Development and Characterization of Long-Acting Injectable Risperidone Microspheres Using Biodegradable Polymers: Formulation Optimization and Release Kinetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of RMs
2.3. Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency of RMs
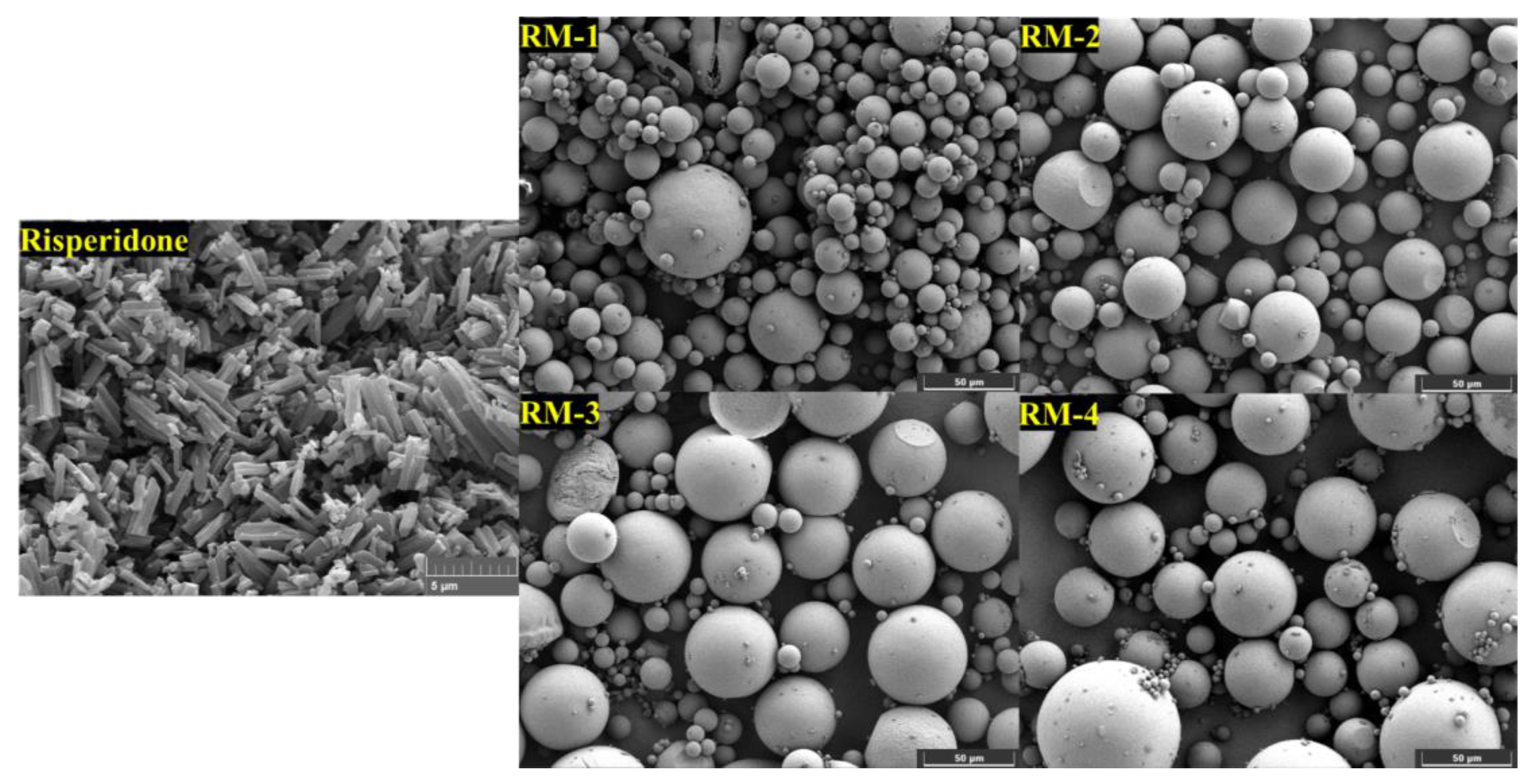
2.4. Morphology
2.5. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
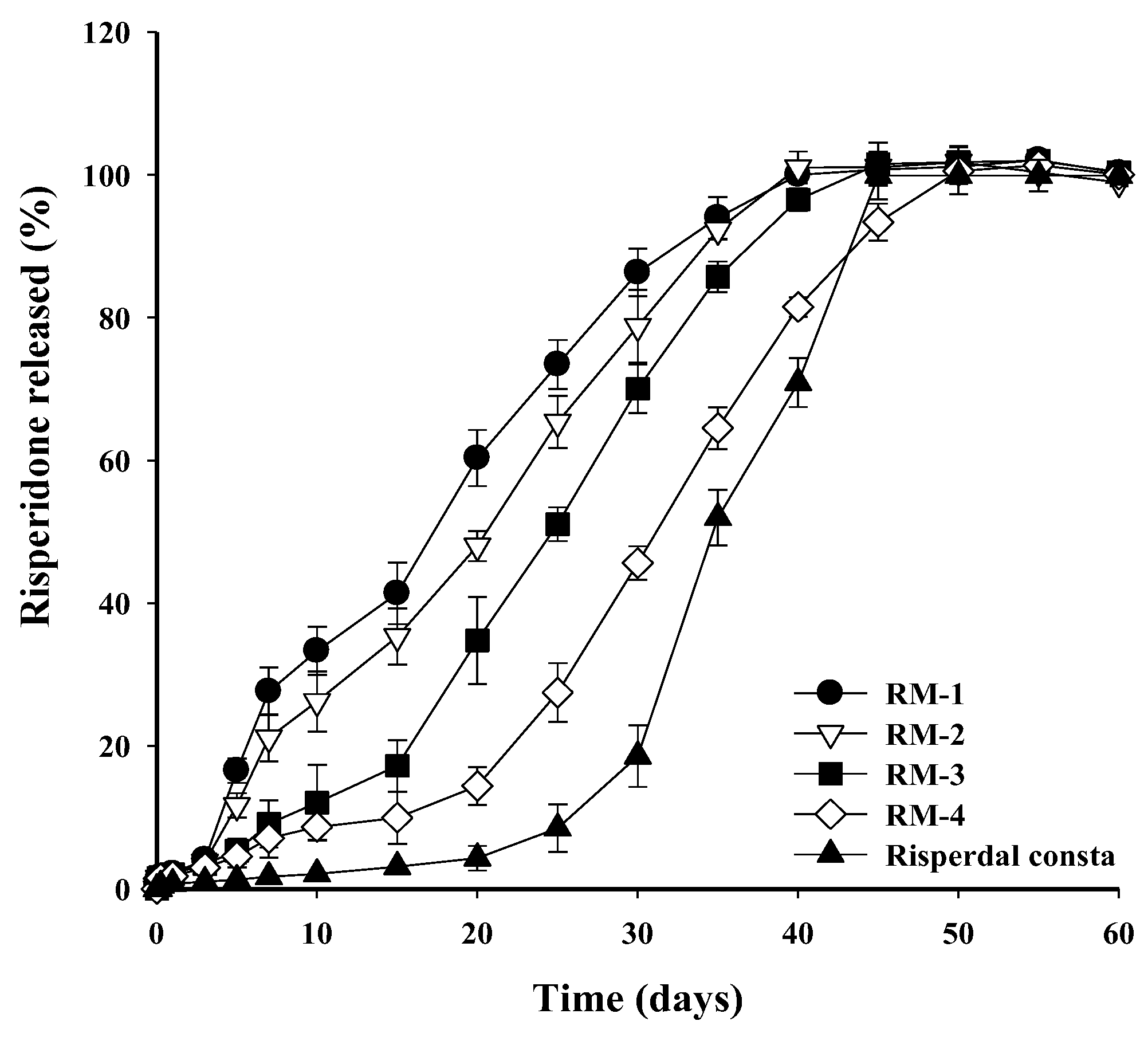
2.6. In Vitro Release Studies
2.7. In Vitro Degradation Studies
3. Results
3.1. Encapsulation of Risperidone in PLGA Microspheres
3.2. Morphological Characteristics of RMs
3.3. Crystallinity Assessment
3.4. In Vitro Release of Risperidone from RMs
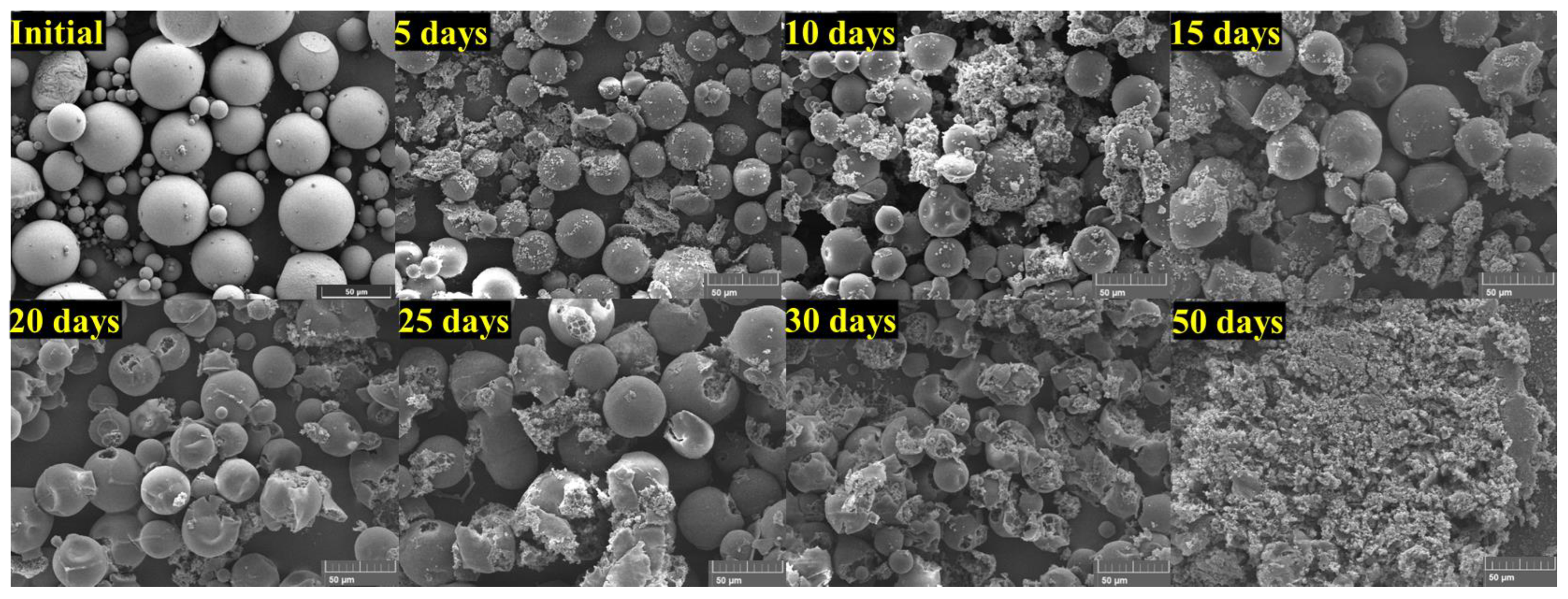
3.5. Degradation Behavior of RM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Marques, T.R.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia—An overview. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisch, R.; Saniotis, A.; Wolf, R.; Bielau, H.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Braun, K.; Jankowski, Z.; Kumaratilake, J. The role of dopamine in schizophrenia from a neurobiological and evolutionary perspective: Old fashioned, but still in vogue. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, J.M. Pharmacologic treatment of schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bartolomeis, A.; Ciccarelli, M.; De Simone, G.; Mazza, B.; Barone, A.; Vellucci, L. Canonical and non-canonical antipsychotics’ dopamine-related mechanisms of present and next generation molecules: A systematic review on translational highlights for treatment response and treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.V.; Grace, A.A. Beyond dopamine receptor antagonism: New targets for schizophrenia treatment and prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, S.; Corves, C.; Arbter, D.; Engel, R.R.; Li, C.; Davis, J.M. Second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Gallego, J.A.; Robinson, D.G.; Malhotra, A.K.; Kane, J.M.; Correll, C.U. Efficacy and safety of individual second-generation vs. first-generation antipsychotics in first-episode psychosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.M.; Metalon, L.; Watanabe, M.D.; Blake, L. Depot antipsychotic drugs: Place in therapy. Drugs 1994, 47, 741–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Illum, L.; Davis, S. A poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) microsphere depot system for delivery of haloperidol. J. Control. Release 1998, 55, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.M.; Eerdekens, M.; Lindenmayer, J.-P.; Keith, S.J.; Lesem, M.; Karcher, K. Long-acting injectable risperidone: Efficacy and safety of the first long-acting atypical antipsychotic. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butreddy, A.; Gaddam, R.P.; Kommineni, N.; Dudhipala, N.; Voshavar, C. PLGA/PLA-based long-acting injectable depot microspheres in clinical use: Production and characterization overview for protein/peptide delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkanga, C.I.; Fisch, A.; Rad-Malekshahi, M.; Romic, M.D.; Kittel, B.; Ullrich, T.; Wang, J.; Krause, R.W.M.; Adler, S.; Lammers, T. Clinically established biodegradable long acting injectables: An industry perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 167, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, M.A.; Coppola, D.; Bailey, N.; Wilson, A.; Kamauu, A.W.C.; Alba, P.R.; Patterson, O.V.; Viernes, B.; Denhalter, D.W.; Solomon, I.D.; et al. Risperdal® CONSTA® Needle Detachment. Incidence Rates Before and After Kit Redesign: A Retrospective Study using Electronic Health Records and Natural Language Processing in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Neurol. Ther. 2019, 8, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megens, A.; Awouters, F.; Schotte, A.; Meert, T.; Dugovic, C.; Niemegeers, C.; Leysen, J. Survey on the pharmacodynamics of the new antipsychotic risperidone. Psychopharmacology 1994, 114, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkoula, M.; Kontoyannis, C. Non-destructive quantitative analysis of risperidone in film-coated tablets. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khang, G.; Rhee, J.M.; Jeong, J.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, H.B. Local drug delivery system using biodegradable polymers. Macromol. Res. 2003, 11, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovagnoli, S.; Blasi, P.; Ricci, M.; Rossi, C. Biodegradable microspheres as carriers for native superoxide dismutase and catalase delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waeckerle-Men, Y.; Groettrup, M. PLGA microspheres for improved antigen delivery to dendritic cells as cellular vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginjupalli, K.; Shavi, G.V.; Averineni, R.K.; Bhat, M.; Udupa, N.; Upadhya, P.N. Poly (α-hydroxy acid) based polymers: A review on material and degradation aspects. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 144, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenberg, S.; Wahlgren, M.; Reslow, M.; Axelsson, A. The mechanisms of drug release in poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; ur Rehman, A. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M.; Shive, M.S. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 28, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Masada, A.; Ichikawa, M. Quantum-confinement effect in individual Ge1−xSnx quantum dots on Si (111) substrates covered with ultrathin SiO2 films using scanning tunneling spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 013109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibe, T.; Maeda, Y.; Terada, T.; Naruse, N.; Mera, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Nakamura, Y. Resistive switching memory performance in oxide hetero-nanocrystals with well-controlled interfaces. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.A. The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly (lactide-co-glycolide)(PLGA) devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, A.; Stippler, E.; Shah, V.P.; Burgess, D.J. Validation of USP apparatus 4 method for microsphere in vitro release testing using Risperdal® Consta®. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, S.; Mounika, K.; Bakshi, V.; Prasad, V. 3-month parenteral PLGA microsphere formulations of risperidone: Fabrication, characterization and neuropharmacological assessments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.E.; Eckenstaler, R.; Syrowatka, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, M.; Benndorf, R.A.; Mäder, K. Has PEG-PLGA advantages for the delivery of hydrophobic drugs? Risperidone as an example. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, C.; Yu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Su, Z.; Sun, F. Development of near zero-order release PLGA-based microspheres of a novel antipsychotic. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.-X.; Shi, Y.-N.; Teng, L.-S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.-X.; Meng, Q.-F.; Teng, L.-R.; Li, Y.-X. Biodegradable poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide)(PLGA) microspheres for sustained release of risperidone: Zero-order release formulation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhian, A.; Siegel, S.J.; Winey, K.I. Production of haloperidol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for extended controlled drug release of haloperidol. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Choi, S.; Qu, W.; Wang, Y.; Burgess, D.J. In vitro-in vivo correlation of parenteral risperidone polymeric microspheres. J. Control. Release 2015, 218, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Schaper, A.; Kissel, T. Effects of process and formulation parameters on characteristics and internal morphology of poly (d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres formed by the solvent evaporation method. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolnik, B.S.; Burgess, D.J. Evaluation of in vivo–in vitro release of dexamethasone from PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Der, O.; Bertola, V. An experimental investigation of oil-water flow in a serpentine channel. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2020, 129, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, W.; Premanadhan, V. Experimental investigation of viscous oil-water flows in pipeline. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 147, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Bao, Q.; Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Burgess, D.J. Effect of polymer source variation on the properties and performance of risperidone microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Palazzo, A.; Hennink, W.E.; Kok, R.J. Effect of particle size on drug loading and release kinetics of gefitinib-loaded PLGA microspheres. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, X.; Pan, F.; Li, F.; Xue, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Y. Evaluation the injectability of injectable microparticle delivery systems on the basis of injection force and discharged rate. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 190, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An add-in program for modeling and comparison of drug dissolution profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Rasool, B.K.; Mohammed, A.A.; Salem, Y.Y. The optimization of a dimenhydrinate transdermal patch formulation based on the quantitative analysis of in vitro release data by DDSolver through skin penetration studies. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Kaffashi, B. Mathematical kinetic modeling on isoniazid release from Dex-HEMA-PNIPAAm nanogels. Nanomed. Res. J. 2016, 1, 90–96. [Google Scholar]


| Formulation | Risperidone (mg) | PLGA (mg) | DCM (mL) | 1% (w/v) PVA (mL) | D.W. (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RM-1 | 75 | 75 | (0.9) | 37.5 | 75 |
| RM-2 | 75 | 100 | (0.9) | 37.5 | 75 |
| RM-3 | 75 | 150 | (0.9) | 37.5 | 75 |
| RM-4 | 75 | 225 | (0.9) | 37.5 | 75 |
| Formulation | D.L (%) | E.E (%) |
|---|---|---|
| RM-1 | 46.2 | 92.3 |
| RM-2 | 39.3 | 91.7 |
| RM-3 | 30.3 | 92.8 |
| RM-4 | 23.1 | 92.2 |
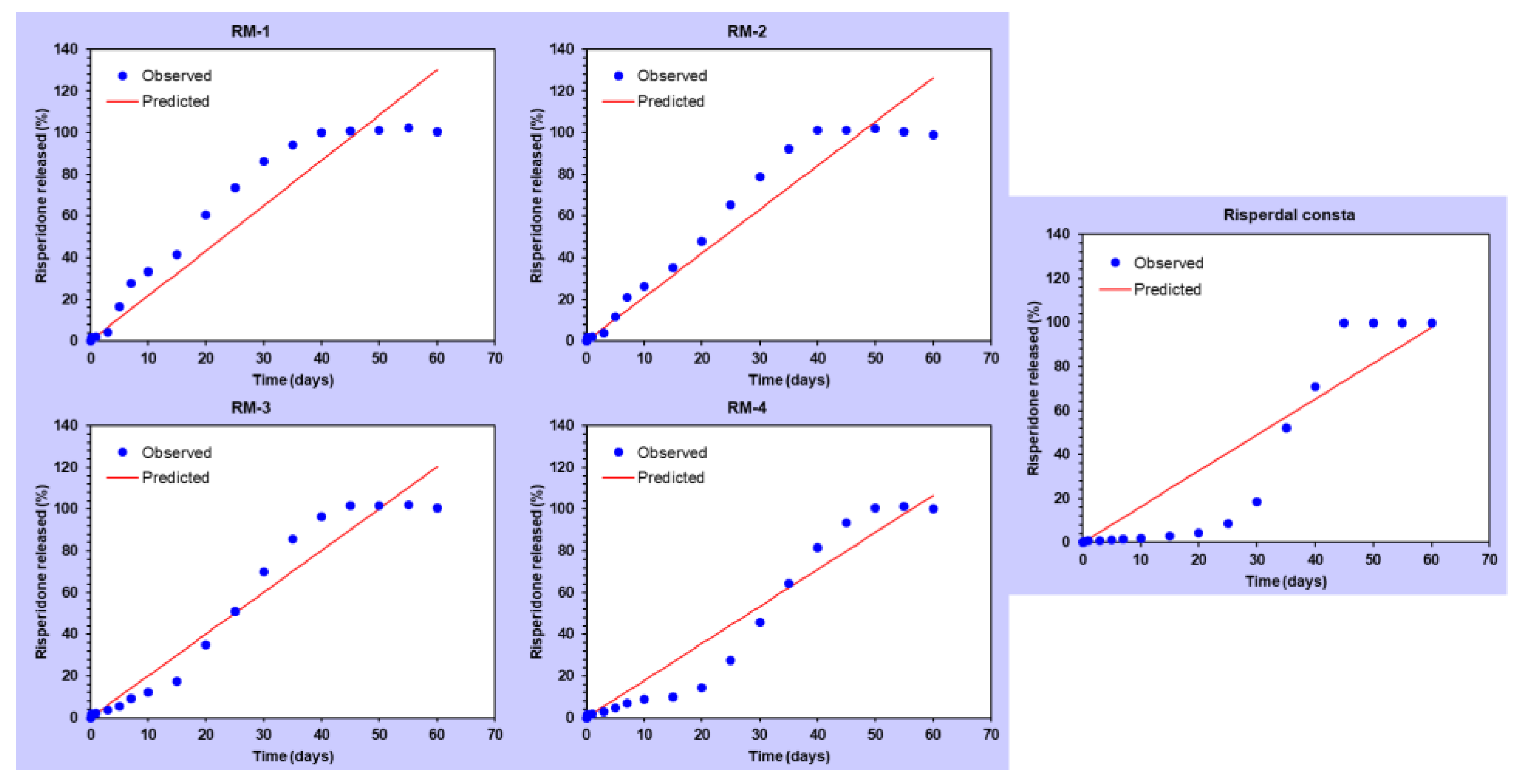
| Modeling | Corresponding Equation | Formulation | Parameters | Rsqr | AIC | MSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-order | f = k0 t f = amount of drug released k0 = reaction rate coefficient t = time | RM-1 | k0 = 2.170 | 0.8920 | 147.6731 | 2.0183 |
| RM-2 | k0 = 2.105 | 0.9276 | 140.5484 | 2.4300 | ||
| RM-3 | k0 = 2.005 | 0.9525 | 133.8190 | 2.8722 | ||
| RM-4 | k0 = 1.778 | 0.9405 | 135.8492 | 2.6620 | ||
| Risperdal Consta® | k0 = 1.630 | 0.8427 | 154.5171 | 1.7056 | ||
| First-order | f = 100 [1 − e−k1t] f = amount of drug released k1 = rate constant t = time | RM-1 | k1 = 0.053 | 0.9680 | 125.7944 | 3.2338 |
| RM-2 | k1 = 0.046 | 0.9486 | 134.3871 | 2.7723 | ||
| RM-3 | k1 = 0.038 | 0.8936 | 148.3252 | 2.0663 | ||
| RM-4 | k1 = 0.028 | 0.8355 | 154.1694 | 1.6442 | ||
| Risperdal Consta® | k1 = 0.023 | 0.7241 | 164.6329 | 1.1436 | ||
| Higuchi | f = kH t0.5 f = amount of drug released kH = dissolution constant t = time | RM-1 | kH = 13.976 | 0.9451 | 135.4998 | 2.6946 |
| RM-2 | kH = 13.398 | 0.9202 | 142.2946 | 2.3330 | ||
| RM-3 | kH = 12.449 | 0.8465 | 154.9272 | 1.6995 | ||
| RM-4 | kH = 10.753 | 0.7612 | 160.8757 | 1.2716 | ||
| Risperdal Consta® | kH = 9.566 | 0.6260 | 170.1084 | 0.8394 | ||
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | f = kKP tn kKP = constant depicting the experimental parameters based on geometry and dosage forms f = amount of drug released n = release exponent | RM-1 | kKP = 8.451 n = 0.640 | 0.9638 | 130.0060 | 2.9998 |
| RM-2 | kKP = 5.837 n = 0.730 | 0.9614 | 131.2244 | 2.9480 | ||
| RM-3 | kKP = 2.362 n = 0.957 | 0.9531 | 135.5830 | 2.7742 | ||
| RM-4 | kKP = 0.537 n = 1.314 | 0.9609 | 130.2830 | 2.9712 | ||
| Risperdal Consta® | kKP = 0.088 n = 1.764 | 0.9234 | 143.5714 | 2.3137 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, Y.J.; Yun, T.H.; Lee, J.G.; Bang, K.H.; Kim, K.S. Development and Characterization of Long-Acting Injectable Risperidone Microspheres Using Biodegradable Polymers: Formulation Optimization and Release Kinetics. Processes 2024, 12, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122858
Son YJ, Yun TH, Lee JG, Bang KH, Kim KS. Development and Characterization of Long-Acting Injectable Risperidone Microspheres Using Biodegradable Polymers: Formulation Optimization and Release Kinetics. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122858
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Young Jin, Tae Han Yun, Jeong Gyun Lee, Kyu Ho Bang, and Kyeong Soo Kim. 2024. "Development and Characterization of Long-Acting Injectable Risperidone Microspheres Using Biodegradable Polymers: Formulation Optimization and Release Kinetics" Processes 12, no. 12: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122858
APA StyleSon, Y. J., Yun, T. H., Lee, J. G., Bang, K. H., & Kim, K. S. (2024). Development and Characterization of Long-Acting Injectable Risperidone Microspheres Using Biodegradable Polymers: Formulation Optimization and Release Kinetics. Processes, 12(12), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122858







