A Comparative Study of the Performance of Orbitally Shaken Bioreactors (OSRs) and Stirred Tank Bioreactors (STRs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioreactor
2.2. CFD Models
2.3. Determination of Bioreactor Power Consumption
2.4. Determination of Oxygen Transfer Rate
2.5. Determination of Mixing Time
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mesh Independence Validation
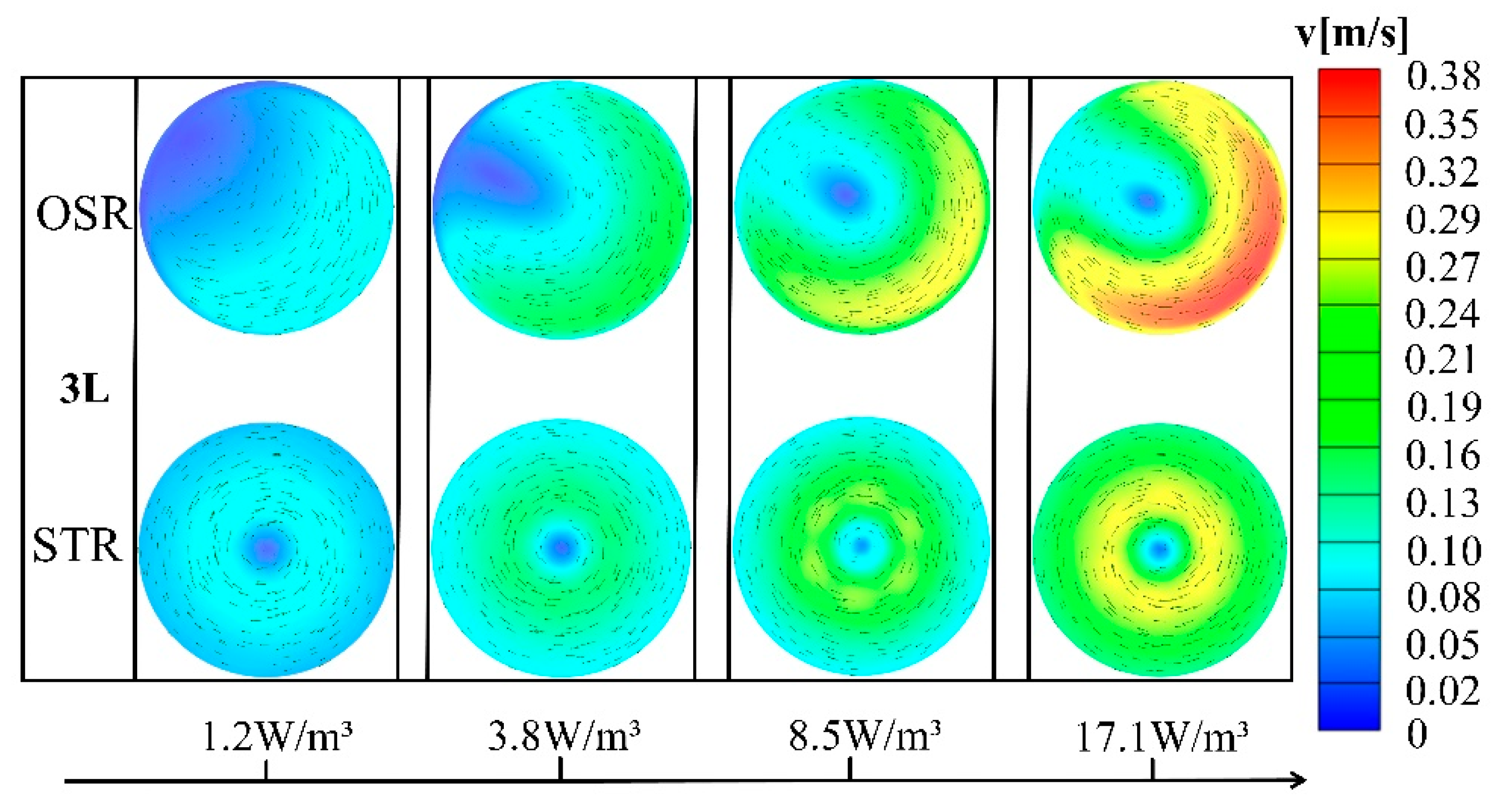
3.2. Comparison of Velocity Vector Field
3.3. Comparison of Aeration Performance
3.4. Comparison of Mixing Characteristics
3.5. Comparison of Shear Damage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, R.; Yang, S.C.; Ren, J.S.; Epstein, R.T. Current situation and future development of the biopharmaceutical industry in China: A mixed-method study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 911165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J.; Cartmell, S.H.; Keramane, A.; Alicia, E.H. Principles and Design of a Novel Magnetic Force Mechanical Conditioning Bioreactor for Tissue Engineering, Stem cell Conditioning, and Dynamic in Vitro Screening. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2006, 5, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jossen, V.; Eibl, R.; Pörtner, R.; Kraume, M.; Eibl, D. Stirred Bioreactors: Current State and Developments, With Special Emphasis on Biopharmaceutical Production Processes. Curr. Dev. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 7, 179–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.K.; Song, B.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Developing an orbitally shaken bioreactor featuring a hollow cylinder vessel wall. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteil, D.T.; Juvet, V.; Paz, J.; Moniatte, M.; Baldi, L.; Hacker, D.L.; Wurm, F.M. A comparison of orbitally-shaken and stirred-tank bioreactors: pH modulation and bioreactor type affect CHO cell growth and protein glycosylation. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yano, M.; Okano, Y.; Masahiro, K.O. Numerical investigation for the movement of cell colonies in bioreactors: Stirring and orbital shaking tanks. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2018, 51, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortsch, R.; Dirk, W.B. Power Consumption and maximum energy dissipation in a milliliter-scale bioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 26, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, M.A.; Marchildon, E.K.; McAuley, K.B.; Cunningham, M.F. Assessment of Mixing Performance and Power Consumption of a Novel Polymerization Reactor System. Chem. Eng. Technol. Ind. Chem.-Plant Equip.-Process Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikenhorst, G.V.; Thomassen, Y.E.; Leo, V.A.; Bakker, A.M. Assessment of mass transfer and mixing in rigid lab-scale disposable bioreactors at low power input levels. Biotechnol. Prog. 2014, 30, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, C.; Nakiboglu, G. Use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) in teaching fluid mechanics. In Proceedings of the ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Conference Proceedings, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24 June 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.N.; Pan, J.Z.; Chen, S.X.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhuang, Y.P. CFD simulation of stirred bioreactor and its application in the inosine production. J. East China Univ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 5, 548–551. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.K.; Song, B.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Analyzing the suitability of a baffled orbitally shaken bioreactor for cells cultivation using the computational fluid dynamics approach. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 35, e2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, M.; Feng, Y.; Ramsey, J.D. Using CFD simulations and statistical analysis to correlate oxygen mass transfer coefficient to both geometrical parameters and operating conditions in a stirred-tank bioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2019, 35, e2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emre, D.T.; Kose, A.; Celik, Y.; Oncel, S.S. Design of a horizontal-dual bladed bioreactor for low shear stress to improve hydrodynamic responses in cell cultures: A pilot study in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 169, 107970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchs, J.; Maier, U.; Milbradt, C.; Zoels, B. Power consumption in shaking flasks on rotary shaking machines: I. power consumption measurement in unbaffled flasks at low liquid viscosity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 68, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchs, J.; Raval, K. Extended method to evaluate power consumption in large disposable shaking bioreactors. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2008, 41, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Peter, C.P.; Akgün, A.; Büchs, J. Power consumption and heat transfer resistance in large rotary shaking vessels. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 21, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Hiraoka, S.; Tada, Y.; Koh, S.T.; Lee, Y.S. Mixing time and power consumption for a liquid in a vertical cylindrical vessel, shaken in a horizontal circle. Trans. Icheme Part A 1996, 74, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Klöckner, W.; Tissot, S.; Wurm, F.M.; Büchs, J. Power input correlation to characterize the hydrodynamics of cylindrical orbitally shaken bioreactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 65, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, N.K.; Appleton, M.; Baganz, F.; Lye, G.J. Quantification of power consumption and oxygen transfer characteristics of a stirred miniature bioreactor for predictive fermentation scale-up. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, S.; Farhat, M.; Hacker, D.L.; Anderlei, T.; Kühner, M.; Comninellis, C.; Wurm, F.M. Determination of a scale-up factor from mixing time studies in orbitally shaken bioreactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 52, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.W.; Wang, T.F.; Wang, J.F. Analysis and measurement of mass transfer in airlift loop reactors. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 14, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.G.; Correia, L.D.C. Oxygen transfer in hydrocarbon aqueous dispersions and its applicability to alkane-based bioprocesses. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, B.M.; Pfefferle, W.; Bachmann, B.; Leuchtenberger, W.; Deckwer, W.D. A special reactor design for investigations of mixing time effects in a scaled-down industrial L-lysine fed-batch fermentation process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 64, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgin, T.; Coronel, J.; Hagens, G.; Hagens, G.; Keebler, M.V.; Genzel, Y.; Reichl, U.; Anderlei, T. Orbitally shaken single-use bioreactor for animal cell cultivation: Fed-batch and perfusion mode. In Animal Cell Biotechnology: Methods and Protocols; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, A.; Chen, S.C.; Jeng, J.C.; Zhu, L.; Leggett, G. Mixing performance analysis of orbitally shaken bioreactors. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.Y.; Li, S.H. Effects of Surface Etch Hole Fault on the Velocity Field in Microchannel Reactors. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 17, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, C. Analysis of hollow wall effect on the fluid dynamics in the orbitally shaken bioreactors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Li, C.; Guo, M.J.; Zhang, S.L.; Ali, M. Numerical simulation of scaling-up an inverted frusto-conical shaking bioreactor with low shear stress for mammalian cell suspension culture. Cytotechnology 2019, 71, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Liao, Y.; Chang, X.; Su, M.; Ou, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Huang, H. A Comparative Study of the Performance of Orbitally Shaken Bioreactors (OSRs) and Stirred Tank Bioreactors (STRs). Processes 2024, 12, 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122849
Zhu L, Liao Y, Chang X, Su M, Ou Y, Wu S, Wu Z, Yang H, Li J, Huang H. A Comparative Study of the Performance of Orbitally Shaken Bioreactors (OSRs) and Stirred Tank Bioreactors (STRs). Processes. 2024; 12(12):2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122849
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Likuan, Yinyu Liao, Xiaoyin Chang, Mingwu Su, Yixian Ou, Shiyun Wu, Zhaozhi Wu, Haolin Yang, Junyan Li, and Haijun Huang. 2024. "A Comparative Study of the Performance of Orbitally Shaken Bioreactors (OSRs) and Stirred Tank Bioreactors (STRs)" Processes 12, no. 12: 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122849
APA StyleZhu, L., Liao, Y., Chang, X., Su, M., Ou, Y., Wu, S., Wu, Z., Yang, H., Li, J., & Huang, H. (2024). A Comparative Study of the Performance of Orbitally Shaken Bioreactors (OSRs) and Stirred Tank Bioreactors (STRs). Processes, 12(12), 2849. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122849





