Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Sediment Abrasion Mechanism at the Leading Edge of an Airfoil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
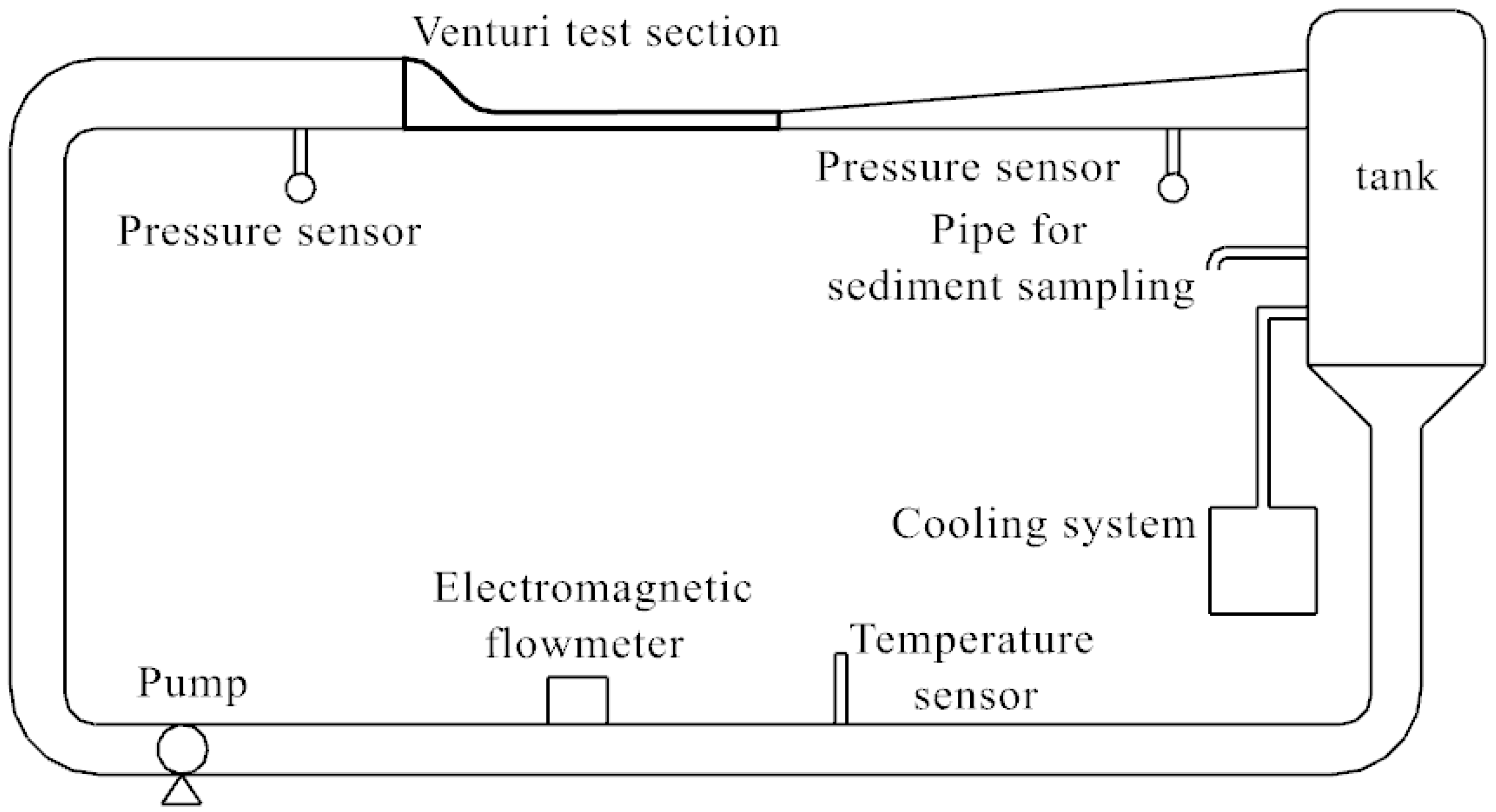
2.1. Introduction to the Tests
2.1.1. Test Conditions
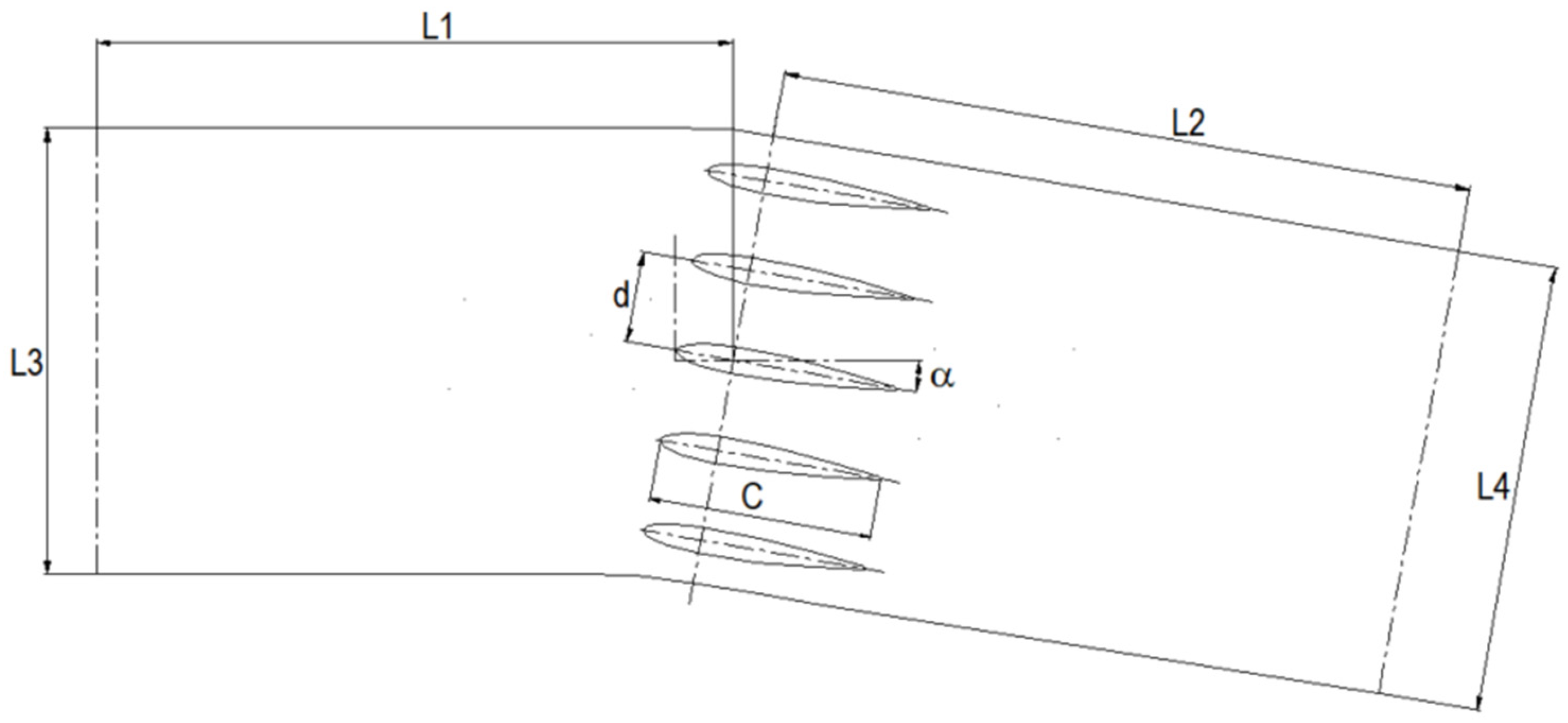
2.1.2. Test Methods
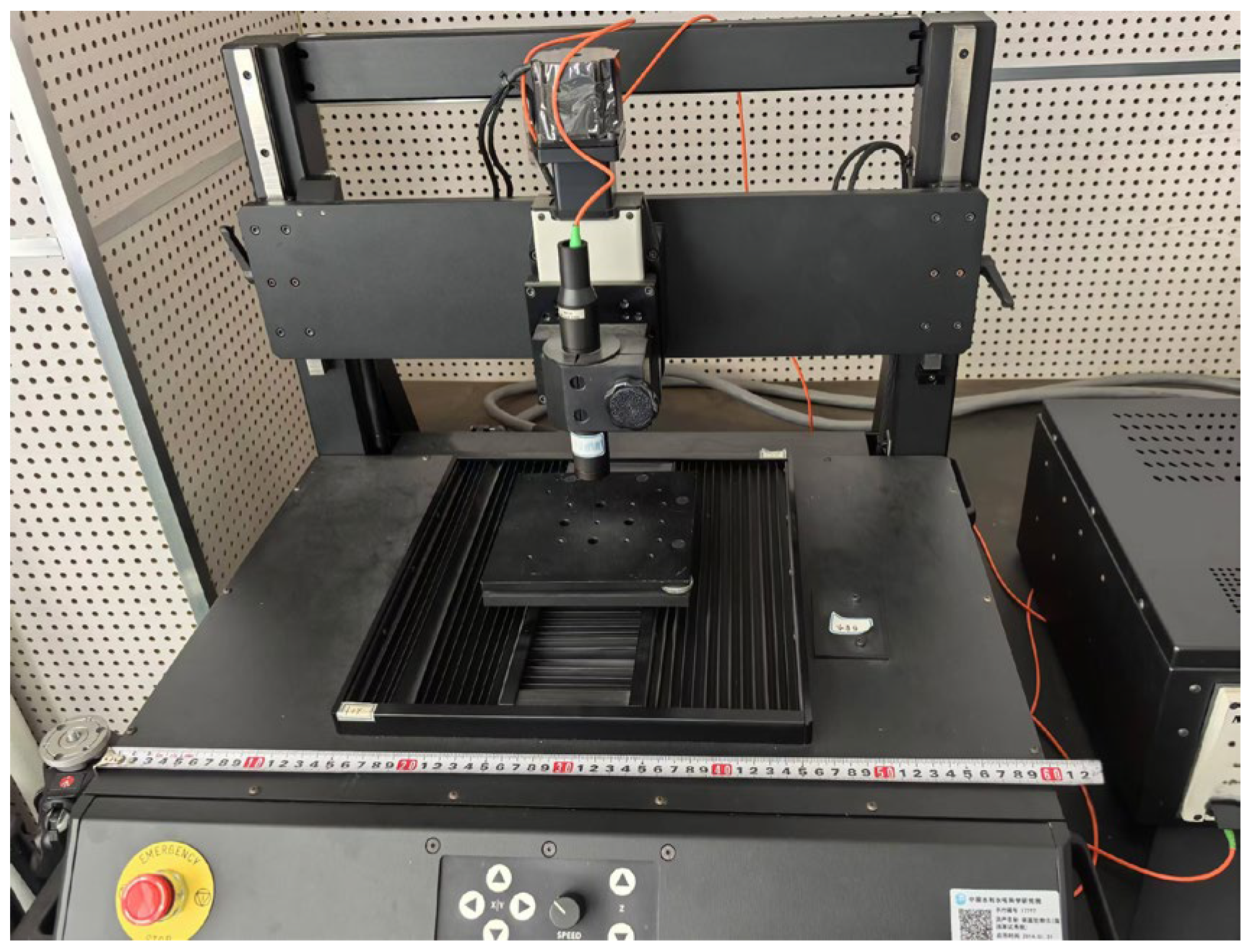
2.1.3. Measurement of the Airfoil’s Outer Profile
2.1.4. Wear Depth Measurements
2.2. Numerical Calculations
2.2.1. Three-Dimensional (3D) Model and Meshing of the Test Section
2.2.2. Numerical Model
2.3. Calculation Methods and Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
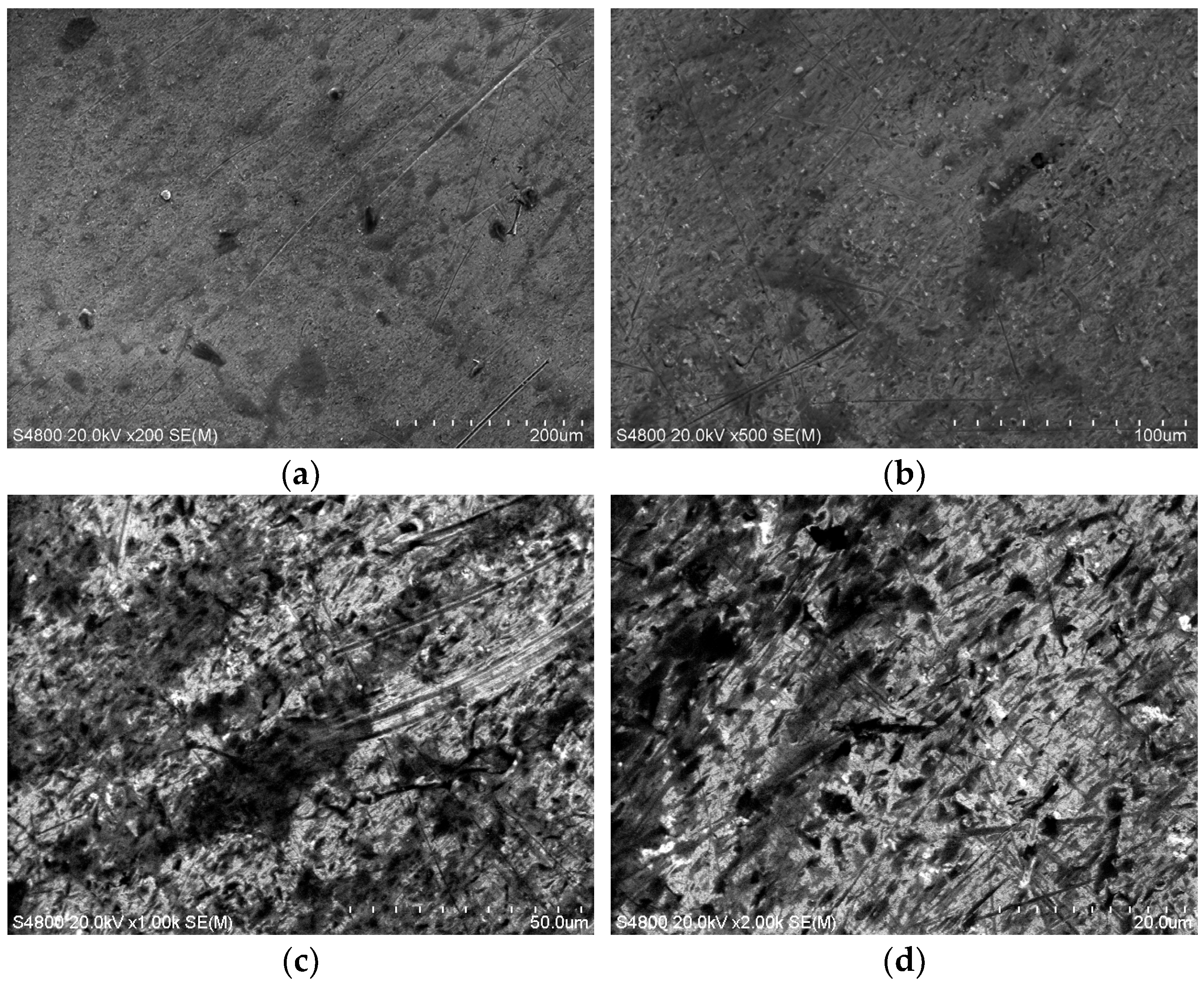
3.1. Wear Test Results and Analysis
3.2. Numerical Simulation Results and Analysis
3.2.1. Comparison of Predicted Airfoil Wear Results with Test Data
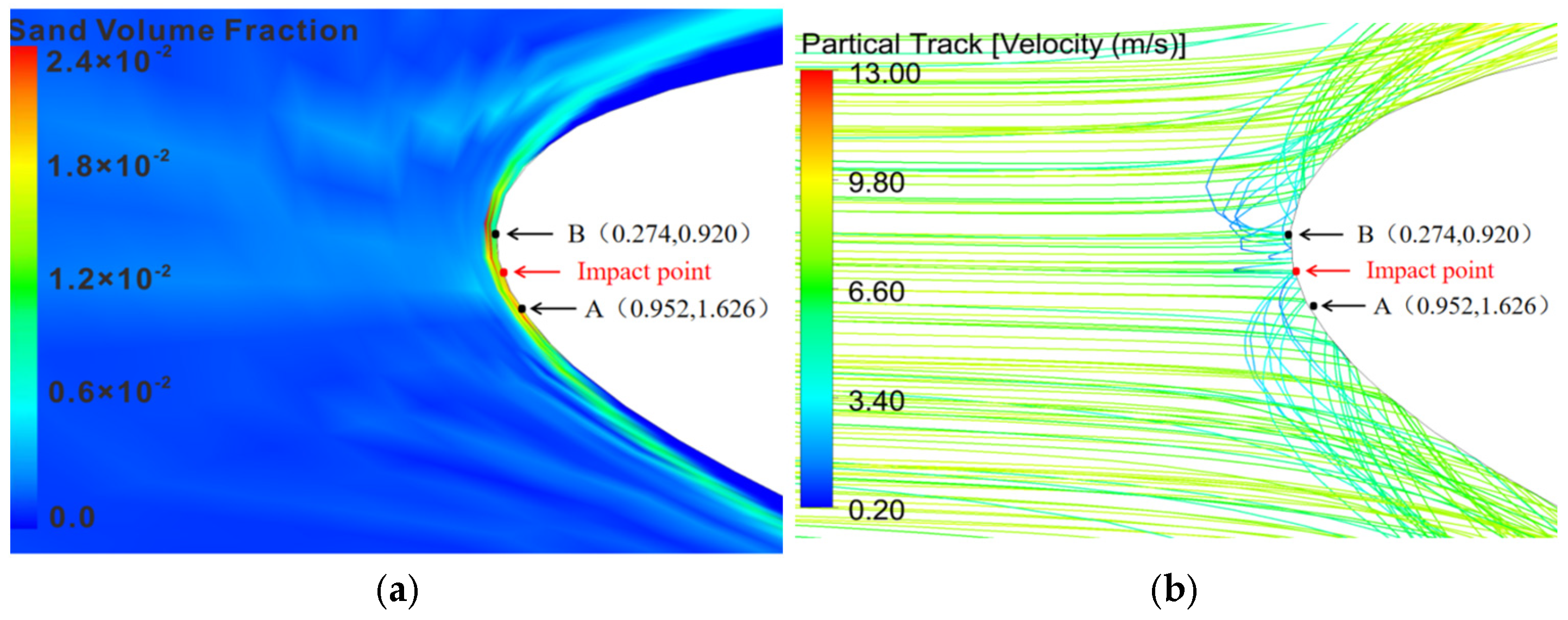
3.2.2. Airfoil’s Wear Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Yi, Y.L. Evaluation of sand abration of hydraulic in Baihetan hydropower Station. J. Hydropower 2016, 35, 67–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Padhy, M.K.; Saini, R.P. Effect of Size and Concentration of Silt Particles on Erosion of Pelton Turbine Buckets. Energy 2009, 34, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.F.; Wei, X.Z. The Particle Induced Energy Loss Mechanism of Pelton Turbine. Renew. Energy 2021, 173, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, M.; Deng, C.; Binama, M.; Zheng, Y. Experimental and Numerical Studies on Opening and Velocity Influence on Sediment Erosion of Pelton Turbine Buckets. Renew. Energy 2021, 173, 1040–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wei, X.Z.; Liu, W.J. Numerical Investigation of Two-Phase Flow in the Guide Vanes Area of a Hydraulic Turbine. J. Large Electr. Mach. Hydraul. Turbine 2015, 2, 42–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Han, W.; Guo, T.; Su, M.; Wei, S. Sediment erosion characteristics and mechanism on guide vane end-clearance of hydro turbine. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Su, M.; Peng, G.; Wei, S. Sediment-wear morphology prediction method of hydraulic machine based on differential-quadrature method. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 33, 1950172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakibuzzaman, M.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, K.; Suh, S.H.; Kim, K.Y. Numerical study of sediment erosion analysis in Francis turbine. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, W. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Sediment Wear of Fixed Guide Vanes of Hydraulic Turbines in Muddy River Based on Discrete Phase Model. Processes 2023, 11, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tan, L.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, D. Solid-liquid multiphase flow and erosion characteristics of a centrifugal pump in the energy storage pump station. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, U.; Chen, Z.; Choi, D.Y. Correlation of the Sediment Properties and Erosion in Francis Hydro Turbine Runner. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2019, 12, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Z.Y.; Wang, J.L. Research on the Influence of Operating Conditions on the Abrasion in the Guide Vane Area of Turbines in Multi-Sand Rivers. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2022, 53, 148–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, S.B.; Trivedi, C.; Dahlhaug, G.O. Design and Development of Guide Vane Cascade for a Low Speed Number Francis Turbine. J. Hydrodyn. 2016, 28, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, R.; Neopane, H.P.; Zhu, B.; Thapa, B. Effect of sediment erosion on flow around guide vanes of Francis turbine. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekke, H.; Wu, Y.L.; Cai, B.Y. Design of Hydraulic Machinery Working in Sand Laden Water, 2nd ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 155–181. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Zhou, X.; Song, H.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z. Study on the Effect of the Guide Vane Opening on the Band Clearance Sediment Erosion in a Francis Turbine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, X. Sediment wear prediction model of ZG06Cr13Ni4Mo turbine guide vane in sediment-laden hydropower station. Mater. Express 2021, 11, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Tang, W.; Liu, X. Sediment wear of turbine guide vane before and after tungsten carbide treatment. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.B.; Dahlhaug, G.O.; Thapa, B. Effects of sediment erosion in guide vanes of Francis turbine. Wear 2017, 390–391, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Meng, X.; Lu, L. Asymmetric Solid–Liquid Two-Phase Flow Around a NACA0012 Cascade in Sediment-Laden Flow. Symmetry 2022, 14, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosanjh, S.; Humphrey, J.A. The influence of turbulence on erosion by a particle-laden fluid jet. Wear 1985, 102, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noon, A.A.; Kim, M.H. Erosion wear on centrifugal pump casing due to slurry flow. Wear 2016, 364, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






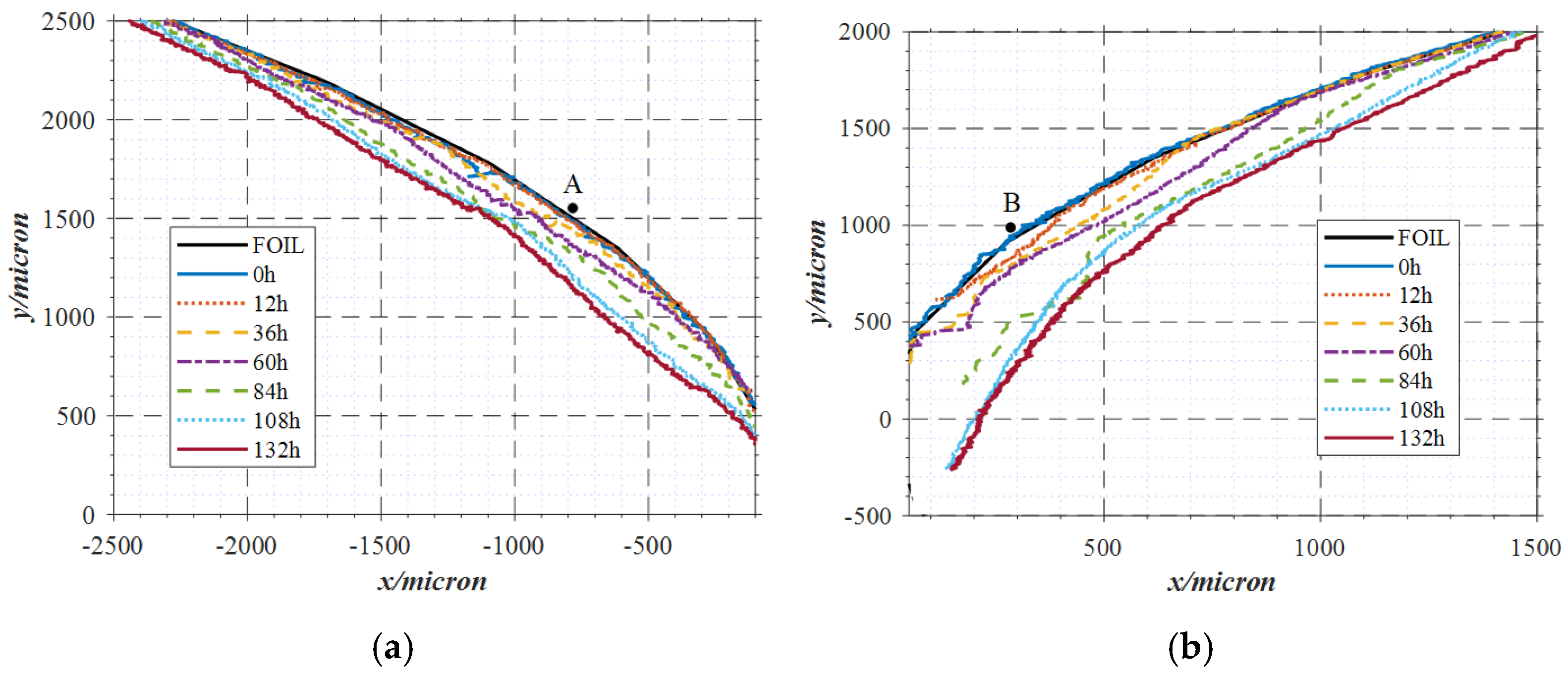

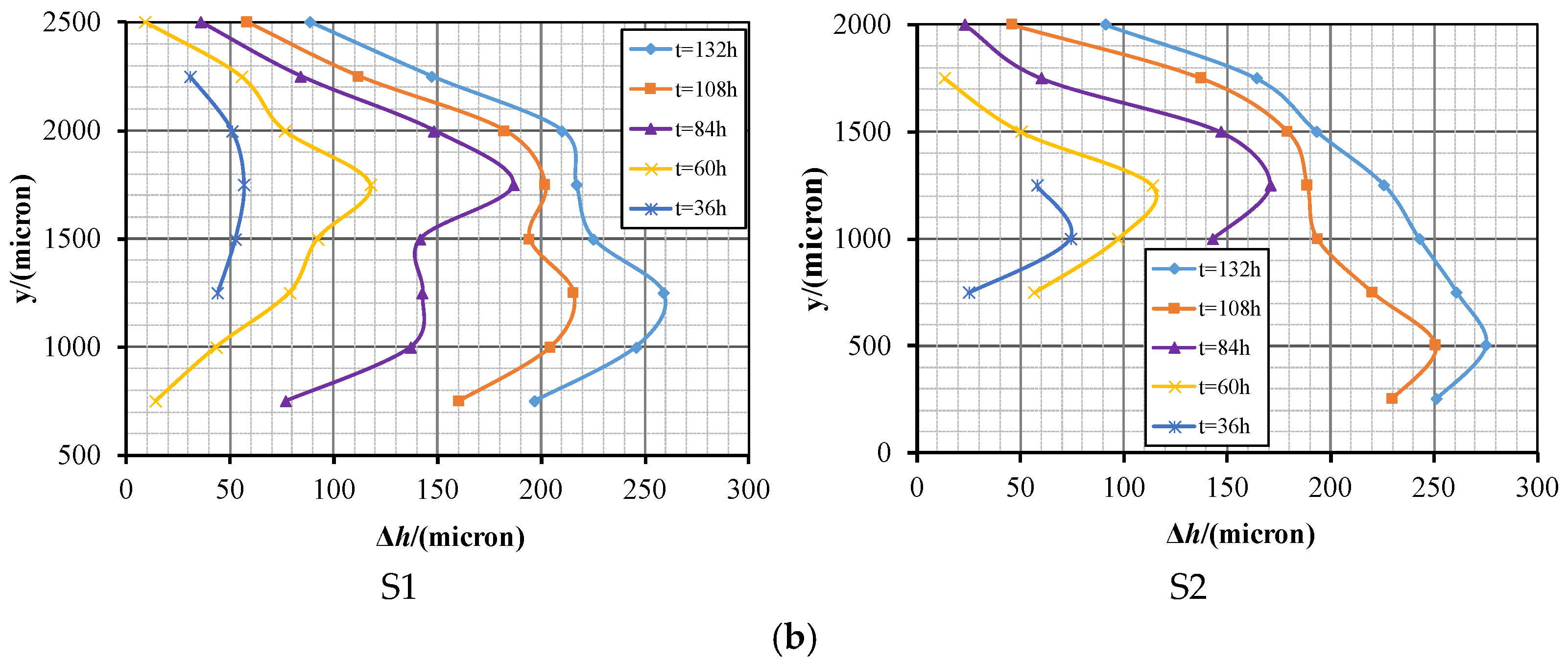



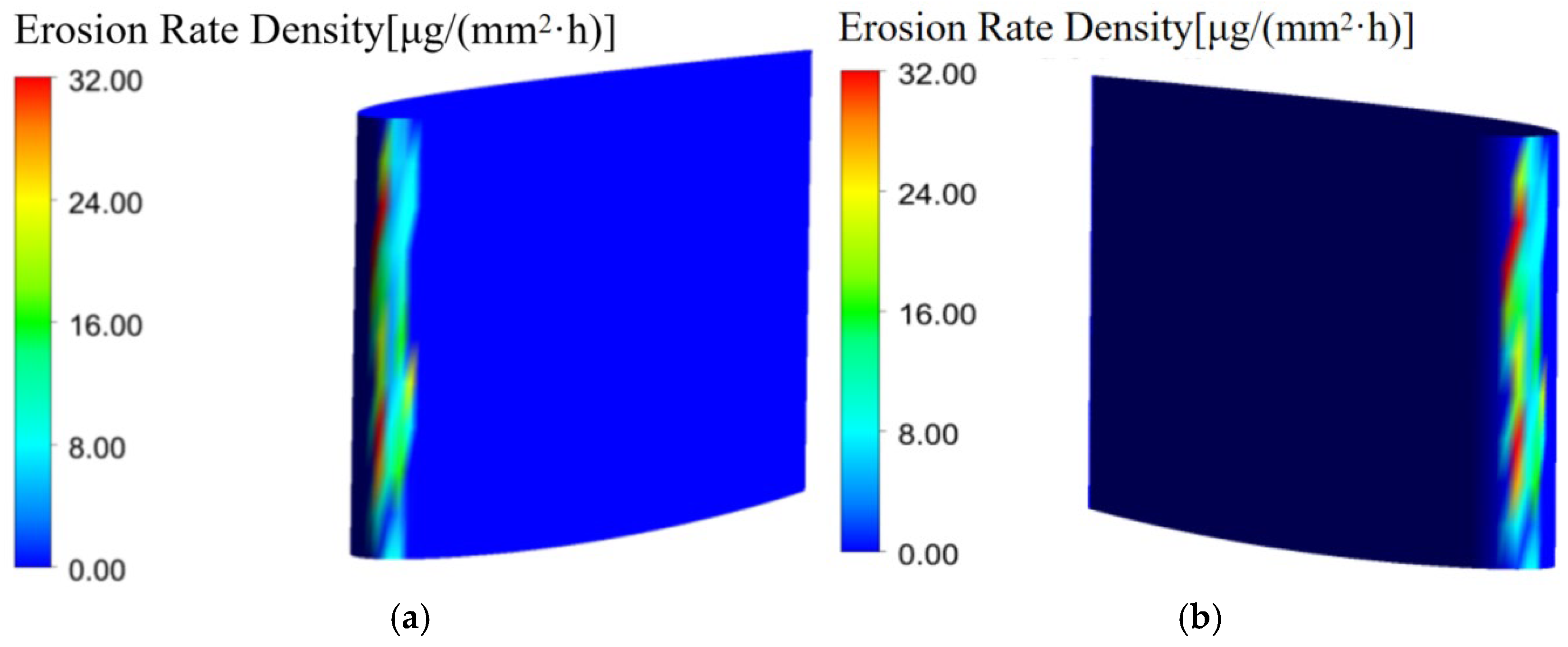


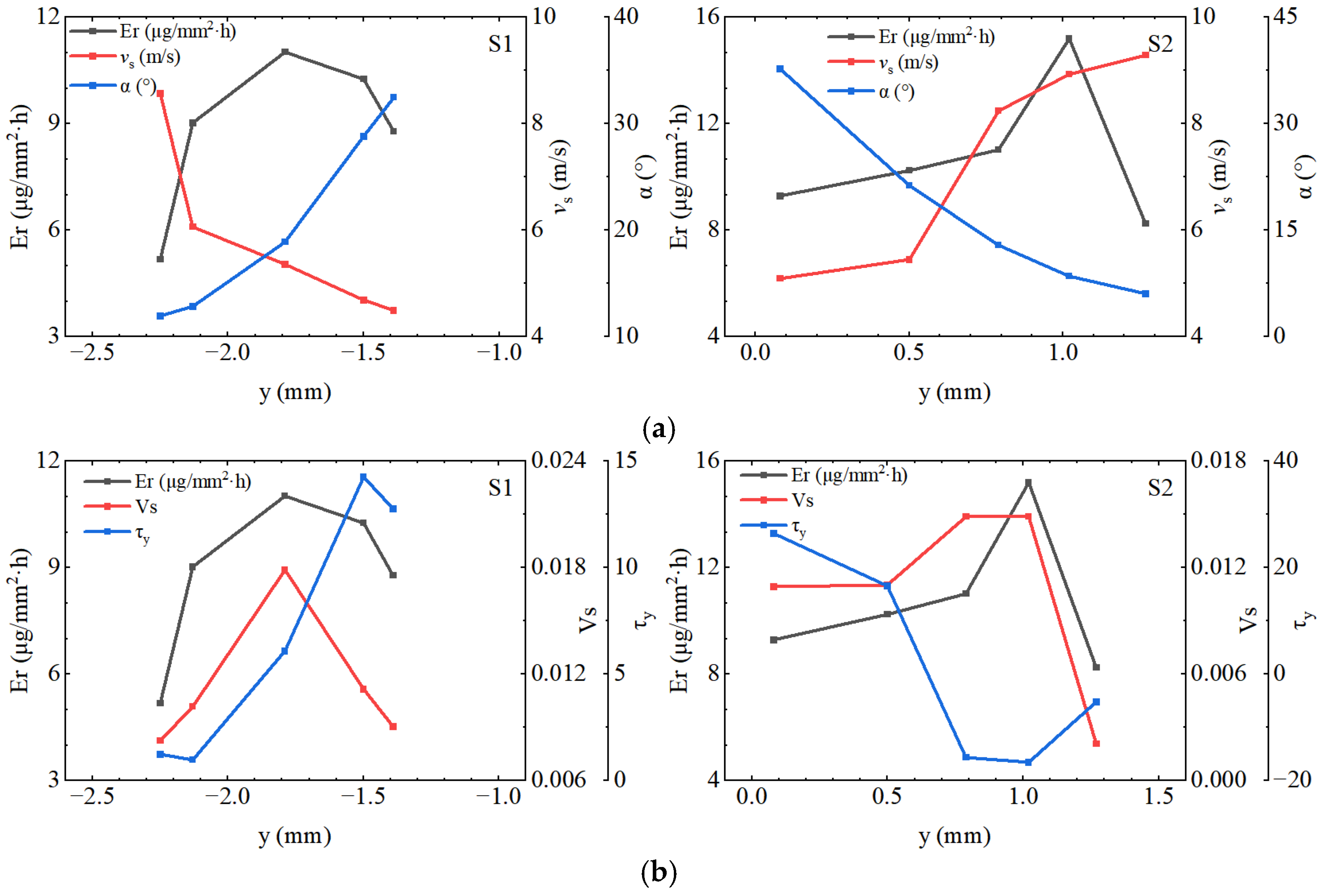
| Material | Hardness | Tensile Strength, σb (MPa) | Conditional Yield Strength, σ0.2 (MPa) | Elongation, δ5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum alloy | 90–95 HBW | 180 | 110 | 14 |
| Element | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zn | Cr | Ti | Si | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass fraction | 0.15–0.4 | 0.15 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.25 | 0.04–0.35 | 0.15 | 0.4–0.8 | 0.7 | Remainder |
| Re | Impact Angle, α | Sediment Mass Concentration, Cm (kg/m3) | Sediment Volume Fraction, CV (%) | Average Sediment Concentration (kg/m3) | Median Particle Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.0 × 105 | 10° | 6.0 | 0.28 | 5.61 | 65.9 |
| Test Time t/h | Maximum Wear Depth | |
|---|---|---|
| S1 Surface | S2 Surface | |
| 36 | 56.6 | 74.0 |
| 60 | 117.8 | 113.8 |
| 84 | 186.3 | 170.9 |
| 108 | 215.5 | 250.7 |
| 132 | 258.9 | 275.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Lu, L.; Li, T.; Wang, W.; Meng, L. Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Sediment Abrasion Mechanism at the Leading Edge of an Airfoil. Processes 2024, 12, 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122790
Liu Z, Zhu L, Lu L, Li T, Wang W, Meng L. Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Sediment Abrasion Mechanism at the Leading Edge of an Airfoil. Processes. 2024; 12(12):2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122790
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhen, Lei Zhu, Li Lu, Tieyou Li, Wanpeng Wang, and Long Meng. 2024. "Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Sediment Abrasion Mechanism at the Leading Edge of an Airfoil" Processes 12, no. 12: 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122790
APA StyleLiu, Z., Zhu, L., Lu, L., Li, T., Wang, W., & Meng, L. (2024). Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Sediment Abrasion Mechanism at the Leading Edge of an Airfoil. Processes, 12(12), 2790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr12122790






