Abstract
Wastewaters generated by the textile industry often contain significant amounts of harmful (carcinogenic and mutagenic) cationic dyes, whose efficient removal is of crucial importance. This study investigates the laccase immobilization on biochar obtained from sour cherry stones (SCS-B), as a cost effective adsorbent, and evaluates its application for brilliant green (BG) degradation. The successful immobilization of laccase on biochar was achieved via adsorption and confirmed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). An immobilization efficiency of 66% was achieved using 0.274 U/mL of laccase at pH 5 and a temperature of 40 °C. The adsorption kinetics of laccase followed a pseudo-second-order model, indicating that chemical adsorption plays a significant role in the immobilization process. The BG degradation by immobilized system was further optimized by evaluating effects of pH, temperature, dye concentration, and contact time. More than 92% of BG (50 mg/L) was removed within 4 h at pH 5 and temperature of 30 °C. These findings suggest that SCS-B can effectively be used as an enzyme carrier and be further utilized for the removal of emerging pollutants, positioning it as a sustainable solution for wastewater treatment.
1. Introduction
Enzymes are proven as a highly efficient tool for biotransformation, enabling catalysis in a wide range of substrates. Their product selectivity, ability to work under mild reaction conditions, and low environmental impact have facilitated their extensive use in various industries [1]. Enzymes, with their supreme and unique catalytic activity and wide selectivity for various pollutants, represent considerable potential for environmental remediation. Previously, several enzymes have been investigated for the removal of water contaminants, and among them, hydrolases and oxidoreductases represent the most used biocatalysts in the treatment of effluents. Oxidoreductase enzymes catalyze the oxidation of a wide range of contaminants, such as phenols, herbicides, pesticides, synthetic textile dyes, pharmaceuticals, and many others. Additionally, after treatment, they can be easily separated by precipitation and centrifugation [2]. Besides lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase, laccases are recognized as the leading oxidoreductases in the environment application category due to their broad substrate range, simple catalysis requirements, apparent stability, and lack of inhibition compared to other enzymes [3]. Laccase is considered a green catalyst, requiring only oxygen as a substrate and producing water as a by-product; thus, it does not generate environmental contamination. Nevertheless, the application of enzymes in their free form is associated with high operational costs, limited stability, a decrease in catalytic activity after one cycle, and poor reusability, limiting their use in large-scale environmental utilization [4,5]. To address these challenges, enzyme immobilization has emerged as an effective strategy. However, the cost of the immobilization of enzymes is high too, and there is the requirement for more economical carriers based on materials derived from waste biomasses. A wide variety of materials, including organic, inorganic, and hybrid supports, have been explored for enzyme immobilization [1]. For optimal efficiency, the support material should maintain the enzyme’s activity, be inert, allow regeneration, minimize enzyme leaching and nonspecific adsorption, and be cost-effective. Recently, there has been increasing interest in using environmentally friendly and affordable carriers for enzyme immobilization, which can be developed from a various carbon-rich materials [4]. Biochar, activated carbon, and chitosan are the most widely utilized biomass-derived carbon materials for enzyme immobilization [6]. Feedstocks include agricultural, industrial, and household wastes, which are available and economical. Biochar, stable, solid renewable-based material possesses numerous desirable features such as functioning as an enzyme carrier, becoming a promising medium for the enzyme immobilization process [7].
Biochar, a carbonaceous product, remains after the thermal decomposition of biomass in oxygen-limited conditions. Thermal degradation (pyrolysis) exposes the biomass to high temperatures, resulting in alterations in its chemical structure [8]. Biochar production is regarded as a carbon-negative process that leads to a decrease in the atmospheric carbon dioxide level [9]. Biochar primarily consists of app. 70% stable carbon, along with hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and trace amounts of other elements, while the precise composition depends on the raw biomass utilized for biochar production and the operational parameters during pyrolysis [6,10]. Owing to its high carbon content, biochar has been utilized in various fields, including waste management, soil quality enhancement, pollutant removal from soil and water, and renewable energy production [4,11,12,13]. Biochar might suitably support high-load enzyme immobilization due to its inert nature, high surface area, rich pore structure, and abundant oxygen-containing functional groups. Biochar demonstrates excellent dispersibility and biocompatibility, as well as physicochemical resistance, owing to its electron exchange properties. These characteristics of biochar, as well as its low cost and widespread availability, make it desirable for laccase immobilization [14]. Recent research has highlighted the effectiveness of biochar as a support material for laccase immobilization in various applications. Lonappan et al. [15] investigated citric acid-modified biochars obtained from Pig manure, almond shell and pine wood in order to enhance laccase binding for diclofenac removal. The results confirmed that near 100% removal was observed using all three laccase-immobilized biochars. Zhang et al. [16] immobilized laccase on biochar, and it was used for BPA removal. The results confirmed that BPA with an initial concentration of 25 mg L−1 could be removed within 75 min due to enzymatic degradation and adsorption.
Brilliant green (BG), a synthetic and toxic dye, is one of the most commonly used dyes in textile and paper printing industries. It is also used in the industrial production of green ink as a bacteriological marker, dermatological agent, an additive to poultry feed to inhibit mold growth, etc. [17,18]. BG is recognized as a mutagenic and carcinogenic dye, posing significant health risks to living organisms. Small dosages of BG can lead to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and renal irritation, while large dosages result in methemoglobinemia, cardiovascular collapse, and death, resulting from respiratory failure [12].
As a cationic dye, BG has more toxic and dangerous effects compared to anionic dyes in both aquatic and terrestrial environments, making its removal essential for environmental protection [19].
On a global scale, waste valorization is becoming a key component of sustainable development, where the reuse of organic waste materials is encouraged to reduce environmental footprints and foster resource efficiency. The re-using of waste fruit stones, by-products from the local food industry, not only prevents their disposal in landfills and subsequent environmental impact but also confers new value to these by-products, aligning with the principles of a circular economy. Serbia is well known for its rich fruit-growing tradition, particularly the cultivation of peaches, plums, and sour cherries, which are among the most abundant fruits in these regions. The conversion of the aforementioned fruit industry waste into high-value biochar for enzyme immobilization contributes to the global trends, promotes a circular economy and offers a sustainable solution for pollutant removal.
This study investigates the possibility of laccase adsorption onto biochar prepared from chemically modified waste biomass: peach stones, sour cherry stones, and plum stones. The laccase immobilized on biochar was further used for the degradation of BG from aqueous solution in a batch system. While there are several papers reporting on laccase immobilization [14,20,21], the use of laccase immobilized on biochar derived from fruit stones for dye degradation is unexplored yet. The novelty of this paper lies in the development of a cost-effective solution that integrates biochar with a biocatalyst, resulting in the efficient removal of a toxic cationic dye.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Peach stones (PSs), sour cherry stones (SCSs), and plum stones (PLSs) were obtained from the local fruit processing factory. The collected stones were separated from the remaining fruit remnants, washed with tap water and dried at room temperature. To reduce their size, the stones were processed using the vibratory disk mill ‘Siebtechnik—T S250’ (Siebtechnik GmbH, Langenfeld, Germany) and then sieved into different size fractions. For this investigation, the class between 0.2 and 0.3 mm was utilized. Grounded PSs, SCSs, and PLSs were pyrolyzed in accordance with the procedure described by Antanasković et al. [12], resulting in the production of biochar PS-B, SCS-B, and PLS-B, respectively. The pyrolysis was carried out in a Nabertherm 1300 muffle furnace (Nabertherm, Lilienthal Germany) in argon atmosphere. Afterward, 2 g of each type of biochar was mixed with a solution containing 50 mL of 5 mol L−1 sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and 5 mol L−1 nitric acid (HNO3) (1:1) in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask; the mixtures were agitated on a magnetic stirrer for 24 h at room temperature. Subsequently, the samples were thoroughly washed using deionized water until they reached neutralization (pH 6–7). The obtained materials, modified peach stone biochar (MPS-B), modified sour cherry stone biochar (MSCS-B), and modified plum stone biochar (MPLS-B), were dried overnight at 80 °C and stored for further experiments.
Laccase from Trametes versicolor (powder, ≥0.5 U/mg) was purchased from Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt Germany. ABTS (2,2-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) and brilliant green were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, and used without further purification. All other chemicals used in this work were of pure analytical grade.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Laccase Characterization
The optimum temperature for free laccase was evaluated by incubating the enzyme in sodium acetate buffer (0.1 mol L−1, pH 5.0) across a temperature range of 20–60 °C, followed by measuring the enzyme’s activity using ABTS as a substrate. The relative activity of laccase as a function of temperature is presented relative to the highest observed activity, which is taken as 100%.
2.2.2. Biochar Supports for Laccase Immobilization
The immobilization of commercial laccase from T. versicolor on acid-functionalized biochar was achieved through the adsorption process. The laccase solution was prepared in 0.1 mol L−1 sodium acetate buffer at pH 5. The optimization was carried out in a range of pH values (4–8; sodium acetate buffer at pH 4 and 5 and potassium phosphate buffer at pH 6, 7, and 8), temperatures (20–50 °C) and contact times (1–6 h), using the single-variable approach. For this purpose, 15 mg of biochar was placed in 2 mL Eppendorf tubes, mixed with 1 mL of laccase solution (with a concentration of 25 mg/mL) and incubated in a shaker at 200 rpm (KS 4000 I, IKA, Staufen, Germany). After a defined time, the supernatant was separated from the biochar and analyzed to measure protein concentration by the Bradford method and laccase activity. The biochar with immobilized laccase was gently washed three times with 1 mL 0.1 mol L−1 buffer (pH 5) and subjected to the determination of enzyme activity. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.2.3. Enzyme Assay
The activity of laccase was evaluated by monitoring the oxidation of ABTS at 420 nm using a UV/VIS Ultrospec 3300 Pro spectrophotometer (Amersham Bioscience, Buckinghamshire, UK). The reaction mixture consisted of 1 mmol L−1 ABTS (0.1 mL), 0.1 mol L−1 sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0, 0.3 mL), and commercial fungal laccase (0.2 mL). The control sample included 0.1 mol L−1 buffer (pH 5.0, 0.4 mL) and commercial fungal laccase (0.2 mL). Incubation was conducted at the optimal temperature for laccase activity (30 °C). The activity of laccase was calculated according the equations given in the study by Ilić et al. [22].
The volumetric activity of free laccase [U/mL] is determined using the following equation:
where E.A. is the volumetric activity of laccase [U/mL], A420 is the absorbance at 420 nm, Vt is the reaction mixture’s total volume [mL], t is the time of incubation [min], Ve is the volume of laccase solution [mL], ɛ is the extinction coefficient of ABTS [36,000 M−1 cm−1], and D is the dilution of laccase.
The total activity of free laccase [U/g] was calculated by the following equation:
where E.A. is the total activity of laccase [U/g], E.A. is the volumetric activity of laccase [U/mL], V is the volume used for laccase extraction [mL], and ms is the laccase powder mass [g]. The protein concentration of laccase was determined using the standard Bradford method [23], with absorbance measured at 540 nm.
The total activity of immobilized laccase [U/g] was calculated according to the following equation:
where A420 is the sample absorbance at 420 nm, Vt is the total reaction mixture volume [mL], t is the time of incubation [min], ms is the solid carrier mass [g], and ɛ is ABTS extinction coefficient [36,000 M−1 cm−1].
In order to determine the optimal conditions for laccase immobilization on biochars, the immobilization efficiency and residual laccase activity were calculated using the equations given in a study of Ilić et al. [22]:
Immobilization efficiency was calculated according to the following equation:
where Ci represents the free laccase protein concentration [mg/mL], and Cs is the concentration of proteins in washed supernatant [mg/mL].
2.2.4. Kinetics of Enzyme Immobilization
Adsorption kinetics assays were performed by analyzing total protein from aliquot supernatant at 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 180 and 240 min. The pseudo-first and pseudo-second-order model were applied in non-linear forms and fitted using non-linear regression analysis with OriginPro (2021 version) software. Summarized data containing applied kinetic models are given in Table S1.
2.2.5. Characterization of Laccase Immobilized Biochar
The functional groups of biochar before and after laccase immobilization were analyzed through Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). FTIR analysis was carried out using a Thermo Nicolet 6700 FTIR spectrometer (International Equipment Trading Ltd., Madison, WI, USA) within the 400–4000 cm−1 spectral range.
The surface morphology of the biochar and laccase-immobilized biochar was examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) to map the distribution of specific elements on surfaces of the material. SEM-EDX analysis was conducted using JEOL JSM-6610 LV SEM (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) on samples coated with a thin layer of gold.
The pH suspension (pHsus) of MSCS-B in water was determined according to the ASTM D6851-02 standard [24]. Moreover, 0.2 g of each sample was added to 30 mL of distilled water and placed in a closed container with stirring at room temperature for 72 h. Subsequently, the pHsus was measured using a SensION3 pH meter (Hach, Loveland, CO, USA).
2.2.6. Brilliant Green Decolorization
To prepare the BG stock solution with an initial concentration of 1000 mg/L, 1.0 g of BG powder was dissolved in distilled water. The experimental solutions of the desired concentration were prepared by the diluting method. To determine the optimal conditions for dye decolorization using laccase immobilized on biochar, the effects of dye concentration (10–500 mg/L), pH (3–7), temperature (20–50 °C), and contact time (1–6 h) were investigated. The specific amount of biochar with immobilized laccase was combined with 1 mL of dye solution. The decolorization efficiency (DE) was determined spectrophotometrically by measuring the absorbance of the dye at 625 nm using Equation (6):
where Ci and Cf are the initial and final dye concentrations [mg/L], respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Laccase Characterization
Laccase activity as a function of temperature is presented in Figure 1. The results demonstrate that laccase activity increases with rising temperatures from 20 °C to 30 °C, with maximum activity observed at 30 °C, indicating its optimal temperature. A similar optimal temperature was found by Taheran et al. [25] for laccase from T. versicolor. However, a further increase in temperature up to 60 °C leads to a significant decrease in the activity of laccase, with the enzyme becoming almost entirely inactive at the highest temperatures, with a relative activity of only 3%. This decline in laccase activity is probably due to enzyme denaturation caused by elevated temperatures, leading to a reduction in catalytic efficiency [16].
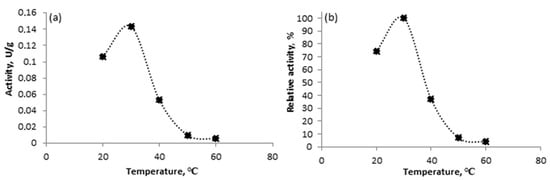
Figure 1.
Effect of temperature on the activity of free laccase from T. versicolor: (a) total activity; (b) relative activity.
3.2. Biochars Supports for Laccase Immobilization
The efficiency of enzyme immobilization onto MPS-B, MSCS-B and MPLS-B is calculated and presented in Figure 2. As shown in Figure 2, the immobilization efficiency was 62% for MSCS-B, 54% for MPLS-B, and 36% for MPS-B. Fatarella et al. [26] demonstrated an immobilization efficiency of 59.4% by immobilizing laccase on Nylon 6 film hydrolyzed by HCl under similar conditions, room temperature and pH = 4.5, but with a significantly longer contact time (12 h). Based on the presented results, MSCS-B demonstrates the highest effectiveness as a support for laccase immobilization, prompting further investigations with this biochar.
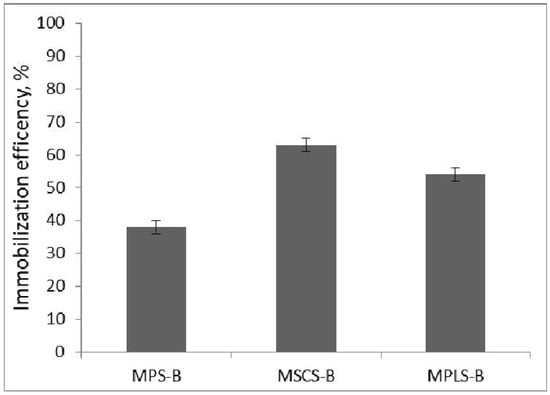
Figure 2.
Immobilization efficiency for different biochars.
Laccase immobilization on MSCS-B was achieved using the adsorption method. To optimize the immobilization conditions, various parameters such as pH, temperature, and incubation time were investigated to improve laccase immobilization. Two crucial parameters (residual activity and immobilization efficiency) were determined to evaluate the success of laccase immobilization on MSCS-B. The optimal pH value is crucial for enzyme activity; an inappropriate pH environment can lead to a loss of laccase activity or inactivation [16]. The effect of pH on immobilization is investigated and presented in Figure 3a. The results revealed that the greatest values of residual activity and immobilization efficiency were reached at pH 5.0, while further increases in pH led to a decrease in these parameters. At pH 5.0, the maximum residual activity was 81% and the highest immobilization efficiency was 74%, making this pH optimal for laccase immobilization on MSCS-B, and it was thus adopted for further investigations. These results align with a study by Al-Sareji et al. [27], who also demonstrated that pH 5 was optimal for the immobilization of laccase from T. versicolor on acid-treated carbon material. Temperature is also one of the key factors in laccase immobilization as enzymes are generally heat-sensitive and are active only within specific temperature ranges [20]. Figure 3b demonstrates the residual activity and immobilization efficiency of the immobilized laccase in relation to temperature. Both parameters increased with rising temperature, reaching their peak at 40 °C, with a residual activity of nearly 83% and immobilization efficiency of 60%. This optimum temperature likely reflects a balance between enhanced molecular mobility and enzyme activity, which facilitates better interactions between the laccase and the biochar as a support. However, at 50 °C, both parameters, residual activity and immobilization efficiency, decreased due to the thermal denaturation of the enzyme, which led to a loss of enzyme structure and function [28]. Taheran et al. [25] also reported that 40 °C is the optimal temperature for immobilizing laccase from T. versicolor onto polyacrylonitrile–biochar. Figure 3c illustrates the effect of contact time on the immobilization of laccase on MSCS-B. The residual activity and immobilization efficiency gradually increase with immobilization time, reaching their maximum values of 85% and 66%, respectively, at 4 h. The initial rise in immobilization efficiency was attributed to the extensive surface area of biochar available for laccase binding [29]. However, the immobilization efficiency declined to 61% and 57% at 5 and 6 h, respectively, revealing that a prolonged immobilization time did not lead to the maximum immobilization efficiency. A prolonged immobilization time can lead to enzyme leaching or detachment from the support due to mechanical forces, so ensuring the rapid immobilization of laccase on biochar is essential.
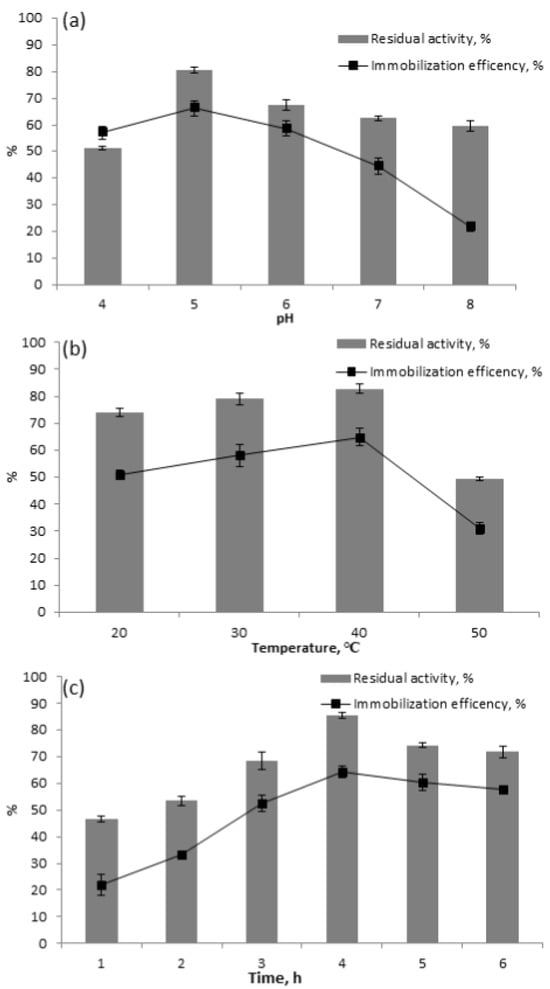
Figure 3.
Influence of (a) pH; (b) temperature; (c) contact time on immobilization efficiency and residual activity in the immobilization of laccase on MSCS-B.
3.3. Kinetics of Enzyme Immobilization
A kinetic study was conducted to determine the adsorption mechanism of laccase on MSCS-B. The experimental data are fitted by pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models; the obtained fitting data are given in Table 1, while the graphs are presented in Figure 4.

Table 1.
Parameters of applied kinetic models.
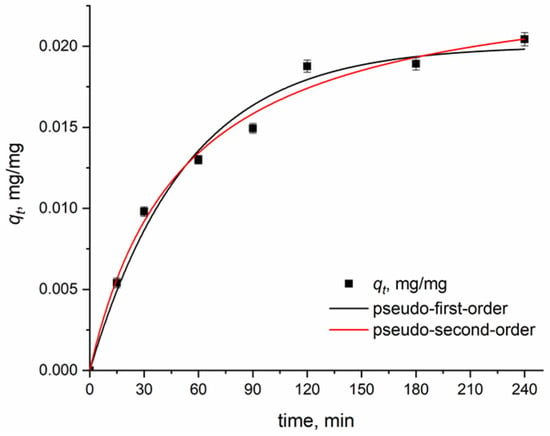
Figure 4.
Experimental data and non-linear fit for pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models for laccase immobilization on MSCS-B.
Based on the results presented in Table 1, it can be observed that the pseudo-second-order model better fits the experimental data compared with the pseudo-first-order model. The calculated qt value for pseudo-second order (0.0226 mg/mg) was closer to the experimental value (0.0214 mg/mg) than the value obtained from the pseudo-first-order model (0.0178 mg/mg). Additionally, the pseudo-first-order model exhibits lower correlation coefficients (R2) and higher chi-squared values (χ2) in relation to the pseudo-second-order model. On the other hand, the correlation coefficient for pseudo-second order was greater than 0.99, and it exhibited a low chi-squared value of only 5.71 × 10−7, which clearly indicated a better fit for the pseudo-second-order model. This implies that the adsorption mechanism is predominantly controlled by the binding interactions involving electron sharing between the enzyme and the support, suggesting that the chemical process might be a limiting factor in laccase adsorption [10]. Jafri et al. [21] also observed that pseudo-second order better describes the laccase adsorption onto magnetically separable hierarchically ordered mesoporous silica, obtaining an adsorption capacity of 0.0275 mg/mg.
3.4. Characterization of Laccase Immobilized Biochar
The material characterization using SEM imaging and EDX mapping provide a detailed analysis of surface morphology and elemental composition of the modified biochar samples before and after laccase immobilization-LMSCS-B (Figure 5). The SEM-EDX analysis of biochar derived from non-modified sour cherry stones conducted in our previous study [30] revealed a porous structure with irregular cracks and channels. After the acid treatment of the biochar (Figure 5a), a heterogeneous surface with deeper pores was observed, attributed to the removal of impurities from the pores by the acid treatment [7]. Similar findings are obtained by the SEM analysis of Al-sareji et al. [27], who investigated the effect of the acid treatment of activated carbon from a coconut shell. The SEM morphology of laccase immobilized on biochar, LMSCS-B (Figure 5b), did not reveal significant alterations in the surface topography. This is probably due to the relatively small dimension of the laccase protein, between 60 and 90 kDa [15], which corresponds to a particle size of less than 5 nanometers. Such a small dimension is difficult to capture by micrographs with a 1 µm magnification [31]. However, after laccase immobilization, the surface of MSCS-B appears smoother, which can be attributed to the enzyme coating on the surface of the biochar. The most important fact observed from the EDX analysis is the significant amount of nitrogen (7.86%) after enzyme adsorption, confirming the successful binding of laccase on the biochar surface. These findings are consistent with other studies that have investigated laccase immobilization on carbon materials [7,32,33].
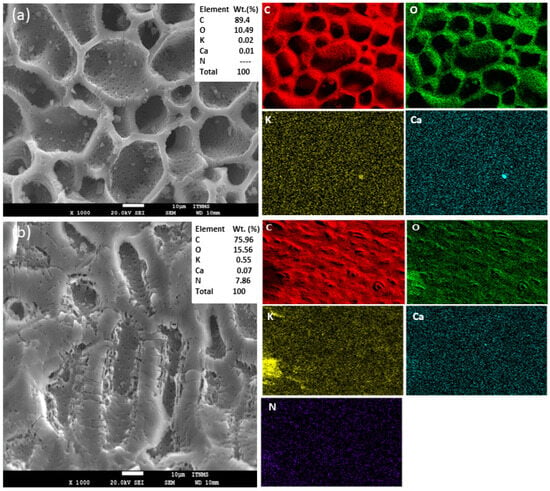
Figure 5.
SEM and EDX before and after immobilized laccase on biochar (a) MSCS-B; (b) LMSCS-B.
The FTIR spectra of MSCS-B and LMSCS-B recorded by FTIR analysis are shown in Figure 6. The sharp peak observed at 2916 cm−1 in LMSCS-B corresponds to the C–H stretching of the -CH2 group [34]. The peak at 2646 cm−1 suggests the presence of aliphatic (–CHn) groups in the biochar [30]. The broad bands at 1600–1703 cm−1 are attributed to the C=O stretching bonds in the carboxylic acid functional groups formed as a result of acid treatment [35]. During the functionalization process, the carbon structure breaks down, leading to an increased generation of an electric dipole. This behavior is due to the bonding of carboxyl groups on the biochar surfaces and the multiplication of defects caused by the oxidation of mixed acid [36]. After laccase immobilization, the signal peak at 1600 cm−1 increased, possibly owing to the additional carbonyl groups of the enzymes [14]. The broad peak observed around 1210 cm−1, related to the C–O stretching vibration of phenolic hydroxyl groups on the biochar’s surface, was followed by the appearance of a triplet at 1116, 1104 and 1080 cm−1 after laccase adsorption, which is characteristic of the laccase protein [37]. This finding supports the results obtained by the EDX analysis, which detected nitrogen, originating from these proteins. The broad absorption peaks between 756 and 872 cm−1 are associated with aromatic compounds present on the investigated sample’s surface [38].
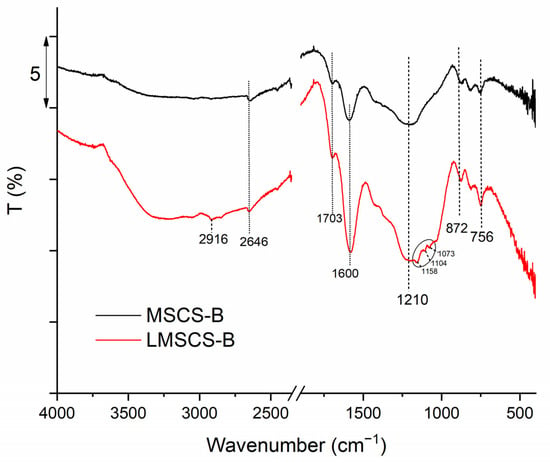
Figure 6.
FTIR spectra of MSCS-B and LMSCS-B.
Contact pH (pHsus) is indicative of the overall content of acidic or basic functional groups present on the biochar’s surface. MSCS-B has a pHsus of 4.18, which is lower compared to the pHsus of native sour cherry stone biochar (6.48) observed in our previous study [30]. The lower pHsus of the modified biochar is a result of acid treatment, which increased the content of acidic functional groups, such as carboxylic and phenolic groups, as confirmed by FTIR analysis. This is favorable for the immobilization of enzymes.
3.5. Brilliant Green Decolorization
After optimizing the immobilization process of laccase on the MSCS-B support, the oxidative activity of the immobilized enzyme was investigated for the decolorization of the toxic dye BG. To achieve efficient dye degradation and further optimize the process, various parameters were examined, including the influence of temperature, pH, time, and dye concentration. The results of these investigations are presented in Figure 7.
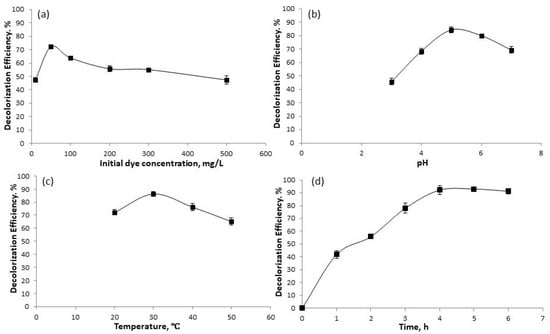
Figure 7.
Influence of operating parameters on decolorization of BG by LMSCS-B: (a) initial dye concentration; (b) pH; (c) temperature; (d) contact time.
The decolorization efficiency of the enzymatic removal of BG by immobilized laccase on biochar was investigated at different initial dye concentrations, ranging from 10 to 500 mg/L. The experiments were conducted at pH 6, a temperature of 20 °C, and a duration of 3 h. As illustrated in Figure 7a, the maximum decolorization efficiency of BG by LMSCS-B was achieved at a BG concentration of 50 mg/L, with a DE of 75%. Further, increased BG concentration led to a decrease in the decolorization of the dye. This can be explained by substrate inhibition and/or the limited availability of enzyme concentration, which led to a decrease in dye decolorization. Thakur et al. [39] reported the same trend in their study using laccase immobilized in alginate for dye removal.
The effect of pH on dye decolorization by laccase immobilized on biochar was investigated in the range of 3 to 7, with a BG concentration of 50 mg/L at a temperature of 20 °C for 3 h, as presented in Figure 7b. As can be seen from Figure 7b, the decolorization of BG improved with increasing the pH up to a value of 5.0 and then gradually decreased. At pH 3, the DE of BG was 45%, probably because the highly acidic pH altered the structure of the enzyme’s amino acid chains, disrupting its conformation and consequently diminishing its catalytic activity [27]. The maximum degradation of BG was recorded at pH 5, with a DE of almost 85%. Similar results were previously reported by Norah et al. [40], who also demonstrated that laccases exhibit optimal activity at pH 5 for dye degradation. It is important to emphasize that at pH 6, the DE of BG was slightly reduced but still reached 80%. This slight decrease in BG decolorization at pH 6 can be attributed to the partial loss of enzyme activity, which results in a change in the ionic form of the active site under suboptimal pH conditions [41].
The DE of BG by LMSCS-B was assessed at an initial dye concentration of 50 mg/L, with optimal pH (pH 5), over a period of 3 h, and across a wide range of temperatures (20, 30, 40, and 50 °C). According to Figure 7c, the decolorization of BG increased with rising temperatures from 20 to 30 °C, with the highest percentage of nearly 87% obtained at 30 °C. However, a further rise in temperature led to a reduction in the enzymatic DE. When the temperature was increased to 50 °C, the decolorization of BG decreased to about 20% caused by immobilized laccase, regarding its maximum values. Temperatures higher than the optimal one caused a negative effect on BG decolorization, likely due to changes in the conformational structure of laccase from thermal denaturation, which in turn decreased its DE [42]. Overall, the optimal temperature for dye degradation by immobilized laccase on different supports has been found to range between 25 and 30 °C in several studies [43,44,45].
The influence of contact time on LMSCS-B for the decolorization of BG was examined over a period of 1–6 h. The experiment was conducted under optimal conditions, including a BG concentration of 50 mg/L, a pH of 5, and a temperature of 30 °C. As can be seen in Figure 7d, LMSCS-B removed 41% of the dye within the first hour, while almost 93% was removed after 4 h. The high DE indicates that LMSCS-B demonstrates a significant capacity for decolorizing toxic dyes. The obtained results are consistent with the study by Chen et al. [46], where laccase immobilized onto magnetic graphene oxide removed 91% of BG within 3 h.
Table 2 summarizes the comparison of decolorization efficiency for commercial laccase immobilized on different solid supports. It is evident from Table 2 that the immobilization of laccase on biochar shows promising results for dye removal.

Table 2.
Comparison decolorization efficiency of commercial laccase immobilized on different solid carriers.
4. Conclusions
This paper presents results of the development of the cost-effective and sustainable enzyme immobilization support based on fruit processing waste biochar. Acid functionalized sour cherry stone biochar was utilized as a carrier for the immobilization of commercial laccase. The successful laccase immobilization was confirmed by characterization, via FTIR analysis, which revealed characteristic peaks corresponding to functional groups associated with the enzyme’s structure, supported by EDX analysis, which detected the presence of nitrogen, originating from the enzyme proteins. Under optimized conditions (pH 5, a temperature of 40 °C and an incubation time of 4 h), a high immobilization efficiency of 66% was achieved. The laccase adsorption on MSCS-B was found to follow the pseudo-second-order model, indicating a chemisorption mechanism, with a high correlation coefficient (R2 ≥ 0.99). Moreover, the immobilized system was applied to degrade BG, wherein almost 93% of dye was removed during 4 h at pH 5 and 30 °C, proving its excellent potential for wastewater treatment.
Despite the high efficiency of laccase immobilization and promising dye degradation results, certain aspects require further exploration. The scalability of the immobilization process could pose challenges in industrial applications, particularly in maintaining consistent biochar quality during large-scale production. Additionally, the long-term stability and reusability of the immobilized enzyme in complex wastewater environments need further investigation. Nonetheless, the current findings underscore the environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness of using waste biomass for enzyme immobilization.
Future research should focus on scaling up this process and integrating it into existing wastewater treatment systems. Exploring different enzymes or pollutants could broaden the application scope, while testing the system in real industrial conditions would enhance its practical value. Overall, this biochar–enzyme system has huge potential to become a versatile and sustainable solution for environmental management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr12112418/s1, Table S1: Kinetic models/equations. References [48,49] are cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and N.I.; methodology, S.D.-B., A.A. and N.I.; software, V.A.; validation, Z.L., S.D.-B. and M.M.; formal analysis, A.A. and N.I.; investigation, A.A.; resources, S.D.-B., A.A. and N.I.; data curation, A.A. and N.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, Z.L., S.D.-B., T.Š. and M.M.; visualization, V.A. and T.Š.; supervision, S.D.-B., M.M. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology Development of the Republic of Serbia (contract number: 451-03-66/2024-03/200023).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chapman, J.; Ismail, A.E.; Dinu, C.Z. Industrial applications of enzymes: Recent advances, techniques, and outlooks. Catalysts 2018, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, L.S.O.; de Oliveira, P.C.O.; Peixoto, B.S.; de Moraes, M.C. Enzyme-coated biochar as a sustainable solution for water and wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 2772–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeau, J.A.; Brar, S.K.; Tyagi, R.D. Laccases for removal of recalcitrant and emerging pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2331–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, D.; Daverey, A.; Arunachalam, K. Biochar: Production, properties and emerging role as a support for enzyme immobilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionowski, T.; Zdarta, J.; Krajewska, B. Enzyme immobilization by adsorption: A review. Adsorption 2014, 20, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijoy, G.; Rajeev, R.; Benny, L.; Jose, S.; Varghese, A. Enzyme immobilization on biomass-derived carbon materials as a sustainable approach towards environmental applications. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Daverey, A.; Dutta, K.; Arunachalam, K. Bioremoval of toxic malachite green from water through simultaneous decolorization and degradation using laccase immobilized biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopičić, Z.R.; Šoštarić, T.D.; Milojković, J.V.; Antanasković, A.V.; Milić, J.S.; Spasić, S.D.; Avdalović, J.S. Efficient Removal of Water Soluble Fraction of Diesel Oil by Biochar Sorption Supported by Microbiological Degradation. Processes 2024, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. Soil carbon sequestration and biochar as negative emission technologies. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopičić, Z.; Avdalović, J.; Milojković, J.; Antanasković, A.; Lješević, M.; Lugonja, N.; Šoštarić, T. Removal of diesel pollution by biochar—Support in water remediation. Hem. Ind. 2021, 75, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Sarkar, B.; Chang, S.X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar composition-dependent impacts on soil nutrient release, carbon mineralization, and potential environmental risk: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antanasković, A.; Lopičić, Z.; Pehlivan, E.; Adamović, V.; Šoštarić, T.; Milojković, J.; Milivojević, M. Thermochemical conversion of non-edible fruit waste for dye removal from wastewater. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 14, 18649–18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Aburiazaiza, A.S.; Miandad, R.; Rehan, M.; Barakat, M.A.; Nizami, A.S. Development of biochar as fuel and catalyst in energy recovery technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Piao, M.; He, L.; Yao, L.; Piao, T.; Liu, Z.; Piao, Y. Immobilization of laccase on magnetically separable biochar for highly efficient removal of bisphenol A in water. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 4795–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Liu, Y.; Rouissi, T.; Pourcel, F.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Covalent immobilization of laccase on citric acid functionalized micro-biochars derived from different feedstock and removal of diclofenac. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y. Laccase immobilization for water purification: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif Ur Rehman, M.; Kim, I.; Rashid, N.; Adeel Umer, M.; Sajid, M.; Han, J.I. Adsorption of Brilliant Green Dye on Biochar Prepared From Lignocellulosic Bioethanol Plant Waste. Clean Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariah, G.K.; Pak, K.S. Removal of brilliant green dye from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation using response surface methodology. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 20, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loqman, A.; El Bali, B.; Lützenkirchen, J.; Weidler, P.G.; Kherbeche, A. Adsorptive removal of crystal violet dye by a local clay and process optimization by response surface methodology. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3649–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sareji, O.J.; Meiczinger, M.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Grmasha, R.A.; Andredaki, M.; Somogyi, V.; Idowu, I.A.; Stenger-Kovács, C.; Jakab, M.; Lengyel, E.; et al. Efficient removal of pharmaceutical contaminants from water and wastewater using immobilized laccase on activated carbon derived from pomegranate peels. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Jafri, N.A.; Rahman, R.A.; Mohd Yusof, A.H.; Sulaiman, N.J.; Sukmawati, D.; Mohd Syukri, M.S. Adsorption kinetics of immobilized laccase on magnetically-separable hierarchically-ordered mesocellular mesoporous silica. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 22, 101445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, N.; Davidović, S.; Milić, M.; Lađarević, J.; Onjia, A.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S.; Mihajlovski, K. Green biocatalyst for decolorization of azo dyes from industrial wastewater: Coriolopsis trogii 2SMKN laccase immobilized on recycled brewer’s spent grain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 32072–32090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford assay for determining protein concentration. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020, 2020, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D6851-02; Standard Guide for Determination of the Water Content of Soil by the Oven Drying Method. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- Taheran, M.; Naghdi, M.; Brar, S.K.; Knystautas, E.J.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Degradation of chlortetracycline using immobilized laccase on Polyacrylonitrile-biochar composite nanofibrous membrane. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatarella, E.; Spinelli, D.; Ruzzante, M.; Pogni, R. Nylon 6 film and nanofiber carriers: Preparation and laccase immobilization performance. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014, 102, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-sareji, O.J.; Meiczinger, M.; Somogyi, V.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Grmasha, R.A.; Stenger-Kovács, C.; Jakab, M.; Hashim, K.S. Removal of emerging pollutants from water using enzyme-immobilized activated carbon from coconut shell. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doǧaç, Y.I.; Çinar, M.; Teke, M. Improving of catalase stability properties by encapsulation in alginate/Fe3O4 magnetic composite beads for enzymatic removal of H2O2. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 45, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, U.U.M.; Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A.; Kamarudin, N.H.A.; Latip, W.; Ali, M.S.M. Immobilization of Hyperthermostable Carboxylesterase EstD9 from Anoxybacillus geothermalis D9 onto Polymer Material and Its Physicochemical Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antanasković, A.; Lopičić, Z.; Šoštarić, T.; Adamović, V.; Cvetković, S.; Perendija, J.; Milivojević, M. Toxic dye removal by thermally modified lignocellulosic wastewaste in a three-phase air-lift reactor: Kinetic insights. Hem. Ind. 2024, 78, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonappan, L.; Liu, Y.; Rouissi, T.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Adsorptive immobilization of agro-industrially produced crude laccase on various micro-biochars and degradation of diclofenac. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yang, Y.; Kim, J.; Yao, L.; Dong, X.; Li, T.; Piao, Y. Multi-layered enzyme coating on highly conductive magnetic biochar nanoparticles for bisphenol A sensing in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristóvão, R.O.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Brígida, A.I.; Loureiro, J.M.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Macedo, E.A.; Coelho, M.A.Z. Immobilization of commercial laccase onto green coconut fiber by adsorption and its application for reactive textile dyes degradation. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 72, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, T.; Güler, S. Characterization and immobilization of Trametes versicolor laccase on magnetic chitosan-clay composite beads for phenol removal. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2015, 43, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, M.; Taheran, M.; Brar, S.K.; Kermanshahi-pour, A.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Immobilized laccase on oxygen functionalized nanobiochars through mineral acids treatment for removal of carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Song, H.J.; Wang, K.; Jiang, W. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes to improve the tribological properties of poly(furfuryl alcohol) composite coatings. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, A.; Sahu, S.K. One-pot synthesis of microporous nanoscale metal organic frameworks conjugated with laccase as a promising biocatalyst. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 4192–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.; Kleber, M. Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, D. Comparative Study of Dye Decolorization using free and Alginate Gel Entrapped Laccase from Cercospora sp. SPF-6. Adv. Biotechnol. Microbiol. 2018, 11, 555813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.M.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Harharah, H.N.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. The biocatalytic degradation of organic dyes using laccase immobilized magnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohidem, N.A.; Mat, H. The Catalytic Activity of Laccase Immobilized in Sol-Gel Silica. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 9, 3141–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilk, S.; Demircan, D.; Saglam, S.; Saglam, N.; Rzayev, Z.M.O. Immobilization of laccase onto a porous nanocomposite: Application for textile dye degradation. Turk. J. Chem. 2016, 40, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, K.; Ciesielczyk, F.; Bachosz, K.; Zdarta, J.; Kaczorek, E.; Jesionowski, T. Laccase immobilized onto zirconia-silica hybrid doped with Cu2+ as an effective biocatalytic system for decolorization of dyes. Materials 2019, 12, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amari, A.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Alsaiari, N.S.; Katubi, K.M.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. Magnetic metal organic framework immobilized laccase for wastewater decolorization. Processes 2021, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arica, M.Y.; Salih, B.; Celikbicak, O.; Bayramoglu, G. Immobilization of laccase on the fibrous polymer-grafted film and study of textile dye degradation by MALDI–ToF-MS. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 128, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Leng, J.; Yang, X.; Liao, L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, A. Enhanced performance of magnetic graphene oxide-immobilized laccase and its application for the decolorization of dyes. Molecules 2017, 22, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagoz, B.; Bayramoglu, G.; Altintas, B.; Bicak, N.; Yakup Arica, M. Amine functional monodisperse microbeads via precipitation polymerization of N-vinyl formamide: Immobilized laccase for benzidine based dyes degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6783–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the theory of so called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Veternskapsakad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).