The Effects of Coexisting Elements (Zn and Ni) on Cd Accumulation and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in the Soil-Tomato System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant Culture
2.4. Determination of Plant Growth
2.5. Determination of HM Contents
2.6. Microbial Analysis of the Soil Samples
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Cd, Zn, and Ni on Plant Growth
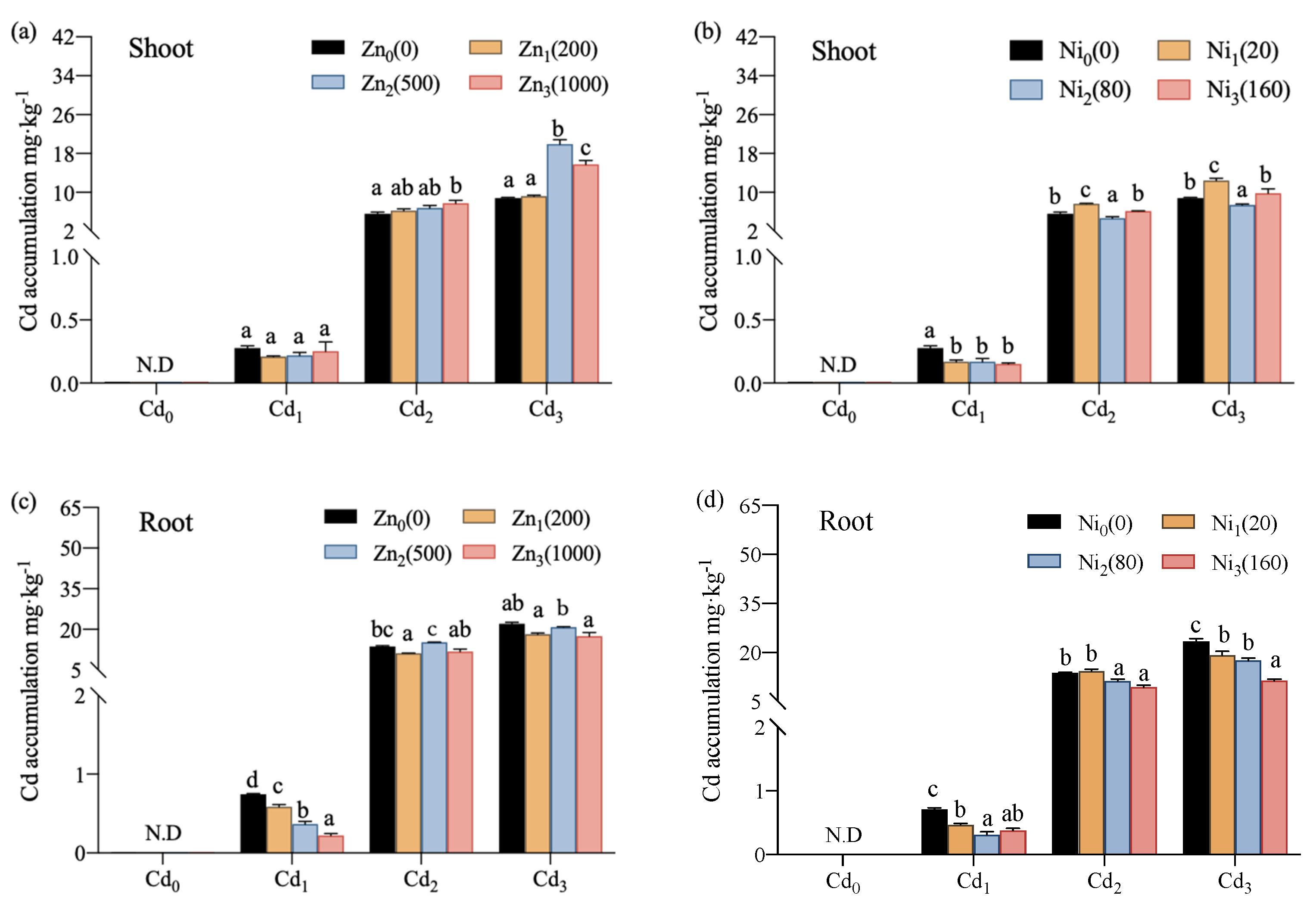
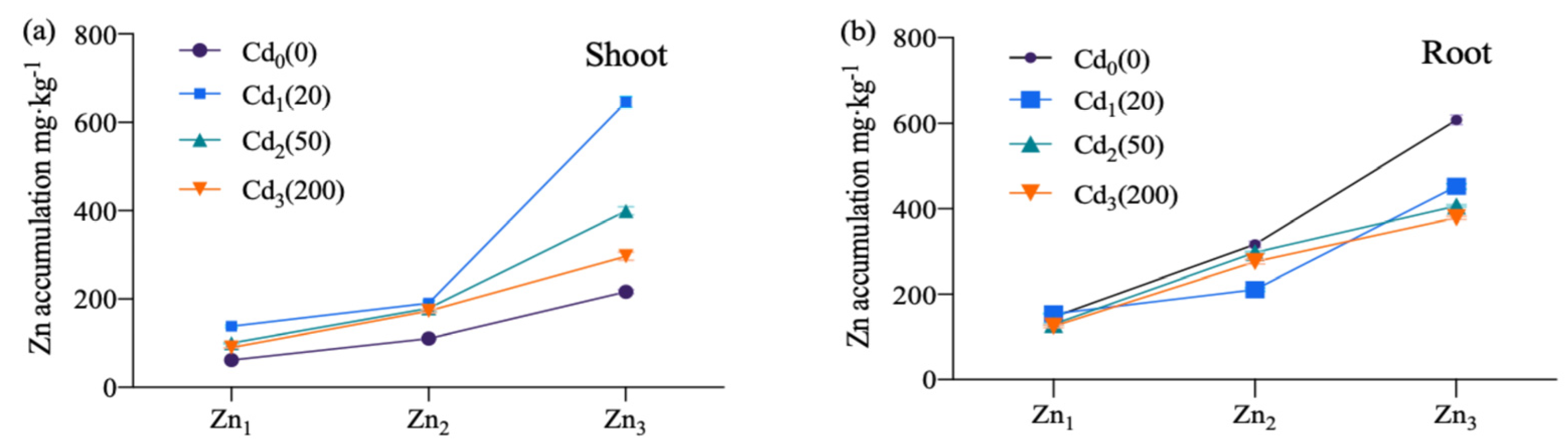
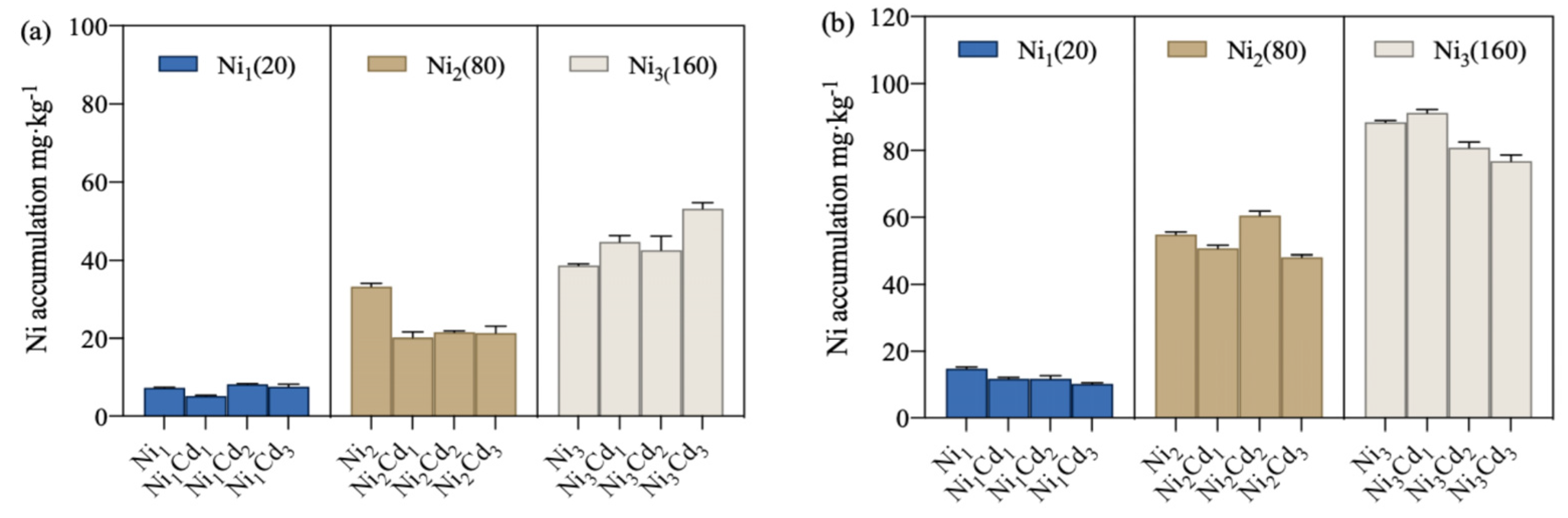
3.2. Accumulation and Transformation of Cd, Zn, and Ni in Tomato Plants
3.3. Effects of Cd, Zn, and Ni on the Community Diversity of the Soil Microorganisms
3.4. Effects of Cd, Zn, and Ni on the Community Structure of the Soil Microorganisms
3.4.1. Microbial Community at the Phylum Level
3.4.2. Microbial Community at the Genus Level
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Fu, W. Risk Assessment, Spatial Patterns and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals in a Typical Chinese Hickory Plantation Region of Southeastern China. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEP); Ministry of Land and Resources of China (MLR). National Soil Pollution Investigation Bulletin; MEP: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- National Environmental Protection Agency of the People’s Republic of China (NEPA); China State Administration for Market Regulation (CSAMR). GB15618-1995; Environmental Quality Standards for Soils. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1995. (In Chinese)
- Shi, J.; Zhao, D.; Ren, F.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal Variation of Soil Heavy Metals in China: The Pollution Status and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEP); China State Administration for Market Regulation (CSAMR). GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar Heavy Metal Uptake, Toxicity and Detoxification in Plants: A Comparison of Foliar and Root Metal Uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Ashraf, M.A.; Rasheed, R.; Iqbal, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Zahid, T.; Thind, S.; Saeed, F. Cadmium-Induced Perturbations in Growth, Oxidative Defense System, Catalase Gene Expression and Fruit Quality in Tomato. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2017, 19, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.M.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant Science: The Key to Preventing Slow Cadmium Poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofy, A.R.; Sofy, M.R.; Hmed, A.A.; Dawoud, R.A.; Alnaggar, A.E.-A.M.; Soliman, A.M.; El-Dougdoug, N.K. Ameliorating the Adverse Effects of Tomato Mosaic Tobamovirus Infecting Tomato Plants in Egypt by Boosting Immunity in Tomato Plants Using Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Molecules 2021, 26, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Rinklebe, J.; Tack, F.M.G.; Ok, Y.S. A Critical Review on Effects, Tolerance Mechanisms and Management of Cadmium in Vegetables. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Rizvi, H.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Hannan, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Hafeez, F.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium Stress in Rice: Toxic Effects, Tolerance Mechanisms, and Management: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17859–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Zhong, H.; Tack, F.M.G.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.-F.; Gao, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Speciation, Transportation, and Pathways of Cadmium in Soil-Rice Systems: A Review on the Environmental Implications and Remediation Approaches for Food Safety. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Millán, A.-F.; Sagardoy, R.; Solanas, M.; Abadía, A.; Abadía, J. Cadmium Toxicity in Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) Plants Grown in Hydroponics. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 65, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küpper, H.; Andresen, E. Mechanisms of Metal Toxicity in Plants. Metallomics 2016, 8, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, K.; Tian, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chai, T. Wheat Cell Number Regulator CNR10 Enhances the Tolerance, Translocation, and Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Shao, S.; Fu, T.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, L.; Chen, S.; Shi, Z. Composite Assessment of Human Health Risk from Potentially Toxic Elements through Multiple Exposure Routes: A Case Study in Farmland in an Important Industrial City in East China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 210, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Nagpal, A.K. Contamination of Vegetables with Heavy Metals across the Globe: Hampering Food Security Goal. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Shabnam, A.A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Malyan, S.K.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Gupta, D.K.; et al. Nickel in Terrestrial Biota: Comprehensive Review on Contamination, Toxicity, Tolerance and Its Remediation Approaches. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Aarts, M.G.M. Opportunities and Feasibilities for Biotechnological Improvement of Zn, Cd or Ni Tolerance and Accumulation in Plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 72, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gui, H. Distribution Features and Internal Relations of Heavy Metals in Soil–Maize System of Mining Area, Anhui Province, Eastern China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Z. The Role of Nickel in Cadmium Accumulation in Rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, X.; Ren, W. Effects of Cadmium on Uptake and Translocation of Nutrient Elements in Different Welsh Onion (Allium fistulosum L.) Cultivars. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y. Mechanisms and Uncertainties of Zn Supply on Regulating Rice Cd Uptake. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gu, C.; Bai, Y.; Zuo, W. Impact of Organic Amendments on the Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Mudflat Soil and Their Uptake by Maize. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63799–63814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.E.; Chaney, R.L.; Bouwkamp, J. Increased Zinc Supply Does Not Inhibit Cadmium Accumulation by Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 40, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Sun, L.; Lu, T.; Qian, H. Shaping Effects of Rice, Wheat, Maize, and Soybean Seedlings on Their Rhizosphere Microbial Community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 35972–35984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Henrik Nilsson, R.; Larsson, K.; Alexander, I.J.; Eberhardt, U.; Erland, S.; Høiland, K.; Kjøller, R.; Larsson, E.; Pennanen, T.; et al. The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification of Fungi—Recent Updates and Future Perspectives. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Yao, H. Effects of Lead and Cadmium Nitrate on Biomass and Substrate Utilization Pattern of Soil Microbial Communities. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Nasir, M.; Lv, J.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J. Understanding the Variation of Microbial Community in Heavy Metals Contaminated Soil Using High Throughput Sequencing. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Composition Affects Cadmium and Arsenic Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, C.; Zheng, X.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; et al. Combined Apatite, Biochar, and Organic Fertilizer Application for Heavy Metal Co-Contaminated Soil Remediation Reduces Heavy Metal Transport and Alters Soil Microbial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.W.; Li, Z.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z.H. The Effect of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) on Arsenic Accumulation and the Growth of Rice Plants (Oryza sativa L.). Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.M.; Saeed, A.; Khan, A.A.; Javid, S.; Fatima, B. Differential Responses of One Hundred Tomato Genotypes Grown under Cadmium Stress. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 13162–13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-M.; Tan, X.-Q.; Mei, X.-Q.; Li, Q.-S.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L.-L.; Ye, H.-J.; Yang, P. Low-Cd Tomato Cultivars (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Screened in Non-Saline Soils Also Accumulated Low Cd, Zn, and Cu in Heavy Metal-Polluted Saline Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27439–27450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Environmental Protection Agency of the People’s Republic of China (NEPA). HJ/T 166-2004; The Technical Specification for soil Environmental monitoring. China Environment Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese)
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Sui, Y.; Suvannang, N.; Zhou, J.; Sun, B. Crop Rotations Alter Bacterial and Fungal Diversity in Paddy Soils across East Asia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaibeh, M.A.; Marschner, B.; Heinze, S. Metal Uptake of Tomato and Alfalfa Plants as Affected by Water Source, Salinity, and Cd and Zn Levels under Greenhouse Conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18894–18905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Z. The Effects of Dark Septate Endophyte (DSE) Inoculation on Tomato Seedlings under Zn and Cd Stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35232–35241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, M.; Ameen, N.; Murtaza, B.; Imran, M.; Shahid, M.; Abbas, G.; Naeem, M.A.; Jacobsen, S. Comparative Physiological and Biochemical Evaluation of Salt and Nickel Tolerance Mechanisms in Two Contrasting Tomato Genotypes. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 168, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.O. Nitric-perchloric wet acid digestion in an open vessel. In Handbook of Reference Methods for Plant Analysis; Kalra, Y.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, G.; Jin, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Qu, J. Organic Amendment Improves Rhizosphere Environment and Shapes Soil Bacterial Community in Black and Red Soil under Lead Stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Liu, X.; Cui, B.; Bai, J.; Wang, X. Concentration-Dependent Alterations in Gene Expression Induced by Cadmium in Solanum Lycopersicum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10528–10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Xie, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, X. Network Response of Two Cherry Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) Cultivars to Cadmium Stress as Revealed by Transcriptome Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shentu, J.; He, Z.; Yang, X.-E.; Li, T. Accumulation Properties of Cadmium in a Selected Vegetable-Rotation System of Southeastern China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6382–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarkson, D.T.; Hanson, J.B. The Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1980, 31, 239–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Hernandez, J.-A.; Solano-Alvarez, N.; Rico-Rodriguez, M.-A.; Rodriguez-Ontiveros, A.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Rico-Garcia, E.; Guevara-Gonzalez, R.-G. Eustressic Dose of Cadmium in Soil Induces Defense Mechanisms and Protection Against Clavibacter Michiganensis in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, W.N.; Green, C.E.; Beyer, M.; Chaney, R.L. Phytotoxicity of Zinc and Manganese to Seedlings Grown in Soil Contaminated by Zinc Smelting. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 179, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Maqbool, A. A Critical Review on the Effects of Zinc at Toxic Levels of Cadmium in Plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6279–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghori, N.-H.; Ghori, T.; Hayat, M.Q.; Imadi, S.R.; Gul, A.; Altay, V.; Ozturk, M. Heavy Metal Stress and Responses in Plants. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzarti, S.; Mohri, S.; Ono, Y. Plant Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity: Comparative Study between the Hyperaccumulator Thlaspi Caerulescens (Ecotype Ganges) and Nonaccumulator Plants: Lettuce, Radish, and Alfalfa. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, I.; Sohail, H.; Sun, J.; Nawaz, M.A.; Li, G.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Liu, J. Heavy Metal and Metalloid Toxicity in Horticultural Plants: Tolerance Mechanism and Remediation Strategies. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Wei, T.; Zhou, R.; Muhammad, H.; Hua, L.; Ren, X.; Guo, J.; Ding, Y. Accumulation and Fixation of Cd by Tomato Cell Wall Pectin under Cd Stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 167, 103829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Hussain, S.; Rengel, Z. Zinc Fertilisation Increases Grain Zinc and Reduces Grain Lead and Cadmium Concentrations More in Zinc-Biofortified than Standard Wheat Cultivar. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Shi, K.; Hu, C.; Guo, J.; Tan, Q.; Sun, X. Non-Invasive Microelectrode Cadmium Flux Measurements Reveal the Decrease of Cadmium Uptake by Zinc Supply in Pakchoi Root (Brassica chinensis L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, U.-H.; Park, J.-O. Distribution and Phytotoxicity of Cadmium in Tomato Seedlings. J. Plant Biol. 1999, 42, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.-L.; Thangavel, P.; Hu, P.-J.; Senthilkumar, P.; Ying, R.-R.; Tang, Y.-T. Interaction of Cadmium and Zinc on Accumulation and Sub-Cellular Distribution in Leaves of Hyperaccumulator Potentilla Griffithii. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ishimaru, Y.; Shimo, H.; Ogo, Y.; Senoura, T.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H. The OsHMA2 Transporter Is Involved in Root-to-Shoot Translocation of Zn and Cd in Rice: Characterization of OsHMA2. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, M.; Tabatabaei, B.E.S.; Akbarzadeh, H. Hyperaccumulation of Cu, Zn, Ni, and Cd in Azolla Species Inducing Expression of Methallothionein and Phytochelatin Synthase Genes. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Phenolic Metabolism and Related Heavy Metal Tolerance Mechanism in Kandelia Obovata under Cd and Zn Stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manquián-Cerda, K.; Escudey, M.; Zúñiga, G.; Arancibia-Miranda, N.; Molina, M.; Cruces, E. Effect of Cadmium on Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Oxidative Stress in Blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) Plantlets Grown in Vitro. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, X.; Guo, X.; Pan, Y.; Yu, B.; Tang, Z.; Guo, Q. Differential Responses to Cd Stress Induced by Exogenous Application of Cu, Zn or Ca in the Medicinal Plant Catharanthus Roseus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkhonsin, B.; Nakbanpote, W.; Hokura, A.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Maneechai, S. Phenolic Compounds Responding to Zinc and/or Cadmium Treatments in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC. Extracts and Biomass. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zeng, J.; Ming, X.; He, Q.; Tao, Q.; Jiang, M.; Gao, S.; Li, X.; Lei, T.; Pan, Y.; et al. The Presence of Zinc Reduced Cadmium Uptake and Translocation in Cosmos Bipinnatus Seedlings under Cadmium/Zinc Combined Stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Liu, D.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.-X.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Chen, X.-P.; Zou, C.-Q. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals (Zn, Cu, Cd, Pb, As and Cr) in Wheat Grain Receiving Repeated Zn Fertilizers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M. A Comparative Study of the Factors Affecting Uptake and Distribution of Cd with Ni in Barley. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.A.; James, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ahmed Saqib, H.S.; Li, H.H.; Jayasuriya, P.; Guo, W. Uptake, Translocation, and Accumulation of Cd and Its Interaction with Mineral Nutrients (Fe, Zn, Ni, Ca, Mg) in Upland Rice. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of P.R. China (NHFPC); National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). GB 27622017; National Standard for Food Security-the Maximum Allowable Levels of Contaminants in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Margesin, R.; Płaza, G.A.; Kasenbacher, S. Characterization of Bacterial Communities at Heavy-Metal-Contaminated Sites. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudjordjie, E.N.; Sapkota, R.; Steffensen, S.K.; Fomsgaard, I.S.; Nicolaisen, M. Maize Synthesized Benzoxazinoids Affect the Host Associated Microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Li, B.; Yang, Y. Cd Accumulation Characteristics of Salvia Tiliifolia and Changes of Rhizospheric Soil Enzyme Activities and Bacterial Communities under a Cd Concentration Gradient. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Bai, L.; Zhang, K.; He, H.; Dai, J. Cultivar-Specific Response of Rhizosphere Bacterial Community to Uptake of Cadmium and Mineral Elements in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 249, 114403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Sun, W.; Chen, Q. Bioavailable Metal(Loid)s and Physicochemical Features Co-Mediating Microbial Communities at Combined Metal(Loid) Pollution Sites. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martínez, V.; Bell, C.W.; Morris, B.E.L.; Zak, J.; Allen, V.G. Long-Term Soil Microbial Community and Enzyme Activity Responses to an Integrated Cropping-Livestock System in a Semi-Arid Region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zou, R.; Li, Y.C.; Tong, Z.; You, M.; Huo, W.; Chi, K.; Fan, H. Effect of Wheat-Solanum Nigrum L. Intercropping on Cd Accumulation by Plants and Soil Bacterial Community under Cd Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-L.; Zheng, M.-M.; Liao, H.-M.; Tan, A.-J.; Feng, D.; Lv, S.-M. Influence of Cadmium and Microplastics on Physiological Responses, Ultrastructure and Rhizosphere Microbial Community of Duckweed. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Cui, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. Improvement of Alfalfa Resistance against Cd Stress through Rhizobia and Arbuscular Mycorrhiza Fungi Co-Inoculation in Cd-Contaminated Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Ecological Responses of Soil Microbial Abundance and Diversity to Cadmium and Soil Properties in Farmland around an Enterprise-Intensive Region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlings, D.E.; Johnson, D.B. The Microbiology of Biomining: Development and Optimization of Mineral-Oxidizing Microbial Consortia. Microbiology 2007, 153, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhong, Q.; Yun, Y.-H.; Chen, W.; Chen, W. Determination of Microbial Diversity and Community Composition in Unfermented and Fermented Washing Rice Water by High-Throughput Sequencing. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. The Variation in Microbial Community Structure under Different Heavy Metal Contamination Levels in Paddy Soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.; Herman, D.J.; Rijkers, R.; Estera, K.; Li, J.; da Rocha, U.N.; He, Z.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Brodie, E.L.; et al. Successional Trajectories of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities over Consecutive Seasons. mBio 2015, 6, e00746-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Lu, D.; Qi, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, L.; Geng, N.; Xu, C.; Hua, E. Removal of Nitrate from Agricultural Runoff in Biochar Electrode Based Biofilm Reactor: Performance and Enhancement Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, R.; Sun, L.; He, L.; Sheng, X. Cadmium-Resistant and Arginine Decarboxylase-Producing Endophytic Sphingomonas Sp. C40 Decreases Cadmium Accumulation in Host Rice (Oryza Sativa Cliangyou 513). Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangaromsuk, J.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Kruatrachue, M.; Upatham, E.S. Cadmium Biosorption by Sphingomonas Paucimobilis Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 85, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Fan, M.; Wang, E.; Chen, W.; Wei, G. Interactions of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria and Soil Factors in Two Leguminous Plants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 8485–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
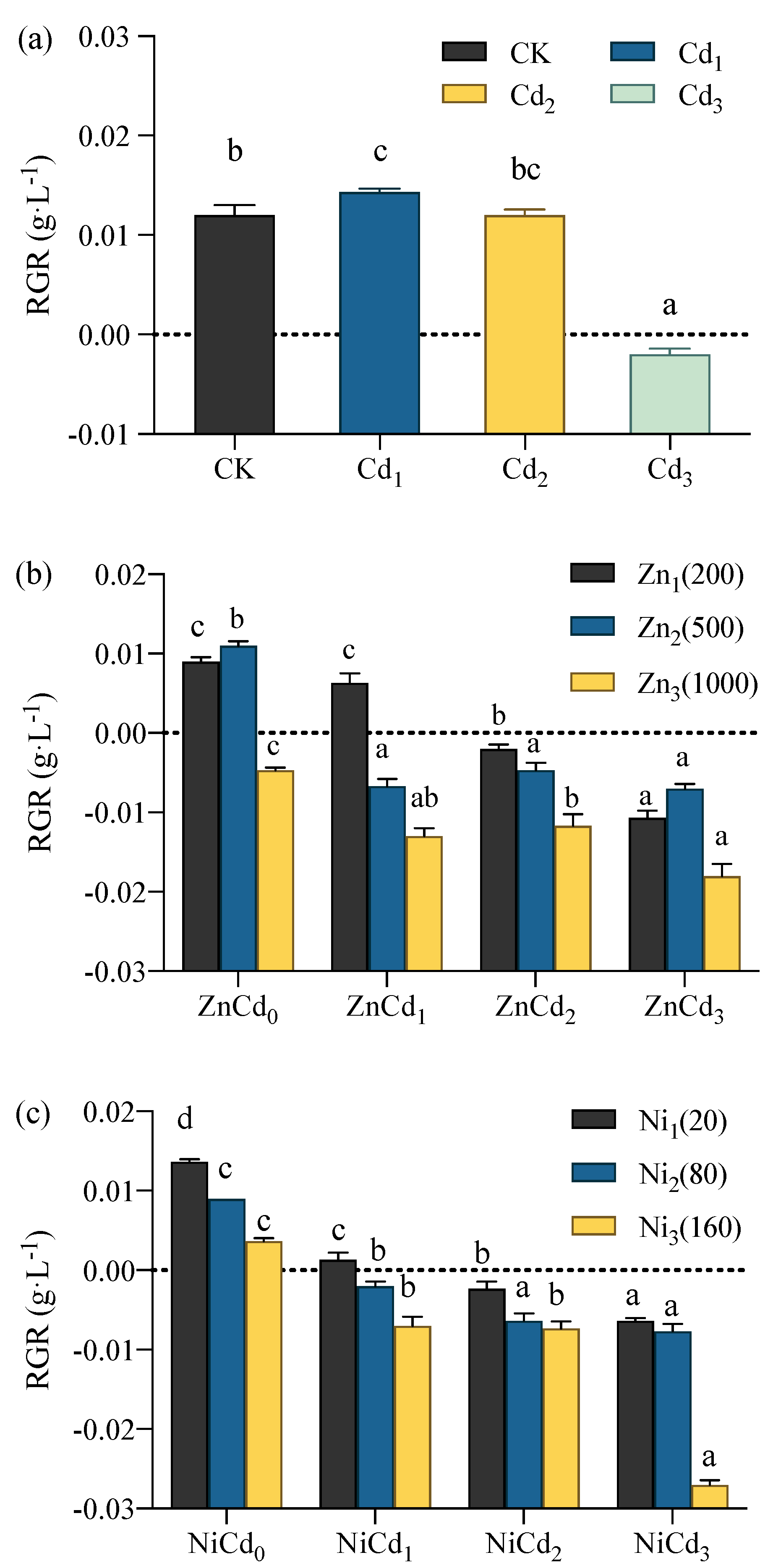
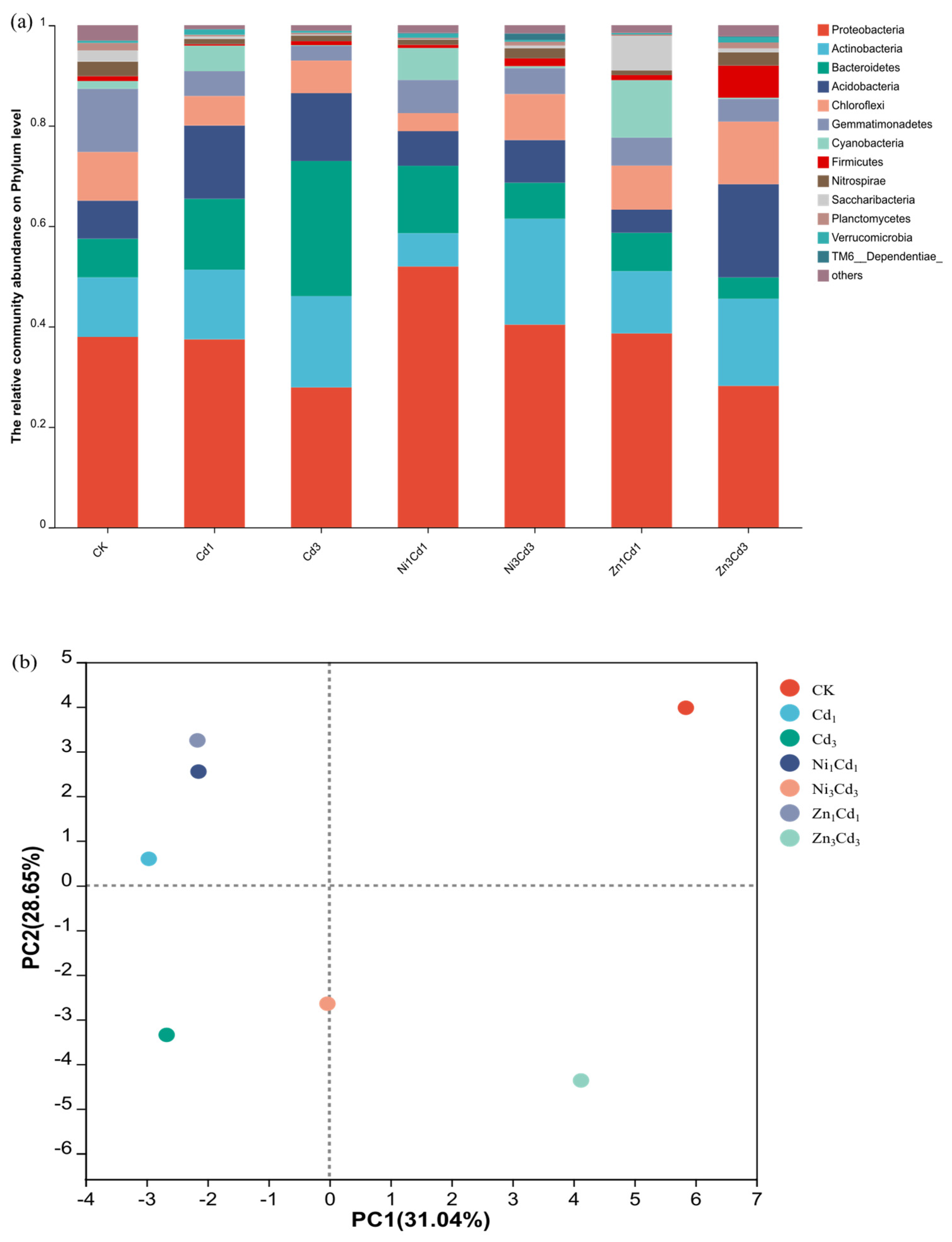
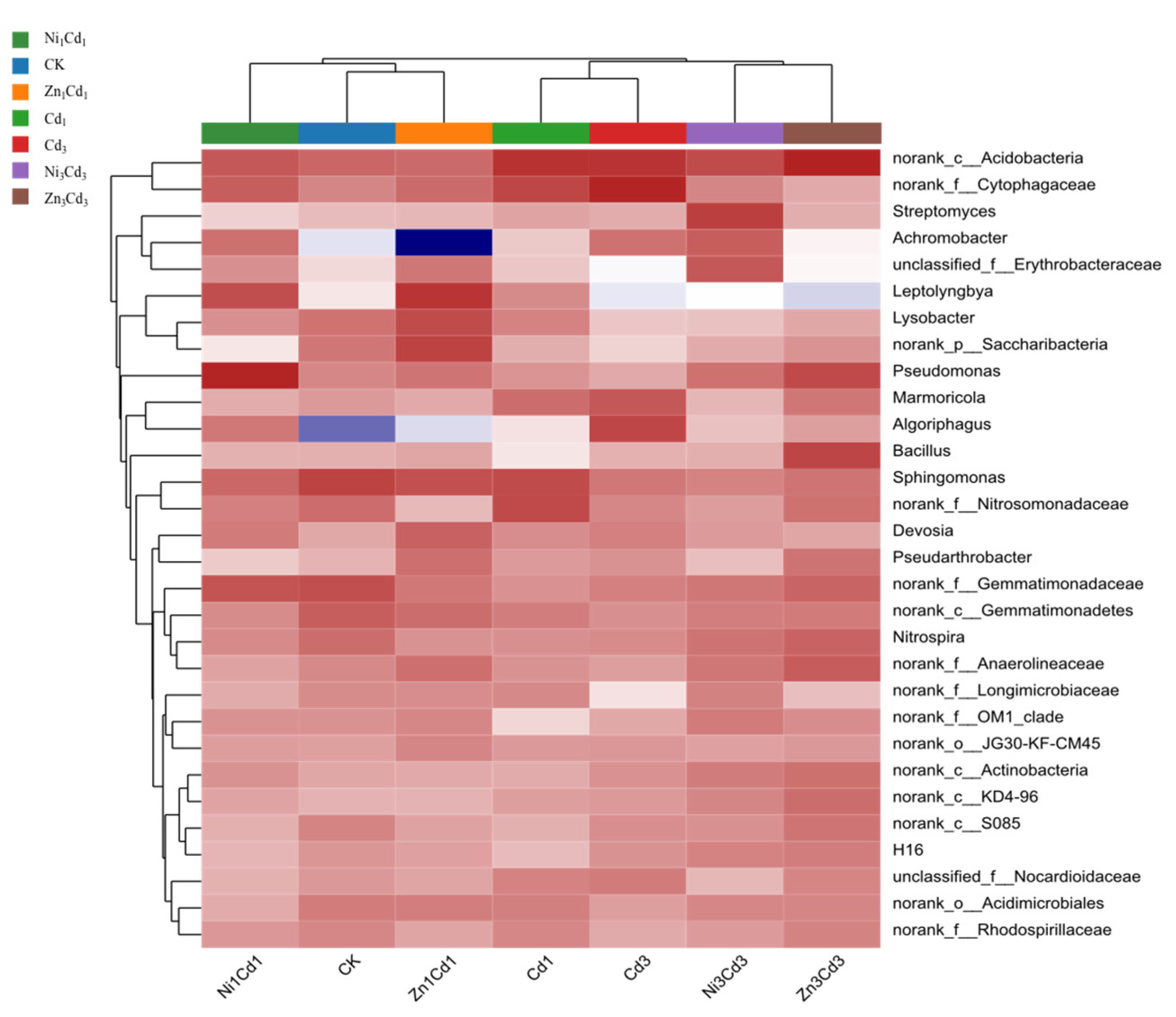
| Treatment Groups | Cd Concentration | Zn Concentration | Ni Concentration | Nomenclature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd single treatment | 0 | 0 | 0 | Cd0(CK) |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Cd1 | |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | Cd2 | |
| 50 | 0 | 0 | Cd3 | |
| Cd combined with Zn treatments | 0 | 200 | 0 | Zn1Cd0 |
| 1 | 200 | 0 | Zn1Cd1 | |
| 20 | 200 | 0 | Zn1Cd2 | |
| 50 | 200 | – | Zn1Cd3 | |
| 0 | 500 | 0 | Zn2Cd0 | |
| 1 | 500 | 0 | Zn2Cd1 | |
| 20 | 500 | – | Zn2Cd2 | |
| 50 | 500 | – | Zn2Cd3 | |
| 0 | 1000 | 0 | Zn3Cd0 | |
| 1 | 1000 | 0 | Zn3Cd1 | |
| 20 | 1000 | 0 | Zn3Cd2 | |
| 50 | 1000 | 0 | Zn3Cd3 | |
| Cd combined with Ni treatments | 0 | 0 | 20 | Ni1Cd0 |
| 1 | 0 | 20 | Ni1Cd1 | |
| 20 | 0 | 20 | Ni1Cd2 | |
| 50 | 0 | 20 | Ni1Cd3 | |
| 0 | 0 | 80 | Ni2Cd0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 80 | Ni2Cd1 | |
| 20 | 0 | 80 | Ni2Cd2 | |
| 50 | 0 | 80 | Ni2Cd3 | |
| 0 | 0 | 160 | Ni3Cd0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 160 | Ni3Cd1 | |
| 20 | 0 | 160 | Ni3Cd2 | |
| 50 | 0 | 160 | Ni3Cd3 |
| System | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.991645 | 0.004494 | 4196.907 | 4198.966 | 0.982454 |
| Cd1 | 6.072421 | 0.006859 | 2857.150 | 2846.419 | 0.984998 |
| Cd3 | 5.823361 | 0.020838 | 3063.735 | 3014.942 | 0.984634 |
| Zn1Cd1 | 6.070820 | 0.007931 | 2932.663 | 2938.172 | 0.985992 |
| Zn3Cd3 | 6.757506 | 0.004557 | 4106.077 | 4030.048 | 0.985002 |
| Ni1Cd1 | 5.706493 | 0.011493 | 2876.45 | 2862.277 | 0.986712 |
| Ni3Cd3 | 6.066191 | 0.012557 | 3875.397 | 3810.785 | 0.979581 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Feng, L. The Effects of Coexisting Elements (Zn and Ni) on Cd Accumulation and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in the Soil-Tomato System. Processes 2023, 11, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051523
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Sun G, Feng L. The Effects of Coexisting Elements (Zn and Ni) on Cd Accumulation and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in the Soil-Tomato System. Processes. 2023; 11(5):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051523
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yufeng, Yuhui Wang, Guojin Sun, and Lu Feng. 2023. "The Effects of Coexisting Elements (Zn and Ni) on Cd Accumulation and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in the Soil-Tomato System" Processes 11, no. 5: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051523
APA StyleZhao, Y., Wang, Y., Sun, G., & Feng, L. (2023). The Effects of Coexisting Elements (Zn and Ni) on Cd Accumulation and Rhizosphere Bacterial Community in the Soil-Tomato System. Processes, 11(5), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051523






