Performance Evaluation of Hydroponic Wastewater Treatment Plant Integrated with Ensemble Learning Techniques: A Feature Selection Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Research Area
2.3. Proposed Models
2.4. Error Ensemble Learning Approach Development
2.4.1. Simple Averaging Ensemble (SAE)
2.4.2. Weighted Averaging Ensemble (WAE)
2.4.3. Nonlinear Neural Ensemble (NNE)
3. Results of Single Models ANN, SVM, ANFIS, and MLR
3.1. Results of TDSt (ANN, SVM, ANFIS, and MLR)
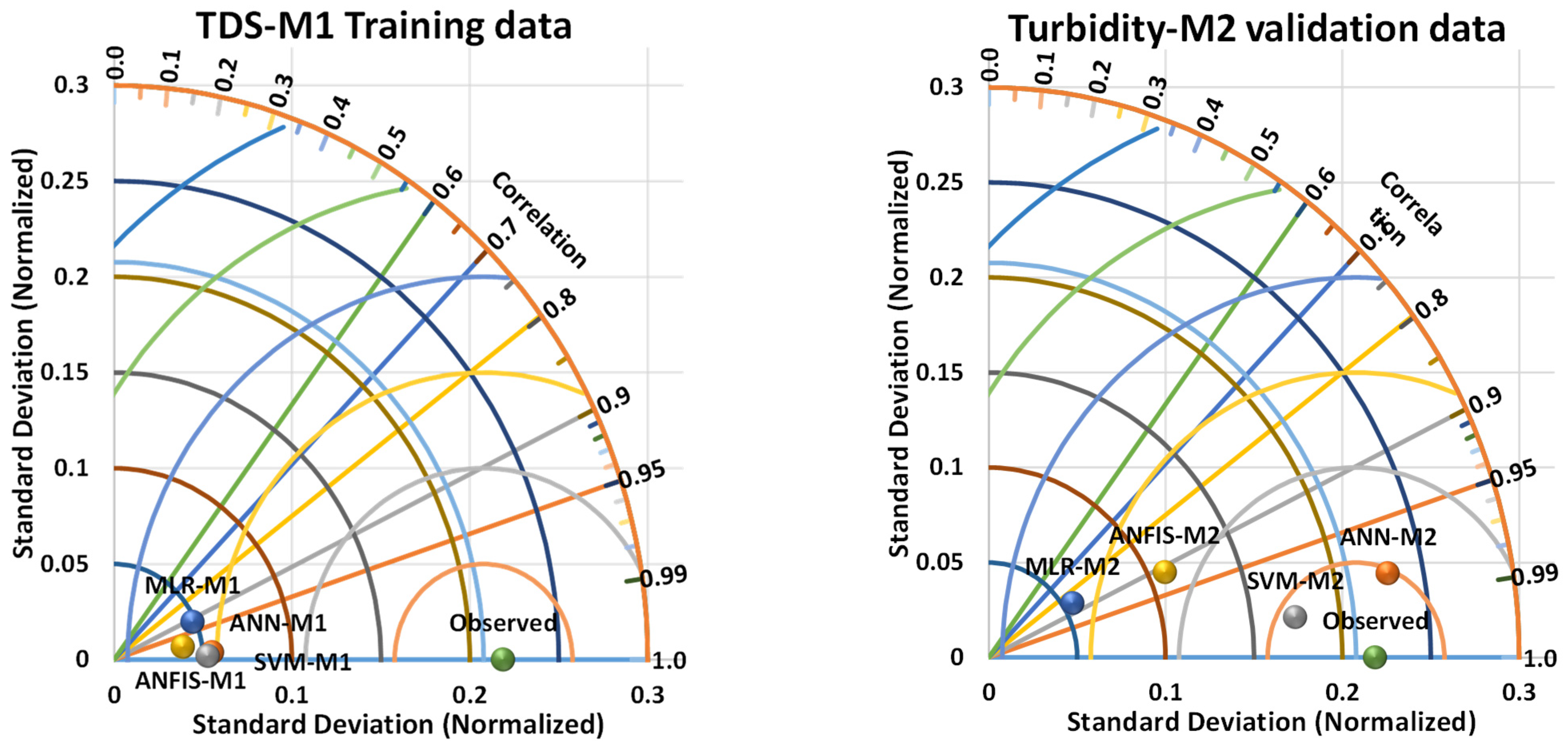
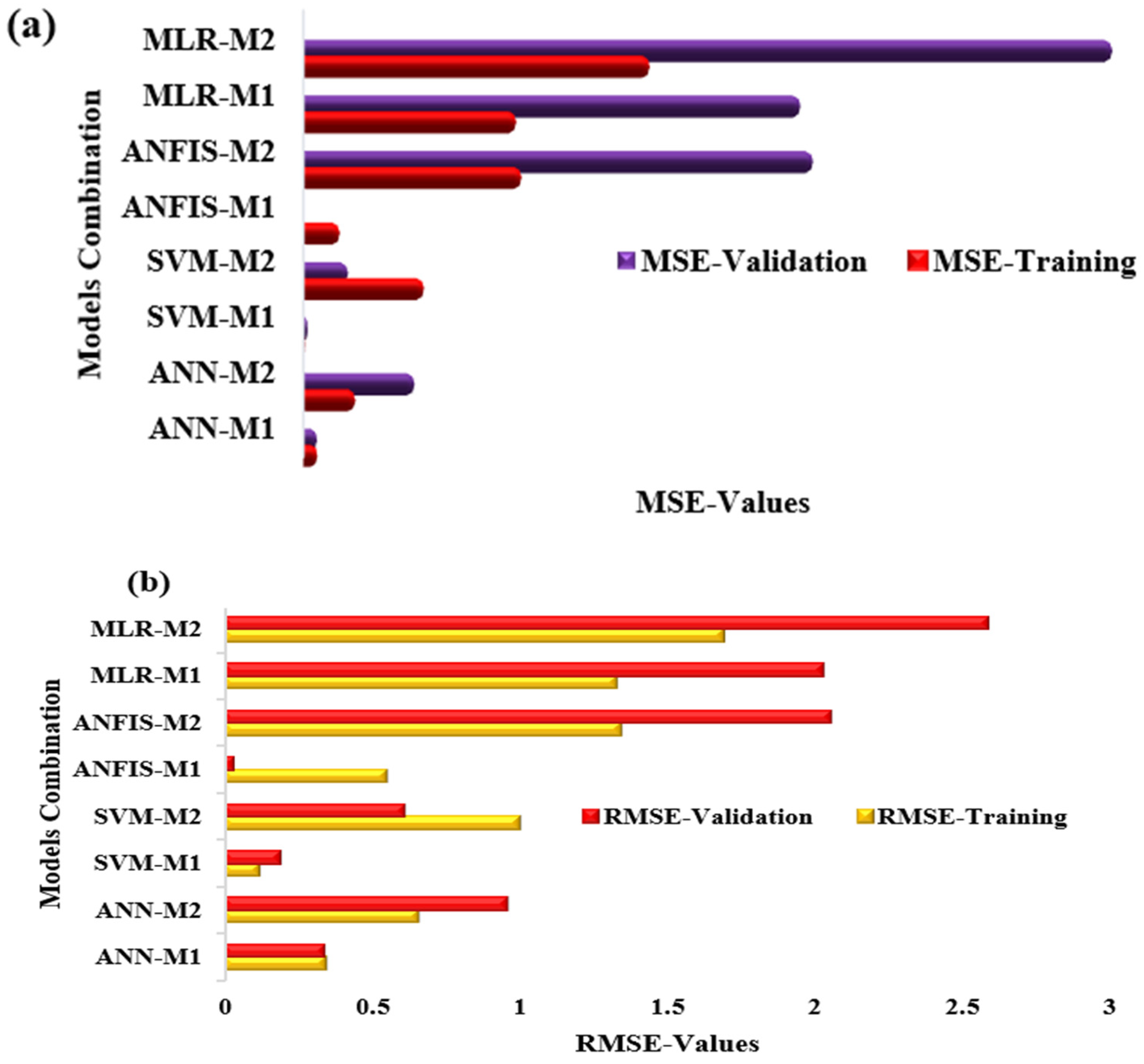
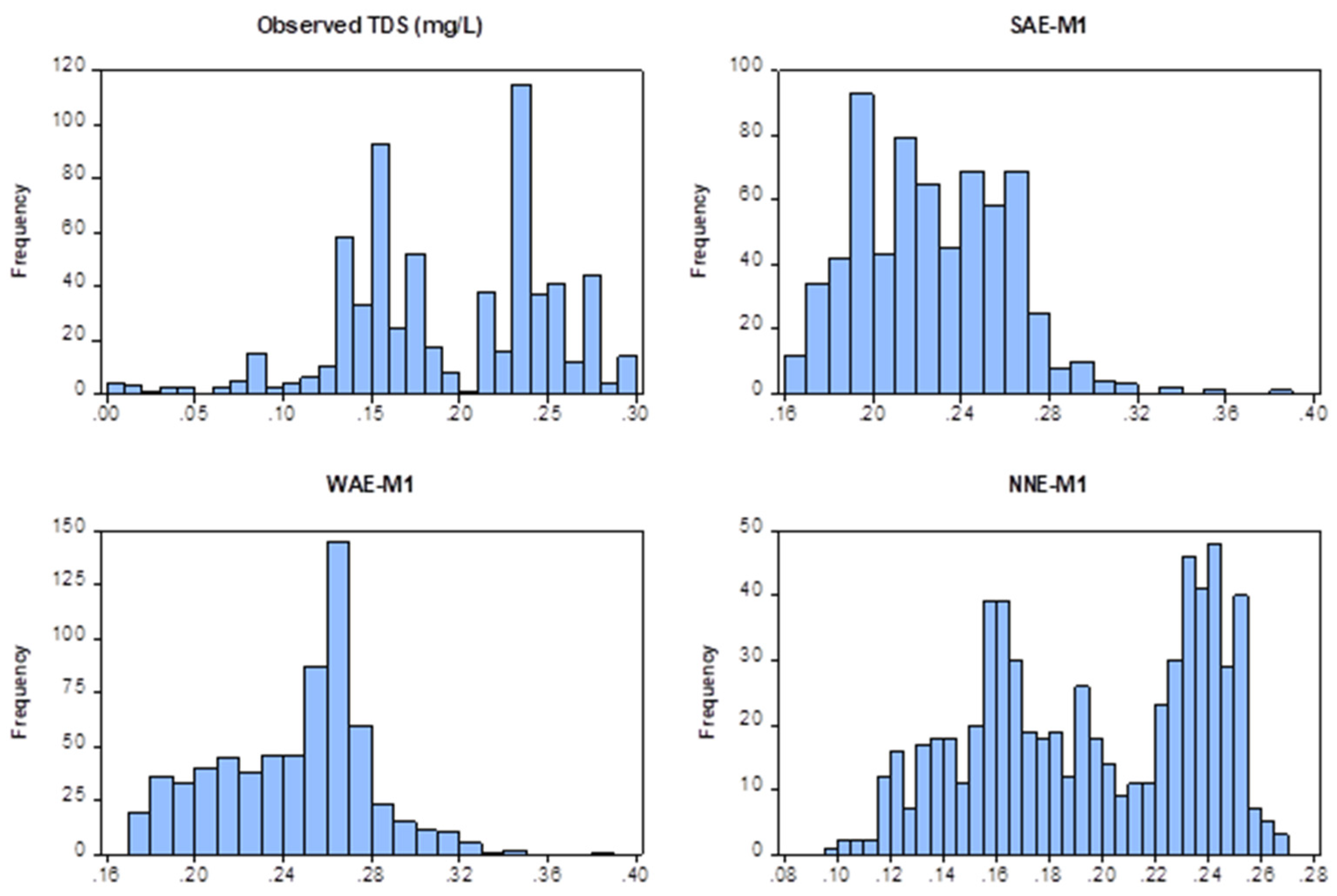
3.2. Error Ensemble Learning Results
4. Conclusions
Recommendations for Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breida, M.; Younssi, S.A.; Ouammou, M.; Bouhria, M.; Hafsi, M. Pollution of Water Sources from Agricultural and Industrial Effluents: Special Attention to NO3ˉ, Cr(VI), and Cu(II). In Water Chemistry; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G. Cultivation of S. molesta plants for phytoremediation of secondary treated domestic wastewater. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2585–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayder, G.; Mustafa, H. Cultivation of Aquatic Plants for Biofiltration of Wastewater. Lett. Appl. NanoBioScience 2021, 10, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G. Performance of Salvinia molesta plants in tertiary treatment of domestic wastewater. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayder, G.; Solihin, M.I.; Mustafa, H.M. Modelling of river flow using particle swarm optimized cascade-forward neural networks: A case study of kelantan river in malaysia. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G. Evaluation of water lettuce, giant salvinia and water hyacinth systems in phytoremediation of domestic wastewater. H2Open J. 2021, 4, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, V.; Parrella, L.; Falcucci, M. Modelling dissolved oxygen dynamics in coastal lagoons. Ecol. Modell. 2008, 211, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouatadid, S.; Adamowski, J. Using extreme learning machines for short-term urban water demand forecasting. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bata, M.H.; Carriveau, R.; Ting, D.S.-K. Short-Term Water Demand Forecasting Using Nonlinear Autoregressive Artificial Neural Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2020, 146, 04020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.I.; Elkiran, G. Effluent prediction of chemical oxygen demand from the astewater treatment plant using artificial neural network application. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 120, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.I.; Elkiran, G.; Nourani, V. Non-linear ensemble modeling for multi-step ahead prediction of treated cod in wastewater treatment plant. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1095, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.; Elkiran, G.; Nourani, V. Improving novel extreme learning machine using PCA algorithms for multi-parametric modeling of the municipal wastewater treatment plant. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 215, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.J.; Abba, S.I.; Sammen, S.S.; Salih, S.Q.; Al-Ansari, N.; Yaseen, Z.M. Non-Linear Input Variable Selection Approach Integrated with Non-Tuned Data Intelligence Model for Streamflow Pattern Simulation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 141533–141548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.M.; Khalafallah, M.G.; Hassanien, E.A. Prediction of wastewater treatment plant performance using artificial neural networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.N.P.; Koottatep, T.; Chapagain, S.K.; Panuvatvanich, A.; Polprasert, C.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Chaiwong, C.; Nguyen, N.L. Removal and monitoring acetaminophen-contaminated hospital wastewater by vertical fl ow constructed wetland and peroxidase enzymes. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 250, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, J.; Kumar, P. Heavy metal uptake by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.) from paper mill effluent (PME): Experimental and prediction modeling studies. no Goheen 2018. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14400–14413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Deswal, S. Estimation of Phosphorus Reduction from Wastewater by Artificial Neural Estimation of Phosphorus Reduction from Wastewater by Artificial Neural Network, Random Forest and M5P Model Tree Approaches. Pollution 2020, 6, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfei, A.; Menapace, A.; Granata, F.; Gargano, R.; Frisinghelli, M.; Righetti, M. An Ensemble Neural Network Model to Forecast Drinking Water Consumption. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenochristou, M.; Kapelan, Z. An ensemble stacked model with bias correction for improved water demand forecasting. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Essalhi, M. Artificial neural network modeling and response surface methodology of desalination by reverse osmosis. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 368, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, E.S.; Ehetshami, M.; Karimi-Jashni, A.; Salari, M.; Sheibani, S.N.; Ehteshami, A. A mathematical method and artificial neural network modeling to simulate osmosis membrane’s performance. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.I.; Pham, Q.B.; Saini, G.; Linh, N.T.T.; Ahmed, A.N.; Mohajane, M.; Khaledian, M.; Abdulkadir, R.A.; Bach, Q.-V. Implementation of data intelligence models coupled with ensemble machine learning for prediction of water quality index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41524–41539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, K.; Son, M.; Yoon, N.; Park, S.; Shim, J.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.-L.; Cho, K.H. Modeling and evaluating performance of full-scale reverse osmosis system in industrial water treatment plant. Desalination 2021, 518, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-herná, P. Water Quality of a Reservoir and Its Major Tributary Located in East-Central Mexic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2014, 6, 6119–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourani, V.; Elkiran, G.; Abba, S.I. Wastewater treatment plant performance analysis using artificial intelligence—An ensemble approach. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarap, A.F.; Azcarraga, A.P. k-Winners-Take-All Ensemble Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference (ICONIP 2021), Bali, Indonesia, 8–12 December 2021; pp. 250–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalehkhondabi, I.; Ardjmand, E.; Young, W.A.; Weckman, G.R. Water demand forecasting: Review of soft computing methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharshini, N.R.; Vanishree, R.; Sebasteenav, P.R. Smart water quality management system. In Proceedings of the Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering | National Conference on Advancement in Emerging Technologies (NCAET’18), Chennai, India, 27–28 April 2018; pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Lu, M.-D. Hybrid feature selection by combining filters and wrappers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 8144–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, X.; Alexandre, L. Weighted Convolutional Neural Network Ensemble. In Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis, Computer Vision, and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizterland, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitt, F.-P.; Will, P.; Robert, E. Arizona Watershed Stewardship Guide: Water Quality & Monitoring. Coll. Agric. Life Sci. Univ. Ariz. 2005, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, K.E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 7183–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.G.; Işik, S.; Abba, S.I. A Novel Multi-model Data-Driven Ensemble Technique for the Prediction of Retention Factor in HPLC Method Development. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, M.S.; Abba, S.I.; Abdu, A.M.; Tukur, A.I.; Saleh, M.A.; Esmaili, P.; Wahab, N.A. Estimation of water quality index using artificial intelligence approaches and multi-linear regression. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2020, 9, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, A.; Esmaili, P.; Ameen, Z.; Abdulkadir, R.; Gaya, M.; Ozsoz, M.; Saini, G.; Abba, S. Metro-environmental data approach for the prediction of chemical oxygen demand in new nicosia wastewater treatment plant. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 221, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.B.; Gaya, M.; Abba, S.; Abdulkadir, R.; Esmaili, P.; Linh, N.T.T.; Sharma, C.; Malik, A.; Khoi, D.N.; Dung, T.D.; et al. Modeling of bunus regional sewage treatment plant using machine learning approaches. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 203, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.I.; Gaya, M.S.; Yakubu, M.L.; Zango, M.U.; Abdulkadir, R.A.; Saleh, M.A.; Hamza, A.N.; Abubakar, U.; Tukur, A.I.; Wahab, N.A. Modelling of Uncertain System: A comparison study of Linear and Non-Linear Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control and Intelligent Systems (I2CACIS 2019—Proc.), Selangor, Malaysia, 29 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, N.; Zaidi, S.; Danish, M. Support vector regression (SVR)-based adsorption model for Ni (II) ions removal. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, P.; Singh, J.; Kumar, P. Use of sugar mill wastewater for Agaricus bisporus cultivation: Prediction models for trace metal uptake and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 26923–26934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.A.; Tawabini, B.; Al-Shaibani, A.; Adetoro, J.A.; Benaafi, M.; Al-Areeq, A.M.; Usman, A.G.; Abba, S.I. Geochemical and Spatial Distribution of Topsoil HMs Coupled with Modeling of Cr Using Chemometrics Intelligent Techniques: Case Study from Dammam Area, Saudi Arabia. Molecules 2022, 27, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



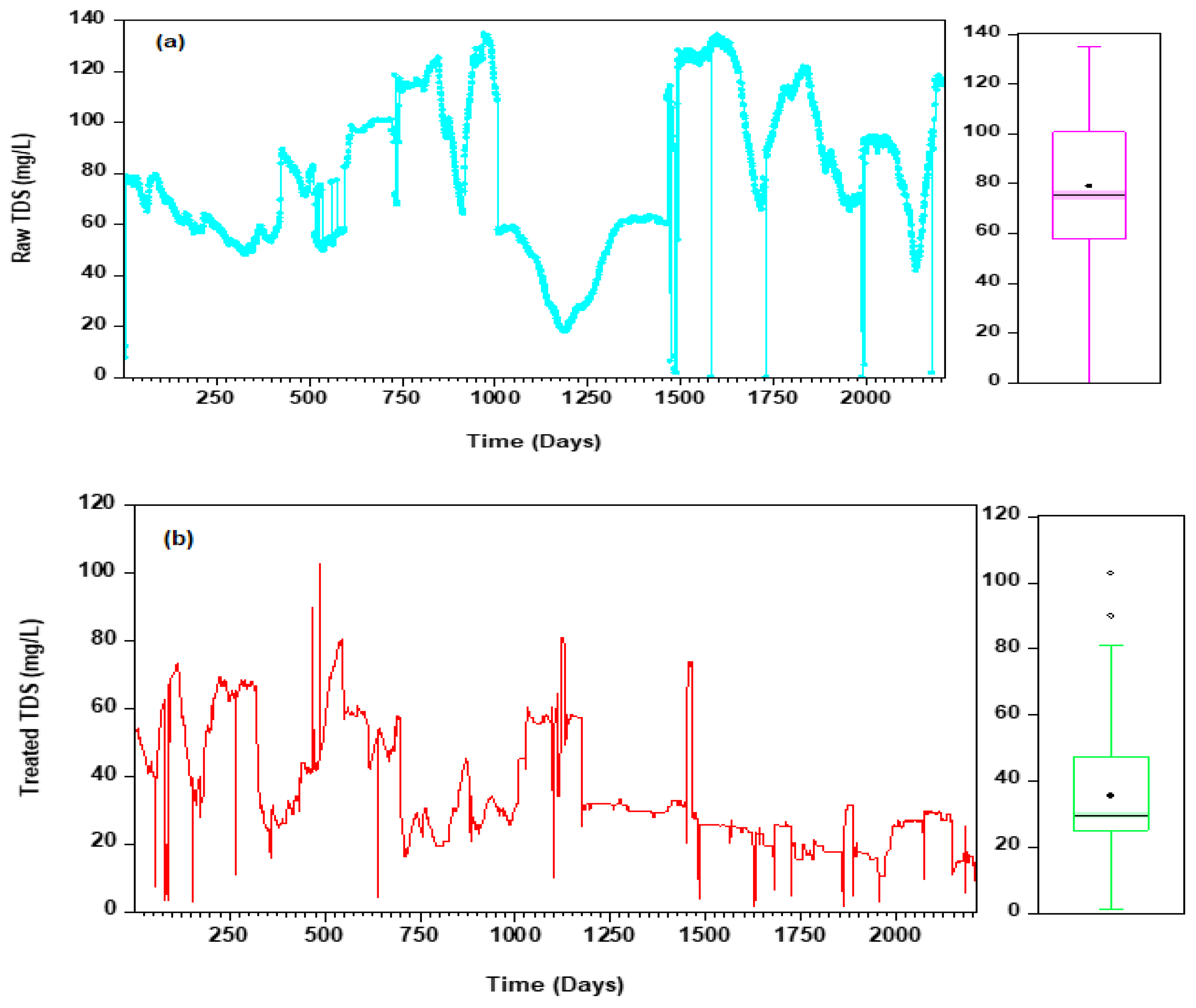






| Parameters | Influent Parameters | Effluent Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Turbidity | TURBr | TDSt |
| Treated Turbidity | TURBt | |
| Raw Total Dissolve Solid | TDSt | |
| Treated Total Dissolve Solid | TDSr | |
| Raw Oxidation-Reduction Potential | ORPr | |
| Treated Oxidation-Reduction Potential | ORPt | |
| Raw Temperature | TEMPr | |
| Treated Temperature | TEMPt |
| Training | Validation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Models | R2 | MSE | R | RMSE | R2 | MSE | R | RMSE |
| ANN-M1 | 0.9995 | 0.1176 | 0.9998 | 0.3430 | 0.9954 | 0.1140 | 0.9977 | 0.3377 |
| ANN-M2 | 0.9982 | 0.4306 | 0.9991 | 0.6562 | 0.9631 | 0.9192 | 0.9814 | 0.9588 |
| SVM-M1 * | 0.9999 | 0.0139 | 1.0000 | 0.1177 | 0.9986 | 0.0356 | 0.9993 | 0.1887 |
| SVM-M2 | 0.9970 | 0.9970 | 0.9985 | 0.9985 | 0.9852 | 0.3696 | 0.9925 | 0.6079 |
| ANFIS-M1 | 0.9988 | 0.3024 | 0.9994 | 0.5499 | 0.9716 | 0.0011 | 0.9857 | 0.0326 |
| ANFIS-M2 | 0.9926 | 1.8033 | 0.9963 | 1.3429 | 0.8309 | 4.2103 | 0.9115 | 2.0519 |
| MLR-M1 | 0.9928 | 1.7588 | 0.9964 | 1.3262 | 0.8350 | 4.1066 | 0.9138 | 2.0265 |
| MLR-M2 | 0.9883 | 2.8616 | 0.9941 | 1.6916 | 0.7316 | 6.6813 | 0.8553 | 2.5848 |
| Ensemble Techniques | MSE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|
| SAE-M1 | 0.0039 | 0.0623 |
| WAE-M1 | 0.0065 | 0.0806 |
| NNE-M1 * | 0.0014 | 0.0379 |
| SAE-M2 | 0.0087 | 0.0933 |
| WAE-M2 | 0.0486 | 0.2204 |
| NNE-M2 | 0.0018 | 0.0426 |
| Techniques | MSE | RMSE | Normalized % Diff MSE | Normalized % Diff RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NNE-M1 * | 0.0014 | 0.0379 | 3.4165 | 15.0820 |
| SVM-1 | 0.0356 | 0.1887 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mustafa, H.M.; Hayder, G.; Abba, S.I.; Algarni, A.D.; Mnzool, M.; Nour, A.H. Performance Evaluation of Hydroponic Wastewater Treatment Plant Integrated with Ensemble Learning Techniques: A Feature Selection Approach. Processes 2023, 11, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020478
Mustafa HM, Hayder G, Abba SI, Algarni AD, Mnzool M, Nour AH. Performance Evaluation of Hydroponic Wastewater Treatment Plant Integrated with Ensemble Learning Techniques: A Feature Selection Approach. Processes. 2023; 11(2):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020478
Chicago/Turabian StyleMustafa, Hauwa Mohammed, Gasim Hayder, S. I. Abba, Abeer D. Algarni, Mohammed Mnzool, and Abdurahman H. Nour. 2023. "Performance Evaluation of Hydroponic Wastewater Treatment Plant Integrated with Ensemble Learning Techniques: A Feature Selection Approach" Processes 11, no. 2: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020478
APA StyleMustafa, H. M., Hayder, G., Abba, S. I., Algarni, A. D., Mnzool, M., & Nour, A. H. (2023). Performance Evaluation of Hydroponic Wastewater Treatment Plant Integrated with Ensemble Learning Techniques: A Feature Selection Approach. Processes, 11(2), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020478










