Bioinformatics Methods for Constructing Metabolic Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Popular Metabolic Pathway Databases
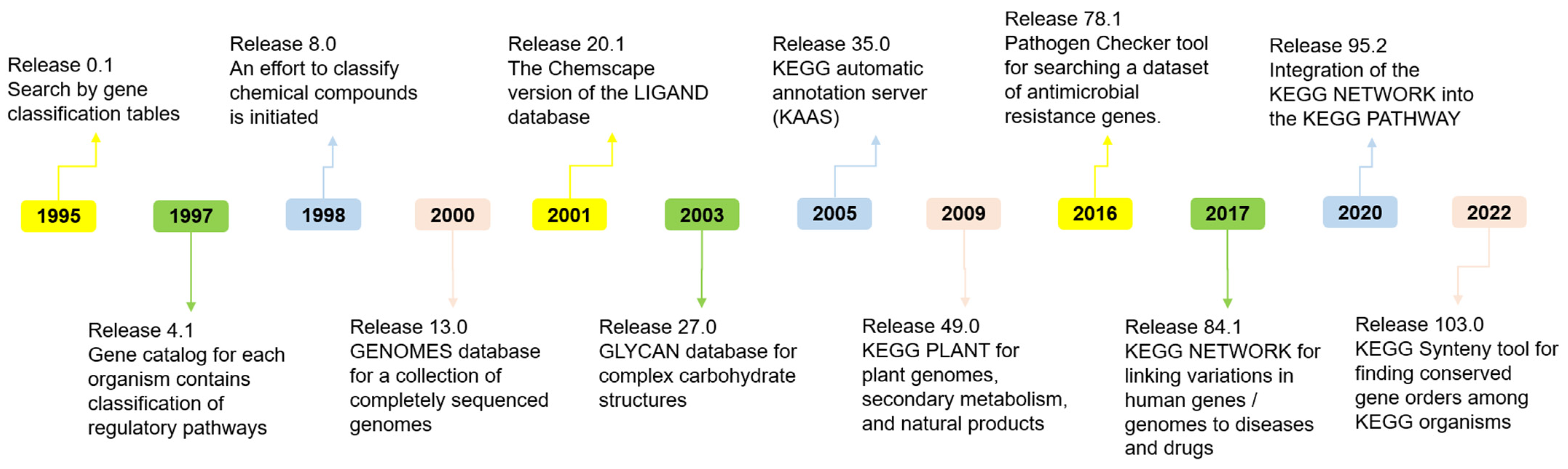
2.1. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
2.2. Reactome Database
2.3. MetaCyc Database
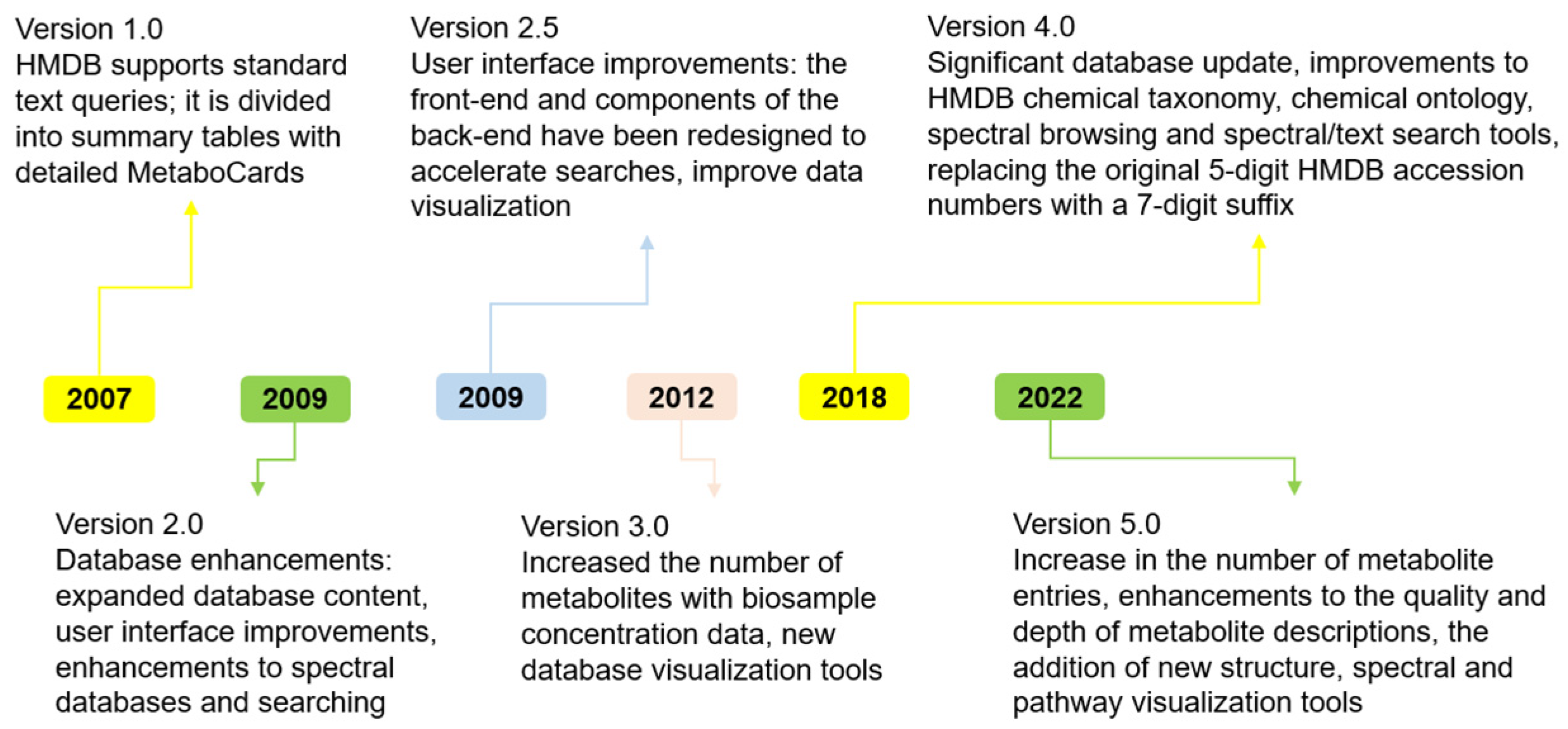
2.4. Human Metabolome Database
- –
- The COVID-19 Community, containing the data on the molecular mechanisms of coronavirus infection in the human body;
- –
- The IMD Community, presenting the data on inherited metabolic disorders;
- –
- The PancCanNet Community, accumulating information about the biological pathways associated with the development of pancreatic cancer, etc. [39].
3. Methods for Constructing Biological Pathway Maps
- –
- Constructing graphs describing the substrate–enzyme–product transformation;
- –
- Stoichiometric analysis of substrate–product transformation;
- –
- Retrosynthesis of the product in compliance with the rules of chemical reactions.
- –
- Choosing the database;
- –
- Metabolic network visualization;
- –
- Reduction (compression) of the metabolic network;
- –
- Searching for a biological pathway/biochemical process;
- –
- Ranking the search results.
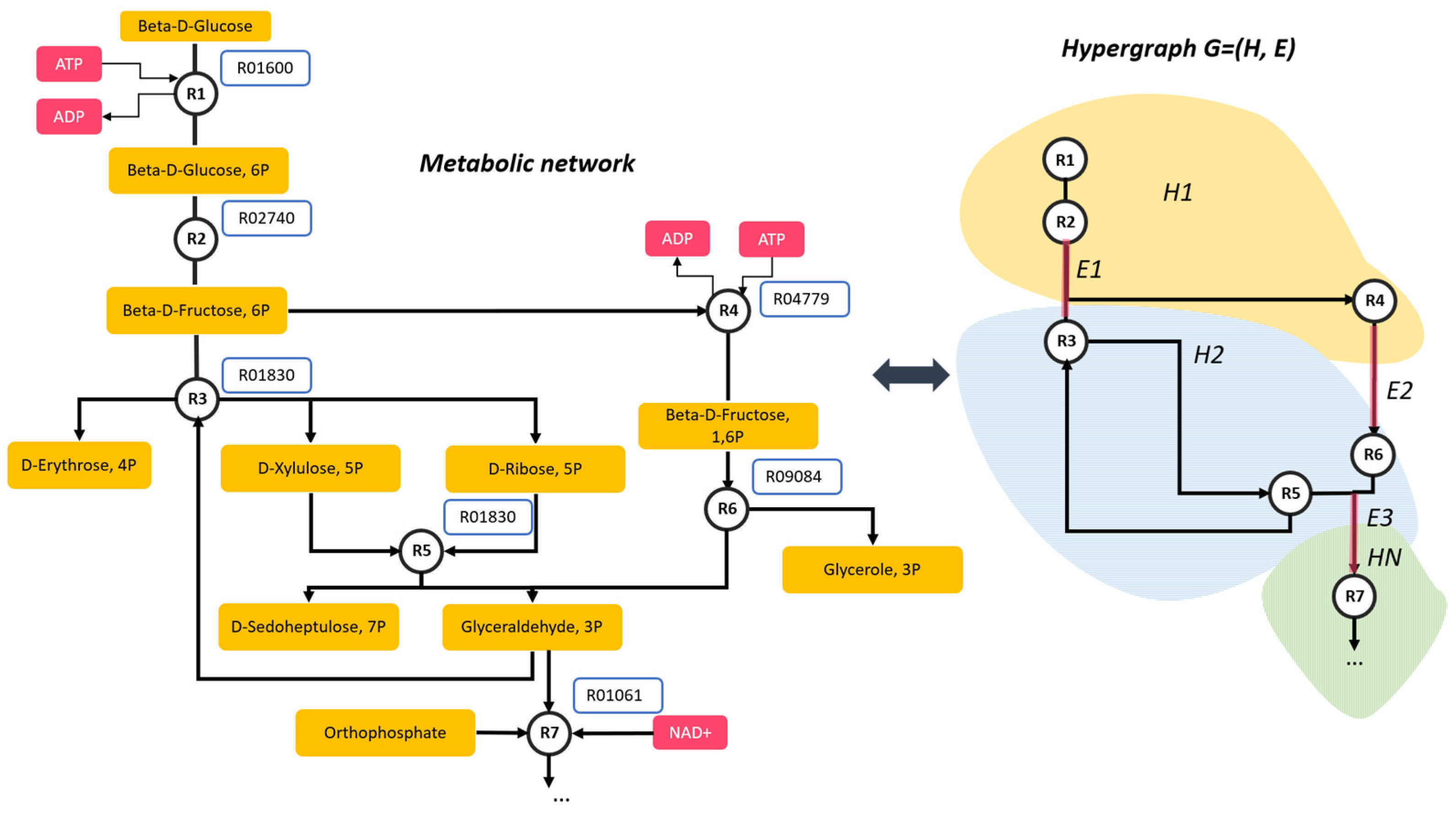
3.1. Methods for Metabolic Network Visualization
3.1.1. Metabolic Network Reduction (Compression) Variants
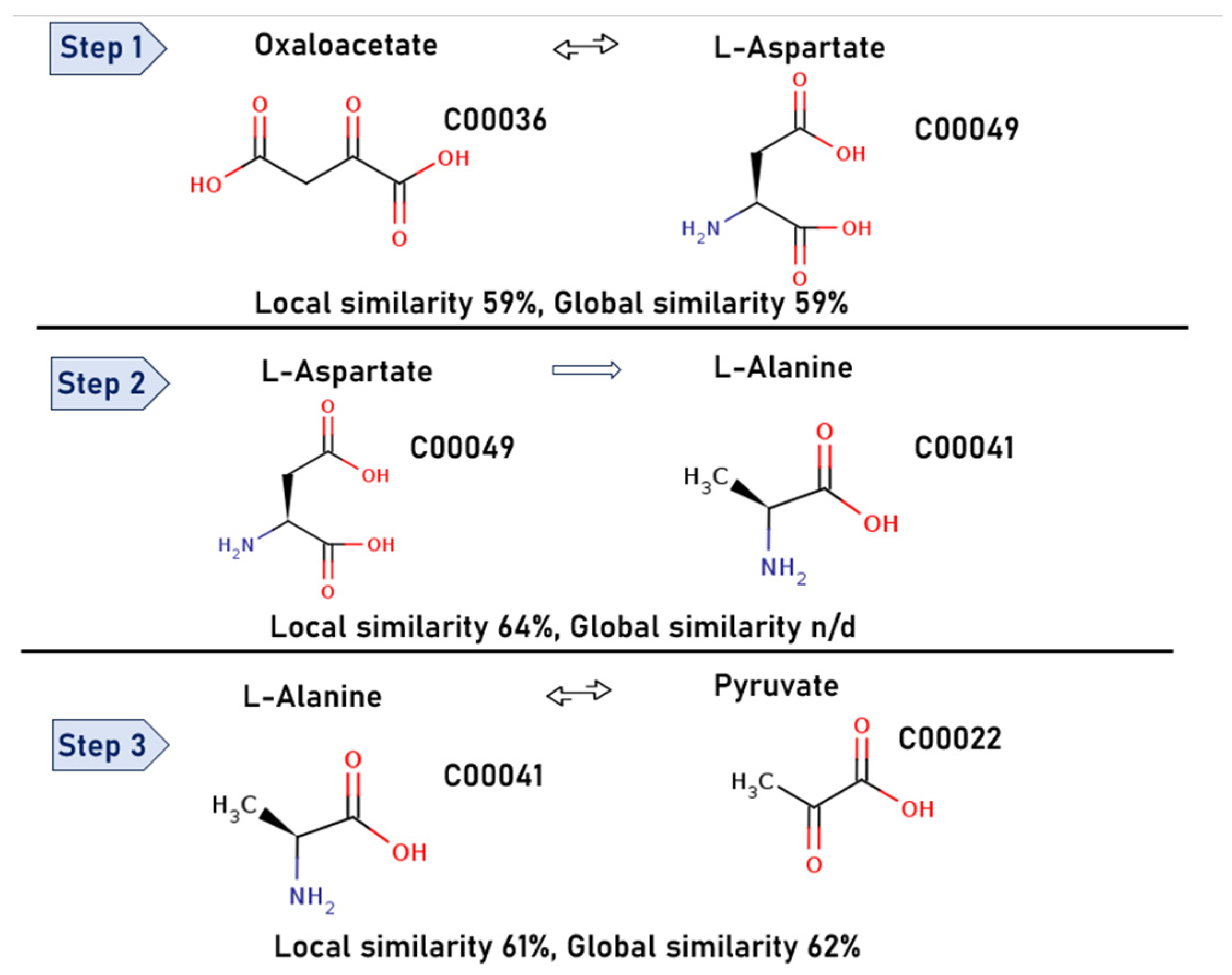
3.1.2. The Search for Biological Pathways
3.1.3. Ranking the Search Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koonin, E.V.; Galperin, M.Y. Evolution of Central Metabolic Pathways: The Playground of Non-Orthologous Gene Displacement. In Sequence—Evolution—Function: Computational Approaches in Comparative Genomics; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Bi, M.; Guo, H.; Li, M. Multi-Omics Approaches for Biomarker Discovery in Early Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis. eBioMedicine 2022, 79, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graw, S.; Chappell, K.; Washam, C.L.; Gies, A.; Bird, J.; Robeson, M.S.; Byrum, S.D. Multi-Omics Data Integration Considerations and Study Design for Biological Systems and Disease. Mol. Omics 2021, 17, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Campos, M.A.; Espinal-Enríquez, J.; Hernández-Lemus, E. Pathway Analysis: State of the Art. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoney, R.; Robertson, D.L.; Nenadic, G.; Schwartz, J.-M. Mapping Biological Process Relationships and Disease Perturbations within a Pathway Network. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2018, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.J.; Orlic-Milacic, M.; Rothfels, K.; Weiser, J.; Trinh, Q.M.; Jassal, B.; Haw, R.A.; Stein, L.D. Evaluating the Predictive Accuracy of Curated Biological Pathways in a Public Knowledgebase. Database 2022, 2022, baac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, W.K.; Paley, S.; Subhraveti, P.; Karp, P.D. The MetaCyc Database of Metabolic Pathways and Enzymes—A 2019 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D445–D453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likić, V.A. Databases of Metabolic Pathways. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2006, 34, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dash, S.; Ng, C.Y.; Maranas, C.D. A Review of Computational Tools for Design and Reconstruction of Metabolic Pathways. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inferring Branching Pathways in Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/1752-0509-3-103 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Chowdhury, A.; Maranas, C.D. Designing Overall Stoichiometric Conversions and Intervening Metabolic Reactions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BiGG Models: A Platform for Integrating, Standardizing and Sharing Genome-Scale Models|Nucleic Acids Research|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/44/D1/D515/2502593 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for Taxonomy-Based Analysis of Pathways and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M. KEGG Mapping Tools for Uncovering Hidden Features in Biological Data. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, S.; Yamada, T.; Hamajima, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Bork, P.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG Atlas Mapping for Global Analysis of Metabolic Pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W423–W426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D.; Billington, R.; Caspi, R.; Fulcher, C.A.; Latendresse, M.; Kothari, A.; Keseler, I.M.; Krummenacker, M.; Midford, P.E.; Ong, Q.; et al. The BioCyc Collection of Microbial Genomes and Metabolic Pathways. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, A.; Korninger, F.; Viteri, G.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Marin-Garcia, P.; Ping, P.; Wu, G.; Stein, L.; D’Eustachio, P.; Hermjakob, H. Reactome Graph Database: Efficient Access to Complex Pathway Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1005968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; Viteri, G.; Gong, C.; Lorente, P.; Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Cook, J.; Gillespie, M.; Haw, R.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D498–D503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.A.; Advani, P.; Schunk, R.; Schrader, R.; Schomburg, D. Metabolic Pathway Analysis Web Service (Pathway Hunter Tool at CUBIC). Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MetaRoute: Fast Search for Relevant Metabolic Routes for Interactive Network Navigation and Visualization|Bioinformatics|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/24/18/2108/190986 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Optimal Metabolic Route Search Based on Atom Mappings|Bioinformatics|Oxford. Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/30/14/2043/2390321 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Tervo, C.J.; Reed, J.L. MapMaker and PathTracer for Tracking Carbon in Genome-scale Metabolic Models. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computing the Shortest Elementary Flux Modes in Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks|Bioinformatics|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/25/23/3158/216440 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia Coli for Direct Production of 1,4-Butanediol|Nature Chemical Biology. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nchembio.580 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Campodonico, M.A.; Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A.; Palsson, B.O.; Feist, A.M. Generation of an Atlas for Commodity Chemical Production in Escherichia Coli and a Novel Pathway Prediction Algorithm, GEM-Path. Metab. Eng. 2014, 25, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, P.; Parutto, P.; Herisson, J.; Pandit, S.B.; Faulon, J.-L. XTMS: Pathway Design in an eXTended Metabolic Space. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W389–W394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Kawashima, S.; Okuno, Y.; Hattori, M. The KEGG Resource for Deciphering the Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D277–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a Reference Resource for Gene and Protein Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vastrik, I.; D’Eustachio, P.; Schmidt, E.; Joshi-Tope, G.; Gopinath, G.; Croft, D.; de Bono, B.; Gillespie, M.; Jassal, B.; Lewis, S.; et al. Reactome: A Knowledge Base of Biologic Pathways and Processes. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi-Tope, G.; Gillespie, M.; Vastrik, I.; D’Eustachio, P.; Schmidt, E.; de Bono, B.; Jassal, B.; Gopinath, G.R.; Wu, G.R.; Matthews, L.; et al. Reactome: A Knowledgebase of Biological Pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D428–D432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, P.D.; Paley, S.M.; Krummenacker, M.; Latendresse, M.; Dale, J.M.; Lee, T.J.; Kaipa, P.; Gilham, F.; Spaulding, A.; Popescu, L.; et al. Pathway Tools Version 13.0: Integrated Software for Pathway/Genome Informatics and Systems Biology. Brief. Bioinform. 2010, 11, 40–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, C.; Ginzburg, D.; Zhao, K.; Dwyer, W.; Xue, B.; Xu, A.; Rice, S.; Cole, B.; Paley, S.; Karp, P.; et al. Plant Metabolic Network 15: A Resource of Genome-wide Metabolism Databases for 126 Plants and Algae. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1888–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Cary, M.P.; Paley, S.; Fukuda, K.; Lemer, C.; Vastrik, I.; Wu, G.; D’Eustachio, P.; Schaefer, C.; Luciano, J.; et al. The BioPAX Community Standard for Pathway Data Sharing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathway Commons: A Resource for Biological Pathway Analysis. Available online: https://www.pathwaycommons.org/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- OWL 2 Web Ontology Language Document Overview (Second Edition). Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/owl2-overview/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Pathway Tools Data-File Formats. Available online: https://bioinformatics.ai.sri.com/ptools/flatfile-format.html (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Martens, M.; Ammar, A.; Riutta, A.; Waagmeester, A.; Slenter, D.N.; Hanspers, K.; Miller, R.A.; Digles, D.; Lopes, E.N.; Ehrhart, F.; et al. WikiPathways: Connecting Communities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D613–D621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathvisio.Github.Io. Available online: https://pathvisio.github.io//pathvisio.github.io/documentation/GPML2013a-doc.html (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- PathVisio Biological Pathway Editor. Available online: https://pathvisio.github.io//pathvisio.github.io/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- The BridgeDb Framework: Standardized Access to Gene, Protein and Metabolite Identifier Mapping Services|BMC Bioinformatics|Full Text. Available online: https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2105-11-5 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Kotera, M.; Goto, S. Metabolic Pathway Reconstruction Strategies for Central Metabolism and Natural Product Biosynthesis. Biophysics 2016, 13, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Hachiya, T.; Saito, Y.; Sato, K.; Sakakibara, Y. An Efficient Algorithm for de Novo Predictions of Biochemical Pathways between Chemical Compounds. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, A.; Yun, H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S. Prediction of Novel Synthetic Pathways for the Production of Desired Chemicals. BMC Syst. Biol. 2010, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Nöllenburg, M.; Viola, I. Graph Models for Biological Pathway Visualization: State of the Art and Future Challenges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.04808. [Google Scholar]
- Mithani, A.; Preston, G.M.; Hein, J. Rahnuma: Hypergraph-Based Tool for Metabolic Pathway Prediction and Network Comparison. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1831–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClymont, K.; Soyer, O.S. Metabolic Tinker: An Online Tool for Guiding the Design of Synthetic Metabolic Pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosraviani, M.; Saheb Zamani, M.; Bidkhori, G. FogLight: An Efficient Matrix-Based Approach to Construct Metabolic Pathways by Search Space Reduction. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yeung, M.; Thiele, I.; Palsson, B.O. Estimation of the Number of Extreme Pathways for Metabolic Networks. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Path Finding Methods Accounting for Stoichiometry in Metabolic Networks|SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-r49 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Erdrich, P.; Steuer, R.; Klamt, S. An Algorithm for the Reduction of Genome-Scale Metabolic Network Models to Meaningful Core Models. BMC Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, C.T.; Wlaschin, A.; Srienc, F. Elementary Mode Analysis: A Useful Metabolic Pathway Analysis Tool for Characterizing Cellular Metabolism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 81, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, L.-E.; Dietmair, S.; Hanscho, M.; Martínez, V.S.; Borth, N.; Nielsen, L.K. Reducing Recon 2 for Steady-State Flux Analysis of HEK Cell Culture. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 184, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdrich, P.; Knoop, H.; Steuer, R.; Klamt, S. Cyanobacterial Biofuels: New Insights and Strain Design Strategies Revealed by Computational Modeling. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reconstruction and Use of Microbial Metabolic Networks: The Core Escherichia Coli Metabolic Model as an Educational Guide|EcoSal Plus. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/full/10.1128/ecosalplus.10.2.1 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Küken, A.; Wendering, P.; Langary, D.; Nikoloski, Z. A Structural Property for Reduction of Biochemical Networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Lercher, M.J. Network Reduction Methods for Genome-Scale Metabolic Models. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambamoorthy, G.; Raman, K. MinReact: A Systematic Approach for Identifying Minimal Metabolic Networks. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4309–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, P.; Negi, S.K.; Tikoo, K.; Kumar, D.; Rao, K.V.S.; Chatterjee, S. Molecular Signatures for Obesity and Associated Disorders Identified through Partial Least Square Regression Models. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wirawan, A.; Kwoh, C.K.; Hieu, N.T.; Schmidt, B. CBESW: Sequence Alignment on the Playstation 3. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhl, A.; Bockmayr, A. A Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Approach to the Reduction of Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataman, M.; Hernandez Gardiol, D.F.; Fengos, G.; Hatzimanikatis, V. redGEM: Systematic Reduction and Analysis of Genome-Scale Metabolic Reconstructions for Development of Consistent Core Metabolic Models. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroukh, C.; Muñoz-Tamayo, R.; Steyer, J.-P.; Bernard, O. DRUM: A New Framework for Metabolic Modeling under Non-Balanced Growth. Application to the Carbon Metabolism of Unicellular Microalgae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, L.-E.; Nielsen, L.K. A Depth-First Search Algorithm to Compute Elementary Flux Modes by Linear Programming. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ravikrishnan, A.; Nasre, M.; Raman, K. Enumerating All Possible Biosynthetic Pathways in Metabolic Networks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanghellini, J.; Ruckerbauer, D.E.; Hanscho, M.; Jungreuthmayer, C. Elementary Flux Modes in a Nutshell: Properties, Calculation and Applications. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ng, C.Y.; Dash, S.; Maranas, C.D. Exploring the Combinatorial Space of Complete Pathways to Chemicals. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Reed, J.L.; Maravelias, C.T. Large-Scale Bi-Level Strain Design Approaches and Mixed-Integer Programming Solution Techniques. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Step | Database Selection | Visual Representation of a Metabolic Network | Reduction (Compression) of the Metabolic Network | Searching for a Biological Pathway/Biochemical Process | Ranking the Search Results | Tool |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph construction | KEGG, MetaCyc, HMDB, CHEBI, BIGG, etc. | Graph of a chemical transformation; Graph of metabolites; Bipartite graph; Hypergraph; Multilayer graph | Exclusion of cofactors and ligands; Weighted graph; Atom mapping; Phylogenetic analysis | Shortest-path search; DFS; Informed search; BFS; The Monte Carlo method | Principle of atom conservation; Metabolite–metabolite association; Structural similarity; Interspecies comparative analysis of biological pathways | Pathway Hunter [21]; MetaRoute [22]; RouteSearch [23]; ReTrace [12] |
| Stoichiometric analysis | KEGG, MetaCyc, HMDB, CHEBI, BIGG, etc. | Scatterplot matrix; Substrate graph | Stoichiometry analysis; Atom mapping | Mixed integer linear programming | Pathway length analysis (common metabolic flux); Pathway length (the most active pathway); Number of heterologous reactions | optStoic [13]; PathTracer [24]; METATOOL 5.0 [25] |
| Retrosynthesis of the product | KEGG, MetaCyc, HMDB, CHEBI, BIGG, etc. | Scatterplot matrix; Substrate graph | Similarity with the substrate (with allowance for the EC number); Structural similarity | Retrosynthetic analysis | Similarity of compounds and pathway assessment;Weight function; Pathway length | Simpheny [26]; GEM-Path [27]; XTMS [28] |
| Algorithm | Approach | Set of Biochemical Transformations | Set of Metabolites | Protection of Minimal Degrees of Freedom * (dof ≥ dofmin) | Computation of Minimal Subnetworks | Set of Phenotypes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Reducer | LP/FVA ** | + | + | + | − | + | [62] |
| MinReact | pFBA *** | − | − | − | + | − | [59] |
| MinNW | MILP **** | + | + | − | + | + | [62] |
| redGEM | Graph algorithms, MILP | + | + | + | + | + | [63] |
| DRUM | EFM ***** | − | + | − | + | + | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrovsky, D.V.; Malsagova, K.A.; Rudnev, V.R.; Kulikova, L.I.; Pustovoyt, V.I.; Balakin, E.I.; Yurku, K.A.; Kaysheva, A.L. Bioinformatics Methods for Constructing Metabolic Networks. Processes 2023, 11, 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123430
Petrovsky DV, Malsagova KA, Rudnev VR, Kulikova LI, Pustovoyt VI, Balakin EI, Yurku KA, Kaysheva AL. Bioinformatics Methods for Constructing Metabolic Networks. Processes. 2023; 11(12):3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123430
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrovsky, Denis V., Kristina A. Malsagova, Vladimir R. Rudnev, Liudmila I. Kulikova, Vasiliy I. Pustovoyt, Evgenii I. Balakin, Ksenia A. Yurku, and Anna L. Kaysheva. 2023. "Bioinformatics Methods for Constructing Metabolic Networks" Processes 11, no. 12: 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123430
APA StylePetrovsky, D. V., Malsagova, K. A., Rudnev, V. R., Kulikova, L. I., Pustovoyt, V. I., Balakin, E. I., Yurku, K. A., & Kaysheva, A. L. (2023). Bioinformatics Methods for Constructing Metabolic Networks. Processes, 11(12), 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11123430







