Impact of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials on the Performance and Emissions of Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel/Biodiesel Blend
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Procedure and the Experimental Setup
2.1. The Experimental Setup
2.2. The Diesel Fuel and WCO Biodiesel Manufacturing
2.3. The Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles
2.4. The Uncertainty Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Combustion Attributes
3.2. Performance Attributes
3.3. Emission Attributes
4. Cost Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
- The peak in-cylinder pressures are increased using different concentrations of nanoparticles due to the high surface area to volume ratio and the high evaporation rate.
- The BSFC and BTE of B40-CNTs and B40-GO improved gradually with increasing nanoparticle concentrations and engine load compared to pure diesel (B0 and B40). Nanoparticle fuels also enhance exhaust gas temperatures (EGTs) due to the higher surface area to volume ratio oxygen content and the lowered combustion duration, which reduced the EGTs compared to B0 and B40.
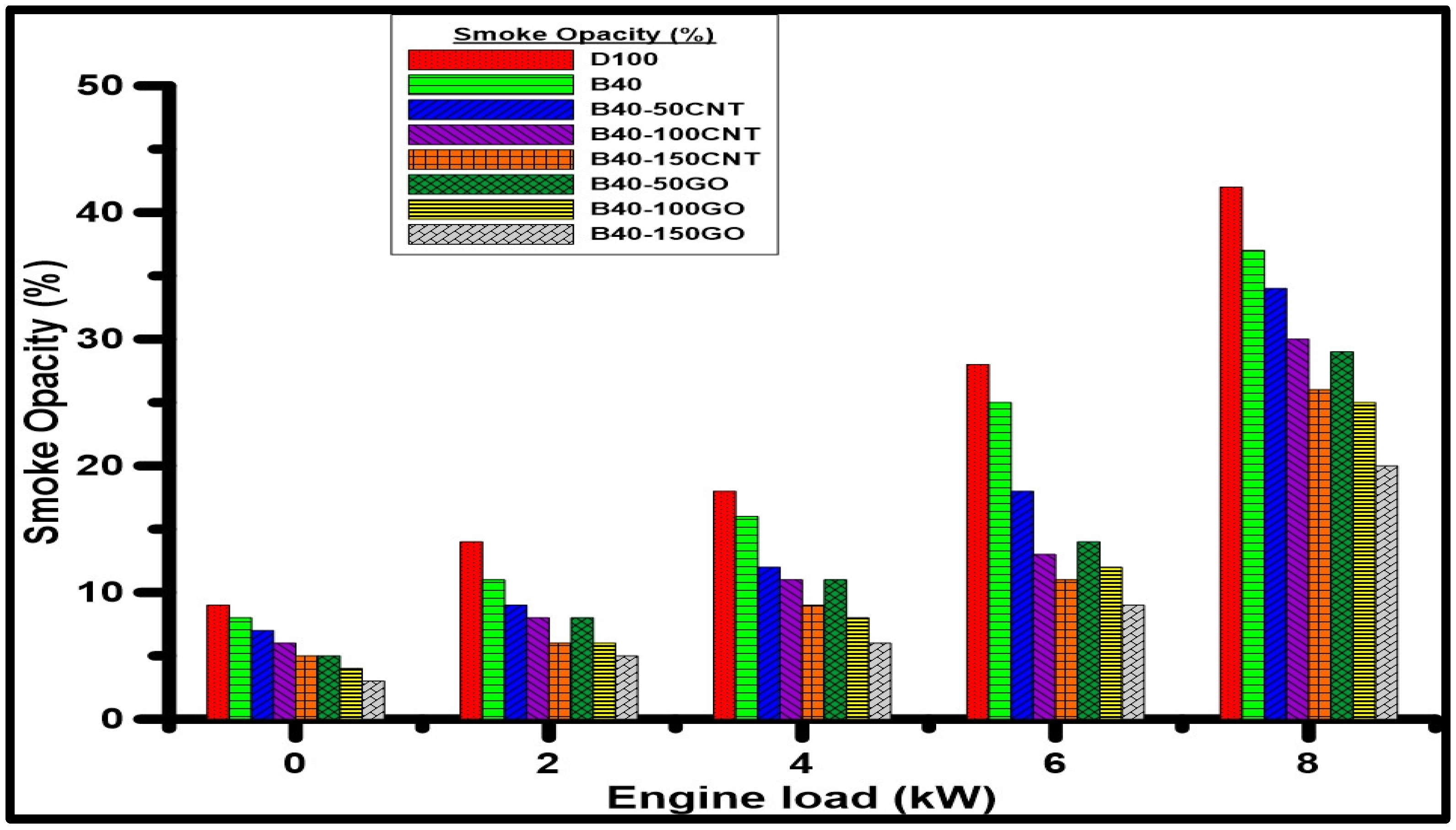
- The percentages of CO2 levels increased with the increasing engine loads and with the use of nanoparticle fuels. B40-GO gives the highest CO2 levels at different concentrations due to its high oxygen content, facilitating more complete combustion. Due to their high cetane number and oxygen content, NOx emissions values are also low for the B40-CNTs and B40-GO nanoparticle fuels. Furthermore, the UHC emissions are significantly reduced using B40-CNTs and B40-GO nanoparticle fuels due to the increased surface area to volume ratio, increased evaporation, and more complete combustion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumaran, P.; Godwin, A.J.; Amirthaganesan, S. Effect of microwave synthesized hydroxyapatite nanorods using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis added waste cooking oil (WCO) methyl ester biodiesel blends on the performance characteristics and emission of a diesel engine. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwaha, A.; Rosha, P.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Mahla, S.K.; Dhir, A. Waste materials as potential catalysts for biodiesel production: Current state and future scope. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 181, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, N.; Belgiorno, G.; Tuner, M.; Tunestal, P.; Di Blasio, G.; Beatrice, C. PPC Operation with Low RON Gasoline Fuel. A Study on Load Range on a Euro 6 Light Duty Diesel Engine. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Diagnostics and Modeling of Combustion in Internal Combustion Engines, Okayama, Japan, 25–28 July 2017; Volume 2017.9, p. C308. [Google Scholar]
- Elkelawy, M.; Bastawissi, H.A.E.; El Shenawy, E.A.; Shams, M.M.; Panchal, H.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Choudhary, A.K. Influence of lean premixed ratio of PCCI-DI engine fueled by diesel/biodiesel blends on combustion, performance, and emission attributes; a comparison study. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 10, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y. Investigation of Effect of Nozzle Numbers on Diesel Engine Performance Operated at Plateau Environment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, C.D.M.; de Andrade, C.C.; e Silva, E.D.S.; Dupas, F.A. Biodiesel production from used cooking oil: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Sharma, D.; Soni, S.L.; Inda, C.S.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Jhalani, A. A comprehensive review of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil and its use as fuel in compression ignition engines: 3rd generation cleaner feedstock. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paone, E.; Tursi, A. 6—Production of biodiesel from biomass. In Advances in Bioenergy and Microfluidic Applications; Rahimpour, M.R., Kamali, R., Makarem, M.A., Manshadi, M.K.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 165–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, M.P. Prospects of biodiesel from Jatropha in India: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.Y.; Ghazi, T.I.M. A review of biodiesel production from Jatropha curcas L. oil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2240–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enweremadu, C.C.; Mbarawa, M.M. Technical aspects of production and analysis of biodiesel from used cooking oil—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2205–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.M.; Teleken, J.G.; de Cinque Almeida, V.; da Silva, C. Biodiesel from waste frying oils: Methods of production and purification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 184, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.M.; Ali, C.H.; Iqbal, T.; Yasin, S.; Sulaiman, M.; Mahmood, H.; Raashid, M.; Pasha, M.; Mu, B. Current scenario and potential of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil in Pakistan: An overview. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 2238–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkelawy, M.; El Shenawy, E.A.; khalaf Abd Almonem, S.; Nasef, M.H.; Panchal, H.; Bastawissi, H.A.E.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Choudhary, A.K.; Sharma, D.; Khalid, M. Experimental study on combustion, performance, and emission behaviours of diesel /WCO biodiesel/Cyclohexane blends in DI-CI engine. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xia, M.; Liu, H.; Shang, R.; Ma, G.; Yao, M. Experimental study on combustion and emissions of n-butanol/biodiesel under both blended fuel mode and dual fuel RCCI mode. Fuel 2018, 226, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhang, X.; Geng, Z.; Pang, X.; Wang, X.; Ji, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, H. Effects of various co-solvents on the solubility between blends of soybean oil with either methanol or ethanol. Fuel 2019, 244, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, E.; Tuner, M.; Verhelst, S. Influence of injection strategies on engine efficiency for a methanol PPC engine. SAE Int. J. Adv. Curr. Pract. Mobil. 2019, 2, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, G.; Pipicelli, M.; Ianniello, R.; Belgiorno, G.; Di Blasio, G. Alcohol fuels in spark ignition engines. In Application of Clean Fuels in Combustion Engines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ealias, A.; Saravanakumar, M. A review on the classification, characterisation, synthesis of nanoparticles and their application. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 263, 032019. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, S.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Albergaria, J.T.; Delerue-Matos, C. Characterization of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced with tree leaf extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Barhoum, A.; Chan, Y.S.; Dufresne, A.; Danquah, M.K. Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: History, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1050–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allah, N.H.A.; Abouelmagd, S.A. Surface functionalization of polymeric nanoparticles for tumor drug delivery: Approaches and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Elkelawy, M.; El Shenawy, E.A.; Bastawissi, H.A.E.; Shams, M.M.; Panchal, H. A comprehensive review on the effects of diesel/biofuel blends with nanofluid additives on compression ignition engine by response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 14, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.Y.; Tai, C.T.; Chang, M.H.; Liu, H.S. Synthesis of Magnesium Hydroxide and Oxide Nanoparticles Using a Spinning Disk Reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 5536–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamun, S.; Belgiorno, G.; Di Blasio, G.; Beatrice, C.; Tunér, M.; Tunestål, P. Performance and emissions of diesel-biodiesel-ethanol blends in a light duty compression ignition engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 145, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, L.; Annamalai, K.; Parthasarathy, M.; Lalvani, I.J.R.; Moorthy, K. Production of Garcinia gummi-gutta methyl ester (GGME) as a potential alternative feedstock for existing unmodified DI diesel engine: Combustion, performance and emission characteristics. J. Test. Eval. 2018, 46, 20170246. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Ampah, J.D.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Veza, I.; Kingsley, U.; Afrane, S.; Jin, C.; Liu, H.; Elfasakhany, A.; Buyondo, K.A. Effects of hybrid nanoparticle additives in n-butanol/waste plastic oil/diesel blends on combustion, particulate and gaseous emissions from diesel engine evaluated with entropy-weighted PROMETHEE II and TOPSIS: Environmental and health risks of plastic waste. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 264, 115758. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzad, F.; Naghib, S.M.; Tabatabaei, S.N.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. An overview of the plant-mediated green synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 94, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.A.; Agunsoye, J.O.; Hassan, S.B. Synthesis of coconut shell nanoparticles via a top down approach: Assessment of milling duration on the particle sizes and morphologies of coconut shell nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Inambao, F.L.; Ampah, J.D. The effect of biodiesel and CeO2 nanoparticle blends on CRDI diesel engine: A special focus on combustion, particle number, PM2.5 species, organic compound and gaseous emissions. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Wei, J.; Tao, C.; Lv, G.; Qian, Y.; Liu, Q.; Han, W. Discussion on the combustion, performance and emissions of a dual fuel diesel engine fuelled with methanol-based CeO2 nanofluids. Fuel 2021, 302, 121096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örs, I.; Sarıkoç, S.; Atabani, A.E.; Ünalan, S.E.; Akansu, S.O. The effects on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of DICI engine fuelled with TiO2 nanoparticles addition in diesel/biodiesel/n-butanol blends. Fuel 2018, 234, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.S.; Lin, M.C.C.; Huang, I.T.; Wang, C.C. Enhancement of thermal conductivity with carbon nanotube for nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 32, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvan, V.A.M.; Anand, R.B.; Udayakumar, M. Effect of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes as fuel-borne additives in Diesterol blends on the performance, combustion and emission characteristics of a variable compression ratio engine. Fuel 2014, 130, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalam, C.S.; Saravanan, C.G.; Kannan, M. Experimental Investigation on CRDI System Assisted Diesel Engine Fulled by Diesel with Nanotubes. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.B.; Ismail, H.M.; Tan, B.T.; Wang, X. Effects of graphite oxide and single-walled carbon nanotubes as diesel additives on the performance, combustion, and emission characteristics of a light-duty diesel engine. Energy 2018, 161, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seesy, A.I.; Abdel-Rahman, A.K.; Bady, M.; Ookawara, S.J. Performance, combustion, and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled by biodiesel-diesel mixtures with multiwalled carbon nanotubes additives. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 135, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, J.S.; Anand, R.B. An experimental investigation in a diesel engine using carbon nanotubes blended water–diesel emulsion fuel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. A J. Power Energy 2011, 225, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, J.S.; Anand, R. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a diesel engine using Carbon Nanotubes blended Jatropha Methyl Ester Emulsions. Alex. Eng. J. 2014, 53, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigandan, S.; Sarweswaran, R.; Devi, P.B.; Sohret, Y.; Kondratiev, A.; Venkatesh, S.; Vimal, M.R.; Joshua, J.J. Comparative study of nanoadditives TiO2, CNT, Al2O3, CuO and CeO2 on reduction of diesel engine emission operating on hydrogen fuel blends. Fuel 2020, 262, 116336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, A.; Rani, G.J.; Balakrishna, B. Effect of MWCNTs as nano additives in C. Inophyllum biodiesel blend (CIB20) on the performance and emission parameters of a diesel engine. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 50, 2581–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Seesy, A.I.; Waly, M.S.; El-Batsh, H.M.; El-Zoheiry, R.M. Enhancement of the diesel fuel characteristics by using nitrogen-doped multiwalled carbon nanotube additives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 561–577. [Google Scholar]
- Hoseini, S.S.; Najafi, G.; Ghobadian, B.; Mamat, R.; Ebadi, M.T.; Yusaf, T. Novel environmentally friendly fuel: The effects of nanographene oxide additives on the performance and emission characteristics of diesel engines fuelled with Ailanthus altissima biodiesel. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.B.; Rajanren, J.R.; Ismail, H.M.; Swamy, V.; Wang, X. Improving combustion characteristics of diesel and biodiesel droplets by graphite oxide addition for diesel engine applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 2258–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seesy, A.I.; Hassan, H.; Ookawara, S. Effects of graphene nanoplatelet addition to jatropha Biodiesel–Diesel mixture on the performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine. Energy 2018, 147, 1129–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, Y.H.; Ookawara, S.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; El-Khouly, M.A.; Elmehasseb, I.M.; El-Shafai, N.M.; Elwardany, A.E. Investigating the engine performance, emissions and soot characteristics of CI engine fueled with diesel fuel loaded with graphene oxide-titanium dioxide nanocomposites. Fuel 2020, 269, 117436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.S.; Najafi, G.; Ghobadian, B.; Ebadi, M.T.; Mamat, R.; Yusaf, T.J. Performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine using graphene oxide (GO) nano-particles additives in biodiesel-diesel blends. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seesy, A.I.; Hassan, H. Investigation of the effect of adding graphene oxide, graphene nanoplatelet, and multiwalled carbon nanotube additives with n-butanol-Jatropha methyl ester on a diesel engine performance. Renew. Energy 2019, 132, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswaran, R.; Balasubramanian, D.; Sastha, B.D.S. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of unmodified diesel engine with titanium dioxide (TiO2) nano particle along with water-in-diesel emulsion fuel. Fuel 2021, 285, 119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramashivaiah, B.M.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Rajashekhar, C.R.; Khandal, S.V. Studies on Effect of Graphene Nanoparticles Addition in Different Levels with Simarouba Biodiesel and Diesel Blends on Performance, Combustion and Emission Characteristics of CI Engine. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 4793–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudagar, M.E.M.; Nik-Ghazali, N.N.; Kalam, M.A.; Badruddin, I.A.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Ali, M.A.B.; Kamangar, S.; Cho, H.M.; Akram, N. An investigation on the influence of aluminium oxide nano-additive and honge oil methyl ester on engine performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 2291–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, S.; Rufuss, D.D.W.; Hossain, A.K. Microscopic characteristics of biodiesel—Graphene oxide nanoparticle blends and their Utilisation in a compression ignition engine. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachander, J.; Gugulothu, S.; Sastry, G. Performance and Emission Reduction Characteristics of Metal Based SiO2 Nanoparticle Additives Blended with Ternary Fuel (Diesel-MME-Pentanol) on CRDI Diesel Engine. Silicon 2021, 14, 2249–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudagar, M.E.M.; Nik-Ghazali, N.N.; Kalam, M.A.; Badruddin, I.A.; Banapurmath, N.; Khan, T.Y.; Bashir, M.N.; Akram, N.; Farade, R.; Afzal, A. The effects of graphene oxide nanoparticle additive stably dispersed in dairy scum oil biodiesel-diesel fuel blend on CI engine: Performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel 2019, 257, 116015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | ZS1115NM |
| Displacement | 1.194 |
| Bore stroke | 115 115 (mm) |
| Power rated | 16.2/2200/min (kw/r/min) |
| Consumption of the fuel | ≤242.1 (g/kW·h) |
| Cooling system | Condenser> |
| Starting method | Electric starting> |
| Lubrication system | Pressure/splash> |
| Net weight | 185 (kg) |
| Compression ratio | 17> |
| Dynamometer Trade Name | ATE-160 LC |
|---|---|
| Load cell capacity | (0–1050) (N·m) |
| Weight sensor | Load cell |
| Length of calibration lever arm | 0.7645 m |
| Type of absorption | Water/Hydraulic |
| Dynamometer with engine connecting | Using half coupling |
| Specification | Diesel | WCO Biodiesel |
|---|---|---|
| Calorific value | 42.10 MJ/kg | 39.51 MJ/kg |
| Density | 830 kg/m3 | 875 kg/m3 |
| Cetane number | 55 | 52 |
| Flashpoint | 45 °C | 158 °C |
| Kinematic viscosity(cSt)@ 25 °C | 3.14 | 5.13 |
| Specific gravity | 0.85 | 0.88 |
| Auto ignition temperature | 263 °C | 273 °C |
| Cloud point | 0 °C | 6 °C |
| Oxygen content | 0 (wt.%) | 9.414 (wt.%) |
| Water content | 0.05 (vol. %) | 0.05 (vol. %) |
| Specification | B40 + 100 CNT | B40 + 100 GO |
|---|---|---|
| Calorific value | 43.73 MJ/kg | 44.4 MJ/kg |
| Density | 846 kg/m3 | 834 kg/m3 |
| Cetane number | 55.8 | 56.1 |
| Kinematic viscosity(cSt)@ 25 °C | 5.07 | 5.02 |
| Specification | CNTs | GO |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Black | Brown black |
| Form | Powder | Powder |
| Ability of Solubility | Dispersed in water | Dispersed in water |
| Average Size | (L: >660 nm) and (D: 15 ± 7 nm) | Microns in length and a few nanometers in thickness |
| Purity | 94.5% | ------------- |
| Shape (TEM) | Tubular-like shape | Sheets |
| Expiration Date | 10/2023 | 11/2023 |
| Equipment | Uncertainty |
|---|---|
| Exhaust gas analyzer | ±0.5% |
| Smoke meter | ±3% |
| In-cylinder pressure transducer | ±1% |
| In-cylinder pressure transmitter | ±1 Kpa |
| Temperature transmitter | ±1 deg. |
| Brake thermal efficiency | ±0.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkelawy, M.; El Shenawy, E.S.A.; Bastawissi, H.A.-E.; Shams, M.M. Impact of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials on the Performance and Emissions of Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel/Biodiesel Blend. Processes 2023, 11, 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113204
Elkelawy M, El Shenawy ESA, Bastawissi HA-E, Shams MM. Impact of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials on the Performance and Emissions of Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel/Biodiesel Blend. Processes. 2023; 11(11):3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113204
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkelawy, Medhat, El Shenawy A. El Shenawy, Hagar Alm-Eldin Bastawissi, and Mahmoud M. Shams. 2023. "Impact of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials on the Performance and Emissions of Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel/Biodiesel Blend" Processes 11, no. 11: 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113204
APA StyleElkelawy, M., El Shenawy, E. S. A., Bastawissi, H. A.-E., & Shams, M. M. (2023). Impact of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Oxide Nanomaterials on the Performance and Emissions of Diesel Engine Fueled with Diesel/Biodiesel Blend. Processes, 11(11), 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11113204










