Evaluation of the Toxicity of Cafeteria Wastewater Treated by a Coupled System (ARFB-SD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction, Drying and Classification of the AR
2.2. Reagents
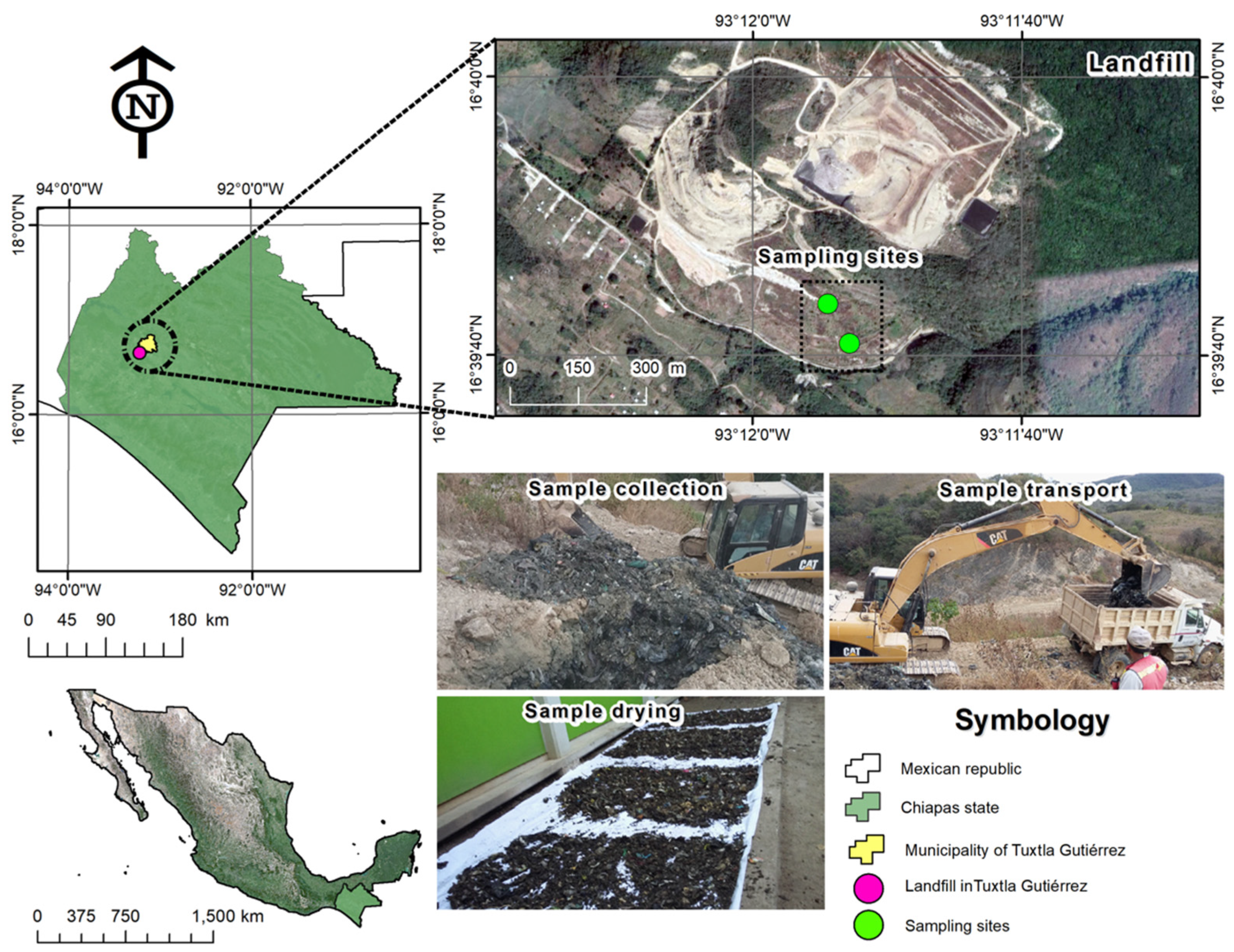
2.2.1. Collection and Characterization of Graywater
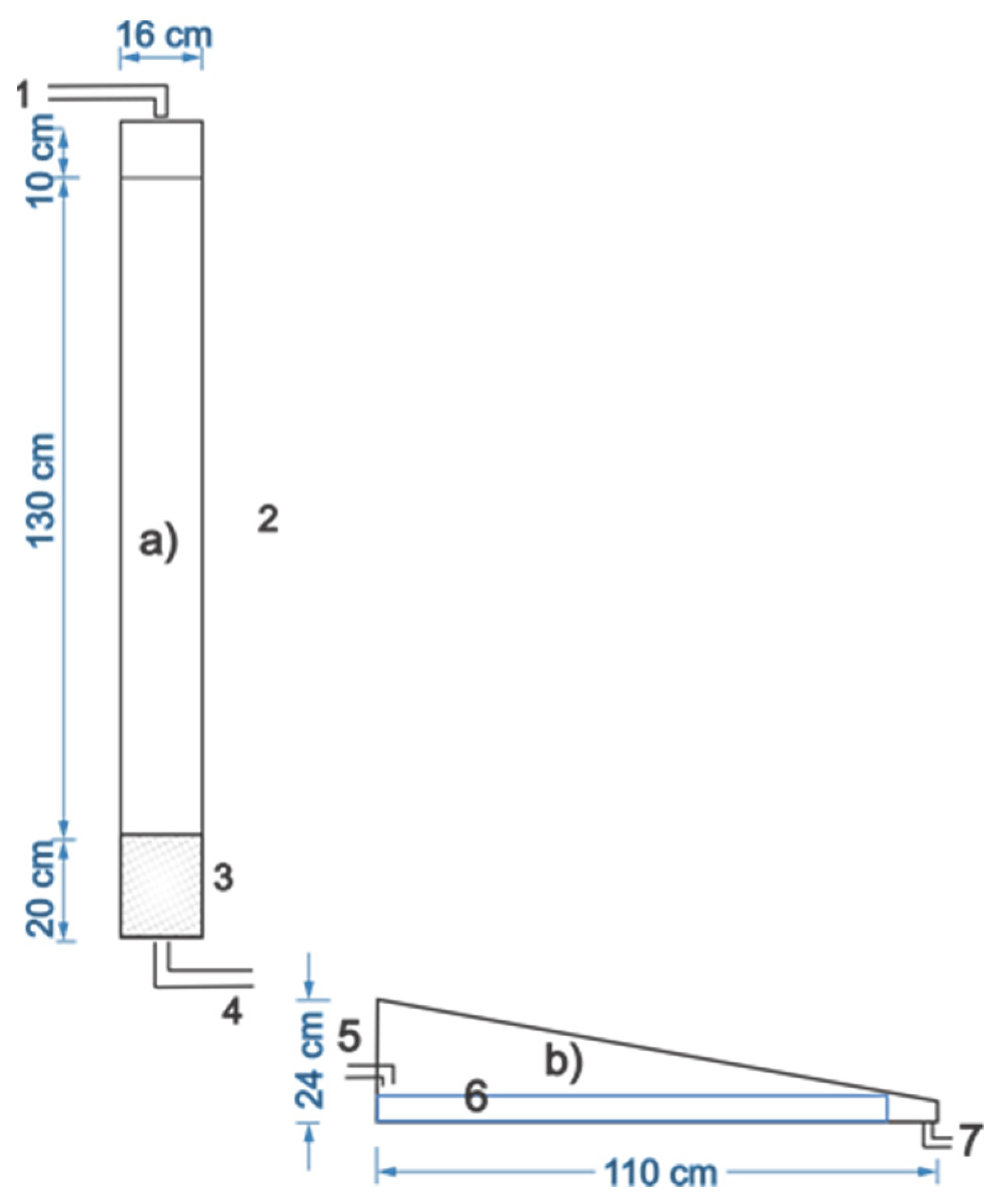
2.2.2. Construction of the ARFB-SD System
2.3. Operation and Monitoring of the ARFB-SD System
2.4. Conducting Toxicity Bioassays
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. AR Extraction, Drying and Classification
3.2. Cafeteria Wastewater Characterization
3.3. Operation and Monitoring of the ARFB-SD System
3.3.1. Stage 1: ARFB
3.3.2. Stage 2: SD
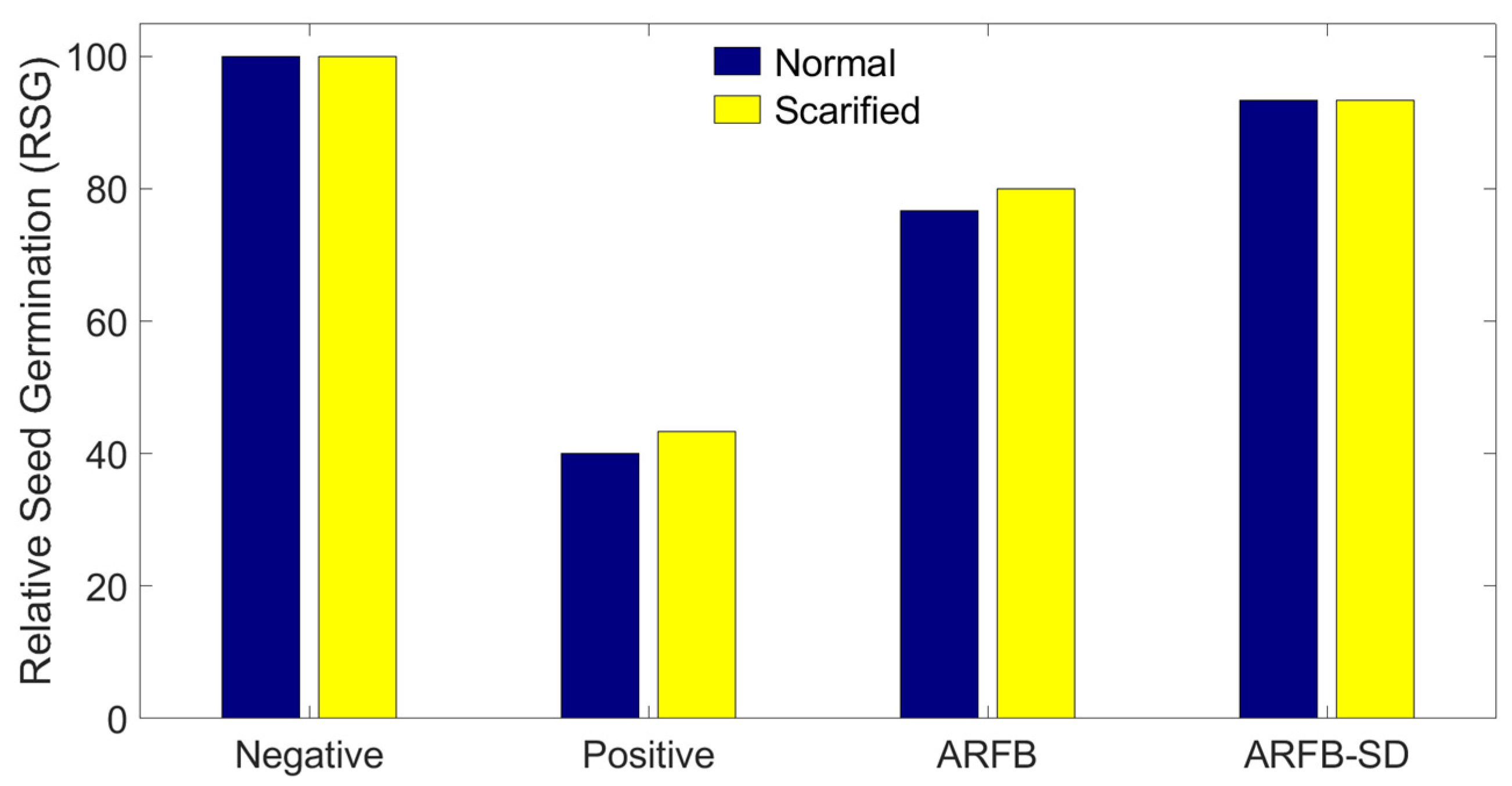
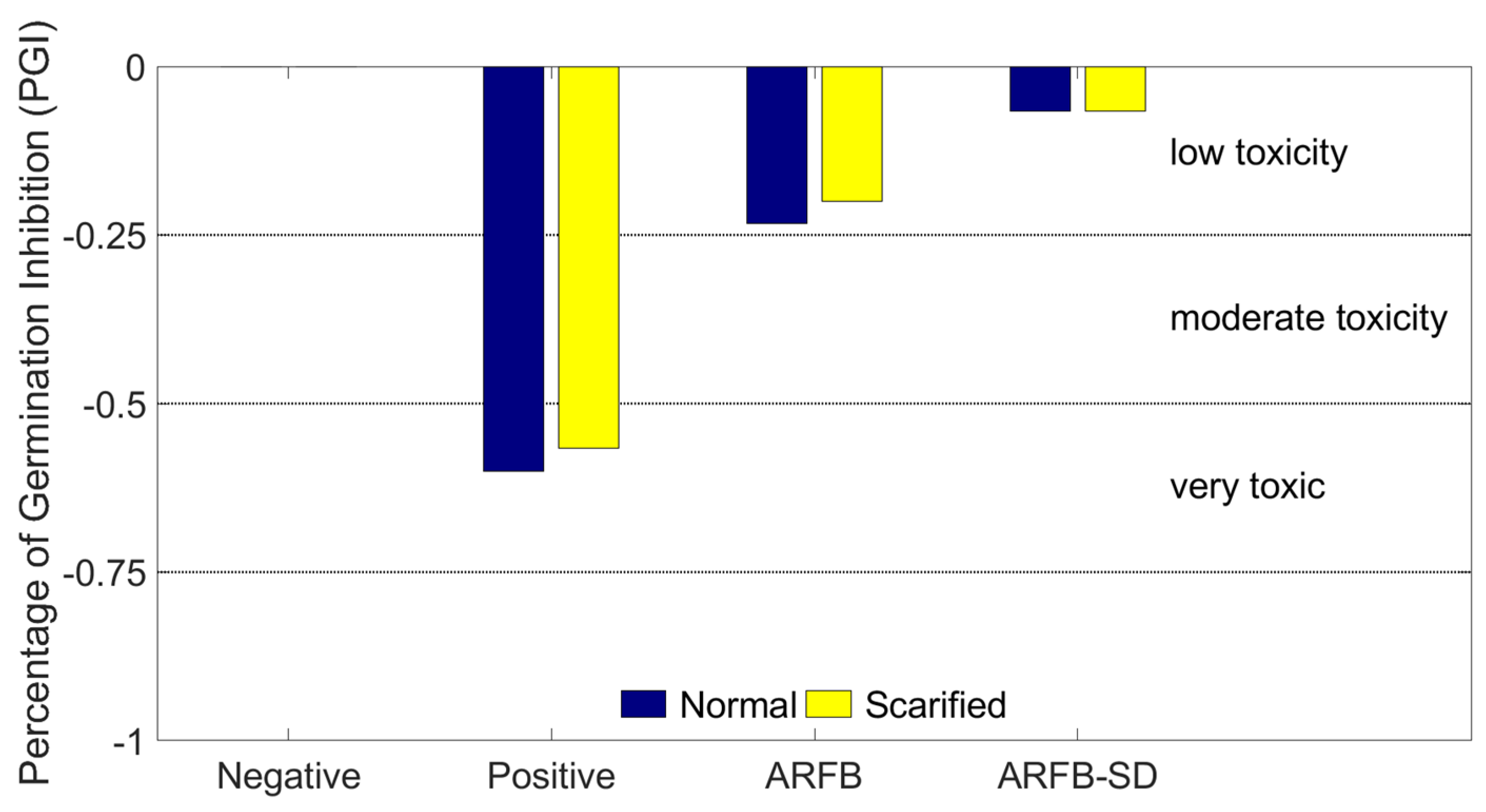
3.4. Toxicity Bioassays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarenga, P.; Mourinha, C.; Farto, M.; Santos, T.; Palma, P.; Sengo, J.; Morais, M.C.; Cunha-Queda, C. Sewage Sludge, Compost and Other Representative Organic Wastes as Agricultural Soil Amendments: Benefits Versus Limiting Factors. Waste Manag. 2015, 40, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, M.; Del Moro, G.; Chimienti, S.; Ritelli, P.; Levantesi, C.; Di Laconi, C. Removal of Pollutants and Pathogens by a Simplified Treatment Scheme for Municipal Wastewater Reuse in Agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, B.; Liang, S. Monitoring Opportunistic Pathogens in Domestic Wastewater from A Pilot-Scale Anaerobic Biofilm Reactor to Reuse in Agricultural Irrigation. Water 2019, 11, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, A.M.; Albarrán, A.; López, D.; Vidal, G. Evaluation of Phytotoxicity of Effluents from Activated Sludge and Constructed Wetland System for Wastewater Reuse. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisión Nacional del Agua–Secretraría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales. Inventario Nacional de Plantas Municipales de Potabilización y de Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales en Operación. Ciudad de México. 2020. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/703303/Inventario_2020.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Murcia-Sarmiento, M.L.; Calderón-Montoya, O.G.; Díaz-Ortiz, J.E. Impacto De Aguas Grises En Propiedades Físicas Del Suelo. Tecnológicas 2014, 17, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Estatal del Agua. Programa Estatal Hídrico 2019–2024: Gobierno del Estado de Chiapas; Instituto Estatal del Agua: Tuxtla Gutiérrez, México, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fichtner, T.; Ibrahim, S.I.; Hamann, F.; Graeber, P.-W. Purification Efficiency for Treated Waste Water in Case of Joint Infiltration with Water Originating from Precipitation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, L.L.; Marder, L.; Benvenuti, T.; Bernardes, A.M. Electrodialysis Applied to The Treatment of a University Sewage for Water Recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, T.; Jefferson, B.; Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Wilde, W.; De Koning, J.; van der Graaf, J.; Wintgens, T. Membrane bioreactor technology for wastewater treatment and reuse. Desalination 2006, 187, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcai, Z.; Hua, L.; Jun, W.; Guowei, G. Treatment of Leachate by Aged-Refuse-Based Biofilter. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 128, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Shen, Z.; Huang, R.; Wang, W. Treatment of Landfill Leachate by Combined Aged-Refuse Bioreactor and Electro-Oxidation. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Xie, B. Use of Aged Refuse-Based Bioreactor/Biofilter for Landfill Leachate Treatment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6543–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Z. Leachate Treatment Using a Demonstration Aged Refuse Biofilter. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erabee, I.K.; Ethaib, S. Treatment of Contaminated Landfill Leachate Using Aged Refuse Biofilter Medium. Orient. J. Chem. 2018, 34, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Tian, J.S.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, Z.L.; Kong, X.J.; Chao, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, D.L. Removal of Phosphorus and Nitrogen From Domestic Wastewater Using A Mineralized Refuse-Based Bioreactor. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nájera-Aguilar, H.A.; Mayorga-Santis, R.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.F.; Araiza-Aguilar, J.A.; Martínez-Salinas, R.I.; García-Lara, C.M.; Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Aged Refuse Filled Bioreactor Using Like a Biological Treatment for Sugar Mill Wastewater. Sugar Tech 2021, 23, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Zeng, L.; Li, Q. Bioremediation of Petroleum-Contaminated Soil by Semi-Aerobic Aged Refuse Biofilter: Optimization and Mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 125354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, R.Z.; Suja, F.; Ruslan, M.H.; Jalil, N.A. The application of a solar still in domestic and industrial wastewater treatment. Sol. Energy 2013, 93, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, A.Q.; Ghawaibeh, S.; Abu Irjei, M. The Application of Solar Distillation Technique as a Mean for Olive Mill Wastewater Management. Water Environ. J. 2017, 32, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur-González, M.G.; Estepa-Molina, C.; Martín-Peinado, F.; Morales-Ruano, S. Toxicity Assessment Using Lactuca sativa L. Bioassay of the Metal (Loid)S As, Cu, Mn, Pb and Zn in Soluble-in-Water Saturated Soil Extracts from an Abandoned Mining Site. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Mafull, C.A.; Hotza, D.; García-Gallardo, R.; Cruz Junior, O.F.; Serafin, J. Adsorption and Thermodynamic Parameters of Activated Carbon-Diazepam Systems in Simulated Gastric Fluid. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priac, A.; Badot, P.M.; Crini, G. Treated Wastewater Phytotoxicity Assessment Using Lactuca Sativa: Focus on Germination and Root Elongation Test Parameters. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2017, 340, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendri, I.; Ben Saad, R.; Khemakhem, B.; Ben Halima, N.; Gdoura, R.; Abdelkafi, S. Effect of Treated and Untreated Domestic Wastewater on Seed Germination, Seedling Growth and Amylase and Lipase Activities in Avena sativa L. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 93, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassama, U.M.; Puteh, A.B.; abd-Halim, M.R.; Kargbo, B. Influence of Municipal Wastewater on Rice Seed Germination, Seedling Performance, Nutrient Uptake, and Chlorophyll Content. J. Crop Sci. Biotech 2015, 18, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcová, D.; Vaverková, M.D.; Brousková, E. The Toxicity of Two Types of Sewage Sludge from Wastewater Treatment Plant for Plants. J. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 17, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, B.; Sheena Kumari, S.K.; Stenstrom, T.A.; Bux, F. Evaluation of Phytotoxicity Effect on Selected Crops Using Treated and Untreated Wastewater from Different Configurative Domestic Wastewater Plants. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Ramírez, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.F.; Nájera-Aguilar, H.A.; Martínez-Salinas, R.I.; Vera-Toledo, P.; Araiza-Aguilar, J.A.; Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Biorreactor Empacado Con Materiales Estabilizados (ARFB), Como Pretratamiento Para Lixiviados De Rellenos Sanitarios. Rev. Mex. De Ing. Química 2018, 17, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Pérez, J.; García-Lara, C.M.; Nájera-Aguilar, H.A.; Vera Toledo, P.; Vázquez-Sánchez, R.A. Desarrollo Y Caracterización De Un Destilador Solar Para Su Aprovechamiento En El Tratamiento De Agua Contaminada. Lacandonia 2010, 4, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ecological effects test guidelines. In Seedling Emergence and Seedling Growth; OPPTS 850.4100; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Oleszczuk, P. Testing of Different Plants to Determine Influence of Physico-Chemical Properties and Contaminants Content on Municipal Sewage Sludges Phytotoxicity. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 25, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañas, P.; de las Heras, J. Phytotoxicity Test Applied to Sewage Sludge Using Lactuca sativa L. and Lepidium sativum L. Seeds. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 15, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, N.J.; Bosker, T.; Lantinga, E.A. Effects of Cattle Dung from Farms with Different Feeding Strategies on Germination and Initial Root Growth of Cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, I.; Martínez, F.; Cala, V. Heavy Metal Speciation and Phytotoxic Effects of Three Representative Sewage Sludges for Agricultural Uses. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Song, L.; Huang, R.; Song, L.; Li, X. Recycling of Aged Refuse from a Closed Landfill. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.F.; Nájera-Aguilar, H.A.; Araiza-Aguilar, J.A.; Martínez-Salinas, R.I.; García-Lara, C.M.; González-Vázquez, U.; Cruz-Salomón, A. Novel Treatment of Sugar Mill Wastewater in a Coupled System of Aged Refuse Filled Bioreactors (ARFB): Full-Scale. Processes 2021, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Yue, P.L. Electrocoagulation and Electroflotation of Restaurant Wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. 2000, 126, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Wang, P.; Jiang, L. Study on Advanced Oxidation of Cafeteria Wastewater Using Fenton Reagent. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 424, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin Mohamed, R.M.S.; Apandi, N.; Matias Peralta, H.M.; Kasim, A.H.M. Removal of Nutrients from Cafeteria Wastewater Using Varying Concentrations of Microalga Scenedesmus Sp. Proceedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melidis, P.; Vaiopoulou, E.; Athanasoulia, E.; Aivasidis, A. Anaerobic Treatment of Domestic Wastewater Using an Anaerobic Fixed-Bed Loop Reactor. Desalination 2009, 248, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez Novelo, R.; Mena Velázquez, R.; Castillo Borges, E.R.; Sauri Riancho, M.R. Evaluación De Un Reactor UASB Para Aguas Porcinas Inoculado Con Líquido Ruminal. Ingeniería 2013, 17, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Shi, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H. Novel Engineering Controls to Increase Leachate Contaminant Degradation by Refuse: From Lab Test to In Situ Engineering Application. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Valencia, M.N.; Orta de Velásquez, M.T.; Franco, V. Urban Agriculture, Using Sustainable Practices That Involve the Reuse of Wastewater and Solid Waste. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaouefi, Z.; Toledo-Cervantes, A.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L.; Muñoz, R. Decolorization and Phytotoxicity Reduction In an Innovative Anaerobic/Aerobic Photobioreactor Treating Textile Wastewater. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Athar, A.R. Textile Effluents Affected Seed Germination and Early Growth of Some Winter Vegetable Crops: A Case Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 2009, 198, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouider, M.; Feki, M.; Sayadi, S. Bioassay and use in irrigation of untreated and treated wastewaters from phosphate fertilizer industry. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Chu, L.M. Phytotoxicity of Veterinary Antibiotics to Seed Germination and Root Elongation of Crops. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamz Piedra, A.; González Cepero, M.C. Salinity as a problem in agriculture: Plant breeding an immediate solution. Cultiv. Trop. 2013, 34, 31–42. [Google Scholar]


| AR Composition (%) | Particle Size Diameter (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon Bags | Rigid Plastics | Others * | Thin Materials | Total | > 40 mm | ≤ 40 mm | Total |
| 11.1 | 10.2 | 21.3 | 57.4 | 100 | 15.05 | 84.95 | 100 |
| Parameter | Units | Average and Range |
|---|---|---|
| COD | mg/L | 3167 (725–5092) |
| BOD | mg/L | 1990 (711–2933) |
| Biodegradability Index (BI) | --- | 0.63 |
| pH | --- | 6.9 (6.7–7.0) |
| Turbidity | UTN | 549.2 (456–622) |
| Color | Pt-Co | 554 (506–602) |
| Chlorides | mg/L | 180 (163–191) |
| Phosphorus | mg/L | 25.1 (21.8–32.7) |
| Nitrogen | mg/L | 11.676 (8.5–15.3) |
| Effluent | Volume (ml) | Number of Seeds | Time (Days) | Seeds | Relative Seed Germination (No Dilution Unless Specified) | Reference | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Textile | 4 | 35 | 14 | Radish | DW | Treated | DW | Untreated | [45] | ||||||
| 89.3 | 91.2 | 89.3 | 89.83 | ||||||||||||
| WWTP | 5 | 100 | 3 | DW | WWTP 1 | WWTP 2 | [46] | ||||||||
| Lettuce | 58.5 | 33 | 3.78 | ||||||||||||
| Radish B. | 89.3 | 58.4 | 31.8 | ||||||||||||
| WWTP | 6 | 10 | 7 | Lettuce | WWTP 1 | WWTP 2 | [27] | ||||||||
| Treated | Untreated | Treated | Untreated | ||||||||||||
| DU 1:4 | ND | DU 1:4 | ND | DU 1:4 | ND | DU 1:4 | ND | ||||||||
| 96.4 | 94.4 | 90.3 | 68.8 | 98.4 | 94.4 | 90.2 | 83.3 | ||||||||
| VAs | 5 | 20 | 5-7 | Lettuce | Aqueous solutions of the five VAs: 0.01 to 1 mg/L | [47] | |||||||||
| TC | SMZ | NOR | ERY | CAP | |||||||||||
| 93 | 93 | 95 | 93 | 95 | |||||||||||
| WWTP | 4 | 30 | 7 | Lettuce | Quality of Water | [23] | |||||||||
| Reverse Osmosis | Distilled | ||||||||||||||
| 98 | 94 | ||||||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Aguilar, H.; García-Lara, C.M.; Nájera-Aguilar, H.A.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.F.; Martínez-Salinas, R.I.; Aguilar, J.A.A. Evaluation of the Toxicity of Cafeteria Wastewater Treated by a Coupled System (ARFB-SD). Processes 2022, 10, 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10081442
Hernández-Aguilar H, García-Lara CM, Nájera-Aguilar HA, Gutiérrez-Hernández RF, Martínez-Salinas RI, Aguilar JAA. Evaluation of the Toxicity of Cafeteria Wastewater Treated by a Coupled System (ARFB-SD). Processes. 2022; 10(8):1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10081442
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Aguilar, Hannia, Carlos M. García-Lara, Hugo A. Nájera-Aguilar, Rubén F. Gutiérrez-Hernández, Rebeca I. Martínez-Salinas, and Juan A. Araiza Aguilar. 2022. "Evaluation of the Toxicity of Cafeteria Wastewater Treated by a Coupled System (ARFB-SD)" Processes 10, no. 8: 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10081442
APA StyleHernández-Aguilar, H., García-Lara, C. M., Nájera-Aguilar, H. A., Gutiérrez-Hernández, R. F., Martínez-Salinas, R. I., & Aguilar, J. A. A. (2022). Evaluation of the Toxicity of Cafeteria Wastewater Treated by a Coupled System (ARFB-SD). Processes, 10(8), 1442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10081442







