Desired Dynamics-Based Generalized Inverse Solver for Estimation Problems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
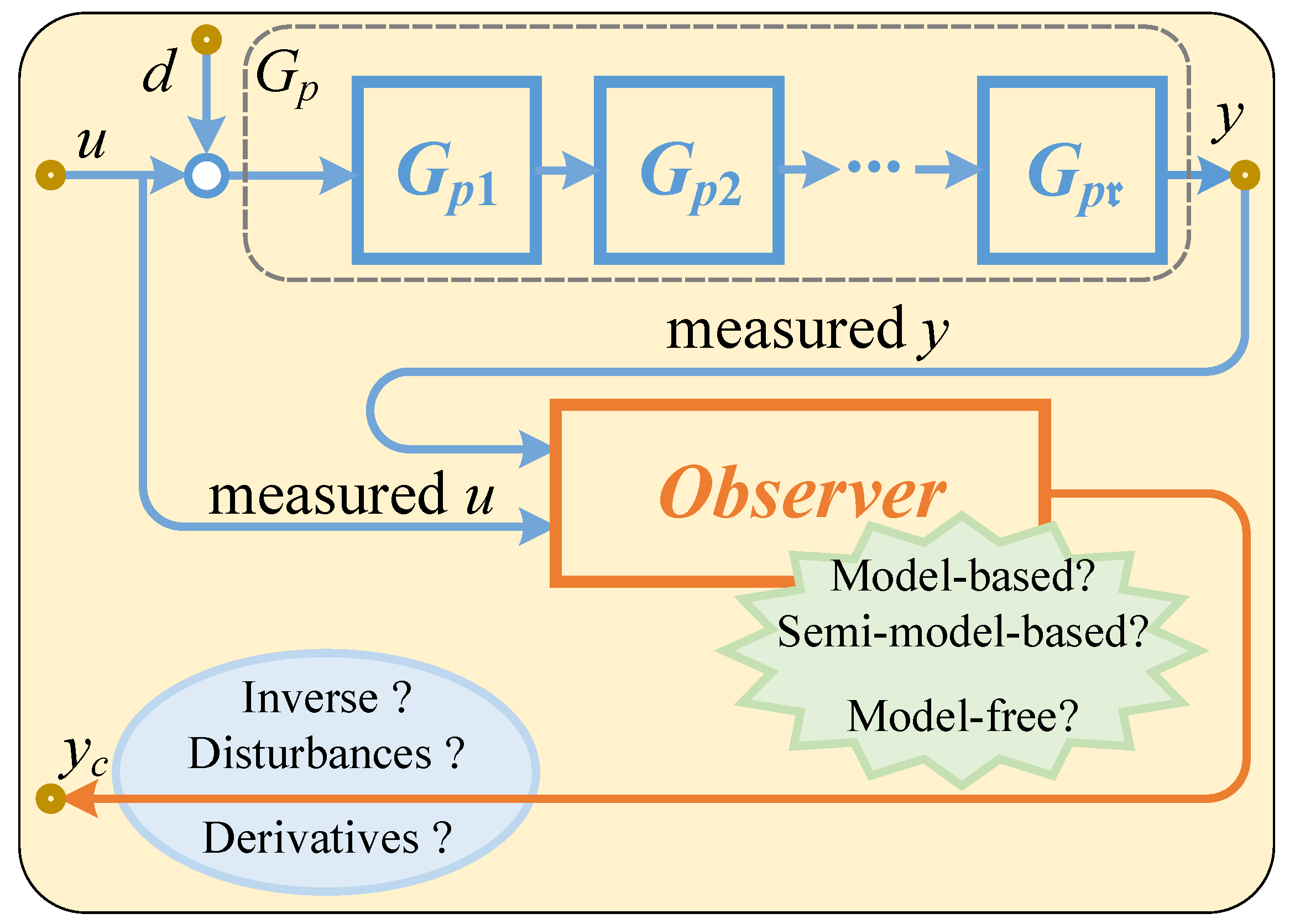
- A novel estimator, named generalized inverse solver (GIS), which is more structurally unified and functionally diverse, is presented. Using GIS to solve the generalized inverse, many estimation problems can be solved; for example, solving the inverse of the system, finding the derivatives of each order of the system, and obtaining the disturbances.
- (2)
- A desired dynamics-based parameterization method is proposed to correct the estimation error of GIS, where states are directly used in the error-correction mechanism (ECM) to accelerate the convergence of GIS. This method is simple and physically meaningful, called desired dynamics-based GIS. Besides, the nominal models in GIS can be model-based, semi-model-based, or even model-free depending on prior knowledge of the system.
- (3)
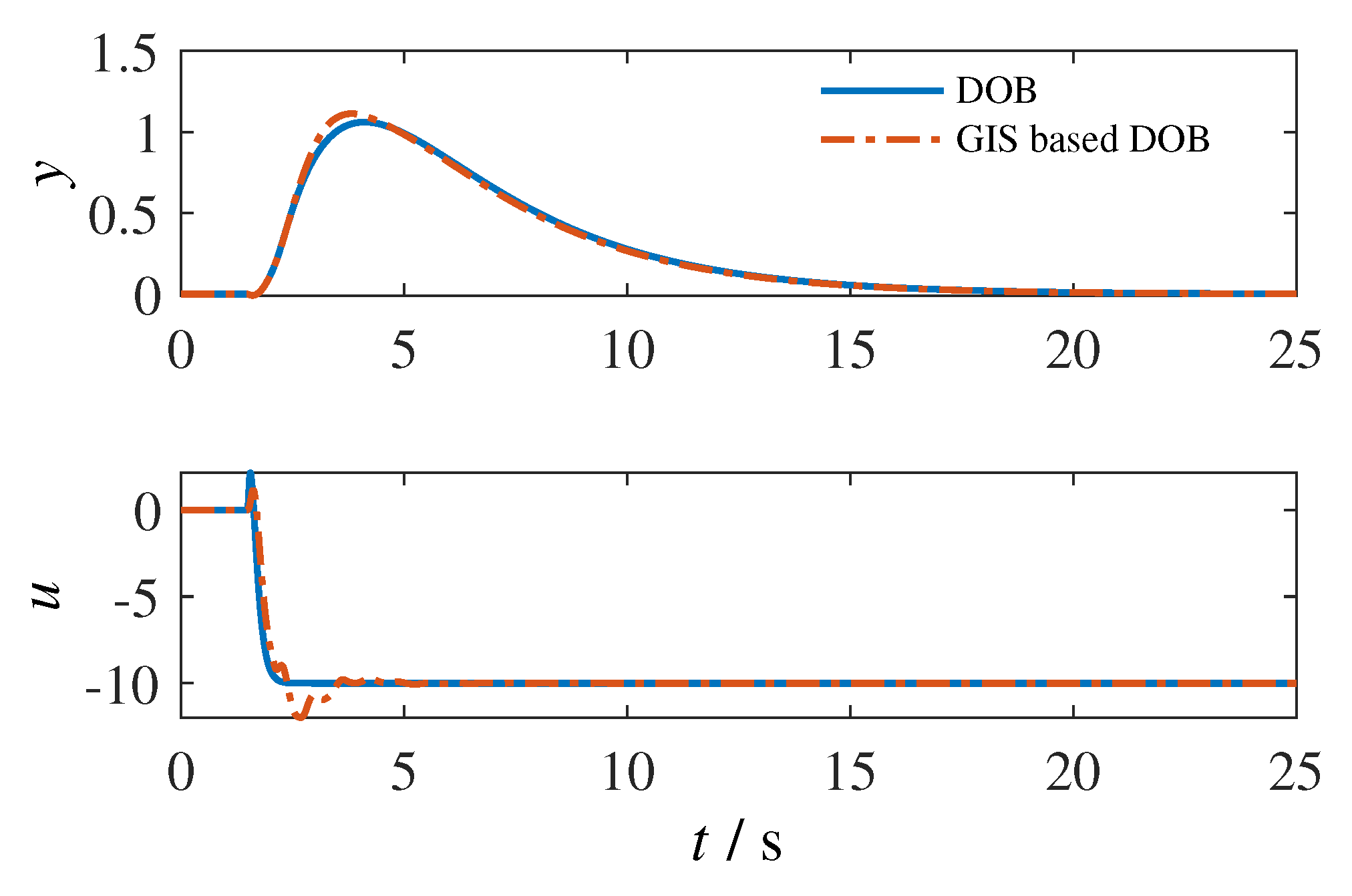
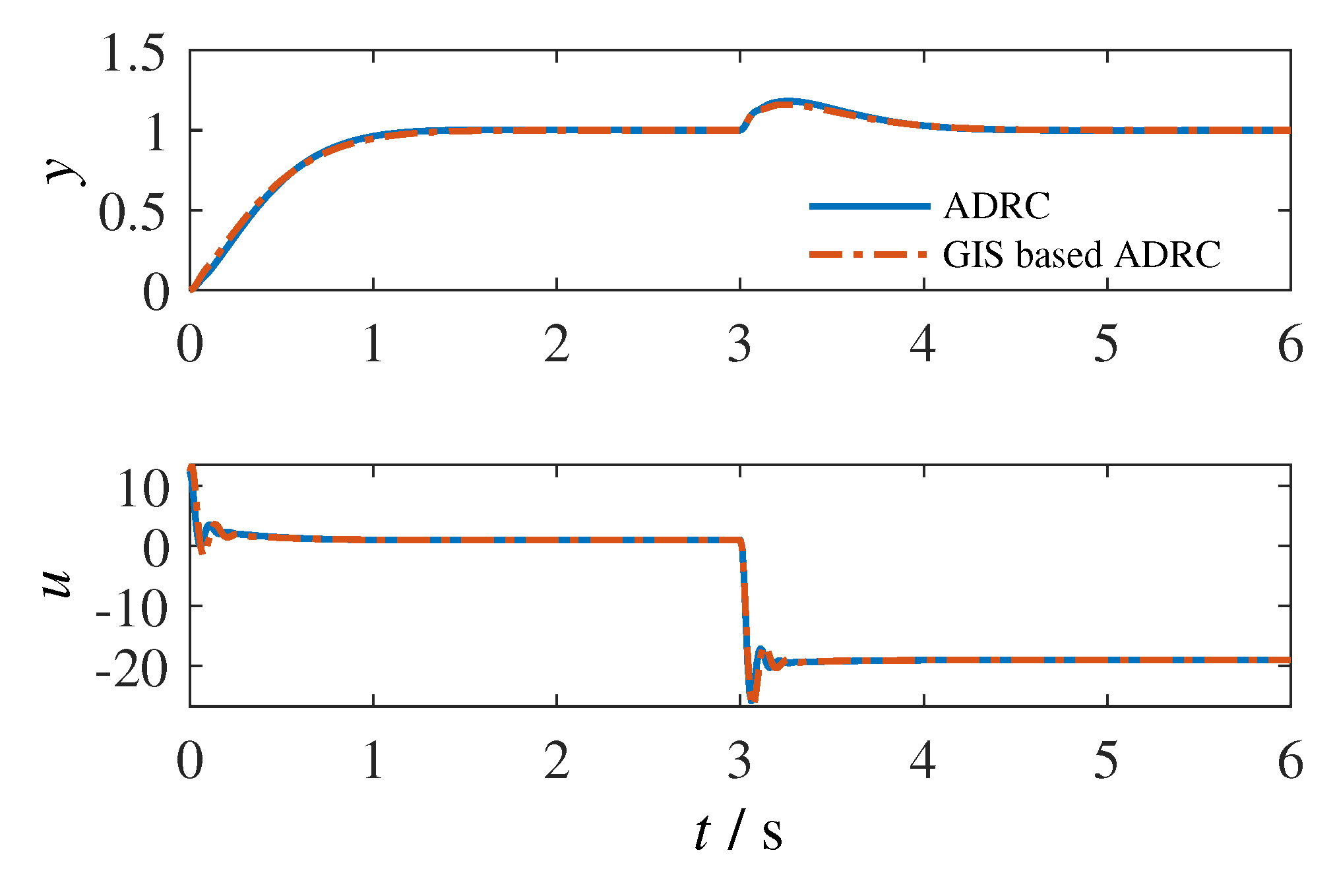
- Case studies of rotary flexible link are presented through the simulation, in order to test the performance of GIS in comparison with that of other observers. Some control cases are studied, including a comparison with DOB and ESO, in order to illustrate their approximate equivalence with GIS.
2. Problem Formulation
3. Fundamentals of General Estimator
4. Asymptotic Analysis
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- In particular, if the nominal model of the controlled system is integral series type, i.e., , in (24) can be rewritten as : that is,
5. Desired Dynamics-Based Parameterization
| Algorithm 1: An algorithm to tune desired dynamic-based GIS via frequency response. |
 |
6. Stability
7. Case Studies
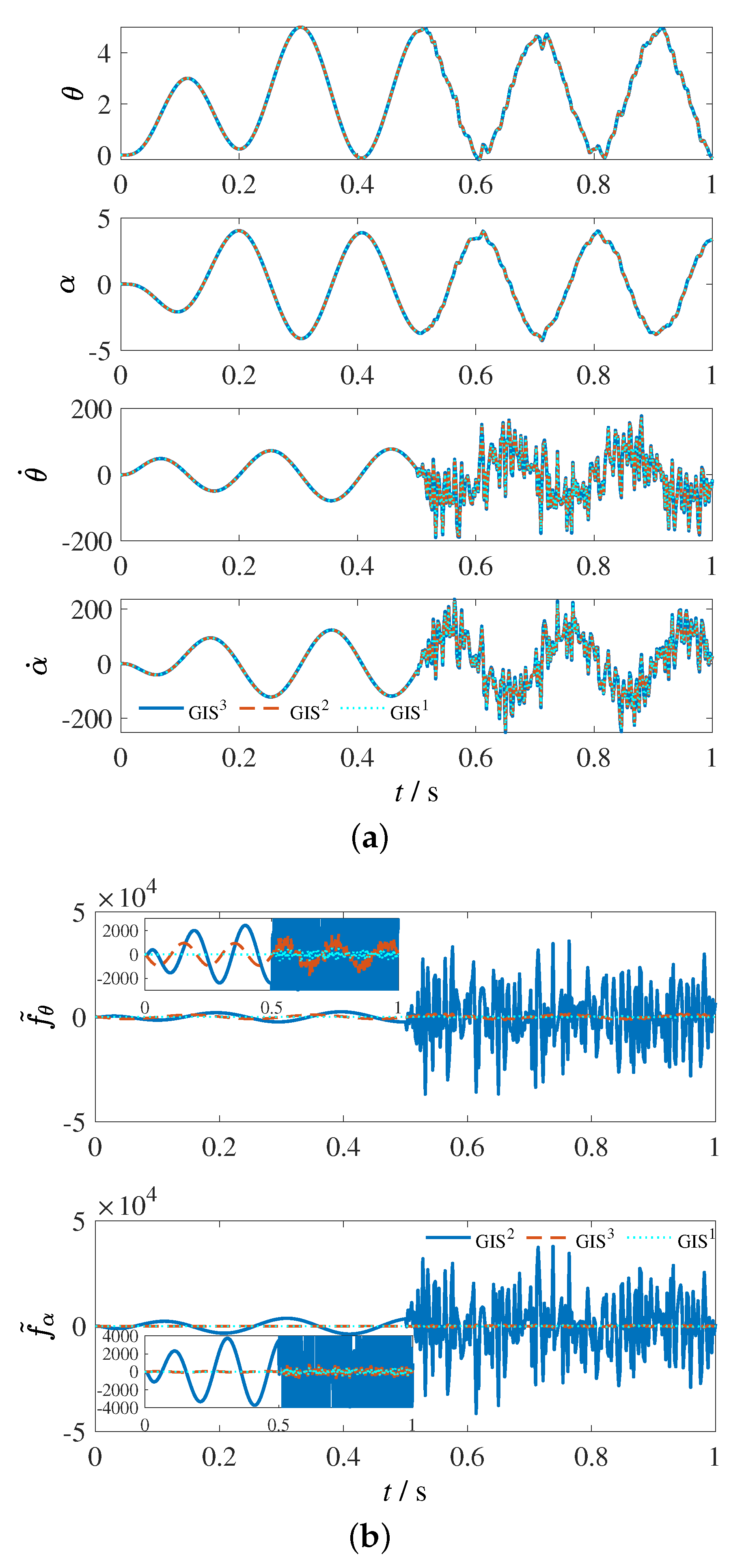
7.1. Estimation Problem for Rotary Flexible Link
7.2. Estimation Problem in Control
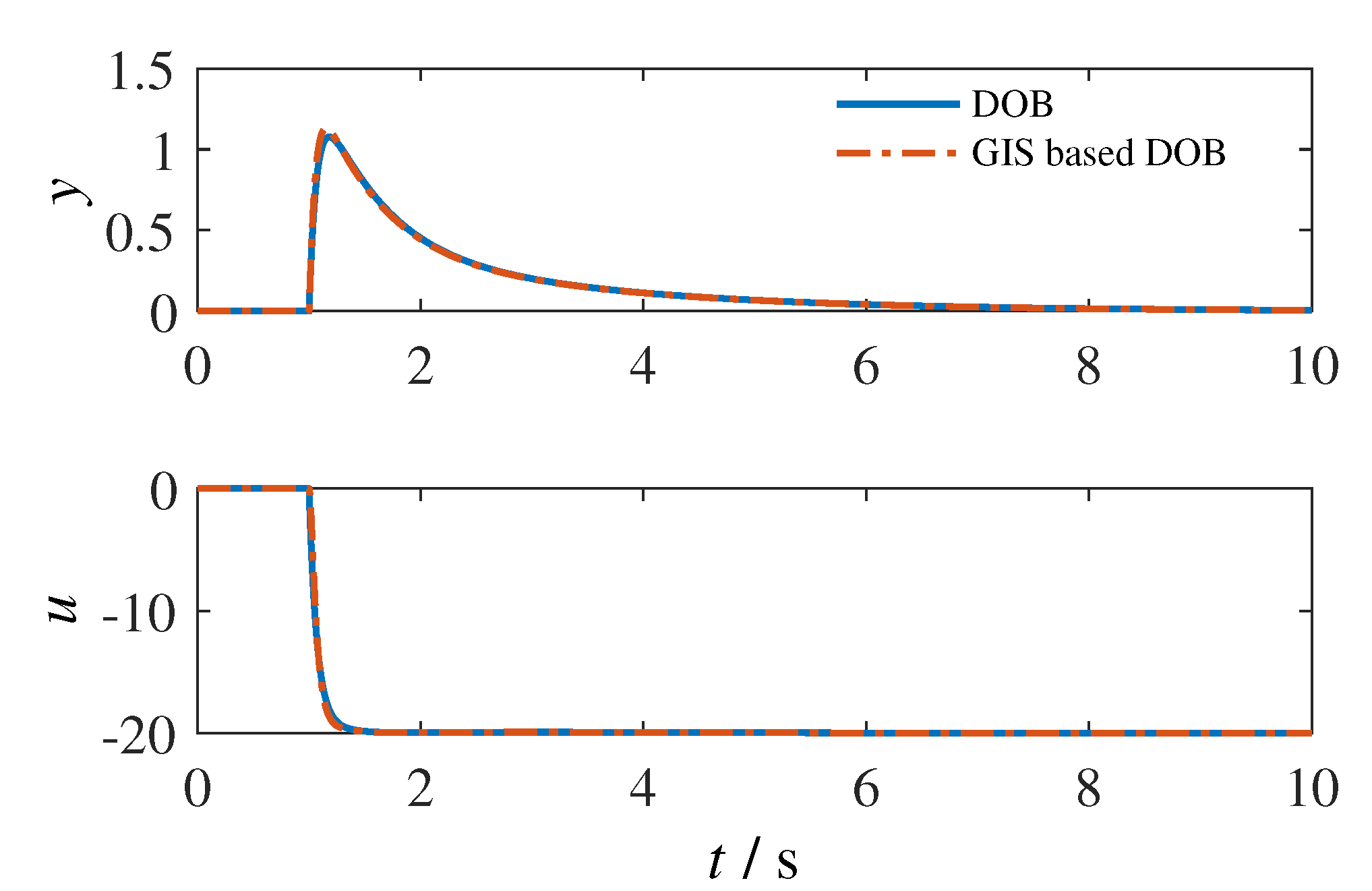
7.2.1. GIS vs. DOB
7.2.2. GIS vs. ESO
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DDE PID | Desired Dynamic Equation proportional-integral-derivative; |
| DOB | Disturbance observer; |
| DOBC | Disturbance observer-based control; |
| ECM | Error-correction mechanism; |
| ESO | Extended state observer; |
| FSO | Full-state observer; |
| GIS | Generalized inverse solver; |
| HGO | High-gain observer; |
| KF | Kalman filter; |
| LO | Luenberger observer. |
Appendix A. The Principle of DDE PID
- (1)
- The relative degree is known.
- (2)
- The spectrum of the polynomial is in the open left half-plane.
- (3)
- The sign of the high frequencies gain is known.
- (4)
- The measure of the output variable and of its time derivatives of order i is available up to order .
Appendix B. The Proof of Theorem 1
Appendix C. The proof of Corollary 1
References
- Bernard, P.; Andrieu, V.; Astolfi, D. Observer design for continuous-time dynamical systems br. Annu. Rev. Control. 2022, 53, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, S.J.; Tang, Z.G.; Xu, J.T.; Wang, W.Z. A novel method of multiple adaptive notch filtering for flexible missile vibration suppression. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2020, 92, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D.G. Observing the state of a linear system. IEEE Trans. Mil. Electron. 1964, 8, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariyildiz, E.; Ohnishi, K. A guide to design disturbance observer. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. Trans. ASME 2014, 136, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Scaling and Bandwidth-Parameterization based Controller Tuning. In Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 27–29 June 2003; pp. 4989–4996. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.Z.; Han, J.Q.; Xi, F.B. Linear tracking-differentiator and application to online estimation of the frequency of a sinusoidal signal with random noise perturbation. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2002, 33, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.Z.; Zhao, Z.L. On convergence of tracking differentiator. Int. J. Control. 2011, 84, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D.G. Observers For Multivariable Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1966, 11, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luenberger, D.G. Introduction to Observers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1971, 16, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, N.H.; Seo, J.H. Input output linearization approach to state observer design for nonlinear system. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2000, 45, 2388–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, R.; van Goor, P.; Hamel, T. Observer Design for Nonlinear Systems with Equivariance. Annu. Rev. Control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 5, 221–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z.; Qian, W. An improved multiple-state observer of Boolean control networks. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 2651–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Leifeld, T.; Zhang, P. Reduced-Order Observer Design for Boolean Control Networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.H. Observer design and stability analysis for a class of PDE chaotic systems. J. Frankl.-Inst.-Eng. Appl. Math. 2021, 358, 3232–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, X. Disturbance Observer-Based Control: Methods and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.H.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Li, S. Disturbance-Observer-Based Control and Related Methods - An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xue, W.; Shi, G.; Zhu, M.; Li, D. Frequency response-based decoupling tuning for feedforward compensation ADRC of distributed parameter systems. Control. Eng. Pract. 2022, 126, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, G.; Li, D. Active disturbance rejection control based on feedforward inverse system for turbofan engines. In Proceedings of the 6th IFAC Conference on Engine Powertrain Control, Simulation and Modeling E-COSM 2021, Tokyo, Japan, 23–25 August 2021; pp. 376–381. [Google Scholar]
- Efimov, D.V.; Fridman, L. A Hybrid Robust Non-Homogeneous Finite-Time Differentiator. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2011, 56, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Zavala, E.; Moreno, J.A. Levant’s Arbitrary-Order Exact Differentiator: A Lyapunov Approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2019, 64, 3034–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Gao, Z.Q.; Aac, A.A.C. A comparison study of advanced state observer design techniques. In Proceedings of the Annual American Control Conference (ACC 2003), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 27–29 June 2003; pp. 4754–4759. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Wei, C.Z.; Wu, R.; Cui, N.G. Non-Recursive Fixed-Time Convergence Observer and Extended State Observer. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62339–62351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Laflamme, S.; Dodson, J.; Joyce, B. Introduction to State Estimation of High-Rate System Dynamics. Sensors 2018, 18, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong, T.T.; Ohishi, K.; Mitsantisuk, C.; Yokokura, Y.; Ohnishi, K.; Oboe, R.; Sabanovic, A. Disturbance Observer and Kalman Filter Based Motion Control Realization. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2018, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.C.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.N.; You, X. Tracking differentiator and extended state observer-based nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode attitude control for a quadrotor. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H. A robust damping controller for DFIG based on variable-gain sliding mode and Kalman filter disturbance observer. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 107, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, G.E.M.; Asirvadam, V.S.; Zulkifli, S.A.B.; Sattar, A.; Kumar, D.; Anwer, A. Effects of unmodelled dynamic factors on an under-actuated quadrotor: A review of hybrid observer design methods. Meas. Control. 2020, 53, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghapani, F.; Babadi, B. Two parameter weighted mixed estimator in linear measurement error models. In Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2020; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Tornambè, A.; Valigi, P. A decentralized controller for the robust stabilization of a class of MIMO linear systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1992, 18, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, D.; Gao, Q.; Wang, C. Two-degrees-of-freedom PID controller tuning method. Qinghua Daxue Xuebao/J. Tsinghua Univ. 2008, 48, 1962–1966. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S. Research on the Desired Dynamic Selection of a Reference Model-Based PID Controller: A Case Study on a High-Pressure Heater in a 600 MW Power Plant. Processes 2022, 10, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y. A Controller Synthesis Method to Achieve Independent Reference Tracking Performance and Disturbance Rejection Performance. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16164–16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

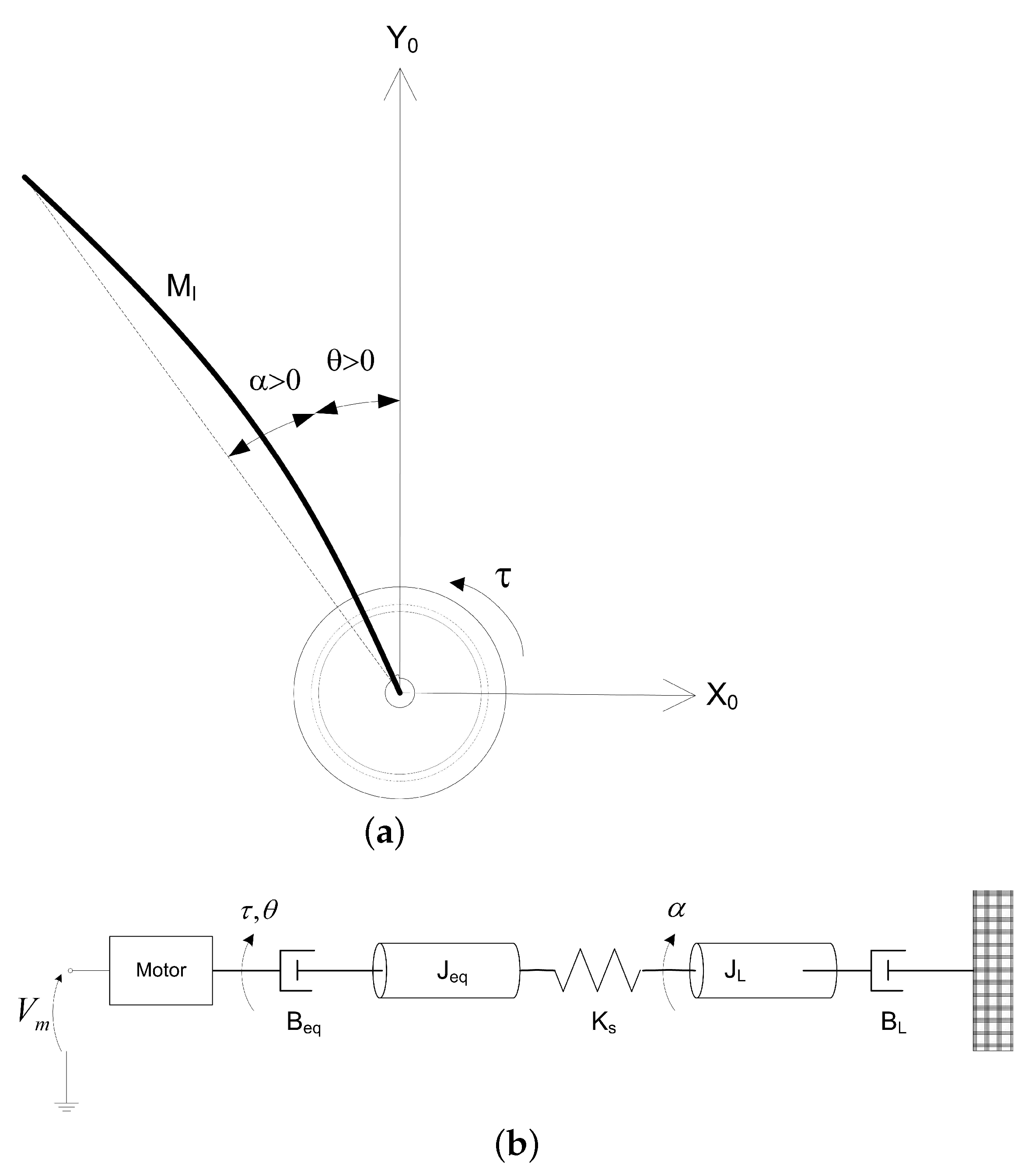


| Symbol | Description | Value | Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| high-gear equivalent viscous damping coefficient | 0.015 N · m/(rad/s) | ||
| viscous damping coefficient | negligible | ||
| geabox efficiency | 0.90 | ||
| motor efficiency | 0.69 | ||
| high-gear equivalent moment of inertia | 2.08 kg | ||
| flexible link moment of inertia | 0.0038 kg | ||
| high-gear total gear ratio low-gear total gear ratio | 70 14 | ||
| stiffness | 1.3 N · m / rad | ||
| motor back-emf constant | 7.68 V/(rad/s) | ||
| motor current-torque constant | 7.68 N · m/A | ||
| motor armature resistance | 2.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, M. Desired Dynamics-Based Generalized Inverse Solver for Estimation Problems. Processes 2022, 10, 2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112193
Liu S, Zhang Y, Gao Z, Chen Y, Li D, Zhu M. Desired Dynamics-Based Generalized Inverse Solver for Estimation Problems. Processes. 2022; 10(11):2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112193
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shaojie, Yulong Zhang, Zhiqiang Gao, Yangquan Chen, Donghai Li, and Min Zhu. 2022. "Desired Dynamics-Based Generalized Inverse Solver for Estimation Problems" Processes 10, no. 11: 2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112193
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhang, Y., Gao, Z., Chen, Y., Li, D., & Zhu, M. (2022). Desired Dynamics-Based Generalized Inverse Solver for Estimation Problems. Processes, 10(11), 2193. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112193








