The Efficacy of Plant Enzymes Bromelain and Papain as a Tool for Reducing Gluten Immunogenicity from Wheat Bran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.2.1. The Conditions of Enzymatic Hydrolysis
2.2.2. Extraction of Gluten Proteins
2.3. Physico-Chemical Analysis of the Composition of Wheat Bran and Hydrolysates
2.3.1. Determination of Soluble Proteins
2.3.2. Evaluation of Protease Activity
2.3.3. Immunological Analysis
2.3.4. Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Influence of Hydrolysis Conditions on the Degradation of Gluten in Wheat Bran
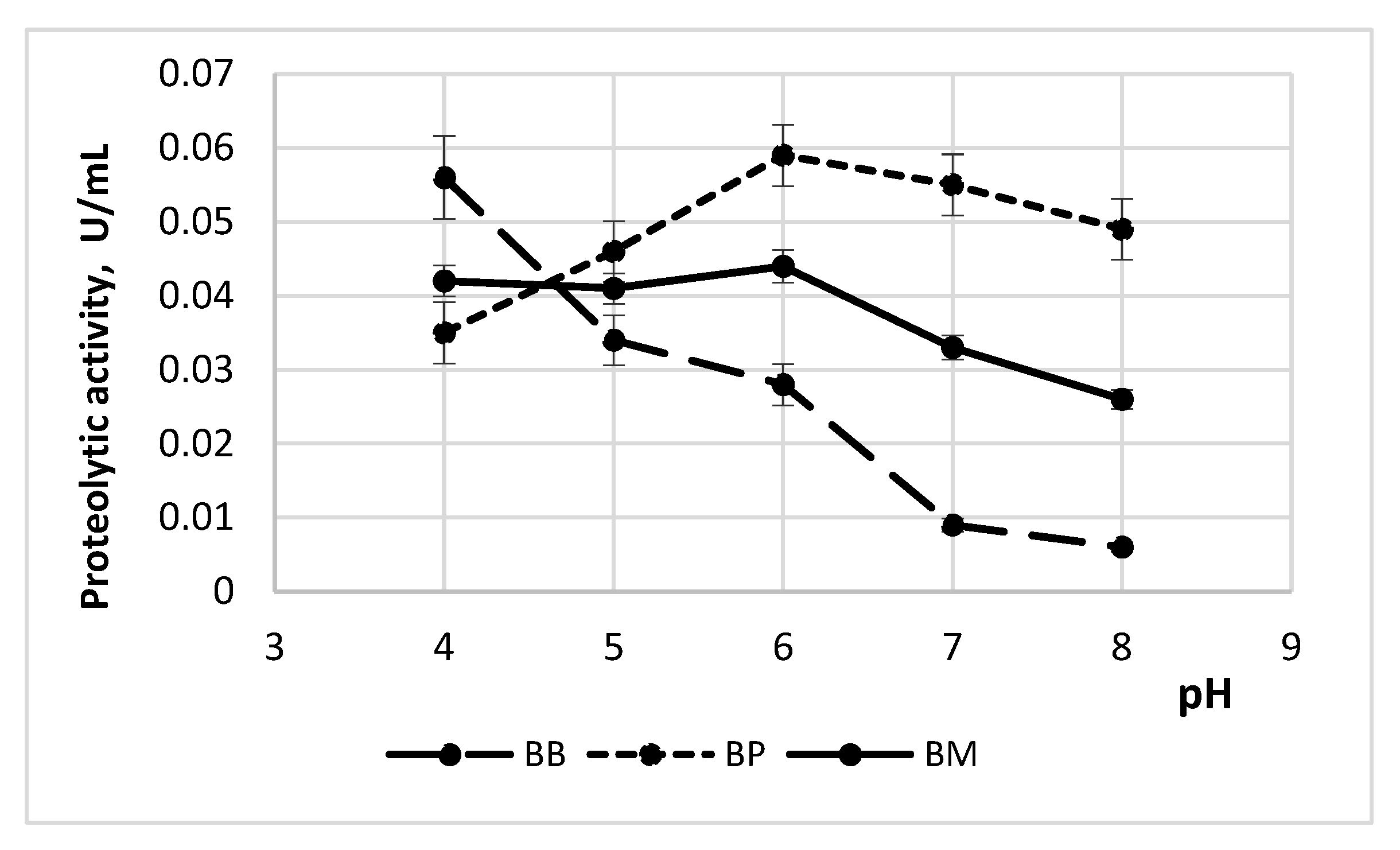
3.1.1. Enzyme Activity Depending on pH
3.1.2. Soluble Protein Content in Wheat Bran Hydrolysates
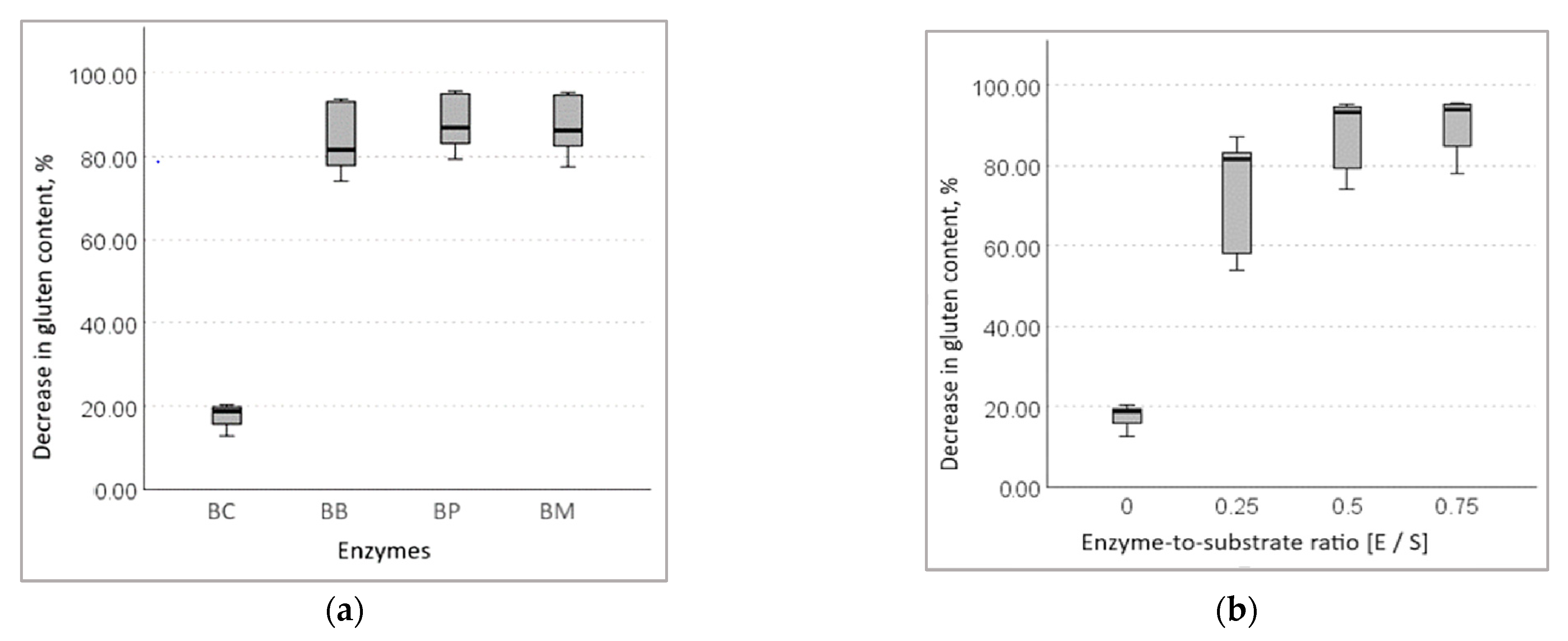
3.1.3. Decrease in Gluten Content in Wheat Bran Hydrolysates
- (a).
- when treated with bromelain:
- (b).
- when treated with papain:
- (c).
- when treated with a combination of bromelain and papain:
3.2. The Changes in the Fractions of Wheat Gliadins Detected by Liquid Chromatography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P.; Arora, A.; Strand, T.A.; Leffler, D.A.; Catassi, C.; Green, P.H.; Kelly, C.P.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Global prevalence of celiac disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, J.A.; Jeong, J.; Underwood, F.E.; Quan, J.; Panaccione, N.; Windsor, J.W.; Ronksley, P.; Shaheen, A.M.; Quan, H.; Van, S.V. Incidence of celiac disease is increasing over time: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, A.S.; Wolter, A.; Czerny, M.; Bez, J.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K.; Czerny, M. Investigation of product quality, sensory profile and ultrastructure of breads made from a range of commercial gluten-free flours compared to their wheat counterparts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, N.; Agostoni, C. Nutritional aspects of gluten-free products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2380–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, S.; Soon, J.M. Nutritional quality, cost and availability of gluten-free food in England. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 2867–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losurdo, G.; Principi, M.; Iannone, A.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. The interaction between celiac disease and intestinal microbiota. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, S145–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascunan, K.A.; Vespa, M.C.; Araya, M. Celiac disease: Understanding the gluten-free diet. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf, K.A.; Wieser, H.; Koehler, P. Novel approaches for enzymatic gluten degradation to create high-quality gluten-free products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 110, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, M.J.; Sánchez-León, S.; Barro, F.; García-Molina, M.D. Gluten free wheat: Are we there? Nutrients 2019, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B. Gluten-related disorders: Celiac disease, wheat allergy, and nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2606–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromilow, S.; Gethings, L.A.; Buckley, M.; Bromley, M.; Shewry, P.R.; Langridge, J.I.; Mills, E.C. A curated gluten protein sequence database to support development of proteomics methods for determination of gluten in gluten-free foods. J. Proteom. 2017, 163, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradauskiene, V.; Vaiciulyte-Funk, L.; Shah, B.R.; Cernauskas, D.; Tita, M.A. Recent advances in biotechnological methods for wheat gluten immunotoxicity abolishment—A review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 71, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel, J.A.; Coda, R.; Limitone, A.; Katina, K.; Raulio, M.; Giuliani, G.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. Manufacture and characterization of pasta made with wheat flour rendered gluten-free using fungal proteases and selected sourdough lactic acid bacteria. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, G.; Benedusi, A.; Di Cagno, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; De Angelis, M.; Gobbetti, M.; Cassone, A. Process of Microbic Biotechnology for Completely Degrading Gluten in Flours. U.S. Patent No. 9,386,777, 12 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Engström, N.; Sandberg, A.S.; Scheers, N. Sourdough fermentation of wheat flour does not prevent the interaction of transglutaminase 2 with α2-gliadin or gluten. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardana, I.A.; Montoya, C.A.; McNabb, W.C.; Boland, M.J. Possibility of minimizing gluten intolerance by co-consumption of some fruits—A case for positive food synergy? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 94, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.; Wieser, H.; Koehler, P. Production of gluten-free wheat starch by peptidase treatment. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, N.D. Gluten-Free Starch and Methods of Producing the Same. U.S. Patent Application No. 039,541, 27 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hemdane, S.; Jacobs, P.J.; Dornez, E.; Verspreet, J.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) bran in bread making: A critical review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, B.; Yan, Q.J.; Jiang, Z.Q. Comparative analysis on the distribution of protease activities among fruits and vegetable resources. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, J.; Sonoyama, K.; Tanabe, S. Novel method for producing hypoallergenic wheat flour by enzymatic fragmentation of the constituent allergens and its application to food processing. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2663–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Goktepe, I.; Ahmedna, M. The potential of papain and alcalase enzymes and process optimizations to reduce allergenic gliadins in wheat flour. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Bromelain treatment of wheat flour to reduce the allergenicity. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2016, 31, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlavan, A.; Sharma, G.M.; Pereira, M.; Williams, K.M. Effects of grain species and cultivar, thermal processing, and enzymatic hydrolysis on gluten quantitation. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, V.; Khatkar, B.S. Microstructural, thermal and IR spectroscopy characterisation of wheat gluten and its sub fractions. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3356–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layne, E. Spectrophotometric and turbidimetric methods for measuring proteins. Meth. Enzymol. 1957, 3, 447–454. [Google Scholar]
- Cupp-Enyard, C. Sigma’s non-specific protease activity assay-casein as a substrate. J. Vis. Exp. 2008, 19, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.; Wieser, H.; Koehler, P. Degradation of gluten in wheat bran and bread drink by means of a proline-specific peptidase. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 4, 10–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard 118–1979. Codex Standard for Foods for Special Dietary Use for Persons Intolerant to Gluten. Codex Alimentarius Commission, Revision 2015. Available online: http://www.codexalimentarius.net/download/standards/291/cxs_118e.pdf (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- Meshram, A.; Singhal, G.; Bhagyawant, S.S.; Srivastava, N. Plant-Derived Enzymes: A Treasure for Food Biotechnology. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology; Kuddus, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of pH, temperature, enzyme-to-substrate ratio and reaction time on the antigenicity of casein hydrolysates prepared by papain. Food Agric. Immunol. 2012, 23, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.C.; Ramli, A.N.M.; Hamid, A.A.A. Comparative modelling studies of fruit bromelain using molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Model. 2020, 26, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Zhao, M.M.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Jiang, Y.M. Antioxidant properties of papain hydrolysates of wheat gluten in different oxidation systems. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.; Grassl, S.; Gänzle, M. Gluten hydrolysis and depolymerization during sourdough fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddrick, O.; Cornell, H.J.; Small, D.M. Reduction of toxic gliadin content of wholegrain bread by the enzyme caricain. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli, A.N.M.; Aznan, T.N.T.; Illias, R.M. Bromelain: From production to commercialisation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Lucas, J.; Castañeda, D.; Hormigo, D. New trends for a classical enzyme: Papain, a biotechnological success story in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, H.J.; Doherty, W.; Stelmasiak, T. Papaya latex enzymes capable of detoxification of gliadin. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Samples | E/S Ratio | Temperature, °C | pH | Soluble Protein Content *, mg/mL | Gluten Content, mg/kg | Decrease in Gluten Content, % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of Enzymatic Hydrolysis, h | ||||||||||
| 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | |||
| BC | 0 | 37 | 6.58 | 6.61 | 2.09 ± 0.02 | 2.21 ± 0.02 | 55,588.47 ± 2800 | 51,250.00 ± 2204 | 5.22 | 12.62 |
| BB | 0.25 | 37 | 6.61 | 6.62 | 2.94 ± 0.03 | 3.13 ± 0.03 | 28,597.74 ± 1212 | 27,060.00 ± 1028 | 51.24 | 53.86 |
| BP | 0.25 | 37 | 6.60 | 6.65 | 3.06 ± 0.04 | 3.47 ± 0.04 | 26,222.42 ± 1055 | 24,548.75 ± 933 | 55.29 | 58.14 |
| BM | 0.25 | 37 | 6.60 | 6.63 | 3.02 ± 0.04 | 3.24 ± 0.04 | 27,500.99 ± 960 | 25,856.25 ± 946 | 53.11 | 55.91 |
| BB | 0.5 | 37 | 6.61 | 6.78 | 3.15 ± 0.05 | 3.28 ± 0.04 | 17,465.97 ± 862 | 15,321.25 ± 734 | 70.22 | 73.88 |
| BP | 0.5 | 37 | 6.60 | 6.79 | 3.21 ± 0.06 | 3.44 ± 0.04 | 14,498.28 ± 740 | 12,167.50 ± 628 | 75.28 | 79.25 |
| BM | 0.5 | 37 | 6.60 | 6.78 | 3.19 ± 0.06 | 3.35 ± 0.05 | 15,559.85 ± 715 | 13,218.75 ± 737 | 73.47 | 77.46 |
| BB | 0.75 | 37 | 6.55 | 6.75 | 3.18 ± 0.06 | 3.31 ± 0.04 | 15,219.68 ± 788 | 12,962.50 ± 720 | 74.05 | 77.90 |
| BP | 0.75 | 37 | 6.57 | 6.77 | 3.29 ± 0.08 | 3.54 ± 0.05 | 11,395.70 ± 656 | 8911.25 ± 619 | 80.57 | 84.81 |
| BM | 0.75 | 37 | 6.55 | 6.76 | 3.28 ± 0.08 | 3.43 ± 0.06 | 12,281.31 ± 745 | 9860.00 ± 716 | 79.06 | 83.19 |
| BC | 0 | 45 | 6.49 | 6.58 | 2.83 ± 0.08 | 2.95 ± 0.05 | 51,870.06 ± 1215 | 47,606.00 ± 1011 | 11.56 | 18.83 |
| BB | 0.25 | 45 | 6.50 | 6.52 | 3.31 ± 0.06 | 3.47 ± 0.04 | 14,269.55 ± 868 | 12,072.60 ± 800 | 75.67 | 79.42 |
| BP | 0.25 | 45 | 6.52 | 6.55 | 3.36 ± 0.06 | 3.45 ± 0.07 | 12,251.99 ± 923 | 9851.00 ± 766 | 79.11 | 83.20 |
| BM | 0.25 | 45 | 6.50 | 6.53 | 3.34 ± 0.05 | 3.41 ± 0.05 | 12,715.32 ± 543 | 10,258.20 ± 770 | 78.32 | 82.51 |
| BB | 0.5 | 45 | 6.50 | 6.52 | 3.05 ± 0.06 | 3.62 ± 0.04 | 6011.63 ± 386.54 | 4100.00 ± 227 | 89.75 | 93.01 |
| BP | 0.5 | 45 | 6.52 | 6.55 | 3.40 ± 0.09 | 3.43 ± 0.04 | 5600.08 ± 354 | 2800.00 ± 215 | 90.45 | 95.23 |
| BM | 0.5 | 45 | 6.50 | 6.54 | 3.15 ± 0.08 | 3.54 ± 0.04 | 5958.84 ± 385.47 | 3150.00 ± 220 | 89.84 | 94.63 |
| BB | 0.75 | 45 | 6.44 | 6.34 | 3.55 ± 0.06 | 3.69 ± 0.05 | 6340.06 ± 421.12 | 3544.50 ± 203 | 89.19 | 93.96 |
| BP | 0.75 | 45 | 6.26 | 6.33 | 3.66 ± 0.05 | 3.86 ± 0.04 | 5348.88 ± 198.56 | 2588.20 ± 199 | 90.88 | 95.59 |
| BM | 0.75 | 45 | 6.25 | 6.34 | 3.64 ± 0.06 | 3.77 ± 0.06 | 5577.62 ± 325 | 2784.60 ± 182 | 90.49 | 95.25 |
| BC | 0 | 50 | 6.47 | 6.51 | 2.94 ± 0.04 | 3.04 ± 0.06 | 50,550.44 ± 1365 | 46,740.00 ± 1012 | 13.81 | 20.31 |
| BB | 0.25 | 50 | 6.50 | 6.52 | 3.02 ± 0.04 | 3.32 ± 0.05 | 13,272.50 ± 866 | 10,785.00 ± 606 | 77.37 | 81.61 |
| BP | 0.25 | 50 | 6.52 | 6.55 | 3.32 ± 0.06 | 3.46 ± 0.06 | 10,169.91 ± 713 | 7606.25 ± 555 | 82.66 | 87.03 |
| BM | 0.25 | 50 | 6.50 | 6.53 | 3.30 ± 0.06 | 3.40 ± 0.06 | 10,580.46 ± 963 | 8062.50 ± 569 | 81.96 | 86.25 |
| BB | 0.5 | 50 | 6.39 | 6.44 | 3.56 ± 0.08 | 3.57 ± 0.05 | 6703.70 ± 695 | 4010.00 ± 176 | 88.57 | 93.16 |
| BP | 0.5 | 50 | 6.36 | 6.39 | 3.67 ± 0.06 | 3.88 ± 0.06 | 5683.19 ± 365 | 2800.00 ± 157 | 90.31 | 95.23 |
| BM | 0.5 | 50 | 6.37 | 6.41 | 3.67 ± 0.05 | 3.75 ± 0.05 | 5964.71 ± 543 | 3197.50 ± 153 | 89.83 | 94.55 |
| BB | 0.75 | 50 | 6.41 | 6.50 | 3.54 ± 0.04 | 3.60 ± 0.08 | 6633.32 ± 415 | 3946.25 ± 163 | 88.69 | 93.27 |
| BP | 0.75 | 50 | 6.40 | 6.56 | 3.69 ± 0.06 | 3.91 ± 0.05 | 5501.37 ± 359 | 2743.75 ± 148 | 90.62 | 95.32 |
| BM | 0.75 | 50 | 6.40 | 6.52 | 3.68 ± 0.06 | 3.77 ± 0.08 | 5647.99 ± 397 | 2855.12 ± 146 | 90.37 | 95.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bradauskiene, V.; Vaiciulyte-Funk, L.; Cernauskas, D.; Dzingeleviciene, R.; Lima, J.P.M.; Bradauskaite, A.; Tita, M.A. The Efficacy of Plant Enzymes Bromelain and Papain as a Tool for Reducing Gluten Immunogenicity from Wheat Bran. Processes 2022, 10, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101948
Bradauskiene V, Vaiciulyte-Funk L, Cernauskas D, Dzingeleviciene R, Lima JPM, Bradauskaite A, Tita MA. The Efficacy of Plant Enzymes Bromelain and Papain as a Tool for Reducing Gluten Immunogenicity from Wheat Bran. Processes. 2022; 10(10):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101948
Chicago/Turabian StyleBradauskiene, Vijole, Lina Vaiciulyte-Funk, Darius Cernauskas, Reda Dzingeleviciene, Joao P. M. Lima, Aida Bradauskaite, and Mihaela Adriana Tita. 2022. "The Efficacy of Plant Enzymes Bromelain and Papain as a Tool for Reducing Gluten Immunogenicity from Wheat Bran" Processes 10, no. 10: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101948
APA StyleBradauskiene, V., Vaiciulyte-Funk, L., Cernauskas, D., Dzingeleviciene, R., Lima, J. P. M., Bradauskaite, A., & Tita, M. A. (2022). The Efficacy of Plant Enzymes Bromelain and Papain as a Tool for Reducing Gluten Immunogenicity from Wheat Bran. Processes, 10(10), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10101948







