Abstract
In this study, the inhibitory activities against human monoamine oxidases (hMAOs) were evaluated using a library of 195 endogenous lichen fungi from Ukraine. Among them, the extract ELF68 of the endogenous fungus Rosellinia corticium from the lichen Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf. exhibited the strongest inhibitory activity against hMAO-A. Using the activity-guided method, (S)-5-methylmellein (5MM) was isolated from the extract and had an IC50 value of 5.31 µM for hMAO-A with a lower potency for hMAO-B (IC50 = 9.15 µM). Compound 5MM also moderately inhibited acetylcholinesterase (IC50 = 27.07 µM) but very weakly inhibited butyrylcholinesterase and β-secretase. Compound 5MM had a Ki value of 2.45 μM and was a reversible competitive inhibitor of hMAO-A. A molecular docking study predicted that (S)-5MM showed higher binding affinity for hMAO-A (−6.8 kcal/mol) than hMAO-B (−6.4 kcal/mol). Its isomer, (R)-5MM, exhibited lower binding affinities for hMAO-A (−6.6 kcal/mol) and hMAO-B (−5.2 kcal/mol), compared to (S)-5MM. The S-form interacted with hMAO-A through hydrogen bonding with the Phe208 residue (distance: 1.972 Å), while the R-form interacted with the Asn181 residue (2.375 Å). The results of an in silico pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that 5MM did not violate Lipinski’s five rules and showed high gastrointestinal absorption and blood–brain barrier permeability. These results suggest that 5MM can be considered a candidate in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression and cardiovascular disease.
1. Introduction
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is a membrane protein, present in the outer mitochondrial membrane, that oxidatively deaminates monoamines (i.e., neurotransmitters) [1]. MAO has two isoforms—A and B—each of which exhibits different substrate specificity and sensitivity to inhibitors [2]. MAO-A mainly breaks down serotonin and norepinephrine, and it may cause depression and cardiovascular disease. On the other hand, MAO-B breaks down phenylethylamine and dopamine, and it is responsible for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) [3]. For this reason, the inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B are used as therapeutic agents for these diseases.
Cholinesterase (ChE) is a choline-based esterase group divided into acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) [4]. AChE breaks down acetylcholine (ACh) into choline and acetate and is found primarily in chemical synapses and red blood cell membranes [5]. BChE breaks down butyrylcholine (BCh) into butyryl and choline and is mainly found in plasma [6,7]. Patients with AD have low levels of ACh and high levels of ChE in the brain. Therefore, ChE inhibitors are used as treatment agents for AD.
Depression patients are usually anxious and lethargic, often experiencing loss of apetite and interest in daily activities and hobbies. Moreover, depression often leads to feelings of hopelessness, worthlessness, and self-loathing of patients. It is medically classified as a psychiatric and behavioral disorder, the core symptom of which is anhedonia [8]. It can be short- or long-term and can lead to feelings of discouragement, sadness, hopelessness and, in severe cases, suicidal thoughts [9]. The main cause of depression is a decrease in monoamines, which are neurotransmitters in nerve synapses, and MAO decomposes monoamines to induce depression [10]. MAO inhibitors are known to be very effective antidepressants. The hydrazine-based compound is a well-known MAO inhibitor and is commercially available as an antidepressant [11]. Although most of them have been withdrawn due to side effects, they are still used for clinical use [12,13]. In addition, various MAO inhibitors are being used, and thus it is necessary to discover new MAO inhibitors for the invention of safer therapeutic agents.
AD is a neurodegenerative disease, which is a leading cause of dementia. It is a progressive disease; the person with AD finds it difficult to remember recent events and gradually loses bodily functions [14]. Genetic causes [15], the cholinergic hypothesis [16], and the amyloid hypothesis [17] can explain the causes of AD. In addition, it has been reported that MAO-B activity is involved as one of the causes of AD [18]. For this reason, it is believed that substances targeting MAO-B have the potential to be used as therapeutic agents for AD.
Lichens are complex organisms that form a symbiotic relationship between lichen-forming fungi and algae, which are photobiotics. It is found in various environments globally and can live in extreme environments. Lichens have long been used not only as a food source [19] but also in traditional medicine [20] and dyes [21]. The secondary metabolites of lichens exhibit various biological activities, such as antibacterial, antifungal, anticancer, and antioxidant activities [22,23,24]. Therefore, their metabolites are being actively studied as a potential source for pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
We previously reported that compounds isolated from the endogenous lichen fungus (ELF) Daldinia fissa [25] within the same library selectively inhibit MAO-B. In this study, the ELF68 extract showed the highest inhibitory activity against MAO-A among the 195 ELF extracts, and it was identified as Rosellinia corticium, an ELF strain of Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf. Based on the activity-guided method, the most potent inhibitor was isolated and identified as (S)-5-methylmellein (5MM) through the separation analysis of the ELF68 extract. Though MAO inhibitory activity of (R)-5MM was reported, but no data of its isomer (S)-5MM is available [26]. In this study, the inhibitory activity of (S)-5MM was tested using purified MAOs, ChEs, and β-secretase (BACE1), and kinetics, reversibility experiments, docking simulations, and in silico pharmacokinetic analysis were performed. Through these experiments, its potential as a therapeutic agent for depression and/or AD was evaluated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining and Preparation of ELF Extracts to Assess MAO-A Inhibitory Activity
To evaluate the inhibitory activity of MAO-A, a library of 195 ethyl acetate or butanol extracts from Ukraine-derived lichen endogenous fungi was obtained from Sunchon University Korea Lichen Research Institute (KOLRI). The extract was dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 10 mg/mL, and the concentration of DMSO in the assay mixture was 0.2% [27]. All other chemicals not specified were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Enzyme Activity Assays
The activities of MAOs were assayed in 0.5 mL of a reaction mixture containing ~1.2 U/mL human recombinant MAOs (hMAO-A or hMAO-B) and substrate (0.06 mM kynuramine for hMAO-A or 0.3 mM benzylamine for hMAO-B) in 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.2). Without preincubation of enzymes and inhibitors, hMAO-A and hMAO-B activities were continuously measured at 316 and 250 nm, respectively, for 30 min in the kinetic mode through UV absorbance analysis using a UV/VIS Spectrophotometer, Optizen pop (Mecasys, Daejeon, Korea) [28].
For the assay of ChE activity, AChE derived from electric eel and BChE derived from horse serum were used and evaluated with a slight modification of the Ellman method [29]. Approximately 0.2 U/mL of ChE enzymes and inhibitors were preincubated for 15 min in 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer, and 0.5 mM 5,5-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) for color development was used with acetylthiocholine iodide for AChE or butyrylthiocholine iodide for BChE, and the activities were continuously measured in 0.5 mL of the reaction mixtures at 412 nm for 15 min in the kinetic mode [30].
The BACE1 assay was performed using a BACE1 activity detection kit with fluorescence (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and a spectrofluorometer (FS-2, Scinco, Seoul, Korea). The enzyme and buffer in the kit were reacted in 100 µL of reaction mixture at 37 °C for 2 h, using excitation at 320 nm and emission at 405 nm [31].
2.3. Culture and Extraction of ELF68
The most potent fungal strain ELF68 was cultured using 90 of 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 200 mL of the potato dextrose broth (PDB) medium for 2 weeks at 27 °C and with shaking at 150 rpm. The same volume of ethyl acetate was added to the culture medium for extraction, and the extract was obtained through rotary vacuum concentration.
2.4. Isolation and Identification of Compounds
Components of the ELF68 extract were separated using Prep TLC plates (PTLC Silica gel 60 F254, 0.5 mm, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The extract was loaded up to 500 µL on a PTLC plate at 100 mg/mL concentration and developed using ethyl acetate and toluene at a ratio of 2:8 (v/v) as the first solvent, and the spots were identified and recovered at a wavelength of 254 nm. The recovered spots were selected using the activity-guided method. Active spots were developed with ethyl acetate and toluene at a ratio of 6:4 (v/v) as the second solvent.
NMR spectra were acquired by using Me4Si as an internal standard on Varian Inova 400 and 100 MHz spectrometers (Varian Medical Systems, Inc., Charlottesville, VA, USA) using solvent DMSO-d6 (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories (CIL), Inc., Tewksbury, MA, USA). Low-resolution LC-MS measurements were performed using the Agilent Technology 1260 quadrupole (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and Waters Micromass ZQ LC-MS system (Waters Corp, Milford, MA, USA) using a reversed-phase column (Phenomenex Luna C18 (2) 100 Å, 50 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min at the National Research Facilities and Equipment Center (NanoBioEnergy Materials Center) at Ewha Womans University. Optical rotations were acquired using a Kruss Optronic P-8000 polarimeter with a 5-cm cell (Kruss, Hambrug, Germany).
2.5. Kinetic Study of the Compounds
The IC50 values of the compounds were measured under the conditions of different inhibitor concentrations. The Ki values were determined with a secondary plot through the Lineweaver–Burk slope by using inhibitors of three concentrations (~1/2 × IC50, IC50, and ~2 × IC50) [32].
2.6. Analysis of Inhibitor Reversibility
The reversibility test of the compound was conducted as a recovery test using dialysis. It was performed at approximately 2 × IC50 concentration of the inhibitor in 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.2). For the recovery comparison, toloxatone, a reversible inhibitor of hMAO-A, and clorgyline, an irreversible inhibitor, were used [33].
2.7. Molecular Docking Simulation of the Compound with hMAO-A and hMAO-B
AutoDock Vina [34], which has an automated docking facility, was used for docking simulations of the compounds to hMAO-A (PDB ID: 2Z5X) and hMAO-B (PDB ID: 3PO7). The PDB files were retrieved from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) (www.rcsb.org, accessed on 9 November 2021) and prepared for docking simulation by removing water molecules and heteroatoms except flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) that acts as a cofactor of MAO enzyme. To locate the ligand-binding pocket for each enzyme, we used a set of predefined active sites obtained from a complex of hMAO-A with 7-methoxy-1-methyl-9H-beta-carboline (HRM) [35] and a complex of hMAO-B 1-(1,2-benzoxazole-3-yl)methanesulfonamide (ZON) [36]. For the docking simulation, we performed the following steps: creation of 2D structures of 5-methylmellein, conversion of the 2D structures into 3D structures, and energy minimization using the ChemOffice program (http://www.cambridgesoft.com, accessed on 9 November 2021) [37]. Docking simulations of hMAO-A and hMAO-B with the compounds were performed using AutoDock Vina in UCSF Chimera [38]. From the docking results, we checked for possible hydrogen bonding using relaxation constraints of 0.4 Å and 20.0 Å with the FindHBond program in UCSF Chimera.
2.8. Analysis of Pharmacokinetic and Physicochemical Parameters In Silico
The pharmacokinetic and physicochemical parameters of the compounds were analyzed using the SwissADME web tool (http://www.swissadme.ch, accessed on 23 October 2021). Gastrointestinal absorption, blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability, cytochrome P inhibitory ability, p-glycoprotein substrate, and Lipinski violation were analyzed [39].
3. Results
3.1. Inhibitory Activity of ELF Extracts against hMAO-A
Among the extracts tested, seven extracts showed less than 60% residual activity against hMAO-A, and five extracts showed less than 30% against hMAO-B at 20 µg/mL (Table 1 and Supplementary Figures S1 and S2). ELF68 showed the highest inhibitory activity against hMAO-A (26.2% of residual activity), followed by ELF100 (42.3%) and ELF71 (43.6%). ELF68 exhibited low inhibitory activity against hMAO-B. ELF68 was identified as an endogenous fungus R. corticium by the 5.8S rRNA sequencing method, with a lichen P. furfuracea (L.) Zopf. The sequence was deposited in GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, accessed on 17 November 2021) under accession number of MN984621.1 and it showed the highest similarity of 100% to R. corticium strain STMA 13324. ELF68 was selected for further study and cultured in large amounts with flasks. The cultured sample was extracted, and the hMAO-A inhibitor was isolated using the activity-guided method.

Table 1.
Inhibitory activities of ELF extracts against hMAO-A and hMAO-B.
3.2. Compound Isolation of ELF68 Using Prep TLC
A total of 18 L of ELF68 culture broth was extracted with the same volume of ethyl acetate and concentrated (1.57 g). When the extract was developed with PTLC using the first solvent, seven spots appeared, and the compounds in the spots were recovered. Among these, spot 1 showed the lowest residual activity against hMAO-A (7.2%), followed by spot 3 (12.6%) (Figure 1). The leading compounds with inhibitory activity against hMAO-A were isolated using an activity-guided method. However, the amount of spot 1 was limited (0.8 mg) for further experiments. Spot 3 was nearly one compound under the second solvent development, and the major compound was isolated (4.0 mg) and identified.
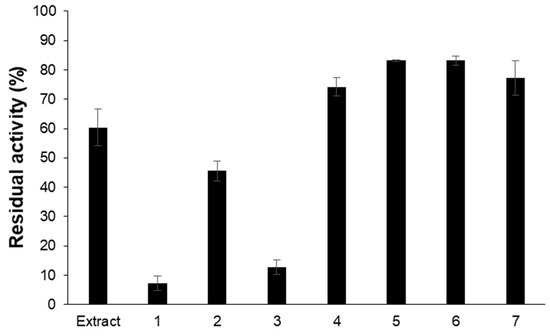
Figure 1.
hMAO-A residual activity of seven spots of PTLC of ELF68 extract. The activity was measured at a concentration of 20 µg/mL of each spot.
3.3. Identification of ELF68
Compound 1 was isolated as yellowish oil. The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 displayed two aromatic protons [δH 6.77 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-6), δH 7.39 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, H-7)], one methylene proton [(δH 2.72 (dd, J =12.4 and 16.8 Hz H-4), (δH 3.04 (dd, J = 3.6 and 16.8 Hz H-4)], one methine proton [δH 4.75 (m, H-3)], two methyl protons [δH 1.45 (d, J = 6.3, H-3), δH 2.17 (s, H-5)], and one exchangeable hydroxyl proton [δH 10.90 (s, H-8)] (Figure S3). The 13C NMR of 1 also indicated that the compound had eleven carbon signals, one carbonyl carbon [C-1 (δC 169.8)], one oxygenated carbon [C-3 (δC 75.6.)], two methyl carbons [3-Me (δC 20.5) and 5-Me (δC 17.7)], two aromatic carbons [C-6 (δC 137.7) and C-7 (δC 115.0)], four aromatic quaternary carbons [C-5 (δC 124.8), C-8 (δC 159.3), C-9 (δC 108.1), and C-10 (δC 138.2)], and one methylene carbon [C-4 (δC 31.1)] (Figure S4). Comprehensive analysis of 2D NMR spectroscopic data allowed the assignment of the structure of compound 1 (Figures S5–S7). The 1H-1H COSY cross-peaks H-3/3-Me, 5-Me/H-6/H-7 and HMBC correlations from H-4 to C-3, C-9, C-10, from H-6 to 5-Me, C-8, C-10, from 3-Me to C-3, C-4, from 5-Me to C-6 permitted the assignment of mullein moiety. LR-ESI-MS spectroscopy data revealed an ionic peat at m/z 193.3 [M + H]+ (Figure S8). Based on the comparison between the NMR data of 1 with those reported, compound 1 was identified as 5-methylmellein (5MM, also known as 3,4-dihydro-8-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylisocoumarin) (Figure 2) [40]. The optical rotation of 1 ( = +22.05°, c 0.11, CH3OH) suggested that the absolute configuration at C-3 should possess an (S)-configuration [41].
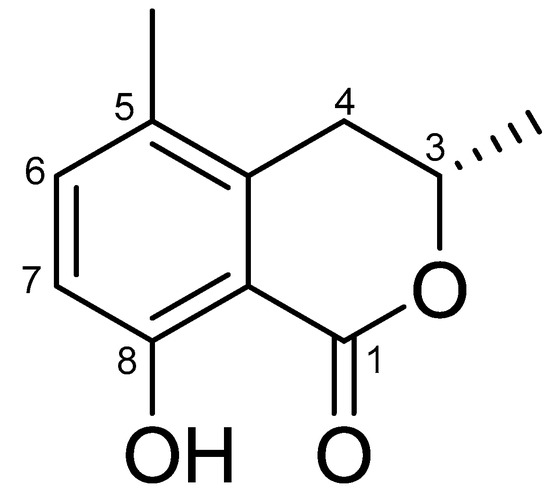
Figure 2.
Chemical structure of 1 ((S)-5-methylmellein, 5MM).
3.4. Inhibitory Activities of 5MM against MAOs, ChEs, and BACE1
The inhibitory activities of 5MM on hMAO-A, hMAO-B, AChE, BChE, and BACE1 were analyzed at 10 µM concentration. Compound 5MM exhibited inhibitory activity against hMAO-A and -B, with 35.2% and 44.5% residual activities, respectively (Table 2). 5MM had an IC50 value of 5.31 µM for hMAO-A, with an effective potency for hMAO-B (IC50 = 9.15 μM), and the selective index (SI) was 1.72 for hMAO-A over hMAO-B (Table 2). In addition, 5MM moderately inhibited AChE (IC50 = 27.07 µM) but very weakly inhibited BChE and BACE1 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Inhibitory activities against hMAOs, ChEs, and BACE1 by compound 5MM.
3.5. Kinetic Studies of 5MM
The mode of inhibition of 5MM against hMAO-A was analyzed using the Lineweaver–Burk plot. The inhibition plots indicated that 5MM was a competitive inhibitor, crossing the y-axis (Figure 3A). In addition, the secondary plot of the slopes derived from each concentration of 5MM showed a Ki value of 2.45 µM for hMAO-A (Figure 3B).
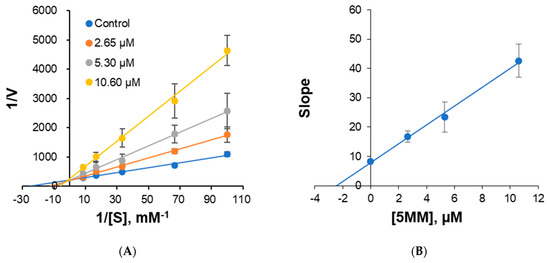
Figure 3.
Lineweaver–Burk plots for hMAO-A inhibition by 5MM (A) and secondary plot with slopes vs. 5MM concentrations (B). Five substrate concentrations (0.01, 0.015, 0.03, 0.06, and 0.12 μM) were used, and three inhibitor concentrations were used (~1/2 × IC50, ~IC50, and ~2 × IC50). Error bars are the results of duplicate experiments.
3.6. Analysis of Reversibility for hMAO-A by 5MM
To analyze the reversibility of hMAO-A inhibition by 5MM, a recovery experiment was performed through dialysis. In hMAO-A inhibition by 5MM, the residual activity was restored from 37.0% to 97.1% through dialysis (Figure 4). Toloxatone, a reversible inhibitor of hMAO-A, also showed a recovery of 37.8–88.4%. In contrast, clorgyline, an irreversible inhibitor of hMAO-A, did not show recovery at all (13.8–4.1%). These results show that 5MM is a reversible inhibitor of hMAO-A.
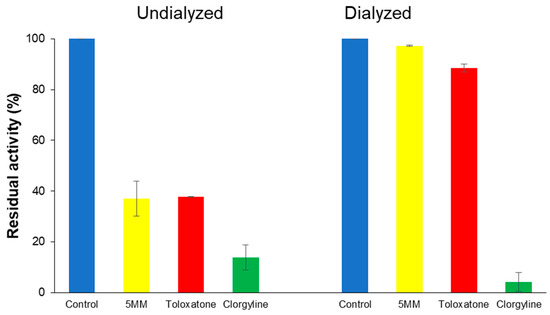
Figure 4.
Inhibition of hMAO-A by 5MM and recovery of hMAO-A activity by dialysis. A concentration of ~2 × IC50 was used as the inhibitor concentration. The data were presented as a result of duplicate experiments.
3.7. Molecular Docking Simulation
The docking simulation results showed that (S)-5MM and (R)-5MM were properly located within the binding site of HRM with hMAO-A (PDB: 2Z5X) and that of ZON with hMAO-B (PDB ID:3PO7). The docking poses and binding scores of the chemicals with hMAO-A or hMAO-B are presented in Figure 5. The simulation result indicated that the binding scores of S-form (−6.8 kcal/mol) and R-form (−6.6 kcal/mol) of 5-MM to hMAO-A were higher than those to hMAO-B (−6.4 kcal/mol and −5.2 kcal/mol, respectively). In addition, intermolecular hydrogen bond interactions of the S-form and R-form to hMAO-A were proposed with the backbone oxygen of Phe208 residue with a distance of 1.972 Å and with the oxygen of amide group in Asn181 residue with a distance of 2.375 Å, respectively, but not to hMAO-B. Besides, O2 of 5MM and C1 in the side chain of Phe208 were located most closely and the distance was 3.011 Å. Therefore, the hydrogen bond contributed to the tighter interaction of both forms with hMAO-A, and the docking results yielded a good correlation with the experimental data obtained from the enzyme inhibition assays.
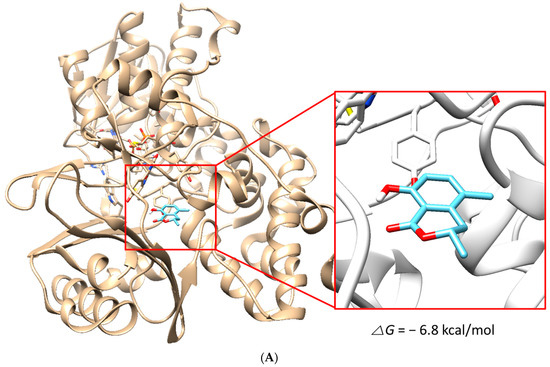
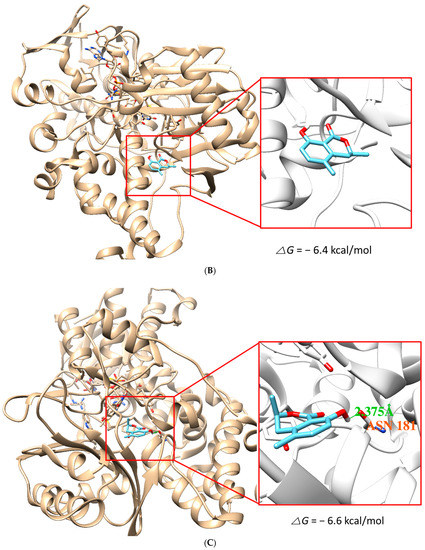
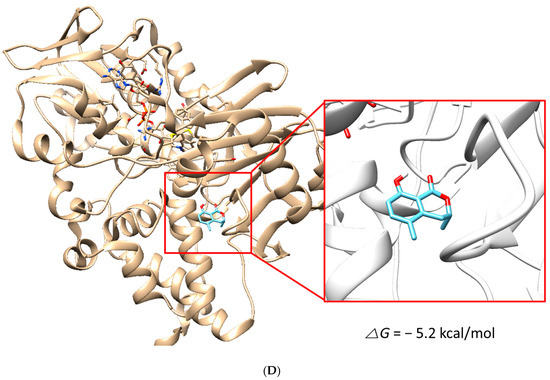
Figure 5.
Docking simulation of 5-methylmellein (S-form) with hMAO-A (2Z5X) (A) and hMAO-B (3PO7) (B) and of R-form with hMAO-A (C) and hMAO-B (D), as determined by the UCSF Chimera. The S- and R-forms interacted with hMAO-A through a hydrogen bond with Phe208 residue (distance: 1.972 Å) and Asn181 residue (distance: 2.375 Å), respectively.
3.8. In Silico Pharmacokinetics of 5MM
The pharmacokinetic analysis of 5MM was performed using the SwissADME web tool. 5MM exhibited high gastrointestinal absorption, permeability to the BBB, and inhibition of CYP1A2 (Table 3). In addition, the results of the Lipinski parameters showed that 5MM did not violate Lipinski’s five rules (Table 4). These results can yield benefits when 5MM is used as a central nervous system (CNS) drug.

Table 3.
Predicted pharmacokinetic properties of 5MM.

Table 4.
Physicochemical parameters and Lipinski violations.
4. Discussion
In this study, the ELF68 extract from the R. corticium strain, which exhibited the highest inhibitory activity against hMAO-A, was selected from a library of 195 ELF extracts. R. corticium was identified as an endogenous fungus of the lichen P. furfuracea (L.) Zopf. P. furfuracea, also known as tree moss, is a lichen that grows on the bark of fir or pine trees. This species has been used in antibacterial activity [42] and for medicinal purposes, especially for respiratory complaints and protection of genotoxicity caused by bismuth compounds [43,44]; moreover, because it adsorbs heavy metals [45], it is used for pollution monitoring [46]. Rosellinia, belonging to the family Xylariaceae, comprises more than 90 species [47]. Some species are known as plant pathogens, and Rosellinia necatrix is a well-known root-rot pathogen [48]. In addition, jammosporin A, recently isolated from Rosellinia sanctae cruciana, exhibits anticancer effects [49]. However, most studies have been conducted on Rosellinia necatrix, and there are few reports on other biological activities of the genus Rosellinia. Little has been reported about R. corticium, except a potent nematicide cyclodepsipeptide PF1022 A purified from the culture medium [50].
5MM exhibits some biological activities, such as Sirtuin inhibition [40] and cytotoxic [51], antibacterial [52], and anticancer [53] effects. In contrast, (R)-5MM, which is an isomer of (S)-5MM, shows an inhibitory activity against hMAO-A (IC50 = 4.6 μM), and its synthetic compounds exhibit more potent activity (IC50 = 0.06~29 µM) [26]. In this study, we isolated a new isomer (S)-5MM and observed that it effectively inhibits hMAO-A (IC50 = 5.31 µM) and moderately inhibits hMAO-B (IC50 = 9.15 µM). Isochroman mellein is known to inhibit MAO (IC50 = 8.93 µg/mL, 50.16 µM) [54]. The MAO-A inhibitory ability of 5 MM was significantly higher than that of mellein.
On the other hand, only a few MAO inhibitors associated with lichens have been reported. The anthraquinone solorinic acid isolated from the lichen Solorina crocea exhibits MAO inhibitory activity (IC50 = 14.3 µM) [55], and 4-acylresorcinol, a synthetic derivative of a lichen compound, exhibits MAO inhibitory activity (IC50 = 4.27 µM) [56]. Alternariol, 5-hydroxy-alternariol, and mycoepoxydiene isolated from ELF Diaporthe mahothocarpus have selective inhibitory activity on hMAO-A [27], and 5-hydroxy-2-methyl-chroman-4-one isolated from ELF Daldinia fissa selectively inhibits hMAO-B [25].
Docking simulation showed that the S-form and R-form of 5MM interacted with a hydrogen bond with different amino acid residues of hMAO-A with different distances, but did not form a hydrogen bond with hMAO-B. Precisely, S-form was predicted to be located under Tyr407 residue of hMAO-A, while R-form was located above the residue as shown in Figure 5. The difference in location was probably derived due to the 3-methyl group attached to the chiral carbon, making different hydrogen bonds. Taken together, the binding affinity of 5MM to hMAO-A exceeded that of hMAO-B.
Collectively, 5MM can be used as a lead compound or a scaffold for developing derivatives, as a natural compound from an ELF. In addition, the high gastrointestinal absorption, BBB permeability, and non-violation of Lipinski’s rule suggest that 5MM has pharmacological potential and can be used as a candidate for treating neuropsychiatric disorders.
5. Conclusions
Among the 195 Ukrainian ELF extracts, ELF68 showed the strongest inhibitory activity against hMAO-A. 5MM was isolated and identified from large cultures, and it showed strong inhibitory activity against hMAO-A as a reversible competitive inhibitor with effective inhibitory activity against hMAO-B. The higher affinity of 5MM to hMAO-A than to hMAO-B was also predicted by a molecular docking simulation. 5MM showed high gastrointestinal absorption and BBB permeability by in silico pharmacokinetic analysis and did not violate Lipinski’s five rules. These results suggest that 5MM can be considered a candidate for developing new therapeutic agents for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr10010166/s1, Supplementary Figures S1 and S2: Inhibitory activity of ELF 195 extracts against MAO-A and MAO-B, respectively; Figures S3–S8: 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and Mass spectra of the compound 1, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.K.; isolation, G.-S.J.; biological activity and in silico analysis, G.-S.J.; identification, E.-Y.L.; molecular docking simulation, M.-G.K.; original draft writing, G.-S.J., E.-Y.L. and M.-G.K.; review and editing, S.-J.N., D.P. and H.K.; supervision, H.K.; funding acquisition, H.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was supported by the Sunchon National University Research Fund in 2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study have been included in this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Korean Lichen and Allied Bioresources Center at the Korean Lichen Research Institute in Sunchon National University, Republic of Korea, for the lichen samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ramsay, R.R. Monoamine Oxidases: The Biochemistry of the Proteins as Targets in Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2189–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The Therapeutic Potential of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joao Matos, M.; Vina, D.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Uriarte, E.; Santana, L. Focusing on New Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Differently Substituted Coumarins As An Interesting Scaffold. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2210–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovic, M.B.; Krstic, D.Z.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T.D.; Bondzic, A.M.; Vasic, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Pharmacology and Toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bierer, L.M.; Haroutunian, V.; Gabriel, S.; Knott, P.J.; Carlin, L.S.; Purohit, D.P.; Perl, D.P.; Schmeidler, J.; Kanof, P.; Davis, K.L. Neurochemical Correlates of Dementia Severity in Alzheimer’s Disease: Relative Importance of the Cholinergic Deficits. J. Neurochem. 1995, 64, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pintus, F.; Di Petrillo, A.; Medda, R.; Caria, P.; Matos, M.J.; Viña, D.; Pieroni, E.; Delogu, F.; Era, B.; et al. Novel 2-Pheynlbenzofuran Derivatives as Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sicinska, P.; Bukowska, B.; Pajak, A.; Koceva-Chyla, A.; Pietras, T.; Nizinkowski, P.; Gorski, P.; Koter-Michalak, M. Decreased Activity of Butyrylcholinesterase in Blood Plasma of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 3, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, P.; Gilbert, P. Psychotherapy and Counselling for Depression; SAGE: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-84920-349-4. [Google Scholar]
- De Zwart, P.L.; Jeronimus, B.F.; de Jonge, P. Empirical Evidence for Definitions of Episode, Remission, Recovery, Relapse and Recurrence in Depression: A Systematic Review. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019, 28, 544–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamon, M.; Blier, P. Monoamine Neurocircuitry in Depression and Strategies for New Treatments. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 45, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Muñoz, F.; Alamo, C. Monoaminergic Neurotransmission: The History of the Discovery of Antidepressants from 1950s until Today. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 1563–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suerinck, A.; Suerinck, E. Depressive states in a sanatorium milieu and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. (Therapeutic results by the combination of iproclozide and chlordiazepoxide). Apropos of 146 cases. J. Med. Lyon 1966, 47, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fagervall, I.; Ross, S.B. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase in Monoaminergic Neurones in the Rat Brain by Irreversible Inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1986, 35, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.; Iliffe, S. Alzheimer’s Disease. BMJ 2009, 338, b158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.-M.; Cuello, A.C.; Farlow, M.R.; Giacobini, E.; Grossberg, G.T.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Cavedo, E.; Snyder, P.J.; et al. The Cholinergic System in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2018, 141, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroni, G.; Bisceglia, P.; Seripa, D. Understanding the Amyloid Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 68, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, P.; Danielczyk, W.; Grünblatt, E. Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibition in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiao, C.-J.; Guo, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.-H.; Li, X.-N.; Li, S.-H. Lobarioid A, Unusual Antibacterial Depsidone Possessing an Eight-Membered Diether Ring from the Edible Lichen Lobaria sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, F.S. Lichens: An Illustrated Guide to the British and Irish Species, Sixth Revised and Enlarged Edition; The Richmond Publishing Co., Ltd.: Slough, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-85546-315-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J. Wild Color; Watson-Guptill Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-8230-5727-6. [Google Scholar]
- Solárová, Z.; Liskova, A.; Samec, M.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D.; Solár, P. Anticancer Potential of Lichens’ Secondary Metabolites. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samanthi, K.; Wickramaarachchi, S.; Wijeratne, E.; Paranagama, P. Two New Antioxidant Active Polyketides from Penicillium Citrinum, an Endolichenic Fungus Isolated from Parmotreama Species in Sri Lanka. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2015, 43, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.; Kim, Y.; Gang, H.-S.; Han, J.; Ha, H.-H.; Kim, H. Antimicrobial Activity of Divaricatic Acid Isolated from the Lichen Evernia Mesomorpha against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Molecules 2018, 23, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, G.-S.; Kang, M.-G.; Han, S.-A.; Noh, J.-I.; Park, J.-E.; Nam, S.-J.; Park, D.; Yee, S.-T.; Kim, H. Selective Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase B by 5-Hydroxy-2-Methyl-Chroman-4-One Isolated from an Endogenous Lichen Fungus Daldinia Fissa. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Xiong, J.; Guan, H.-D.; Wang, C.-H.; Lei, X.; Hu, J.-F. Discovery, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Study of (R)-5-Methylmellein and Its Analogs as Selective Monoamine Oxidase A Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 2027–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.S.; Hillman, P.F.; Kang, M.-G.; Hwang, S.; Park, J.-E.; Nam, S.-J.; Park, D.; Kim, H. Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Human Monoamine Oxidase A from an Endogenous Lichen Fungus Diaporthe Mahothocarpus. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.C.; Choi, B.; Nam, S.-J.; Kim, H. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase A and B by Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.P.; Kang, M.-G.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, J.M.; Baek, S.C.; Leem, H.H.; Park, D.; Cho, M.-L.; Kim, H. Potent Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase by Sargachromanol I from Sargassum Siliquastrum and by Selected Natural Compounds. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 89, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.N.; Do Carmo, S.; Iulita, M.F.; Hall, H.; Ducatenzeiler, A.; Marks, A.R.; Allard, S.; Jia, D.T.; Windheim, J.; Cuello, A.C. BACE1 Inhibition by Microdose Lithium Formulation NP03 Rescues Memory Loss and Early Stage Amyloid Neuropathology. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, S.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Kang, M.-G.; Park, D.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, M.-L.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, H. Selective Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase A by Hispidol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.C.; Park, M.H.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, J.P.; Kang, M.-G.; Park, D.; Park, C.M.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, H. Rhamnocitrin Isolated from Prunus Padus Var. Seoulensis: A Potent and Selective Reversible Inhibitor of Human Monoamine Oxidase A. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, S.-Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of Human Monoamine Oxidase A at 2.2-A Resolution: The Control of Opening the Entry for Substrates/Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binda, C.; Aldeco, M.; Mattevi, A.; Edmondson, D.E. Interactions of Monoamine Oxidases with the Antiepileptic Drug Zonisamide: Specificity of Inhibition and Structure of the Human Monoamine Oxidase B Complex. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, J.E.J.; Dean, P.M. Three-Dimensional Hydrogen-Bond Geometry and Probability Information from a Crystal Survey. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 1996, 10, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera? A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shigemoto, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Masuo, S.; Takaya, N. 5-Methylmellein Is a Novel Inhibitor of Fungal Sirtuin and Modulates Fungal Secondary Metabolite Production. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okuno, T.; Oikawa, S.; Goto, T.; Sawai, K.; Shirahama, H.; Matsumoto, T. Structures and Phytotoxicity of Metabolites from Valsa Ceratosperma. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, H.; Yılmaz, M.; Tay, T.; Türk, A.Ö.; Kıvanç, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Extracts of Chemical Races of the Lichen Pseudevernia Furfuracea and Their Physodic Acid, Chloroatranorin, Atranorin, and Olivetoric Acid Constituents. Z. Für Nat. C 2006, 61, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Tejero, M.R.; Martínez-Lirola, M.J.; Casares-Porcel, M.; Molero-Mesa, J. Three Lichens Used in Popular Medicine in Eastern Andalucia (Spain). Econ. Bot. 1995, 49, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyikoglu, F.; Turkez, H.; Aslan, A. The Protective Roles of Some Lichen Species on Colloidal Bismuth Subcitrate Genotoxicity. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2007, 23, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, A.; Yildiz, A.; Yildiz, N.; Calimli, A. Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solution by Pseudevernia Furfuracea (L.) Zopf. Ann. Chim. 2007, 97, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.; Rosso, A.; Minciardi, M.R.; Troiani, F.; Piervittori, R. Analysis of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Particulates in Relation to Their Bioaccumulation in Explanted Pseudevernia Furfuracea Thalli. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 69, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, L.E.; Petrini, O. Morphological Studies in Rosellinia (Xylariaceae): The First Step towards a Polyphasic Taxonomy. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliego, C.; López-Herrera, C.; Ramos, C.; Cazorla, F.M. Developing Tools to Unravel the Biological Secrets of Rosellinia Necatrix, an Emergent Threat to Woody Crops: Tools to Study Rosellinia Necatrix. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Kushwaha, M.; Arora, D.; Jain, S.; Singamaneni, V.; Sharma, S.; Shankar, R.; Bhushan, S.; Gupta, P.; Jaglan, S. New Cytochalasin from Rosellinia sanctae-cruciana, an Endophytic Fungus of Albizia lebbeck. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittstein, K.; Cordsmeier, A.; Lambert, C.; Wendt, L.; Sir, E.B.; Weber, J.; Wurzler, N.; Petrini, L.E.; Stadler, M. Identification of Rosellinia Species as Producers of Cyclodepsipeptide PF1022 A and Resurrection of the Genus Dematophora as Inferred from Polythetic Taxonomy. Stud. Mycol. 2020, 96, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunyapaiboonsri, T.; Yoiprommarat, S.; Srikitikulchai, P.; Srichomthong, K.; Lumyong, S. Oblongolides from the Endophytic Fungus Phomopsis Sp. BCC 9789. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Yao, F.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, W.; Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, R. A New Phthalide from the Endophytic Fungus Xylaria Sp. GDG-102. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, D.; Sharma, N.; Singamaneni, V.; Sharma, V.; Kushwaha, M.; Abrol, V.; Guru, S.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, A.P.; Bhushan, S.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Bioactive Metabolites from Xylaria Psidii, an Endophytic Fungus of the Medicinal Plant Aegle Marmelos and Their Role in Mitochondrial Dependent Apoptosis against Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2016, 23, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Yang, Z.-D.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Yu, H.-T.; Sun, J.-Y.; Yao, X.-J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, H.-Y. Colletotrilactam A–D, Novel Lactams from Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides GT-7, a Fungal Endophyte of Uncaria Rhynchophylla. Fitoterapia 2016, 113, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, E.; Hossain, C.F.; Yamazaki, M. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors from a Lichen, Solorina crocea (L.) ACH. Jpn. J. Pharmacogn. 1991, 45, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, K.; Saito, D.; Koyama, K.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, Y.; Okuyama, E.; Fujimoto, H.; Yamazaki, M. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Effects of Some Lichen Compounds and Their Synthetic Analogues. J.-Hattori Bot. Lab. 2002, 92, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).