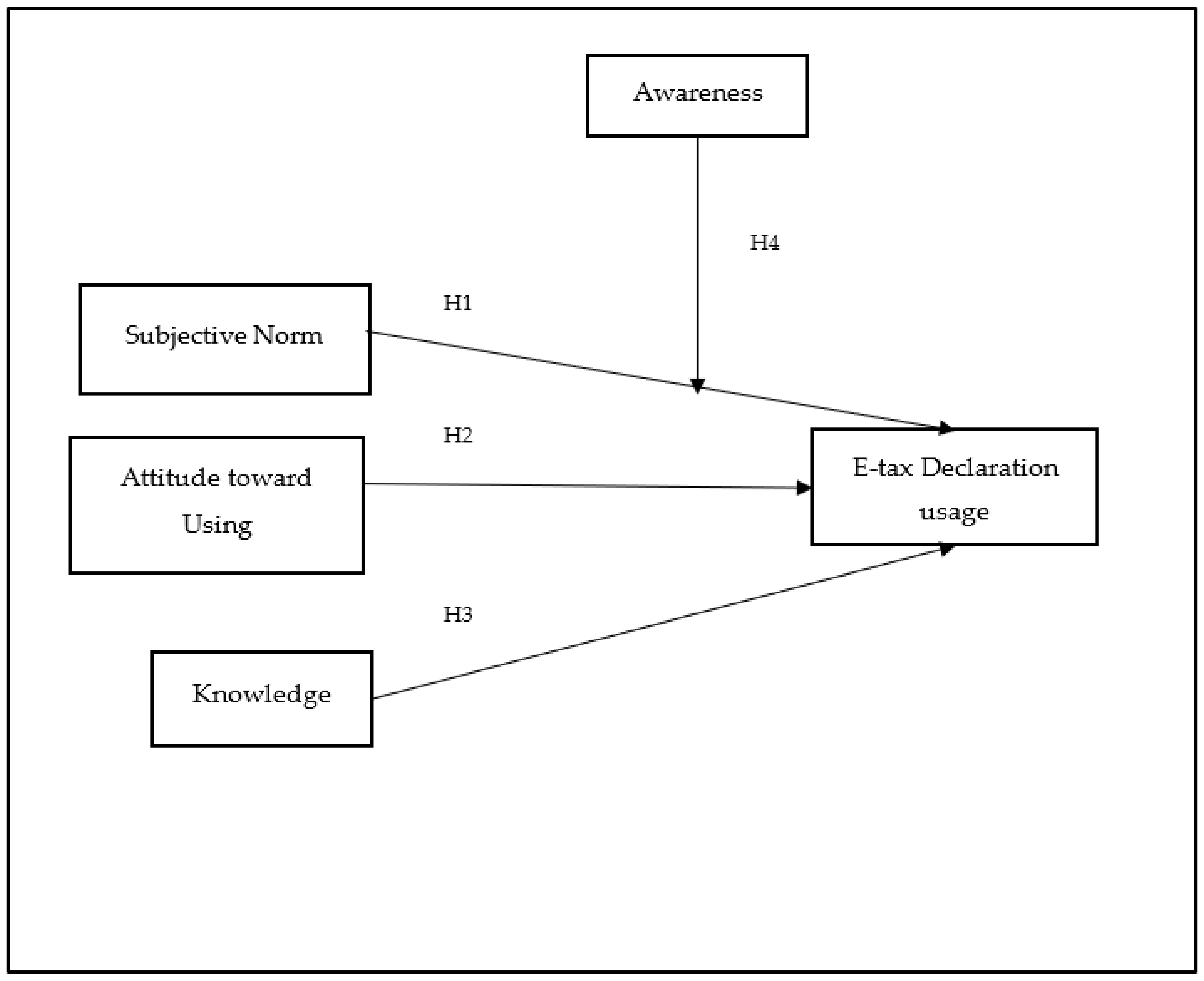
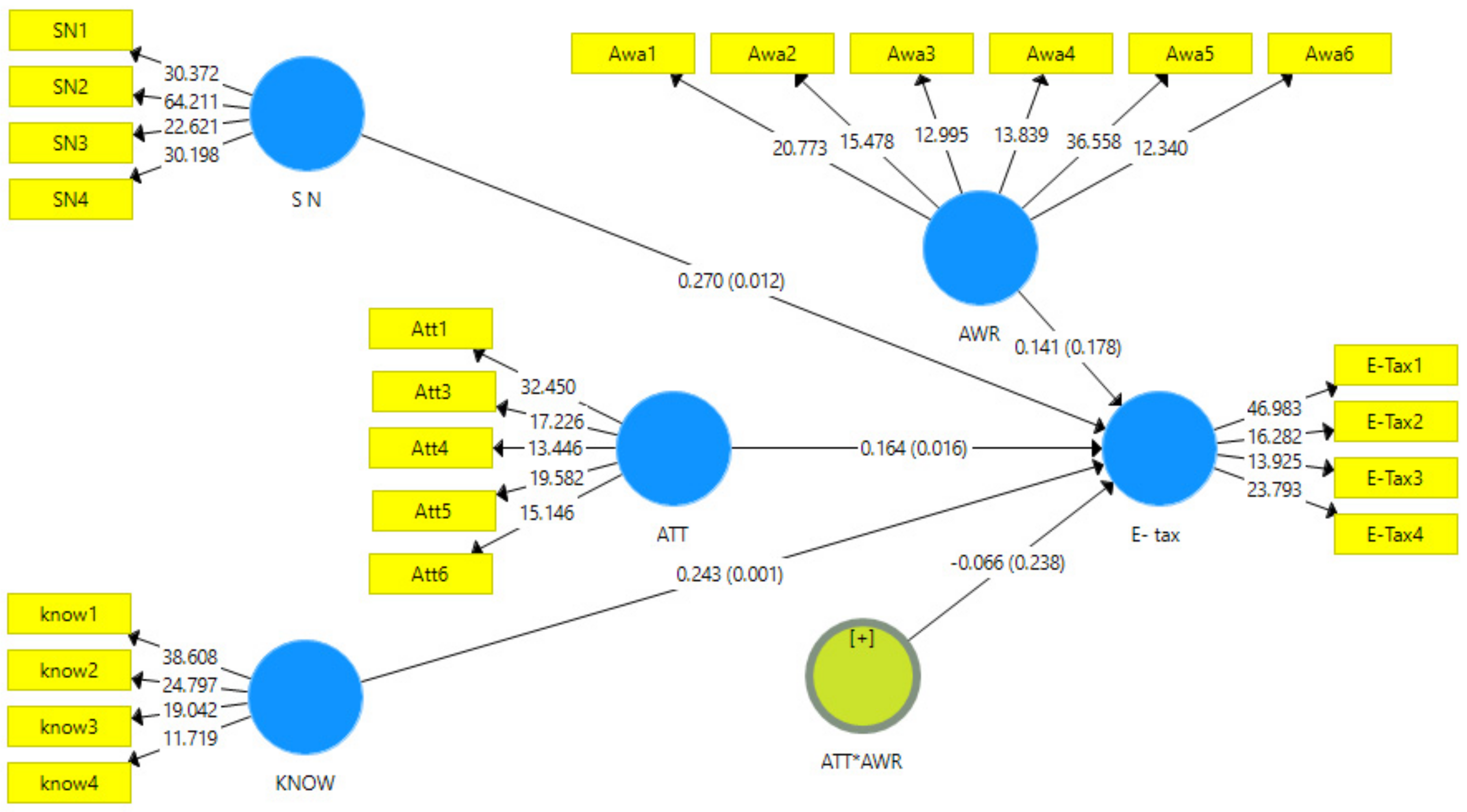
1. Introduction
The rapid proliferation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has fundamentally revolutionized the way governments operate, particularly as technologies continue to bridge us closer together in light of the ongoing ICT advancements [
1]. Dramatic changes have been made in people’s use of digital communication methods as a consequence of the period of self-isolation and contagion. As a result, both public and private sectors need to reinvent themselves to be in line with these changes [
2]. Although there has been a significant and discernible improvement, the public sector tends to fall behind in the process of implementing new technologies and business reinvention [
3].
There is a reasonable doubt that the low acceptance by citizens of e-services in developing countries is still evident despite the quality of services provided by governments [
4]. It is argued that their low acceptance results from governments’ poor efforts in implementing good governance in terms of transparency, accountability, and anti-corruption [
5]. As a result, their citizens are used to dealing with poor services and corruption which plays a role in their uncertainty and trust in e-government adoption which has already been conceived [
6].
Furthermore, public trust in governmental organizations plays a moderating role in the acceptance of governmental services [
7]. Those countries that have higher public trust from their citizens have the advantage of implementing services much more efficiently than those with a lower public trust [
7], due to citizens voluntarily abiding by regulations and demands of governments without aggressively resisting them [
8]. It is argued that increasing citizens’ knowledge regarding governmental policies and allowing them open access to data as well as informing them of the benefits of using e-services shape their attitude and intention in the adoption of the e-services [
5].
Moreover, economic inequality is prevalent in developing countries, meaning that e-governmental services will be accessible only to those privileged in a population which could further contribute to corruption and rising economic inequality [
9]. Additionally, developing countries often have poor IT infrastructures which further strains the government’s efforts to implement the use of e-governmental services; the need to build a solid technological infrastructure is necessary to ensure equal access to all citizens, including reliable electricity and Internet access [
9].
Jordan is a developing country in the Middle East, that has recently been following the trend of moving towards transforming services using ICTs. There are several projects and initiatives that have been carried out by the Jordanian government aimed to accomplish digital transformation across all governmental sectors such as “digital educational content, open government information and data”. According to the Ministry of Digital Economy and Entrepreneurship, digital transformation has numerous advantages, including reduced time and cost, increased flexibility and efficiency in production and data processing, improved quality, streamlined procedures, and the ability to provide innovative and creative services that are not possible with traditional methods [
10].
In 2018, the Income and Tax Department digitalized tax filing which is one of their most essential services. Since the 1920s, the department conducted a conventional filing system for PIT Return (Personal income tax Return) until the Electronic Tax Filing (ETF) was first launched in 2005 to facilitate PIT Return services provided by tax authorities to taxpayers [
11]. The application of ETF is intended to enhance competitiveness through cost reduction and timesaving compared with conventional filing systems. It is also intended to enhance compliance with tax law and uncover tax evasion [
12].
In 2018, ETF became mandatory for all taxpayers in Jordan, including all citizens with an annual income of more than JOD 10,000 (Income Sales Tax Department, 2018). Total income tax revenue collected during the first seven months from this year or about 413 million dinars which is accounted for 34.3% from total revenue amounted 1.225 billion dinars within the first seven months of this year [
13]. The ministry of finance later amended the tax law to require all citizens with an annual income of JOD 9000 to provide ETF. Hence, the Finance Ministry directed the efforts toward producing a user-friendly interface for the ETF system, making it more convenient for taxpayers to provide their Income Tax Declaration through e-tax means. According to several researchers, the main factors impacting the use of e-tax PIT Return are user satisfaction, technology acceptance and knowledge, incentives to use, and social influence [
14].
The adoption of the e-tax PIT Return System is expected to increase the trust between taxpayers and tax authorities by enhancing the efficiency of tax performance in Jordan, in addition to better compliance with tax law and hence higher tax collection [
15].
Digitalizing services yields efficiency and better flexibility in processing collected data, subsequently improving the overall quality of provided services. It also reduces the time and cost compared with the traditional paper processing [
16]. However, the factors impacting the users’ usage of digital services, including e-tax filing, are still largely unexplored. Therefore, this paper aims to shed light on factors that determine the e-tax declaration usage.
This paper proceeds as follows: the next section presents the literature and related theories. The third section discusses the methodology while the fourth section introduces the analyses and results. The fifth section discusses the results while the sixth section shows the contribution of this study. Lastly, and finally, the seventh section presents the limitations and the agenda for future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.A.-M. and A.R.A.N.; methodology, H.A.-M.; software, A.R.A.N.; validation, F.S., H.Z. and G.A.R.; formal analysis, H.A.-M.; investigation, F.S.; resources, A.R.A.N.; data curation, H.Z. and A.R.A.N.; writing—original draft preparation, H.A.-M.; writing—review and editing, F.S. and H.Z.; visualization, G.A.R.; supervision, H.A.-M. and F.S.; project administration, H.A.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Valencia, K.; Rusu, C.; Quiñones, D.; Jamet, E. The Impact of Technology on People with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, L.; Al-Karaghouli, W.; Weerakkody, V. Analysing the critical factors influencing trust in e-government adoption from citizens’ perspective: A systematic review and a conceptual framework. Int. Bus. Rev. 2017, 26, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndou, V. E–Government for developing countries: Opportunities and challenges. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Ctries. 2004, 18, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soneka, P.N.; Phiri, J. A Model for Improving E-Tax Systems Adoption in Rural Zambia Based on the TAM Model. Open J. Bus. Manag. 2019, 7, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanto, T.D.; Aljoza, M. Individual Acceptance of e-Government Services in a Developing Country: Dimensions of Perceived Usefulness and Perceived Ease of Use and the Importance of Trust and Social Influence. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 72, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusamhadana, G.A.; Bakon, K.A.; Elias, N.F. E-Government in Ghana: The benefits and challenges. Abusamhadana, GAO, Bakon KA, & Elias NF (2021)" E-Government in Ghana: The Benefits and Challenges". Asia-Pac. J. Inf. Technol. Multimed. 2021, 10, 124–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jameel, A.; Asif, M.; Hussain, A.; Hwang, J.; Sahito, N.; Bukhari, M.H. Assessing the Moderating Effect of Corruption on the E-Government and Trust Relationship: An Evidence of an Emerging Economy. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, A.; Asif, M.; Hussain, A. Good Governance and Public Trust: Assessing the Mediating Effect of E-Government in Pakistan. Lex Localis-J. Local Self-Gov. 2019, 17, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, D. The Failure of E-Government in Developing Countries: A Literature Review. Electron. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Ctries. 2006, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaileh, M.; Alshawawreh, A. Measuring digital transformation impact in Jordan: A proposed framework. J. Innov. Digit. Mark. 2021, 2, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Akel, S.A.A.; Ibrahim, M. The Factors Effecing E-Filing Adoption Among Jordanian Firms: The Moderating Role Oftrust. Palarch’s J. Archaeol. Egypt/Egyptol. 2020, 17, 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hammouri, Q.; Abu-Shanab, E. Exploring the factors influencing employees’ satisfaction toward e-tax systems. Int. J. Public Sect. Perform. Manag. 2017, 3, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department, I.S.T. 13% Increase in Tax Revenue. Available online: https://istd.gov.jo/En/NewsDetails/13_increase_in_tax_revenue (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Al-Okaily, M.; Al Natour, A.R.; Shishan, F.; Al-Dmour, A.; Alghazzawi, R.; Alsharairi, M. Sustainable FinTech Innovation Orientation: A Moderated Model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswadeh, S.N.; Hanandeh, T.S. The Effect of Computerized Tax Services in Improving Tax Performance Moderated by Governance. J. Asian Finance, Econ. Bus. 2020, 7, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entrepreneurship, T.M.o.D.E.a. Jordan Digital Transformation Strategy. 2020. Available online: https://www.modee.gov.jo (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Fishbein, M.; Ajzen, I. Predicting and Changing Behavior: The Reasoned Action Approach; Psychology Press: London, England, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ajzen, I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process 1991, 50, 179–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, A.; Valois, P.; Ajzen, I.; Schmidt, P. Using the theory of planned behavior to identify key beliefs underlying pro-environmental behavior in high-school students: Implications for educational interventions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2015, 42, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Law, R.; Schuckert, M. Mediating effects of attitude, subjective norms and perceived behavioural control for mobile payment-based hotel reservations. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 84, 102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mital, M.; Chang, V.; Choudhary, P.; Papa, A.; Pani, A.K. Adoption of Internet of Things in India: A test of competing models using a structured equation modeling approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhowaiter, W.A. Digital payment and banking adoption research in Gulf countries: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Perceived risk, usage frequency of mobile banking services. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2013, 23, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I. From Intentions to Actions: A Theory of Planned Behavior. In Action Control; Kuhl, J., Beckmann, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 11–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, H. A study of mobile banking loyalty in Iran. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 44, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Choi, B.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.-J. Culture-Technology Fit: Effects of Cultural Characteristics on the Post-Adoption Beliefs of Mobile Internet Users. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2007, 11, 11–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Literacy, S.F.a.B. Central Bank of Jordan. Available online: http://www.cbj.gov.jo/Pages/viewpage.aspx?pageID=202 (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Seale, C.; Gobo, G.; Gubrium, J.F.; Silverman, D. Qualitative Research Practice; Sage: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Palinkas, L.A.; Horwitz, S.M.; Green, C.A.; Wisdom, J.P.; Duan, N.; Hoagwood, K. Purposeful Sampling for Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis in Mixed Method Implementation Research. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 2015, 42, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G. Pros and cons of different sampling techniques. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2017, 3, 749–752. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdoost, H. Sampling methods in research methodology; how to choose a sampling technique for research. Int. J. Acad. Res. Manag. 2016, 5, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, H.L. Conducting online surveys. J. Hum. Lact. 2019, 35, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, M.A.; Ting, H.; Cheah, J.-H.; Thurasamy, R.; Chuah, F.; Cham, T.H. SAMPLE SIZE FOR SURVEY RESEARCH: REVIEW AND RECOMMENDATIONS. J. Appl. Struct. Equ. Modeling 2020, 4, 1–20. Available online: https://jasemjournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/Memon-et-al_JASEM_-Editorial_V4_Iss2_June2020.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Oladapo, I.A.; Hamoudah, M.M.; Alam, M.; Olaopa, O.R.; Muda, R. Customers’ perceptions of FinTech adaptability in the Islamic banking sector: Comparative study on Malaysia and Saudi Arabia. J. Model. Manag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatimah, H.; Halim, F. The effect of attitude and its decomposed, perceived behavioral control and its decomposed and awareness on intention to use e-money mobile in Indonesia. J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2016, 3, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Finstad, K. Response interpolation and scale sensitivity: Evidence against 5-point scales. J. Usability Stud. 2010, 5, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, J.; Amran, A.; Yahya, S. External oriented resources and social enterprises’ performance: The dominant mediating role of formal business planning. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Abu Talib, M. Emotional intelligence moderates perfectionism and test anxiety among Iranian students. Sch. Psychol. Int. 2015, 36, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, N.P. Sources of method bias in social science research and recommendations on how to control it. Annu. Rev. Psychol 2012, 63, 539–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, H.H. Modern Factor Analysis; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N.; Lynn, G. Lateral collinearity and misleading results in variance-based SEM: An illustration and recommendations. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2012, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, N. Common Method Bias: A Full Collinearity Assessment Method for PLS-SEM. In Partial Least squares Path Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Tiwari, J. Order reducing of linear system using clustering method factor division algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Syst. 2012, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Falahat, M.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Soto-Acosta, P.; Ramayah, T. Entrepreneurial, market, learning and networking orientations as determinants of business capability and international performance: The contingent role of government support. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2021, 17, 1759–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair Jr, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; saGe: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al Natour, A.R.; Meqbel, R.; Kayed, S.; Zaidan, H. The Role of Sustainability Reporting in Reducing Information Asymmetry: The Case of Family-and Non-Family-Controlled Firms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronbach, L.J.; Meehl, P.E. Construct validity in psychological tests. Psychol. Bull. 1955, 52, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöreskog, K.G. Simultaneous factor analysis in several populations. Psychometrika 1971, 36, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics; Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.H.; Malhotra, A.; Segars, A.H. Knowledge Management: An Organizational Capabilities Perspective. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2001, 18, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.W. PLS-Graph User’s Guide; CT Bauer College of Business, University of Houston: Houston, TX, USA, 2001; Volume 15, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Fassott, G. Testing Moderating Effects in PLS Path Models: An Illustration of Available Procedures. In Handbook of Partial Least Squares; Vinzi, V., Wynne, W., Chin, W., Henseler, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 713–735. ISBN 978-3-540-32825-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Hair, J.F. Treating unobserved heterogeneity in PLS-SEM: A multi-method approach. In Partial Least Squares Path Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 197–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Hopkins, L.; Kuppelwieser, V.G. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): An emerging tool in business research. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2014, 26, 21–106. [Google Scholar]
- Teo, T. Factors influencing teachers’ intention to use technology: Model development and test. Comput. Educ. 2011, 57, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).