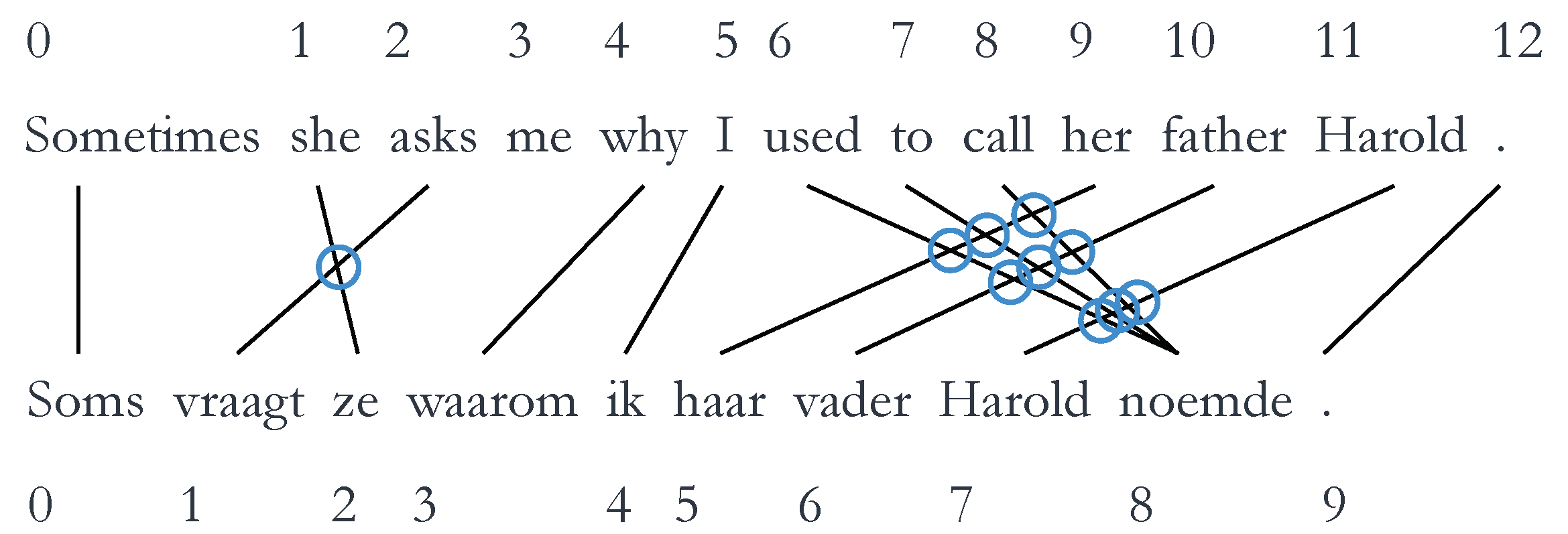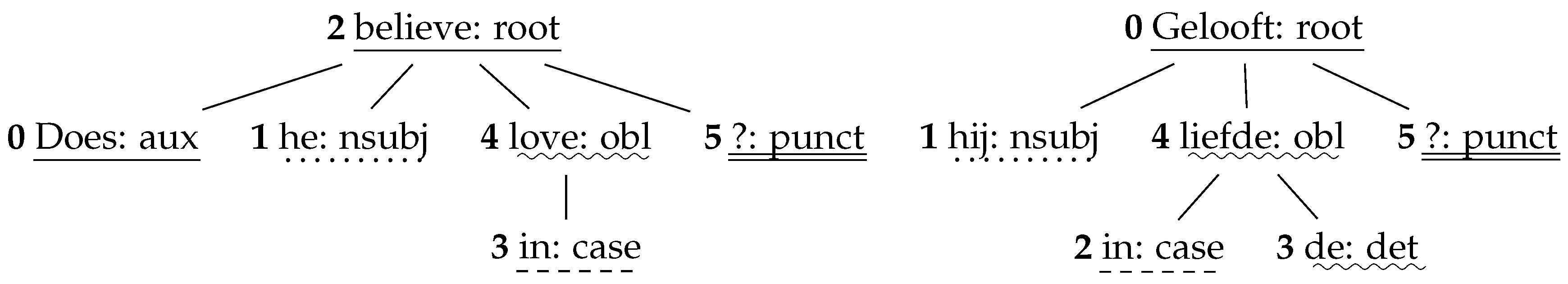Abstract
Due to the growing success of neural machine translation (NMT), many have started to question its applicability within the field of literary translation. In order to grasp the possibilities of NMT, we studied the output of the neural machine system of Google Translate (GNMT) and DeepL when applied to four classic novels translated from English into Dutch. The quality of the NMT systems is discussed by focusing on manual annotations, and we also employed various metrics in order to get an insight into lexical richness, local cohesion, syntactic, and stylistic difference. Firstly, we discovered that a large proportion of the translated sentences contained errors. We also observed a lower level of lexical richness and local cohesion in the NMTs compared to the human translations. In addition, NMTs are more likely to follow the syntactic structure of a source sentence, whereas human translations can differ. Lastly, the human translations deviate from the machine translations in style.
1. Introduction
Although machine translation (MT) is widely accepted in everyday translation situations, using it to translate literary texts can still cause some hesitation [1]. Voigt and Jurafsky [2] even state that literary MT may at first seem a “near-contradiction in terms”, due to MT traditionally only being employed for informative texts. However, with the continuous advancements made in the field of neural machine translation (NMT), some researchers have tried to remove this stigma and provide more information on the applicability of NMT to literary texts [1,3,4,5]. The aim of this article is to assess the performance of generic NMT systems on literary texts, by not only providing insights into the quality of the NMT, but by also examining more in-depth features such as lexical richness, local cohesion, syntactic and stylistic difference.
In this article, we will consider the NMT outputs generated by Google’s NMT system (GNMT) and DeepL’s NMT system (DeepL) for four literary classics from English into Dutch. In order to discuss the performance of NMT on literary texts, we completed two types of analyses. The first concerns an error analysis, which is the more traditional approach of assessing translation quality. The error analysis is based on approximately the first 3000 words of each novel, annotated according to an adapted version of the SCATE error taxonomy [6]. However, as the quality of MT systems has improved enormously over the past years, it is worthwhile to investigate in what other aspects human- and machine-generated translations differ. Therefore, the second type of analysis is a key feature analysis performed on the novels as a whole, in which the NMT outputs are compared to the human translations (HT) and the source texts (ST) in order to gather information on lexical richness, local cohesion (i.e., cohesion between smaller chunks of text, such as a number of consecutive sentences), syntactic and stylistic difference.
In Section 2, we first mention some research relevant to the assessment of literary NMT. We discuss our method for text selection, error analysis, and key feature analysis in Section 3. Then, in Section 4, we present our results and bring these together in a brief discussion in Section 5. Section 6 contains a conclusion and possible future research.
2. Related Research
Assessing the quality of MT can either be done automatically or manually. The former is typically achieved by comparing an MT output to a reference translation and generating metrics such as BLEU [7], whereas the latter concerns the human assessment of an MT output, such as the annotations of errors or the ranking of translations. Although manual assessment is much more time-consuming, its automatic variant has often been criticized as being problematic [8], having the tendency to underestimate the quality of NMT systems [9], or not even being a representation of the actual quality of the translation [1]. Sceptical of the reliability of automatic assessment, Matusov [1] performed a manual assessment of literary NMT with his own classification system, specifically designed for NMT. He concluded that NMT of German fiction into English has a higher quality than NMT of English literature into Russian. For English to Russian, he observed a high number of omission errors, but a low number of serious syntax errors. He also stated that up to 30% of the German to English sentences were of acceptable quality, although these were mostly shorter sentences. Fonteyne et al. [4] likewise manually assessed the quality of literary NMT, but for English into Dutch. Their study consisted of annotating various fluency and accuracy errors in The Mysterious Affair At Styles, a 58,039 word novel by Agatha Christie translated from English into Dutch with GNMT. They concluded that 43.9% of the sentences contained no errors, which is a considerably higher amount than other language pairs, such as English-Slovene, English-Russian, and German-English (p. 3789). They also added that the main issues for literary NMT seem to be mistranslation, coherence, and style & register.
However, it is often argued that a good literary translation does not simply maintain meaning, but also the reading experience [3]. A phenomenon which in turn requires us to address “larger-scale textual features beyond the sentence-level” [2]. For these reasons, many researchers have started to look beyond the possible constraints of judging NMT by an error analysis and have pinpointed other, broader factors that are equally important in literary texts, such as lexical richness and cohesion. Vanmassenhove et al. [10] have noted that the process of NMT causes a decrease of lexical diversity and richness, due to the NMT system increasing/decreasing the usage of more/less frequent words as a consequence of overgeneralization. Tezcan et al. [5] also examined lexical richness in literary NMT from English into Dutch and offered a cautionary tale. They discovered that their NMT achieved higher lexical richness than the HT, but warned that this may be more related to the tendency of NMT to mistranslate certain words.
Voigt and Jurafsky [2] observed that literary texts have a higher level of referential cohesion than everyday texts, such as newspapers. They then examined whether MT systems were capable of maintaining this cohesion when translating from Chinese into English. Eventually, they concluded that MT systems did indeed have difficulty maintaining the greater referential cohesion present in literary texts, while human translations were capable of capturing this greater referential cohesion.
An article that has already recognized the importance of combining multiple approaches to literary NMT, and is hence woven throughout this literature review, is written by Tezcan et al. [5]. They firstly conducted a quality assessment of the first chapter of Agatha Christie’s The Mysterious Affair at Styles, translated by GNMT from English into Dutch. This was achieved manually, in the form of annotations according to an adapted version of the SCATE error taxonomy [6]. Secondly, they took a look at more in-depth features of the NMT, by examining lexical richness, cohesion and syntactic divergence. on the whole novel (58,309 words). Syntactic divergence measures how (dis)similar sentences/texts are syntactically and will be explained in more detail later on. The Agatha Christie novel was chosen to enable future comparisons with the GECO eyetracking corpus of monolingual and bilingual sentence reading [11]. However, as this novel was specifically selected due to its relatively short length and its similarity to natural language, we have to be careful when interpreting the results for this single piece of work. In an attempt to provide a more thorough interpretation of the applicability of NMT to literature and to discover the common features between different human- and machine-translated literary texts, we will perform similar analyses on four novels from different time periods and authors, with varying lengths, using two different NMT systems. Moreover, we will employ a metric from stylometry, namely Burrows’ Delta [12], to discuss the styles of the translated novels, and extend the analysis on syntactic divergence with metrics that examine deeper syntactic structures.
3. Methodology
3.1. Text Selection
Our four English classics were obtained from Gutenberg.org, an open-access resource which provides multiple novels in an electronic format for free. The selection was based on the availability of the modern Dutch (human) translations of these four novels in digital format. The novels are also from different time periods, from three different authors and have varying lengths; this ensures a fairly diverse corpus. The chosen novels are: A Christmas Carol by Charles Dickens (1843) (Human translation by Else Hoog (1995)), Sense and Sensibility by Jane Austen (1811) (Human translation by W.A. Dorsman-Vos (1982)), The Memoirs of Sherlock Holmes (1893) and The Sign of the Four (1890) by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (Human translation of the former by Paul Heijman (2015) and of the latter by Fanneke Cnossen (2014)).
Each novel was then translated from English into Dutch with GNMT (August 2019) and DeepL (October 2019). As a consequence, there are always four versions of each novel: the English source text, the Dutch human translation, the Dutch translation generated by GNMT and the Dutch translation generated by DeepL. For each novel, all four versions underwent sentence alignment.
Due to certain inconsistencies in the data, the data used for each of the two analyses had to be adapted slightly. The data used for the first analysis, i.e., the error analysis, originally consisted of approximately the first 3000 words of each novel. However, due to two errors appearing in the data which were only noticed after the annotation work had been completed, some segments had to be removed. Firstly, an error during preprocessing led to the source texts that were used for each version of the same novel not always being identical (e.g., the source text used for GNMT would contain a sentence that was not present in the source text used for DeepL). To ensure that each version was based on the same source text and hence contained the same (number of) segments, these extra segments were removed from the data. A second error occurred in the error analysis data when certain segments were incompletely translated in the NMTs. These incomplete segments were then manually copied back into the NMT systems and re-translated before the annotation process began. When processing the data for analysis, however, it was discovered that this error was caused by curly quotation marks which provoked an incomplete translation by GNMT. When the segments were entered into GNMT for re-translation, straight quotation marks were used, which led to this mistake no longer occurring in the translation. Due to this then seeming to be an inherent characteristic of GNMT for literary texts, we decided to remove these re-translated segments from the data, in order to prevent providing GNMT with an unfair advantage. In total, this led to the length of our data decreasing by 21 sentences or 615 words (Table 1).

Table 1.
Overview of data used for error analysis: Number of words and sentences in each novel before and after data was removed.
The data used for the second analysis, i.e., the key feature analysis, was also adapted due to so-called ‘empty lines’. This means that certain segments were not present in all four versions (e.g., a segment would be present in the ST, HT and DeepL, but not in the GNMT). Since we wanted to compare the different versions of the novels in our key feature analysis, it was important that all four versions contained an equal number of segments. Hence, if a segment was not present in one of the four versions, it was removed from all four versions. This led to 165 sentences or 1132 words being removed from our total data set (Table 2). It should also be mentioned that this data set similarly contained incomplete translations, such as in the error analysis data mentioned above. These instances were, however, kept in the second data set.

Table 2.
Overview of data for key feature analysis: Number of words and sentences in each novel before and after data was removed.
3.2. Error Analysis
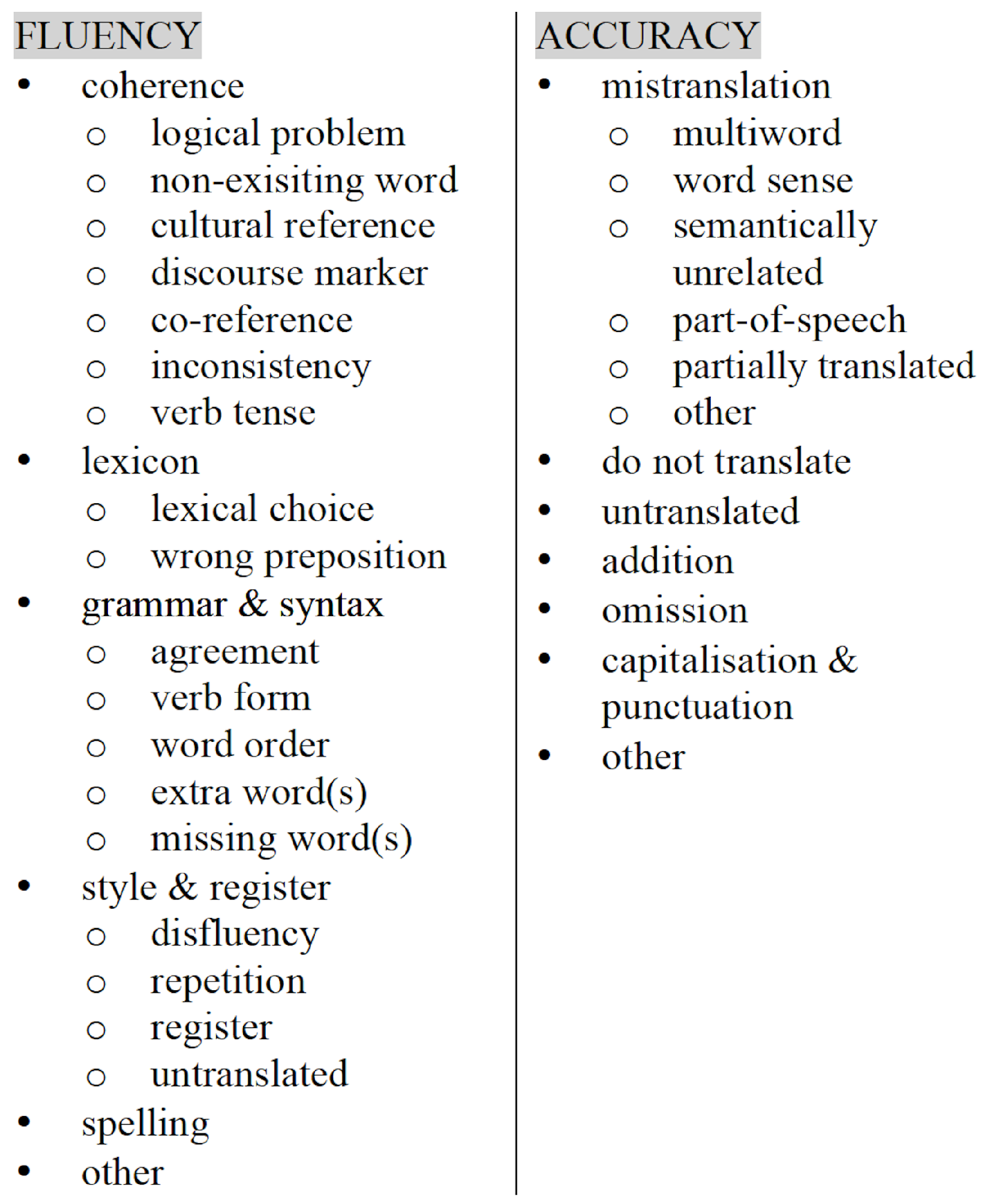
In order to discuss the quality of each NMT system, approximately the first 3000 words of each book were annotated according to an adapted version of the SCATE error taxonomy. The SCATE error taxonomy is a hierarchical error taxonomy based on the distinction between accuracy and fluency errors. Accuracy errors are errors that can only be detected by comparing the source and target text (TT), whereas fluency errors are errors that can be detected by only looking at the target text. Its hierarchical nature also allows errors to be categorized according to three potential levels of detail, ranging from the fairly broad level 1 (e.g., fluency) to the more fine-grained level 3 (e.g., fluency→grammar→word form). Since this error taxonomy was published in 2017 [6], it has undergone two main adaptations. Firstly, Van Brussel et al. [13] adapted the taxonomy to NMT by adding two extra categories: one fluency classification concerning needlessly repeated words and one accuracy classification concerning mistranslations which are semantically unrelated to the source word. Secondly, Tezcan et al. [5] adapted the taxonomy further to make it more applicable to errors made in literary MT. The two categories of ’style & register’ and ’coherence’ were added as fluency errors, and the grammar category ‘word form’ was also split into ‘agreement’ and ‘verb form’. An overview of this updated SCATE taxonomy, which was used for our study, can be found in Figure 1. The detailed annotation guidelines are publicly available at GitHub (https://github.com/margotfonteyne/StylesNMT/blob/master/AnnotationGuidelines.pdf). To check the validity of the error annotation scheme and the annotation guidelines, an inter-annotator study has been carried out in earlier work [4]. The results showed that the two annotators agreed on error detection for 73% of all annotations, but that they tended not to agree on the length of the error annotation span.
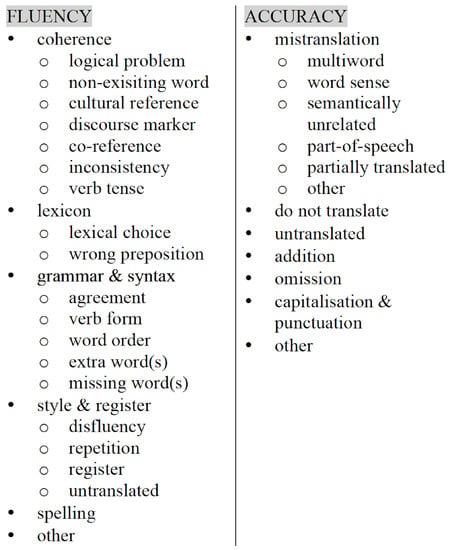
Figure 1.
Overview of the SCATE error taxonomy.
The annotator of the previous study (a student with a Master’s degree in translation) also provided the annotations for this study, which took approximately 46 h. In order to comply with the requirements of the SCATE error taxonomy, the annotation work was completed in two steps; first, the fluency errors were indicated in the target and then the accuracy errors were annotated by comparing the source to the target. Hence, we used the online annotation tool WebAnno (https://webanno.github.io/webanno/), due to its ability to annotate both on a monolingual (for the fluency errors) and a bilingual level (for the accuracy errors). Furthermore, the tool also allows for multiple error types to be annotated on the same text span.
3.3. Key Feature Analysis
In addition to the error analysis, we decided to take a look at four key features: lexical richness, cohesion, syntactic and stylistic difference. These four analyses were conducted on the novels as a whole.
3.3.1. Lexical Richness
Since lexical richness plays a fairly large part in the literary genre, we compared the lexical richness of the NMTs to the lexical richness of the HTs and the STs. In order to do this, we first employed the type-token ratio measure. Type-token ratio refers to the number of unique words (types) averaged by the total number of words in a text (tokens). The lower this number is, the less lexically rich the text is; the higher, the more lexically rich.
TTR (type-token ratio), with t = number of types and n = number of tokens:
Although the TTR measure is useful in its own right, it can be influenced by text length, an aspect which may become problematic when comparing novels of varying lengths. For this reason, we also calculated the mass index (MASS) and the mean segmental type-token ratio (MSTTR), metrics that are not influenced by text length. The latter divides the text into equal segments, calculates the TTR of these segments, and then averages them by taking the mean [14]. The former has the following formula (2), but, in contrast with the previous TTR measures, the smaller the mass index, the larger the lexical richness.
3.3.2. Local Cohesion
A noteworthy characteristic of literature, when compared to everyday writing, is its higher level of cohesion [2], not to be confused with the category ’coherence’ in the MT error taxonomy we used for our error analysis above. Hence, another textual feature worth focusing on when examining literary NMT is whether or not it is capable of maintaining this characteristic high level of cohesion.
As context-agnostic NMT systems often produce plausible translations of isolated sentences, the translation errors due to lack of context are becoming more noticeable [15,16]. An increasing number of studies tackle this problem by focusing on building context-aware NMT systems, some of which led to improvements measured by automatic quality evaluation metrics, as well as local cohesion indices (i.e., cohesion between neighboring sentences) [16,17]. Cohesion is a complex phenomenon to be measured by computational methods. Previous attempts combine a variety of indices, such as local, global (paragraph-level), and text-level indices, to predict expert judgments for a variety of text types [18,19], based on the previous work on context-aware NMT. In this study, we only focus on local cohesion indices by measuring lexical and semantic overlaps for each sentence (i) with two succeeding sentences (i+1 and i+2).
Lexical overlap refers to the same content word occurring in succeeding sentences, whereas semantic overlap refers to the occurrence of semantically related content words (such as synonyms, near-synonyms, co-hyponyms, antonyms, etc. alongside identical words) in succeeding sentences. These semantically related words are accumulated by using WordNets and comparing shared synsets of content words (i.e., groupings of synonymous words referring to the same concept) in the NLTK package (https://www.nltk.org/). Both lexical and semantic cohesion have been calculated on the lemma level and sentence level. The former refers to the total number of overlapping lemmas, while the latter refers to the number of sentences that contain at least one overlap.
3.3.3. Syntactic Divergence
The third key feature which we will discuss is syntactic divergence. Syntactic divergence is a measure of syntactic (dis)similarity between e.g., a source and a target sentence; the higher the syntactic divergence is, the more dissimilar the structures of the two sentences are and the more reordering is required to move from source to target. This feature is perhaps not as characteristic of literary texts as the previous two, but it can give us a clear indication of the literary reading experience in the target language. If the HT structure deviates more from the ST than the NMT structure, this likely indicates that the reading experience for both will be different. This observation can in turn carry implications of the fluency of the translation.
Syntactic divergence can be quantified through various different metrics. We will briefly explain these metrics so they can be interpreted correctly during the discussion of the results; however, for a more thorough explanation, we refer to the works of Vanroy et al. [20,21]. The scripts used to calculate these metrics can be found at https://github.com/BramVanroy/astred. The first metric is word_cross. This examines the reordering of words necessary when comparing source to target [21]. Concretely, it is calculated by the number of times word alignment links cross each other averaged by the total number of alignment links. The word alignments between the source and target are obtained automatically by using GIZA++. In Figure 2 below, there are 12 links (indicated by arrows) and 10 crosses (indicated by circles). This means that the word_cross value is or 0.833; a fairly high score, which indicates that a large amount of word reordering, is necessary.
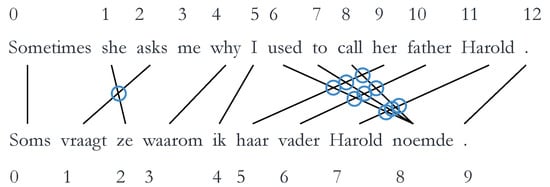
Figure 2.
Example of word_cross, with a word_cross value of … (example taken from Vanroy et al. [21]). (Literal translation of Dutch sentence: * Sometimes asks she why I her father Harold used to call.)
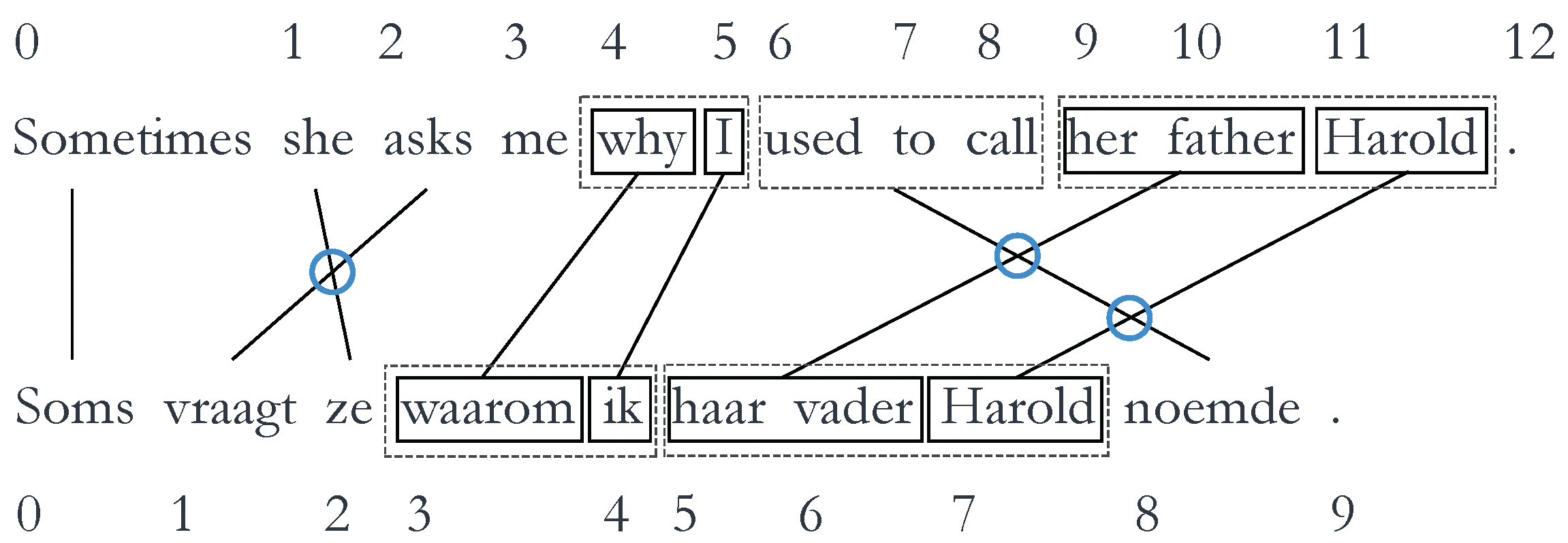
The second metric is Syntactically Aware Cross (SACr), which refers to the reordering of linguistically motivated groups, based on dependency representations [21]. The dependency representation assumes that sentence and clause structure result from dependency relationships between words, unlike the phrase structure representation, which sees sentences and clauses structured in terms of constituents [22]. To be considered a linguistically motivated word group, in SACr, all words in each given word group must exhibit one or more child–parent dependency relationships with other words in the same group. If not all words of a group adhere to the criterion, new sub-groups will be created for which the criterion does hold. Similarly to word_cross, SACr is calculated by the number of times linguistically motivated groups cross each other averaged by the total number of alignment links. An example can be seen in Figure 3, where the SACr value is or 0.375.
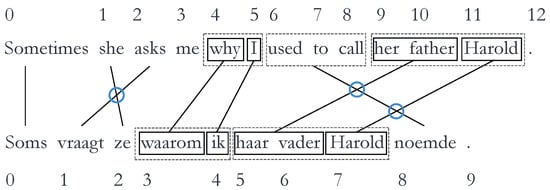
Figure 3.
Example of SACr, with a SACr value of 3/8 = 0.375 (example taken from Vanroy et al. [21]). The dotted boxes indicate word groups that are not linguistically motivated; they are simply words that remain in the same order in the translation. These boxes are then split into linguistically motivated groups (solid boxes) to calculate SACr. (Literal translation of Dutch sentence: * Sometimes asks she why I her father Harold used to call.)
The third metric is called Aligned Syntactic Tree Edit Distance (ASTrED), a metric which examines the deeper, structural differences between a source and a target sentence, by calculating the tree edit distance between the word-aligned dependency trees of a source and a target sentence, which are directed acyclic graphs with words as nodes and dependency relations as edges. Tree edit distance is defined as the minimum-cost sequence of node edit operations (i.e., deletion, insertion, and substitution) that transform one tree into another [23], as visualized in Figure 4 [21].
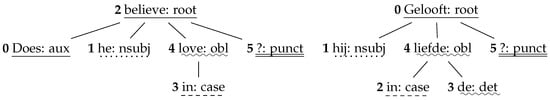
Figure 4.
Example of the source dependency tree of ’Does he believe in love?’ (left) and the target dependency tree of its Dutch translation ’Gelooft hij in de liefde’ (right) (example sentences taken from Vanroy et al. [21]). The word alignments between the two sentences have been indicated by underlinings. In order to calculate ASTrED, the tree edit distance between these two trees is measured. (Literal translation of the Dutch sentence: * Believes he in the love?).
Despite the availability of different automatic parsers, their annotation schemes vary significantly across languages [21]. Universal Dependencies is an initiative to mitigate this problem by developing a framework for cross-linguistically consistent morphosyntactic annotation [24]. In this study, we obtain the dependency trees by using the stanza parser of the Stanford NLP group [25] and annotate the dependency labels for English and Dutch by using Universal Dependencies (UD).
3.3.4. Stylistic Difference: Burrows’ Delta
Finally, Burrows’ Delta was also calculated for our data. Burrows’ Delta is a word frequency based metric from the field of stylometry, which is often used as a method for authorship attribution (i.e., to determine the author of a text of unknown or disputed authorship), but can also be employed as a measure of stylistic difference [12]. We will be using Burrows’ Delta in the latter application.
Evert et al. [26] point out how Burrows’ Delta is a distance measure, i.e., ”it describes the distance between one text and a group of texts”. Hence, the smaller the Delta score, the smaller the distance between the texts, and the more similar these texts are stylistically. We will now briefly explain how Burrows’ Delta is calculated, but, for a more extensive explanation and formulae, refer to the work of Burrows himself [12] and Evert et al. [26]. In short, in order to compare one text (text a) to a corpus consisting of various other texts (texts b and c), the n most frequent words from that corpus are collected. To prevent the larger frequencies (of the very frequent words) from overpowering the smaller frequencies in the ‘n most frequent word list’, ‘z-scores’ are used to give each word equal weight. The z-scores of each of the texts from the corpus (texts b and c) are then compared to the z-score of text a, in order to measure how similar these texts are. This score is Burrows’ Delta, or to put it in the words of Burrows himself:
“A delta- score […] can be defined as the mean of the absolute differences between the z-scores for a set of word-variables in a given text-group and the z-scores for the same set of word-variables in a target text” [12].
For calculating Burrows’ Delta, we used a Python script retrieved from GitHub (https://github.com/programminghistorian/jekyll/blob/gh-pages/en/lessons/introduction-to-stylometry-with-python.md). Due to the varying lengths of the novels, e.g., A Christmas Carol with approximately 29,000 words and Sense and Sensibility with 120,000, we decided to shorten each novel to an equal length. We wanted to represent each novel equally in the corpus, but also wanted to ensure that, when each novel was compared to that corpus, it was given the same chances as the other texts. Proisl et al. [27] discovered an increase in accuracy for longer texts while calculating Cosine Delta, which is another type of delta measure that is also used for authorship attribution, So it seemed inaccurate to potentially allow Sense and Sensibility to exceed the others so much in length. Proisl et al. [27] also discovered that texts under the 7000 words fared the worst. Hence, in order to have the texts as long as possible and above the 7000 words, we decided to limit the length of all novels to the length of the shortest novel, i.e., 29,000 words. The first 29,000 words of each novel were then used to create ’the corpus’ and the text which was to be compared to said corpus. The main issue when calculating Burrows’ Delta was deciding how large the aforementioned n should be (in the n most frequent words). Burrows himself states that a larger n leads to more accurate results [12]; however, a too large n-value would lead to the list of ’most frequent words’, containing words that are not frequent at all. We decided to discover the impact of different n-values ourselves, such as n = 100 and n = 500. The 100th most frequent word appeared 157 times in the corpus, while the 500th word appeared 23 times. In order to find a balance between the highest possible n and avoiding the list containing too many non-frequent words, we decided to go with an n between these two values: n = 150 (the 150th most frequent word appeared 92 times). These settings were preserved for both the comparison of the different novels, as well as the comparison of the different translations of one novel.
4. Results
4.1. Comparison of Four Novels
Before discussing the results of the error and key feature analysis, it might be useful to compare the four novels used in this study. Differences between the novels could possibly be related to deviant results in the error or key feature analysis. In order to discover if there are any ’peculiar’ novels, we firstly looked at the distribution of sentence lengths per novel, and secondly calculated Burrows’ Delta, a measure of stylistic difference.
When examining the distribution of sentence lengths in our source novels, it appears that there is one outlier: Sense and Sensibility (Table 3). Whereas the majority of the sentences in A Christmas Carol, The Memoirs of Sherlock Holmes and The Sign of the Four hover between the 5 and 14 tokens (i.e., category 5+ and 10+), Sense and Sensibility mostly contains sentences of 45 tokens or above. When calculating the average sentence length, by simply dividing the number of tokens in the novel by the number of sentences, the same tendency comes to light.

Table 3.
Distribution of sentence length (in tokens) and average sentence length (in tokens) in the STs of each novel.
Although Burrows’ Delta has been mentioned as a part of our key feature analysis, it can also be employed in order to compare the styles of the four novels. Therefore, we calculated the Delta scores of the first 29,000 words of each source novel; the results of which can be seen in Table 4. The stylistic distance between each novel and Sense and Sensibility is large, which can be observed in the high Delta scores. Again, this points to Sense and Sensibility deviating from the other novels. Another observation, is that A Christmas Carol is rather similar to The Memoirs of Sherlock Holmes and The Sign of the Four. The stylistic distance between The Memoirs of Sherlock Holmes and The Sign of the Four is also fairly small. This makes sense to a certain degree, since both novels are written by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Burrows’ Delta will be applied to our data again later on, as a part of the key feature analysis.

Table 4.
Delta scores of first 29,000 words of each source novel (n = 150).
4.2. Error Analysis
The first analysis of this study concerns an error analysis. The aim of this analysis is to discover the quality of the NMTs based on error annotations made according to an adapted version of the SCATE taxonomy. These annotations will also allow us to discover which types of errors are most problematic for literary NMT.
4.2.1. Overall Quality
When looking at the number of sentences containing no errors, 142 GNMT sentences (23%) and 129 DeepL sentences (21%) contain no errors. This is a surprisingly small amount, when compared to previous studies on literary NMT. Both Fonteyne et al. [4] and Tezcan et al. [5] discussed the quality of Agatha Christie’s The Mysterious Affair at Styles, translated by GNMT from English into Dutch and came to the conclusion that approximately 44% of the sentences contained no errors.
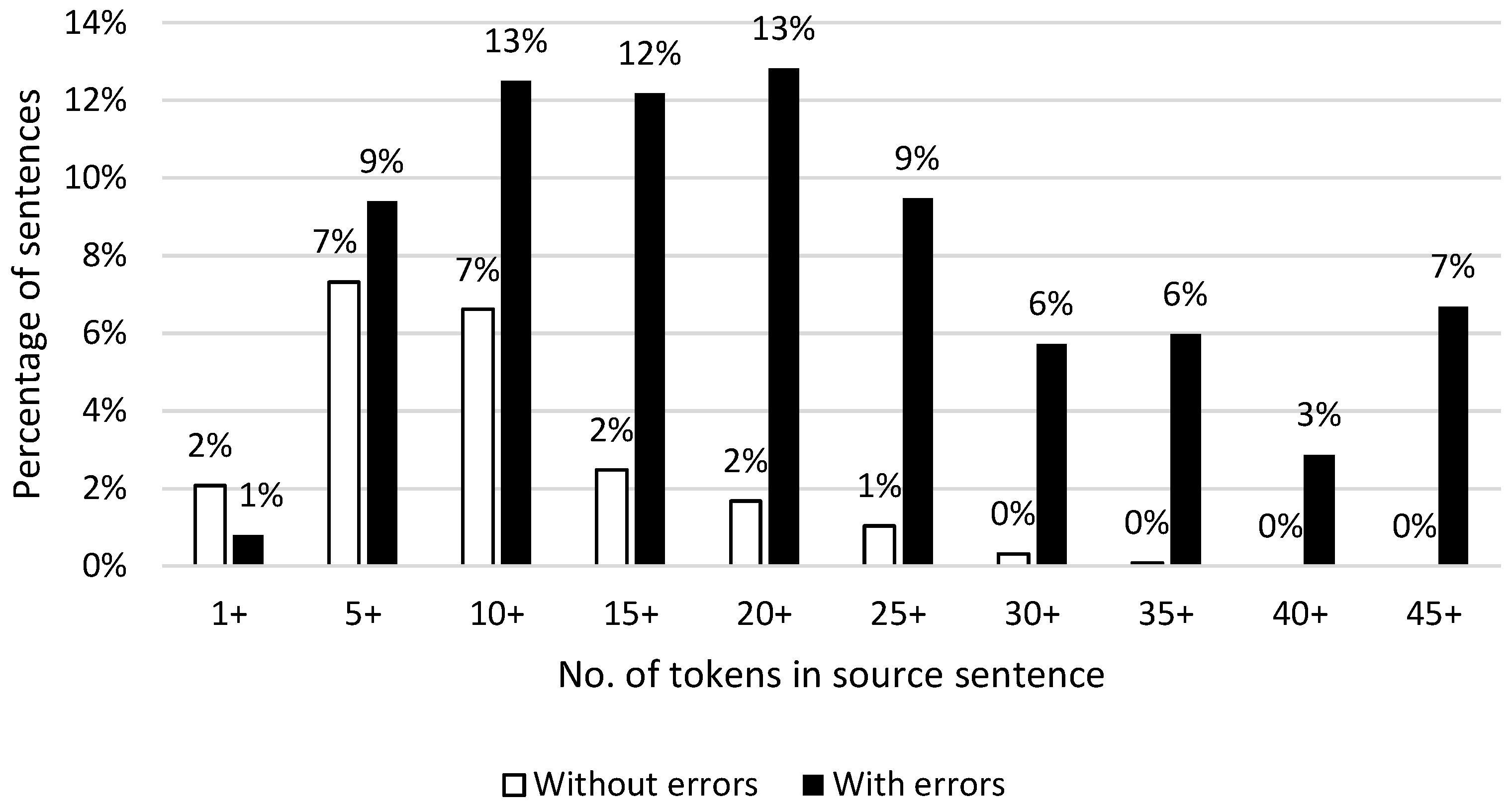
When looking at the quality of each novel separately, one novel seems to catch the eye. Sense and Sensibility only has 5% of the GNMT sentences without errors and 4% of the DeepL sentences. The other three novels hover around ±25% without errors. This may raise questions as to why Sense and Sensibility performed so poorly. As mentioned earlier in this article, Sense and Sensibility also distinguished itself from the other novels by its style and fairly long sentences. When looking at all the sentences with or without errors in the whole corpus as shown in Figure 5, we see that, on average, the longer a sentence is, the less likely it is to be error free. This is also confirmed in previous research, and longer sentences are simply more difficult for NMT to translate [28,29,30]. The aforementioned observation could also indicate that there is a possible relation between authorial style and quality of NMT.
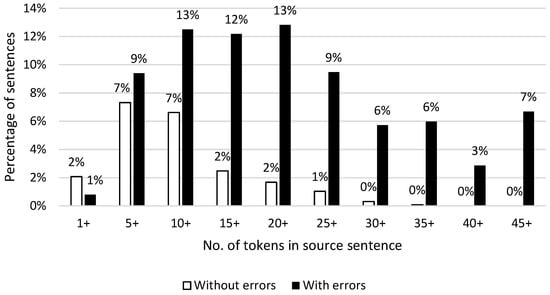
Figure 5.
Distribution of sentences with and without errors per source sentence length in tokens (for all four novels and both MT systems).
4.2.2. Error Distribution
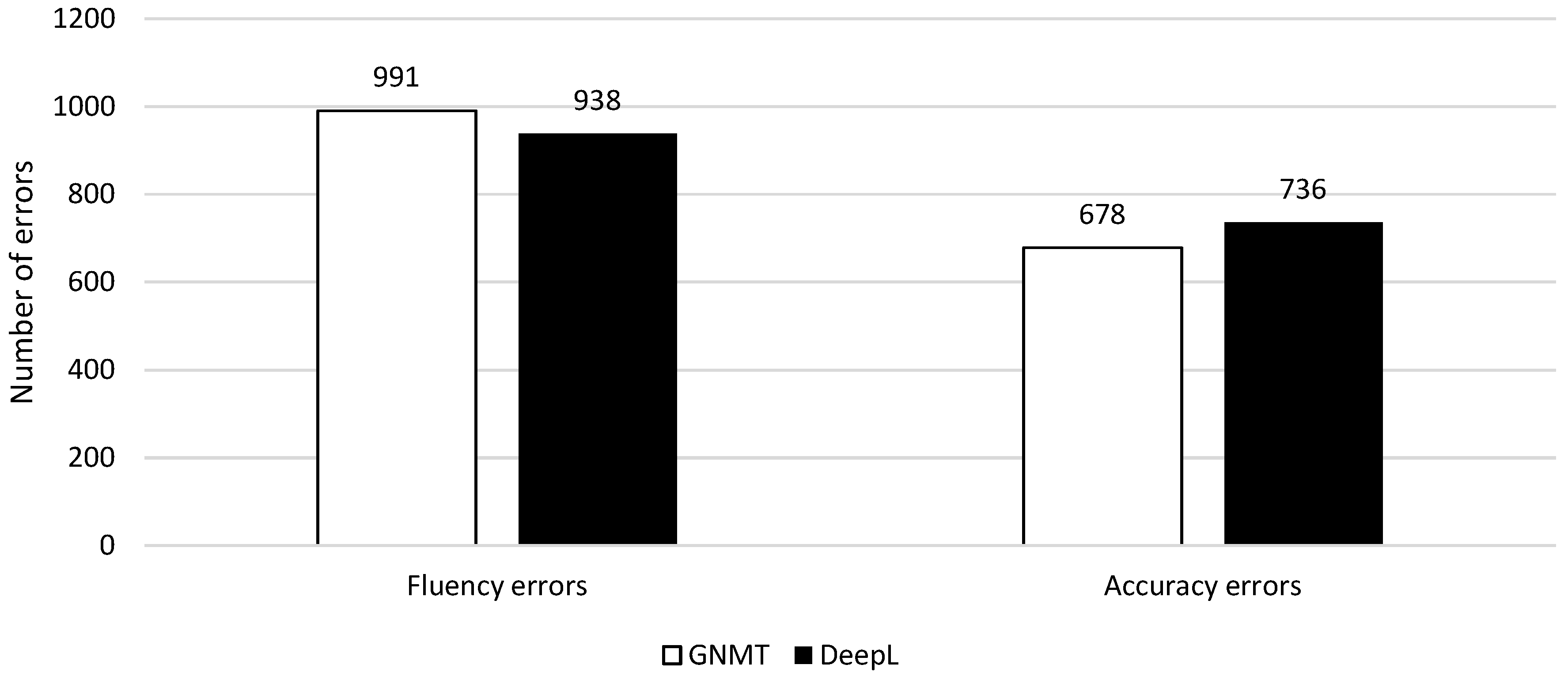
In order to discover the most problematic errors for literary NMT, we took a look at the most frequent errors’ types. Similar to previous research on English to Dutch NMT [4,5,13], our data set contains more fluency errors (1,929) than accuracy errors (1414). In total, GNMT makes 1669 errors, 991 of which are fluency (59%) and 678 accuracy (41%); DeepL makes 1674 errors, 938 of which are fluency (56%) and 736 accuracy (44%) (Figure 6). This would seem to indicate that GNMT struggles more with fluency errors than DeepL and DeepL more with accuracy errors than GNMT, but more research would be needed to substantiate this claim further.
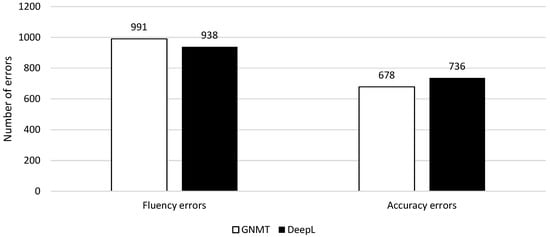
Figure 6.
Distribution of fluency and accuracy errors per NMT system for all four novels.
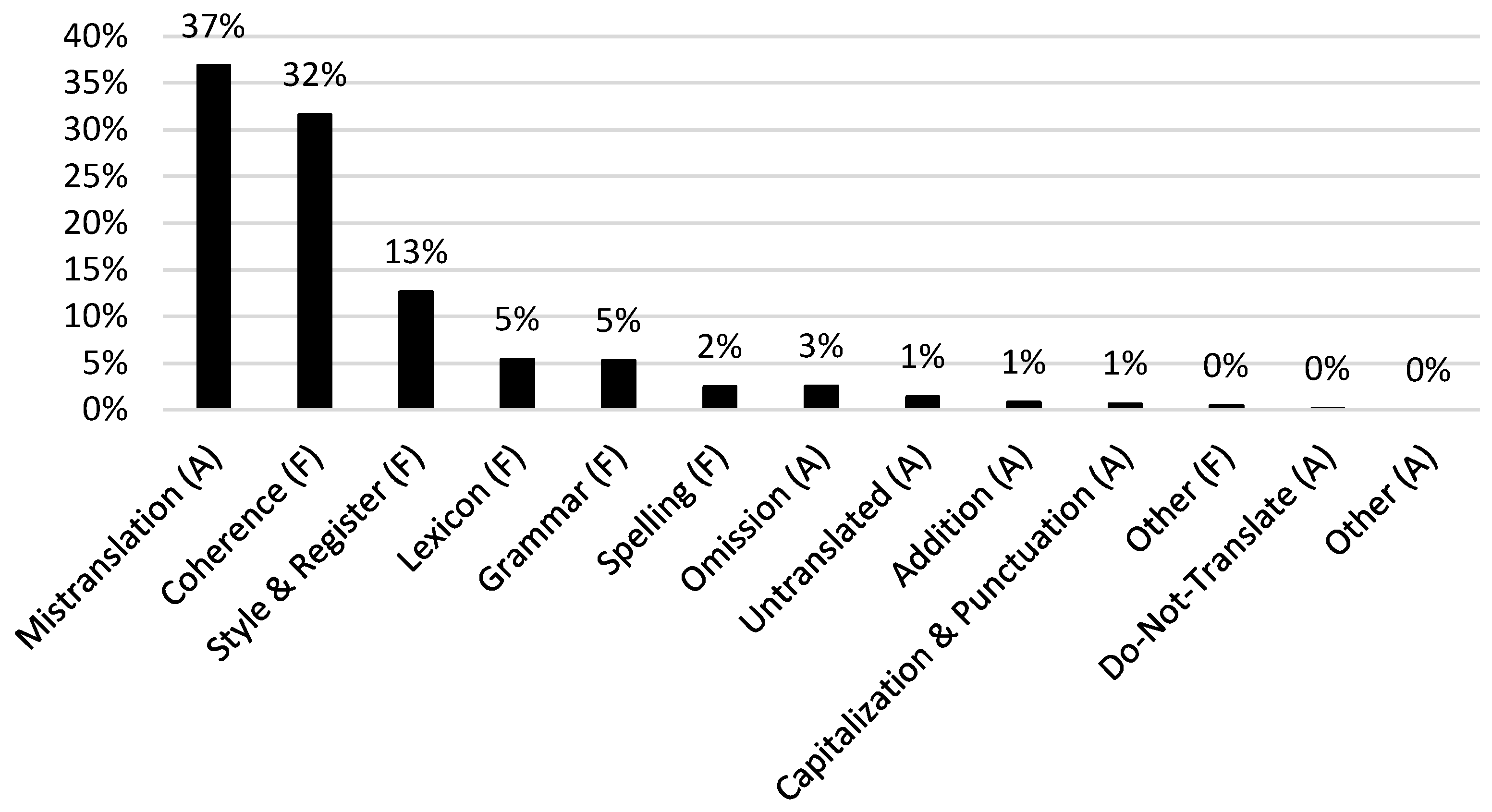
On a more fine-grained level, the most frequent errors made in our whole data set of literary NMT (3343 errors) are mistranslation (1231 errors or 37%), coherence (1056 errors or 32%), and style & register (422 errors or 13%). An example of a mistranslation error occurred in the GNMT version of The Sign of the Four. In a sentence where someone’s wrist was described as ‘scarred with innumerable puncture-marks’, GNMT mistranslated ‘puncture-marks’ as ‘flat/leaking tires’ (i.e., ‘lekke banden’). While a ‘puncture’ can indeed be a hole in a tire, this is not the correct word sense in this particular sentence. For someone reading the target text without access to the source text, such a mistranslation also leads to coherence issues, our second most frequent error type. Although a reader familiar with the English language and machine translation errors may be able to infer that a wrist looking like a flat tire implies the wrist being wounded or damaged, there are other coherence issues that have the ability of being even more problematic for intelligibility. Consider the following coherence-error-ridden sentence taken from the DeepL translation of A Christmas Carol: ‘Be here all the earlier next morning’. This was translated as ‘De volgende ochtend hier de hele ochtend eerder zijn’ (*‘The next morning here the whole morning earlier be’), a sentence which makes about as much sense in the Dutch translation as in the word-for-word English translation with an asterisk. The third most frequent error type is style & register. A sentence containing such an error can usually be understood, but there is a more idiomatic way of expressing the same thing in the target language. For example, ‘the city clocks had just gone three’ in A Christmas Carol was translated by GNMT as ‘de stadsklokken waren net pas drie geworden’ (‘the city clocks had just become three’). Although this is intelligible to a Dutch speaker, in Dutch clocks do not ‘become’ a time (‘geworden’), but they ‘strike’ a time (‘geslagen’). Of these error types, the style subcategory ‘disfluency’ is perhaps the most subjective one, as what is perceived as ‘disfluent’ by one native speaker is not necessarily perceived as such by all native speakers. Findings related to this specific error type must therefore be interpreted with caution.
The abovementioned top three most frequent error types remains the same for each novel and each NMT system separately. These frequent errors also correspond to previous research by Tezcan et al. [5] and Fonteyne et al. [4]. Most mistranslation issues are related to issues without a specific subcategory (39.6%), word sense (37.5%), and multi word expressions (13.4%). Coherence issues are mostly caused by logical problems (79%) and style & register issues by disfluent sentences or constructions (87.2%). Figure 7 shows the different frequency distributions of each error type for all novels and both NMT systems. Fluency and accuracy errors often overlap. The most common error categories appearing together are mistranslation errors and coherence errors, accounting for 84% of the overlapping errors in our data.
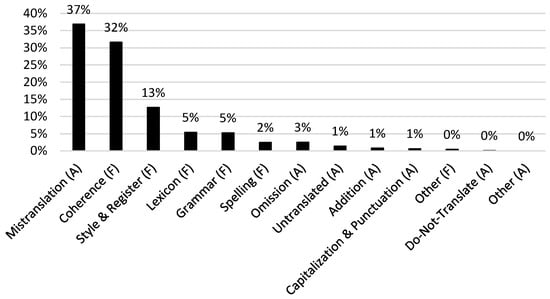
Figure 7.
Frequency distributions of error types expressed as percentage of all errors (from all four novels and both NMT systems).
4.3. Key Feature Analysis
The second analysis performed on our four novels was a key feature analysis. This analysis was carried out on the novels as a whole. Whereas the error analysis primarily focused on the quality of the NMT in its own right, this analysis will allow us to compare the NMTs to the HTs and the STs by highlighting certain features, such as lexical richness, cohesion, syntactic and stylistic difference. In the following sections, the ST is mostly included as a point of reference, as any differences between the ST and the translations are likely caused by linguistic differences between English and Dutch rather than by differences between source and target. Our main goal is to establish differences between the HT and NMT versions of the text.
4.3.1. Lexical Richness
Table 5 clearly shows that the number of unique words in the human translations always exceeds the number of unique words in the machine translations (e.g., A Christmas Carol has 4260 unique words in the ST, 5064 in HT, 4799 in the GNMT and 4804 in the DeepL). This would seem to indicate that human translations tend more strongly towards lexical richness than machine translations. This is confirmed by Vanmassenhove et al. [10], who state that MT causes a loss in terms of lexical richness and diversity when compared to a human-generated or human-translated texts. An interesting illustration of this decline of lexical richness can be found in Sense and Sensibility. In the source text, the adjective ‘charming’ appears 17 times; both GNMT and DeepL use the fairly evident translation ‘charmant’ 17 times, whereas the human translation uses 14 different formulations, remarkably none of which is the ‘evident’ ‘charmant’ Other examples of human translations of ‘charming’ are: ‘schattig’ (x1), ‘allerliefst’ (x4), ‘riant’ (x1), ’lief’ (x1), ’oergezellig’ (x1), ’dol’ (x1), ‘innemend’ (x1), ‘fijn’ (x1), ‘heerlijk’ (x1), ‘betoverend’ (x1), etc.

Table 5.
Number of unique and total words per novel for ST, HT, GNMT, and DeepL.
The observation that the HTs are lexically richer than the NMTs can also be recognized in all three measures in Table 6. It can be observed that the HT always has the largest TTR-values and smallest MASS indices for each novel.

Table 6.
Overview TTR-values per novel for ST, HT, GNMT, and DeepL.
4.3.2. Local Cohesion
As previously mentioned, a high level of cohesion is characteristic of literary texts [2]. Therefore, it is also important that this high level of cohesion is maintained in the machine translation of said text. In order to explore this matter further, we calculated lexical cohesion and semantic cohesion for our four novels. Given that different languages have different ways to express cohesion and have different levels of tolerance for lexical repetition [31], we expect these values to be different for the English STs and Dutch TTs, but the question is whether the NMT texts exhibit levels of cohesion that more closely resemble those of the English ST or those of the Dutch HT.
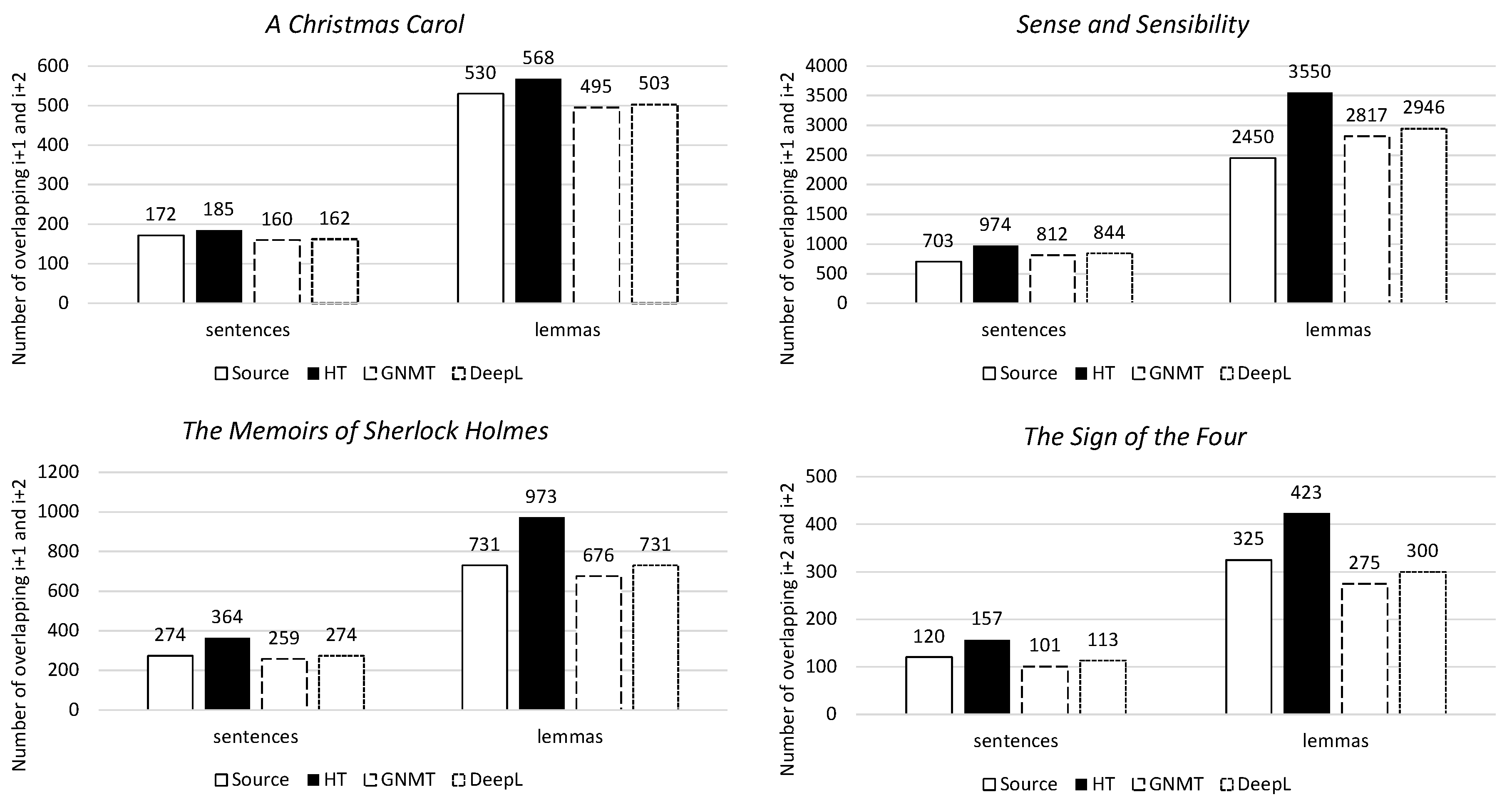
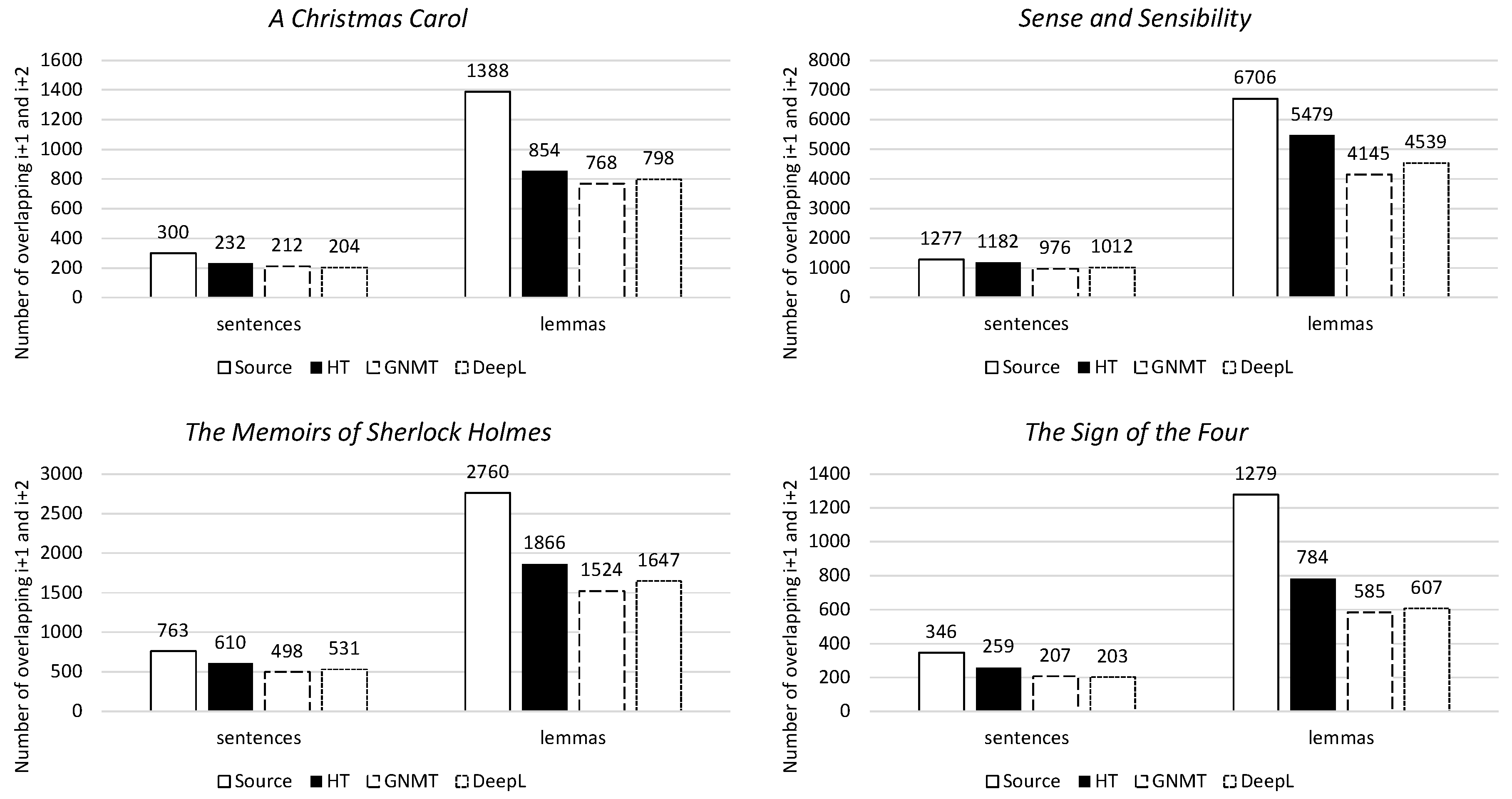
Firstly, lexical cohesion indicates the overlaps created by identical words in sentence i, sentence i+1, and sentence i+2. For all four novels, the human translation has the highest lexical cohesion, both on the sentence and lemma levels. The machine translation has a level of lexical cohesion that is much lower than that of the human translation. Its level of lexical cohesion more closely resembles that of the source text (Figure 8).
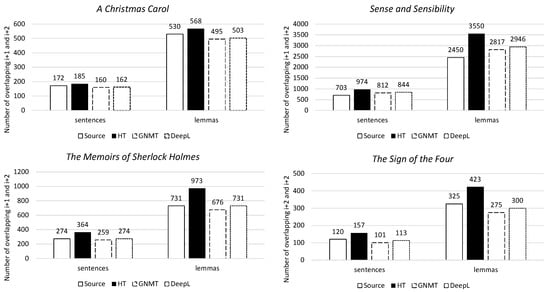
Figure 8.
Lexical cohesion for i+1 and i+2 per novel, on both the sentence and lemma levels.
Secondly, semantic cohesion discusses the overlaps created by semantically related words in sentence i, sentence i+1, and sentence i+2. For all four novels, the highest semantic cohesion is achieved in the human translation, both on the sentence level and the lemma level (Figure 9). Please note that due to the synsets (which contain the semantically related words) being much larger for English than Dutch, it would not be accurate to compare the semantic cohesion calculated by these synsets across the two languages. The performance of the ST for semantic cohesion can still be viewed in Figure 9, but only as a reference. Again, both machine translations have a lower semantic cohesion than the human translation.
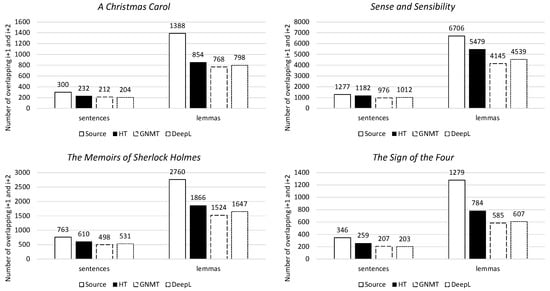
Figure 9.
Semantic cohesion for i+1 and i+2 per novel, on both sentence and lemma levels.
To summarize, both types of machine translations seem to maintain the level of lexical cohesion of the source text, but they do not seem to achieve the level of lexical or semantic cohesion of the human translation. It would therefore appear that machine translations have a lower level of cohesion than human translations.
4.3.3. Syntactic Divergence
The penultimate key feature to be discussed in this paper is syntactic divergence. This feature will allow for a discussion of the changes the source text undergoes when being translated by the human translator or the NMT systems.
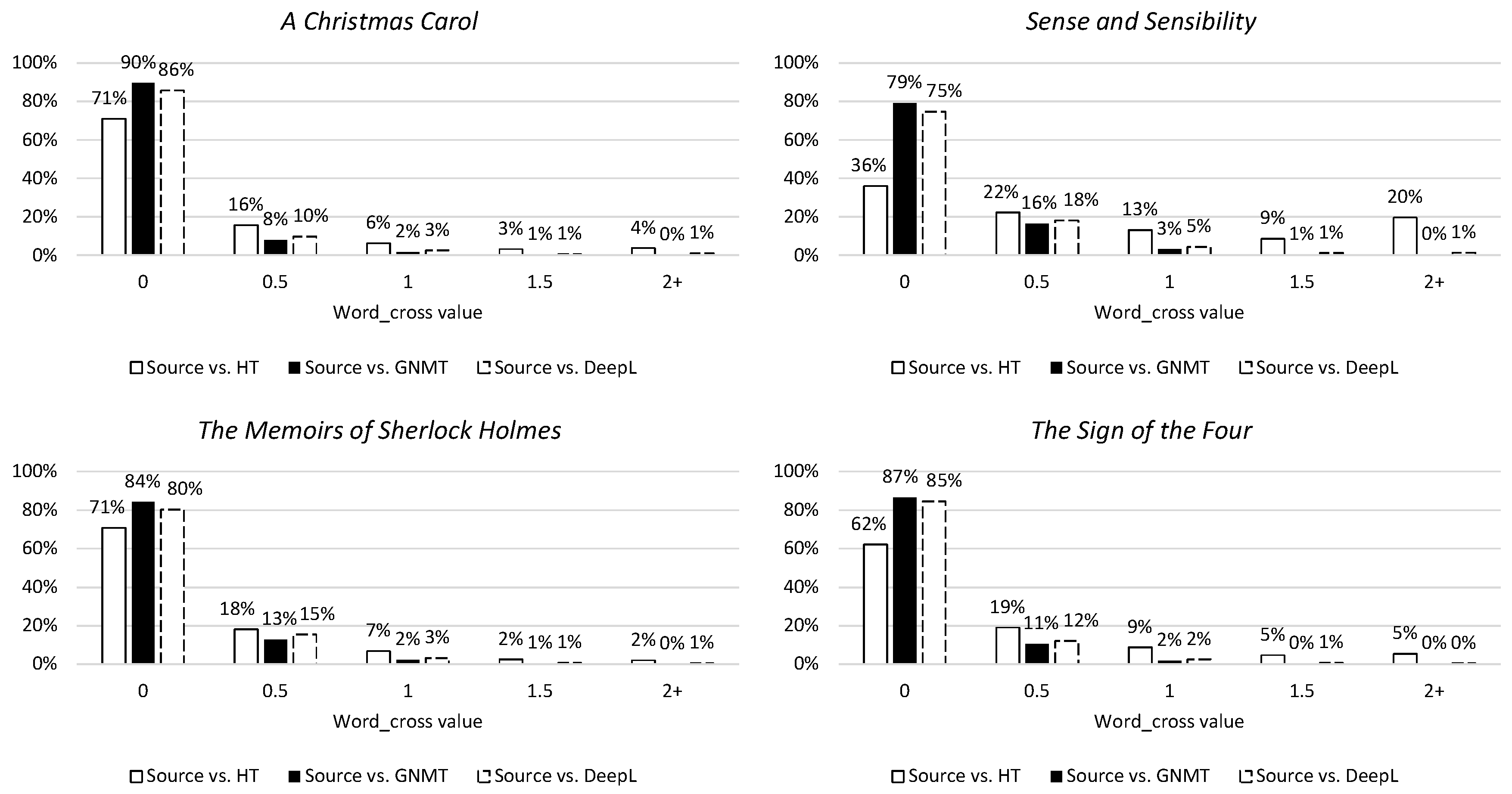
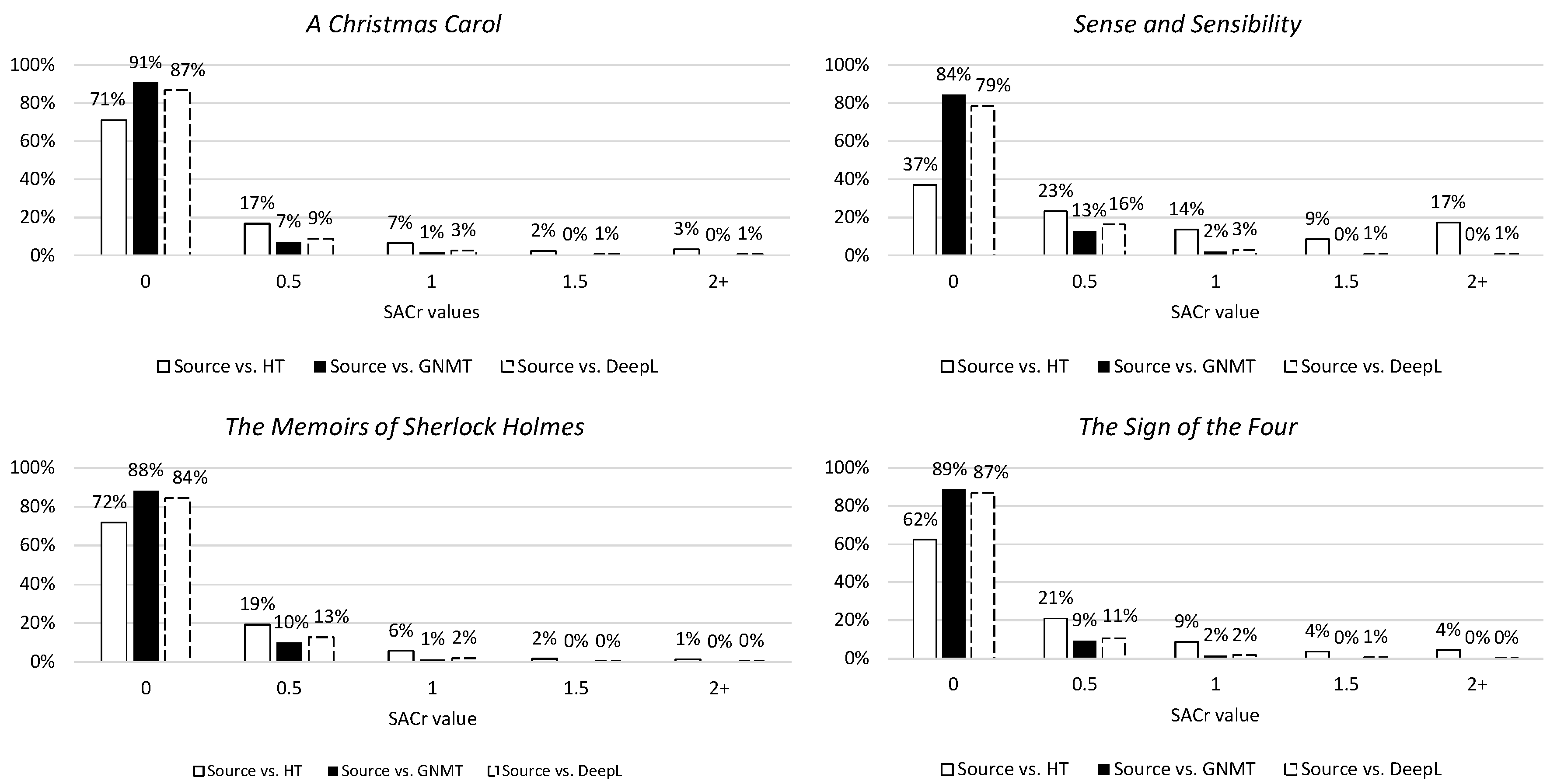
The first metric is word_cross, which concerns the reordering of words by measuring crossing links. As can be seen in Figure 10, the NMTs tend to make no or fairly small deviations from the source word order (0 and 0.5) and scarcely make any large changes (1+). The tendency for making large changes to word order lies more with the human translation, although this also seems capable of copying or more or less following source word order. This observation can also be recognized when looking at the second metric for syntactic divergence, namely SACr (Figure 11). This metric describes the reordering of linguistically motivated word groups by measuring crossing links and shows the same tendencies indicated by the word_cross values.
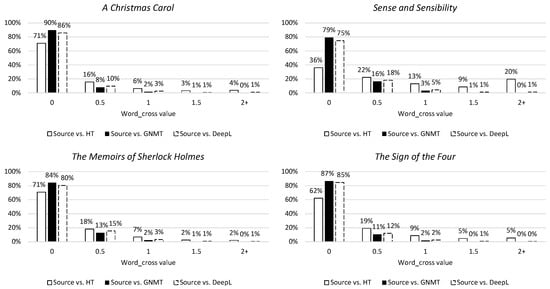
Figure 10.
Distribution of word_cross values in percentages per novel. The 0 column contains values [0:0.5[, the 0.5 column values [0.5:1[, etc.
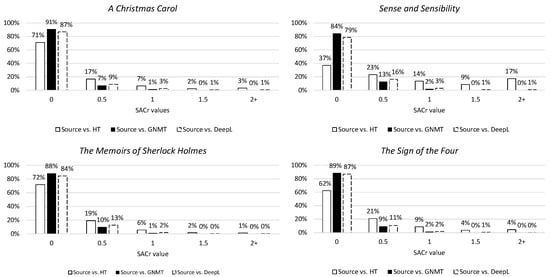
Figure 11.
Distribution of SACr values in percentages per novel. The 0 column contains values [0:0.5[, the 0.5 column [0.5:1[, etc.
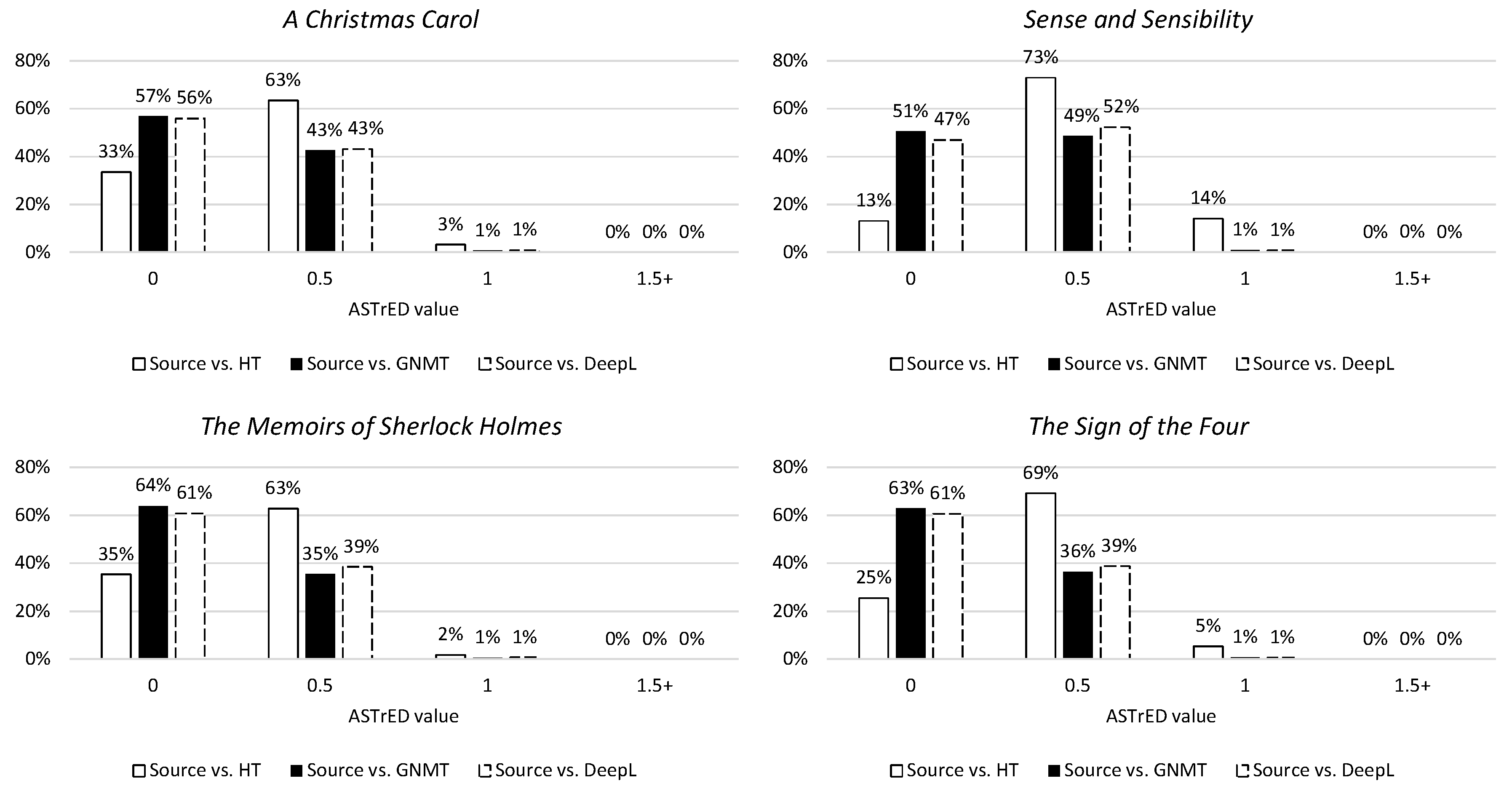
The last metric of syntactic divergence is ASTrED, a metric used to illustrate reordering on a deeper (linguistic) level by employing edit distance between dependency trees. The results of this metric are similar to the results of the previously mentioned metrics (Figure 12). Although the scores cannot be equated across the three metrics, the tendency of the NMTs to remain close to the structure of the ST (while the HT may deviate more from the ST) can be observed throughout.
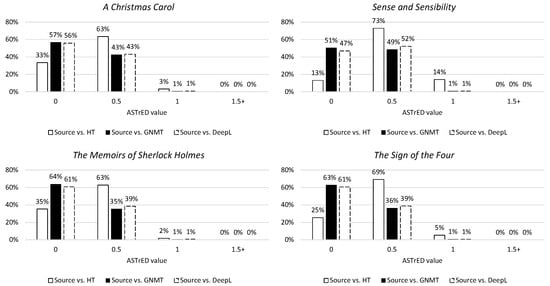
Figure 12.
Distribution of ASTrED values in percentages per novel. The 0 column contains values [0:0.5[, the 0.5 column [0.5:1[, etc.
The fact that NMT mostly follows the source structure can also be connected to the large number of fluency errors noted in the annotations. Besacier and Schwartz [32] similarly translated English literature, but they translated into French and with a phrase-based MT (PBMT). They noted that the human evaluator observed a defective syntactic calque in the MT, stating that the structure did not sound “very French” (i.e., fluent). The fact that our Dutch NMT deviates little from the English source order (whereas the HT sometimes does) could indicate that our NMT also does not sound ’very Dutch’, which in turn perhaps points to non-native-like language (or fluency errors) still remaining an issue for the successor of PBMT, NMT. Note, for example, the following sentence taken from A Christmas Carol: ’By the bye, how he ever knew that, I don’t know.’ The word_cross value between the sentences in the ST and the HT is 2, which indicates that quite some reordering was needed to move from the source to the correct target. However, the word_cross value between the sentences in the ST and the GNMT is 0, which indicates that the word order from the English source has been copied into the Dutch translation (’Trouwens, hoe hij ooit wist dat ik het niet weet.’ (or in more fluent Dutch: ’Trouwens, hoe hij dat ooit wist, weet ik niet’). i.e., *’By the bye, how he ever knew that I it do not know’). GNMT follows the source order in this sentence, which leads to an incorrect word order in Dutch, which is classified as a ’fluency’ error in the SCATE taconomy.
4.3.4. Stylistic Difference
Another interesting application of Burrows’ Delta is to measure the stylistic differences between the three translations (HT, GNMT, and DeepL). Rybicki et al. [33] have previously indicated Burrows’ Delta as an accurate metric to measure translator styles, when it is applied to different translations of a single novel. Hence, we compared the styles of the three translations of a novel by calculating Burrows’ Delta on the first 29,000 words of each novel with n = 150. An example of these Delta scores can be seen in Table 7, which shows the Delta scores for the different translations of A Christmas Carol. These scores indicate large distances between the styles of the human translation and the machine translations, but small distances between the styles of the machine translations (GNMT and DeepL). This trend can also be observed in the scores of the other novels. Therefore, the aforementioned results suggest that human translators employ a different style than machine translations, but that both GNMT and DeepL employ a similar style.

Table 7.
Delta scores of each translation of A Christmas Carol (n = 150).
5. Discussion
The aim of this study was to consider the performance of literary NMT from English into Dutch. In order to do this, we translated four novels with GNMT and DeepL and also obtained their human translations. The quality of the NMTs was then measured through an error analysis and the different versions of the same novel were compared through a key feature analysis.
At first sight, the quality of literary NMT does not seem at all satisfactory. The translated novels showed that a large majority of the sentences contained errors (±75%). Sense and Sensibility exceeded the other novels, by only translating 5% of the sentences without errors. These amounts are striking when compared to a study on ’general-domain NMT’ from English into Dutch. Van Brussel et al. [13] observed that 33% of their NMT sentences were error-free. Their translations were also collected two years prior to ours, so, if this study was performed now, with the continuous improvements of NMT, this number may even increase.
Due to the above-mentioned erroneous sentences being linked to annotations, we were able to see which errors led to these fairly unfavorable numbers. A first observation is that there are more fluency errors (59% in GNMT and 56% in DeepL) than accuracy errors (41% in GNMT and 44% in DeepL); or, in other words, literary NMT struggles more with producing correct sentences in the target language than with accurately representing what is being said in the source. It must be noted that the number of accuracy errors also remain rather high and are especially represented by mistranslations. Mistranslation is generally seen as a common type of mistake for NMT, no matter the genre [13,34] and, in particular, word sense mistranslations can lead to comical utterances, such as how Scrooge wishes to buy a country at Christmas in A Christmas Carol (i.e., the food ‘turkey’ is translated as the country ‘Turkey’ in both GNMT and DeepL) or how Elinor from Sense and Sensibility is continuously declaring herself to be a homosexual (i.e., the emotion of being ‘gay’ is translated as the sexual orientation in both GNMT and DeepL). Despite the small chuckles, these mistakes may allow the reader, they remain problematic for literary translations; the possibility of changing the plot of a novel or making the story incomprehensible remains a danger for literary NMT. Although mistranslation may be seen as an error type that is fairly common to all types of NMT, coherence and style & register are specific to literary NMT. It must not be forgotten that these two categories were added to the SCATE taxonomy specifically to adapt it to the context of literary NMT.
On the one hand, one could argue that we cannot expect a generic NMT system to produce accurate literary translations if literary translations were not included in the training data. On the other hand, research has shown that even a system trained on large amounts of literary text produces a maximum of 34% accurate sentences [3]. As such, it becomes increasingly important to look at specific textual features in addition to quality. Aside from the types of errors in the NMTs, one could also wonder how these machine generated translations compare to the actual human translations: Do they achieve the same level of lexical richness and cohesion, the same syntactic structures, or even the same style? Our results indicate that lexical richness decreases from human translation to machine translation, indicating a certain homogenization of the lexicon used by the NMT systems (cf. [10]). NMT systems do not only have a lower lexical richness than human translations, but also a lower level of lexical and semantic cohesion. Even though these results need to be confirmed by expert judgements, compared to the human-translations, they point to a lack of context awareness in the NMT systems used in this study. The impact of this lack of context awareness can also be seen in the error annotations in the form of coherence errors, which cover a number of context-related factors such as co-reference and discourse markers. Considering that coherence issues often overlap with mistranslation errors (84% of all overlapping errors), further developments in context-aware NMT could lead to fewer errors in both coherence and mistranslation error categories, which make up of 69% of all error annotations in our data, and greatly improve overall NMT quality for literary text.
Furthermore, the low scores of word_cross, SACr, and ASTrED show the NMTs to have a less diverse approach to syntactic structure; whereas the NMTs tend to follow the structures of the source closely, the HTs show the ability to deviate from the source structure. Lastly, the style of the human translation is different from that of the machine translations, but the styles of the machine translations are remarkably similar. This can also be seen as a convergence of the machine translations, which in turn implies a normalized language form generated by NMTs. All in all, these findings point to the translations generated by NMT systems being less diverse and cohesive than those generated by humans.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, it would appear that literary human translations are lexically richer, more cohesive, and syntactically more diverse than their literary NMTs. Although the NMTs do not perform disastrously, they offer a passable attempt at what the human translator is capable of, with little input of diversity or creativity and fairly many errors. In the meantime, NMT systems can definitely be employed in the field of literary translation, but perhaps more as an aid during translation.
Although this may seem a fairly bleak ending to a paper which started by trying to discover the possibilities of literary NMT, it must be remembered that these NMT systems are general-domain NMT systems, which are not specifically trained to cope with literary texts. It was precisely our goal to determine to what extent such generic NMT systems contain textual features comparable to those found in literary human translation. The improvements over the past years for general-domain NMT have been colossal. Although literary translation is often described as a skillful process, a delicate balancing act of capturing style, register, cohesion, meaning, reading experience, etc. while remaining creative and diverse, NMT systems seem to be already taking a step in the right direction.
In the future, we would like to continue this study by delving deeper into the capability of literary NMT on an even larger data set, i.e., examining different languages and more novels. In addition, we would like to explore the impact of Dutch compounds on lexical richness by applying a compound splitter to the data. Lastly, by annotating and linking cohesive and stylistic devices across all versions of our novels (source, HT, GNMT, and DeepL), we would like to compare the cohesion and style of different versions of a novel on document level. This will in turn give us an idea of how NMT systems cope with translating whole novels and if they are capable of maintaining the all-important literary reading experience. From a broader perspective, the features presented in this study offer an initial methodology to observe different aspects of translation, which allow for a comparison between translations of the same text. While applied here on human translation and neural machine translation of literary texts, it would be interesting to see the same comparison for different human translations of the same source text, which, for example, could also be used to study differences between different student translations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.D., L.M., A.T., M.F., and R.W.; methodology, J.D., L.M., A.T., M.F., and R.W.; software, A.T. and M.F.; validation, J.D., L.M., A.T., and M.F.; formal analysis, R.W.; investigation, R.W.; resources, M.F.; data curation, J.D. and L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, R.W.; writing—review and editing, R.W., L.M., A.T., M.F., and J.D.; visualization, R.W.; supervision, L.M. and J.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is part of the ArisToCAT project (Assessing The Comprehensibility of Automatic Translations), which is a four-year research project (2017–2020) funded by the Research Foundation—Flanders (FWO)—Grant No. G.0064.17N.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Bram Vanroy for generating the syntactic metrics on our data sets and the Master’s student for the manual error annotation of the NMT output.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ASTrED | aligned syntactic tree edit distance |
| DeepL | neural machine translation system of DeepL |
| GNMT | neural machine translation system of Google |
| HT | human translation |
| MASS | mass index |
| MSTTR | mean segmental type-token ratio |
| MT | machine translation |
| NMT | neural machine translation |
| PBMT | phrase-based machine translation |
| SACr | syntactically aware cross |
| ST | source text |
| TT | target text |
| TTR | type-token ratio |
| UD | universal dependencies |
References
- Matusov, E. The Challenges of Using Neural Machine Translation for Literature. In Proceedings of the Qualities of Literary Machine Translation, Dublin, Ireland, 19 August 2019; pp. 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, R.; Jurafsky, D. Towards a Literary Machine Translation: The Role of Referential Cohesion. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT 2012 Workshop on Computational Linguistics for Literature, Montréal, QB, Canada, 8 June 2012; pp. 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Toral, A.; Way, A. What Level of Quality Can Neural Machine Translation Attain on Literary Text? In Translation Quality Assessment; Moorkens, J., Castilho, S., Gaspari, F., Doherty, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 263–287. [Google Scholar]
- Fonteyne, M.; Tezcan, A.; Macken, L. Literary Machine Translation under the Magnifying Glass: Assessing the Quality of an NMT-Translated Detective Novel on Document Level. In Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 3790–3798. [Google Scholar]
- Tezcan, A.; Daems, J.; Macken, L. When a ‘sport’ is a person and other issues for NMT of novels. In Proceedings of the Qualities of Literary Machine Translation; Hadley, J., Popović, M., Afli, H., Way, A., Eds.; European Association for Machine Translation: Lisbon, Portugal, 2019; pp. 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tezcan, A.; Hoste, V.; Macken, L. SCATE taxonomy and corpus of machine translation errors. In Trends in E-Tools and Resources for Translators and Interpreters; Pastor, G.C., Durán-Muñoz, I., Eds.; Approaches to Translation Studies; Brill | Rodopi: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 45, pp. 219–244. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. BLEU: A Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PL, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Aue, A.; Chen, C.; Chowdhary, V.; Clark, J.; Federmann, C.; Huang, X.; Junczys-Dowmunt, M.; Lewis, W.; Li, M.; et al. Achieving Human Parity on Automatic Chinese to English News Translation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.05567. [Google Scholar]
- Shterionov, D.; Superbo, R.; Nagle, P.; Casanellas, L.; O’Dowd, T.; Way, A. Human versus automatic quality evaluation of NMT and PBSMT. Mach. Transl. 2018, 32, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmassenhove, E.; Shterionov, D.; Way, A. Lost in Translation: Loss and Decay of Linguistic Richness in Machine Translation. In Proceedings of Machine Translation Summit XVII Volume 1: Research Track; European Association for Machine Translation: Dublin, Ireland, 2019; pp. 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Cop, U.; Dirix, N.; Drieghe, D.; Duyck, W. Presenting GECO: An eyetracking corpus of monolingual and bilingual sentence reading. Behav. Res. Methods 2017, 49, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, J. ’Delta’: A Measure of Stylistic Difference and a Guide to Likely Authorship. Lit. Linguist. Comput. 2002, 17, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brussel, L.; Tezcan, A.; Macken, L. A fine-grained error analysis of NMT, PBMT and RBMT output for English-to-Dutch. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation; Calzolari, N., Choukri, K., Cieri, C., Declerck, T., Goggi, S., Hasida, K., Isahara, H., Maegaard, B., Mariani, J., Mazo, H., et al., Eds.; European Language Resources Association (ELRA): Paris, France, 2018; pp. 3799–3804. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W. Sudies in Language Behavior. Psychol. Monogr. 1944, 56, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läubli, S.; Sennrich, R.; Volk, M. Has Machine Translation Achieved Human Parity? A Case for Document-level Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 4791–4796. [Google Scholar]
- Voita, E.; Sennrich, R.; Titov, I. When a Good Translation is Wrong in Context: Context-Aware Machine Translation Improves on Deixis, Ellipsis, and Lexical Cohesion. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1198–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Werlen, L.M.; Ram, D.; Pappas, N.; Henderson, J. Document-Level Neural Machine Translation with Hierarchical Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 2947–2954. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, D.S.; Graesser, A.C.; McCarthy, P.M.; Cai, Z. Automated Evaluation of Text and Discourse with Coh-Metrix; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, S.A.; Kyle, K.; McNamara, D.S. The tool for the automatic analysis of text cohesion (TAACO): Automatic assessment of local, global, and text cohesion. Behav. Res. Methods 2016, 48, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanroy, B.; Tezcan, A.; Macken, L. Predicting syntactic equivalence between source and target sentences. Comput. Linguist. Neth. J. 2019, 9, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Vanroy, B.; De Clercq, O.; Tezcan, A.; Daems, J.; Macken, L. Metrics of syntactic equivalence to assess translation difficulty. In Explorations in Empirical Translation Process Research; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, P. Syntax. In Cambridge Textbooks in Linguistics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, K.C. The tree-to-tree correction problem. J. ACM 1979, 26, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivre, J.; De Marneffe, M.C.; Ginter, F.; Goldberg, Y.; Hajic, J.; Manning, C.D.; McDonald, R.; Petrov, S.; Pyysalo, S.; Silveira, N.; et al. Universal dependencies v1: A multilingual treebank collection. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 1659–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bolton, J.; Manning, C.D. Stanza: A Python Natural Language Processing Toolkit for Many Human Languages. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meetingof the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Seattle, WA, USA, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Evert, S.; Proisl, T.; Jannidis, F.; Reger Isabella, P.S.; Schöch, C.; Vitt, T. Understanding and explaining Delta measures for authorship attribution. Digit. Scholarsh. Humanit. 2017, 32, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proisl, T.; Evert, S.; Jannidis, F.; Schöch, C.; Konle, L.; Pielström, S. Delta vs. N-Gram Tracing: Evaluating the Robustness of Authorship Attribution Methods. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018), Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bentivogli, L.; Bisazza, A.; Cettolo, M.; Federico, M. Neural versus Phrase-Based Machine Translation Quality: A Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–4 November 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Tu, Z.; Shi, S.; Hovy, E.; Zhang, T. Neural machine translation with adequacy-oriented learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 6618–6625. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, P.; Knowles, R. Six Challenges for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the First, Workshop on Neural Machine Translation; Association for Computational Linguistics: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2017; pp. 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M. In Other Words/Mona Baker; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Besacier, L.; Schwartz, L. Automated Translation of a Literary Work: A Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop on Computational Linguistics for Literature, Denver, CO, USA, 4 June 2015; pp. 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicki, J.; Heydel, M. The stylistics and stylometry of collaborative translation: Woolf’s Night and Day in Polish. Lit. Linguist. Comput. 2013, 28, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X. The Gap between NMT and Professional Translation from the Perspective of Discourse. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Innovation in Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 14–17 March 2019; Volume ICIAI 2019, pp. 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).