Big Data Management with Incremental K-Means Trees–GPU-Accelerated Construction and Visualization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Construction of the Tree Hierarchy
3.1. GPU-Accelerated Incremental K-Means
| Algorithm 1: Incremental K-Means |
Input: data points P, distance threshold t Output: clusters C C = empty set for each un-clustered point p in P if C is empty then Make p a new cluster center and add it into C else p = next un-clustered point Find the cluster center c in C that is closest to p d = distance(c, p) if d < t then Cluster p into c else Make p a new cluster center and add it into C end if end if end for return C |
| Algorithm 2: Parallel Incremental K-Means |
Input: data points P, distance threshold t, batch size s Output: clusters C C = empty set while number of un-clustered points in P > 0 Perform Alg. 1 until a number of s clusters B emerge in parallel: for each un-clustered point pi Find the cluster center bi in B that is closest to pi di = distance(bi, pi) ci = bi if di < ti, otherwise ci = null end for end parallel Assign each point pi to ci if ci exists Add B to C end while return C |
3.2. Construction of the Tree Hierarchy
| Algorithm 3: Incremental K-Means Tree |
Input: data points P, initial distance threshold t, batch size s Output: root node of the tree Set each data point in P as a leaf node L = leaves t’ = t while L does not meet the stop condition Perform Alg. 2 with t’ and s to generate C clusters (nodes) from L Make nodes in L as children of the corresponding nodes in C t’ = update_threshold(t) L = C end while if L contains only one node then Return L[0] as the root else Make and return the root with L as its children |
3.3. Determine the Distance Threshold
4. Low Level Implementation
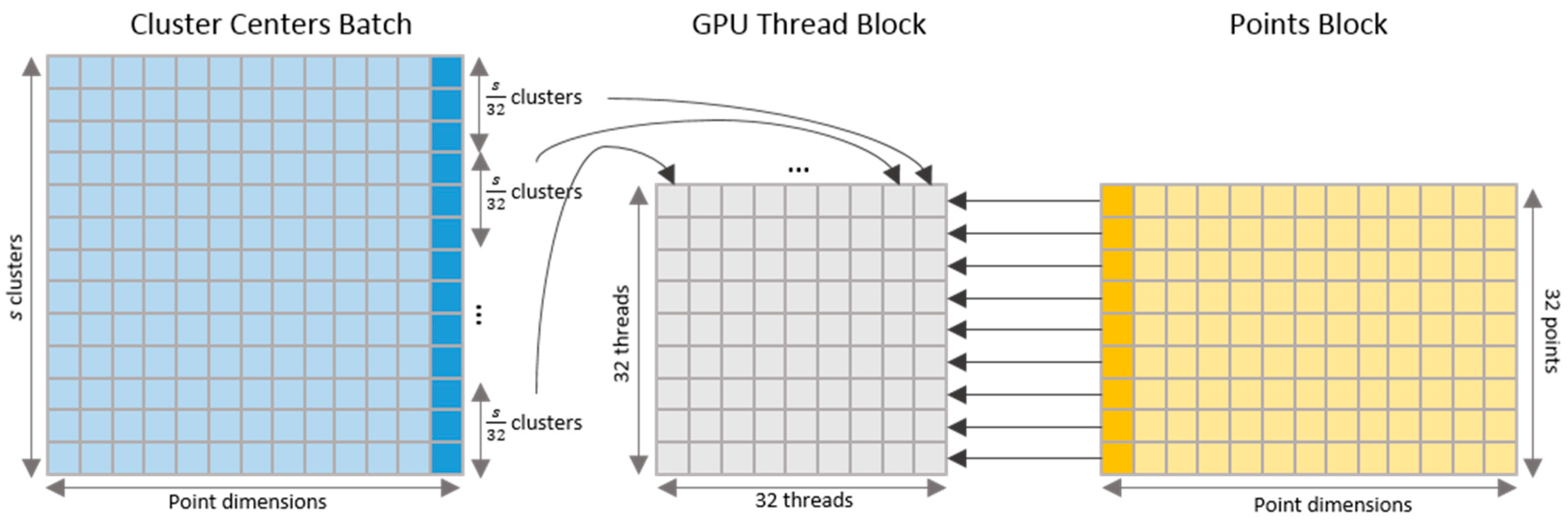
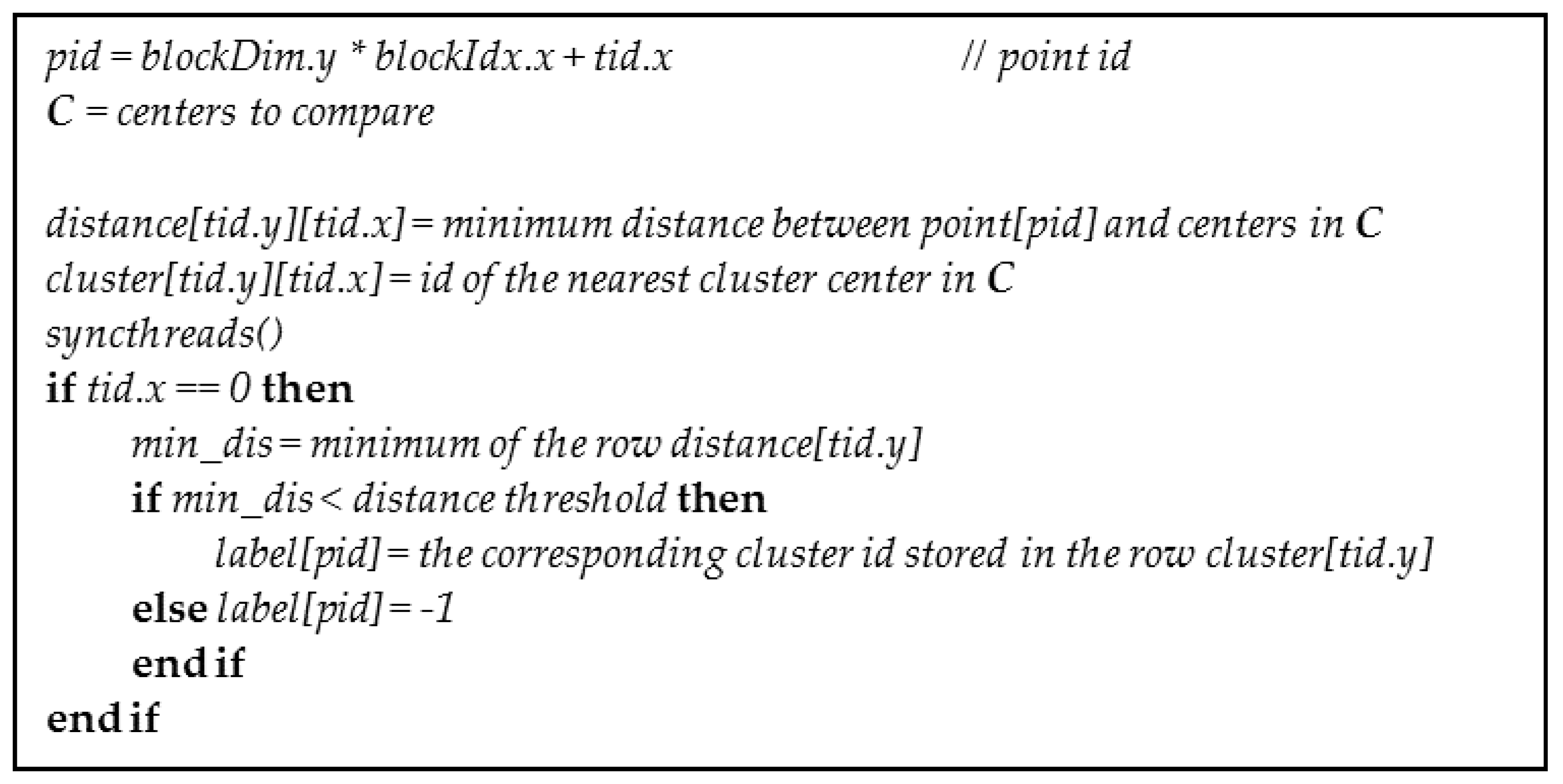
4.1. Kernel for Parallel Clustering
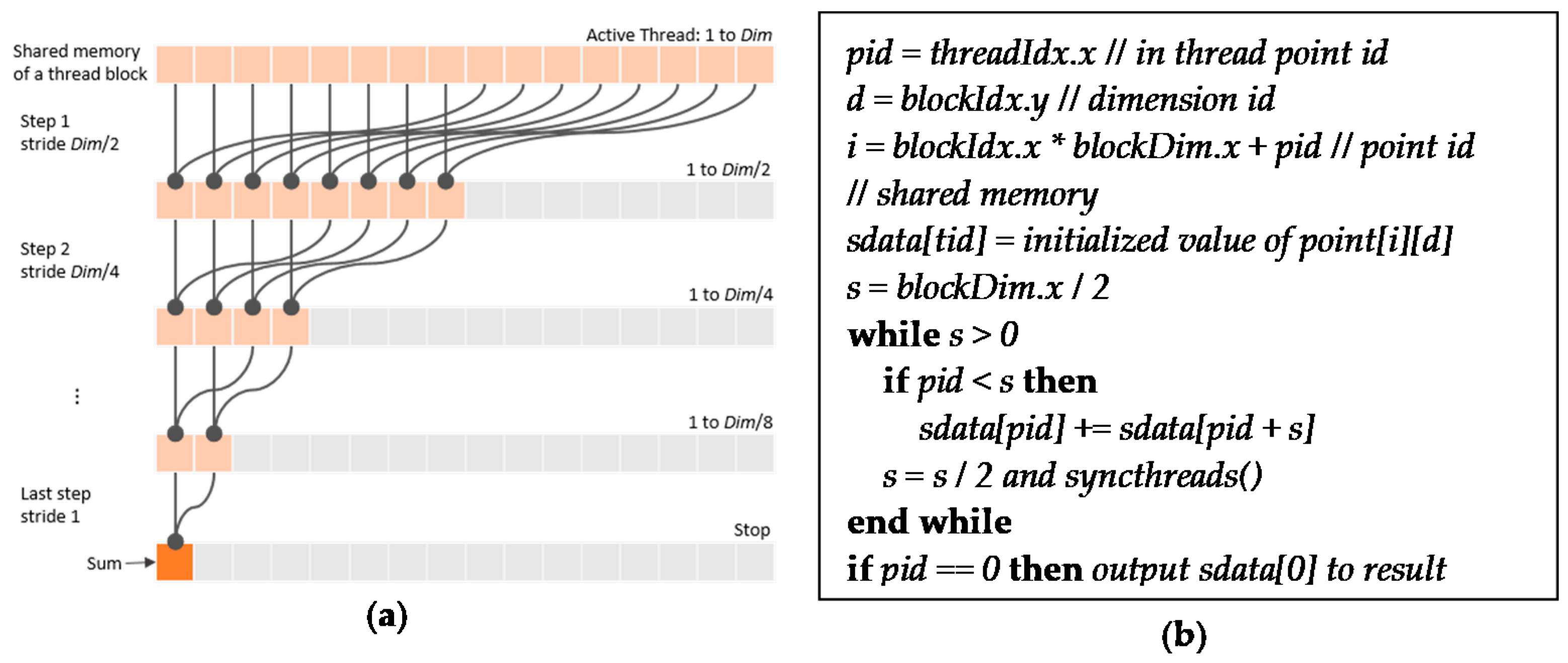
4.2. Parallel Computing of Standard Deviations and Pairwise distances
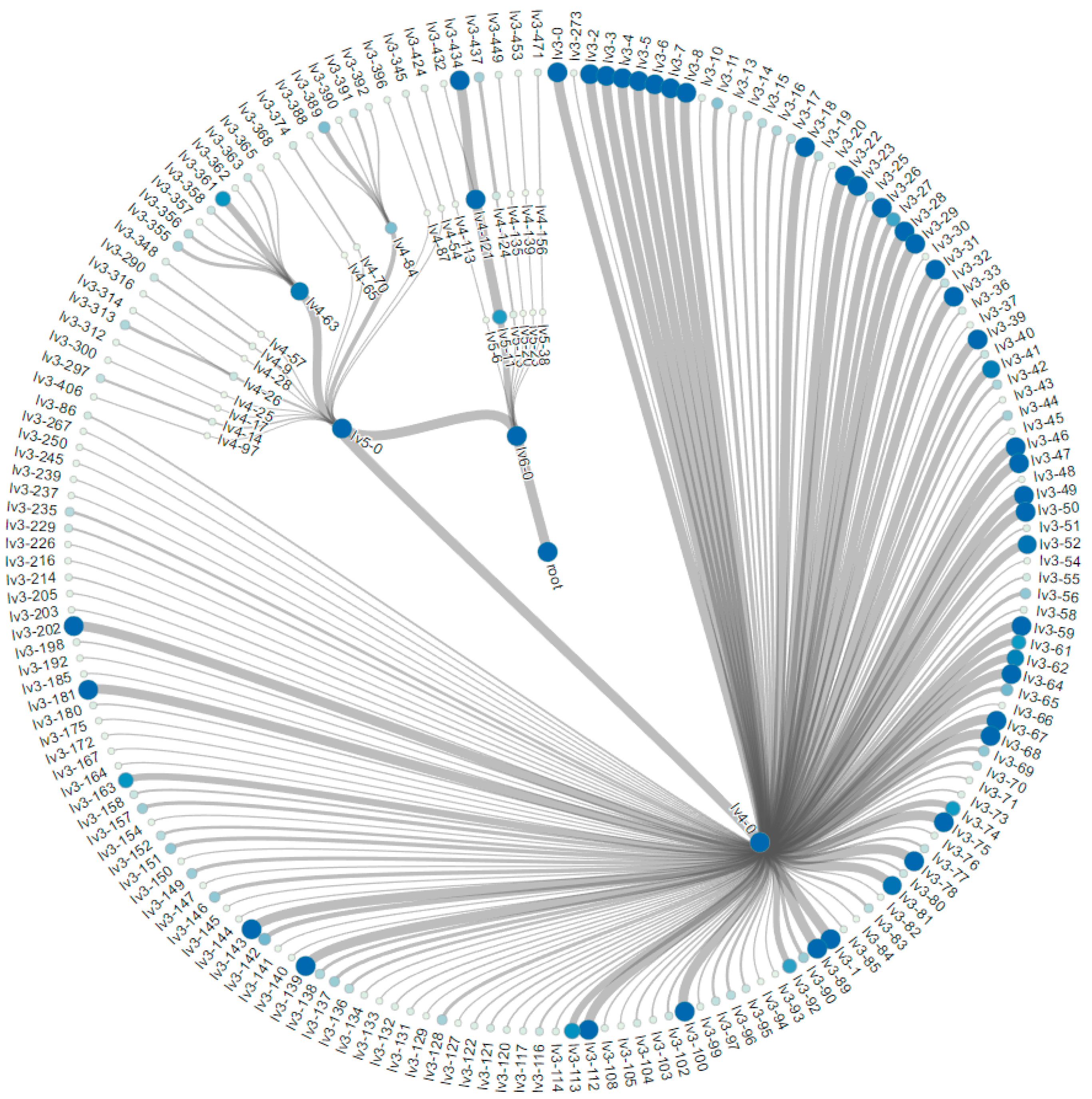
5. Experiments and Visualization
5.1. The MNIST Dataset
5.2. The Aerosol Dataset
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Big data. Nature 2008, 455, 1–136.
- Dealing with data. Science 2011, 331, 639–806.
- Muja, M.; Lowe, D.G. Scalable nearest neighbor algorithms for high dimensional data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, S.; Hsu, D. Hierarchical sampling for active learning. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, 5–9 July 2008; pp. 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Fahad, A.; Alshatri, N.; Tari, Z.; Alamri, A.; Khalil, I.; Zomaya, A.Y.; Foufou, S.; Bouras, A. A survey of clustering algorithms for big data: Taxonomy and empirical analysis. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2014, 2, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.C.; Shen, H.W.; Johnson, C.R.; Chen, C.; Ross, R.B. The top 10 challenges in extreme-scale visual analytics. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2012, 32, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Berkeley, CA, USA, 21 June–18 July 1965 and 27 December 1965–7 January 1966; Lucien, C., Jerzy, N., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1967; Volume 1, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Farivar, R.; Rebolledo, D.; Chan, E. A parallel implementation of k-means clustering on GPUs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Processing Techniques and Applications, PDPTA 2008, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 14–17 July 2008; Volume 13, pp. 340–345. [Google Scholar]
- Bezdek, J. C.; Ehrlich, R.; Full, W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 1984, 10, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Livny, M. BIRCH: An Efficient Data Clustering Method for Very Large Databases; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 25, pp. 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, S.; Rastogi, R.; Shim, K. CURE: An efficient clustering algorithm for large databases. Inf. Syst. 2001, 26, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karypis, G.; Han, E.H.; Kumar, V. Chameleon: hierarchical clustering using dynamic modeling. Computer 1999, 32, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ankerst, M.; Breunig, M.M.; Kriegel, H.; Sander, J. OPTICS: Ordering Points to Identify the Clustering Structure; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 28, pp. 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.; Gehrke, J.; Gunopulos, D.; Raghavan, P. Automatic Subspace Clustering of High Dimensional Data for Data Mining Applications; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 27, pp. 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Muntz, R. STING: A statistical information grid approach to spatial data mining. Int. Conf. Very Large Data 1997, 97, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fraley, C.; Raftery, A.E. MCLUST: Software for Model-Based Cluster Analysis. J. Classif. 1999, 16, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data via the EM Algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bentley, J.L. Multidimensional binary search trees used for associative searching. Commun. ACM 1975, 18, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidman, J.H.; Bentley, J.L.; Finkel, R.A. An Algorithm for Finding Best Matches in Logarithmic Expected Time. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1977, 3, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silpa-Anan, C.; Hartley, R. Optimised KD-trees for fast image descriptor matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lamrous, S.; Taileb, M. Divisive Hierarchical K-Means. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Inteligence for Modelling Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents Web Technologies and International Commerce, Sydney, Australia, 28 November–1 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jose Antonio, M.H.; Montero, J.; Yanez, J.; Gomez, D. A divisive hierarchical k-means based algorithm for image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 15–16 November 2010; pp. 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Nister, D.; Stewenius, H. Scalable Recognition with a Vocabulary Tree. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 2161–2168. [Google Scholar]
- Imrich, P.; Mueller, K.; Mugno, R.; Imre, D.; Zelenyuk, A.; Zhu, W. Interactive Poster: Visual data mining with the interactive dendrogram. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Visualization Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 28–29 October 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Satish, N.; Harris, M.; Garland, M. Designing efficient sorting algorithms for manycore gpus. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, Rome, Italy, 23–29 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Papenhausen, E.; Wang, B.; Ha, S.; Zelenyuk, A.; Imre, D.; Mueller, K. GPU-accelerated incremental correlation clustering of large data with visual feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, 6–9 October 2013; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero-lopez, S.; Williams, J.R.; Sanchez, A. Parallel Multiclass Classification Using SVMs on GPUs. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on General-Purpose Computation on Graphics Processing Units, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14 March 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jian, L. A CUDA-based parallel implementation of K-nearest neighbor algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cyber-Enabled Distributed Computing and Knowledge Discovery, Zhangjiajie, China, 10–11 October 2009; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuseler, M.; Schumann, H. A flexible approach for visual data mining. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2002, 8, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beham, M.; Herzner, W.; Groller, M.E.; Kehrer, J. Cupid: Cluster-Based Exploration of Geometry Generators with Parallel Coordinates and Radial Trees. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Maaten, L.J.P.; Hinton, G.E. Visualizing high-dimensional data using t-sne. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, M. Optimizing Parallel Reduction in CUDA. In NVIDIA CUDA SDK 2. 2008; NVIDIA Developer: Santa Clara, CA, USA, August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zelenyuk, A.; Yang, J.; Choi, E.; Imre, D. SPLAT II: An Aircraft Compatible, Ultra-Sensitive, High Precision Instrument for In-Situ Characterization of the Size and Composition of Fine and Ultrafine Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

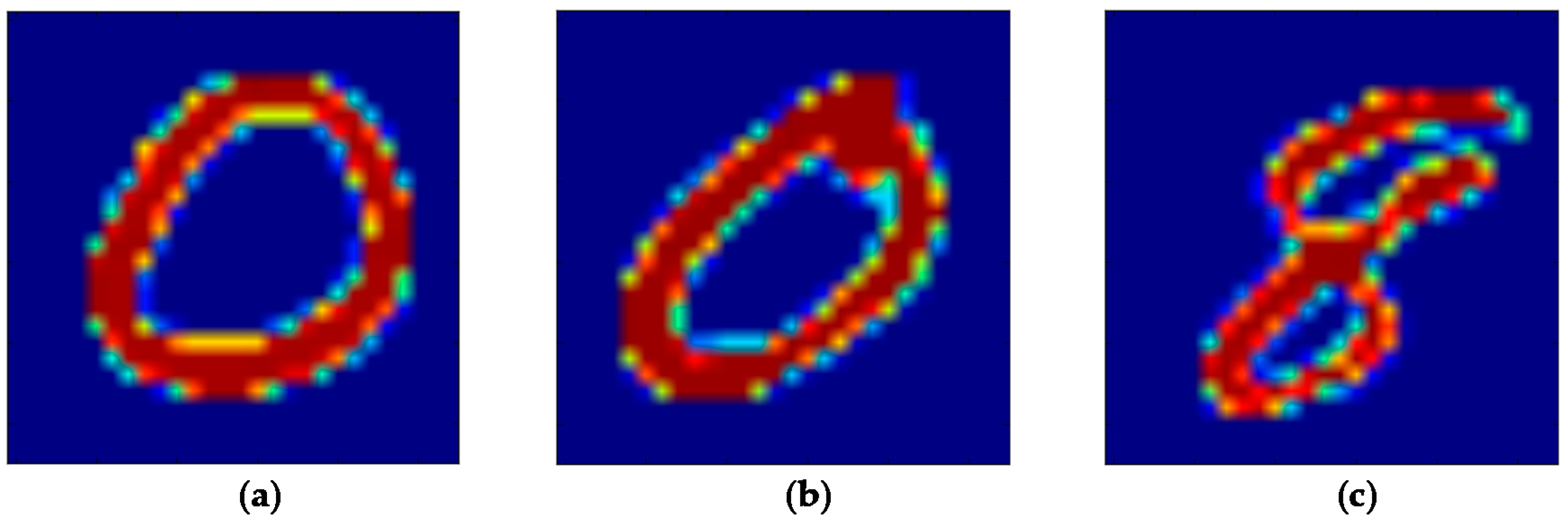
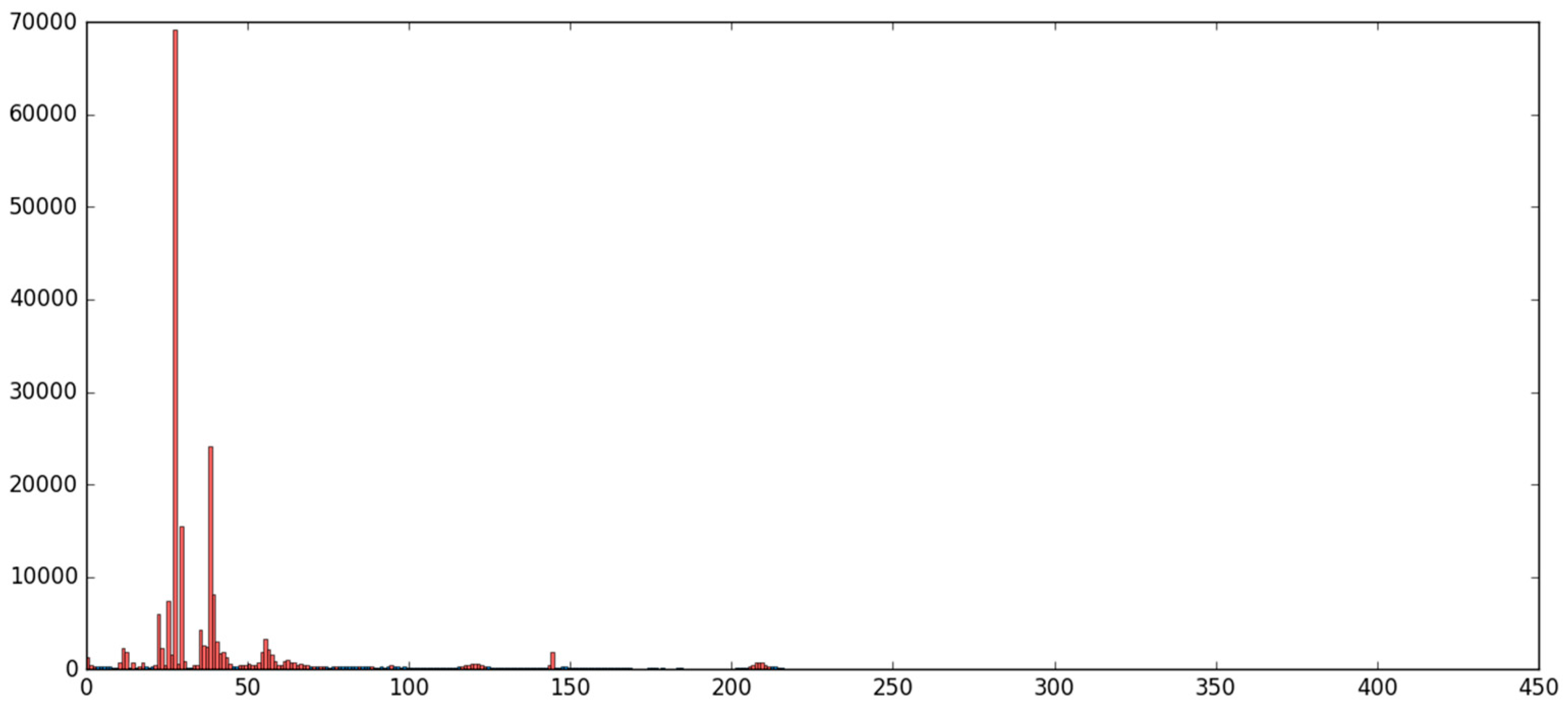

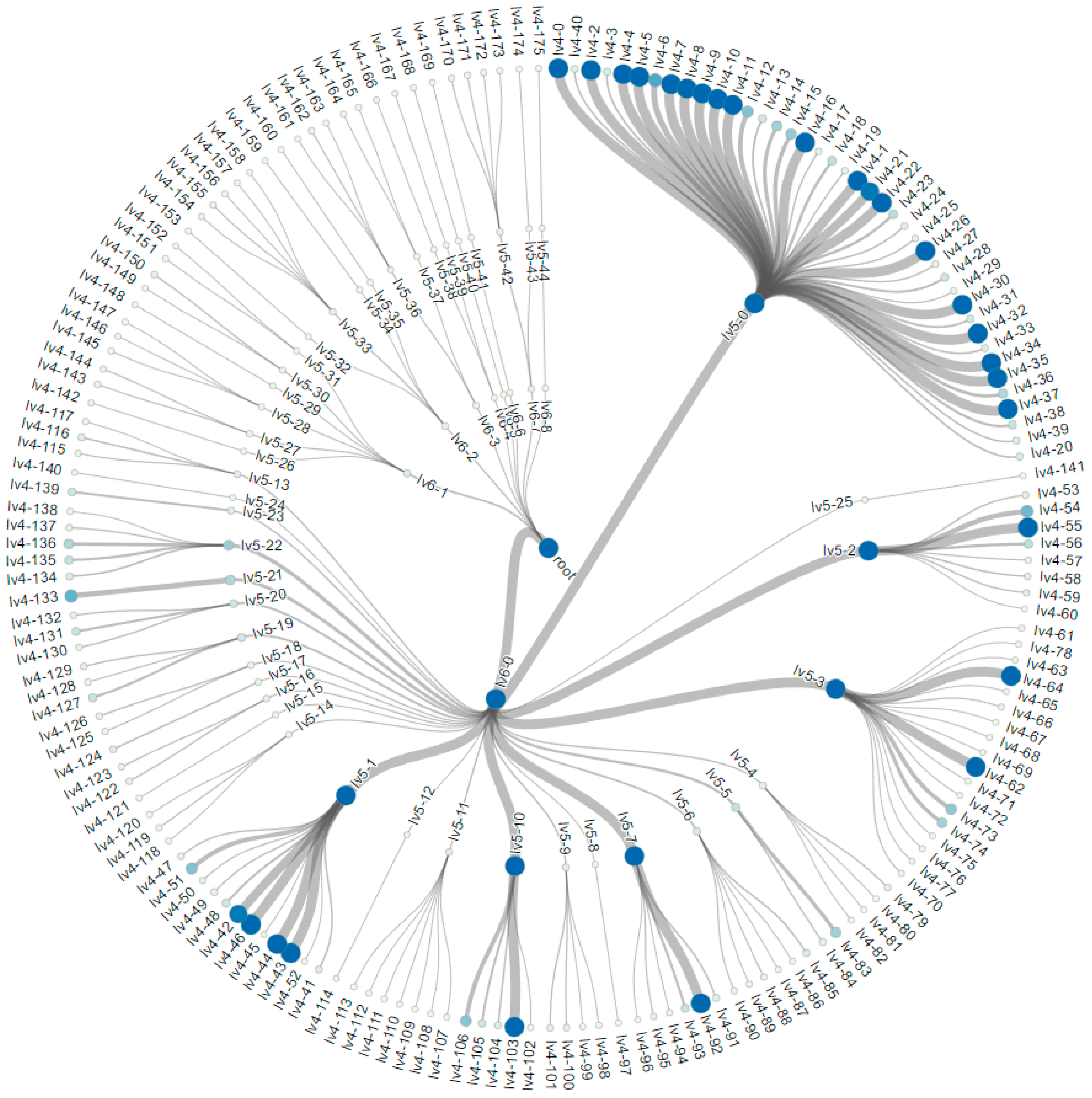
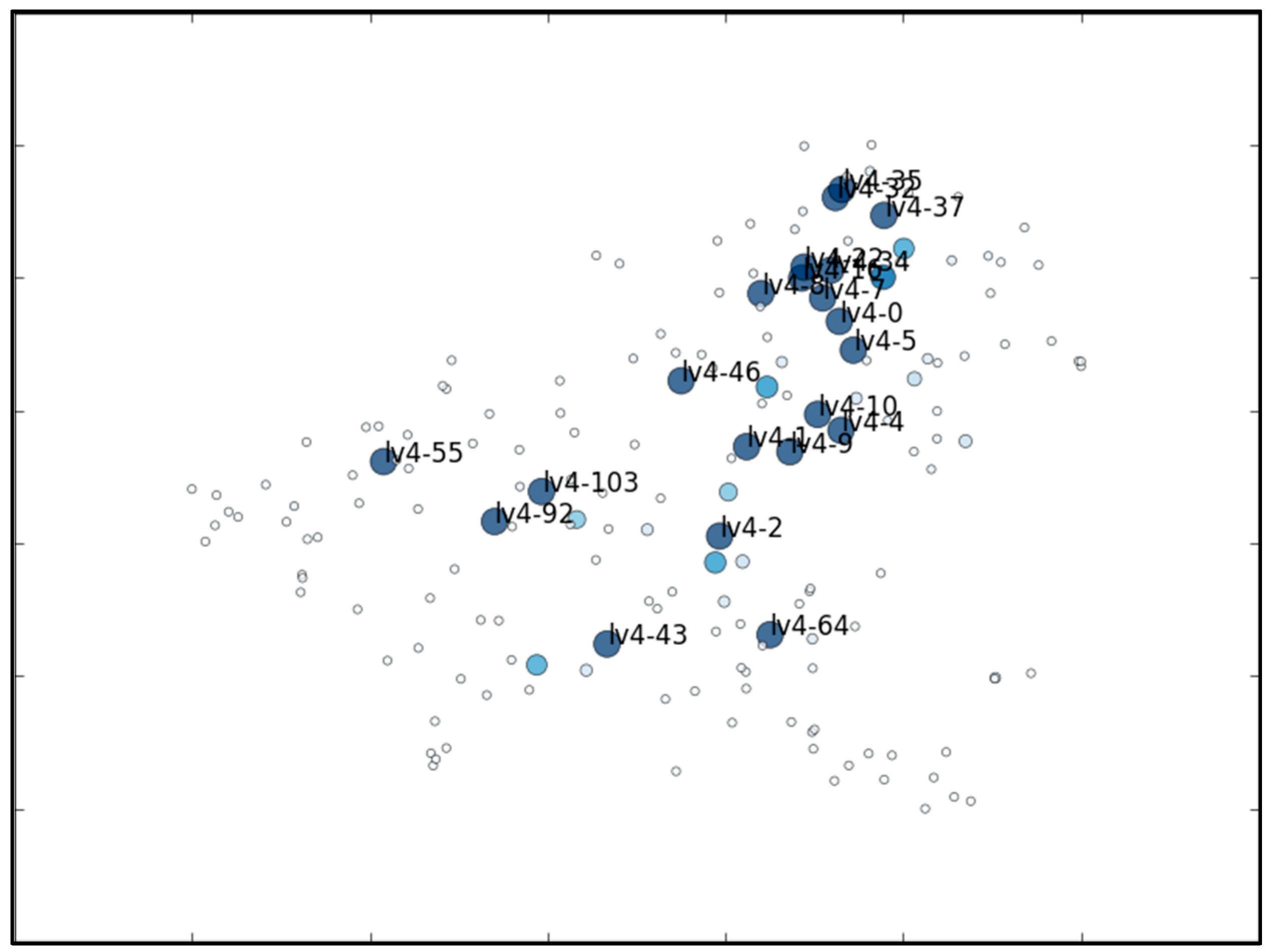
| Level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 8 (root) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance threshold | 1.4 | 1.54 | 1.70 | 1.86 | 2.05 | 2.25 | 2.48 |
| Number of nodes | 20,610 | 2928 | 521 | 205 | 83 | 19 | 1 |
| Level | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 (root) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance threshold | 5 k | 10 k | 20 k | 40 k | 80 k | 160 k | 320 k |
| Number of nodes | 196,591 | 4549 | 709 | 176 | 45 | 9 | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zelenyuk, A.; Imre, D.; Mueller, K. Big Data Management with Incremental K-Means Trees–GPU-Accelerated Construction and Visualization. Informatics 2017, 4, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics4030024
Wang J, Zelenyuk A, Imre D, Mueller K. Big Data Management with Incremental K-Means Trees–GPU-Accelerated Construction and Visualization. Informatics. 2017; 4(3):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics4030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jun, Alla Zelenyuk, Dan Imre, and Klaus Mueller. 2017. "Big Data Management with Incremental K-Means Trees–GPU-Accelerated Construction and Visualization" Informatics 4, no. 3: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics4030024
APA StyleWang, J., Zelenyuk, A., Imre, D., & Mueller, K. (2017). Big Data Management with Incremental K-Means Trees–GPU-Accelerated Construction and Visualization. Informatics, 4(3), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics4030024







