Automated Detection of Persuasive Content in Electronic News
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Models
3.1. Text Summarization
3.2. Classifier
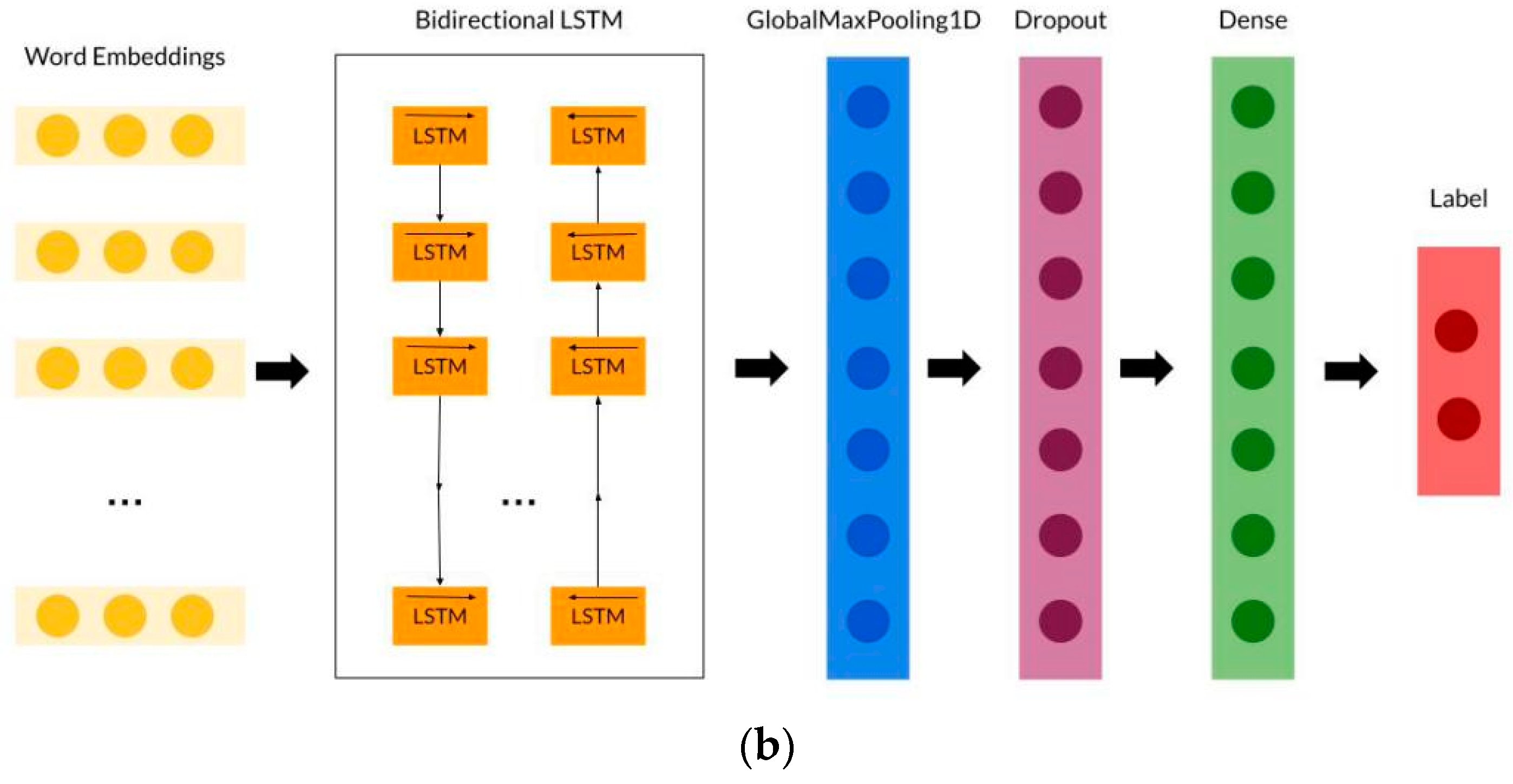
3.2.1. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM)
3.2.2. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
3.3. Proposed Method
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Compared Method
4.3. Experimental Setup
F1-Score = (2 (Recall × Precision))/(Recall + Precision) Accuracy = (TP + TN)/(TP + FP + FN + TN)
True Positive Rate (TPR) = TP/(TP + FN)
5. Results
5.1. Evaluation Metrics
5.2. Discussion
5.3. Theoretical and Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
7. Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molina, M.D.; Sundar, S.S.; Le, T.; Lee, D. “Fake News” Is Not Simply False Information: A Concept Explication and Taxonomy of Online Content. Am. Behav. Sci. 2019, 65, 180–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatandas, S. Gazete Haberlerinde Korku Sunumunun Göstergebilimsel Çözümlemesi (COVID-19 Örneğinde). Elektron. Sos. Bilim. Derg. 2021, 20, 1060–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, D.; Murray, N. When Being Positive Might Be Negative: An Analysis of Australian and New Zealand Newspaper Framing of Vaccination Post Australia’s No Jab No Pay Legislation. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5627–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanova, I.D.; Smirnova, I.V. Persuasive Techniques in Advertising. Train. Lang. Cult. 2019, 3, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Bidgoly, A.J.; Amirkhani, H. Fake News Detection on Social Media Using a Natural Language Inference Approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 33801–33821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawaid, J.; Awalina, A.; Krisnabayu, R.Y.; Yudistira, N. Indonesia’s Fake News Detection Using Transformer Network. In ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, J.A.; Khan, O.S.; Varlamis, I. Fake News Detection: A Hybrid CNN-RNN Based Deep Learning Approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2021, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, D.M.; Simons, G.F.; Fennig, C.D. What Are the Top 200 Most Spoken Languages? Ethnologue. 2020. Available online: https://www.ethnologue.com/guides/ethnologue200 (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Suryavanshi, A.; Gujare, B.; Mascarenhas, A.; Tekwani, B. Hindi Multi-Document Text Summarization Using Text Rank Algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2021, 174, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnoto, B.R.P.; Siahaan, D.; Purwitasari, D. Deep Learning for Native Advertisement Detection in Electronic News: A Comparative Study. In Proceedings of the 2022 11th Electrical Power, Electronics, Communications, Controls and Informatics Seminar (EECCIS), Malang, Indonesia, 23–25 August 2022; pp. 304–309. [Google Scholar]
- Quoc Tran, K.; Trong Nguyen, A.; Hoang, P.G.; Luu, C.D.; Do, T.H.; Van Nguyen, K. Vietnamese Hate and Offensive Detection Using PhoBERT-CNN and Social Media Streaming Data. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 573–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, K.M.; Sabbeh, S.F.; Medhat, W. Arabic Fake News Detection Using Deep Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 71, 3647–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, S.P.; Eswari, R. Attention-Based Deep Learning Models for Detection of Fake News in Social Networks. Int. J. Cogn. Inform. Nat. Intell. 2021, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.Z.; Habib, A.; Habib, A.; Khan, A.; Ali, R.; Khattak, A. Exploring Deep Neural Networks for Rumor Detection. J. Ambient. Intell Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 4315–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, M.; Mousavian, M.; Momtazi, S. Deep Contextualized Text Representation and Learning for Fake News Detection. Inf. Process Manag. 2021, 58, 102723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Yu, G. Automatic Keyphrase Extraction from Scientific Chinese Medical Abstracts Based on Character-Level Sequence Labeling. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2021, 6, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalcea, R.; Tarau, P. TextRank: Bringing Order into Texts. In Proceedings of the 2004 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2004—A Meeting of SIGDAT, a Special Interest Group of the ACL Held in Conjunction with ACL 2004, Catalunya, Spain, 25–26 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- To, H.Q.; Nguyen, K.V.; Nguyen, N.L.T.; Nguyen, A.G.T. Monolingual versus Multilingual BERTology for Vietnamese Extractive Multi-Document Summarization. In Proceedings of the 35th Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation, PACLIC 2021, Shanghai, China, 7–12 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Beskow, D.M.; Kumar, S.; Carley, K.M. The Evolution of Political Memes: Detecting and Characterizing Internet Memes with Multi-Modal Deep Learning. Inf. Process Manag. 2020, 57, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Gautam, D.; Mamidi, R. Volta at SemEval-2021 Task 6: Towards Detecting Persuasive Texts and Images Using Textual and Multimodal Ensemble. Available online: https://aclanthology.org/2021.semeval-1.149/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Luhn, H.P. The Automatic Creation of Literature Abstracts. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1958, 2, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmundson, H.P. New Methods in Automatic Extracting. J. ACM 1969, 16, 264–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, G.; Radev, D.R. LexRank: Graph-Based Lexical Centrality as Salience in Text Summarization. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2004, 22, 457–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, X. Generic Text Summarization Using Relevance Measure and Latent Semantic Analysis. In Proceedings of the SIGIR Forum (ACM Special Interest Group on Information Retrieval), Online, 11–15 July 2021; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanah, N.A.; Suciati, N.; Purwitasari, D. Identifying Degree-of-Concern on COVID-19 Topics with Text Classification of Twitters. Regist. J. Ilm. Teknol. Sist. Inf. 2021, 7, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, J. A Sentiment Analysis Method of Capsule Network Based on BiLSTM. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 37014–37020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, I.; Cotton, C. A Novel LSTM–CNN–Grid Search-Based Deep Neural Network for Sentiment Analysis. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 13911–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhanoui, M.; Mikram, M.; Yousfi, S.; Barzali, S. A CNN-BiLSTM Model for Document-Level Sentiment Analysis. Mach Learn. Knowl Extr. 2019, 1, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, N.; Ullah Khan, I.; Alotaibi, F.S.; Aldaej, L.A.; Aldubaikil, A.K. Fake Detect: A Deep Learning Ensemble Model for Fake News Detection. Complexity 2021, 2021, 5557784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaeed, E.; Ouda, O.; Elmogy, M.M.; Atwan, A.; El-Daydamony, E. Detecting Fake News in Social Media Using Voting Classifier. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 161909–161925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Deep Learning Based Text Classification Methods. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 34, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Asthana, R.; Upadhyay, S.; Upreti, N.; Akbar, M. Fake News Detection Using Deep Learning Models: A Novel Approach. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020, 31, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Pal, S.; Om, H. A Comparative Analysis on Hindi and English Extractive Text Summarization. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings Using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019—2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Hong Kong, China, 4 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dataset Persuasive News. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/Dataset_Persuasive_xlsx/23805354/1 (accessed on 30 July 2023).





| URL | Description | Category | Scraping Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kompas.com (2000 Article) | Indonesia’s leading online news platform that provides up-to-date and reliable information on various aspects of life, from political news, economics, to sports and entertainment | Politics, economics, business, technology, sports, entertainment, and lifestyle | August–September 2022 |
| Detik.com (2000 Article) | A news portal that presents a variety of the latest information from within and outside the country including political, economic, and entertainment news with a simple appearance | National, regional, business, technology, entertainment, sports, science, automotive, property, and travel | September–October 2022 |
| Tempo.co (2000 Article) | A news portal that presents various investigative reports, political, economic news, and a variety of other interesting content with a critical and in-depth approach | Politics, economics, business, law, technology, sports, entertainment, lifestyle, and travel | October–November 2022 |
| Cnnindonesia.com (2000 Article) | A news site that presents national and international news in a style that combines multimedia journalism, covering political, economic, to technological and lifestyle news | National, international, political, economic, technological, sports, entertainment, lifestyle, health, and science | November–December 2022 |
| Viva.co.id (2000 Article) | A news and entertainment platform that provides the latest and interesting news about politics, economy, and lifestyle with a fresh look and varied content | Politics, economy, business, technology, entertainment, sports, lifestyle, property, travel, and automotive | December 2022–January 2023 |
| Sindonews.com (2000 Article) | A news portal that provides a variety of up-to-date information, especially in terms of politics, economics, sports, and law, with an in-depth and factual approach. | National, political, legal, economic, sports, technology, entertainment, and lifestyle. | January–February 2023 |
| Category | Total Data | News Label | Persuasive Label | Average Sentences | Average Words |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education | 92 | 46 | 46 | 25 | 617 |
| Finance | 126 | 63 | 63 | 28 | 623 |
| Food | 145 | 72 | 73 | 24 | 683 |
| Health | 146 | 73 | 73 | 30 | 634 |
| Lifestyle | 150 | 75 | 75 | 25 | 617 |
| Megapolitan | 151 | 76 | 75 | 25 | 712 |
| National | 154 | 76 | 76 | 29 | 661 |
| Automotive | 161 | 80 | 81 | 24 | 701 |
| Regional | 164 | 82 | 82 | 25 | 636 |
| Sport | 165 | 83 | 82 | 20 | 607 |
| Technology | 166 | 83 | 83 | 24 | 617 |
| Travel | 72 | 36 | 36 | 27 | 684 |
| SME | 16 | 8 | 8 | 21 | 711 |
| Methods | Layers |
|---|---|
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional layer (units = 100), GlobalMaxPooling1D layer, dropout layer (rate = 0.2), dense layer (units = 2, activation = sigmoid) |
| CNN | Convo1D layer (filter = 32, kernel size = 3, activation = relu), GlobalMaxPooling1D, dropout layer (rate = 0.2), and dense layer (units = 2, activation = sigmoid) |
| Text Summarization | Word Embedding | Classifier | Accuracy | F1 Score | Precision | Recall | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | BERT | BiLSTM | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| LSA | BERT | BiLSTM | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| TextRank | BERT | BiLSTM | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| - | BERT | CNN | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| LSA | BERT | CNN | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| TextRank | BERT | CNN | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| - | roBERTa | BiLSTM | 0.85 | 0.846 | 0.856 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| LSA | roBERTa | BiLSTM | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| TextRank | roBERTa | BiLSTM | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| - | roBERTa | CNN | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.79 |
| LSA | roBERTa | CNN | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| TextRank | roBERTa | CNN | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | AUC Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BiLSTM–BERT–TextRank | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| BiLSTM–BERT | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| CNN–BERT–TextRank | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| CNN–BERT | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| BERT–BiLSTM FNID–FakeNewsNet dataset [5] | 0.90 |
| BERT–BiLSTM FNID-LIAR dataset [5] | 0.39 |
| BERT for Indonesia fake news [6] | 0.90 |
| Ensemble-based deep learning model [29] | 0.898 |
| BiLSTM for Arabic fake news [12] | 0.848 |
| BERT–BiLSTM for detection of native ads [10] | 0.95 |
| Ours (TextRank–BERT–BiLSTM) | 0.95 |
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BERT (transformer) | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.9 | 0.93 |
| BiLSTM–CNN–attention (attention) | 0.9 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.9 |
| BiLSTM–LSTM (ensemble model) | 0.57 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.45 |
| MLP (feed forward) | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| TextRank–BERT–BiLSTM (proposed method) | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darnoto, B.R.P.; Siahaan, D.; Purwitasari, D. Automated Detection of Persuasive Content in Electronic News. Informatics 2023, 10, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10040086
Darnoto BRP, Siahaan D, Purwitasari D. Automated Detection of Persuasive Content in Electronic News. Informatics. 2023; 10(4):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarnoto, Brian Rizqi Paradisiaca, Daniel Siahaan, and Diana Purwitasari. 2023. "Automated Detection of Persuasive Content in Electronic News" Informatics 10, no. 4: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10040086
APA StyleDarnoto, B. R. P., Siahaan, D., & Purwitasari, D. (2023). Automated Detection of Persuasive Content in Electronic News. Informatics, 10(4), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics10040086


_Bryant.png)



