A Study on Global Investors’ Criteria for Investment in the Local Currency Bond Markets Using AHP Methods: The Case of the Republic of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Decision Framework
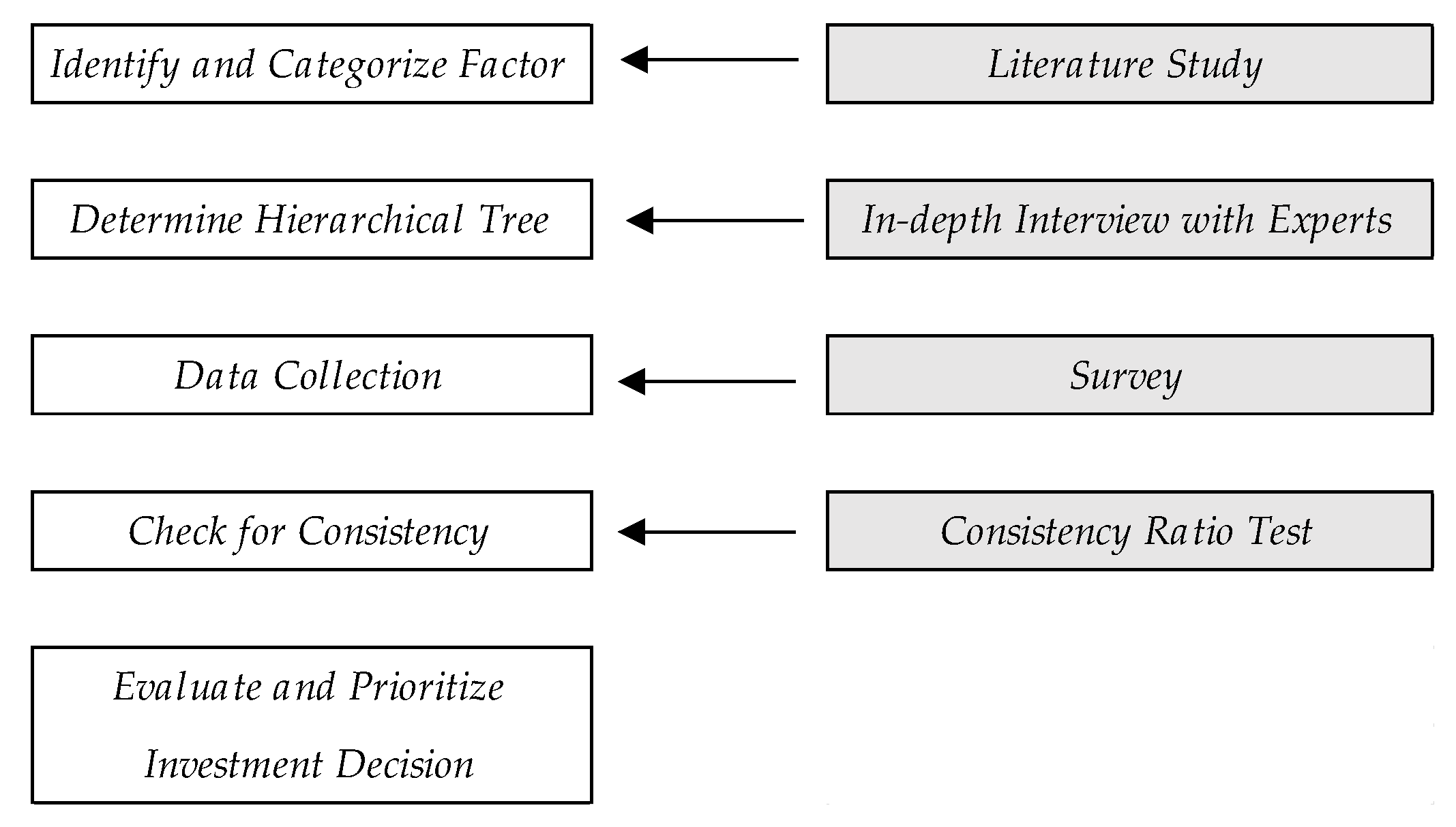
3.1.1. Application of the AHP Method
- Step 1:
- Identify the determinants of the investors’ investment decisions through literature research and point out limitations and problems of existing studies. This was completed in the literature review section of this paper.
- Step 2:
- By analyzing the results of the literature research and conducting expert interviews and brainstorming sessions, construct a hierarchical structure of decision-making factors.
- Step 3:
- Design the questionnaire for pairwise comparison, distribute it to experts, and gather results.
- Step 4:
- Check for consistency.
- Step 5:
- Evaluate it and prioritize the factors.
3.1.2. Derivation of Components
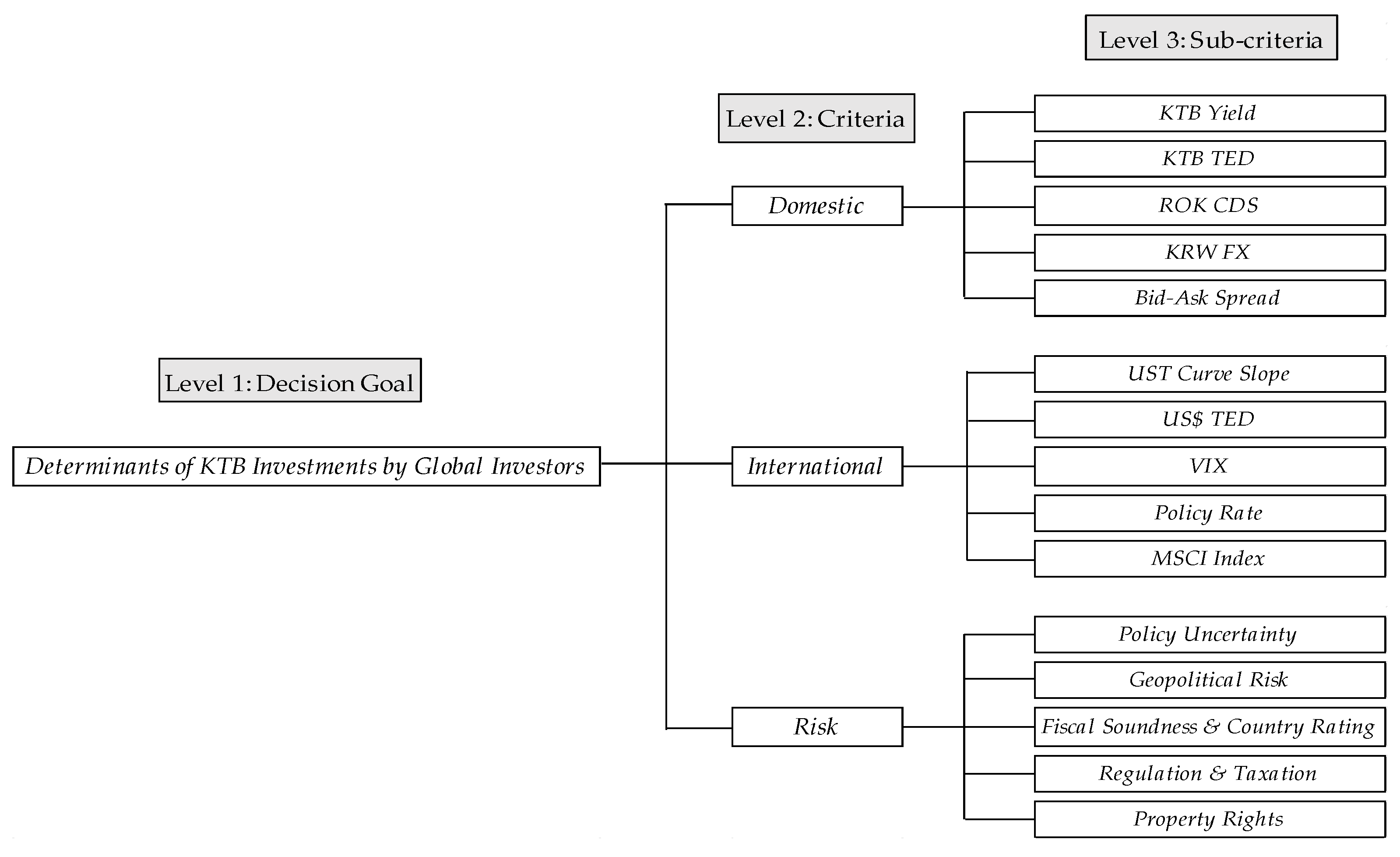
4. Composition of Hierarchical Structure
4.1. Developing the Assessment Criteria
4.2. Respondent Selection and Survey
- Working period: at least 15 years of investment experience
- Institution of employment: a variety in the types of institutions that the experts are employed at. At least one from each of the categories: investment banks, central bank, pension fund, insurances company, trust and asset management company, brokerage firm, government, and monetary authority.
- Location of the investment institution: a variety in the location of the institutions that the experts are employed at. At least, one from each of the categories: East Asian, South Asia, Europe, U.S., and Australia.
5. Empirical Results
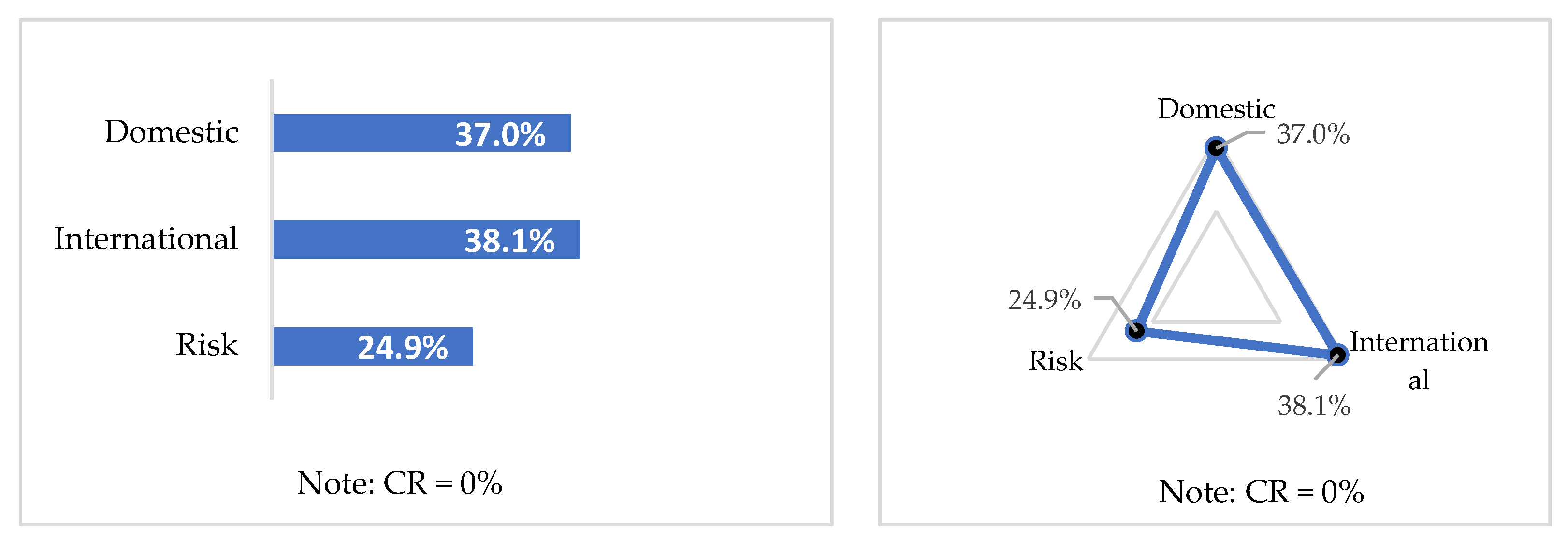
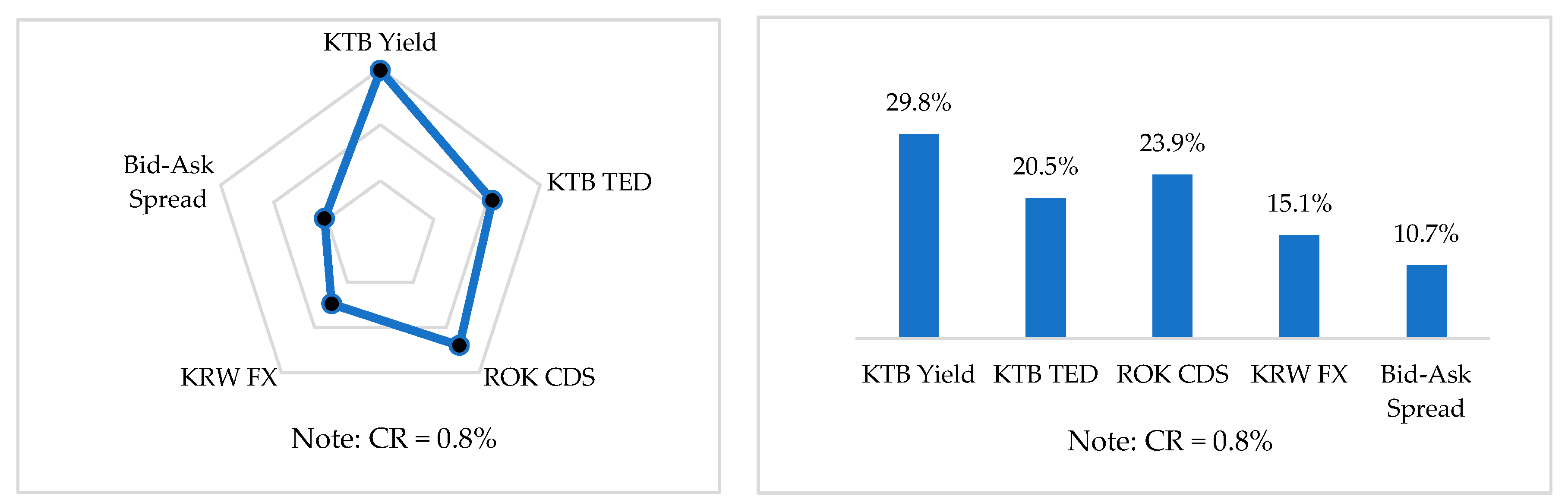
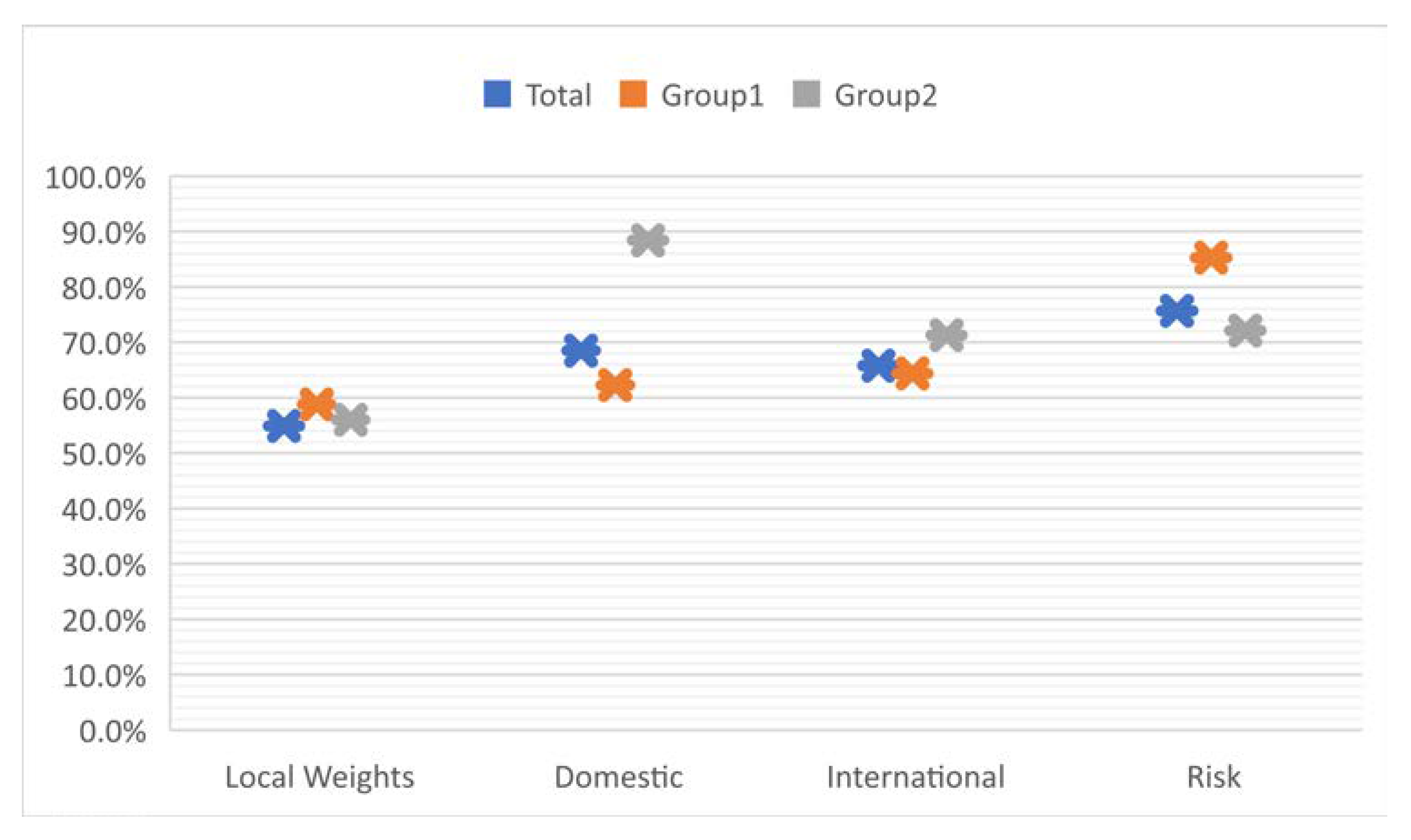
5.1. Weights of the Factors and Attributes
5.1.1. Local Weights for Level 2
5.1.2. Local Weights for Level 3
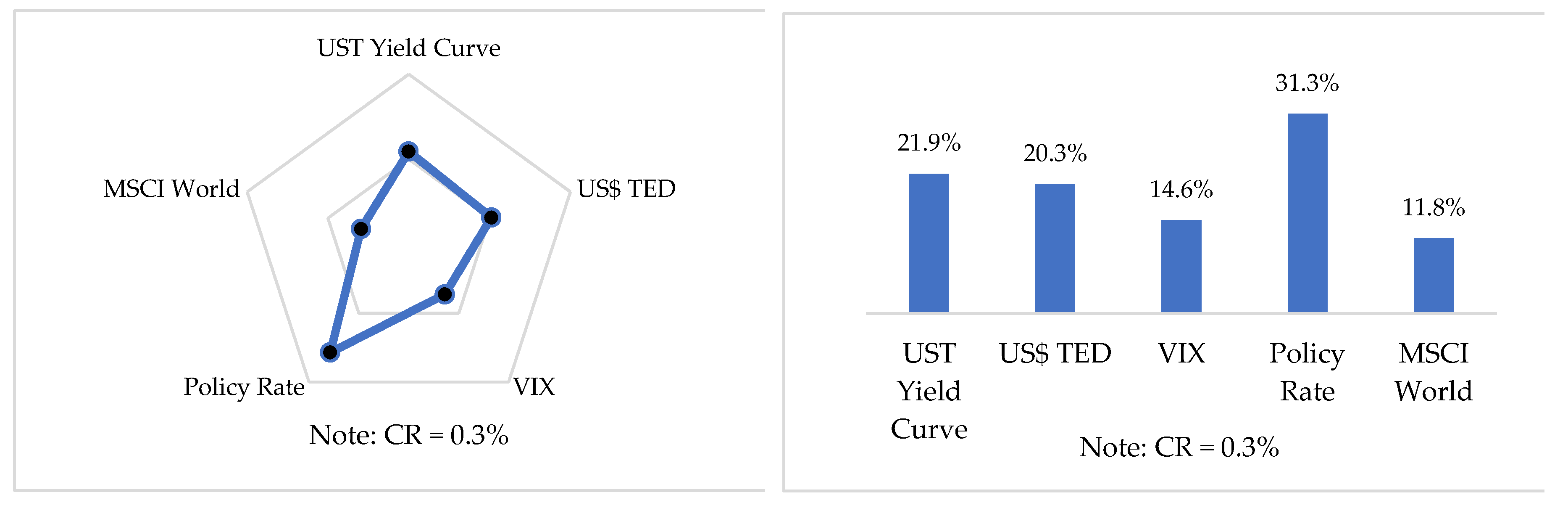
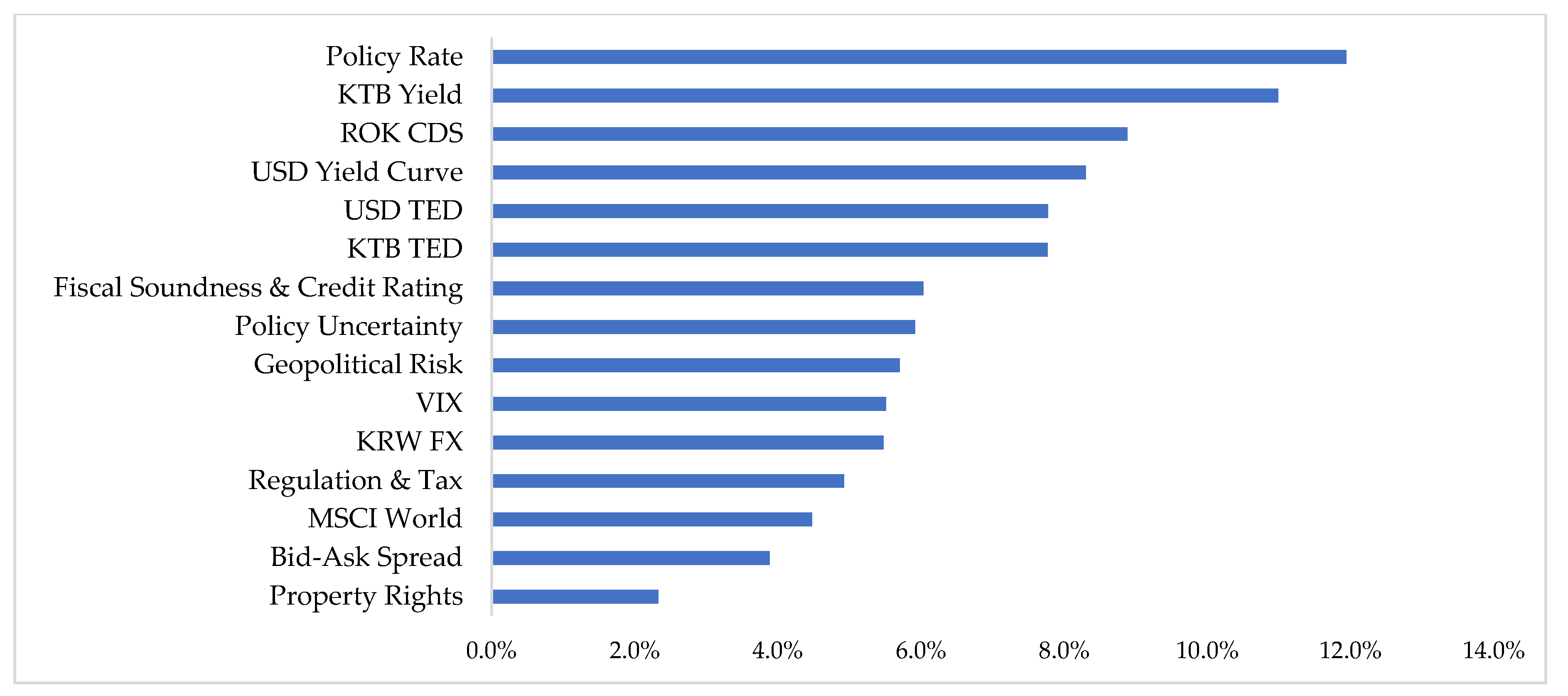
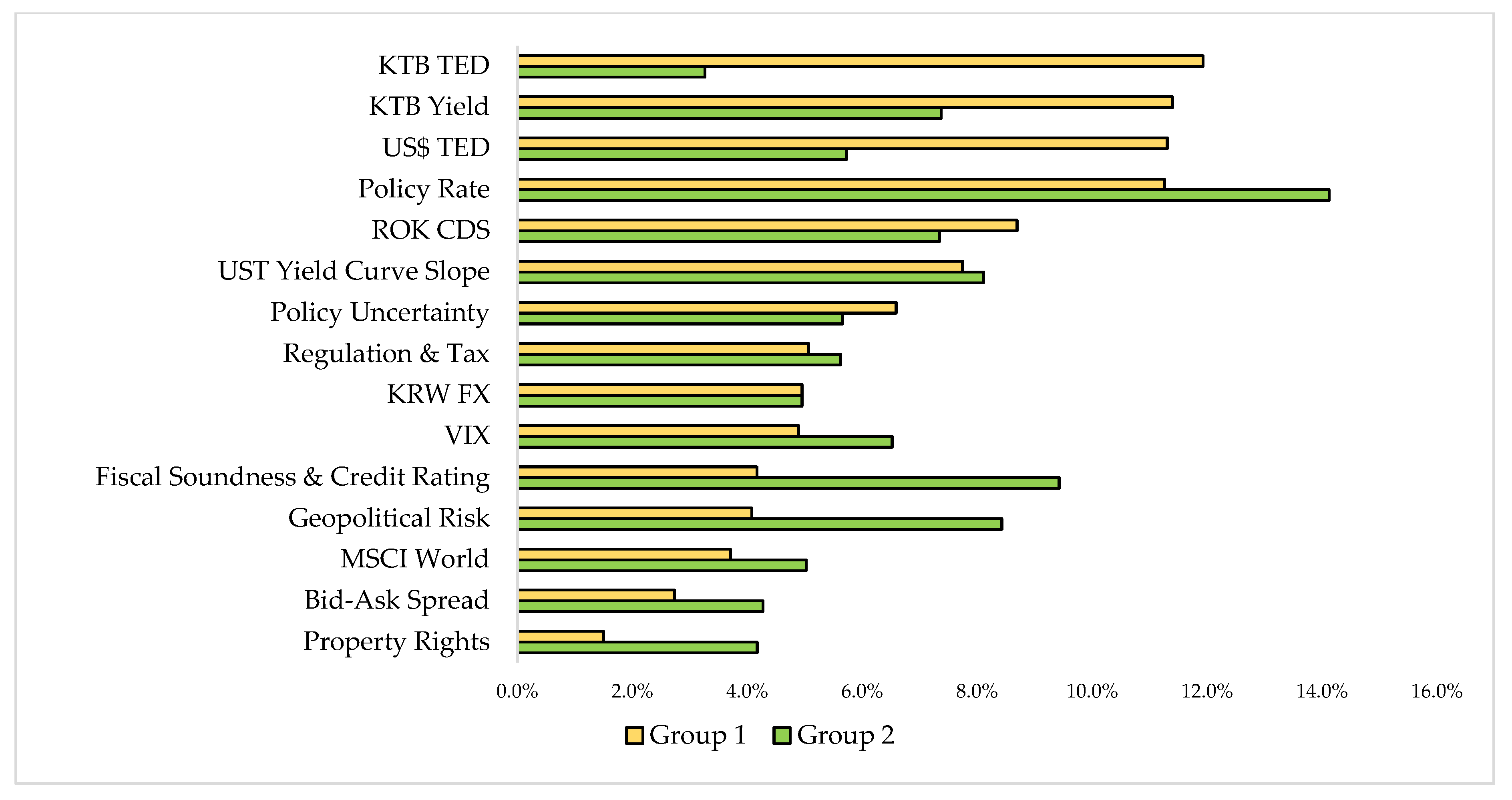
5.1.3. Global Weights for Level 3
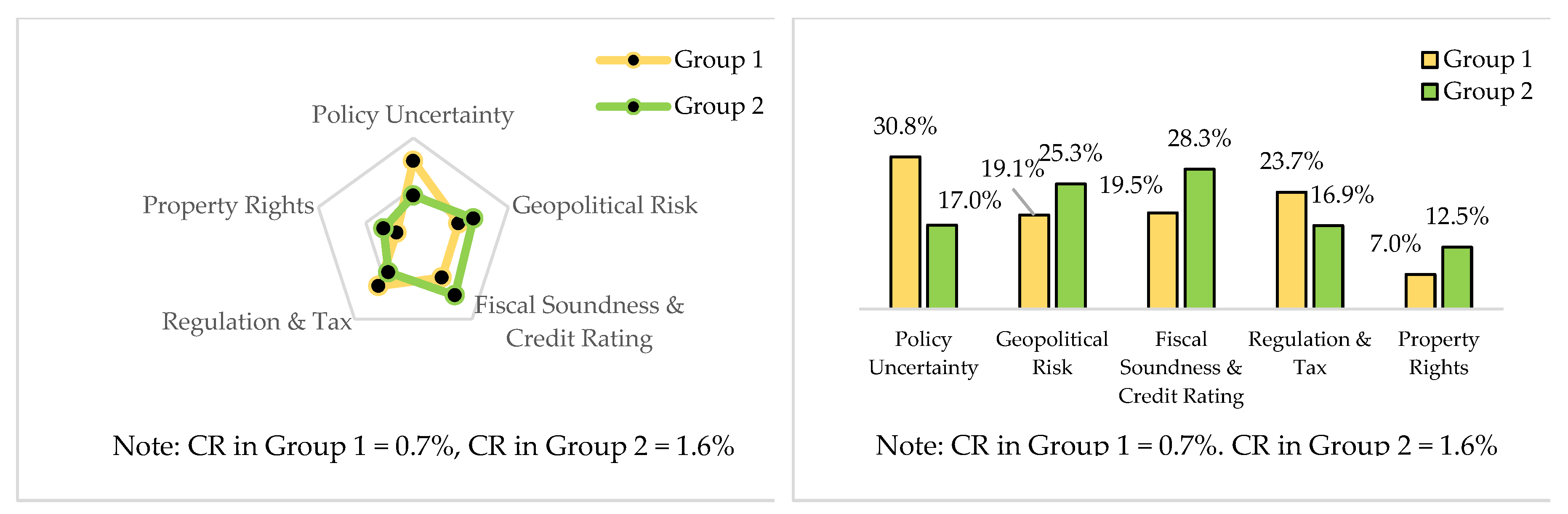
5.2. Weights of the Factors and Attributes Divided by Two Groups
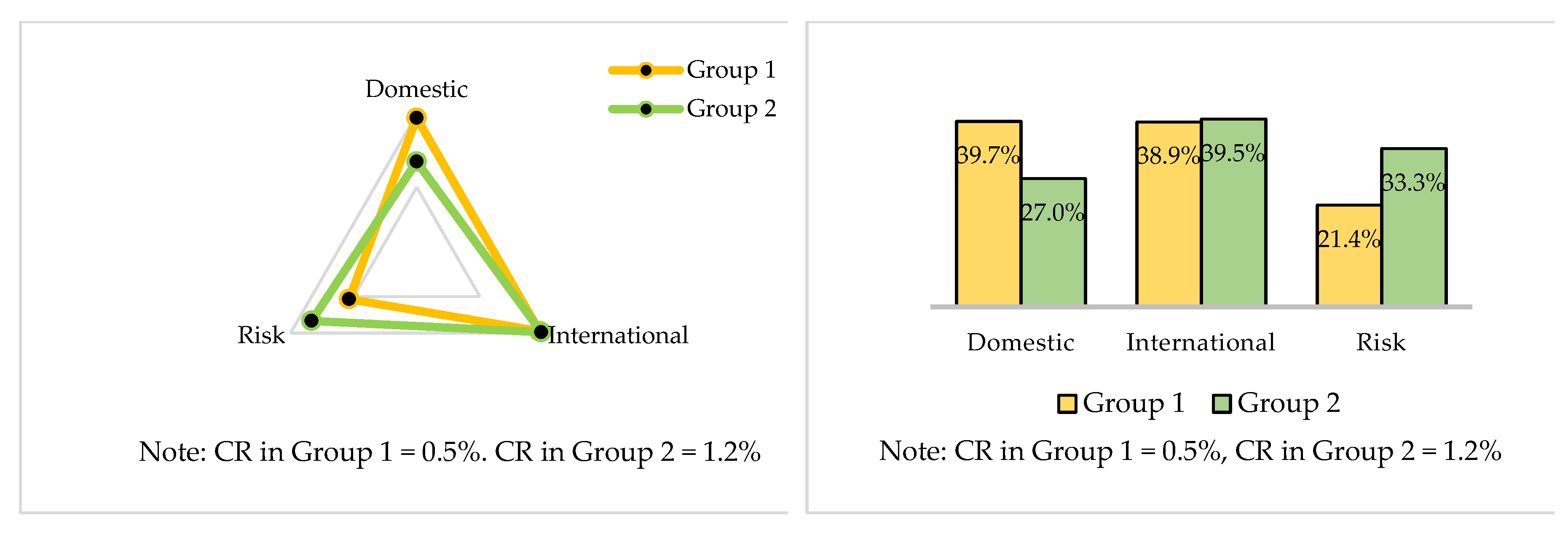
5.2.1. Local Weights for Level 2 between Group 1 and Group 2
5.2.2. Local Weights for Level 3 between Group 1 and Group 2
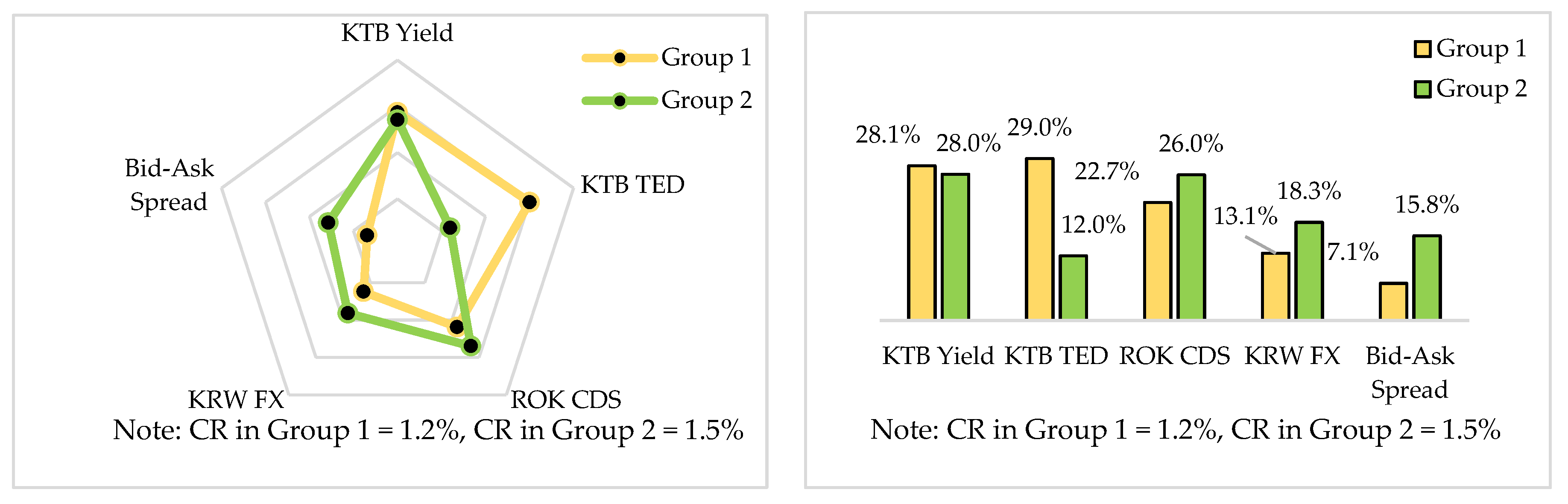
5.2.3. Global Weights for level 3 in Two Groups
5.3. Consensus Level
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, Hee-Joon, Seung-Pyo Jeon, and Jong-Bum Chay. 2010. The Effects of the News Related to the North-South Korean Relationship on the Korean Stock Markets. Journal of Korean Economic Analysis 16: 199–238. [Google Scholar]
- Aizenman, Joshua, and JaeWoo Lee. 2007. International Reserves: Precautionary versus Mercantilist Views, Theory and Evidence. Open Economies Review 18: 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, Esra, and Yasemin Claire Erensal. 2004. Using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to Improve Human Performance: An Application of Multiple Criteria Decision-Making Problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 15: 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, Kamal M. Al-Subhi. 2001. Application of the AHP in project management. International Journal of Project Management 19: 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, Andrew, and Monika Piazzesi. 2003. No-Arbitrage Vector Autoregression of Term Structure Dynamics with Macroeconomic and Latent Variables. Journal of Monetary Economics 50: 745–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakakis, Nikolaos, Ioannis Chatziantoniou, and George Filisb. 2013. Dynamic Co-Movements of Stock Market Returns, Implied Volatility and Policy Uncertainty. Economics Letters 120: 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armacost, Robert L., Paul J. Componation, Michael A. Mullens, and William W. Swart. 1994. An AHP Framework for Prioritizing Customer Requirements in QFD: An Industrialized Housing Application. IIE Transactions 26: 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian Development Bank. 2018. Asian Bond Monitor, November 2018. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/467066/abm-nov-2018.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2019).
- Asian Development Bank. 2019. Asian Bond Monitor, March 2019. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/491531/abm-mar-2019.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Baele, Lieven, Geert Bekaert, and Koen Inghelbrecht. 2010. The Determinants of Stock and Bond Return Comovements. The Review of Financial Studies 23: 2374–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, Nick, David Yamoah PotkinBasseer, and Farahmand Rezvani. 1987. Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process to Select Investment in a Heterogenous Environment. Mathematical Modelling 8: 157–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Basu, Susanto, and Brent Bundick. 2017. Uncertainty Shocks in a Model of Effective Demand. The Journal of The Econometrica Society 85: 937–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, Geert, Robert J. Hodrick, and Xiaoyan Zhang. 2009. International Stock Return Comovements. The Journal of Finance 64: 2591–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernanke, Ben, and Alan S. Blinder. 1992. The Federal Funds Rate and the Transmission of Monetary Policy. American Economic Review 82: 901–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bilson, Christopher M., Timothy J. Brailsford, and Vincent C. Hooper. 2002. The Explanatory Power of Political Risk in Emerging Markets. International Review of Financial Analysis 11: 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornland, Hilde C., and Kai Lietemo. 2009. Identifying the Interdependence between US Monetary Policy and the Stock Market. Journal of Monetary Economics 56: 275–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, Nicholas. 2014. Fluctuations in Uncertainty. Journal of Economic Perspectives 28: 153–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordo, Michael D. 2008. An Historical Perspective on the Crisis of 2007–2008 No. 14569. NBER Working Paper 14569: 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, John D., and Francis E. Warnock. 2007. Foreign Participation in Local Currency Bond Markets. Review of Financial Economics 16: 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, John Y. Campbell, Yeung Lewis Chanb, and Luis M. Viceira. 2013. Handbook of the Fundamentals of Financial Decision Making. World Scientific Handbook in Financial Economics Series; Singapore: World Scientific, pp. 809–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Ching-Fu. 2006. Applying the Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) Approach to Convention Site Selection. Journal of Travel Research 45: 167–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Michael Tow, and Ziqi Liao. 2009. Investing in Real-World Equity Markets with an AHP-based Decision Framework. Journal of Decision Systems 18: 149–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, Jens H. E., Eric Fischer, and Patrick Shultz. 2019. Bond Flows and Liquidity: Do Foreigners Matter? Working Paper 2019-08. San Francisco: Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, pp. 1–31.
- Christiano, Lawrence J., and Martin Eichenbaum. 1992. Liquidity Effects and the Monetary Transmission Mechanism. American Economic Review 82: 346–53. [Google Scholar]
- Christiano, Lawrence J., Martin Eichenbaum, and Charles L. Evans. 1996. The Effects of Monetary Policy Shocks: Evidence from the Flow of Funds. Review of Economics and Statistics 78: 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, Robert, Chris Stivers, and Licheng Sun. 2005. Stock Market Uncertainty and the Stock-Bond Return Relation. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 40: 161–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, Fabio, Antonella Petrillo, and Claudio Autorino. 2015. Development of a framework for sustainable outsourcing: Analytic Balanced Scorecard Method (A-BSC). Sustainability 7: 8399–8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diebolda, Francis X., Glenn D. Rudebusch, and S. Boragăn Aruoba. 2006. The Macroeconomy and the Yield Curve: A dynamic Latent Factor Approach. Journal of Econometrics 131: 309–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Wenxin, Alexander Tepper, and Adrien Verdelhan. 2018. Deviations from Covered Interest Rate Parity. The Journal of Finance 73: 915–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffie, Darrell. 1998. Defaultable Term Structure Models with Fractional Recovery of Par. Stanford: Graduate School of Business, Stanford University. [Google Scholar]
- Estrella, Arturo, and Frederic S. Mishkin. 1995. The Term Structure of Interest Rates and Its Role in Monetary Policy for The European Central Bank. European Economic Review 41: 1375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goepel, Klaus D. 2013. Implementing the Analytic Hierarchy Process as a Standard Method for Multi-Criteria Decision Making in Corporate Enterprises—A New AHP Excel Template with Multiple Inputs. Paper presented at International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, June 23–26; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, David B., and Eric M. Leeper. 1994. The Dynamic Impacts of Monetary Policy: An Exercise in Tentative Identification. Journal of Political Economy 102: 1228–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group of Thirty. 2013. Long-Term Finance and Economic Growth. Washington: Working Group on Long-Term Finance. [Google Scholar]
- Gyntelberg, Jacob, Mico Loretan, Tientip Subhanij, and Eric Chan. 2014. Exchange Rate Fluctuations and International Portfolio Rebalancing. Emerging Markets Review 18: 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, James D. 2003. What is an Oil Shock? Journal of Econometrics 13: 363–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, Anthony F., and Craig W. Slinkman. 1984. Political-Economic Cycles in the U.S. Stock Market. Financial Analysts Journal 40: 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Daniel, Graeme Newell, and Anthony Walker. 2005. The Importance of Property-specific Attributes in Assessing CBD Office Building Quality. Journal of Property Investment and Finance 23: 424–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Chung Hyo. 2011. An Empirical Study on Price Discovery among CDS Spread, Won/Dollar Spot and Futures Markets. Korean Journal of Financial Engineering 10: 103–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houweling, Patrick, and Ton Vorst. 2005. Pricing Default Swaps: Empirical Evidence. Journal of International Money and Finance 24: 1200–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Rong-Yau, and Cheng-Hung Yeh. 2011. Development of an Assessment Framework for Green Highway Construction. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers 31: 573–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, John, Mirela Predescu, and Alan White. 2004. The Relationship between Credit Default Swap Spreads, Bond Yields, and Credit Rating Announcements. Journal of Banking & Finance 28: 2789–811. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Jae Young, and Erdal Atukeren. 2019. Sustainable Local Currency Debt: An Analysis of Foreigners’ Korea Treasury Bonds Investments Using a LA-VARX Model. Sustainability 11: 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, Lou. 2006. Entropy and Diversity. OIKOS 113: 363–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaller, Ira G. 1997. The TED Spread. Derivatives Quarterly 3: 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kil, Sung-Ho, Dong Kun Lee, Jun-Hyun Kim, Ming-Han Li, and Galen Newman. 2016. Utilizing the Analytic Hierarchy Process to Establish Weighted Values for Evaluating the Stability of Slope Revegetation based on Hydroseeding Applications in South Korea. Sustainability 8: 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Chi-Wook. 2011. Inter-Korean Relations and Korea Discount: An Analysis of Foreign Investors Stock Trading. Journal of Peace and Unification Studies 3: 219–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Do Yeon. 2012. Effects of Foreign Exchange Risk on International Portfolio Investment in Northeast Asian Countries and Korea. The Journal of Northeast Asian Economic Studies 24: 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Dong Soon, and Yu Jin Jung. 2015. The Effect of the Global Financial and Eurozone Debt Crises on European and Emerging Market Countries’ Sovereign Bond Markets and Foreign Investment in the Korean Government Bonds. Korean Academy of International Business 26: 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Hong Bae, Myoung Jong Kim, and Sung Jae Rowe. 2013. Price Discovery and Volatility Transmission between Korean Sovereign CDS and ROK Bond Markets. The Korean Journal of Financial Engineering 12: 51–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kontonikas, Alexandros, and Zivile Zekaite. 2018. Monetary Policy and Stock Valuation: Structural VAR Identification and Size Effects. Quantitative Finance 18: 837–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, Robert, Subrata Sarker, and Garima Vasishtha. 2014. Spillover Effects of Quantitative Easing on Emerging-Market Economies. Bank of Canada Review (Autumn) 2014: 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Quan Vu, and Paul J. Zak. 2006. Political Risk and Capital Flight. Journal of International Money and Finance 25: 308–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, KeunYeoung. 2002. The Correlation Analysis of Volatility on Stock, Bond and Money Market. Kukje Kyungje Yongu 8: 191–212. [Google Scholar]
- Leeper, Eric M., and David B. Gordon. 1992. In Search of the Liquidity Effect. Journal of Monetary Economics 29: 341–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Ziqi, and Michael Tow Cheung. 2012. A Multi-dimensional Decision Framework to Support Corporate Bond Investment. Journal of Decision System 21: 161–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, Wan Mansor, and Nazihah Mohd Dinniah. 2009. Stock Returns and Macroeconomics Variables: Evidence from the Six Asian-Pacific Countries. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics 30: 154–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mawapanga, Mwana N., and David L. Debertin. 1996. Choosing between Alternative Farming Systems: An Application of the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Review of Agricultural Economies 18: 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, C. Duncan. 1977. A Political Model of the Business Cycle. Journal of Political Economy 85: 239–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Economy and Finance. 2019. 2018 Korea Treasury Bonds. Available online: http://ktb.moef.go.kr/eng/main.do (accessed on 2 June 2019).
- Miron, Paul, and Philip Swannell. 1991. Pricing and Hedging Swaps. London: Euromoney Publications PLC. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, Kyun Chun. 2007. Volatility and Correlation in International Stock Markets and the Role of Exchange Rate Fluctuations. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money 17: 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordhaus, William D. 1975. The Political Business Cycle. Review of Economic Studies 42: 169–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Jae Hwan, and Chun Kyu Kim. 2013. The Effect of Policy Rate Adjustments in US on the Korean Bond. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association 13: 344–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, Lubos, and Pietro Veronesi. 2012. Uncertainty about Government Policy and Stock Prices. The Journal of Finance 67: 1219–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, Shanaka J. 2010. Foreign Participation in Emerging Markets’ Local Currency Bond Markets. IMF Working Paper, WP/10/88. Washington: International Monetary Fund, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, David L., David G. Silsbee, and Daniel L. Schmoldt. 1995. A Case Study of Resources Management Planning with Multiple Objectives and Projects. Environmental Management 18: 729–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, Helen. 1993. Long-term Covered Interest Parity: Evidence from Currency Swaps. Journal of International Money and Finance 12: 439–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, Thomas L., Paul C. Rogers, and Ricardo Pell. 1980. Portfolio Selection through Hierarchies. Journal of Portfolio Management 6: 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A. C. 2006. Multinational Financial Management, 5th ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Jae Ho, Yoon Seob Nam, and Hwa Soon Lim. 2013. A study for JeJu-Tourism Policy Importance with use AHP. TamLa MunHwa 43: 321–42. [Google Scholar]
- Steiguer, Joseph E., Jennifer Duberstein, and Vicente Lopes. 2003. The Analytic Hierarchy Process as a Means for Integrated Watershed Management. Paper presented at Conference on Research on the Watersheds, Benson, AZ, USA, October 27–30; pp. 736–40. [Google Scholar]
- Strongin, Steven. 1995. The Identification of Monetary Policy Disturbances Explaining the Liquidity Puzzle. Journal of Monetary Economics 35: 463–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, Nobuya. 1995. Currency Swaps and Long-term Covered Interest Parity. Economics Letters 49: 181–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantaphyllou, Evangelos. 2000. Multi-criteria Decision-Making Methods. A Comparative Study. Applied Optimization Book Series 44: 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, Jonathan H., and Hao Zhou. 2009. Bond Risk Premia and Realized Jump Risk. Journal of Banking & Finance 33: 2333–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Yue-Jun, and Yi-Ming Wei. 2010. The Crude Oil Market and the Gold Market: Evidence for Cointegration, Causality and Price Discovery. Resources Policy 35: 168–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

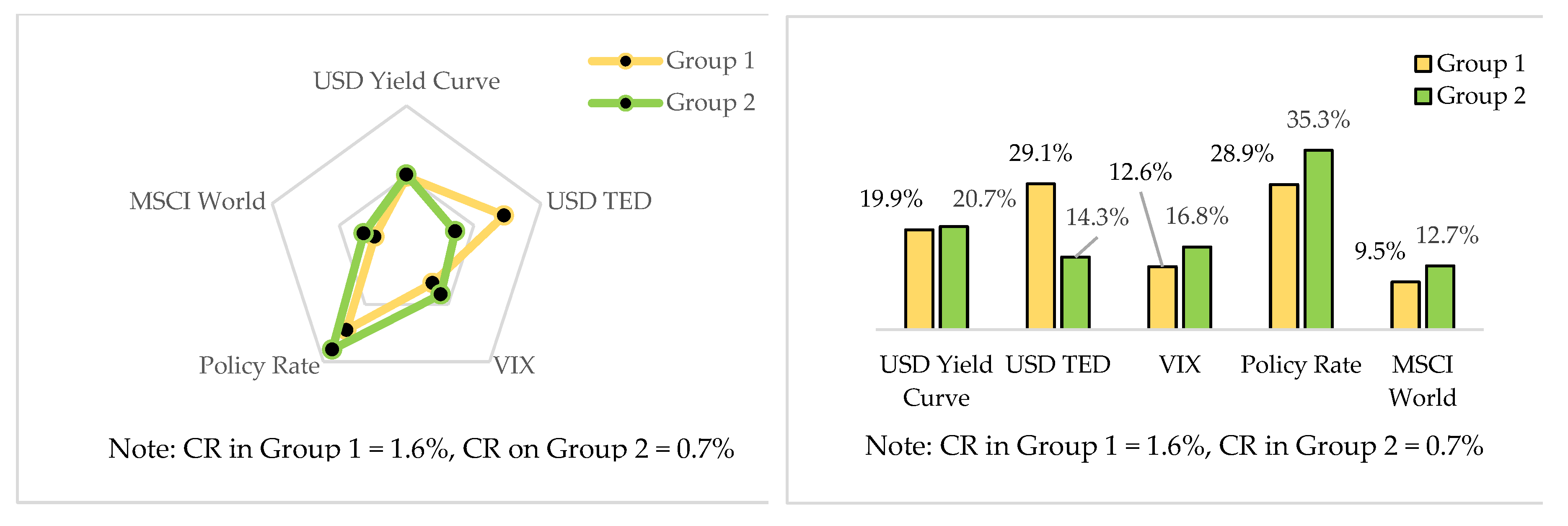
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total * | 57.5 | 74.2 | 83.0 | 91.0 | 94.7 | 100.4 | 101.4 | 89.3 | 98.5 | 113.8 |
| (% **) | 5.6 | 6.6 | 6.9 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 6.6 |
| KTBs * | 28.7 | 47.7 | 60.9 | 56.9 | 58.3 | 65.9 | 67.9 | 72.5 | 77.8 | 86.3 |
| (% **) | 9.8 | 15.4 | 17.9 | 15.7 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 13.8 | 14.0 | 14.2 | 15.2 |
| MSBs * | 28.1 | 25.4 | 20 | 31.6 | 34.4 | 33.2 | 32.7 | 15.5 | 19.5 | 26.2 |
| (% **) | 18.3 | 15.5 | 11.9 | 19.4 | 20.8 | 18.7 | 17.9 | 9.2 | 11.4 | 1.3 |
| Factor | Sub-Factor |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Policy Rate, Short term Interest Rate (KRW Call and US$ LIBOR), KTB (or MSB) Yields, U.S. Treasury Yields, Turnover Ratio, Bid-Ask Spread, EMBI (Emerging Market Bond Index) |
| Spread and Curve | KTB (or MSB) TED CCIRS Spread, Basis Swap, US$ TED, Yield Curve Scope |
| FX | FX Spot (and Dollar Index), FX Swap, FX Volatility |
| Stock | KOSPI, Dow, S&P 200, MSCI G7, MSCI World, VIX |
| CDS | ROKCDS, CDX, PIIGS CDS |
| Oil | Crude Oil |
| Macroeconomic Indicators | CPI, M2, GDP, Current Account, CLI |
| Others | Credit Rating, Sovereign Debt, Fiscal Deficit, Foreign Reserve, Property Rights, Settlement System, Market Transparency, Political Events, Geopolitical Risk, Policy Uncertainty, Regulation, Taxation |
| Criteria | Sub-Criteria | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic Factors | KTBs Yield | The KTB Yield is the benchmark return on the Korean LCY bond market. |
| KTB TED CCIRS Spread | The KTB TED spread is the interest rate difference between the KTB and the KRW/US$ cross currency interest rate swap, which is the KTB risk-free arbitrage spread, excluding sovereign default risks. | |
| ROK CDS | The ROK CDS is the Republic of Korea’ Credit Default Swap that can transfer Korea’s sovereign risk exposure to others. | |
| KRW FX | The KRW FX is KRW against US$ FX rate. | |
| Bid–Ask Spread | The bid-ask spread is market liquidity in the price dimension. | |
| International Factors | UST Yield Curve Slope | The UST yield curve slope is the rate difference between long-term and short-term bonds, and an inverted yield curve is often considered a bad sign for the economy. |
| US$ TED | The US$ TED is the rate difference between the three-month Treasury bill and the three-month US$ LIBOR. The TED spread is used as an indicator of credit risk. | |
| VIX | The CBOE variability index, VIX, is commonly referred to as the fear index. | |
| Policy Rate | The policy rate is the rate determined by monetary authorities such as the central bank. | |
| MSCI World | The MSCI World is a market cap weighted stock market index of 1,636 stocks from companies throughout the world and is intended to represent a broad cross-section of the global markets. | |
| Risk Factors | Policy Uncertainty | Policy uncertainty is one of the risk factors for an economy that can delay spending and investment decisions by businesses and individuals. |
| Geopolitical Risk | Geopolitical risks can affect or upset the domestic political and social policies of other countries, including military conflicts, civil wars, terrorist attacks, riots, sanctions, etc. | |
| Fiscal Soundness and Sovereign Rating | Fiscal soundness consists of debt, spending and tax revenues, and worsening fiscal soundness could lead to a sovereign debt crisis. The sovereign rating is an independent assessment of a country’s creditworthiness and an implicit prediction of sovereign debt repayment ability and possible default. | |
| Regulations and Taxes | Regulations are rules created to control what the government or other agencies do or what people do. Taxes are compulsory financial charges of levy imposed upon taxpayers by governmental organizations in order to fund various public expenditures. | |
| Property Rights | Property rights are the legal rights that entities have on a property and have four components: the right to use the good, to earn an income from it, to transfer it to others, and the right to enforce property rights. |
| Investment Institution | Frequency | % | Region | Frequency | % | Working Period | Frequency | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment Bank | 6 | 30 | East Asia | 5 | 25 | 10–19 years | 3 | 15 |
| Asset Management and Trust | 3 | 15 | South Asia | 5 | 25 | 20–29 years | 5 | 25 |
| Central Bank | 4 | 20 | Australia | 2 | 10 | Over 30 years | 12 | 60 |
| Pension Fund | 2 | 10 | Europe | 5 | 25 | - | - | - |
| Insurance Company | 3 | 15 | U.S. | 3 | 15 | - | - | - |
| Monetary Authority and Gov’t | 2 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 | Total | 20 | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.Y.; Park, M.J. A Study on Global Investors’ Criteria for Investment in the Local Currency Bond Markets Using AHP Methods: The Case of the Republic of Korea. Risks 2019, 7, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7040101
Jang JY, Park MJ. A Study on Global Investors’ Criteria for Investment in the Local Currency Bond Markets Using AHP Methods: The Case of the Republic of Korea. Risks. 2019; 7(4):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7040101
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Jae Young, and Min Jae Park. 2019. "A Study on Global Investors’ Criteria for Investment in the Local Currency Bond Markets Using AHP Methods: The Case of the Republic of Korea" Risks 7, no. 4: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7040101
APA StyleJang, J. Y., & Park, M. J. (2019). A Study on Global Investors’ Criteria for Investment in the Local Currency Bond Markets Using AHP Methods: The Case of the Republic of Korea. Risks, 7(4), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks7040101





