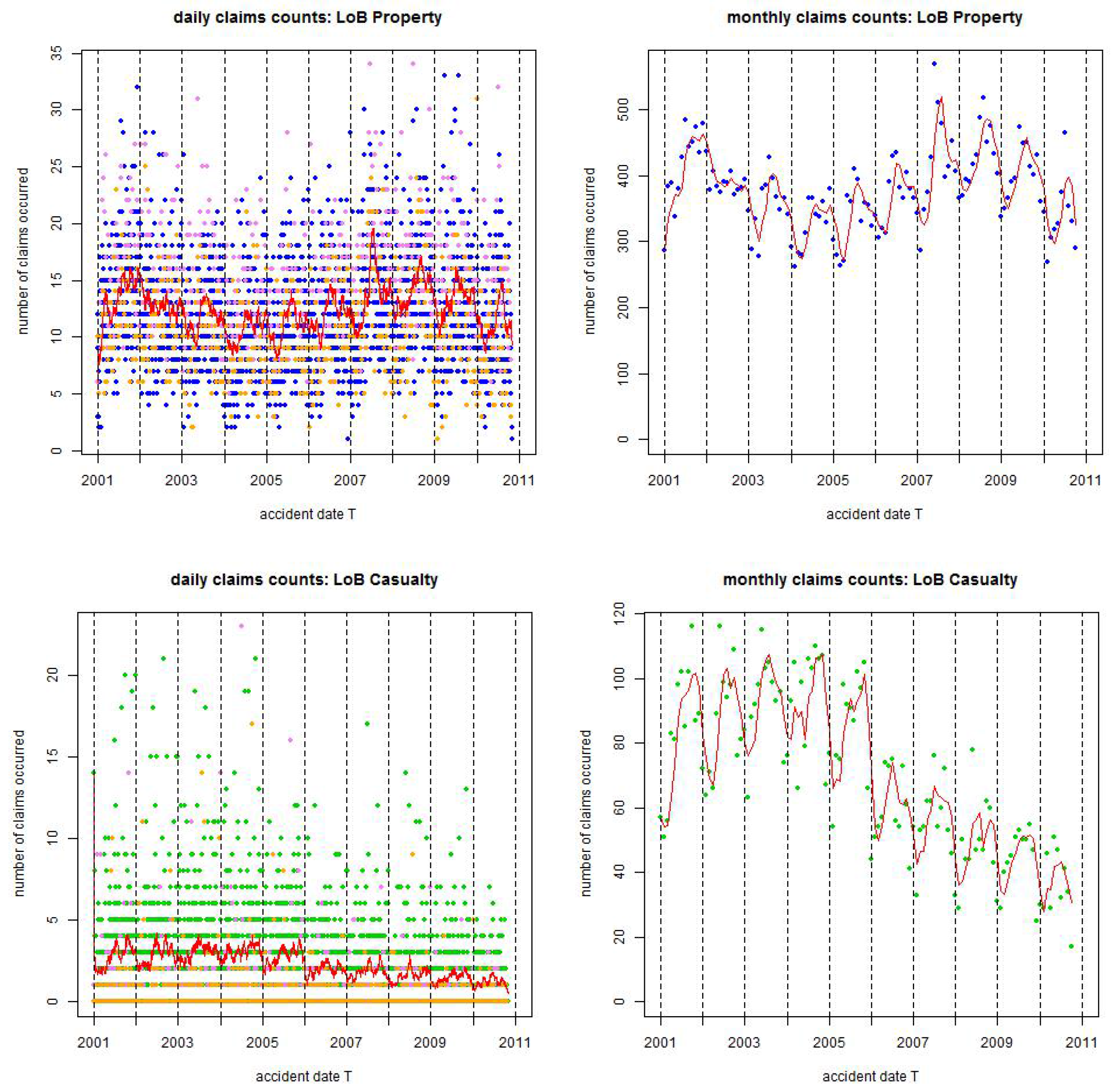
Figure 1.
Observed claims counts from 1/1/2001 until 31/10/2010: (top) LoB Property colored blue and (bottom) LoB Casualty colored green. The lhs gives daily claims counts and the rhs monthly claims counts; the red lines are the rolling averages over 30 days on the lhs and over 2 months on the rhs; violet dots show claims occurrence on Saturdays and orange dots claims occurrence on Sundays, the resulting statistics are provided in
Table 1.
Figure 1.
Observed claims counts from 1/1/2001 until 31/10/2010: (top) LoB Property colored blue and (bottom) LoB Casualty colored green. The lhs gives daily claims counts and the rhs monthly claims counts; the red lines are the rolling averages over 30 days on the lhs and over 2 months on the rhs; violet dots show claims occurrence on Saturdays and orange dots claims occurrence on Sundays, the resulting statistics are provided in
Table 1.
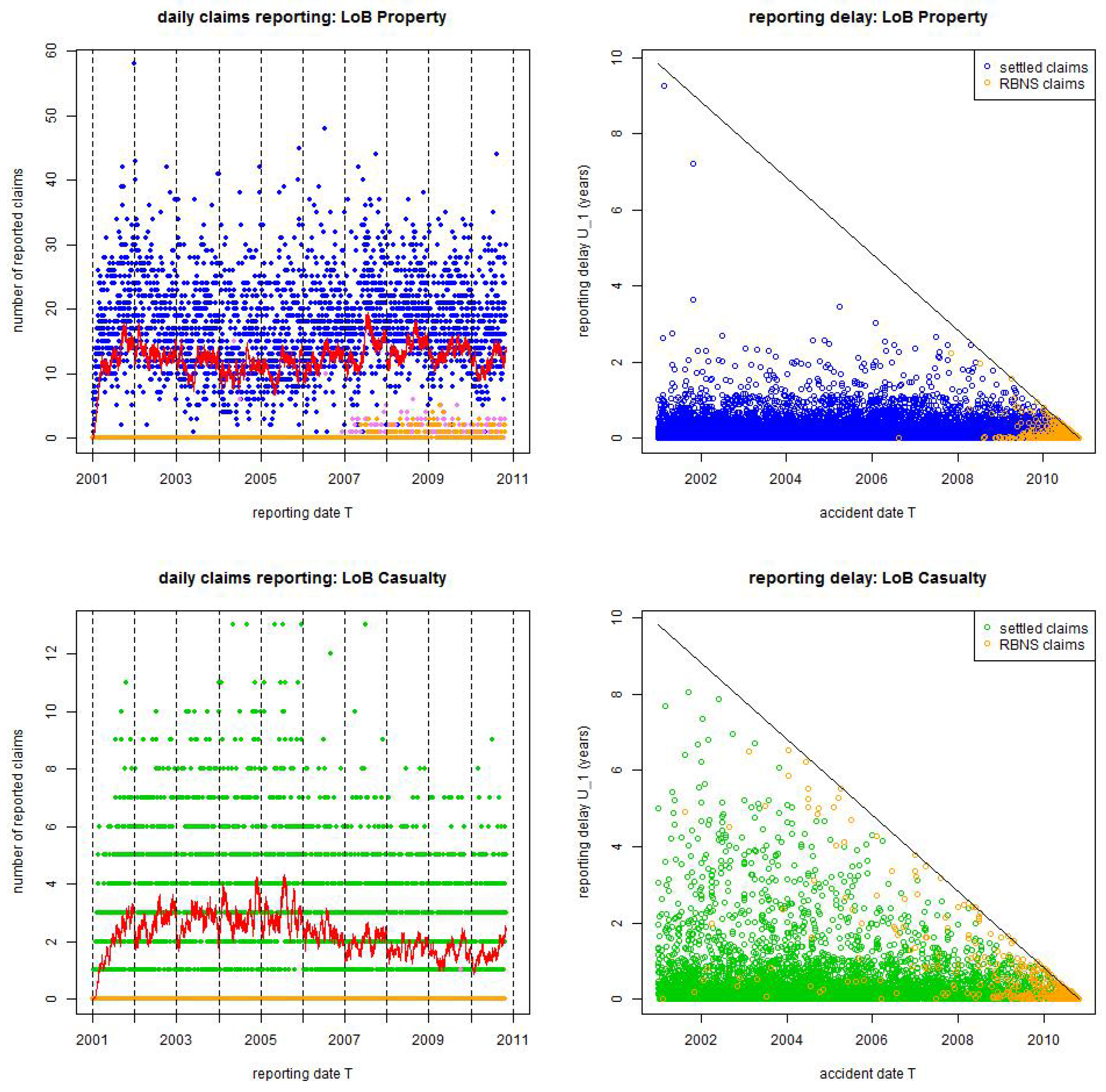
Figure 2.
Observed and reported claims counts from 1/1/2001 until 31/10/2010: (top) LoB Property colored blue and (bottom) LoB Casualty colored green. The lhs gives daily claims reporting; the red lines are the 30 days rolling averages; violet dots show claims reporting on Saturdays and orange dots claims reporting on Sundays. The rhs plots accident dates versus reporting delays ; the upper-right (white) triangle corresponds to the missing data (IBNYR claims); the blue/green dots illustrate reported and settled claims; the orange dots reported but not settled (RBNS) claims.
Figure 2.
Observed and reported claims counts from 1/1/2001 until 31/10/2010: (top) LoB Property colored blue and (bottom) LoB Casualty colored green. The lhs gives daily claims reporting; the red lines are the 30 days rolling averages; violet dots show claims reporting on Saturdays and orange dots claims reporting on Sundays. The rhs plots accident dates versus reporting delays ; the upper-right (white) triangle corresponds to the missing data (IBNYR claims); the blue/green dots illustrate reported and settled claims; the orange dots reported but not settled (RBNS) claims.
Figure 3.
Box plots of the logged reporting delays on the yearly scale (lhs) LoB Property, (rhs) LoB Casualty.
Figure 3.
Box plots of the logged reporting delays on the yearly scale (lhs) LoB Property, (rhs) LoB Casualty.
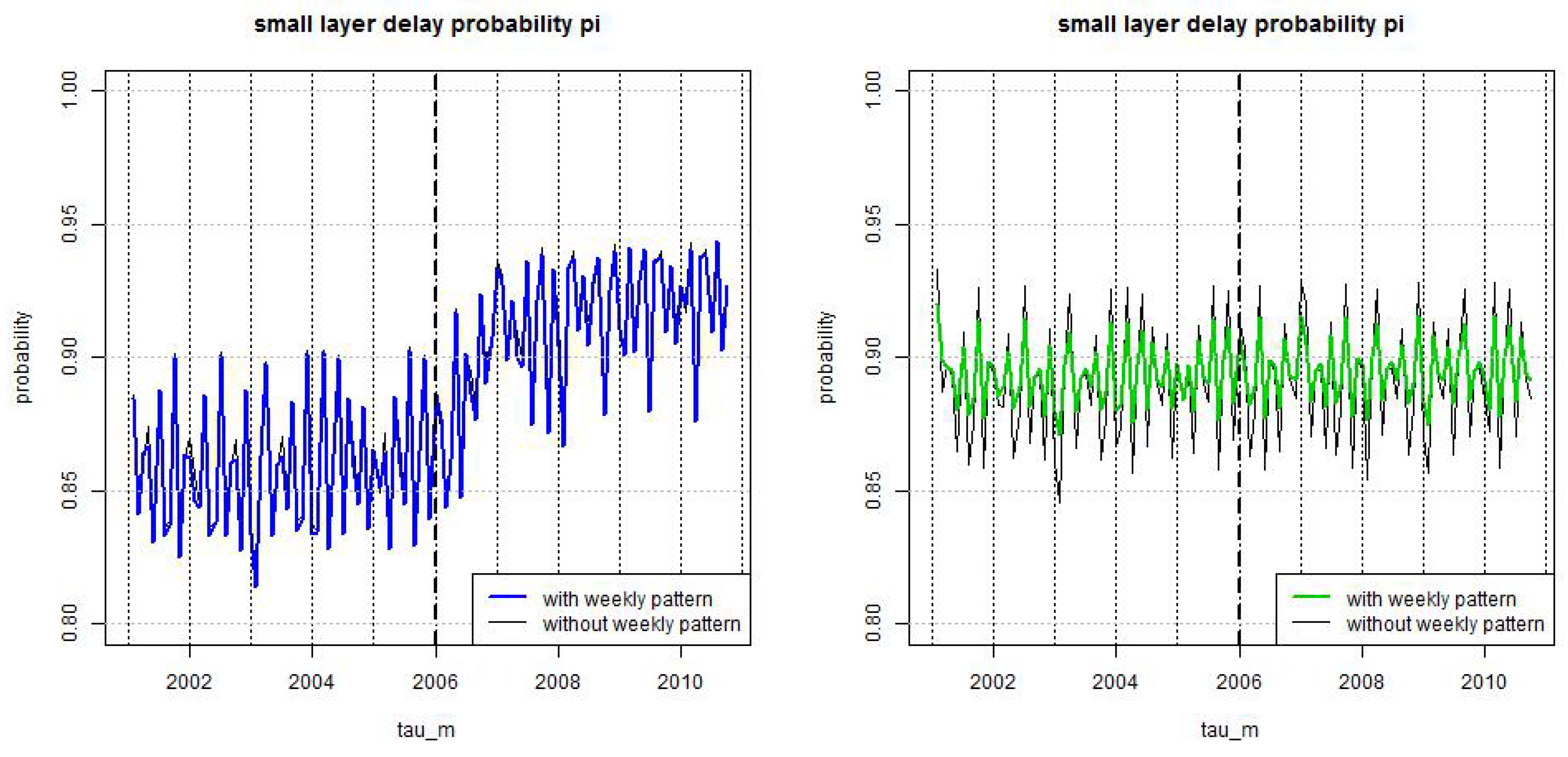
Figure 4.
Estimated probability , see (23), for using weekly periodic pattern (blue/green) and setting (black) for (lhs) LoB Property under the full model (21), and (rhs) LoB Casualty under the null hypothesis reduced model.
Figure 4.
Estimated probability , see (23), for using weekly periodic pattern (blue/green) and setting (black) for (lhs) LoB Property under the full model (21), and (rhs) LoB Casualty under the null hypothesis reduced model.
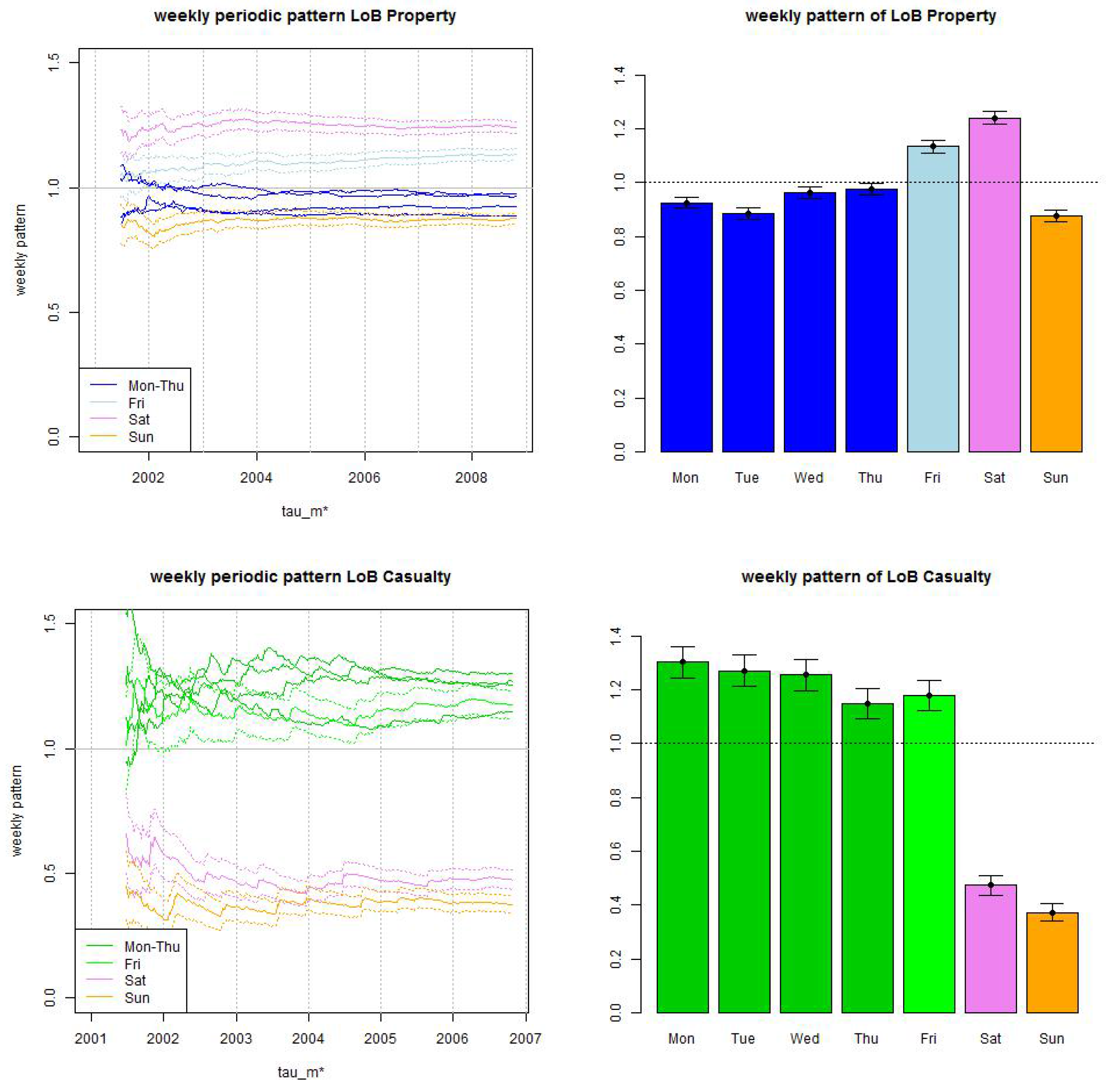
Figure 5.
Weekly periodic pattern estimate (top) LoB Property and (bottom) LoB Casualty: (lhs) time series as a function of and (rhs) for maximal such that (11) holds at time for a maximal reporting delay of 2 years (LoB Property) and of 4 years (LoB Casualty). The confidence bounds in all plots are given by (12) for confidence level .
Figure 5.
Weekly periodic pattern estimate (top) LoB Property and (bottom) LoB Casualty: (lhs) time series as a function of and (rhs) for maximal such that (11) holds at time for a maximal reporting delay of 2 years (LoB Property) and of 4 years (LoB Casualty). The confidence bounds in all plots are given by (12) for confidence level .
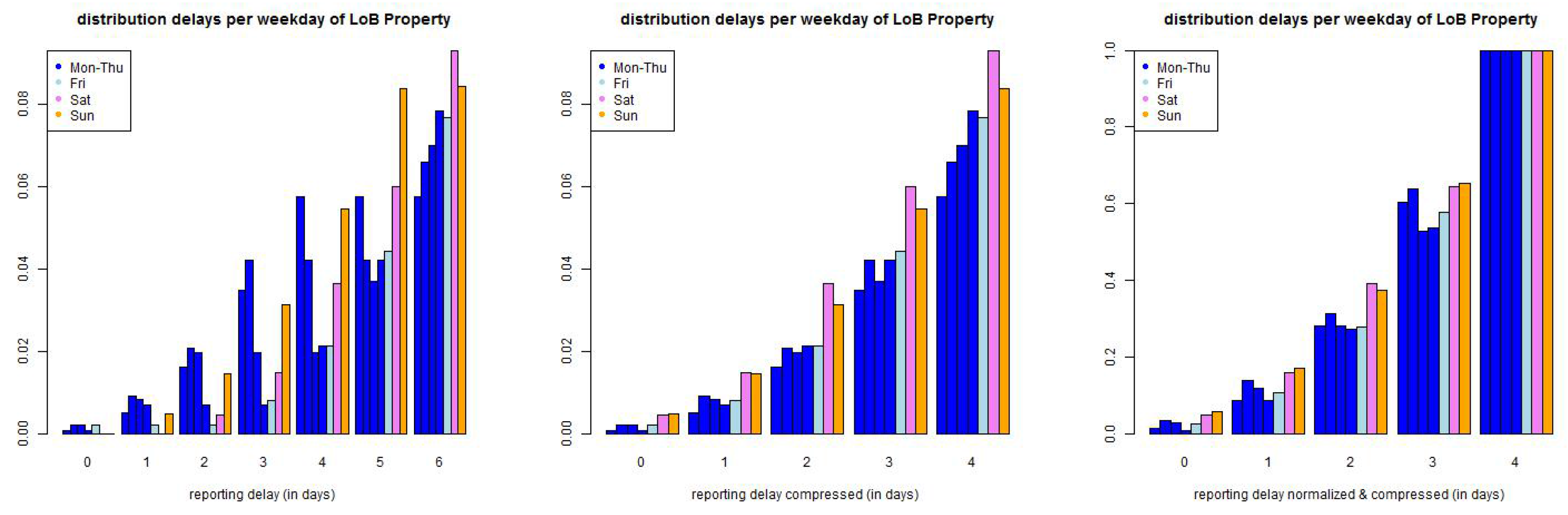
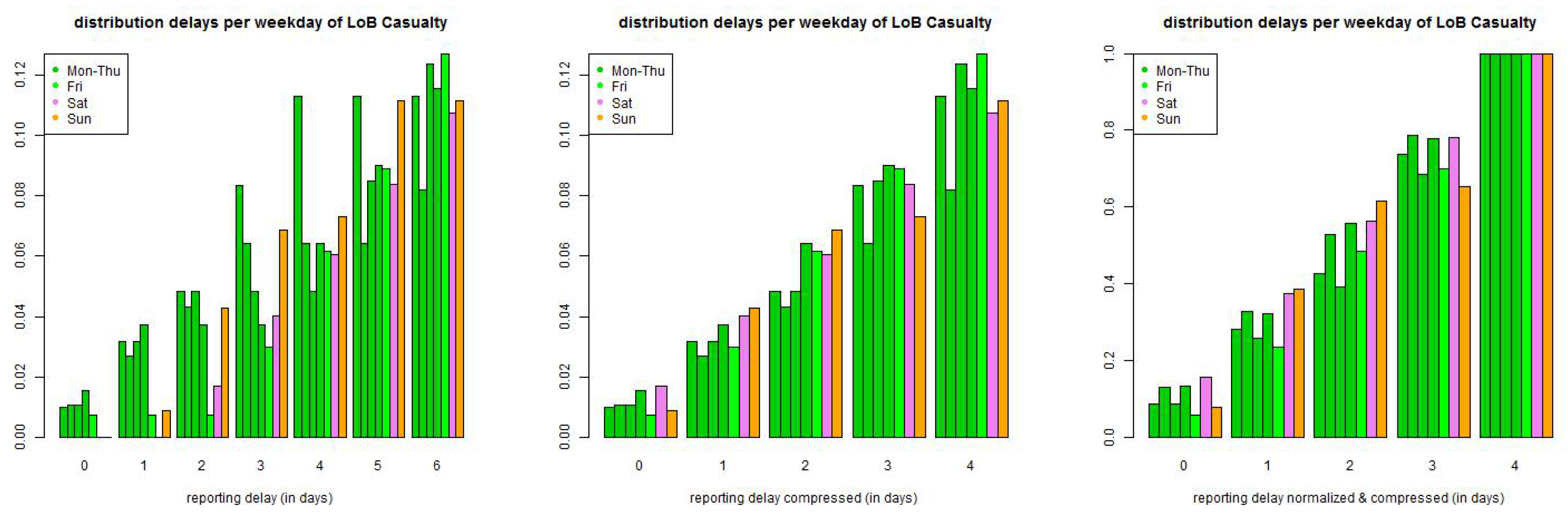
Figure 6.
(top) LoB Property and (bottom) LoB Casualty: empirical distribution of reporting delays separated by weekdays of claims occurrence of all data with accident date prior to 01/2006 and maximal reporting delay of days (lhs) per day, (middle) compressed by weekends, and (rhs) compressed and normalized to 1 after a delay of one week.
Figure 6.
(top) LoB Property and (bottom) LoB Casualty: empirical distribution of reporting delays separated by weekdays of claims occurrence of all data with accident date prior to 01/2006 and maximal reporting delay of days (lhs) per day, (middle) compressed by weekends, and (rhs) compressed and normalized to 1 after a delay of one week.
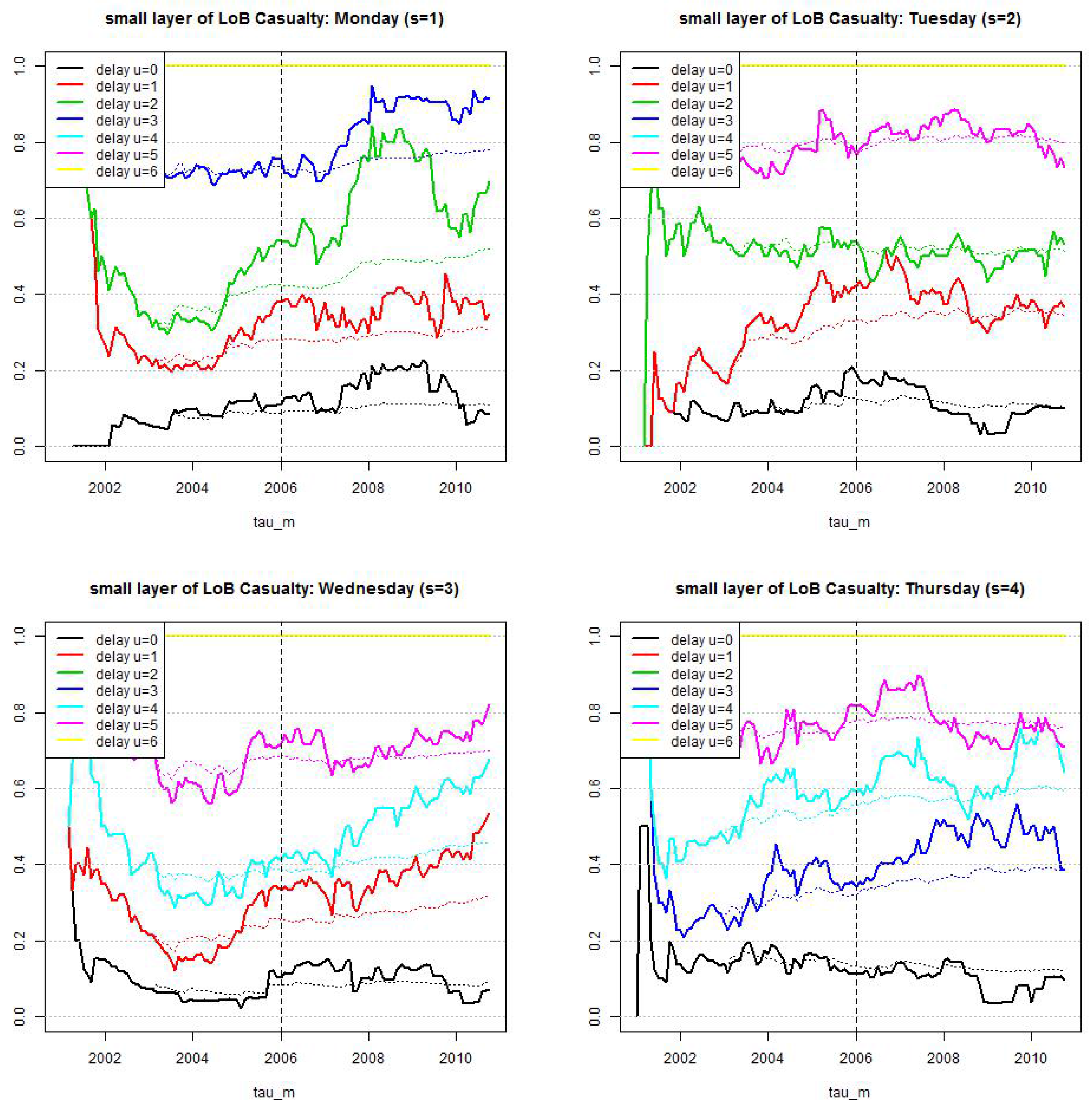
Figure 7.
(lhs) small reporting delay layer as of 31/10/2010 for occurrence dates in 10/2010 of LoB Property, and (rhs) estimated trend parameter α at times for LoB Property (blue/light blue) and LoB Casualty (green/light green) with dark colors are for months and light colors for months.
Figure 7.
(lhs) small reporting delay layer as of 31/10/2010 for occurrence dates in 10/2010 of LoB Property, and (rhs) estimated trend parameter α at times for LoB Property (blue/light blue) and LoB Casualty (green/light green) with dark colors are for months and light colors for months.
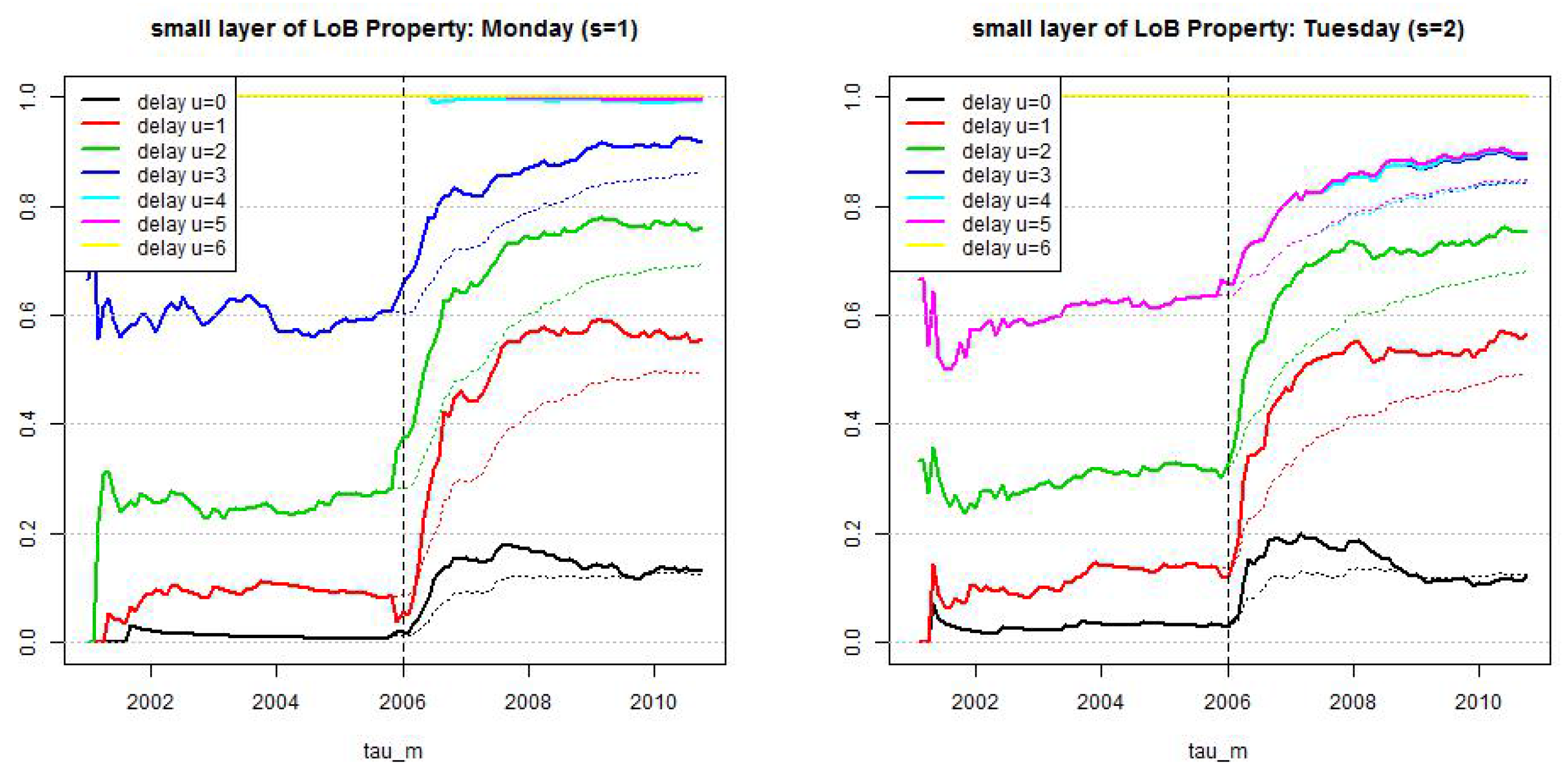
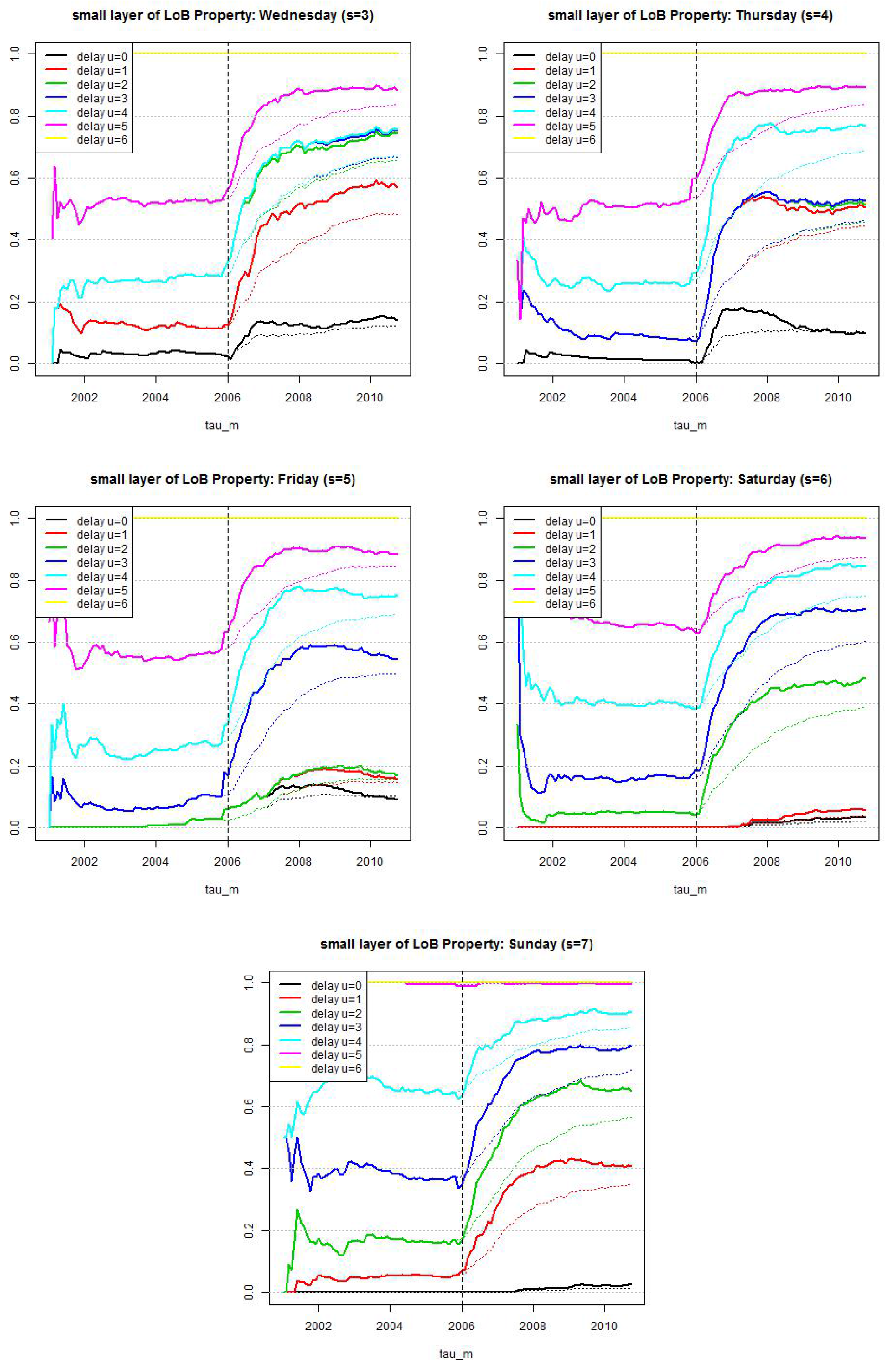
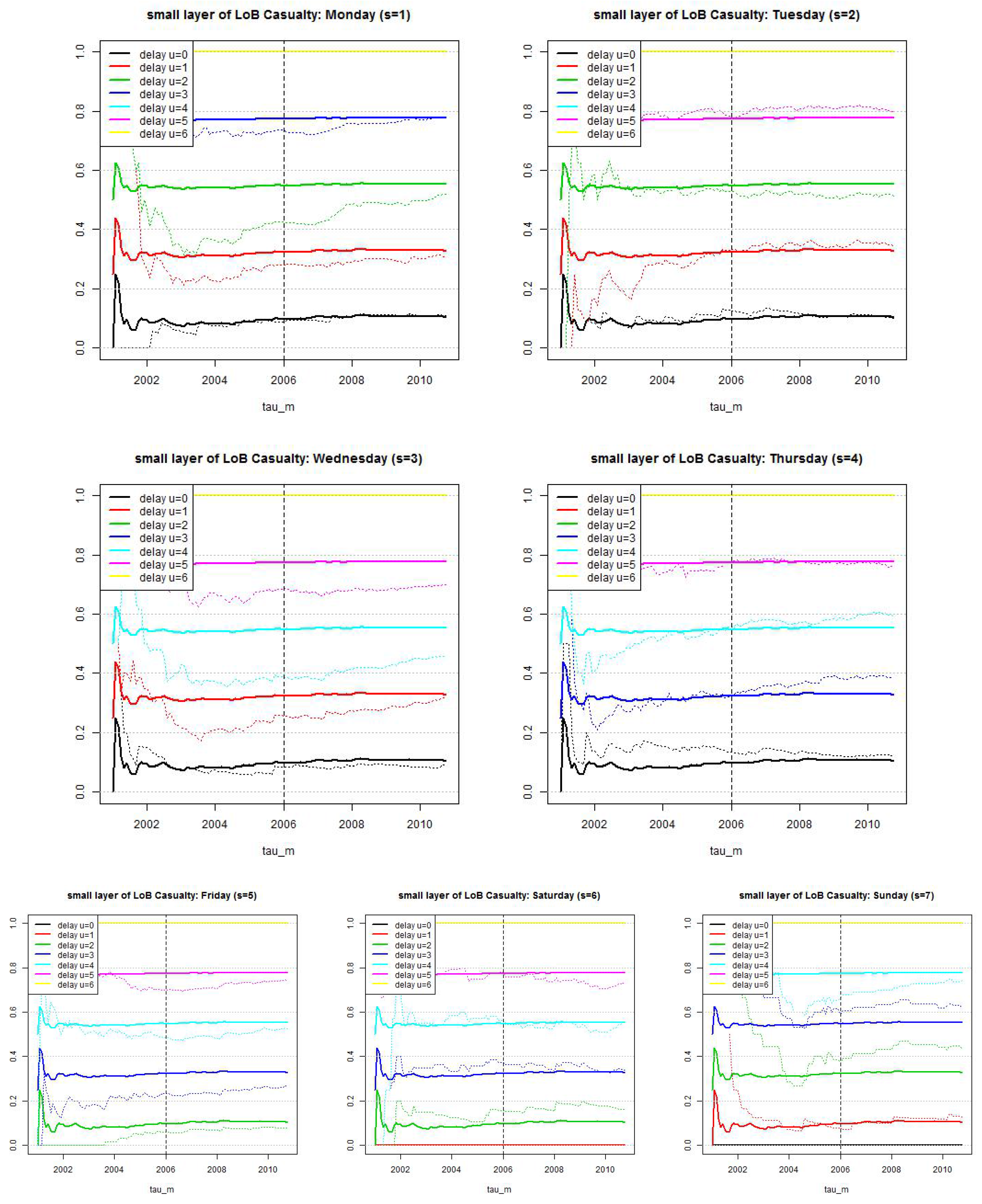
Figure 8.
LoB Property, small reporting delay layer: estimated cumulative distribution per weekday . Dotted lines show calibration based on all observations since and lines show calibration based on a rolling window of length 2·365 days.
Figure 8.
LoB Property, small reporting delay layer: estimated cumulative distribution per weekday . Dotted lines show calibration based on all observations since and lines show calibration based on a rolling window of length 2·365 days.
Figure 9.
LoB Casualty, small reporting delay layer: estimated cumulative distribution per weekday . Dotted lines show calibration based on all observations since and lines show calibration based on a rolling window of length 2·365 days.
Figure 9.
LoB Casualty, small reporting delay layer: estimated cumulative distribution per weekday . Dotted lines show calibration based on all observations since and lines show calibration based on a rolling window of length 2·365 days.
Figure 10.
LoB Casualty, small reporting delay layer: estimated cumulative distribution per weekday . Dotted lines show calibration based on individual weekdays and reporting delays and lines show calibration under compressed weekends and the null hypothesis that we only need three parameters.
Figure 10.
LoB Casualty, small reporting delay layer: estimated cumulative distribution per weekday . Dotted lines show calibration based on individual weekdays and reporting delays and lines show calibration under compressed weekends and the null hypothesis that we only need three parameters.
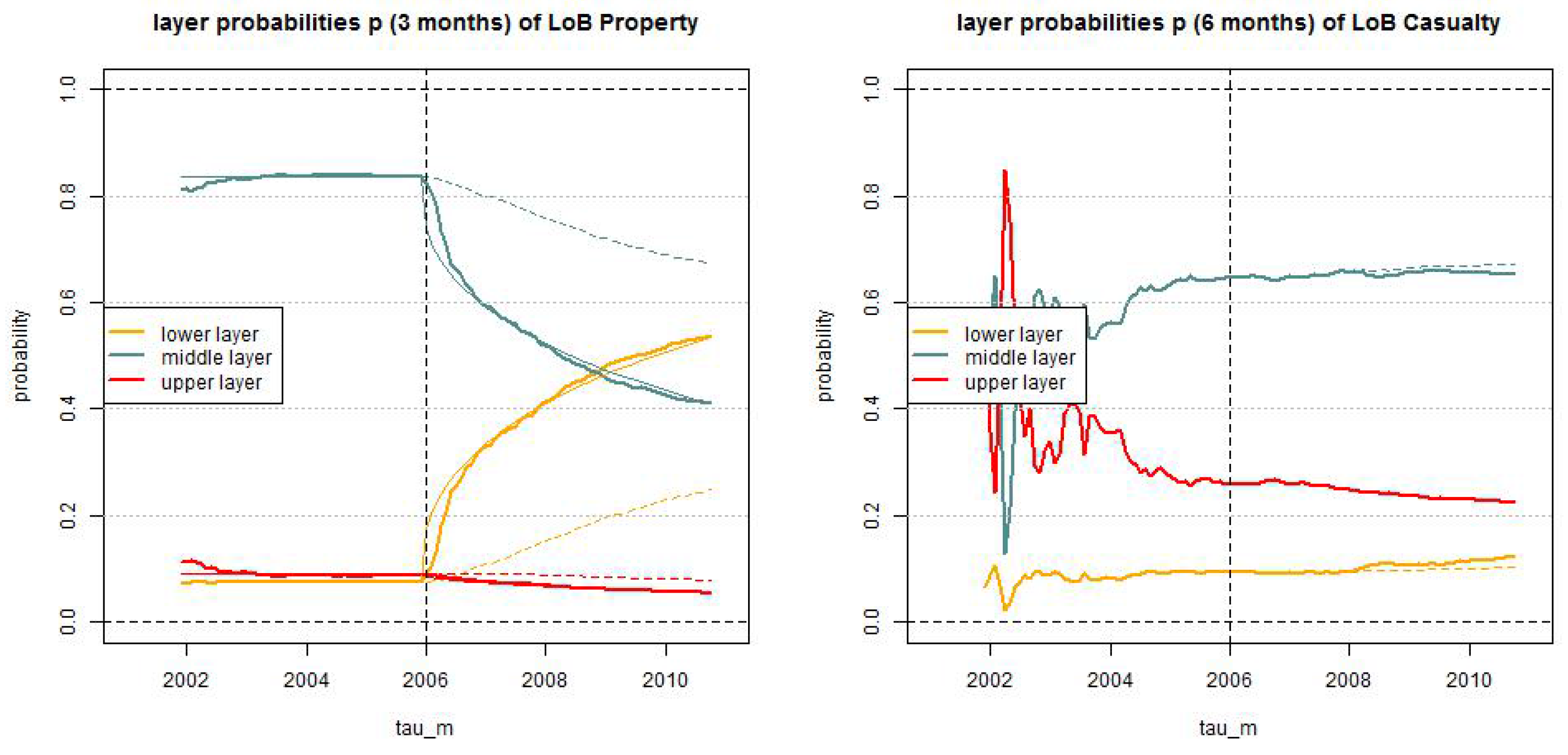
Figure 11.
Estimated layer probabilities , , in the truncated/shifted log-normal model (lhs) LoB Property with and (rhs) LoB Casualty with months for ; the solid lines give the dynamic versions with and the dotted lines the static versions .
Figure 11.
Estimated layer probabilities , , in the truncated/shifted log-normal model (lhs) LoB Property with and (rhs) LoB Casualty with months for ; the solid lines give the dynamic versions with and the dotted lines the static versions .
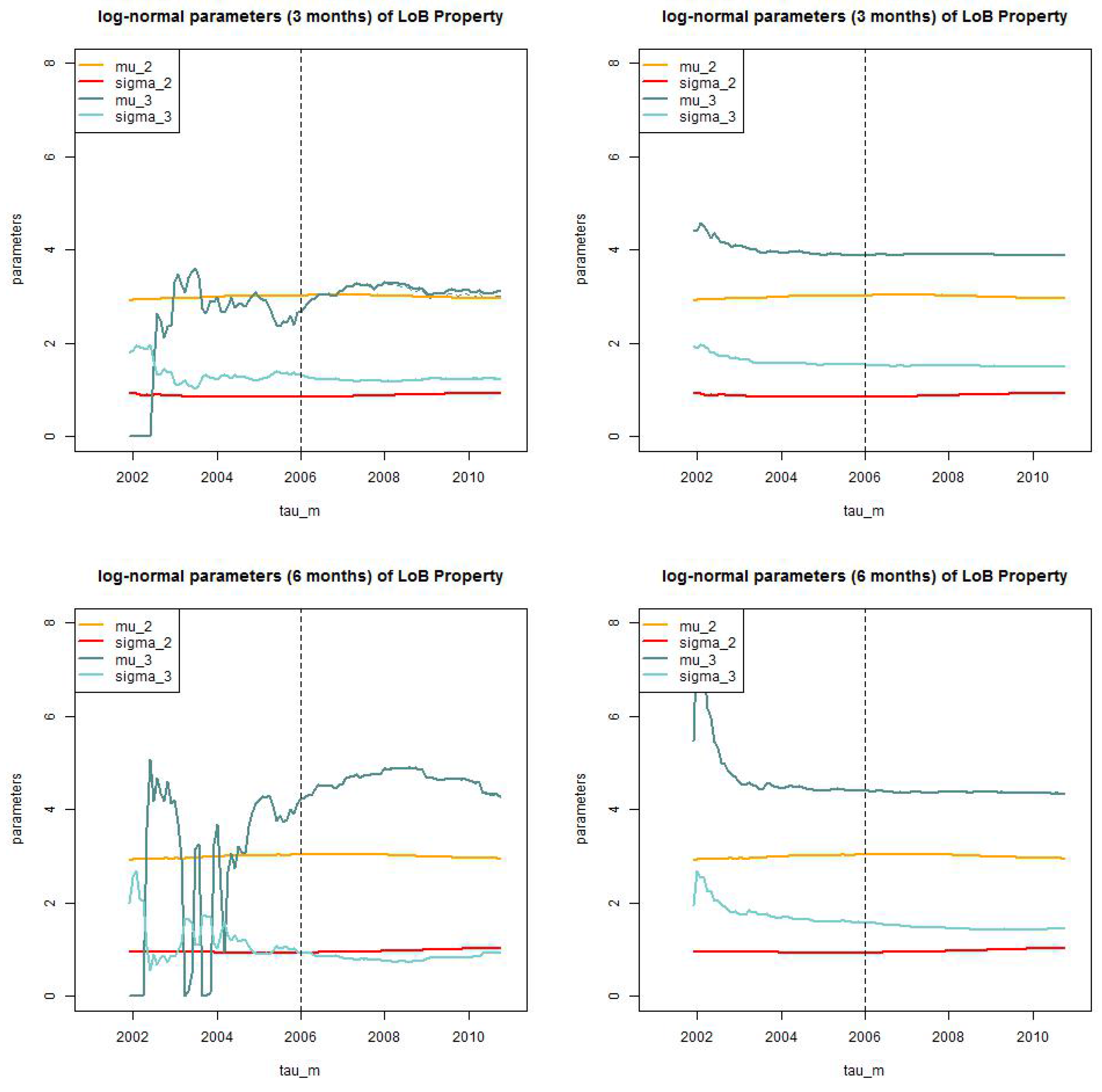
Figure 12.
LoB Property: parameter estimates of for the dynamic model with for (top, lhs) months truncated/truncated and (top, rhs) and truncated/shifted; and (bottom, lhs) months truncated/truncated and (bottom, rhs) and truncated/shifted.
Figure 12.
LoB Property: parameter estimates of for the dynamic model with for (top, lhs) months truncated/truncated and (top, rhs) and truncated/shifted; and (bottom, lhs) months truncated/truncated and (bottom, rhs) and truncated/shifted.
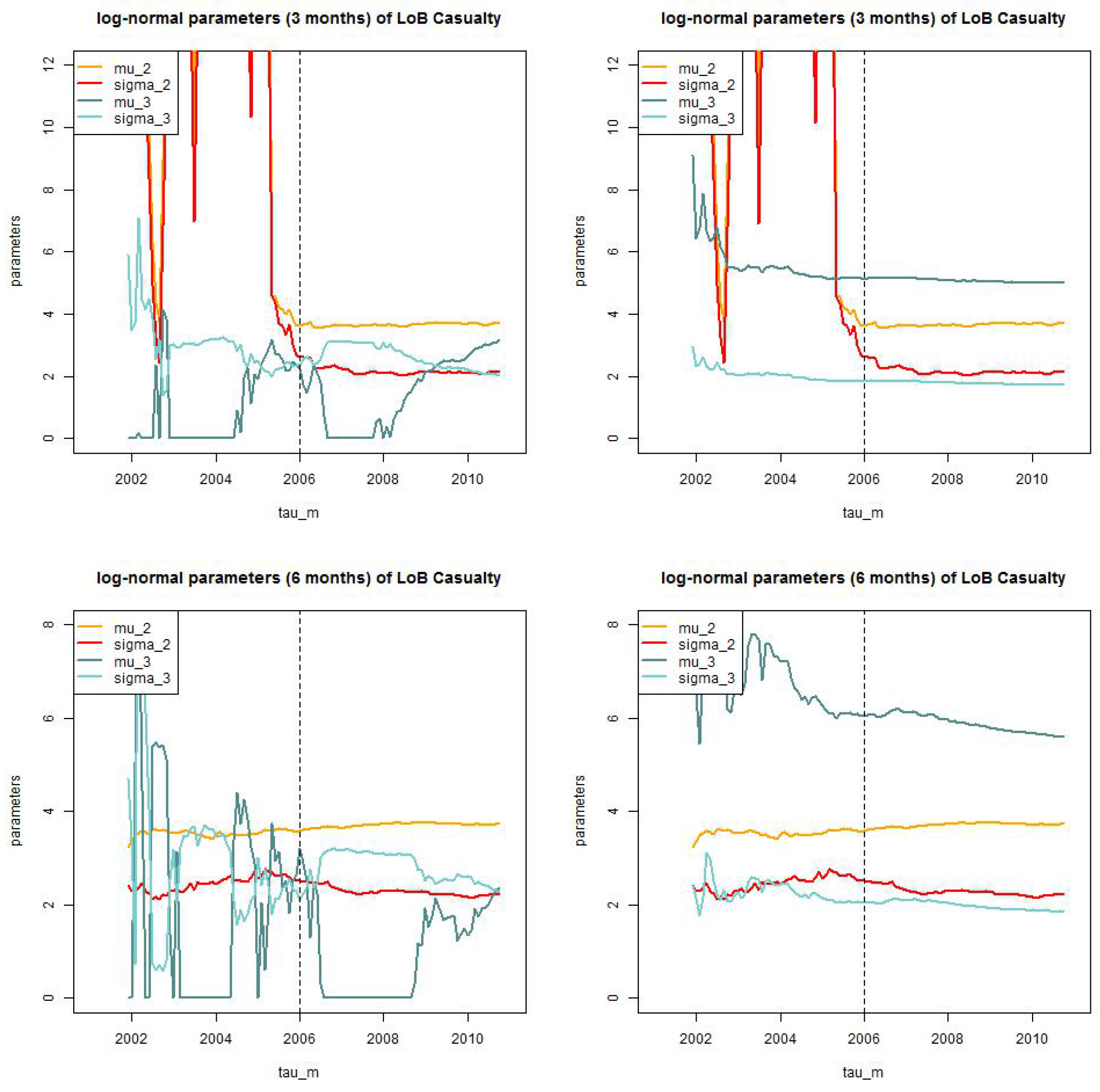
Figure 13.
LoB Casualty: parameter estimates of for the static model for (top, lhs) months truncated/truncated and (top, rhs) and truncated/shifted; and (bottom, lhs) months truncated/truncated (bottom, rhs) and truncated/shifted.
Figure 13.
LoB Casualty: parameter estimates of for the static model for (top, lhs) months truncated/truncated and (top, rhs) and truncated/shifted; and (bottom, lhs) months truncated/truncated (bottom, rhs) and truncated/shifted.
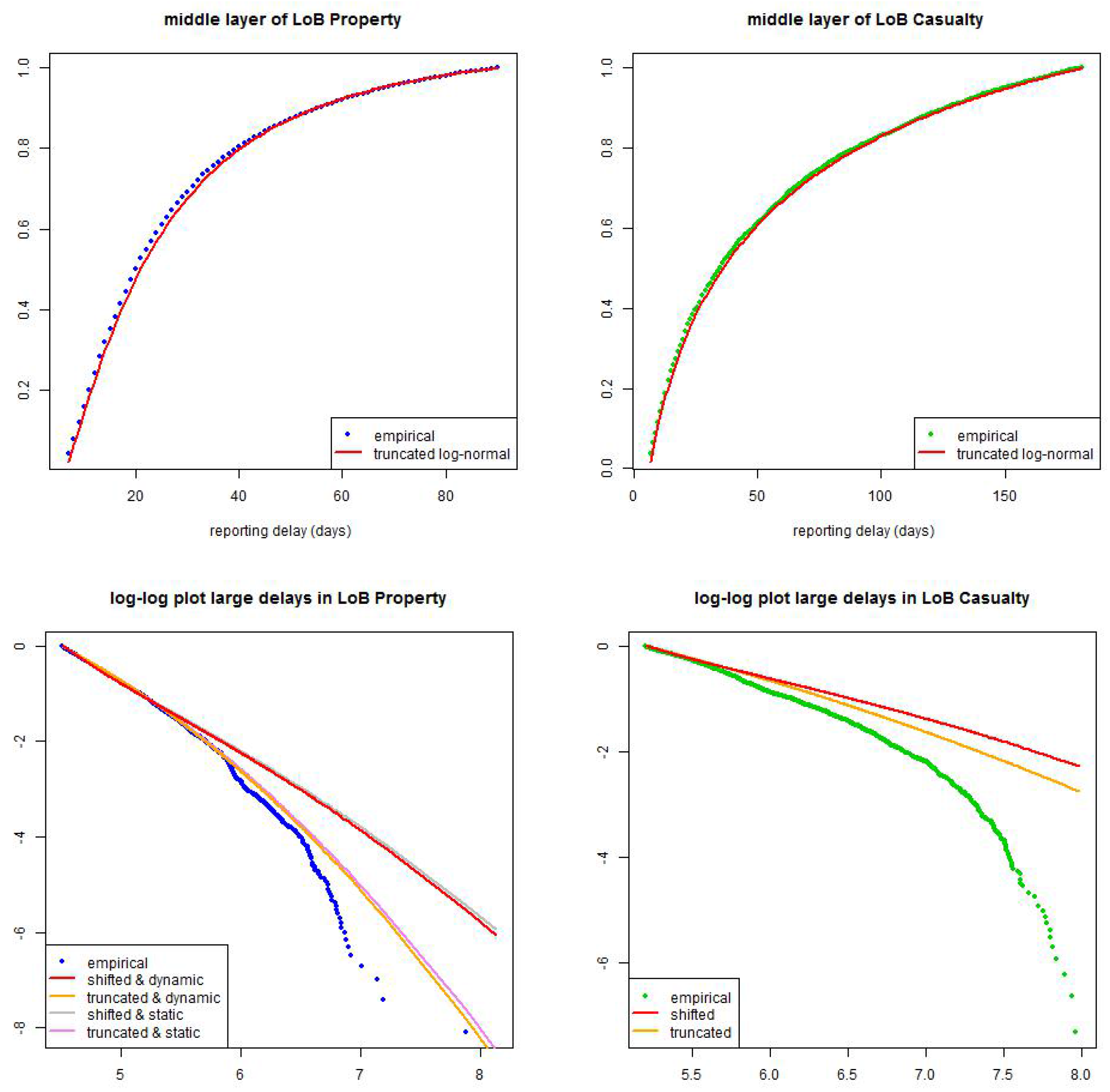
Figure 14.
(top) calibration of truncated log-normal distribution in the middle layer for (lhs) LoB Property with months and (rhs) LoB Casualty with months; (bottom) calibration of shifted and truncated log-normal distributions in the large layer for (lhs) LoB Property with months (static and dynamic versions) and (rhs) LoB Casualty with months (only static versions).
Figure 14.
(top) calibration of truncated log-normal distribution in the middle layer for (lhs) LoB Property with months and (rhs) LoB Casualty with months; (bottom) calibration of shifted and truncated log-normal distributions in the large layer for (lhs) LoB Property with months (static and dynamic versions) and (rhs) LoB Casualty with months (only static versions).
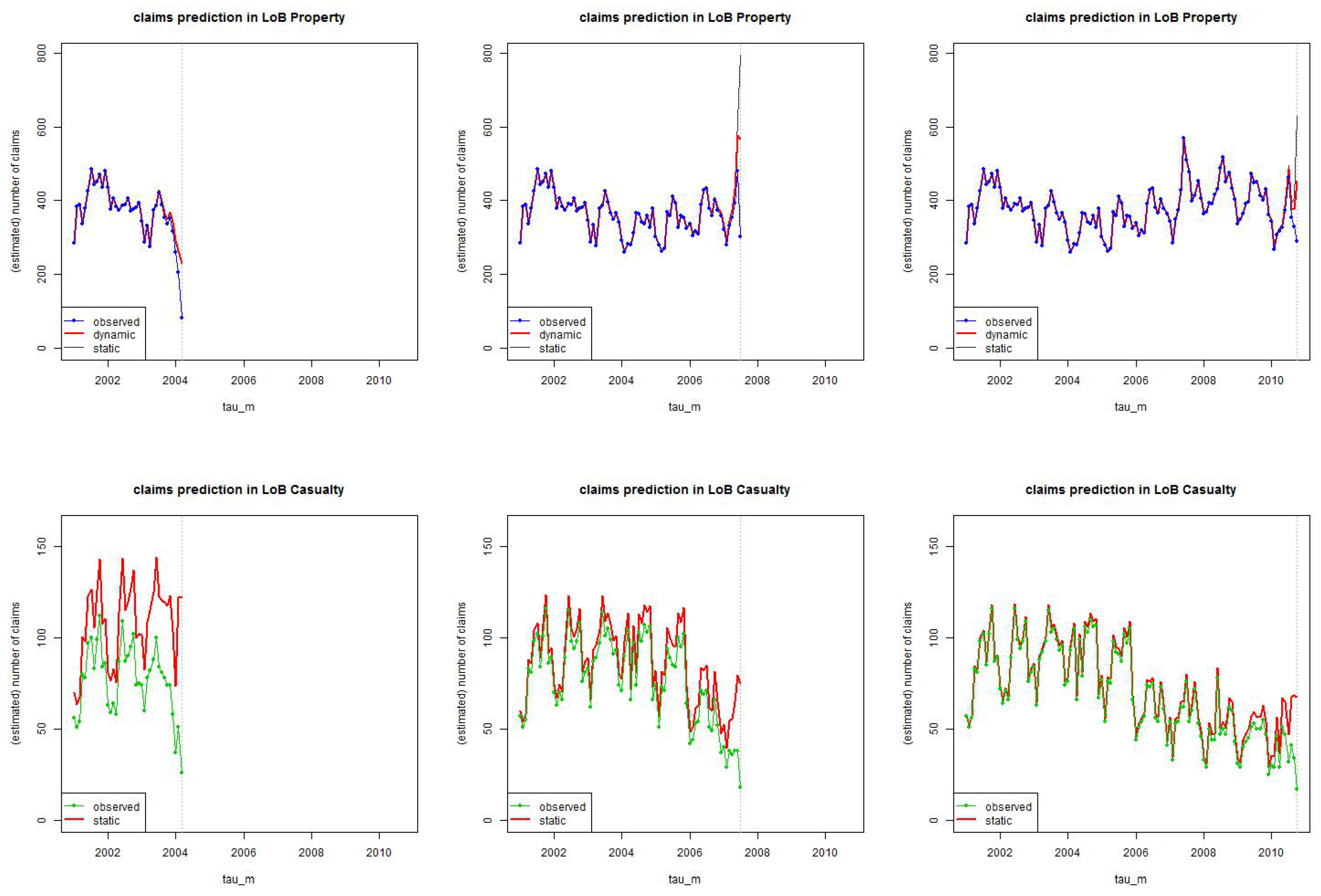
Figure 15.
Estimation of the number of incurred claims for (top) LoB Property and (bottom) LoB Casualty at times using the truncated/shifted log-normal model with months and months, respectively; “observed” (blue/green) gives the number of reported claims in each period at time , “dynamic/static” (red) gives the total number of estimated claims (the spread giving the estimated number of IBNYR claims).
Figure 15.
Estimation of the number of incurred claims for (top) LoB Property and (bottom) LoB Casualty at times using the truncated/shifted log-normal model with months and months, respectively; “observed” (blue/green) gives the number of reported claims in each period at time , “dynamic/static” (red) gives the total number of estimated claims (the spread giving the estimated number of IBNYR claims).
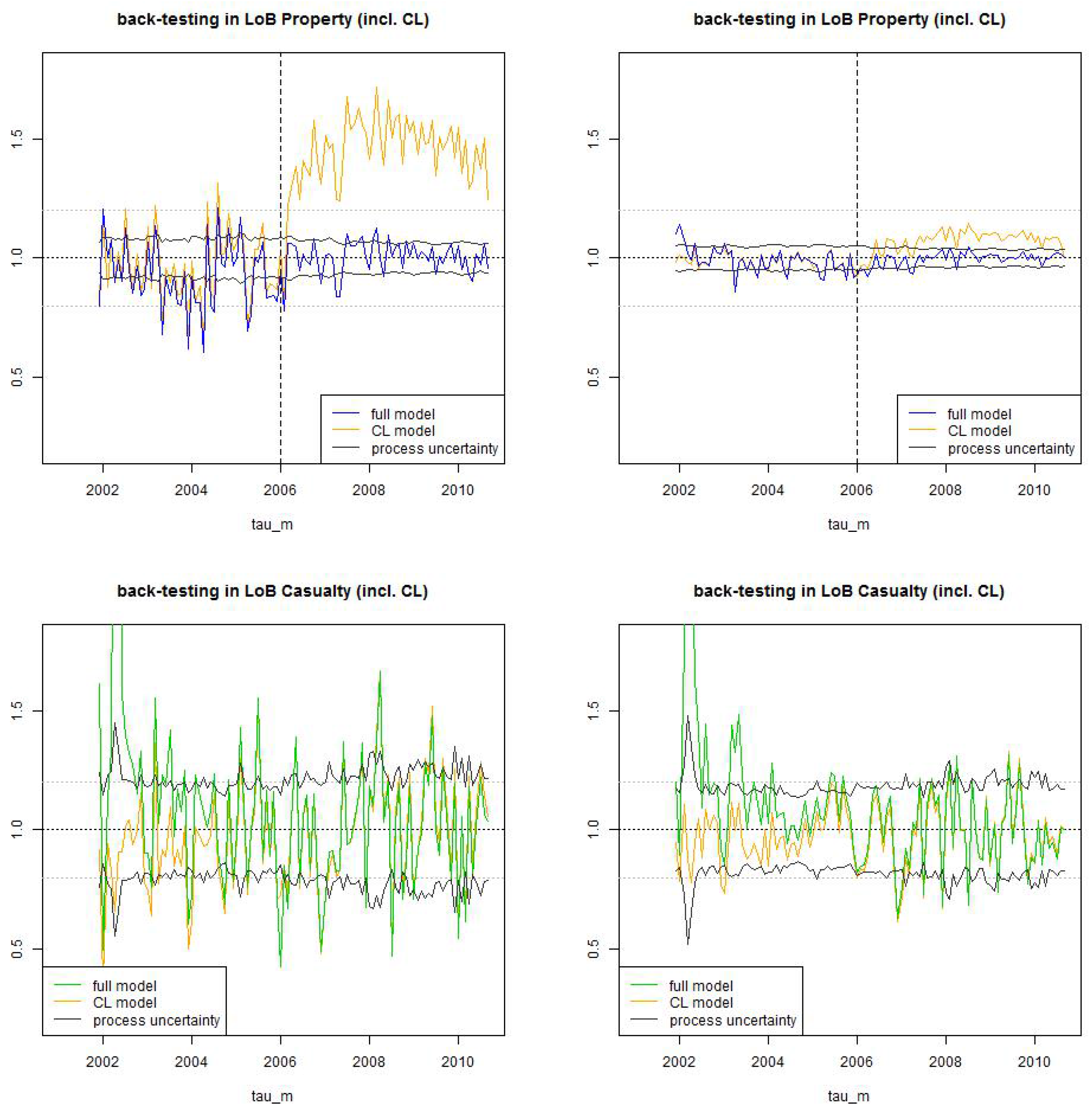
Figure 16.
Back-test LoB Property (top) and LoB Casualty (bottom): we compare the (non-stationary) estimate (blue/green) to the (stationary) chain-ladder estimate (orange) for (lhs) time lag and (rhs) time lag . The black line shows the process uncertainty confidence bounds of 2 (relative) standard deviations .
Figure 16.
Back-test LoB Property (top) and LoB Casualty (bottom): we compare the (non-stationary) estimate (blue/green) to the (stationary) chain-ladder estimate (orange) for (lhs) time lag and (rhs) time lag . The black line shows the process uncertainty confidence bounds of 2 (relative) standard deviations .
Table 1.
Statistics per weekday: average daily claims counts and empirical standard deviation for LoB Property and LoB Casualty.
Table 1.
Statistics per weekday: average daily claims counts and empirical standard deviation for LoB Property and LoB Casualty.
| | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
|---|
| LoB Property | | | | | | | |
| average | 11.48 | 11.02 | 11.87 | 12.15 | 14.23 | 15.46 | 10.73 |
| standard deviation | 4.51 | 4.05 | 4.26 | 4.30 | 4.66 | 4.95 | 4.26 |
| LoB Casualty | | | | | | | |
| average | 2.89 | 2.92 | 2.89 | 2.65 | 2.61 | 1.09 | 0.82 |
| standard deviation | 2.72 | 2.82 | 2.63 | 2.40 | 2.45 | 2.08 | 1.80 |
Table 2.
Observed number of reported claims for weekdays and reporting delays at time for claims with accident dates before 26/10/2010 of LoB Property.
Table 2.
Observed number of reported claims for weekdays and reporting delays at time for claims with accident dates before 26/10/2010 of LoB Property.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|
| Mon | 164 | 482 | 254 | 220 | 172 | 5 | 3 |
| Tue | 172 | 504 | 255 | 221 | 3 | 5 | 207 |
| Wed | 178 | 545 | 258 | 17 | 4 | 246 | 248 |
| Thu | 163 | 542 | 20 | 9 | 355 | 239 | 257 |
| Fri | 193 | 88 | 15 | 651 | 369 | 296 | 287 |
| Sat | 49 | 33 | 754 | 445 | 314 | 266 | 266 |
| Sun | 20 | 470 | 307 | 211 | 195 | 197 | 6 |
Table 3.
Observed number of reported claims for weekdays and reporting delays at time for claims with accident dates before 26/10/2010 of LoB Casualty, the rhs is compressed by weekends.
Table 3.
Observed number of reported claims for weekdays and reporting delays at time for claims with accident dates before 26/10/2010 of LoB Casualty, the rhs is compressed by weekends.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 0* | 1* | 2* | 3* | 4* |
|---|
| Mon | 17 | 31 | 33 | 41 | 34 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 31 | 33 | 41 | 34 |
| Tue | 15 | 36 | 25 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 15 | 36 | 25 | 42 | 30 |
| Wed | 16 | 40 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 43 | 53 | 16 | 40 | 25 | 43 | 53 |
| Thu | 19 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 27 | 38 | 19 | 43 | 33 | 27 | 38 |
| Fri | 12 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 40 | 33 | 40 | 12 | 29 | 40 | 33 | 40 |
| Sat | 0 | 0 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 15 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 15 |
| Sun | 0 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 5 | 10 |
Table 4.
p-values of the -tests under the corresponding null hypotheses for test statistics , see Equation (22), for weekdays (with 4 degrees of freedom).
Table 4.
p-values of the -tests under the corresponding null hypotheses for test statistics , see Equation (22), for weekdays (with 4 degrees of freedom).
| | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
|---|
| p-values | 79% | 29% | 3.2% | 37% | 44% | 52% | 47% |
Table 5.
AIC and BIC as of 31/10/2010 (top) and months and (bottom) LoB Property truncated/truncated dynamic () log-normal model with and LoB Casualty truncated/truncated static () log-normal model.
| Method: Log-normal Distribution | AIC | BIC |
|---|
| LoB Property | | |
| truncated/shifted (static ) | 347’532 | 347’592 |
| truncated/truncated (static ) | 347’461 | 347’522 |
| truncated/shifted (dynamic ) | 339’270 | 339’348 |
| truncated/truncated (dynamic ) | 339’204 | 339’274 |
| LoB Casualty | | |
| truncated/shifted (static ) | 87’979 | 88’028 |
| truncated/truncated (static ) | 87’941 | 87’990 |
| truncated/shifted (dynamic ) | 87’973 | 88’028 |
| truncated/truncated (dynamic ) | 87’934 | 87’990 |
| Threshold | AIC | BIC |
|---|
| LoB Property | | |
| months | 339’033 | 339’103 |
| months | 339’204 | 339’274 |
| months | 339’291 | 339’361 |
| months | 339’376 | 339’445 |
| LoB Casualty | | |
| months | 87’908 | 87’957 |
| months | 87’941 | 87’990 |
| months | 87’963 | 88’013 |
| months | 87’988 | 88’037 |
Table 6.
AIC and BIC as of 31/10/2010 for LoB Property truncated/truncated dynamic log-normal model with months.
Table 6.
AIC and BIC as of 31/10/2010 for LoB Property truncated/truncated dynamic log-normal model with months.
| Threshold | AIC | BIC |
|---|
| LoB Property | | |
| months | 339’594 | 339’663 |
| months | 339’267 | 339’337 |
| months | 339’204 | 339’274 |
| months | 339’222 | 339’292 |
Table 7.
AIC and BIC as
Table 5 (top) but with log-normal distributions replaced by gamma distributions.
Table 7.
AIC and BIC as Table 5 (top) but with log-normal distributions replaced by gamma distributions.
| Method: Gamma Distribution | AIC | BIC |
|---|
| LoB Property | | |
| truncated/shifted (static ) | 348’121 | 348’174 |
| truncated/truncated (static ) | 348’109 | 348’161 |
| truncated/shifted (dynamic ) | 339’935 | 340’005 |
| truncated/truncated (dynamic ) | 339’856 | 339’926 |
| LoB Casualty | | |
| truncated/shifted (static ) | 88’000 | 88’042 |
| truncated/truncated (static ) | 88’887 | 88’929 |
| truncated/shifted (dynamic ) | 87’995 | 88’051 |
| truncated/truncated (dynamic ) | 88’888 | 88’943 |