Developing a System for Monitoring Human Resource Risks in a Digital Economy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The HR risks of an organization were analyzed using the methods of the generalization of scientific sources and by collecting relevant information from participants of the sociological survey.
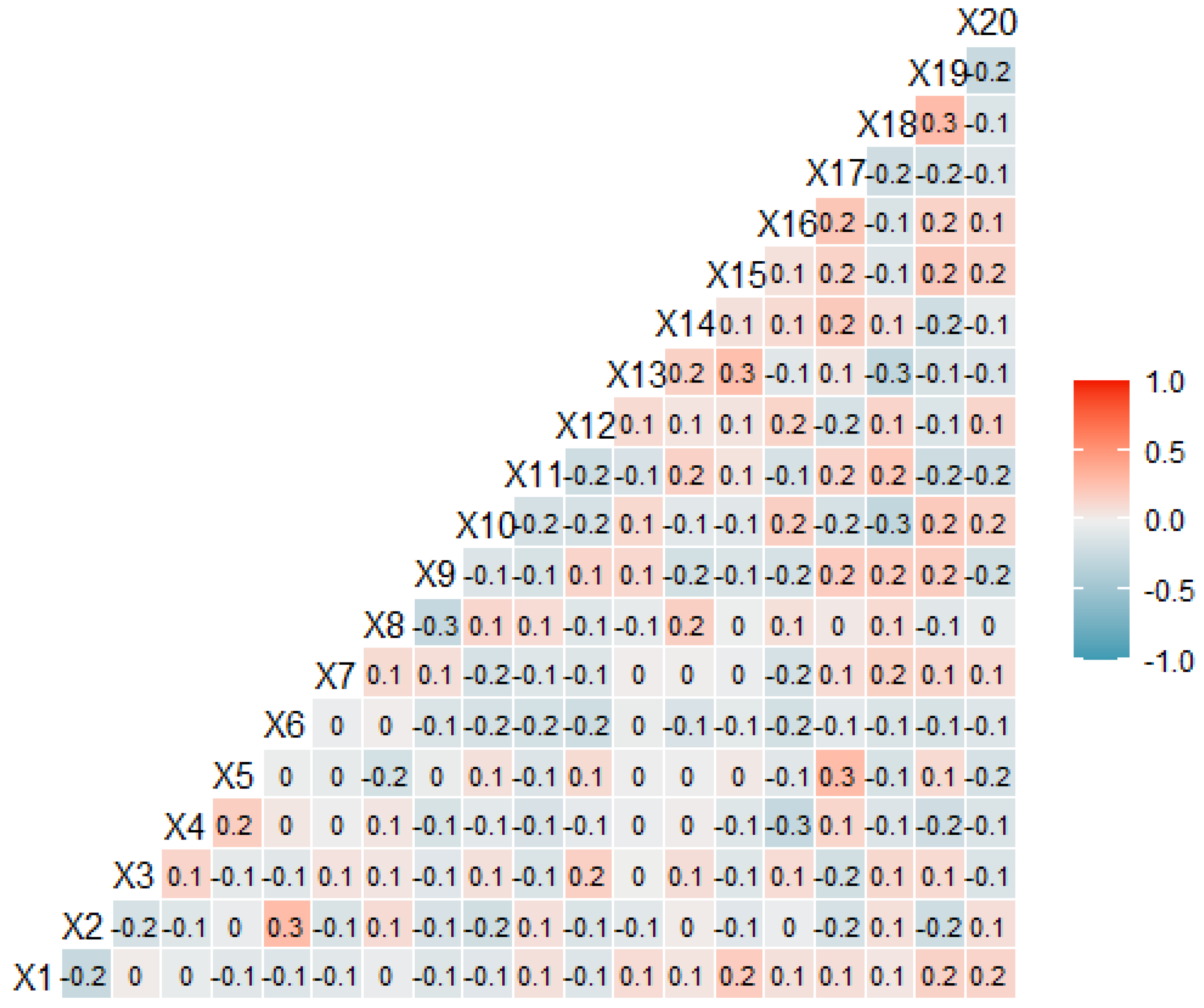
- Significant correlations were identified in the respondents’ answers to determine the significance and impact of HR risks on the security of the organization based on the cluster and correlation–regression analysis.
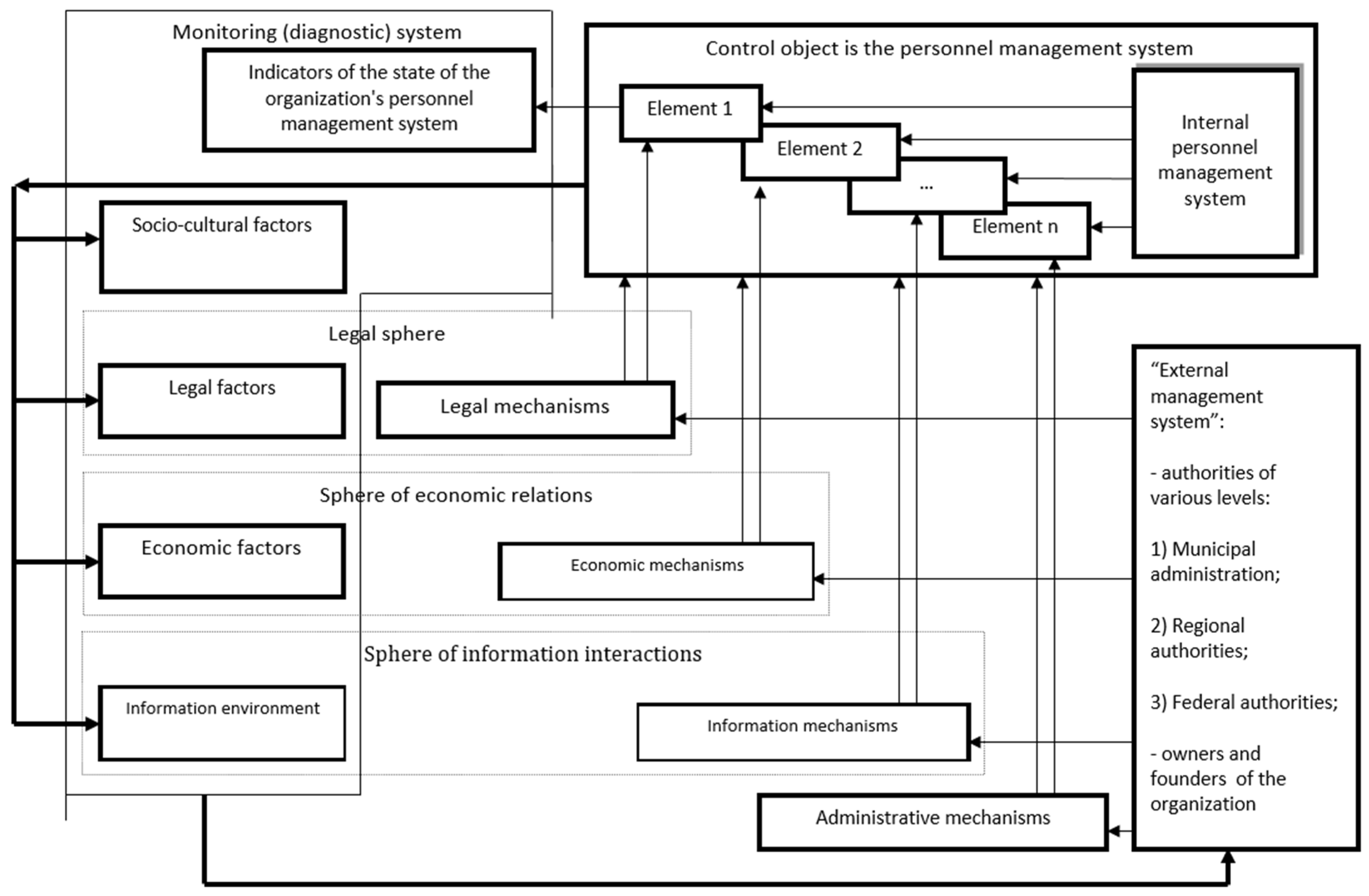
- A conceptual model of HR risk management was developed.
2. Literature Review
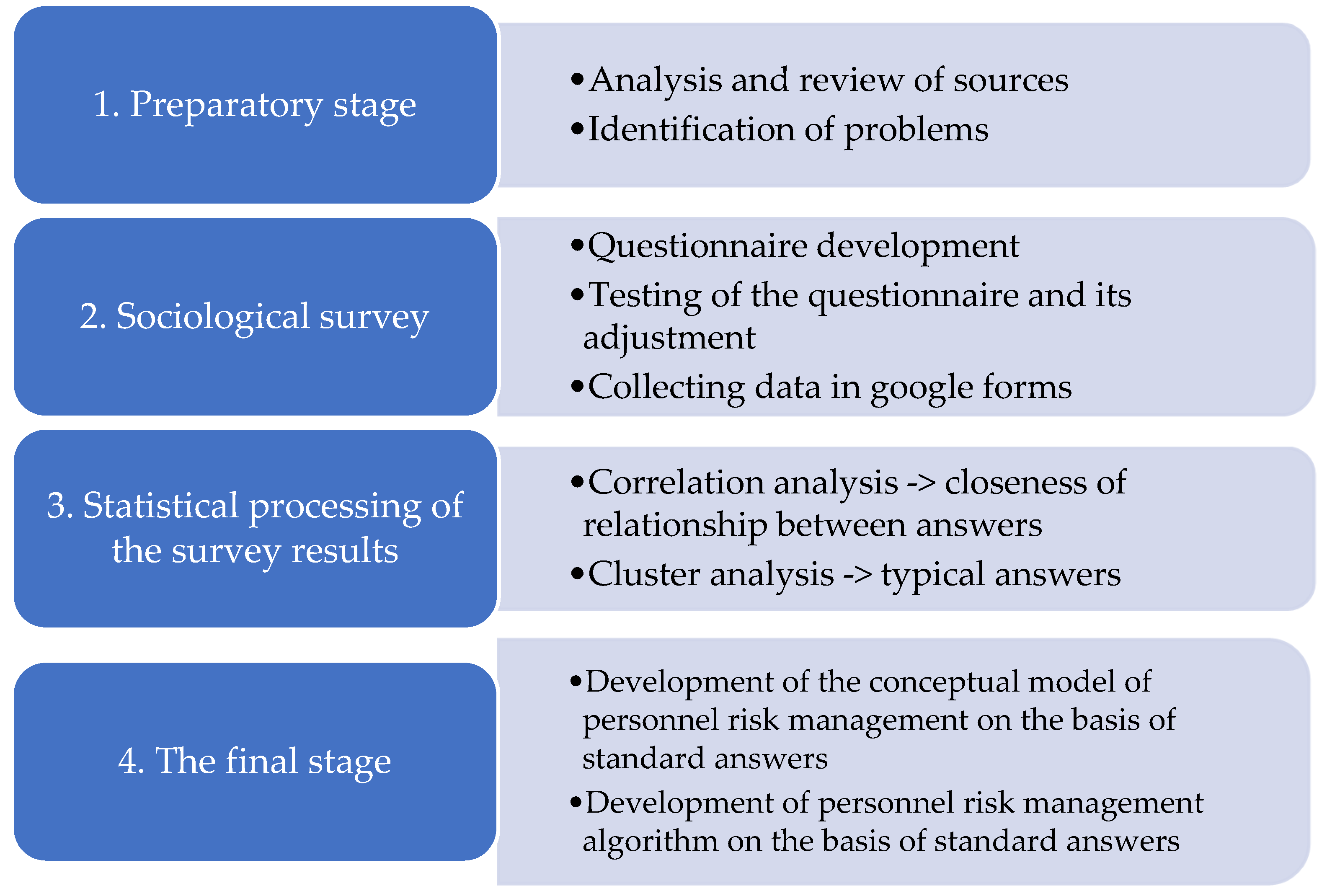
3. Materials and Methods
- Study Participants
- Research Tools
4. Results
4.1. Correlation Analysis
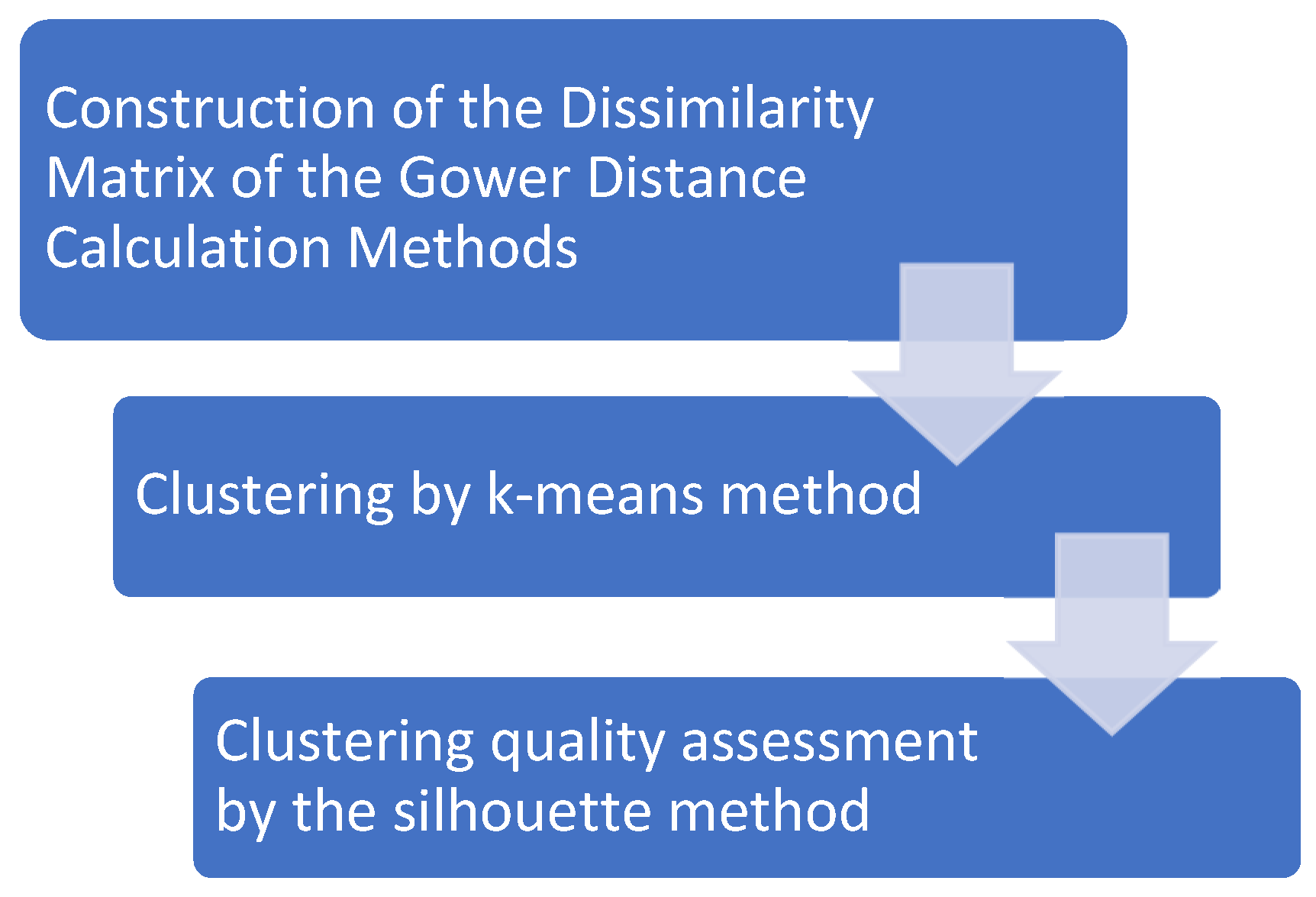
4.2. Cluster Analysis
- (1)
- The basis for clustering is a dissimilarity matrix, which, in mathematical terms, describes how the points in the dataset are different (remote) from each other. It allows for the further grouping of the points that are closest to each other or for separating the points that are most distant from each other, which is the main idea of clustering. This study uses Gower’s distance.
- (2)
- The k-means method was chosen as a clustering method.
- (3)
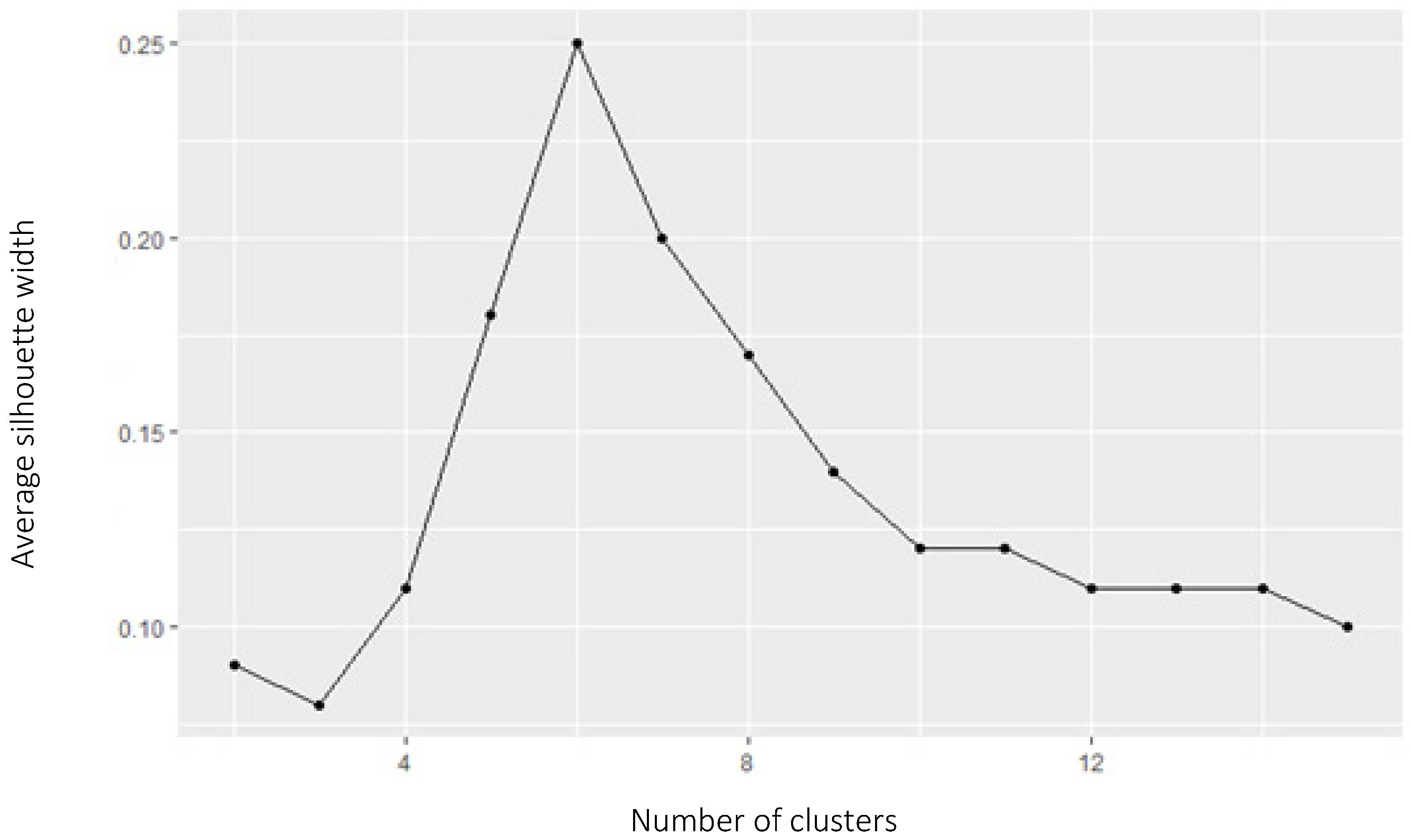
- The k-number of clusters was evaluated using a silhouette evaluation method: the silhouette graph used for measuring the data consistency shows how close each of the points within one cluster is to points in the neighboring clusters. The graph in Figure 4 shows the distribution of the silhouette width of the clusters (consistency of the data within the clusters). The sharp inflections of the graph demonstrate the optimal number of partitions.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Your gender
- (a)
- male
- (b)
- female
- Your age
- (a)
- under 25
- (b)
- 26–35
- (c)
- 36–45
- (d)
- 46–60
- (e)
- over 60
- What sector does your organization operate in?
- (a)
- industrial production
- (b)
- trade
- (c)
- construction
- (d)
- health care
- (e)
- education
- (f)
- financial services
- (g)
- consulting services
- (h)
- IT
- (i)
- agriculture
- (j)
- public service
- (k)
- other _______________
- The headcount of your organization is
- (a)
- less than 50 people
- (b)
- 51–100
- (c)
- 101–500
- (d)
- 501–1000
- (e)
- from 1000 to 5000
- (f)
- over 5000
- Your work experience in this organization is
- (a)
- less than 6 months
- (b)
- from 6 months to 1 year
- (c)
- 1–3 years
- (d)
- 3–5 years
- (e)
- 5–10 years
- (f)
- more than 10 years
- Do you hold a managerial position in your organization?
- (a)
- yes
- (b)
- no
- What statement do you associate HR risk?
- (a)
- loss or shortfall in the organization’s income
- (b)
- probability of deviation from the planned result
- (c)
- security threat to the organization
- (d)
- decreased labor efficiency
- In your opinion, which stage of work process causes the highest probability of HR risks?
- (a)
- selection and assessment of candidates
- (b)
- hiring (concluding labor relations)
- (c)
- direct work of the personnel in the organization
- (d)
- dismissal or resignation of an employee
- In your opinion, which sphere is mostly damaged by HR risks in the organization? (choose no more than 3 answers)
- (a)
- financial
- (b)
- informational
- (c)
- material-technical
- (d)
- moral
- (e)
- professional competence
- (f)
- personnel
- In your opinion, which kinds of HR risks are most threatening to effective operation of the organization? (choose from 1 to 3 answers)
- (a)
- imbalance of the personnel age groups
- (b)
- no monitoring of threats to vital interests of the organization
- (c)
- no measures are taken to reveal and prevent unwanted actions of personnel
- (d)
- selection of personnel that is not competent enough
- (e)
- insufficiency of measures aimed at forming motivation and loyalty of employees working in the organization
- (f)
- conflicts of interests between employees and the employer
- (g)
- dismissal or resignation of key employees
- In your opinion, in which of the functional personnel management subsystems do HR risks prevail? (choose no more than 3 answers)
- (a)
- personnel planning
- (b)
- labor relations management
- (c)
- provision of decent working conditions
- (d)
- formation of organizational structure
- (e)
- corporate culture development
- (f)
- legal support of personnel management
- (g)
- organization’s social development management
- (h)
- personnel development management
- (i)
- personnel motivation management
- (j)
- personnel assessment
- In which form do HR risks manifest in your organization? (choose any number of answers)
- (a)
- violation of labor discipline and ethic code
- (b)
- destructive conflicts and stress in the organizational environment
- (c)
- the organizational structure is not effective or optimal
- (d)
- insufficient professional competence of employees
- (e)
- high staff turnover
- (f)
- fraud, financial losses
- (g)
- threats to information security
- (h)
- resistance of personnel to innovations
- (i)
- our organization does not have any substantial HR risks
- Have you ever encountered with employees’ mistakes your professional activity that entailed serious negative effects for the organization (legal costs, financial and/or material losses, expired deadlines and broken agreements, etc.)
- (a)
- never
- (b)
- very rarely
- (c)
- rarely
- (d)
- sometimes
- (e)
- often
- (f)
- very often
- In your opinion, what caused these mistakes?
- (a)
- poor qualification
- (b)
- lack of loyalty on the part of personnel
- (c)
- interpersonal conflicts
- (d)
- fraud
- (e)
- sabotage and other forms of deviant behavior
- (f)
- other ________________
- (g)
- I find it difficult to answer
- Have you ever encountered in your professional experience with a situation when a dismissal or resignation of a key employee brought your organization substantial losses?
- (a)
- never
- (b)
- very rarely
- (c)
- rarely
- (d)
- sometimes
- (e)
- often
- (f)
- very often
- In your opinion, what causes violations of labor discipline (choose no more than 3 answers)
- (a)
- lack of clear understanding of the goals of the organization by employees
- (b)
- barriers in communications between front-line employees and/or management team
- (c)
- unstable work rates
- (d)
- abuse of authority by the heads of departments, inconsistency of their requirements, etc.
- (e)
- unjustified disciplinary rules and restrictions
- In your opinion, what causes conflict situations among workforce (choose no more than 3 answers)
- (a)
- breach of promises between departments and employees
- (b)
- constraints of any type of resources
- (c)
- imperfect remuneration system
- (d)
- presence of informal leadership and counterculture
- (e)
- resistance to change
- In your opinion, staff turnover is caused by: (choose no more than 3 answers)
- (a)
- low pay grade
- (b)
- lack of respectful business relationships with the management team
- (c)
- unsatisfactory labor conditions
- (d)
- unfavorable socio-psychological climate in the team
- (e)
- high intensity of work
- Which properties should the HR risk management methodology of the organization have (any number of answers can be chosen):
- (a)
- comprehensibility for the management team and employees
- (b)
- low labor costs of the implementation
- (c)
- flexibility for adapting the methodology to meet the changes in the organization;
- (d)
- ability to continuously monitor the HR situation
- (e)
- ability to get integrated into the corporate general security system
- (f)
- meeting the requirements of international standards
- In your opinion, which actions should be taken to minimize the risks of negative situations in the work with the personnel (any number of answers can be chosen)
- (a)
- training (professional development) of employees
- (b)
- stricter control over the activities of the personnel
- (c)
- informing employees about their liability
- (d)
- forming a signaling system (informing about the negative situation in the organization)
- (e)
- “exemplary dismissals”
- (f)
- other______________
References
- Balykhin, Gennadiy A., Sergey G. Radko, Sergey G. Dembitskyi, and Elena V. Berezina. 2015. The formation of human capital and risks in personnel management. Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Seriya Teknologiya Tekstil’noi Promyshlennosti 359: 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Campo Elías, Lopez-Rodríguez, and Espinosa-Rodríguez Miguel Alejandro. 2021. Operational risk: Behavior of its factors in the banking sector of Bogotá Colombia. Revista Venezolana de Gerencia 26: 439–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, Michael R., John W. Jones, and Brian W. Dreschler. 2018. Personnel risk management assessment for newly emerging forms of employee crimes. International Journal of Selection and Assessment 26: 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlenko, Olga A., and Tatyana P. Mozhaeva. 2017. Personnel Risk Control in System of Company Quality Management. Bryansk: Bulletin of Bryansk State Technical University. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, John C. 1983. Comparing classifications. In Numerical Taxonomy. Berlin: Springer, pp. 137–55. [Google Scholar]
- Guzairova, Alfiya F., Nadezhda V. Lipatkina, and Vladimir V. Tarasenko. 2018. HR risks in training the managerial personnel of educational organization: Concept definition, typology, detection algorithm. In The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences EpSBS. Future Academy, UK: vol. 50, pp. 1278–84. Available online: https://www.europeanproceedings.com/article/10.15405/epsbs.2018.12.157 (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Hudáková, Mária, Matej Masár, Josef Vodák, Patrik Lahuta, Wiesław Ciechomski, and M. Gabryśová. 2021. Personnel risks and their impact on business in the V4 countries. Polish Journal of Management Studies 23: 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illiashenko, Olena, Olena Zhehus, Lesia Matviychuk, Viktor Lopatovskyi, Yevhenii Rudnichenko, and Nataliia Havlovska. 2020. Improving accounting-analytical processes of personnel management in the context of relevant threats and risks for an enterprise economic security system. International Journal of Scientific and Technology Research 9: 105–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, Irina A., and Valentina N. Pulyaeva. 2022. Employment management in the focus of conceptual provisions and current trends in labor market regulation and population support. Labor Economics 9: 209–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jennex, Murray E. 2013. A method for assessing knowledge loss risk with departing personnel. In Knowledge Management and Competitive Advantage: Issues and Potential Solutions. Hershey: IGI Global, pp. 256–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kotaskova, Anna, Jaroslav Belás, Yuriy Bilan, and Khurram Ajaz Khan. 2020. Significant Aspects of Managing Personnel Risk in the SME Sector. Management and Marketing 15: 203–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlova, Olga, Mariya Makarova, and Zhanna Mingaleva. 2016. Corporative social responsibility as a factor of reducing the occupational health risk of personnel. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research 14: 10981–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lishchuk, Elena N., and Elena A. Zolotareva. 2017. Assessing the personnel-related risks in the audit of material misstatements in financial reporting. In Modern Trends in the Theory and Practice of Economic Analysis, Accounting, Financial Management. Collection of Materials of the International Scientific Conference. Edited by Elena N. Lishchuk, Elena I. Leonenko, Ekaterina S. Eremenko, Vera A. Surovtseva, Maria K. Chernyakova and Ludmila P. Nagovitsina. Novosibirsk: Siberian University of Consumer Cooperation, pp. 119–26. [Google Scholar]
- Manakhova, Irina, Ekaterina Levchenko, Veronika Bekher, and Andrey Bystrov. 2020. Quality of human resources and personnel security risk management in digital economy. Quality Access to Success 21: 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Masár, Matej, and Mária Hudáková. 2020. Personnel Risks and Their Impact on Business in the Transport Sector in Slovakia. Conference: Transport Means, 142–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrofanova, Alexandra E. 2003. The Concept of Personnel Risk Management in Working with the Personnel of the Organization [Text]. Moscow: Competence, vol. 3, pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Paurova, Veronika, Darina Chlebikova, and Juraj Kolencik. 2020. Management of psychosocial risks as part of personnel management. Paper presented at the 33rd International Business Information Management Association Conference, IBIMA 2019: Education Excellence and Innovation Management through Vision, Granada, Spain, April 10–11; pp. 9618–962. [Google Scholar]
- Polyanin, Andrey, Lydmila Proniayeva, Viktor Matveyev, Anna Amelina, and Maria Klevtsova. 2018. Personnel risks management in the competency approach at state service bodies. Paper presented at the 32nd International Business Information Management Association Conference, IBIMA 2018—Vision 2020: Sustainable Economic Development and Application of Innovation Management from Regional expansion to Global Growth, Seville, Spain, November 15–16; pp. 2376–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rozsa, Zoltan, Jaroslav Belas, Khurram Ajaz Khan, and Katarina Zvarikova. 2021. Corporate social responsibility and essential factors of personnel risk management in smes. Polish Journal of Management Studies 23: 449–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpilina, Tatyana M., Sergey G. Erokhin, and Maria V. Abramova. 2019. Personnel risks of the knowledge economy: On the example of science-based companies. Paper presented at the 33rd International Business Information Management Association Conference, IBIMA 2019: Education Excellence and Innovation Management through Vision, Granada, Spain, April 10–11; pp. 1033–39. [Google Scholar]
- Solovova, Natalya V., Natalia V. Sukhankina, and Dmitriy G. Slatov. 2021. HR risks management in the context of labour market precarization. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems 161: 633–43. [Google Scholar]
- Swartz, Paulus, Adele Da Veiga, and Nico Martins. 2021. Validating an information privacy governance questionnaire to measure the perception of employees. Information and Computer Security 29: 761–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapman, Leonid N. 2002. Risks in Economics: Studies. Handbook for Universities. Moscow: L.N. Tapman.–UNITY-DANA. [Google Scholar]
- Tikhonov, Alexey. 2020. Modem approaches to the integrated assessment of personnel risks of an industrial enterprise. Research in World Economy 11: 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselyutina, Tatyana V., Olga A. Timokhina, Tatyana A. Vlasova, and Yana V. Maslova. 2019. Development of the personnel risks assessment and supply chain strategy as a basis of the risk management system of modern organizations. International Journal of Supply Chain Management 8: 1030. [Google Scholar]
- Veres, Oleh, Pavlo Ilchuk, Olha Kots, Ihor Rishnyak, and Halyna Rishniak. 2020. Choosing a means of implementing an information system to minimize the risks of personnel management. Paper presented at 2020 IEEE 15th International Scientific and Technical Conference on Computer Sciences and Information Technologies, CSIT 2020, Zbarazh, Ukraine, September 23–26; pp. 127–30. [Google Scholar]
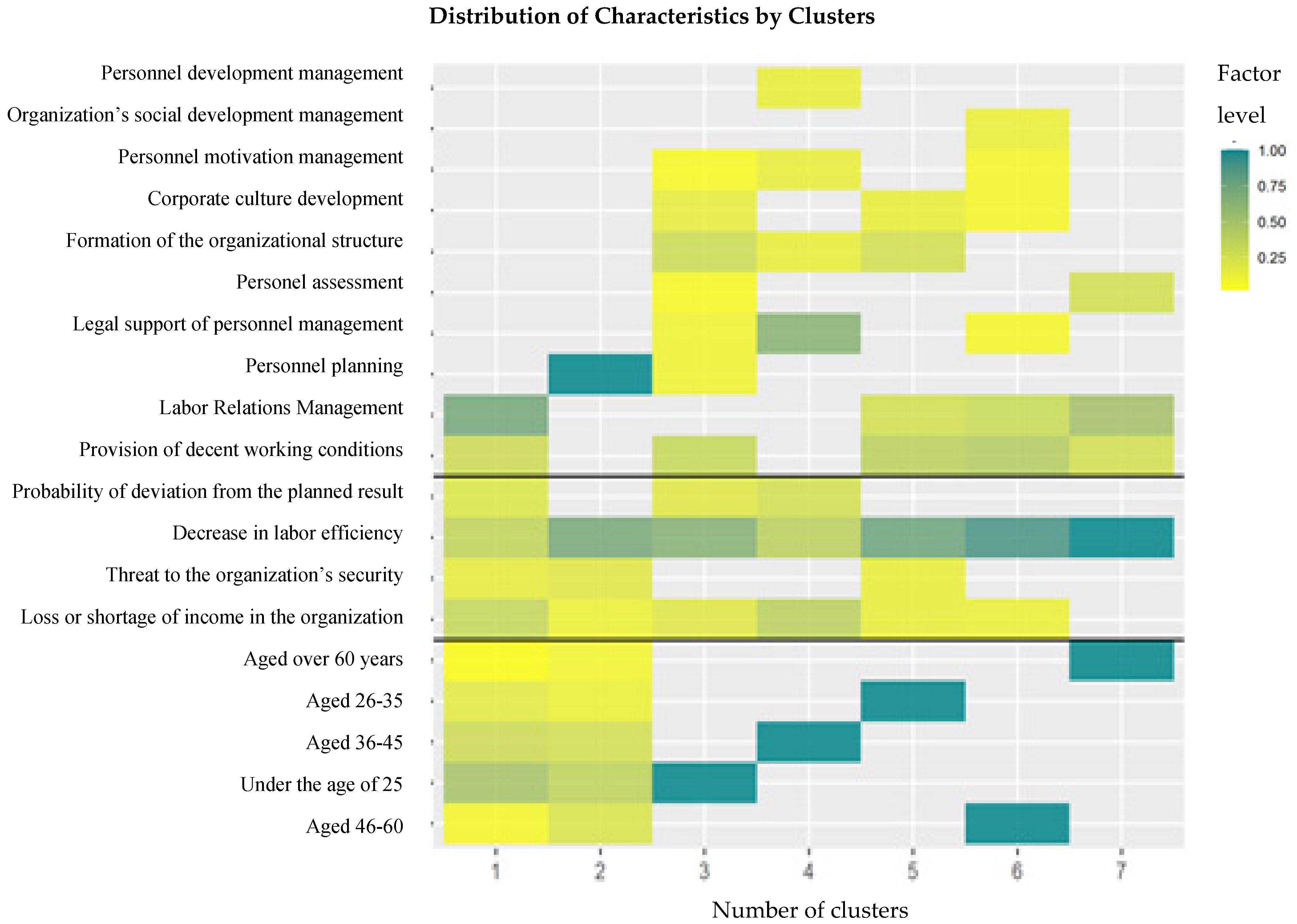
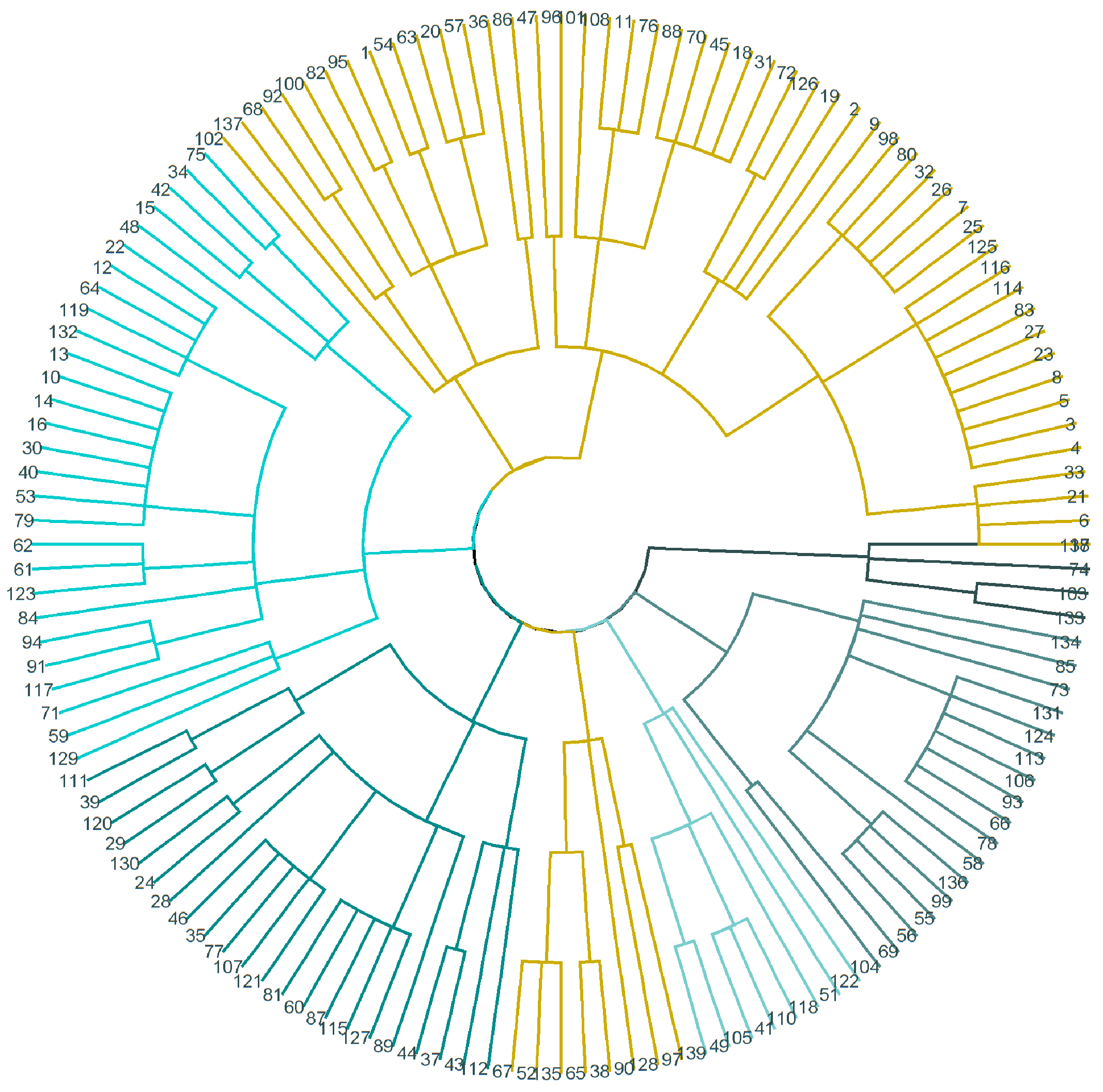
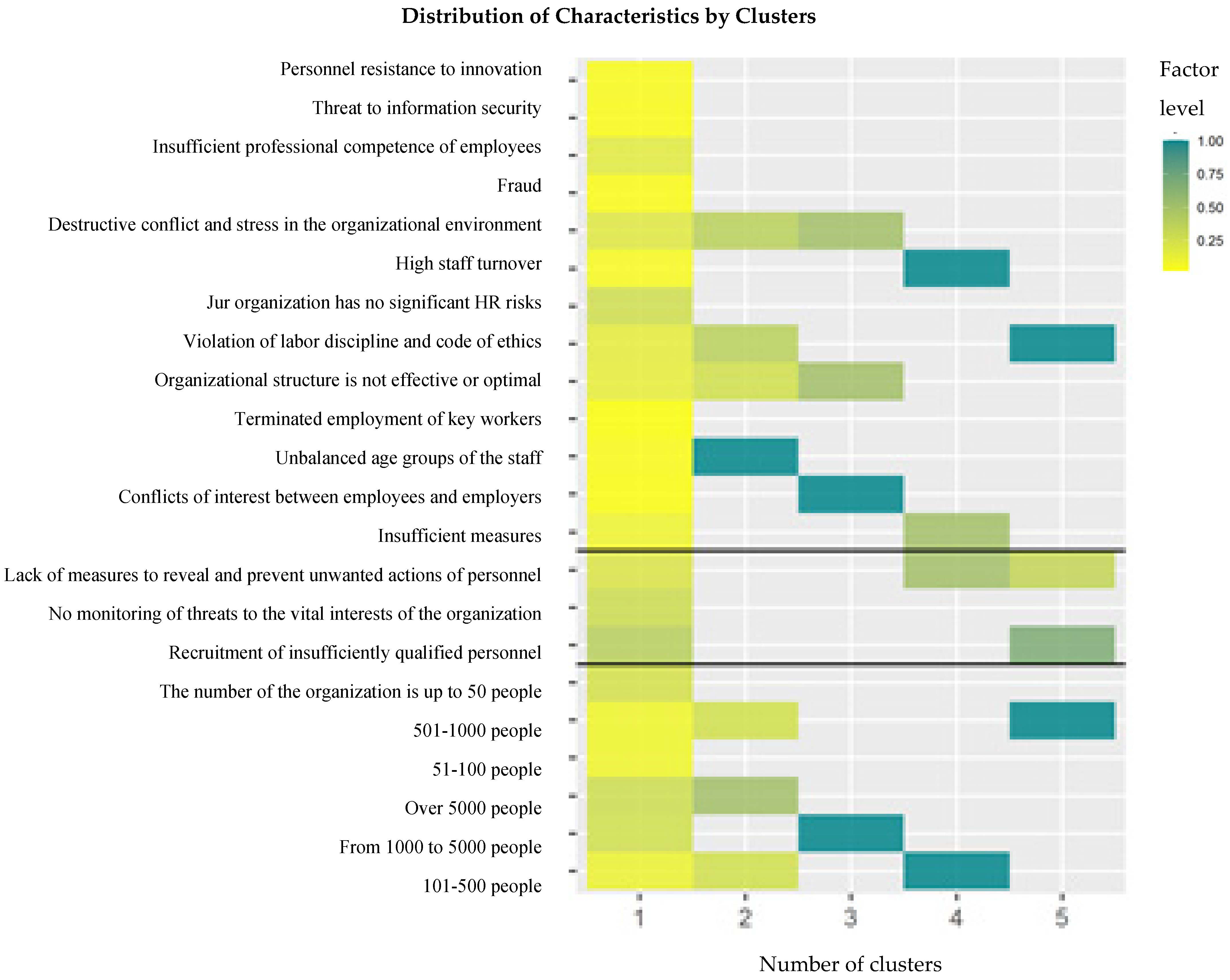
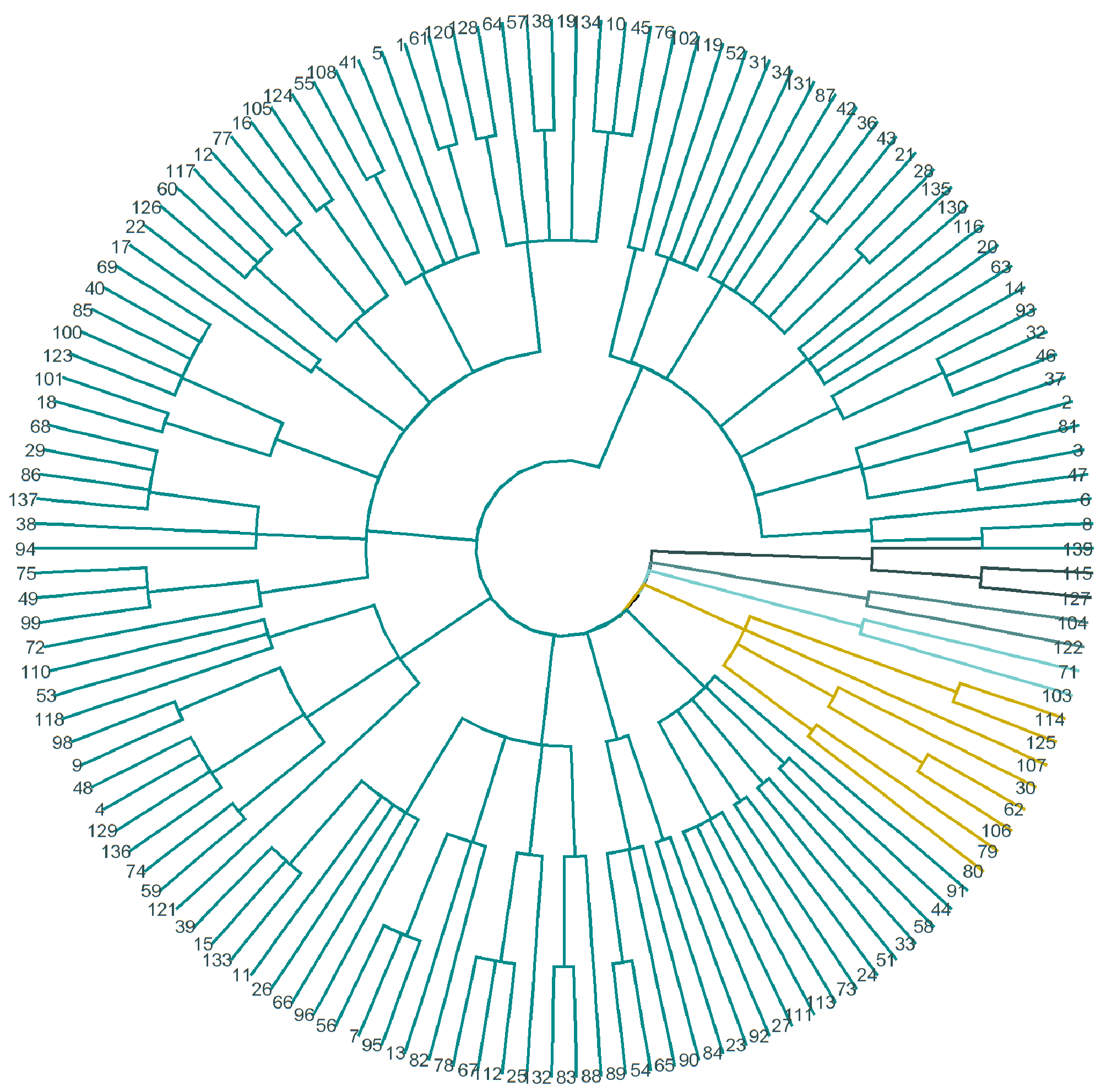
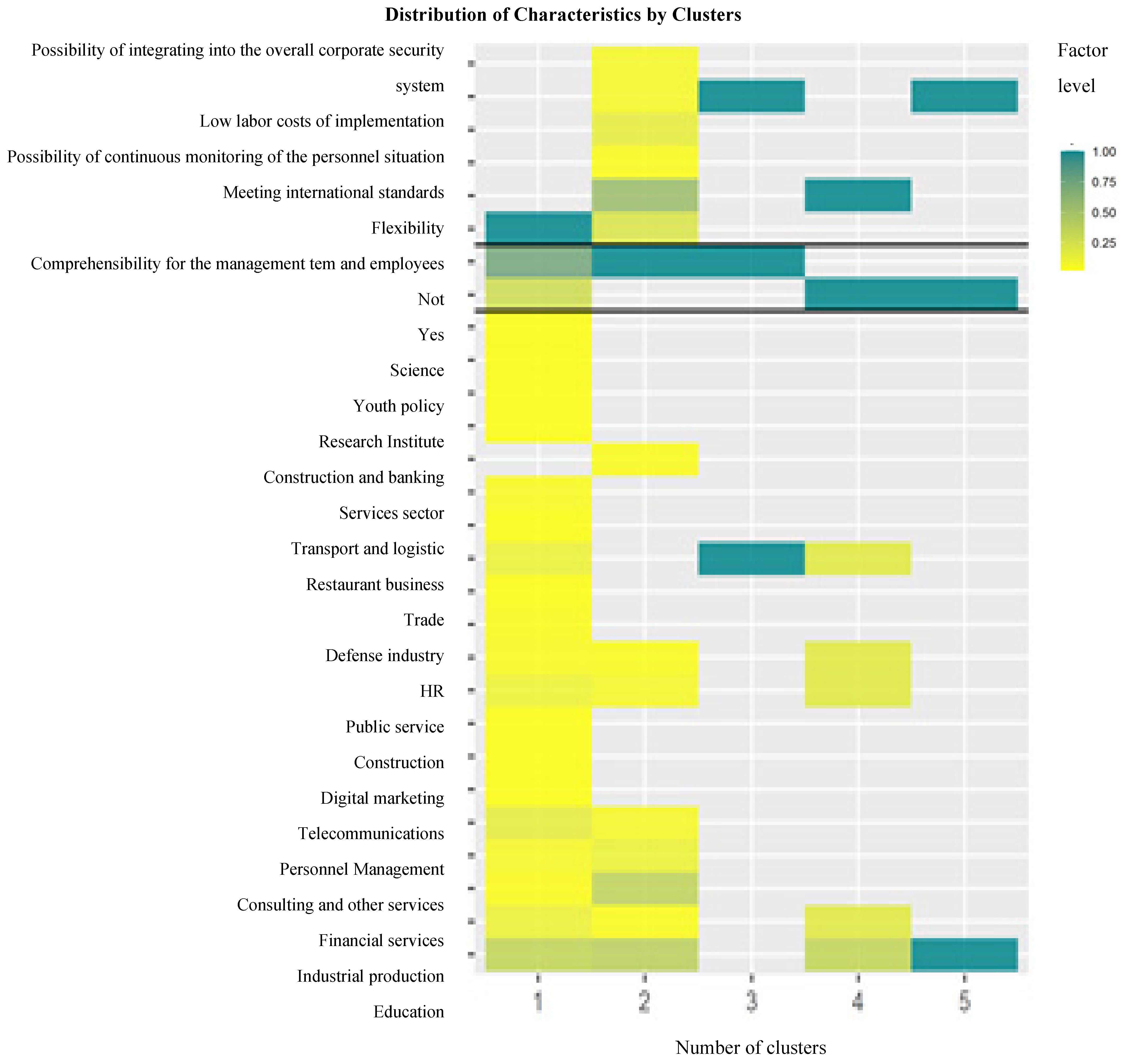
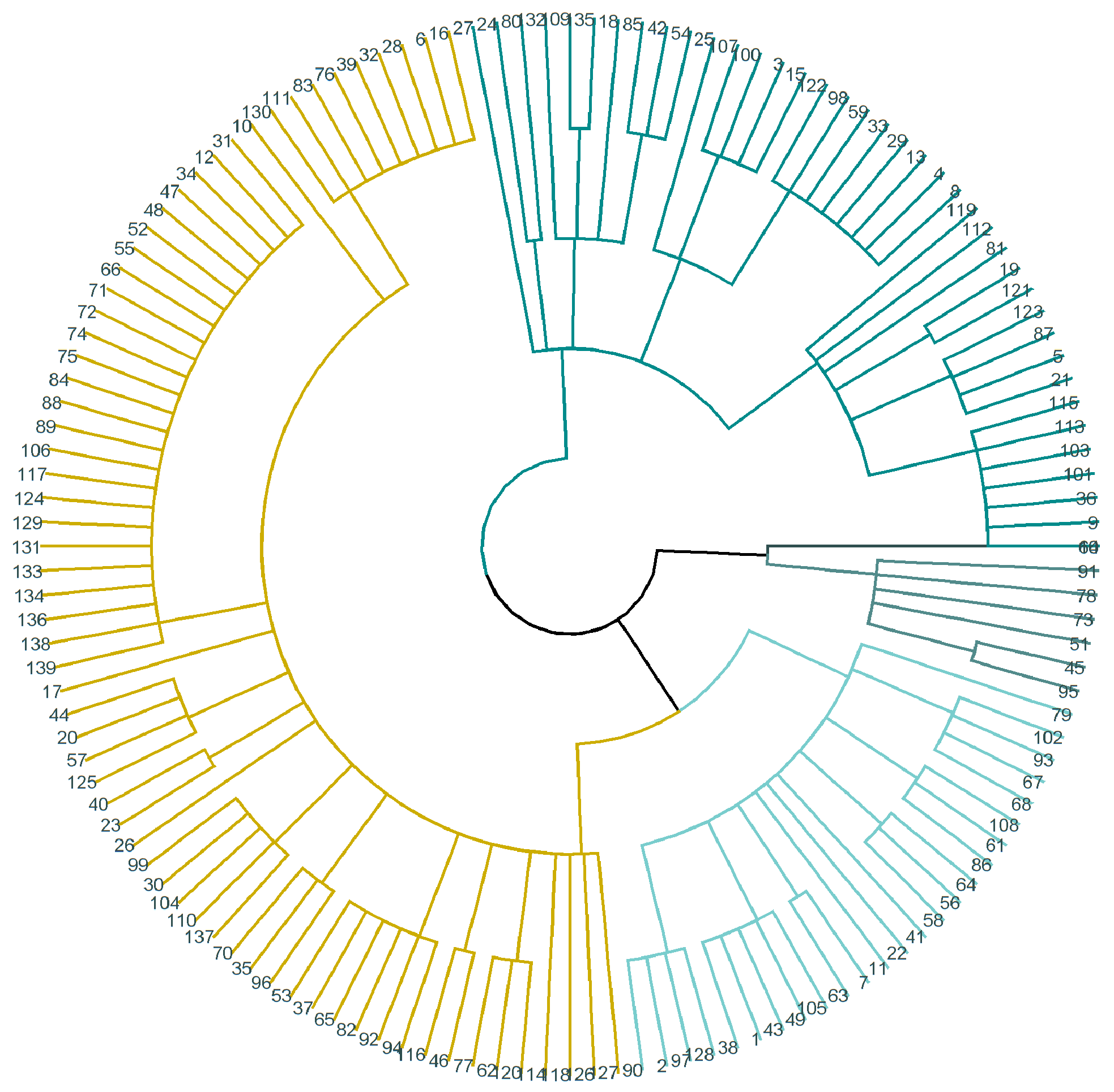
| Group | I | II | III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of clusters | 7.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Sum of squared distances between observations in the cluster (Gower’s distance.) | 25.32 | 35.94 | 17.65 |
| Average silhouette width (si) | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.50 |
| Size of cluster 1, people | 21.00 | 16.00 | 25.00 |
| Size of cluster 2, people | 9.00 | 32.00 | 20.00 |
| Size of cluster 3, people | 70.00 | 67.00 | 86.00 |
| Size of cluster 4, people | 14.00 | 9.00 | 4.00 |
| Size of cluster 5, people | 9.00 | 15.00 | 4.00 |
| Size of cluster 6, people | 2.00 | ||
| Size of cluster 7, people | 14.00 |
| Stage | Content | Measures |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Analytical | 1.1 Analyze the external and internal environment of the organization. 1.2 Form a strategy for HR risk management. 1.3 Benchmarking |
| 2 | Development of a consistent vision of the organization’s future | 2.1 Determine the key competences of the organization. 2.2 Set goals and objectives of HR risk management. 2.3 Determine the needs of HR risk management subjects (information–analytical, administrative, etc.) 2.4 Determine metrics for evaluating the results of HR risk management. |
| 3 | Investment and formation of personnel by the organization | 3.1 Search for and attract talent on the external and internal labor market. 3.2 Conclude labor relations and additional agreements. 3.3 Teach and develop the personnel. 3.4 Create favorable working conditions. 3.5 Develop a corporate culture to support the process of HR risk management. 3.6 Develop the employer’s brand |
| 4 | Personnel use | 4.1 Assess human capital and talents (potential and results). 4.2 Develop and introduce an incentive system. |
| 5 | Personnel accumulation | 5.1 Plan the careers and success of the organization’s workers. 5.2 Retain talent through incentives, increased involvement, loyalty, and job satisfaction |
| 6 | Personnel reproduction | 6.1 Succession planning. 6.2 Work with the personnel reserve. 6.3 Transfer experience through mentoring. |
| 7 | Result assessment and continuous improvement | 7.1 Evaluate the efficiency of HR risk management and profitability. 7.2 Audit the personnel and HR risks. 7.3 Continuously improve the system. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babkin, I.; Pulyaeva, V.; Ivanova, I.; Veys, Y.; Makhmudova, G. Developing a System for Monitoring Human Resource Risks in a Digital Economy. Risks 2023, 11, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks11050082
Babkin I, Pulyaeva V, Ivanova I, Veys Y, Makhmudova G. Developing a System for Monitoring Human Resource Risks in a Digital Economy. Risks. 2023; 11(5):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks11050082
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabkin, Ivan, Valentina Pulyaeva, Irina Ivanova, Yulya Veys, and Guljakhon Makhmudova. 2023. "Developing a System for Monitoring Human Resource Risks in a Digital Economy" Risks 11, no. 5: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks11050082
APA StyleBabkin, I., Pulyaeva, V., Ivanova, I., Veys, Y., & Makhmudova, G. (2023). Developing a System for Monitoring Human Resource Risks in a Digital Economy. Risks, 11(5), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/risks11050082






