The Role of Arthroereisis in Improving Sports Performance, Foot Aesthetics and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Flexible Flatfoot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
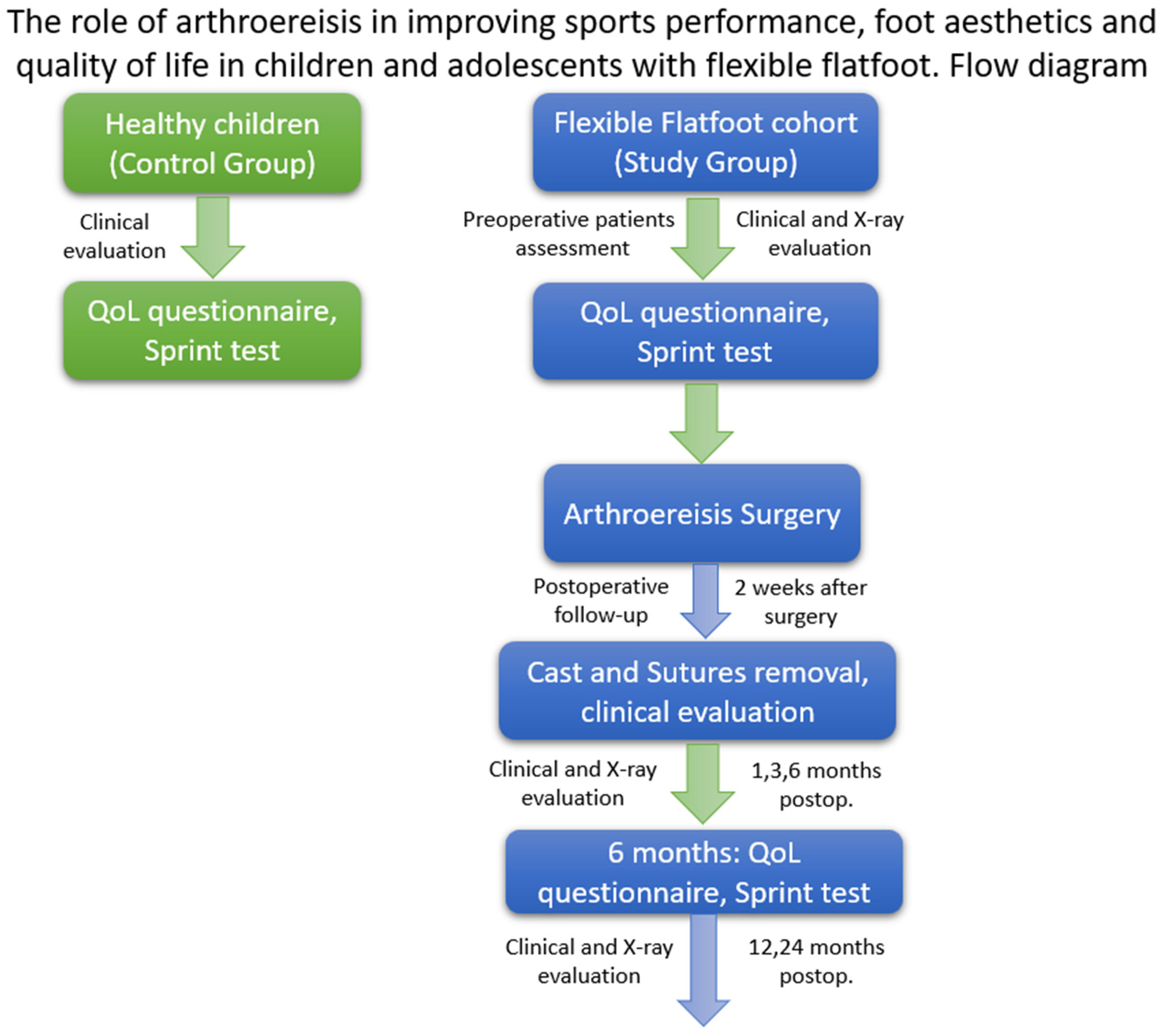
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Study Procedure
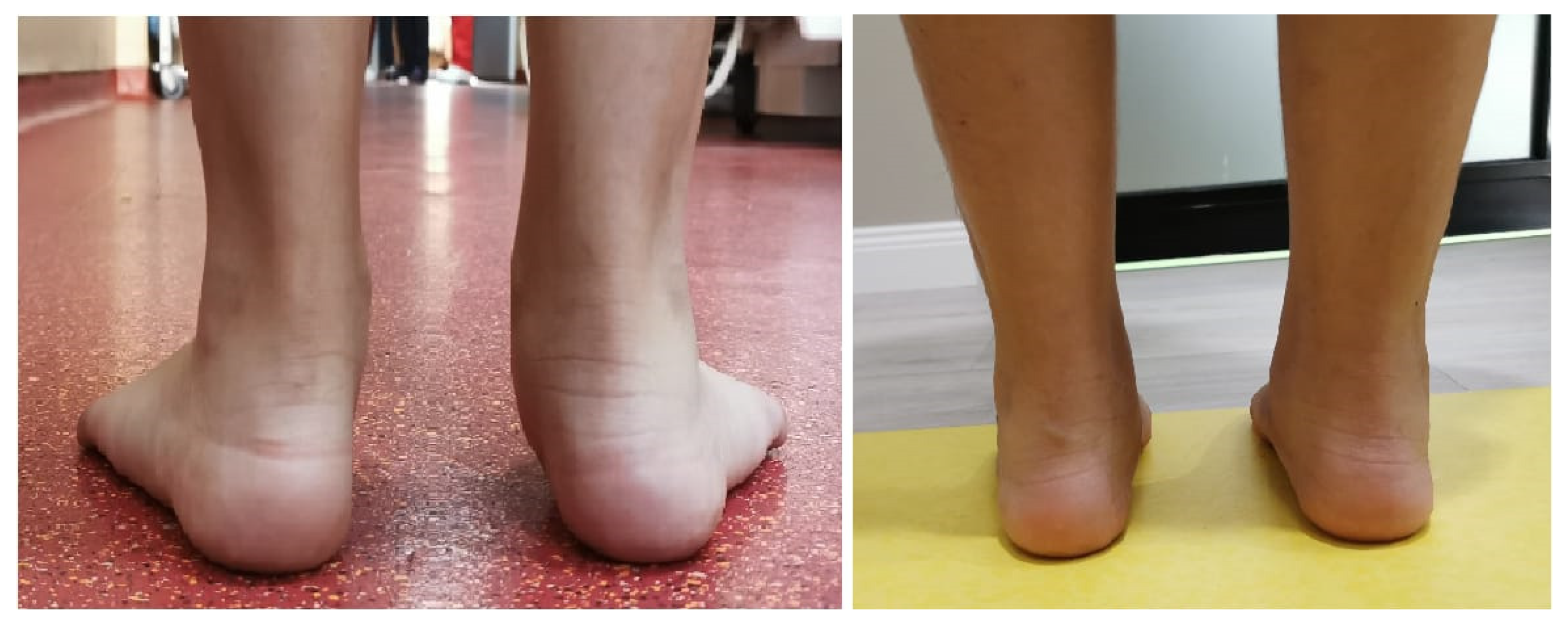
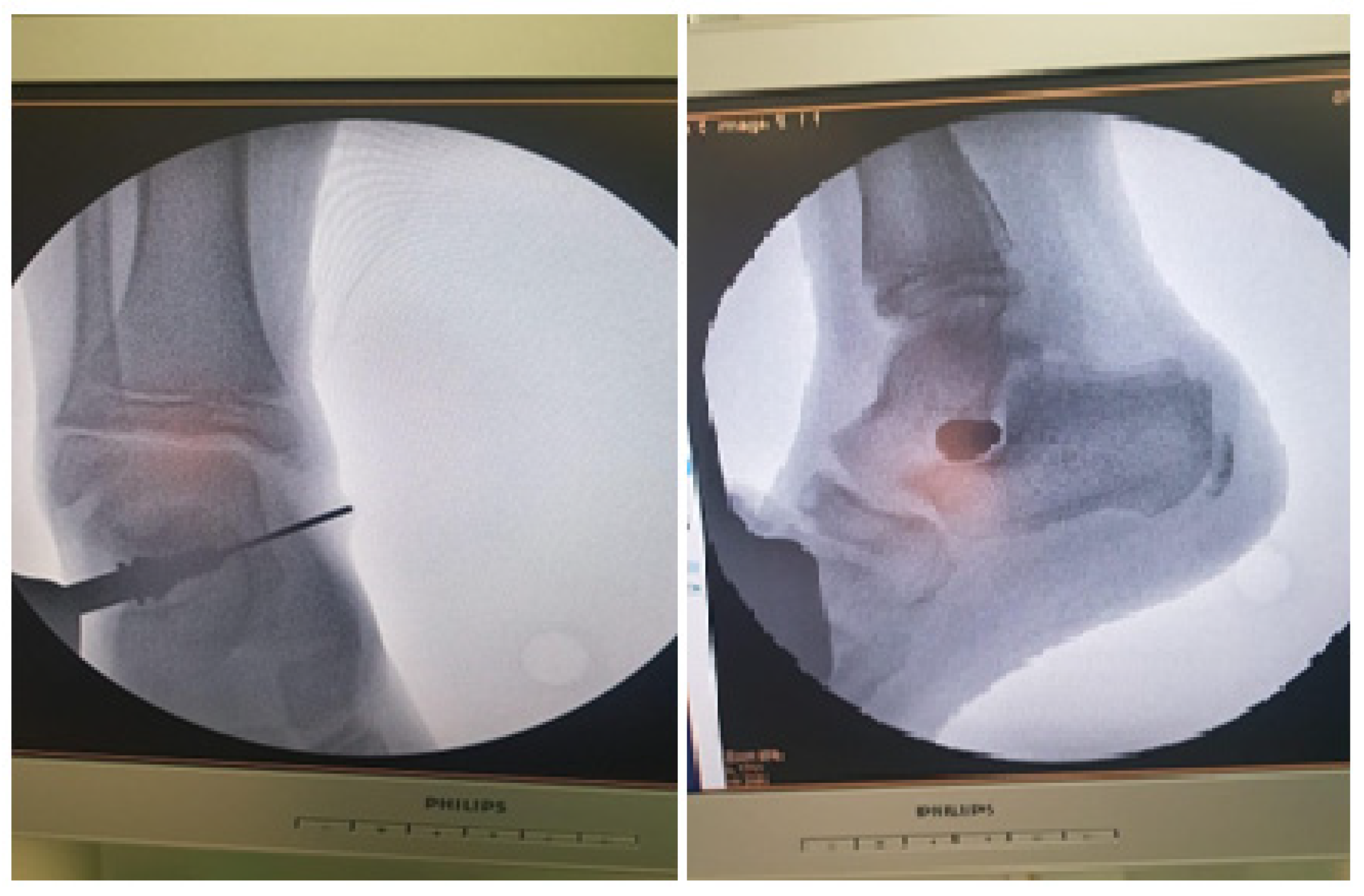
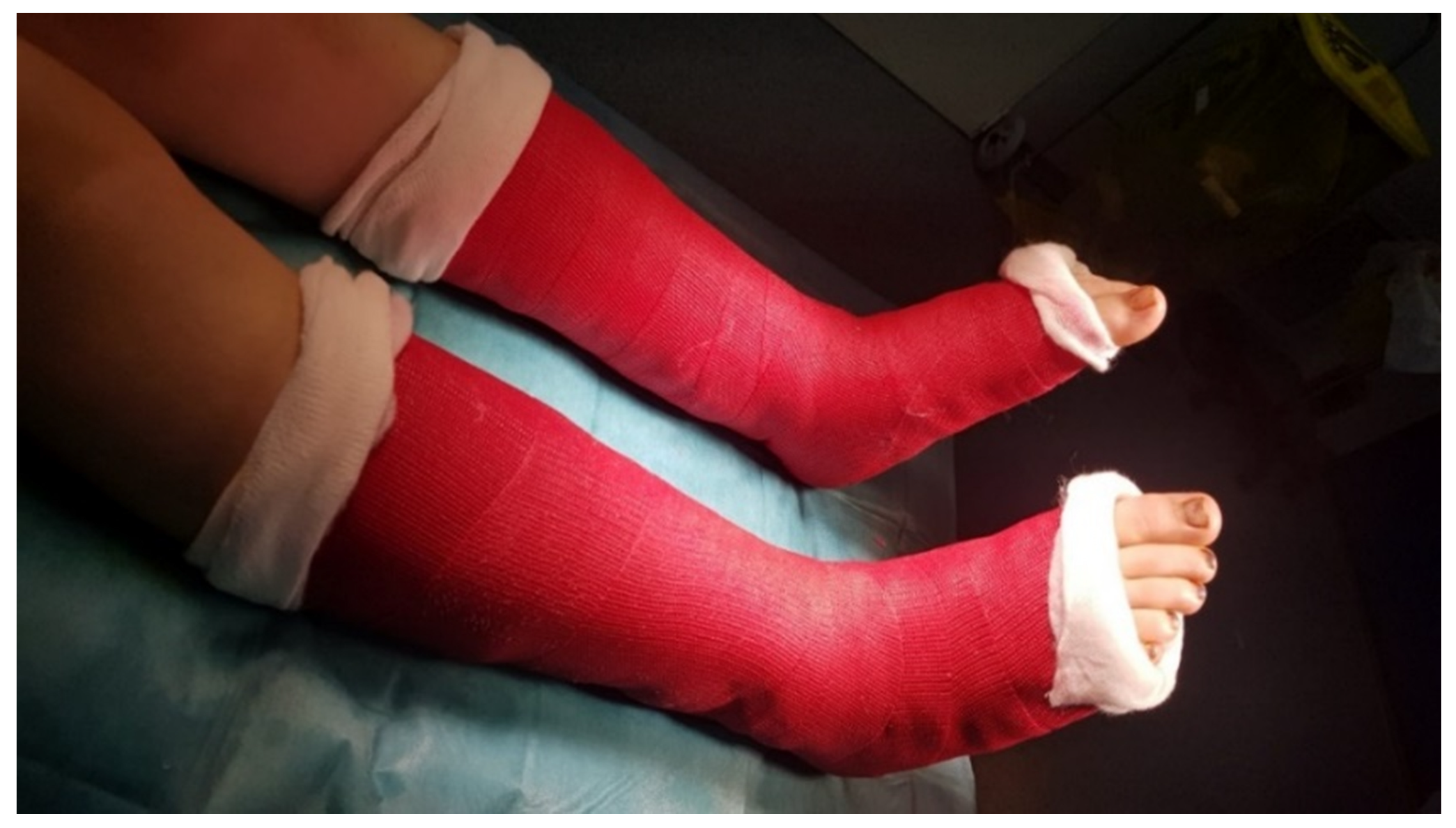
2.4. Surgical Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Needleman, R.L. Current topic review: Subtalar arthroereisis for the correction of flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005, 26, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyting, S. King Tut Felled by His Feet, Not His Foes. The Globe and Mail. 16 February 2010. Available online: www.theglobeandmail.com/technology/science/king-tut-felled-by-his-feet-not-his-foes/article4306421 (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Pourghasem, M.; Kamali, N.; Farsi, M.; Soltanpour, N. Prevalence of flatfoot among school students and its relationship with BMI. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2016, 50, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jay, R.M.; Din, N. Correcting pediatric flatfoot with subtalar arthroereisis and gastrocnemius recession: A retrospective study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, S.E.; Scannell, B.P. Pediatric Flatfoot: Pearls and Pitfalls. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017, 22, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, V.S. Flexible flatfoot in children and adolescents. J. Child. Orthop. 2010, 4, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spratley, E.M.; Matheis, E.A.; Hayes, C.W.; Adelaar, R.S.; Wayne, J.S. Validation of a population of patient-specific adult acquired flatfoot deformity models. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2013, 31, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.H. Pes cavus and pes planus: Analyses and Treatment. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raj, M.A.; Tafti, D.; Kiel, J. Pes Planus; [Updated 5 February 2022]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, January 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430802/ (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Yontar, N.S.; Ogut, T.; Guven, M.F.; Botanlioglu, H.; Kaynak, G.; Can, A. Surgical treatment results for flexible flatfoot in adolescents. Acta Orthop. Et Traumatol. Turc. 2016, 50, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levine, D.F.; Richards, J.; Whittle, M. Whittle’s Gait Analysis Whittle’s Gait Analysis Elsevier Health Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-0702042652. [Google Scholar]
- Dicharry, J. Kinematics and Kinetics of Gait: From Lab to Clinic. Clin. Sports Med. 2010, 29, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, S.; Catani, F.; Benedetti, M.; Leardini, A. Gait Analysis: Methodologies and Clinical Applications; BTS Bioengineering Technology and Systems: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Video Gait Analysis. Total Foot Health. 26 May 2022. Available online: https://totalfoothealth.co.uk/biomechanics/video-gait-analysis (accessed on 17 March 2022).
- Sadeghi-Demneh, E.; Jafarian, F.; Melvin, J.M.; Azadinia, F.; Shamsi, F.; Jafarpishe, M. Flatfoot in school-age children: Prevalence and associated factors. Foot Ankle Spec. 2015, 8, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, U.B.; Joseph, B. The influence of footwear on the prevalence of flat foot. A survey of 2300 children. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 1992, 74, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, H. Growing pains. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 33, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canada: Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada, Ghana: Recruitment Criteria for the Ghanaian Armed Forces (Age, Preferred Educational, Professional or Ethnic Profiles, Promotion, Practice of Rewarding Individuals with Positions in the Army), 1 June 1999, GHA32053.E. Available online: https://www.refworld.org/docid/3ae6aad68c.html (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Dars, S.; Uden, H.; Banwell, H.A.; Kumar, S. The effectiveness of non-surgical intervention (Foot Orthoses) for paediatric flexible pes planus: A systematic review: Update. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwell, H.A.; Mackintosh, S.; Thewlis, D.; Landorf, K.B. Consensus-based recommendations of Australian podiatrists for the prescription of foot orthoses for symptomatic flexible pes planus in adults. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2014, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, L.S.; Redmond, A.C.; Landorf, K.B.; Rome, K.; Keenan, A.-M.; Waxman, R.; Alcacer-Pitarch, B.; Siddle, H.J.; Backhouse, M.R. A survey of foot orthoses prescription habits amongst podiatrists in the UK, Australia and New Zealand. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herchenröder, M.; Wilfling, D.; Steinhäuser, J. Evidence for foot orthoses for adults with flatfoot: A systematic review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2021, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Hong, W.H.; Suh, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Lee, D.J.; Lee, Y.J. The long-term structural effect of orthoses for pediatric flexible flat foot: A systematic review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.C.; Kim, M.O.; Kim, H.S.; Hong, S.E. Changes in Resting Calcaneal Stance Position Angle Following Insole Fitting in Children with Flexible Flatfoot. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanatli, U.; Aktas, E.; Yetkin, H. Do corrective shoes improve the development of the medial longitudinal arch in children with flexible flat feet? J. Orthop. Sci. 2016, 21, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, V.; De Maio, F.; Caterini, A.; Marsiolo, M.; Petrungaro, L.; Ippolito, E.; Farsetti, P. Surgical Treatment of Severe Idiopathic Flexible Flatfoot by Evans-Mosca Technique in Adolescent Patients: A Long-Term Follow-Up Study. Adv. Orthop. 2021, 2021, 8843091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, D.S. An extra-articular arthrodesis of the subastragalar joint for correction of paralytic flat feet in children. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1952, 34, 927–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraldsson, S. Pes Plano-Valgus staticus juvenilis and its operative treatment. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1965, 35, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.R. The operative treatment of hypermobile flatfeet in the young child. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1977, 122, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.F. An operation for the correction of flexible flat feet of adolescents. West. J. Surg. Obstet. Gynecol. 1946, 54, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bernasconi, A.; Lintz, F.; Sadile, F. The role of arthroereisis of the subtalar joint for flatfoot in children and adults. EFORT Open Rev. 2017, 2, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, M.S. Tarsal coalition. In Comprehensive Textbook of Foot Surgery: Volume 1; McGlamry, E.D., Banks, A.S., Downey, M.S., Eds.; Williams Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jack, E.A. Naviculo-cuneiform fusion in the treatment of flat foot. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1953, 35, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free Online AOFAS Ankle-Hindfoot Scale Calculator, Orthotoolkit, [Online]. Available online: https://orthotoolkit.com/aofas-ankle-hindfoot/ (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- D’agostino, R.B.; Belanger, A.; D’Agostino, R.B., Jr. A suggestion for using powerful and informative tests of normality. Am. Stat. 1990, 44, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- William, S. The probable error of a mean. Biometrika 1908, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, W.J. Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 3rd ed.; John Wiley Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; p. 350. ISBN 0-471-16068-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether one of Two Random Variables is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.; Mosca, V.S.; Zionts, L.E. What’s New in Pediatric Flatfoot? J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2016, 36, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.M.; Rome, K. A Cochrane review of the evidence for non-surgical interventions for flexible pediatric flat feet. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 47, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jane MacKenzie, A.; Rome, K.; Evans, A.M. The efficacy of nonsurgical interventions for pediatric flexible flat foot: A critical review. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2012, 32, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, R.L.; Peng, H.L.; Lee, W.C. Short-term effects of customized arch support insoles on symptomatic flexible flatfoot in children: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2018, 97, e10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, N.; Bianchi, A.; Martinkevich, P.; Sartorelli, E.; Romeo, G.; Bonifacini, C.; Malerba, F. Return to sport activities after subtalar arthroereisis for correction of pediatric flexible flatfoot. J. Pediatr. Orthop. Part B 2018, 27, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhuang, G.; Liang, X.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Fan, X.; Cao, Y. Flexible flatfoot of 6-13-year-old children: A cross-sectional study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Lee, C.-C.; Tseng, T.-H.; Wu, K.-W.; Chang, J.-F.; Wang, T.-M. Body Weight Effects on Extra-Osseous Subtalar Arthroereisis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abich, Y.; Mihiret, T.; Akalu, T.Y.; Gashaw, M.; Janakiraman, B. Flatfoot and associated factors among Ethiopian school children aged 11 to 15 years: A school-based study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldívar-Cerón, H.I.; Ramírez, A.G.; Acevedo, M.A.R.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P. Obesidad infantil: Factor de riesgo para desarrollar pie plano [Childhood obesity: A risk factor for development of flatfoot]. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2015, 72, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megremis, P.; Megremis, O. Arthroereisis for Symptomatic Flexible Flatfoot Deformity in Young Children: Radiological Assessment and Short-Term Follow-Up. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019, 58, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández de Retana, P.; Álvarez, F.; Viladot, R. Subtalar Arthroereisis in Pediatric Flatfoot Reconstruction. Foot Ankle Clin. 2010, 15, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, S.; Ceccarelli, F.; Benedetti, M.G.; Catani, F.; Faldini, C. Surgical treatment of flexible flatfoot in children a four-year follow-up study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2001, 83, S73–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, P.R.; Lara, M.H. Giannini Prosthesis for Flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005, 26, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaret, D.I.; Myerson, M.S. Arthroerisis of the subtalar joint. Foot Ankle Clin. 2003, 8, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.C.; Haycock, D.M.; Little, E.R. Flexible flatfoot treatment with arthroereisis: Radiographic improvement and child health survey analysis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2004, 43, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Nguyen, A. Preliminary radiographic findings and sizing implications on patients undergoing bioabsorbable subtalar arthroereisis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2007, 46, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Group | Control Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total: | 33 Patients (19 M, 14 F) | 36 Children (20 M, 16 F) | |||||
| Age (years) | BMI | QoL | Age (years) | BMI | QoL | ||
| Preoperative values: | Average | 11.93 | 19.1 | 37.39 | 11.72 | 17.01 | 98.02 |
| S.D. | 1.56 | 3.15 | 14.2 | 1.89 | 1.84 | 0.5 | |
| 95% CI | 11.93 ± 0.55 | 19.1 ± 1.11 | 37.39 ± 5.03 | 11.72 ± 0.64 | 17.01 ± 0.62 | 98.02 ± 1.02 | |
| Postoperative values: | Average | 12.43 | 19.44 | 98.84 | |||
| S.D. | 1.56 | 2.39 | 2.29 | ||||
| 95% CI | 12.43 ± 0.55 | 19.44 ± 0.85 | 98.84 ± 0.81 | ||||
| p | 0.54 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||||
| Study Group | Control Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative Data | Postoperative Data | ||
| Number of patients | 33 | 33 | 36 |
| Mean time (s) | 24.55 | 22.30 | 20.94 |
| S.D. | 1.95 | 1.87 | 3.20 |
| Max. time (s) | 29.02 | 25.18 | 23.61 |
| Min. time (s) | 19.00 | 18.30 | 14.96 |
| CI 95% | [23.7, 24.3] | [21.7, 22.3] | [19, 21] |
| p | <0.0001 | 0.01 | |
| Preoperative | Postoperative | Wilcoxon Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | Max. | Median | CI 95% | Min. | Max. | Median | CI 95% | p Value | ||
| Pitch (left) | 10° | 30° | 15° | [16.52 ± 1.45] | Pitch (left) | 12° | 30° | 19° | [19.18 ± 1.35] | <0.0001 |
| Pitch (right) | 9° | 28° | 15° | [16.67 ± 1.59] | Pitch (right) | 12° | 28° | 19° | [19.42 ± 1.45] | <0.0001 |
| Meary (left) | 2° | 24° | 10° | [10.76 ± 1.63] | Meary (left) | −1° | 9° | 1° | [2 ± 0.71] | <0.0001 |
| Meary (right) | 2° | 20° | 11° | [10.42 ± 1.7] | Meary (right) | 0° | 6° | 2° | [2.06 ± 0.549] | <0.0001 |
| Kite face (left) | 19° | 61° | 36° | [37.3 ± 3.41] | Kite face (left) | 17° | 39° | 25° | [27 ± 2.18] | <0.0001 |
| Kite face (right) | 21° | 52° | 35° | [35.94 ± 3.15] | Kite face (right) | 14° | 40° | 27° | [27.7 ± 2.27] | <0.0001 |
| Kite profile (left) | 31° | 66° | 56° | [53.76 ± 2.79] | Kite profile (left) | 26° | 58° | 49° | [47.15 ± 2.58] | <0.0001 |
| Kite profile (right) | 34° | 66° | 55° | [52.94 ± 2.33] | Kite profile (right) | 27° | 56° | 48° | [46.64 ± 2.39] | <0.0001 |
| Talonavicular coverage angle (left) | 5° | 35° | 21° | [20.36 ± 3.08] | Talonavicular coverage angle (left) | 1° | 16° | 6° | [6.15 ± 1.16] | <0.0001 |
| Talonavicular coverage angle (right) | 5° | 39° | 19° | [19.36 ± 3.11] | Talonavicular coverage angle (right) | 0° | 15° | 5° | [5.36 ± 1.12] | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herdea, A.; Neculai, A.-G.; Ulici, A. The Role of Arthroereisis in Improving Sports Performance, Foot Aesthetics and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Flexible Flatfoot. Children 2022, 9, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9070973
Herdea A, Neculai A-G, Ulici A. The Role of Arthroereisis in Improving Sports Performance, Foot Aesthetics and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Flexible Flatfoot. Children. 2022; 9(7):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9070973
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerdea, Alexandru, Adrian-Gabriel Neculai, and Alexandru Ulici. 2022. "The Role of Arthroereisis in Improving Sports Performance, Foot Aesthetics and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Flexible Flatfoot" Children 9, no. 7: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9070973
APA StyleHerdea, A., Neculai, A.-G., & Ulici, A. (2022). The Role of Arthroereisis in Improving Sports Performance, Foot Aesthetics and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Flexible Flatfoot. Children, 9(7), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9070973








