Multidisciplinary Treatment for Childhood Obesity: A Two-Year Experience in the Province of Naples, Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Setting
2.2. Intervention and Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analyses
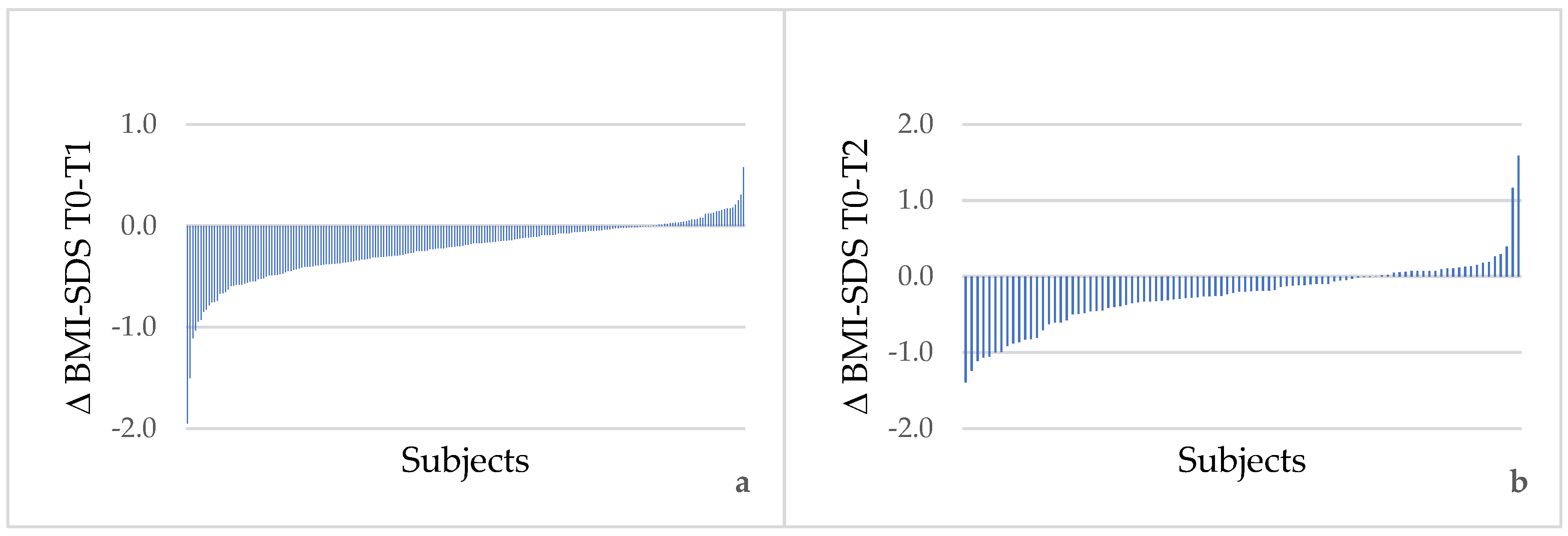
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Obesity and overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Freemark, M. Childhood obesity in the modern age: Global trends, determinations, complications, and costs. In Pediatric Obesity: Etiology, Pathogenesis and Treatment; Freemark, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wilding, S.; Ziauddeen, N.; Smith, D.; Roderick, P.; Chase, D.; Alwan, N.A. Are environmental area characteristics at birth associated with overweight and obesity in school-aged children? Findings from the SLOPE (Studying Lifecourse Obesity PrEdictors) population-based cohort in the south of England. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Falconer, C.; Viner, R.M.; Kinra, S. The impact of childhood obesity on morbidity and mortality in adulthood: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandoni, M.; Calcaterra, V.; Carnevale Pellino, V.; De Silvestri, A.; Marin, L.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Tranfaglia, V.; Giuriato, M.; Codella, R.; Lovecchio, N. An Italian Cross-Sectional Study. Children 2021, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Kovacs, V.A.; Yngve, A.; Spiroski, I.; Obreja, G.; Starc, G.; Pérez, N.; Rito, A.I.; Kunešová, M.; et al. Prevalence of Severe Obesity among Primary School Children in 21 European Countries. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italian Institute of Health. Okkio Alla Salute. Indagine 2019. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/okkioallasalute/indagine-2019 (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Rahman A, M.; Chandrasekaran, B. Estimating the Impact of the Pandemic on Children’s Physical Health: A Scoping Review. J. Sch. Health 2021, 91, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Report of the Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity. In Implementation Plan: Executive Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Spear, B.A.; Barlow, S.E.; Ervin, C.; Ludwig, D.S.; Saelens, B.E.; Schetzina, K.E.; Taveras, E.M. Recommendations for treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics 2007, 120, S254–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valerio, G.; Maffeis, C.; Saggese, G.; Ambruzzi, M.A.; Balsamo, A.; Bellone, S.; Bergamini, M.; Bernasconi, S.; Bona, G.; Calcaterra, V.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of pediatric obesity: Consensus position statement of the Italian Society for Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology and the Italian Society of Pediatrics. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cade, J.; Thompson, R.; Burley, V.; Warm, D. Development, validation and utilization of food-frequency questionnaires—A review. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES): Anthropometry Procedures Manual; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Frisancho, A.R. Anthropometric Standards: An Interactive Nutritional Reference of Body Size and Body Composition for Children and Adults; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciari, E.; Milani, S.; Balsamo, A.; Spada, E.; Bona, G.; Cavallo, L.; Cerutti, F.; Gargantini, L.; Greggio, N.; Tonini, G.; et al. Italian cross-sectional growth charts for height, weight and BMI (2 to 20 yr). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO child growth standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 450, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, A.C.; Bartok, C.; Schoeller, D.A. The validity of bioelectrical impedance models in clinical populations. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2004, 19, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prochaska, J.O.; Di Clemente, C.C. Transtheoretical therapy: Toward a more integrative model of change. Theory Res. Pract. 1982, 19, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.R.; Rollnick, S. (Eds.) Motivational Interviewing; Preparing People for Change; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Crocker, P.R.; Bailey, D.A.; Faulkner, R.A.; Kowalski, K.C.; McGrath, R. Measuring general levels of physical activity: Preliminary evidence for the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, M.W.; Shields, C.A.; Oh, P.I.; Fowles, J.R. Health care provider confidence and exercise prescription practices of Exercise is Medicine Canada workshop attendees. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Reyes, A.; Cámara-Martos, F.; Molina-Luque, R.; Romero-Saldaña, M.; Molina-Recio, G.; Moreno-Rojas, R. Changes in body composition with a hypocaloric diet combined with sedentary, moderate and high-intense physical activity: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Womens Health. 2019, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiess, W.; Reich, A.; Müller, G.; Galler, A.; Kapellen, T.; Raile, K.; Böttner, A.; Seidel, B.; Kratzsch, J. Obesity in childhood and adolescence: Clinical diagnosis and management. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 14, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Oude Luttikhuis, H.; Baur, L.; Jansen, H.; Shrewsbury, V.A.; O’Malley, C.; Stolk, R.P.; Summerbell, C.D. Interventions for treating obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD001872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gussinyer, S.; García-Reyna, N.I.; Carrascosa, A.; Gussinyer, M.; Yeste, D.; Clemente, M.; Albisu, M. Anthropometric, dietetic and psychological changes after application of the “Niñ@s en movimiento” program in childhood obesity. Med. Clin. 2008, 131, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemet, D.; Oren, S.; Pantanowitz, M.; Eliakim, A. Effects of a Multidisciplinary Childhood Obesity Treatment Intervention on Adipocytokines, Inflammatory and Growth Mediators. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2013, 79, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-García, M.; Alegre, L.M.; García-Cuartero, B.; Bryant, E.J.; Gutin, B.; Ara, I. Effects of a 3-month vigorous physical activity intervention on eating behaviors and body composition in overweight and obese boys and girls. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lek, D.; Haveman-Nies, A.; Bezem, J.; Zainalabedin, S.; Schetters-Mouwen, S.; Saat, J.; Gort, G.; Roovers, L.; van Setten, P. Two-year effects of the community-based overweight and obesity intervention program Gezond Onderweg! (GO!) in children and adolescents living in a low socioeconomic status and multi-ethnic district on Body Mass Index-Standard Deviation Score and quality of life. EclinicalMedicine 2021, 42, 101217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, E.; Davoren, M.P.; Harrington, J.M.; Shiely, F.; Perry, I.J.; McHugh, S.M. Barriers and facilitators to initial and continued attendance at community-based lifestyle programmes among families of overweight and obese children: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wild, C.E.; Rawiri, N.T.; Willing, E.J.; Hofman, P.L.; Anderson, Y.C. Determining barriers and facilitators to engagement for families in a family-based, multicomponent healthy lifestyles intervention for children and adolescents: A qualitative study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, J.; Nosworthy, N.M.; Holt, N.L.; Zwaigenbaum, L.; Avis, J.L.; Rasquinha, A.; Ball, G.D. Attrition and the management of pediatric obesity: An integrative review. Child Obes. 2014, 10, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elvsaas, I.; Giske, L.; Fure, B.; Juvet, L.K. Multicomponent Lifestyle Interventions for Treating Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. J. Obes. 2017, 2017, 5021902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecoraro, P.; Gallè, F.; Muscariello, E.; Di Mauro, V.; Daniele, O.; Forte, S.; Ricchiuti, R.; Liguori, G.; Valerio, G. A telehealth intervention for ensuring continuity of care of pediatric obesity during the COVID-19 lockdown in Italy. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 3502–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsdottir, T.; Njardvik, U.; Olafsdottir, A.S.; Craighead, L.W.; Bjarnason, R. The role of parental motivation in family-based treatment for childhood obesity. Obesity 2011, 19, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T. Effectiveness of lifestyle intervention in overweight children. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zolotarjova, J.; ten Velde, G.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. Effects of multidisciplinary interventions on weight loss and health outcomes in children and adolescents with morbid obesity. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uysal, Y.; Wolters, B.; Knop, C.; Reinehr, T. Components of the metabolic syndrome are negative predictors of weight loss in obese children with lifestyle intervention. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gailite, J.; Apela, D.; Dzīvīte-Krišāne, I.; Gardovska, D. Short-Term Predictors for Weight Correction Success of the First Paediatric Weight Correction Programme in Children’s Clinical University Hospital in Riga. Medicina 2019, 55, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiland, A.; Nannette, L.K.; Zipfel, S.; Ehehalt, S.; Ziser, K.; Junne, F.; Mack, I. Predictors of Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance in Children and Adolescents with Obesity After Behavioral Weight Loss Intervention. Front. Public Health 2022, 25, 813822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, T. Lifestyle intervention in childhood obesity: Changes and challenges. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Non-Returners n = 253 | Returners n = 220 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.832 | ||
| male | 162 (53.5) | 150 (54.3) | |
| female | 141 (46.5) | 126 (45.7) | |
| Age years (mean, range) | 10.0 (9.5–10.7) | 10.6 (9.9–11.1) | 0.046 |
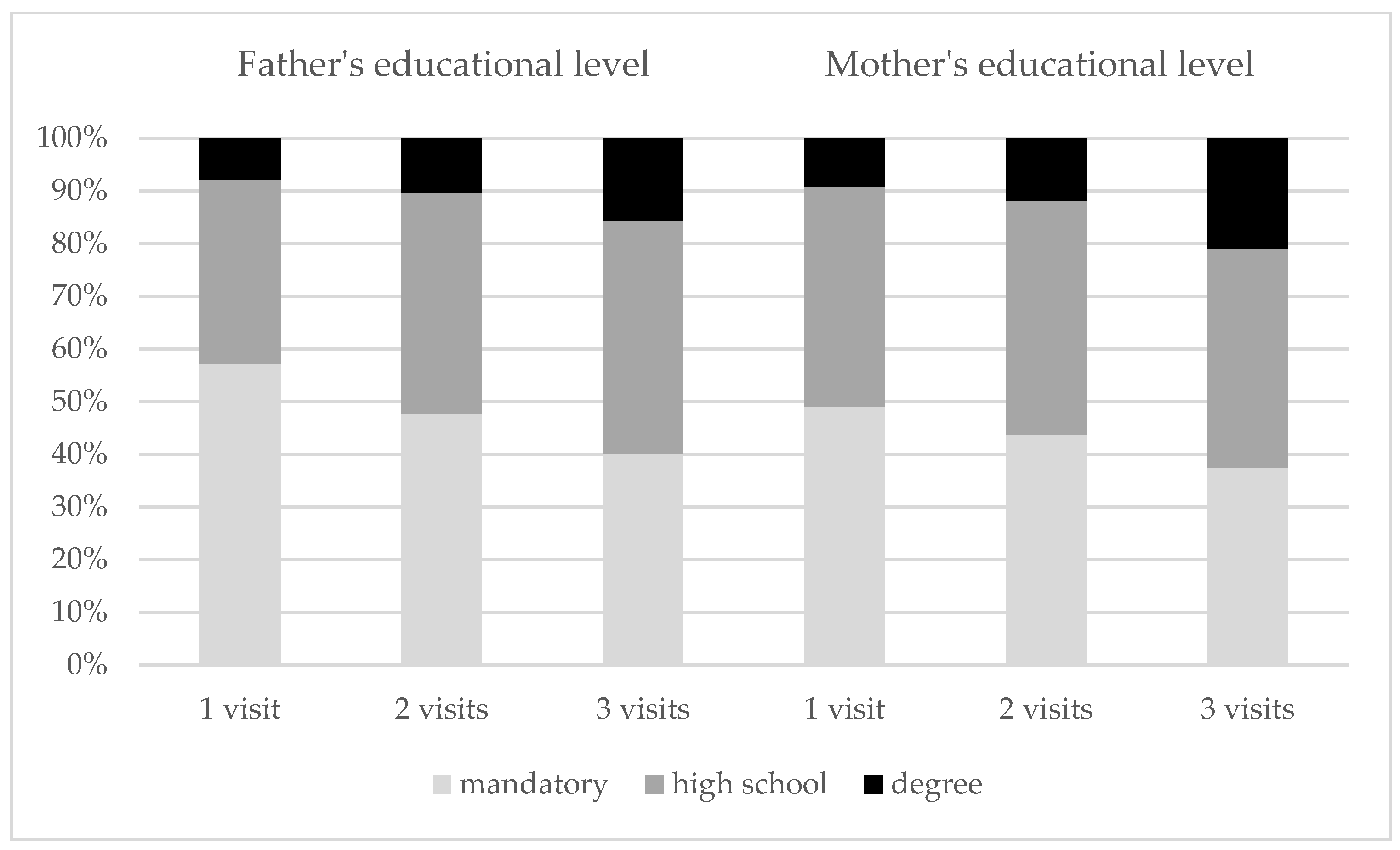
| Father’s educational level | 0.041 | ||
| mandatory | 116 (57.1) | 88 (44.9) | |
| high school | 71 (35) | 84 (42.9) | |
| degree | 16 (7.9) | 24 (12.2) | |
| Mother’s educational level mandatory high school degree | 106 (49.1) 90 (41.7) 20 (9.3) | 86 (41.5) 90 (43.5) 31 (15) | 0.118 |
| Weight (kg) median (IQR) | 58.1 (7.9) | 62.9 (9.2) | 0.326 |
| Height (m) median (IQR) | 1.5 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.1) | 0.237 |
| BMI (kg/m2) median (IQR) | 28.4 (1.7) | 28.6 (1.3) | 0.999 |
| BMI-SDS median (IQR) | 2.29 (0.14) | 2.22 (0.17) | 0.271 |
| WC (cm) median (IQR) | 90 (4.5) | 92 (3) | 0.646 |
| WC/H median (IQR) | 0.63 (0.02) | 0.63 (0.01) | 0.278 |
| FM (%) median (IQR) | 37.1 (2.1) | 37.8 (2.1) | 0.985 |
| FM (Kg) median (IQR) | 23.2 (3.6) | 23.2 (2.7) | 0.670 |
| FFM (%) median (IQR) | 62.8 (2.1) | 62.1 (2.1) | 0.913 |
| FFM (Kg) median (IQR) | 37.1 (3.4) | 38.4 (3.2) | 0.646 |
| Weekly PA median (IQR) (CPAQ score) median (IQR) | 1.6 (0.2) | 1.6 (0.4) | 0.569 |
| Parent’s weekly PA (min/week) median (IQR) | 1593 (413) | 1656 (575) | 0.484 |
| Variable | T0 | T1 (6 ± 3 Months after T0) | p (T0–T1) | T2 (12 ± 3 Months after T0) | p (T1–T2) | p (T0–T2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 451 | n = 141 | n = 79 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.6 (1.3) | 27.4 (1.3) | <0.001 | 27.3 (1.4) | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| BMI-SDS | 2.2 (0.2) | 2.0 (0.2) | <0.001 | 1.9 (0.3) | 0.159 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 92 (3) | 88.5 (4.5) | <0.001 | 88 (5) | 0.092 | <0.001 |
| WC/H | 0.63 (0.01) | 0.60 (0.02) | <0.001 | 0.59 (0.03) | 0.263 | <0.001 |
| FM (%) | 37.8 (2.1) | 35.2 (3) | <0.001 | 36.4 (4,9) | 0.336 | 0.903 |
| FM (kg) | 23.2 (2.7) | 22.4 (4.1) | <0.001 | 22.4 (6.6) | 0.123 | 0.651 |
| FFM (%) | 62.1 (2.1) | 63.8 (3) | <0.001 | 63.6 (4.3) | 0.464 | 0.891 |
| FFM (kg) | 38.4 (3.2) | 40.3 (5.3) | 0.007 | 39.5 (8.9) | 0.232 | 0.549 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallè, F.; Valerio, G.; Daniele, O.; Di Mauro, V.; Forte, S.; Muscariello, E.; Ricchiuti, R.; Sensi, S.; Balia, M.; Liguori, G.; et al. Multidisciplinary Treatment for Childhood Obesity: A Two-Year Experience in the Province of Naples, Italy. Children 2022, 9, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060834
Gallè F, Valerio G, Daniele O, Di Mauro V, Forte S, Muscariello E, Ricchiuti R, Sensi S, Balia M, Liguori G, et al. Multidisciplinary Treatment for Childhood Obesity: A Two-Year Experience in the Province of Naples, Italy. Children. 2022; 9(6):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060834
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallè, Francesca, Giuliana Valerio, Ornella Daniele, Valentina Di Mauro, Simone Forte, Espedita Muscariello, Roberta Ricchiuti, Serena Sensi, Mario Balia, Giorgio Liguori, and et al. 2022. "Multidisciplinary Treatment for Childhood Obesity: A Two-Year Experience in the Province of Naples, Italy" Children 9, no. 6: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060834
APA StyleGallè, F., Valerio, G., Daniele, O., Di Mauro, V., Forte, S., Muscariello, E., Ricchiuti, R., Sensi, S., Balia, M., Liguori, G., & Pecoraro, P. (2022). Multidisciplinary Treatment for Childhood Obesity: A Two-Year Experience in the Province of Naples, Italy. Children, 9(6), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060834









