Changes in Platelet Function in Preterm Newborns with Prematurity Related Morbidities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cases Selection
2.2. Reagents and Equipment
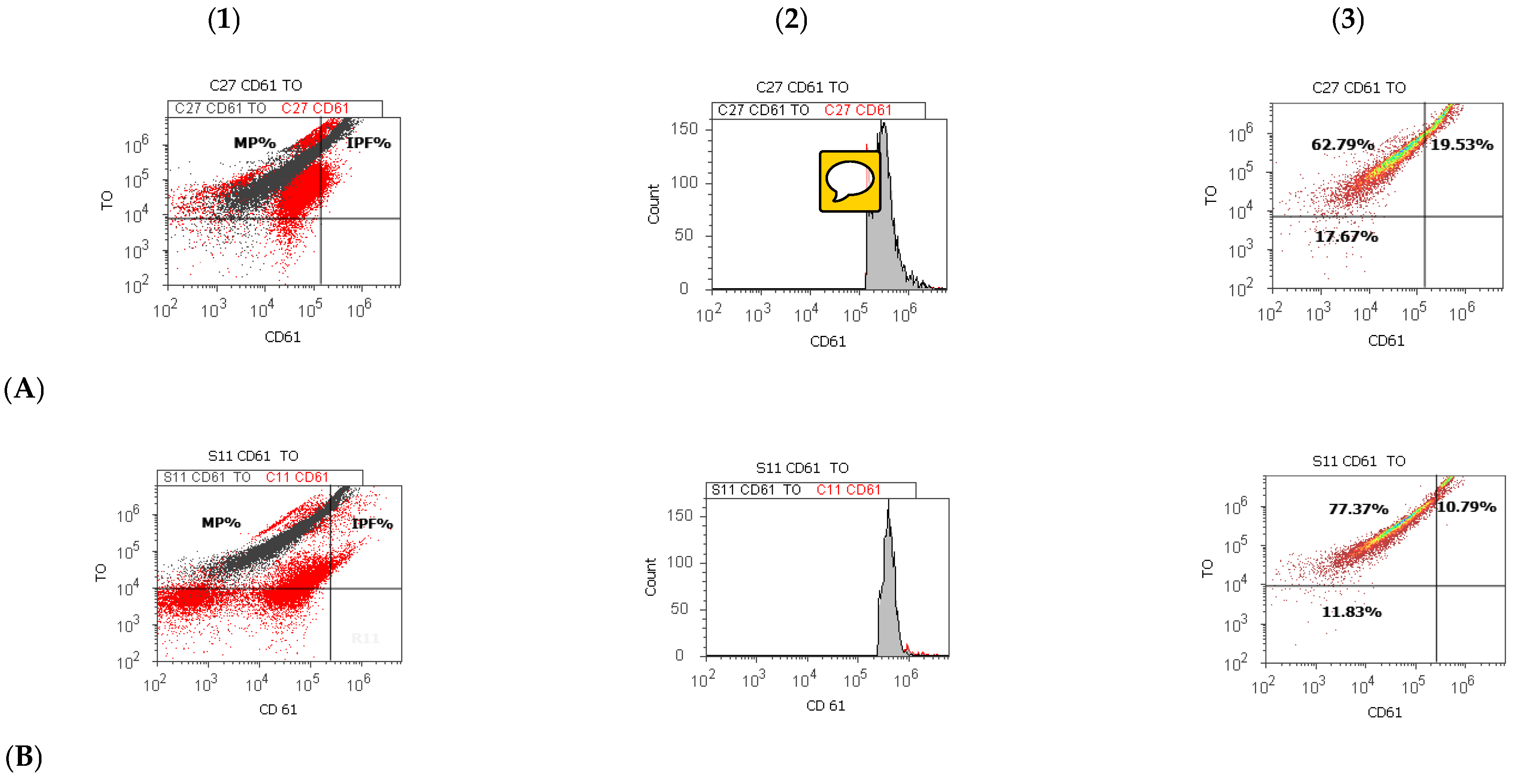
2.3. CD 61 Platelet Membrane Glycoproteins and Thiazole Orange Detections by Flow Cytometry Dual Stain
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Platelet Parameters at Preterm Newborns Reported to Healthy Full-Term Newborns Cases
3.2. Incidence of Prematurity Related Morbidities in Preterm Newborn Cases
3.3. Platelet Parameters in Preterm Newborns Cases, in the Function of Presence or Absence of Prematurity Related Morbidities
3.4. Correlations between Platelet Parameters and Clinicopathological Aspects in Preterm Newborns
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Harrison, P. Platelet function analysis. Blood Rev. 2005, 19, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, M. Beyond clotting: The powers of platelets. Science 2010, 328, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, T.R.; Kampmann, B.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Marchant, A.; Levy, O. Protecting the newborn and young infant from infectious diseases: Lessons from immune ontogeny. Immunity 2017, 46, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallevi, H.; Walker, K.C.; Kasam, M.; Bornstein, N.; Grotta, J.C.; Savitz, S.I. Inflammatory response to intraventricular hemorrhage: Time course, magnitude, and effect of t-PA. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 315, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esiaba, I.; Mousselli, I.; Faison, G.M.; Angeles, D.M.; Boskovic, D.S. Platelets in the Newborn. In Neonatal Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ballabh, P. Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants: Mechanism of disease. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 567, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helwich, E.; Rutkowska, M.; Bokiniec, R.; Gulczynska, E.; Hożejowski, R. Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome treated with surfactant: Incidence and risk factors in the prospective cohort study. Dev. Period Med. 2017, 21, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romantsik, O.; Bruschettini, M.; Zappettini, S.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Calevo, M.G. Heparin for the treatment of thrombosis in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD012185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiluk, A.; Mantur, M.; Kemona-Chetnik, I.; Szczepanski, M.; Warda, J.; Bochenko-Luczynska, J. Does prematurity affect thrombocytopoiesis? Platelets 2007, 18, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola-Visner, M. Platelets in the neonatal period: Developmental differences in platelet production, function, and hemostasis and the potential impact of therapies. Hematology 2012, 2012, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxonhouse, M.A.; Sola, M.C.; Pastos, K.M.; Ignatz, M.E.; Hutson, A.D.; Christensen, R.D.; Rimsza, L.M. Reticulated platelet percentages in term and preterm neonates. J. Pediatric Hematol. Oncol. 2004, 26, 797–802. [Google Scholar]
- Sitaru, A.-G.; Holzhauer, S.; Speer, C.P.; Singer, D.; Obergfell, A.; Walter, U.; Grossmann, R. Neonatal platelets from cord blood and peripheral blood. Platelets 2005, 16, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannar, V.; Deepthi, A.; Kumar, M.L.H.; Junjegowda, K.; Mariyappa, N. Effect of gestational age, prematurity, and birth asphyxia on platelet indices in neonates. J. Clin. Neonatol. 2014, 3, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiluk, A.; Dabrowska, M.; Osada, J.; Jasinska, E.; Laudanski, T.; Redzko, S. Platelet indices in SGA newborns. Adv. Med. Sci. 2011, 56, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekin, A.; Gezer, C.; Kulhan, G.; Avci, M.E.; Taner, C.E. Can platelet count and mean platelet volume during the first trimester of pregnancy predict preterm premature rupture of membranes? J. Obstet. Gynecol. Res. 2015, 41, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canpolat, F.E.; Yurdakok, M.; Armangil, D.; Yigit, S. Mean platelet volume in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr. Int. 2009, 51, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Q.; Qin, J.; Plow, E.F. Platelet integrin α (IIb) β (3): Activation mechanisms. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattil, S.J.; Newman, P.J. Integrins: Dynamic scaffolds for adhesion and signaling in platelets. Blood 2004, 104, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruggeri, Z.M. The role of von Willebrand factor in thrombus formation. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, S5–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobocka, M.B.; Sobocki, T.; Babinska, A.; Hartwig, J.H.; Li, M.; Ehrlich, Y.H.; Kornecki, E. Signaling pathways of the F11 receptor (F11R; a.k.a. JAM-1, JAM-A) in human platelets: F11R dimerization, phosphorylation and complex formation with the integrin GPIIIa. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2004, 24, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, N.; Andre, P.; Bao, M.; Clauser, K.; Deguzman, F.; Howie, D.; Conley, P.B.; Terhorst, C.; Phillips, D.R. Platelet aggregation induces platelet aggregate stability via SLAM family receptor signaling. Blood 2005, 106, 3028–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andre, P.; Prasad, K.S.; Denis, C.V.; He, M.; Papalia, J.M.; Hynes, R.O.; Phillips, D.R.; Wagner, D.D. CD40L stabilizes arterial thrombi by a beta3 integrin–dependent mechanism. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurden, A.T. Platelets, inflammation, and tissue regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, S13–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.S.; Black, M.; Silvia, U.; Fischer, S.; Morgenstern, E.; Hammes, H.P.; Preissner, K.T. The functional role of blood platelet components in angiogenesis. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 92, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.J. Reticulated platelets: Analytical aspects and clinical utility. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dusse, L.M.; Freitas, L.G. Clinical applicability of reticulated platelets. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiluk, A.; Mantur, M.; Kemona, H.; Szczepański, M.; Jasińska, E.; Milewski, R. Thrombopoiesis in small for gestational age newborns. Platelets 2009, 20, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasiluk, A.; Osada, J.; Dabrowska, M.; Szczepański, M.; Jasinska, E. Does prematurity affect platelet indices? Adv. Med. Sci. 2009, 54, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiedmeier, S.E.; Henry, E.; Sola-Visner, M.C.; Christensen, R.D. Platelet reference ranges for neonates, defined using data from over 47,000 patients in a multihospital healthcare system. J. Perinatol. 2009, 29, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagy, B., Jr.; Debreceni, I.B.; Kappelmayer, J. Flow cytometric investigation of classical and alternative platelet activation markers. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 23, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Niu, J.; Mu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Impact of preeclampsia on megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet homeostasis of preterm infants. Platelets 2016, 27, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, H.; El Beshlawy, A.; Badrawi, N.; Mohsen, L.; Mansour, E.; Ramy, N.; Patel, K. Thrombopoietin level is increased in the serum of asphyxiated neonates: A prospective controlled study. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stoppelaar, S.F.; van’t Veer, C.; Poll, T.V.D. The role of platelets in sepsis. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strauss, R.G. Anemia of Prematurity: Pathophysiology & Treatment. Blood Rev. 2010, 24, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strauss, R.G.; Mock, D.M.; Widness, J.A.; Johnson, K.; Cress, G.; Schmidt, R.L. Post-transfusion 24-hour recovery and subsequent survival of allogeneic red blood cells in the bloodstream of newborn infants. Transfusion 2004, 44, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maier, R.F.; Sonntag, J.; Walka, M.M.; Liu, G.; Metze, B.; Obladen, M. Changing practices of red blood cell transfusions in infants with birth weights less than 1000 g. J. Pediatr. 2000, 136, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuko, S.; Takeda, T.; Hirota, A.; Hisaeda, Y.; Amakata, S.; Nakao, A.; Kawakami, T. Examination of the percentage of immature platelet fraction in term and preterm infants at birth. J. Clin. Neonatol. 2013, 2, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cremer, M.; Weimann, A.; Szekessy, D.; Hammer, H.; Bührer, C.; Dame, C. Low immature platelet fraction suggests decreased megakaryopoiesis in neonates with sepsis or necrotizing enterocolitis. J. Perinatol. 2013, 33, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofoli, F.; Ciardelli, L.; Angelini, M.; Gentile, R.; Mazzucchelli, I.; Tinelli, C.; Bollani, L.; Tzialla, C. The role of immature platelet fraction (IPF%) in full-term and preterm infants: Italian data of a promising clinical biomarker in neonates. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, e10–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, B.C.; Christensen, R.D.; Henry, E.; Romrell, A.M.; Pysher, T.J.; Bennett, S.T.; Sola-Visner, M.C. The immature platelet fraction: Creating neonatal reference intervals and using these to categorize neonatal thrombocytopenias. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.; Kunka, S.; Hart, D.; Oguni, S.; Machin, S.J. Assessment of an immature platelet fraction (IPF) in peripheral thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Hematol. 2004, 126, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasi, R.A.; Cardelli, P.; Costante, A.; Sandri, M.; Mercieri, M.; Arcioni, R. Immature platelet fraction in predicting sepsis in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, R.M.E.; Rodrigues, M.V.; Andreguetto, B.D.; Santos, T.M.; Gilberti, M.D.F.P.; de Castro, V.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M.; Dragosavac, D.; Carvalho-Filho, M.A.; De Paula, E.V. Association of the immature platelet fraction with sepsis diagnosis and severity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.H.; Song, M.Y.; Yang, B.X.; Xia, R.X. Clinical significance of measuring reticulated platelets in infectious diseases. Medicine 2017, 96, e9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, I.; Cetin, C.; Baydemir, C.; Günlemez, A. Can immature platelet fraction be an early predictor for congenital pneumonia? Turk. Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 55, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, D. Are platelet volume indices related to mortality in hospitalized children on mechanical ventilation? J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohsen, L.; Akmal, D.M.; Ghonaim, E.K.E.; Riad, N.M. Role of mean platelet volume and ischemia modified albumin in the evaluation of oxidative stress and its association with postnatal complications in infants of diabetic mothers. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 3, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, H.; Ohto, H.; Nollet, K.E.; Takano, S.; Kashiwabara, N.; Chishiki, M.; Maeda, H.; Imamura, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Momoi, N. Using Platelet Parameters to Anticipate Morbidity and Mortality among Preterm Neonates: A Retrospective Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becchi, C.; Malyan, A.L.M.; Fabbri, L.P.; Marsili, M.; Boddi, V.; Boncinelli, S. Mean platelet volume trend in sepsis: Is it a useful parameter? Minerva Anestesiol. 2006, 72, 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Cekmez, F.; Tanju, I.A.; Canpolat, F.E.; Aydinoz, S.; Aydemir, G.; Karademir, F.; Sarici, S.U. Mean platelet volume in very preterm infants: A predictor of morbidities? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazze, J.; Gioia, S.; Spagnuolo, A.; Cerekja, A. Platelets in pregnancy. J. Prenat. Med. 2011, 5, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Missfelder-Lobos, H.; Teran, E.; Lees, C.; Albaiges, G.; Nicolaides, K.H. Platelet changes and subsequent development of pre-eclampsia and fetal growth restriction in women with abnormal uterine artery Doppler screening. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2002, 19, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzin, K.; Tomruk, S.; Tuncay, Y.A.; Naki, M.; Sezginsoy, S.; Zemheri, E.; Yucel, N.; Kanadikirik, F. The relation of increased uterine artery blood flow resistance and impaired trophoblast invasion in pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2005, 272, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erikci, A.A.; Muhcu, M.; Dundar, O.; Ozturk, A. Could mean platelet volume be a predictive marker for gestational diabetes mellitus? Hematology 2008, 13, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, S.; Cerekja, A.; Larciprete, G.; Vallone, C.; Demaliaj, E.; Evangelista, M.T.; Guglietta, M.; Piazze, J. Gestational diabetes: Is it linked to platelets hyperactivity? Platelets 2009, 20, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera, M.C.; Parant, O.; Vayssiere, C.; Arnal, J.F.; Payrastre, B. Physiologic and pathologic changes of platelets in pregnancy. Platelets 2010, 21, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, B.C.; Levine, R.J.; Karumanchi, S.A. Pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Krieger, B.P. Pulmonary complications of pregnancy. Review. Clin. Chest Med. 2004, 25, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaivani, K. Prevalence & consequences of anaemia in pregnancy. Indian J. Med. Res. 2009, 130, 627–633. [Google Scholar]

| Nb. | Parameters | Experimental (E) X ± SD | Control (C) X ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Age (days) | 8.79 ± 8.34 ** | 1.13 ± 0.35 ** |
| p-value | 0.004 | ||
| 2. | Weight (grams) | 1433.57 ± 467.77 ** | 3316.66 ± 440.67 ** |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||
| 3. | Gestational age (weeks) | 30.14 ± 2.98 ** | 38.66 ± 0.89 ** |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||
| 4. | Platelets number (103/µL) | 325.64 ± 144.33 | 288.86 ± 107.70 |
| p-value | 0.441 | ||
| 5. | Platelet’s volume (fL) | 11.42 ± 1.07 ** | 9.90 ± 0.62 ** |
| p-value | 0.000 | ||
| 6. | Platelets index mass (103/µL × fL) | 3724.83 ± 1563.82 | 2840.00 ± 1019.48 |
| p-value | 0.087 | ||
| 7. | Immature platelet fraction (%) | 11.83 ± 3.92 * | 15.78 ± 4.91 * |
| p-value | 0.024 | ||
| 8. | Mature platelets (%) | 74.70 ± 6.39 | 70.79 ± 9.68 |
| p-value | 0.211 | ||
| 9. | RBC number at birth (106/µL) | 4.16 ± 0.49 * | 4.61 ± 0.51 * |
| p-value | 0.024 | ||
| 10. | Hemoglobin value at birth (g/dL) | 15.75 ± 0.97 | 16.44 ± 1.85 |
| p-value | 0.220 | ||
| Nb. | Prematurity Related Morbidities | Experimental Cases Number (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Respiratory distress syndrome | RDS+: 33 (79) RDS−: 9 (21) |
| 2. | Intraventricular bleeding | IVH+: 24 (57) IVH−: 18 (43) |
| 3. | Anemia of prematurity (after one month, at hospital discharge) | AoP+: 30 (71) AoP−: 12 (29) |
| Nb. | Parameters | RDS+ X ± SD | RDS− X ± SD | IVH+ X ± SD | IVH− X ± SD | AoP+ X ± SD | AoP− X ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Age (days) | 8.92 ± 9.02 | 9.00 ± 2.00 | 11.25 ± 10.38 | 5.50 ± 2.66 | 9.56 ± 10.40 | 7.40 ± 2.40 |
| p values | 0.986 | 0.171 | 0.662 | ||||
| 2. | Weight (grams) | 1397.50 ± 498.19 | 1650.00 ± 57.73 | 1256.25 ± 408.09 | 1670.00 ± 467.29 | 1263.33 ± 492.72 * | 1740.00 ± 207.36 * |
| p values | 0.340 | 0.103 | 0.027 | ||||
| 3. | Gestational age (weeks) | 29.58 ± 2.84 * | 33.50 ± 0.57 * | 28.75 ± 2.91 * | 32.00 ± 2.00 * | 29.22 ± 3.07 | 31.80 ± 2.16 |
| p values | 0.018 | 0.038 | 0.125 | ||||
| 4. | Platelets number (103/µL) | 320.16 ± 115.89 | 358.50 ± 283.47 | 331.12 ± 133.41 | 318.33 ± 170.67 | 280.33 ± 69.98 | 407.20 ± 212.07 |
| p values | 0.696 | 0.877 | 0.257 | ||||
| 5. | Platelet’s volume (fL) | 11.58 ± 1.07 * | 10.50 ± 0.46 * | 11.61 ± 1.20 | 11.18 ± 0.92 | 11.66 ± 1.07 | 11.00 ± 1.03 |
| p values | 0.015 | 0.481 | 0.283 | ||||
| 6. | Platelets index mass (103/µL x fL) | 3701.90 ± 1240.91 | 3862.45 ± 3142.11 | 3813.81 ± 1363.61 | 3606.20 ± 1930.18 | 3315.03 ± 1026.97 | 4462.48 ± 2186.47 |
| p values | 0.881 | 0.817 | 0.200 | ||||
| 7. | Immature platelet fraction (%) | 11.51 ± 4.30 * | 18.75 ± 9.32 * | 11.13 ± 3.22 | 15.10 ± 7.70 | 10.65 ± 2.79 * | 16.76 ± 7.77 * |
| p values | 0.047 | 0.210 | 0.050 | ||||
| 8. | Mature platelets (%) | 75.62 ± 6.41 | 70.27 ± 3.88 | 77.77 ± 6.47 * | 70.68 ± 3.63 * | 76.40 ± 6.89 | 71.73 ± 4.51 |
| p values | 0.078 | 0.034 | 0.202 | ||||
| 9. | RBC number at birth (106/µL) | 4.15 ± 0.53 | 4.25 ± 0.19 | 4.18 ± 0.62 | 4.35 ± 0.17 | 4.28 ± 0.47 | 3.96 ± 0.51 |
| p values | 0.615 | 0.529 | 0.267 | ||||
| 10. | Hemoglobin value at birth (g/dL) | 15.73 ± 1.05 | 15.90 ± 0.04 | 15.71 ± 1.11 | 16.01 ± 0.62 | 15.74 ± 1.22 | 15.78 ± 0.34 |
| p values | 0.597 | 0.561 | 0.936 | ||||
| 11. | RBC number after one month, at hospital discharge (106/µL) | 3.37 ± 0.43 | 3.49 ± 0.28 | 3.53 ± 0.45 | 3.56 ± 0.44 | 3.30 ± 0.42 ** | 3.56 ± 0.38 ** |
| p values | 0.552 | 0.907 | 0.002 | ||||
| 12. | Hemoglobin value after one month, at hospital discharge (g/dL) | 11.15 ± 1.20 * | 12.00 ± 0.04 * | 11.50 ± 0.88 | 11.55 ± 1.33 | 10.66 ± 0.95 | 12.38 ± 0.35 |
| p values | 0.034 | 0.934 | 0.274 | ||||
| Immature Platelets Fraction | Platelet Volume | Need of Respiratory Support | Intraventricular Bleeding | Anemia of Prematurity | Mature Platelets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.389 * | 0.398 * | 0.376 * | 0.390 * | −0.682 ** |
| p values | 0.037 | 0.033 | 0.045 | 0.036 | 0.000 |
| Platelet Volume | Need of Respiratory Support | Intraventricular Bleeding | Anemia of Prematurity | Immature Platelets Fraction | Mature Platelets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.698 ** | −0.529 ** | −0.549 ** | −0.389 * | −0.417 * |
| p values | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.037 | 0.024 |
| Gestational Age (Weeks) | Age | Weight | Platelet Volume | Need of Respiratory Support | Intraventricular Bleeding | Anemia of Prematurity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.612 * | 0.934 * | −0.604 * | 0.880 * | 0.755 * | 0.681 * |
| p values | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Weight | Age | Platelet Volume | Need of Respiratory Support | Intraventricular Bleeding | Anemia of Prematurity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | −0.559 * | −0.527 * | 0.818 * | 0.685 * | 0.652 * |
| p values | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franciuc, I.; Matei, E.; Aschie, M.; Mitroi, A.; Chisoi, A.; Poinareanu, I.; Dobrin, N.; Stoica, A.G.; Surdu, T.V.; Manea, M.; et al. Changes in Platelet Function in Preterm Newborns with Prematurity Related Morbidities. Children 2022, 9, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060791
Franciuc I, Matei E, Aschie M, Mitroi A, Chisoi A, Poinareanu I, Dobrin N, Stoica AG, Surdu TV, Manea M, et al. Changes in Platelet Function in Preterm Newborns with Prematurity Related Morbidities. Children. 2022; 9(6):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060791
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranciuc, Irina, Elena Matei, Mariana Aschie, Anca Mitroi, Anca Chisoi, Ionut Poinareanu, Nicolae Dobrin, Andreea Georgiana Stoica, Traian Virgiliu Surdu, Mihaela Manea, and et al. 2022. "Changes in Platelet Function in Preterm Newborns with Prematurity Related Morbidities" Children 9, no. 6: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060791
APA StyleFranciuc, I., Matei, E., Aschie, M., Mitroi, A., Chisoi, A., Poinareanu, I., Dobrin, N., Stoica, A. G., Surdu, T. V., Manea, M., Topliceanu, S., & Cozaru, G. C. (2022). Changes in Platelet Function in Preterm Newborns with Prematurity Related Morbidities. Children, 9(6), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9060791








