Serum Allergen-Specific IgE among Pediatric Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
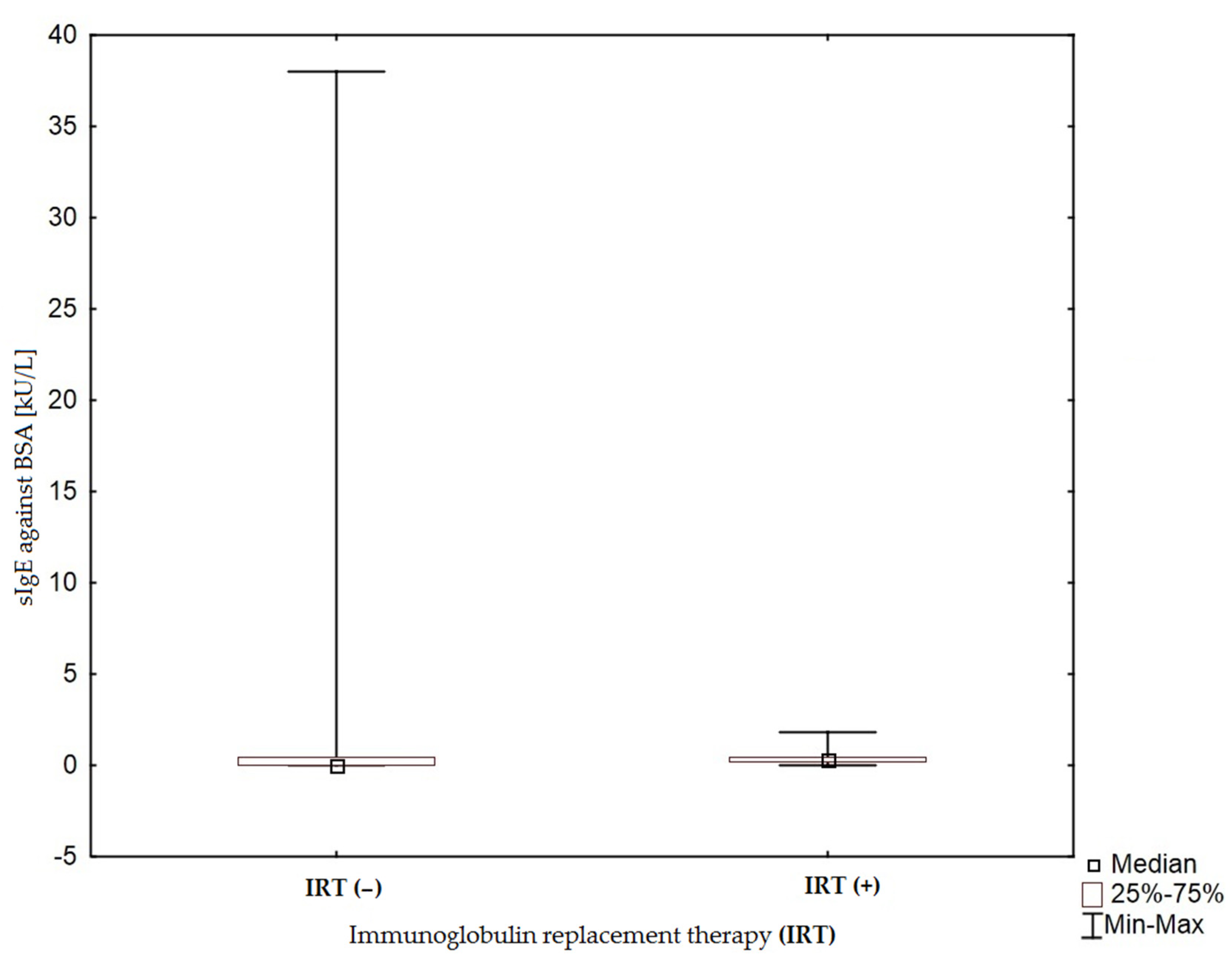
3.1. Allergen-Specific IgE
3.2. Total IgE Level
3.3. Blood Eosinophilia
3.4. Clinical Manifestations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A | asthma |
| Ab | antibody(ies) |
| AC | allergic conjunctivitis |
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| AR | allergic rhinitis |
| A-T | ataxia–telangiectasia |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CVID | common variable immunodeficiency |
| FA | food allergy |
| HSCT | hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| ICD-10 | International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems |
| IEI | inborn errors of immunity |
| IFN-γ | interferon-gamma |
| IgE/G/A/M | immunoglobulin(s) class E/G/A/M |
| IPEX syndrome | immunodysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy X-linked syndrome |
| IRT | immunoglobulin replacement therapy |
| IUIS | International Union of Immunodeficiency Societies |
| n | number |
| NBS | Nijmegen breakage syndrome |
| NHANES | The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| PAD | predominantly antibody deficiencies |
| PID | primary immunodeficiency |
| PRKDC | Protein Kinase, DNA-Activated, Catalytic Subunit |
| sIgE | allergen-specific immunoglobulin class E |
| sIgAD | selective IgA deficiency |
| SCID | severe combined immunodeficiency |
| SPT | skin prick test |
| U | urticaria |
| USIDNET | US Immunodeficiency Network |
| WAS | Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome |
| X-linked | gene is located in the X chromosome |
References
- Bucciol, G.; Moens, L.; Bosch, B.; Bossuyt, X.; Casanova, J.L.; Puel, A.; Meyts, I. Lessons learned from the study of human inborn errors of innate immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyts, I.; Bosch, B.; Bolze, A.; Boisson, B.; Itan, Y.; Belkadi, A.; Pedergnana, V.; Moens, L.; Picard, C.; Cobat, A.; et al. Exome and genome sequencing for inborn errors of immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangye, S.G.; Al-Herz, W.; Bousfiha, A.; Chatila, T.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Etzioni, A.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2019 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 24–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauracher, A.A.; Gujer, E.; Bachmann, L.M.; Güsewell, S.; Schmid, J.P. Patterns of Immune Dysregulation in Primary Immunodeficiencies: A Systematic Review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 792–802.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowicz-Uszyńska, A.; Pasternak, G.; Świerkot, J.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Primary Immunodeficiencies: Diseases of Children and Adults—A Review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1289, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, K.; Milner, J.D. The overlap between allergy and immunodeficiency. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.K.; Gelfand, E.W. Primary Immunodeficiency Masquerading as Allergic Disease. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2015, 35, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsford, M.J.; Klocperk, A.; Pulvirenti, F.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; Milota, T.; Cinetto, F.; Chovancova, Z.; Rial, M.J.; Sediva, A.; Litzman, J.; et al. Hyper-IgE in the allergy clinic—When is it primary immunodeficiency? Allergy 2018, 73, 2122–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lougaris, V.; Sorlini, A.; Monfredini, C.; Ingrasciotta, G.; Caravaggio, A.; Lorenzini, T.; Baronio, M.; Cattalini, M.; Meini, A.; Ruggeri, L.; et al. Clinical and Laboratory Features of 184 Italian Pediatric Patients Affected with Selective IgA Deficiency (SIgAD): A Longitudinal Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 39, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urm, S.H.; Yun, H.D.; Fenta, Y.A.; Yoo, K.H.; Abraham, R.S.; Hagan, J.; Juhn, Y.J. Asthma and risk of selective IgA deficiency or common variable immunodeficiency: A population-based case-control study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuano, K.S.; Orange, J.S.; Sullivan, K.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Bonilla, F.A.; Davis, C.M. Food allergy in patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases: Prevalence within the US Immunodeficiency Network (USIDNET). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Aghamohammadi, A.; Cheraghi, T.; Gharagozlou, M.; Movahedi, M.; Rezaei, N.; Yeganeh, M.; Parvaneh, N.; Abolhassani, H.; Pourpak, Z.; Moin, M. IgA deficiency: Correlation between clinical and immunological phenotypes. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzi, M.; Kull, I.; Sjöberg, R.; Wan, J.; Melén, E.; Bayat, N.; Ostblom, E.; Pan-Hammarström, Q.; Nilsson, P.; Hammarström, L. Selective IgA deficiency in early life: Association to infections and allergic diseases during childhood. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, H.J.; Belloit, J.; De Fillippi, I.; Royal, G. Age-related serum immunoglobulin E levels in healthy subjects and in patients with allergic disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1980, 66, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansotegui, I.J.; Melioli, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Caraballo, L.; Villa, E.; Ebisawa, M.; Passalacqua, G.; Savi, E.; Ebo, D.; Gómez, R.M.; et al. IgE allergy diagnostics and other relevant tests in allergy, a World Allergy Organization position paper. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agondi, R.C.; Barros, M.T.; Rizzo, L.V.; Kalil, J.; Giavina-Bianchi, P. Allergic asthma in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Allergy 2010, 65, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Palacios-Kibler, T.V.; Workman, L.J.; Schuyler, A.J.; Steinke, J.W.; Payne, S.C.; McGowan, E.C.; Patrie, J.; Fuleihan, R.L.; Sullivan, K.E.; et al. Low Serum IgE Is a Sensitive and Specific Marker for Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID). J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ara, M.C.; Boyano-Martínez, M.T.; Díaz-Pena, J.M.; Martín-Muñoz, M.F.; Martín-Esteban, M. Cow’s milk-specific immunoglobulin E levels as predictors of clinical reactivity in the follow-up of the cow’s milk allergy infants. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, H.A. Utility of food-specific IgE concentrations in predicting symptomatic food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, F.; Caubet, J.C.; Ramadan, S.; Spoerl, D.; Eigenmann, P.A. Specific IgE Decision Point Cutoffs in Children with IgE-Mediated Wheat Allergy and a Review of the Literature. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, T.T.; Matsui, E.C.; Kay Conover-Walker, M.; Wood, R.A. The relationship of allergen-specific IgE levels and oral food challenge outcome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.D.; Ryu, G.; Seo, M.Y.; Jeong, J.I.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, S.-K.; Dhong, H.-J. Optimal cutoff values of allergen-specific immunoglobulin E to house dust mites and animal dander based on skin-prick test results: Analysis in 16,209 patients with allergic rhinitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, D.M.; Bock, S.A.; Spears, G.C.; Wilson, C.G.; Miyazawa, N.K.; Gleason, M.C.; Gyorkos, E.A.; Murphy, J.R.; Atkins, D.; Leung, D.Y.M. Oral food challenges in children with a diagnosis of food allergy. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 578–583.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel; Boyce, J.A.; Assa’ad, A.; Burks, A.W.; Jones, S.M.; Sampson, H.A.; Wood, R.A.; Plaut, M.; Cooper, S.F.; Fenton, M.J.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of food allergy in the United States: Report of the NIAID-sponsored expert panel. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126 (Suppl. 6), S1–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Allen, K.; Lack, G.; Taylor, S.L.; Donovan, S.M.; Oria, M. Critical Issues in Food Allergy: A National Academies Consensus Report. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20170194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, D.B.; Marsh, D.G.; Freidhoff, L.R.; Kwiterovich, K.A.; Addison, B.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Natural history of Hymenoptera venom sensitivity in adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100 Pt 1, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, M.D.; Sellins, S.; Grube, E.; Schroer, K.; Gupta, J.; Wang, N.; Hershey, G.K.K. Aeroallergen sensitization in healthy children: Racial and socioeconomic correlates. J. Pediatr. 2007, 151, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, B.; Venter, C.; Grundy, J.; Clayton, C.B.; Arshad, S.H.; Dean, T. Prevalence of sensitization to food allergens, reported adverse reaction to foods, food avoidance, and food hypersensitivity among teenagers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E.; Frew, A.J.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Bochner, B.S.; Golden, D.B.K.; Finkelman, F.D.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Lotvall, J.; Marone, G.; Metcalfe, D.D.; et al. Risk assessment in anaphylaxis: Current and future approaches. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120 (Suppl. 1), S2–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Primary Immunodeficiencies with Elevated IgE. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 35, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.M.; Pastorino, A.C.; Fahl, K.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Monteiro, R.C. Autoimmunity in IgA deficiency: Revisiting the role of IgA as a silent housekeeper. J. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 28 (Suppl. 1), S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadkhah, M.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Movahedi, M.; Gharagozlou, M. Atopic Manifestations: Dermatitis, Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma in Patients With Hypogammaglobulinemia. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2015, 25, e2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Herz, W.; Nanda, A. Skin manifestations in primary immunodeficient children. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2011, 28, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowska, J.; Sobocińska, A.; Kałuzińska-Parzyszek, I.; Jerzyńska, J.; Brzozowska, A. Allergic Manifestation in Paediatric Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases. JMS 2020, 89, e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiec, A.; Sybilski, A.; Komorowski, J.; Furmańczyk, K.; Namysłowski, A.; Zieliński, W.; Raciborski, F.; Białoszewski, A.Z.; Samoliński, B. Sensitisation to airborne allergens as a risk factor for allergic rhinitis and asthma in the Polish population. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2020, 37, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, K.; Ghibu, F.; Sommerville, W.; Toledano, B.J.; Bastein, Y.; Cameron, L.; Hamid, Q.A.; Mazer, B. Intravenous immunoglobulin inhibits IgE production in human B lymphocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 102, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, H.S.; Lee, H.B.; Oh, J.W. Long-term Efficacy of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy for Moderate to Severe Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2011, 3, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durandy, A.; Fischer, A.; Griscelli, C. Dysfunctions of pokeweed mitogen stimulated T and B lymphocyte responses induced by gammaglobulin therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 67, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, G.; Lee, K.Y. Intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) therapy in steroid-resistant atopic dermatitis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 1999, 14, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, P.J.; Kakakios, A.; Wong, L.C.; Wong, M.; Campbell, D.E. Intravenous immunoglobulin to treat severe atopic dermatitis in children: A case series. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, J.J.; Milner, J.D. Primary atopic disorders. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient No | Age | Gender | PID Type | Previous Diagnosis of Allergic Disease | Reported Allergy Symptoms | sIgE [kU/L] | Total IgE [IU/mL] | Correlation between sIgE and Allergy Symptoms | Eosinophil Count [103/uL] | Antihistamines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | M | IgM, IgG subclass deficiency | A, AR, FA | Nasal obstruction Sneezing Nose/eyes itching Trouble breathing with mouth closed Recurrent bronchitis | 6 Grass mix = 2.9 D. pteronyssinus > 100 D. farinae > 100 Cat = 33.0 Dog = 0.89 A. alternata = 12 | 587 [0.5–393] | Yes | 1.77 | Yes |
| 2 | 14 | M | IgM deficiency | AR, FA | Rhinorrhea Diarrhea | D. pteronyssinus = 13.0 D. farinae = 65.0 Cat = 0.81 BSA = 0.5 | 207 [1.9–170] | Possible | 0.12 | No |
| 3 | 13 | M | IgA deficiency | AD | Nose/eyes itching Eczema Pruritus | Horse = 0.53 Cow’s milk = 2.0 BSA = 38.0 | 34,2 [1.9–170] | Possible | 0.17 | No |
| 4 | 7 | M | IgM and IgG subclass deficiency | No | Sneezing | D. pteronyssinus > 100 D. farinae > 100 Cat = 1.2 Dog = 2.2 Horse = 0.45 | 328 [0.5–393] | Yes | 3.75 | No |
| 5 | 6 | F | IgG subclass deficiency | A, AD, FA | Eczema Pruritus Sneezing Nose/eyes itching Trouble breathing with mouth closed | 6 Grass mix > 100 Birch pollen > 100 Mugwort pollen = 0.86 D. pteronyssinus = 4.5 D. farinae = 48 Cat = 0.27 Dog = 74 C. herbarum = 1.9 A. alternata = 5.0 Egg white = 0.94 Cow’s milk = 0.94 Casein = 0.36 Flour Mix 0.46 Rice = 0.86 Peanut = 54.0 Hazelnut = 0.91 Carrot = 0.77 Potato = 1.8 Apple = 0.99 | 823.5 [0.5–393] | Yes | 0.32 | Yes |
| 6 | 12 | F | IgG subclass deficiency | AR | Sneezing Nose/eyes itching Watery eyes Need to rub eyes/nose Nasal obstruction | 6 Grass mix > 100 Birch pollen = 3.5 Mugwort pollen = 0.81 D. pteronyssinus = 1.3 D. farinae = 11 Cat = 4.1 Dog = 0.6 A. alternata = 1.2 Flour Mix = 0.43 Rice = 0.48 Carrot = 0.50 | 466 [1.9–170] | Yes | 0.17 | Yes |
| 7 | 6 | M | IgA deficiency | A, AR | Sneezing Nose/eyes itching Watery eyes Need to rub eyes/nose Nasal obstruction Nasal congestion Rhinorrhea Abdominal cramping Recurrent bronchitis | D. pteronyssinus > 100 D. farinae > 100 BSA = 4.8 Cow’s milk = 0.44 | 699 [0.5–393] | Yes | 0.35 | Yes |
| 8 | 4 | F | IgG subclass deficiency | A | Sneezing Nose/eyes itching Watery eyes Need to rub eyes/nose Recurrent bronchitis | Birch pollen = 1.3 Cat = 15 | 38.4 [0.4–351] | Yes | 0.72 | Yes |
| 9 | 6 | F | IgA and IgG subclass deficiency | AD, AR, FA | Sneezing Nose/eyes itching Watery eyes Need to rub eyes/nose Rhinorrhea Nasal obstruction Eczema | 6 Grass mix = 60 Birch pollen = 1.7 | 134 [<90] | Yes | 0.12 | Yes |
| 10 | 10 | F | IgG subclass deficiency | AR | Rhinorrhea | 6 Grass mix > 100 Birch pollen = 0.63 Mugwort pollen = 0.64 | 227 [<200] | Yes | 0.22 | No |
| 11 | 16 | M | IgM deficiency | AD, AR | Eczema Rhinorrhea | 6 Grass mix > 100 Birch pollen = 0.50 Mugwort pollen = 0.51 Cow’s milk = 0.54 BSA = 4.9 | 1157 [1.5–100] | Possible | 0.17 | Yes |
| 12 | 9 | M | PRKDC mutation, IgG subclass deficiency | AD, AR, FA | Eczema Nasal congestion Cough Sneezing Nose/eyes itching | 6 Grass mix = 4.1 Birch pollen = 0.36 Mugwort pollen = 0.88 Cat = 0.96 Dog = 0.63 | 131 [0.5–393] | Yes | 0.23 | Yes |
| 13 | 3 | F | Complement deficiency | AD | Eczema Pruritus Excoriatio Rhinorrhea Cough | Dog = 0.37 Horse = 0.36 BSA = 9.9 Cow’s milk = 0.73 | 10.5 [<60] | Possible | 0.2 | No |
| 14 | 2 | M | Phagocyte number/function deficiency | U | Urticaria | Cow’s milk = 0.77 BSA = 7.0 | 17.3 [<60] | Possible | 0.22 | No |
| 15 | 7 | F | Congenital asplenia | AR | Rhinorrhea Nose/eyes itching | 6 Grass mix = 4.0 Horse = 0.72 A. alternata = 9.4 | 47.3 [0.5–393] | Yes | 0.27 | Yes |
| 16 | 10 | F | Lymphocyte T deficiency | U | Urticaria Flushing | 6 Grass mix = 2.7 Birch pollen = 0.36 Mugwort pollen = 0.58 D. pteronyssinus = 0.81 D. farinae = 0.94 Cow’s milk = 0.52 BSA = 4.4 Flour Mix = 0.37 Rice = 0.44 Carrot = 0.39 Potato = 0.93 Apple = 1.00 | 908 [1.9–170] | Possible | 0.19 | Yes |
| Type of PID (n = 72) | Clinical Symptoms of Allergy (n = 44) | sIgE ≥ 0.35 kUa/L (n = 36) | Elevated Total IgE (n = 13) | Sensitization to Food Allergens (sIgE ≥ 0.35 kUa/L) + Clinical Symptoms (n = 23) | Skin Eczema (n = 21) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selected Parameter | |||||
| SCID (n = 2) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 1 (50.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) |
| Ataxia-telangiectasia (n = 4) | n = 3 (75.00%) | n = 3 (75.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 2 (50.00%) | n = 1 (25.00%) |
| Nijmegen syndrome (n = 3) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 1 (33.33%) |
| DiGeorge syndrome (n = 2) | n = 1 (50.00%) | n = 1 (50.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 1 (50.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) |
| Kabuki syndrome (n = 1) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) |
| PRKDC mutation (n = 1) | n = 1 (100.00%) | n = 1 (100.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 1 (100.00%) |
| Predominantly Ab deficiency (n = 51): | n = 31 (60.78%) | n = 24 (47.06%) | n = 12 (23.53%) | n = 15 (29.41%) | n = 16 (31.37%) |
| CVID (n = 3) | n = 2 (66.67%) | n = 2 (66.67%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 2 (66.67%) | n = 1 (33.33%) |
| X-linked agammaglobulinemia (n = 1) | n = 1 (100.00%) | n = 1 (100.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 1 (100.00%) | n = 1 (100.00%) |
| other hypo-gammaglobulinemia’s (n = 20) | n = 12 (60.00%) | n = 10 (50.00%) | n = 4 (20.00%) | n = 4 (20.00%) | n = 6 (30.00%) |
| IgG subclass deficiency (n = 20) | n = 12 (60.00%) | n = 7 (35.00%) | n = 6 (30.00%) | n = 5 (25.00%) | n = 7 (35.00%) |
| selective IgA deficiency (n = 7) | n = 4 (57.14%) | n = 4 (57.14%) | n = 2 (28.57%) | n = 3 (42.86%) | n = 1 (14.29%) |
| Congenital defects of phagocyte number, function or both (n = 3) | n = 2 (66.67%) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 0 (0.00%) |
| Complement deficiency (n = 2) | n = 2 (100.00%) | n = 2 (100.00%) | n = 0 (0.00%) | n = 2 (100.00%) | n = 1 (50.00%) |
| Others (n = 3) | n = 3 (100.00%) | n = 2 (66.67%) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 1 (33.33%) | n = 1 (33.33%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pieniawska-Śmiech, K.; Lewandowicz-Uszyńska, A.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M.; Jutel, M. Serum Allergen-Specific IgE among Pediatric Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency. Children 2022, 9, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9040466
Pieniawska-Śmiech K, Lewandowicz-Uszyńska A, Zemelka-Wiacek M, Jutel M. Serum Allergen-Specific IgE among Pediatric Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency. Children. 2022; 9(4):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9040466
Chicago/Turabian StylePieniawska-Śmiech, Karolina, Aleksandra Lewandowicz-Uszyńska, Magdalena Zemelka-Wiacek, and Marek Jutel. 2022. "Serum Allergen-Specific IgE among Pediatric Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency" Children 9, no. 4: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9040466
APA StylePieniawska-Śmiech, K., Lewandowicz-Uszyńska, A., Zemelka-Wiacek, M., & Jutel, M. (2022). Serum Allergen-Specific IgE among Pediatric Patients with Primary Immunodeficiency. Children, 9(4), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9040466








