Deliberative and Affective Risky Decisions in Teenagers: Different Associations with Maladaptive Psychological Functioning and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
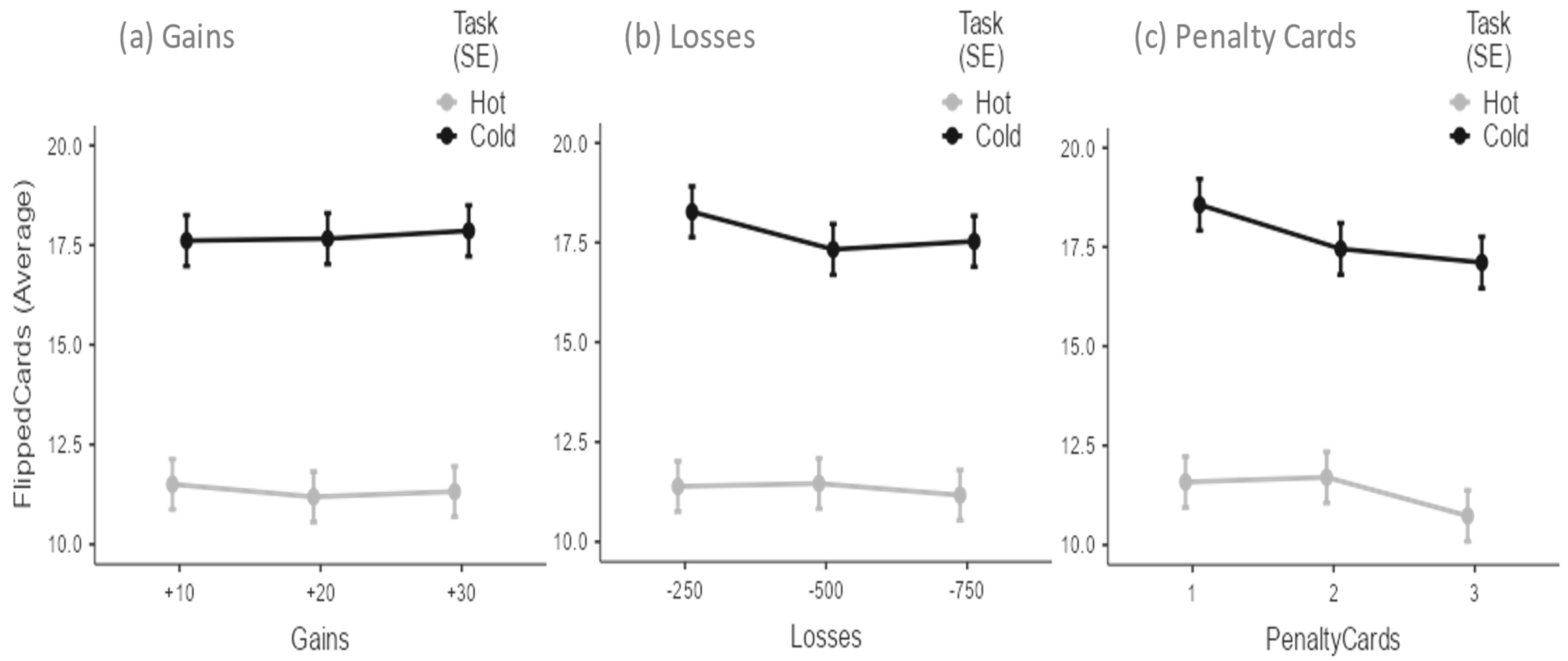
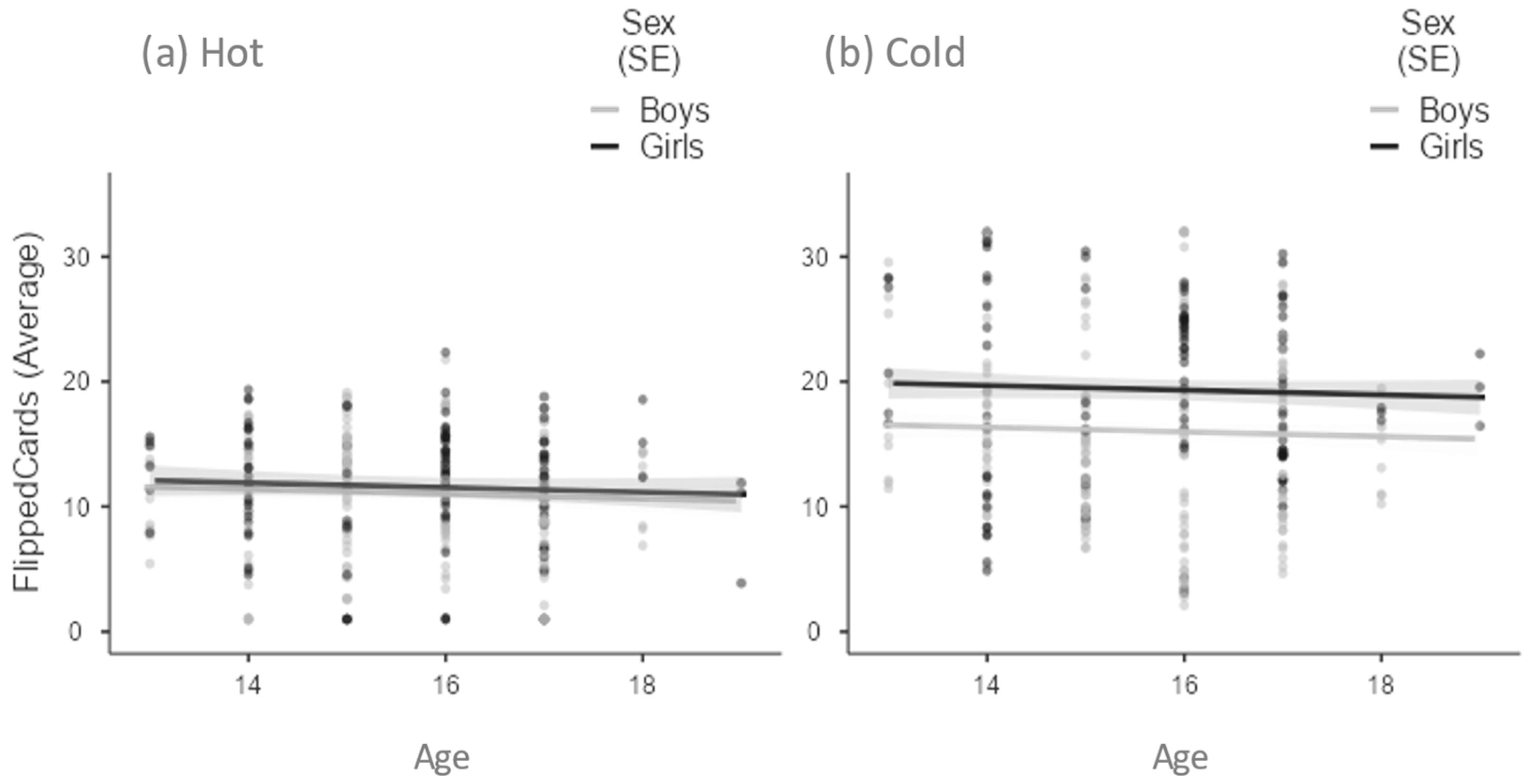
2.2.1. Columbia Card Task
2.2.2. Youth Self-Report (YSR)
2.2.3. Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Strategies (DERS)
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Preliminary Analysis
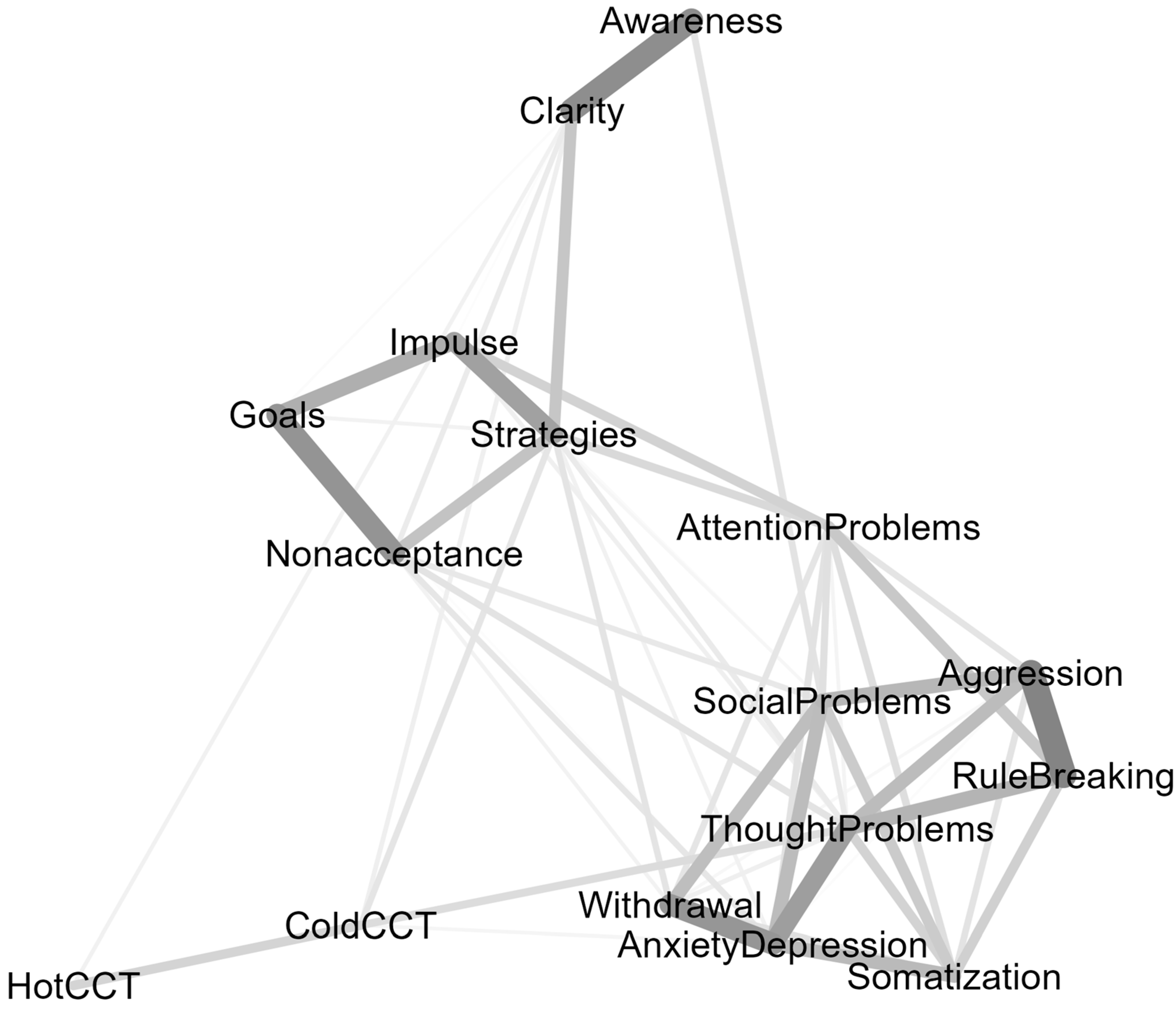
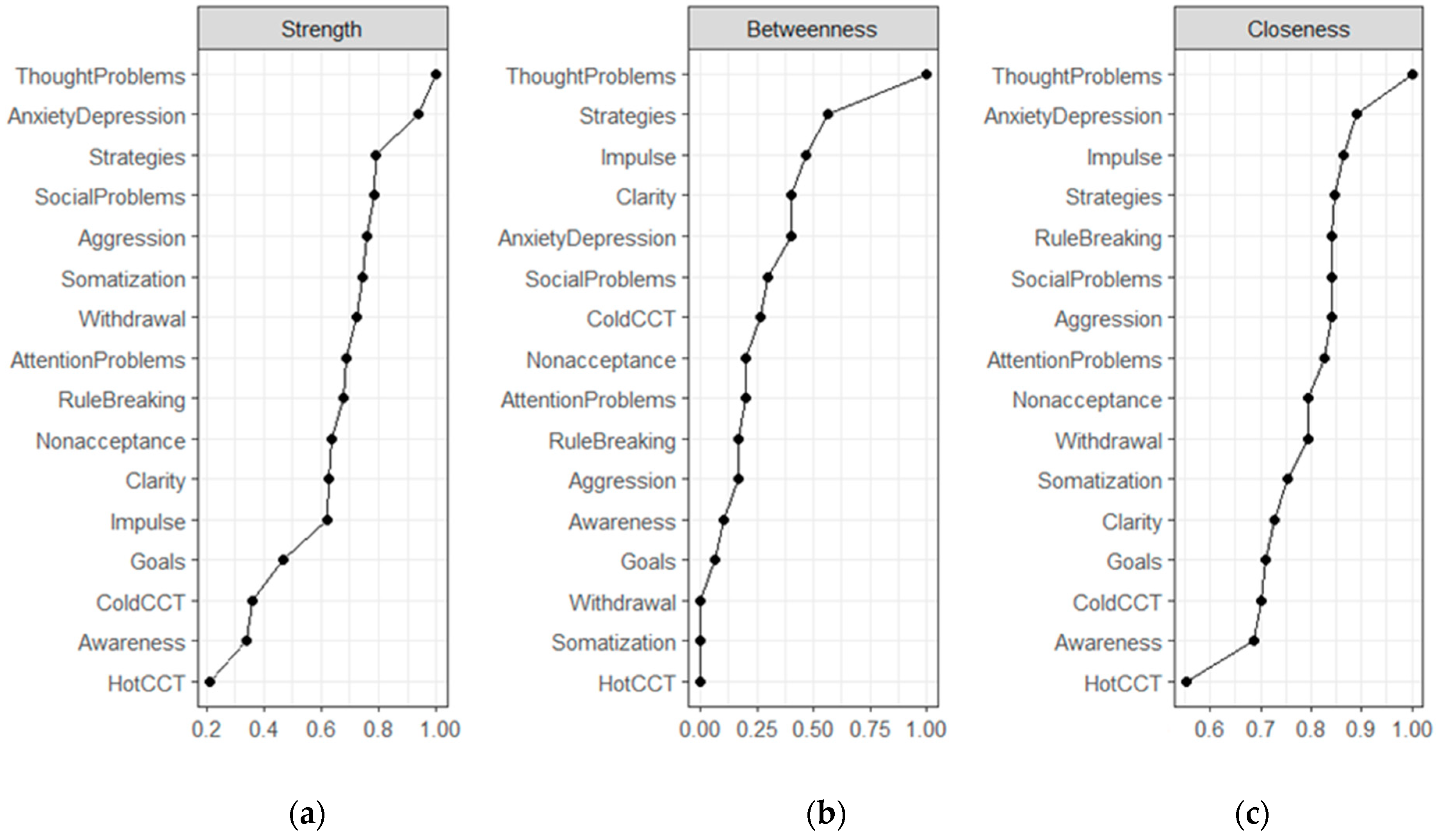
2.3.2. Network Analysis
2.3.3. Mediation Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
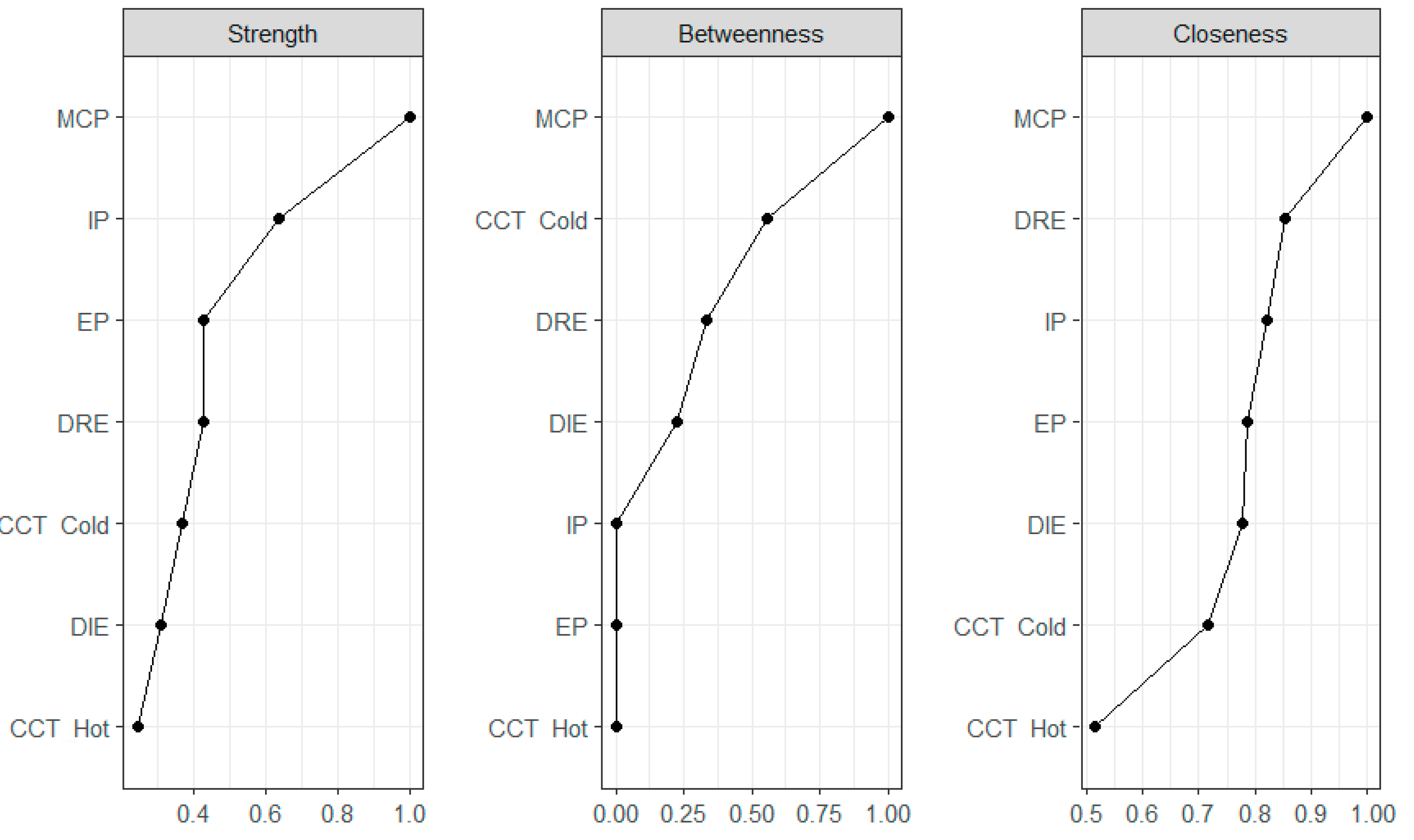
3.2. Network Analysis
3.3. Mediation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahn, W.-Y.; Busemeyer, J.R. Challenges and Promises for Translating Computational Tools into Clinical Practice. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adoue, C.; Jaussent, I.; Olié, E.; Beziat, S.; Van den Eynde, F.; Courtet, P.; Guillaume, S. A Further Assessment of Decision-Making in Anorexia Nervosa. Eur. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuin, N.; Masthoff, E.; Kramer, M.; Scherder, E. The Role of Risky Decision-Making in Aggression: A Systematic Review. Aggress. Violent 2015, 25, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, H.; Kaufman, J.; Martin, A. Amygdala and Hippocampal Volumes in Adolescents and Adults with Bipolar Disorder. Arch. Gen. 2003, 60, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineberg, N.; Chamberlain, S.; Goudriaan, A. New Developments in Human Neurocognition: Clinical, Genetic, and Brain Imaging Correlates of Impulsivity and Compulsivity. CNS 2014, 19, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, G.; Drevets, W.; Manji, H. Discovering Endophenotypes for Major Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 1765–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, A.; Lam, L. Neurocognitive Profiles of People with Borderline Personality Disorder. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2013, 26, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauls, D.; Abramovitch, A.; Rauch, S. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: An Integrative Genetic and Neurobiological Perspective. Nat. Rev. 2014, 15, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-J.; Turpyn, C.C.; Duell, N.; Telzer, E.H. Neural Underpinnings of Social Contextual Influences on Adolescent Risk-Taking. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2020, 7, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, L.; Steinberg, L.; Chein, J. Connecting Brain Responsivity and Real-World Risk Taking: Strengths and Limitations of Current Methodological Approaches. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 33, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, M. Psychopathological Development Across Adolescence. J. Youth Adolesc. 2007, 36, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, B.J. Beyond Simple Models of Self-Control to Circuit-Based Accounts of Adolescent Behavior. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, E.P.; Smith, A.R.; Silva, K.; Icenogle, G.; Duell, N.; Chein, J.; Steinberg, L. The Dual Systems Model: Review, Reappraisal, and Reaffirmation. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrenkohl, T.I.; Kosterman, R.; Mason, W.A.; Hawkins, J.D.; McCarty, C.A.; McCauley, E. Effects of Childhood Conduct Problems and Family Adversity on Health, Health Behaviors, and Service Use in Early Adulthood: Tests of Developmental Pathways Involving Adolescent Risk Taking and Depression. Dev. Psychopathol. 2010, 22, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, K.N.; Mayes, L.C.; Potenza, M.N. Risk-Taking and Decision-Making in Youth: Relationships to Addiction Vulnerability. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelazo, P.D. Executive Function and Psychopathology: A Neurodevelopmental Perspective. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 16, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehinejad, M.A.; Ghanavati, E.; Rashid, M.H.A.; Nitsche, M.A. Hot and Cold Executive Functions in the Brain: A Prefrontal-Cingular Network. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2021, 5, 239821282110077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, S.-J.; Robbins, T.W. Decision-Making in the Adolescent Brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelazo, P.D.; Carlson, S.M. Hot and Cool Executive Function in Childhood and Adolescence: Development and Plasticity. Child. Dev. Perspect. 2012, 6, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández García, L.; Merchán, A.; Phillips-Silver, J.; Daza González, M.T. Neuropsychological Development of Cool and Hot Executive Functions between 6 and 12 Years of Age: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 687337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, H.J.; Brunsdon, V.E.A.; Bradford, E.E.F. The Developmental Trajectories of Executive Function from Adolescence to Old Age. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoraki, T.E.; McGeown, S.P.; Rhodes, S.M.; MacPherson, S.E. Developmental Changes in Executive Functions during Adolescence: A Study of Inhibition, Shifting, and Working Memory. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 38, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brevers, D.; Bechara, A.; Cleeremans, A.; Noël, X. Iowa Gambling Task (IGT): Twenty Years after—Gambling Disorder and IGT. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechara, A.; Damasio, A.; Damasio, H.; Anderson, S. Insensitivity to Future Consequences Following Damage to Human Prefrontal Cortex. Cognition 1994, 50, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almy, B.; Kuskowski, M.; Malone, S.M.; Myers, E.; Luciana, M. A Longitudinal Analysis of Adolescent Decision-Making with the Iowa Gambling Task. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prencipe, A.; Kesek, A.; Cohen, J.; Lamm, C.; Lewis, M.D.; Zelazo, P.D. Development of Hot and Cool Executive Function during the Transition to Adolescence. J. Exp. Child. Psychol. 2011, 108, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G.; Xiao, L.; Bechara, A. Decision Making in Children and Adolescents: Impaired Iowa Gambling Task Performance in Early Adolescence. Dev. Psychol. 2012, 48, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, L. A Dual Systems Model of Adolescent Risk-Taking. Dev. Psychobiol. 2010, 52, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, L.P. Adolescent Neurodevelopment. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52, S7–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, L. A Social Neuroscience Perspective on Adolescent Risk-Taking. Dev. Rev. 2008, 28, 78–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambelli, R.; Cerniglia, L.; Cimino, S.; Ballarotto, G. Parent-Infant Interactions in Families with Women Diagnosed with Postnatal Depression: A Longitudinal Study on the Effects of a Psychodynamic Treatment. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Snyder, H.R.; Friedman, N.P.; Hankin, B.L. Transdiagnostic Mechanisms of Psychopathology in Youth: Executive Functions, Dependent Stress, and Rumination. Cognit. Ther. Res. 2019, 43, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimes-Dougan, B.; Garber, J. Regulatory Control and Depression in Adolescents: Findings from Neuroimaging and Neuropsychological Research. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2016, 45, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulik, M.J. Introduction to the Special Section on Executive Functions and Externalizing Symptoms. J. Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017, 45, 1473–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brieant, A.; King-Casas, B.; Kim-Spoon, J. Transactional Relations between Developmental Trajectories of Executive Functioning and Internalizing and Externalizing Symptomatology in Adolescence. Dev. Psychopathol. 2022, 34, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morea, A.; Calvete, E. Cognitive Flexibility and Selective Attention’s Associations with Internalizing Symptoms in Adolescents: Are They Reciprocal? J. Youth Adolesc. 2021, 50, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Kable, J.W. Value-Based Decision Making in Mental Illness A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 2, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriola, M.; Weller, J. Personality and Risk: Beyond Daredevils-Risk Taking from a Temperament Perspective. In Psychological Perspectives on Risk and Risk Analysis: Theory, Models, and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–36. ISBN 9783319924786. [Google Scholar]
- Buelow, M.T.; Blaine, A. The Assessment of Risky Decision Making: A Factor Analysis of Performance on the Iowa Gambling Task, Balloon Analogue Risk Task, and Columbia Card Task. Psychol. Assess. 2015, 27, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figner, B.; Mackinlay, R.J.; Wilkening, F.; Weber, E.U. Affective and Deliberative Processes in Risky Choice: Age Differences in Risk Taking in the Columbia Card Task. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn Mem. Cogn. 2009, 35, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, K.; Strien, J.W. Event-related Potentials in Response to Feedback Following Risk-taking in the Hot Version of the Columbia Card Task. Psychophysiology 2019, 56, e13390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holper, L.; Murphy, R.O. Hemodynamic and Affective Correlates Assessed during Performance on the Columbia Card Task (CCT). Brain Imaging Behav. 2014, 8, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Buelow, M.T. Predicting Performance on the Columbia Card Task. Assessment 2015, 22, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz, Ł.; Kubińska, E. Information Use Differences in Hot and Cold Risk Processing: When Does Information About Probability Count in the Columbia Card Task? Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panno, A.; Lauriola, M.; Figner, B. Emotion Regulation and Risk Taking: Predicting Risky Choice in Deliberative Decision Making. Cogn. Emot. 2013, 27, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohm, C.L.; Clore, G.L. Affect as Information: An Individual-Differences Approach. In The Wisdom in Feeling: Psychological Processes in Emotional Intelligence; Barrett, L.F., Salovey, P., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 89–113. [Google Scholar]
- McNally, R.J. Can Network Analysis Transform Psychopathology? Behav. Res. Ther. 2016, 86, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsboom, D.; Cramer, A.O.J. Network Analysis: An Integrative Approach to the Structure of Psychopathology. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2013, 9, 91–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, K.L.; Roemer, L. Multidimensional Assessment of Emotion Regulation and Dysregulation: Development, Factor Structure, and Initial Validation of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2004, 26, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lafferty, J.; Wasserman, L. The Nonparanormal: Semiparametric Estimation of High Dimensional Undirected Graphs. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 2295–2328. [Google Scholar]
- Epskamp, S.; Borsboom, D.; Fried, E.I. Estimating Psychological Networks and Their Accuracy: A Tutorial Paper. Behav. Res. Methods 2018, 50, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Rockwood, N.J. Regression-Based Statistical Mediation and Moderation Analysis in Clinical Research: Observations, Recommendations, and Implementation. Behav. Res. Ther. 2017, 98, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.R.; Fergus, T.A.; Hannan, S.M.; Orcutt, H.K. Addressing Psychometric Limitations of the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale through Item Modification. J. Pers. Assess. 2016, 98, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, I.; Keeley, H.; Corcoran, P.; Lynch, F.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Devlin, N.; Molloy, C.; Roddy, S.; Clarke, M.C.; Harley, M.; et al. Clinicopathological Significance of Psychotic Experiences in Non-Psychotic Young People: Evidence from Four Population-Based Studies. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 201, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, S.; Rizvi, S.H.; Freeman, L.K.; Youngstrom, J.K.; Findling, R.L.; Youngstrom, E.A. Diagnostic Efficiency of the CBCL Thought Problems and DSM-Oriented Psychotic Symptoms Scales for Pediatric Psychotic Symptoms. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 27, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, G.; Rossi, R.; Ribolsi, M.; di Lorenzo, G.; Parisi, C.; Siracusano, M.; Morciano, L.; de Stefano, A.; Pesaresi, A.; Niolu, C.; et al. ‘Too Many BeEPs in Our Teens!’ Behavioral and Emotional Problems in a Large Group of Italian Adolescents. Psychol. Med. 2020, 52, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, M.; Nelson, B.; Yung, A.R.; Ross, M.; Birchwood, M.; Girardi, P.; Nastro, P.F. Psychotic-like Experiences and Correlation with Distress and Depressive Symptoms in a Community Sample of Adolescents and Young Adults. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 119, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, M.; Woodman, T.; Chapman, C.; Milton, M.; Stone, D.; Dodds, T.; Allen, B. Who Takes Risks in High-Risk Sport?: The Role of Alexithymia. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2015, 37, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, A.; Sarrionandia, A.; Lauriola, M.; Giacomantonio, M. Alexithymia and Risk Preferences: Predicting Risk Behaviour across Decision Domains. Int. J. Psychol. 2019, 54, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, B.W.; Basso, M.R.; Miller, A.K.; Whiteside, D.M.; Combs, D. Executive Function, Impulsivity, and Risky Behaviors in Young Adults. Neuropsychology 2019, 33, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Pettifor, A.; Duta, M.; Demeyere, N.; Wagner, R.G.; Selin, A.; MacPhail, C.; Laeyendecker, O.; Hughes, J.P.; Stein, A.; et al. Executive Function Associated with Sexual Risk in Young South African Women: Findings from the HPTN 068 Cohort. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, L.H.; Haddara, N.; Sasse, S.F.; Skwara, A.C.; Moran, J.M.; Figner, B. Dissecting “Peer Presence” and “Decisions” to Deepen Understanding of Peer Influence on Adolescent Risky Choice. Child. Dev. 2019, 90, 2086–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, M.A.; Chiesi, F.; Iozzi, A.; Manfredi, A.; Fagni, F.; Primi, C. Gambling-Related Distortions and Problem Gambling in Adolescents: A Model to Explain Mechanisms and Develop Interventions. Front. Psychol. 2018, 8, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figner, B.; Weber, E.U. Who Takes Risks When and Why? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 20, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, A.; Donati, M.A.; Milioni, M.; Chiesi, F.; Primi, C. Why Women Take Fewer Risk Than Men Do: The Mediating Role of State Anxiety. Sex Roles 2018, 78, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelow, M.T.; Cayton, C. Relationships between the Big Five Personality Characteristics and Performance on Behavioral Decision Making Tasks. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2020, 160, 109931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A.; Ling, D.S. Conclusions about Interventions, Programs, and Approaches for Improving Executive Functions That Appear Justified and Those That, despite Much Hype, Do Not. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Correlation Coefficients | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| --- | 0.52 ** | 0.52 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.33 ** | 0.11 | 0.44 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.25 * | 0.39 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.21 * | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.14 |
| 0.54 ** | --- | 0.32 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.02 | 0.28 ** | 0.27 ** | 0.09 | 0.31 ** | 0.20* | 0.25* | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.04 | −0.06 |
| 0.49 ** | 0.39 ** | --- | 0.49 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.25 * | 0.47 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.25 * | 0.29 ** | 0.11 | 0.24 * |
| 0.35 ** | 0.47 ** | 0.55 ** | --- | 0.24 * | 0.14 | 0.37 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.50 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.34 ** | −0.09 | 0.05 |
| 0.30 ** | 0.24 * | 0.38 ** | 0.26 ** | --- | 0.49 ** | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.23 * | 0.20 * | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.20 * | 0.27 ** |
| 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.24 * | 0.15 | 0.50 ** | --- | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.24 * | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.20 * | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.17 |
| 0.48 ** | 0.33 ** | 0.48 ** | 0.35 ** | 0.14 | 0.05 | --- | 0.74 ** | 0.67 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.57 ** | −0.10 | 0.24 * |
| 0.42 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.75 ** | --- | 0.62 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.52 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.49 ** | −0.07 | 0.18 |
| 0.33 ** | 0.16 | 0.39 ** | 0.23 * | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.71 ** | 0.61 ** | --- | 0.60 ** | 0.61 ** | 0.52 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.61 ** | −0.15 | 0.10 |
| 0.45 ** | 0.22 * | 0.44 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.16 | 0.29 ** | 0.73 ** | 0.67 ** | 0.67 ** | --- | 0.54 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.47 ** | 0.57 ** | −0.14 | 0.17 |
| 0.47 ** | 0.21 * | 0.49 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.78 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.69 ** | 0.67 ** | --- | 0.58 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.66 ** | 0.05 | 0.28 ** |
| 0.23 * | 0.23 * | 0.47 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.59 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.58 ** | --- | 0.59 ** | 0.54 ** | −0.07 | 0.19 * |
| 0.15 | −0.06 | 0.32 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.53 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.71 ** | 0.58 ** | --- | 0.74 ** | −0.07 | 0.16 |
| 0.21 * | 0.11 | 0.36 ** | 0.30 ** | −0.01 | 0.23 * | 0.63 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.68 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.77 ** | --- | −0.12 | 0.12 |
| 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.14 | −0.04 | 0.20 * | 0.05 | −0.03 | −0.08 | −0.09 | −0.05 | 0.05 | −0.01 | −0.02 | −0.09 | --- | 0.33 |
| 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.30 ** | 0.06 | 0.24 * | 0.16 | 0.31 ** | 0.22 * | 0.16 | 0.25 * | 0.35 ** | 0.24 * | 0.21 * | 0.19 | 0.27 ** | --- |
| 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | 9. | 10. | 11. | 12. | 13. | 14. | 15. | 16. | |
| M | 12.83 | 12.33 | 19.42 | 13.07 | 12.10 | 7.52 | 7.12 | 4.26 | 3.90 | 4.20 | 5.47 | 5.44 | 6.34 | 8.35 | 11.28 | 17.23 |
| SD | 5.89 | 4.36 | 5.65 | 4.79 | 4.30 | 3.01 | 4.96 | 3.22 | 3.43 | 4.06 | 4.72 | 3.26 | 5.11 | 5.48 | 4.24 | 7.34 |
| Label | Indirect Effect | Estimate | SE | Lower | Upper | β |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IE1 | MCP ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| IE2 | DIE ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| IE3 | DRE ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.02 |
| IE4 | EP ⇒ MCP ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| IE5 | EP ⇒ DRE ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| IE6 | EP ⇒ DIE ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.00 | 0.00 | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| IE7 | IP ⇒ MCP ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| IE8 | IP ⇒ DRE ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | −0.01 | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −.01 |
| IE9 | IP ⇒ DIE ⇒ Cold CCT ⇒ Hot CCT | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauriola, M.; Cerniglia, L.; Tambelli, R.; Cimino, S. Deliberative and Affective Risky Decisions in Teenagers: Different Associations with Maladaptive Psychological Functioning and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation? Children 2022, 9, 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121915
Lauriola M, Cerniglia L, Tambelli R, Cimino S. Deliberative and Affective Risky Decisions in Teenagers: Different Associations with Maladaptive Psychological Functioning and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation? Children. 2022; 9(12):1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121915
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauriola, Marco, Luca Cerniglia, Renata Tambelli, and Silvia Cimino. 2022. "Deliberative and Affective Risky Decisions in Teenagers: Different Associations with Maladaptive Psychological Functioning and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation?" Children 9, no. 12: 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121915
APA StyleLauriola, M., Cerniglia, L., Tambelli, R., & Cimino, S. (2022). Deliberative and Affective Risky Decisions in Teenagers: Different Associations with Maladaptive Psychological Functioning and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation? Children, 9(12), 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9121915








