Pediatric Patient with Ischemic Stroke: Initial Approach and Early Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Classification
3. Epidemiology
4. Risk Factors
5. Presentation and Diagnosis
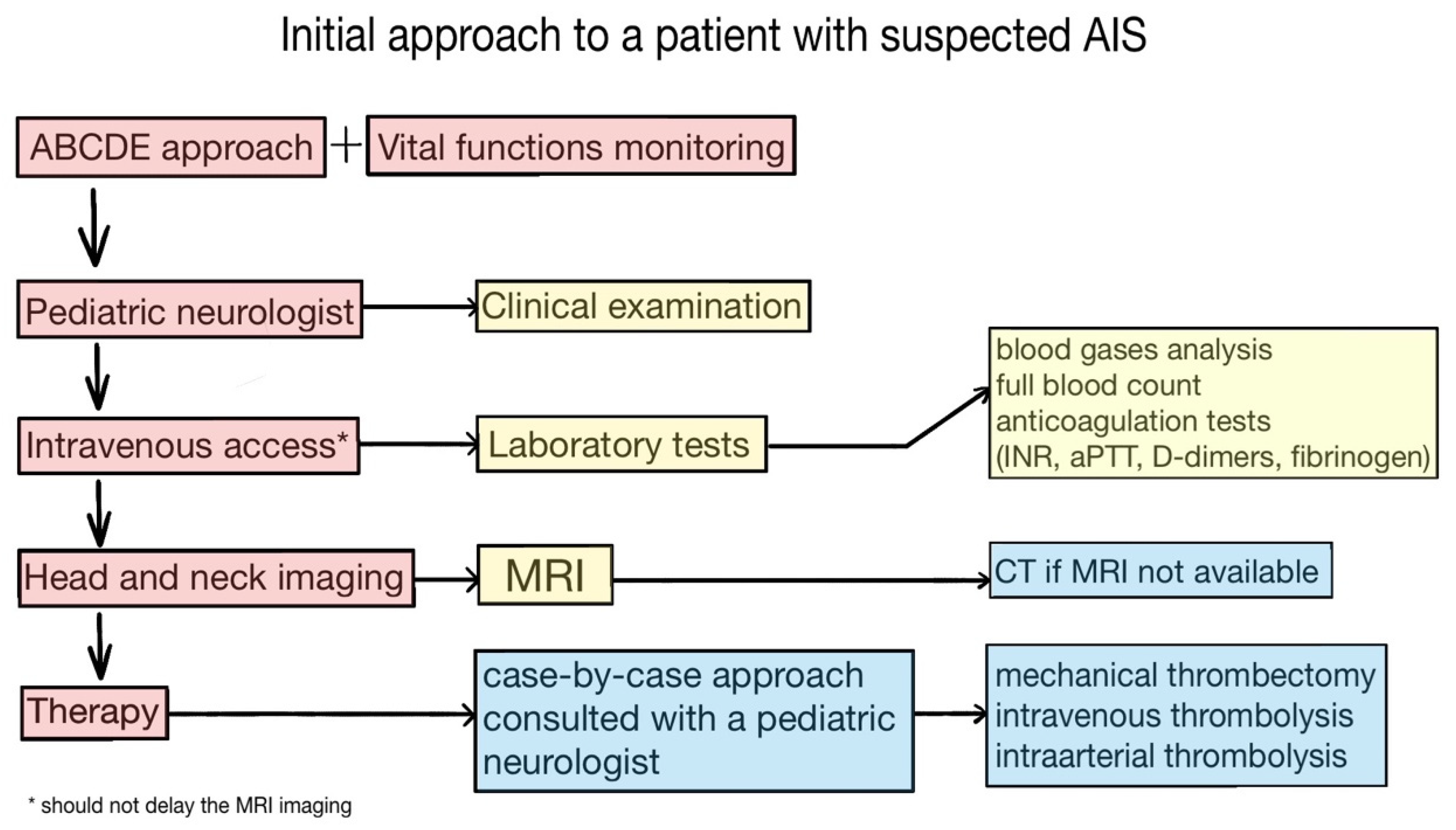
6. Initial Approach
7. Imaging
8. Specific AIS Therapy
9. Further Treatment and Recurrence Prevention
10. Outcome
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. MONICA Project Principal Investigators. The World Health Organization Monica Project (monitoring trends and determinants in cardiovascular disease): A major international collaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; Connors, J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. An Updated Definition of Stroke for the 21st Century. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldenberg, N.A.; Bernard, T.J.; Fullerton, H.J.; Gordon, A.; de Veber, G. Antithrombotic treatments, outcomes, and prognostic factors in acute childhood onset arterial ischaemic stroke: A multicentre, observational, cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Yau, I.; Moharir, M. Current Concepts in Pediatric Stroke. Indian J. Pediatr. 2014, 82, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissela, B.M.; Khoury, J.C.; Alwell, K.; Moomaw, C.J.; Woo, D.; Adeoye, O.; Flaherty, M.L.; Khatri, P.; Ferioli, S.; De Los Rios La Rosa, F.; et al. Age at stroke: Temporal trends in stroke in-cidence in a large, biracial population. Neurology 2012, 79, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golomb, M.R.; Fullerton, H.J.; Nowak-Gottl, U.; Deveber, G. Male predominance in childhood ischemic stroke: Findings from the international pediatric stroke study. Stroke 2009, 40, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grysiewicz, R.A.; Thomas, K.; Pandey, D. Epidemiology of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke: Incidence, Prevalence, Mortality, and Risk Factors. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 871–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statler, K.D.; Dong, L.; Nielsen, D.M.; Bratton, S.L. Pediatric stroke: Clinical characteristics, acute care utilization patterns, and mortality. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2010, 27, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.A.; Hills, N.K.; Sidney, S.; Johnston, S.C.; Fullerton, H.J. The 5-year direct medical cost of neonatal and child-hood stroke in a population-based cohort. Neurology 2010, 74, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, W.; Zamel, K.; Ponnappa, K.; Allen, A.; Chisolm, D.; Tang, M.; Kerlin, B.; Yeates, K. The Cost of Pediatric Stroke Care and Rehabilitation. Stroke 2008, 39, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perkins, E.; Stephens, J.; Xiang, H.; Lo, W. The Cost of Pediatric Stroke Acute Care in the United States. Stroke 2009, 40, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, W.; Huang, H.; Seiber, E.; Lo, W. Cost and Outcome in Pediatric Ischemic Stroke. J. Child Neurol. 2015, 30, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriero, D.M.; Fullerton, H.; Bernard, T.J.; Billinghurst, L.; Daniels, S.R.; DeBaun, M.R.; DeVeber, G.; Ichord, R.N.; Jordan, L.C.; Massicotte, P.; et al. Management of Stroke in Neonates and Children: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e51–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, K.B.; Lynch, J.K. Stroke in newborn infants. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivkin, M.J.; Bernard, T.J.; Dowling, M.M.; Amlie-Lefond, C. Guidelines for Urgent Management of Stroke in Children. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 56, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodan, L.; McCrindle, B.W.; Manlhiot, C.; MacGregor, D.L.; Askalan, R.; Moharir, M.; de Veber, G. Stroke recurrence in chil-dren with congenital heart disease. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, M.; Lemesle, M.; Madinier, G.; Manceau, E.; Osseby, G.V.; Dumas, R. Stroke in children under 16 years of age. Clinical and etiological difference with adults. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 96, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsze, D.; Valente, J.H. Pediatric Stroke: A Review. Emerg. Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mallick, A.A.; O’Callaghan, F.J. The epidemiology of childhood stroke. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.K.; McKinney, J.S.; Sedjro, J.E.; Cosgrove, N.M.; Cabrera, J.; Kostis, J.B. Temporal trends in incidence and long-term case fatality of stroke among children from 1994 to 2007. Neurology 2012, 78, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirton, A.; DeVeber, G. Advances in Perinatal Ischemic Stroke. Pediatr. Neurol. 2009, 40, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Veber, G.; Roach, E.S.; Riela, A.R.; Wiznitzer, M. Stroke in children: Recognition, treatment, and future directions. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2000, 7, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinlin, M.; Pfister, I.; Pavlovic, J.; Everts, R.; Boltshauser, E.; Mori, A.C.; Mercati, D.G.; Hänggeli, C.-A.; Keller, E.; Luetschg, J.; et al. The First Three Years of the Swiss Neuropaediatric Stroke Registry (SNPSR): A Population-Based Study of Incidence, Symptoms and Risk Factors. Neuropediatrics 2005, 36, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christerson, S.; Strömberg, B. Childhood stroke in Sweden I: Incidence, symptoms, risk factors and short-term outcome. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, A.; Ganesan, V.; Kirkham, F.; Fallon, P.; Hedderly, T.; McShane, T.; Parker, A.P.; Wassmer, E.; Wraige, E.; Amin, S.; et al. Childhood arterial ischaemic stroke incidence, presenting features, and risk factors: A prospective population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintermark, M.; Hills, N.K.; DeVeber, G.A.; Barkovich, A.J.; Elkind, M.S.; Sear, K.; Zhu, G.; Leiva-Salinas, C.; Hou, Q.; Dowling, M.M.; et al. Arteriopathy diagnosis in childhood arterial ischemic stroke: Results of the vascular effects of infection in pediatric stroke study. Stroke 2014, 45, 3597–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yock-Corrales, A.; Mackay, M.T.; Mosley, I.; Maixner, W.; Babl, F.E. Acute Childhood Arterial Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in the Emergency Department. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2011, 58, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simma, B.; Martin, G.; Müller, T.; Huemer, M. Risk Factors for Pediatric Stroke: Consequences for Therapy and Quality of Life. Pediatr. Neurol. 2007, 37, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveber, G.A.; Kirton, A.; Booth, F.A.; Yager, J.Y.; Wirrell, E.C.; Wood, E.; Shevell, M.; Surmava, A.-M.; McCusker, P.; Massicotte, M.P.; et al. Epidemiology and Outcomes of Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Children: The Canadian Pediatric Ischemic Stroke Registry. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 69, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, L.L.; Khoury, J.C.; Taylor, J.M.; Yeramaneni, S.; Sucharew, H.; Alwell, K.; Moomaw, C.J.; Peariso, K.; Flaherty, M.; Khatri, P.; et al. Pediatric Stroke Rates Over 17 Years: Report From a Population-Based Study. J. Child Neurol. 2018, 33, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullerton, H.; Wu, Y.W.; Zhao, S.; Johnston, S.C. Risk of stroke in children: Ethnic and gender disparities. Neurology 2003, 61, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLaroche, A.M.; Sivaswamy, L.; Farooqi, A.; Kannikeswaran, N. Pediatric Stroke Clinical Pathway Improves the Time to Diagnosis in an Emergency Department. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 65, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, G.; Lim, B.C.; Chae, J.-H. Pediatric Stroke. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2015, 57, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Günther, G.; Junker, R.; Sträter, R.; Schobess, R.; Kurnik, K.; Heller, C.; Kosch, A.; Nowak-Göttl, U. Symptomatic ischemic stroke in full-term neonates: Role of acquired and genetic prothrombotic risk factors. Stroke 2000, 31, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Croen, L.A.; Backstrand, K.H.; Yoshida, C.K.; Henning, L.H.; Lindan, C.; Ferriero, D.M.; Fullerton, H.J.; Barkovich, A.J.; Wu, Y.W. Maternal and infant characteristics associated with perinatal arterial stroke in the infant. JAMA 2005, 293, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, C.; Mineyko, A.; Massicotte, P.; Leaker, M.; Jiang, X.Y.; Floer, A.; Kirton, A. Thrombophilia risk is not increased in children after perinatal stroke. Blood 2017, 129, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felling, R.J.; Sun, L.R.; Maxwell, E.C.; Goldenberg, N.; Bernard, T. Pediatric arterial ischemic stroke: Epidemiology, risk factors, and management. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2017, 67, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchen, M.; Goldstein, G.; Lubetsky, A.; Strauss, T.; Schiff, E.; Kenet, G. Factor V Leiden and Antiphospholipid Antibodies in Either Mothers or Infants Increase the Risk for Perinatal Arterial Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curry, C.J.; Bhullar, S.; Holmes, J.; Delozier, C.D.; Roeder, E.R.; Hutchison, H.T. Risk Factors for Perinatal Arterial Stroke: A Study of 60 Mother-Child Pairs. Pediatr. Neurol. 2007, 37, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J.; Fox, C.; Ichord, R.N.; Almond, C.S.; Bernard, T.J.; Beslow, L.A.; Chan, A.K.C.; Cheung, M.; Deveber, G.; Dowling, M.M.; et al. Stroke in Children With Cardiac Disease: Report From the International Pediatric Stroke Study Group Symposium. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 52, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganesan, V.; Prengler, M.; McShane, M.A.; Wade, A.M.; Kirkham, F. Investigation of risk factors in children with arterial ischemic stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 53, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.K.; Sidney, S.; Fullerton, H. Community-based case-control study of childhood stroke risk associated with congenital heart disease. Stroke 2015, 46, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haywood, S.; Liesner, R.; Pindora, S.; Ganesan, V. Thrombophilia and first arterial ischaemic stroke: A systematic review. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Baun, M.R.; Armstrong, F.D.; McKinstry, R.C.; Ware, R.E.; Vichinsky, E.; Kirkham, F.J. Silent cerebral infarcts: A review on a prevalent and progressive cause of neurologic injury in sickle cell anemia. Blood 2012, 119, 4587–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBaun, M.R. Secondary Prevention of Overt Strokes in Sickle Cell Disease: Therapeutic Strategies and Efficacy. Hematology 2011, 2011, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grunt, S.; Mazenauer, L.; Buerki, S.E.; Boltshauser, E.; Mori, A.C.; Datta, A.N.; Fluss, J.; Mercati, D.; Keller, E.; Maier, O.; et al. Incidence and Outcomes of Symptomatic Neonatal Arterial Ischemic Stroke. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e1220–e1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernard, T.J.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Lo, W.; Mackay, M.; Ganesan, V.; DeVeber, G.; Goldenberg, N.A.; Armstrong-Wells, J.; Dowling, M.M.; Roach, E.S.; et al. Towards a Consensus-Based Classification of Childhood Arterial Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2012, 43, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, M.T.; Wiznitzer, M.; Benedict, S.L.; Lee, K.J.; DeVeber, G.A.; Ganesan, V. Arterial ischemic stroke risk factors: The international pediatric stroke study. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafay, M.F.; Pontigon, A.-M.; Chiang, J.; Adams, M.; Jarvis, D.A.; Silver, F.; MacGregor, D.; DeVeber, G.A. Delay to Diagnosis in Acute Pediatric Arterial Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, K.; Lee, J.H.; Cheng, P.; Ajani, Z.; Salem, M.M.; Sangha, N. Pediatric stroke associated with a sedentary lifestyle during the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic: A case report on a 17-year-old. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, L.; Shekhar, S.; Bansal, A.; Kumar, S. COVID-19 associated arterial ischaemic stroke and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: A case report. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beslow, L.A.; Msc, A.B.L.; Fox, C.K.; Kossorotoff, M.; Zambrano, Y.C.Z.; Hernández-Chávez, M.; Hassanein, S.M.A.; Byrne, S.; Lim, M.; Maduaka, N.; et al. Pediatric Ischemic Stroke: An Infrequent Complication of SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 89, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, M.T.; Lee, M.; Churilov, L.; Yock-Corrales, A.; Donnan, G.; Monagle, P.; Babl, F. Pediatric brain attacks: Differentiating between stroke and mimics in the emergency room. International Stroke Conference oral abstract 37. Stroke 2014, 45, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinghurst, L.L.; Beslow, L.A.; Abend, N.S.; Uohara, M.; Jastrzab, L.; Licht, D.J.; Ichord, R.N. Incidence and predictors of epilepsy after pediatric arterial ischemic stroke. Neurology 2017, 88, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbers, J.; Wainwright, M.S.; Amlie-Lefond, C. The Pediatric Stroke Code: Early Management of the Child with Stroke. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 19–24.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichord, R.N.; Bastian, R.; Abraham, L.; Askalan, R.; Benedict, S.; Bernard, T.J.; Beslow, L.; de Veber, G.; Dowling, M.; Friedman, N.; et al. Interrater reliability of the Pediatric Na-tional Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (PedNIHSS) in a multicenter study. Stroke 2011, 42, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ichord, R.; Smith, S.E.; Garg, B.P.; Garcia-Espana, F.J.; Licht, D.J.; O’Tool, E.; Clancy, R. Pediatric adaptation of the NIH stroke scale predicts outcome after arterial ischemic stroke in children. Stroke 2005, 36, 480–481. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, W.J.; Derdeyn, C.; Biller, J.; Coffey, C.S.; Hoh, B.L.; Jauch, E.C.; Johnston, K.C.; Johnston, S.C.; Khalessi, A.A.; Kidwell, C.S.; et al. 2015 American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Focused Update of the 2013 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Regarding Endovascular Treatment: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American. Stroke 2015, 46, 3020–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van der Lugt, A.; de Miquel, M.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkin, M.J.; DeVeber, G.; Ichord, R.N.; Kirton, A.; Chan, A.K.C.; Hovinga, C.A.; Gill, J.C.; Szabo, A.; Hill, M.; Scholz, K.; et al. Thrombolysis in Pediatric Stroke Study. Stroke 2015, 46, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, B.G.; Cavelti, A.; Arnold, M.; Bigi, S.; Regényi, M.; Mattle, H.P.; Gralla, J.; Fluss, J.V.; Weber, P.; Hackenberg, A.; et al. Long-term outcome after arterial ischemic stroke in children and young adults. Neurology 2015, 84, 1941–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Bigi, S.; Laughlin, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Sinclair, A.; Dirks, P.; Pontigon, A.M.; Moharir, M.; Askalan, R.; MacGregor, D.; et al. Association Between Prolonged Seizures and Malignant Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction in Children With Acute Ischemic Stroke. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 64, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beslow, L.A.; Kasner, S.E.; Smith, S.E.; Mullen, M.T.; Kirschen, M.P.; Bastian, R.A.; Dowling, M.M.; Lo, W.; Jordan, L.C.; Bernard, T.J.; et al. Concurrent Validity and Reliability of Retrospective Scoring of the Pediatric National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale. Stroke 2012, 43, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Davalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K.R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T.; et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Putaala, J.; Metso, T.M.; Metso, A.J.; Mäkelä, E.; Haapaniemi, E.; Salonen, O.; Kaste, M.; Tatlisumak, T. Thrombolysis in young adults with is-chemic stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, J.T.; Siepmann, T.; Barlinn, J.; Winzer, S.; Penzlin, A.I.; Puetz, V.; von der Hagen, M.; Barlinn, K. Safety and efficacy of recanalization therapy in pediatric stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satti, S.; Chen, J.; Sivapatham, T.; Jayaraman, M.; Orbach, D. Mechanical thrombectomy for pediatric acute ischemic stroke: Review of the literature. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2016, 9, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, E.S.; Golomb, M.; Adams, R.; Biller, J.; Daniels, S.; DeVeber, G.; Ferriero, D.; Jones, B.V.; Kirkham, F.; Scott, R.M.; et al. Management of Stroke in Infants and Children: A scientific statement from a Special Writing Group of the American Heart Association. Stroke 2008, 39, 2644–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schechter, T.; Kirton, A.; Laughlin, S.; Pontigon, A.-M.; Finkelstein, Y.; MacGregor, D.; Chan, A.K.C.; DeVeber, G.; Brandão, L.R. Safety of anticoagulants in children with arterial ischemic stroke. Blood 2012, 119, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sträter, R.; Kurnik, K.; Heller, C.; Schobess, R.; Luigs, P.; Nowak-Göttl, U. Aspirin versus low-dose low-molecular-weight heparin: Antithrombotic therapy in pediatric ischemic stroke patients: A prospective follow-up study. Stroke 2001, 32, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fullerton, H.J.; Wu, Y.W.; Sidney, S.; Johnston, S.C. Risk of Recurrent Childhood Arterial Ischemic Stroke in a Population-Based Cohort: The Importance of Cerebrovascular Imaging. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullerton, H.J.; Wintermark, M.; Hills, N.K.; Dowling, M.M.; Tan, M.; Rafay, M.F.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Barkovich, A.J.; DeVeber, G.A.; Plumb, P.A.; et al. Risk of Recurrent Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Childhood: A prospective international study. Stroke 2016, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beslow, L.A.; Smith, S.E.; Vossough, A.; Licht, D.J.; Kasner, S.E.; Favilla, C.; Halperin, A.R.; Gordon, D.M.; Jones, C.I.; Cucchiara, A.J.; et al. Hemorrhagic Transformation of Childhood Arterial Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simma, B.; Höliner, I.; Luetschg, J. Therapy in pediatric stroke. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 172, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simma, B.; Tscharre, A.; Hejazi, N.; Krasznai, L.; Fae, P. Neurologic outcome after decompressive craniectomy in children. Intensiv. Care Med. 2002, 28, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.E.; Kirkham, F.J.; DeVeber, G.; Millman, G.; Dirks, P.B.; Wirrell, E.; Telfeian, A.E.; Sykes, K.; Barlow, K.; Ichord, R. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant middle cerebral artery infarction in children. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 53, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klucka, J.; Stourac, P.; Stoudek, R.; Toukalkova, M.; Harazim, H.; Kosinova, M.; Stouracova, A.; Mrlian, A.; Suk, P.; Malaska, J. Ischemic stroke in paediatrics—Narrative review of the literature and two cases. Biomed. Pap. 2017, 161, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cnossen, M.H.; Aarsen, F.K.; Akker, S.L.V.D.; Danen, R.; Appel, I.M.; Steyerberg, E.; E Catsman-Berrevoets, C. Paediatric arterial ischaemic stroke: Functional outcome and risk factors. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, J.; Kaufmann, F.; Boltshauser, E.; Mori, A.C.; Mercati, D.G.; Haenggeli, C.-A.; Keller, E.; Lütschg, J.; Marcoz, J.-P.; Ramelli, G.-P.; et al. Neuropsychological Problems after Paediatric Stroke: Two Year Follow-Up of Swiss Children. Neuropediatrics 2006, 37, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Studer, M.; Boltshauser, E.; Mori, A.C.; Datta, A.; Fluss, J.; Mercati, D.; Hackenberg, A.; Keller, E.; Maier, O.; Marcoz, J.-P.; et al. Factors affecting cognitive outcome in early pediatric stroke. Neurology 2014, 82, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeVeber, G.A.; MacGregor, D.; Curtis, R.; Mayank, S. Neurologic Outcome in Survivors of Childhood Arterial Ischemic Stroke and Sinovenous Thrombosis. J. Child Neurol. 2000, 15, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.K.; Johnston, S.C.; Sidney, S.; Fullerton, H. High critical care usage due to pediatric stroke: Results of a population-based study. Neurology 2012, 79, 420-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallick, A.A.; Ganesan, V.; Kirkham, F.J.; Fallon, P.; Hedderly, T.; McShane, T.; Parker, A.P.; Wassmer, E.; Wraige, E.; Amin, S.; et al. Outcome and recurrence 1 year after pediatric arterial ischemic stroke in a population-based cohort. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elbers, J.; DeVeber, G.; Pontigon, A.-M.; Moharir, M. Long-Term Outcomes of Pediatric Ischemic Stroke in Adulthood. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 29, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.K.; Hirtz, D.G.; DeVeber, G.; Nelson, K.B. Report of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke workshop on perinatal and childhood stroke. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajek, C.A.; Yeates, K.O.; Anderson, V.; Mackay, M.; Greenham, M.; Gomes, A.; Lo, W. Cognitive Outcomes Following Arterial Ischemic Stroke in Infants and Children. J. Child Neurol. 2013, 29, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolk, A.; Ennok, M.; Laugesaar, R.; Kaldoja, M.-L.; Talvik, T. Long-Term Cognitive Outcomes after Pediatric Stroke. Pediatr. Neurol. 2011, 44, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Most Common Risk Factors According to Age Group (According to Jeong et al. [33]) | |
|---|---|
| Age Group | Most Common Risk Factor |
| 1–11 months | CNS infection |
| Cardiac disease Severe dehydration | |
| 1–5 years | Moyamoya disease |
| Cardiac disease | |
| Inflammatory vasculopathy | |
| 6–11 years | Moyamoya disease |
| Prothrombotic condition | |
| Metabolic disease | |
| ≥12 years | Cardiac disease |
| Prothrombotic condition | |
| Metabolic disease | |
| Clinical AIS Presentation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Perinatal AIS | Childhood AIS | Stroke-Like Symptoms |
| Seizures (focal and unilateral) | Hemiparesis | Migraine |
| Cardiorespiratory symptoms | Facial unilateral weakness | Headache |
| Altered consciousness | Speech disorder | Confusion |
| Failure to thrive | Vision abnormalities | Syncope |
| Feeding intolerance | Altered consciousness | Nausea and vomiting |
| seizures with Todd paresis | ||
| Bell palsy | ||
| Altered consciousness |
| ABCDE Approach by ERC and EPALS * | ||
|---|---|---|
| ABCDE Approach | Aim | Action/Management |
| A—Airway | Airway patency, cervical spine protection if indicated | Open the mouth, bend the head (over 1 year), use airway if needed, MILS **, cervical collar or head blocks |
| B—Breathing | Spontaneous breathing efficacy, normoxemia, normocapnia | Pulse oximetry, oxygen, mechanical ventilation if indicated, capnography and blood gases analysis |
| C—Circulation | Oxygen delivery to meet the demand, blood pressure (50–95% according to age), adequate heart rate, capillary refill time ≤2 s, lactate ≤2 mmol/L | Fluid resuscitation (10 mL/kg fluid challenge), vasopressors or antihypertensives to meet target blood pressure |
| D—Disability | GCS ≥ 9, seizures control | Tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation if GCS ≤ 8 and anticonvulsants |
| E—Exposure/Examination | Clinical examination, temperature management, normoglycemia (6–10 mmol/L) | Insulin or glucose to meet target glycemia and normothermia |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klučka, J.; Klabusayová, E.; Musilová, T.; Kramplová, T.; Skříšovská, T.; Kratochvíl, M.; Kosinová, M.; Horák, O.; Ošlejšková, H.; Jabandžiev, P.; et al. Pediatric Patient with Ischemic Stroke: Initial Approach and Early Management. Children 2021, 8, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080649
Klučka J, Klabusayová E, Musilová T, Kramplová T, Skříšovská T, Kratochvíl M, Kosinová M, Horák O, Ošlejšková H, Jabandžiev P, et al. Pediatric Patient with Ischemic Stroke: Initial Approach and Early Management. Children. 2021; 8(8):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080649
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlučka, Jozef, Eva Klabusayová, Tereza Musilová, Tereza Kramplová, Tamara Skříšovská, Milan Kratochvíl, Martina Kosinová, Ondřej Horák, Hana Ošlejšková, Petr Jabandžiev, and et al. 2021. "Pediatric Patient with Ischemic Stroke: Initial Approach and Early Management" Children 8, no. 8: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080649
APA StyleKlučka, J., Klabusayová, E., Musilová, T., Kramplová, T., Skříšovská, T., Kratochvíl, M., Kosinová, M., Horák, O., Ošlejšková, H., Jabandžiev, P., & Štourač, P. (2021). Pediatric Patient with Ischemic Stroke: Initial Approach and Early Management. Children, 8(8), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8080649






