Multimodal Treatment of Pediatric Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Presentation
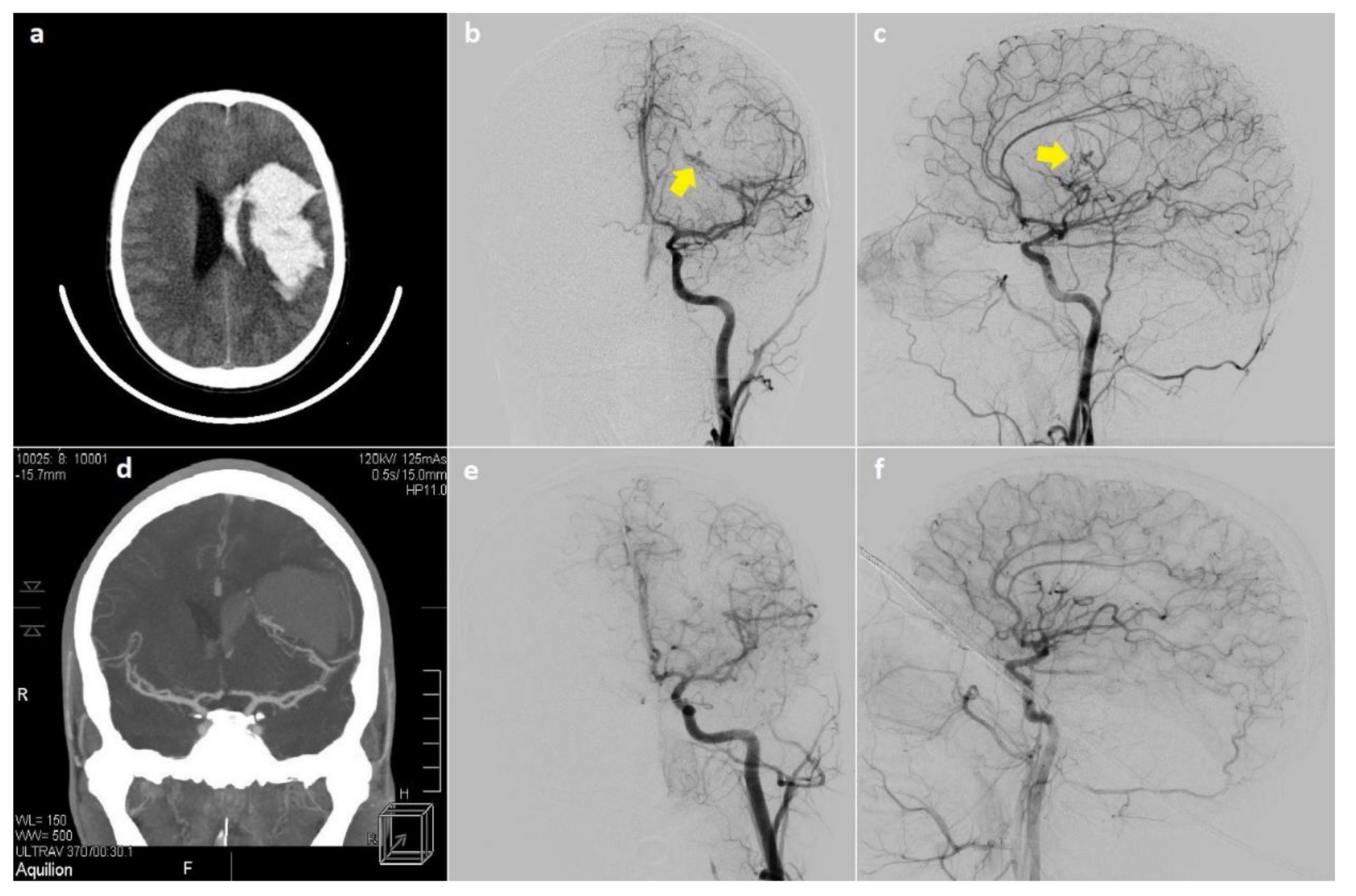
3.2. Radiological Presentation
3.3. Outcomes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.R.; Butler, W.E.; Ogilvy, C.S. Surgical approaches to vascular anomalies of the child’s brain. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2002, 15, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, Q.-J.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Cui, X.-B.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Lai, L.-F.; Su, S.-X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.-F.; He, X.-Y.; et al. Clinical features and endovascular treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2014, 30, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, L.C.; Johnston, S.C.; Wu, Y.W.; Sidney, S.; Fullerton, H.J. The importance of cerebral aneurysms in childhood hemorrhagic stroke: A population-based study. Stroke 2009, 40, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buis, D.R.; Dirven, C.M.F.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Mandl, E.S.; Nijeholt, G.J.L.Á.; Eshghi, D.S.; Berg, R.V.D.; Baayen, J.C.; Meijer, O.W.M.; Slotman, B.J.; et al. Radiosurgery of brain arteriovenous malformations in children. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.A.; Storey, A.; Orbach, D.B.; Scott, R.M.; Smith, E.R. Microsurgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients: The Boston Children’s Hospital experience. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2015, 15, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Ye, Z.; Xu, J.; You, C.; Jiang, Y. The factors associated with hemorrhagic presentation in children with untreated brain arteriovenous malformation: A meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2018, 23, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, L.; Wallace, M.C.; Ter Brugge, K.G.; O’Kelly, C.; Willinsky, R.A.; Tymianski, M. The natural history and predictive features of hemorrhage from brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 2009, 40, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernesniemi, J.A.; Dashti, R.; Juvela, S.; Väärt, K.; Niemelä, M.; Laakso, A. Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: A long-term follow-up study of risk of hemorrhage in 238 patients. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Martin, N.A. A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemer, A.B.; Bank, O.W.; Armonda, R.A.; Liu, A.-H.; Herzig, D.W.; Bell, R.S. Acute embolization of ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2013, 5, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondziolka, D.; Kano, H.; Yang, H.-C.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L. Radiosurgical management of pediatric arteriovenous malformations. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2010, 26, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.L.; Macdonald, R.L. Surgical Strategies for Acutely Ruptured Arteriovenous Malformations. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2015, 37, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.-T.; Fong, D. Ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations in children: Correlation of clinical outcome with admission parameters. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2010, 46, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abecassis, I.J.; Xu, D.S.; Batjer, H.H.; Bendok, B.R. Natural history of brain arteriovenous malformations: A systematic review. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 37, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, C.P.; McDowell, M.M.; Phan, M.Q.; Connolly, E.S.; LaVine, S.D.; Meyers, P.M.; Sahlein, D.; Solomon, R.A.; Feldstein, N.A.; Anderson, R.C. Number and location of draining veins in pediatric arteriovenous malformations: Association with hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2014, 14, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, M.J.; Armstrong, D.; Vachhrajani, S.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Dirks, P.B.; Drake, J.M.; Smith, E.R.; Scott, R.M.; Orbach, D.B. Angioarchitectural features associated with hemorrhagic presentation in pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2013, 5, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Starke, R.M.; Kano, H.; Mathieu, D.; Huang, P.P.; Feliciano, C.; Rodriguez-Mercado, R.; Almodovar, L.; Grills, I.S.; Silva, D.; et al. International multicenter cohort study of pediatric brain arteriovenous malformations. Part 1: Predictors of hemorrhagic presentation. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.T.; Kim, H.; McCulloch, C.E.; Mikhak, B.; Young, W.L. A supplementary grading scale for selecting patients with brain arteriovenous malformations for surgery. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidert, M.C.; Lawton, M.T.; Mader, M.; Seifert, B.; Valavanis, A.; Regli, L.; Bozinov, O.; Burkhardt, J.-K. The AVICH Score: A Novel Grading System to Predict Clinical Outcome in Arteriovenous Malformation-Related Intracerebral Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2016, 92, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.A.; Lai, P.M.R.; Du, R.; A Aziz-Sultan, M.; Patel, N.J. The Ruptured Arteriovenous Malformation Grading Scale (RAGS): An Extension of the Hunt and Hess Scale to Predict Clinical Outcome for Patients With Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kırış, T.; Sencer, A.; Şahinbaş, M.; Sencer, S.; Imer, M.; Izgi, N. Surgical results in pediatric Spetzler-Martin grades I-III intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristol, R.E.; Albuquerque, F.C.; Spetzler, R.F.; Rekate, H.L.; McDougall, C.G.; Zabramski, J.M. Surgical management of arteriovenous malformations in children. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105 (Suppl. 2), 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatci, I.; Geyik, S.; Yavuz, K.; Cekirge, H.S. Endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations with prolonged intranidal Onyx injection technique: Long-term results in 350 consecutive patients with completed endovascular treatment course. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Stapf, C.; Sciacca, R.; Faulstich, A.; Mohr, J.; Schumacher, H.; Mast, H. Risk of endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 2002, 33, 1816–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Nagata, I.; Nozaki, K.; Morimoto, M.; Taki, W.; Kikuchi, H. Posttreatment sequelae of palliatively treated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2000, 46, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, A.; Dashti, R.; Seppänen, J.; Juvela, S.; Väärt, K.; Niemelä, M.; Sankila, R.; Hernesniemi, J.A. Long-term excess mortality in 623 patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Norat, P.; Ding, D.; Mendes, G.A.C.; Tvrdik, P.; Park, M.S.; Kalani, M.Y. Transvenous embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations: A review of techniques, indications, and outcomes. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 45, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, G.Z.; Ghali, M.G.Z.; Ghali, E.Z. Transvenous embolization of arteriovenous malformations. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 178, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyns, N.; Blond, S.; Gauvrit, J.-Y.; Touzet, G.; Coche, B.; Pruvo, J.-P.; Dhellemmes, P. Role of radiosurgery in the management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations in the pediatric age group: Data from a 100-patient series. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharia, B.E.; Vaughan, K.A.; Jacoby, A.; Hickman, Z.L.; Bodmer, D.; Connolly, E.S., Jr. Management of ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2012, 14, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauwblomme, T.; Bourgeois, M.; Meyer, P.; Puget, S.; Di Rocco, F.; Boddaert, N.; Zerah, M.; Brunelle, F.; Rose, C.S.; Naggara, O. Long-term outcome of 106 consecutive pediatric ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations after combined treatment. Stroke 2014, 45, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Long-term outcomes and prognostic predictors of 111 pediatric hemorrhagic cerebral arteriovenous malformations after microsurgical resection: A single-center experience. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No. of Patients (%) | |
|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 22 |
| Male | 11 (50) |
| Female | 11 (50) |
| Age in years (mean, SD, range) | 11.86 (range 2–17) |
| Presentation | |
| Altered level of consciousness | 6 (27.3) |
| Seizures | 3 (13.6) |
| Neurologic deficit | 8 (36.4) |
| Headache | 16 (72.7) |
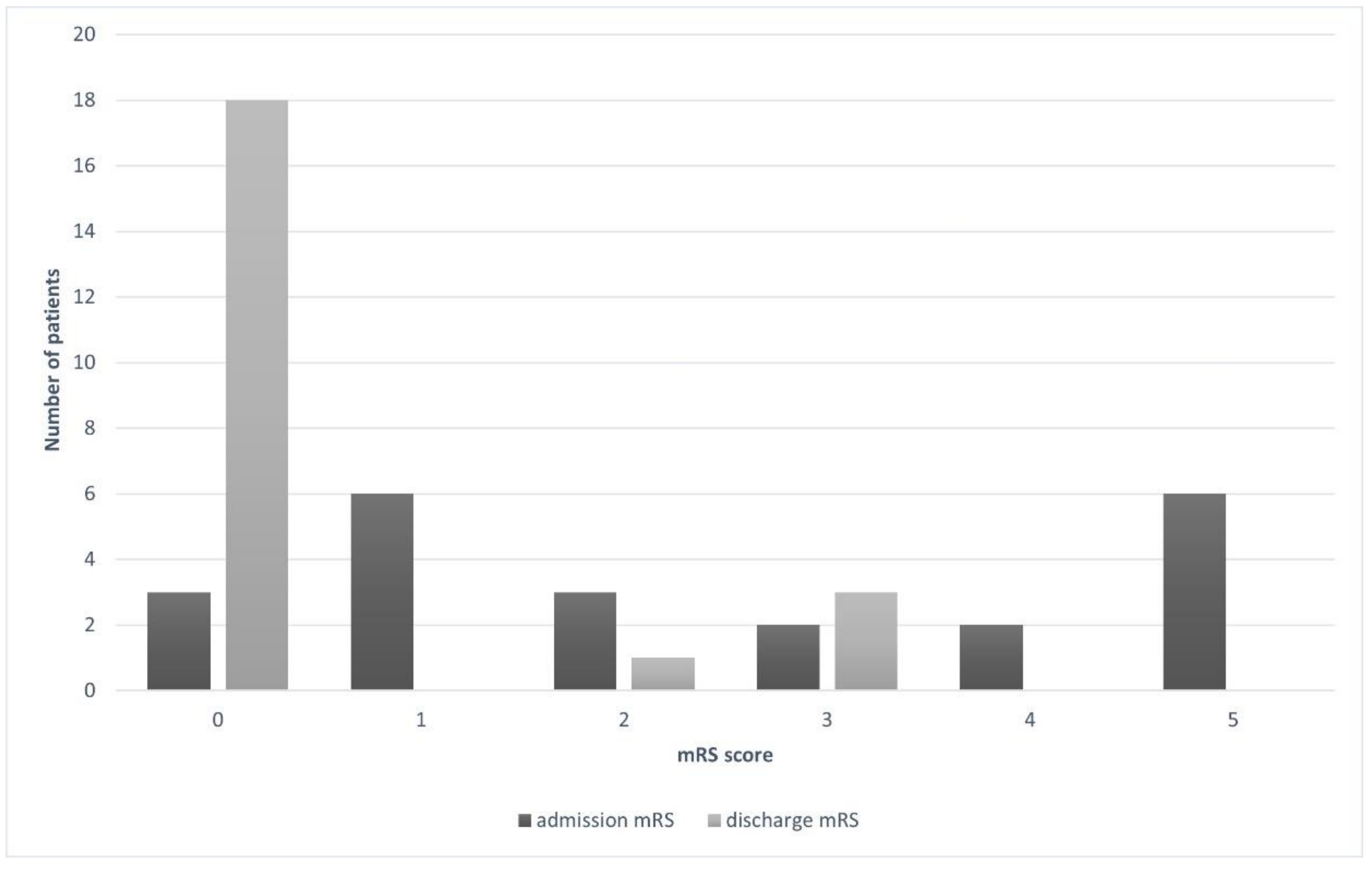
| mRS at admission | |
| 0 | 3 (13.6) |
| 1 | 6 (27.3) |
| 2 | 3 (13.6) |
| 3 | 2 (9.1) |
| 4 | 2 (9.1) |
| 5 | 6 (27.3) |
| mRS at discharge | |
| 0 | 18 (81.8) |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 (4.6) |
| 3 | 3 (13.6) |
| 4 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 |
| Hunt-Hess score | |
| 1 | 5 (22.7) |
| 2 | 6 (27.3) |
| 3 | 5 (22.7) |
| 4 | 6 (27.3) |
| 5 | 0 |
| No. of Patients (%) | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Frontal | 6 (27.3) |
| Fronto-parietal | 1 (4.6) |
| Parietal | 5 (22.7) |
| Occipital | 4 (18.2) |
| Temporal | 2 (9.1) |
| Deep | 4 (18.2) |
| Laterality | |
| Right | 11 (50) |
| Left | 11 (50) |
| Hemorrhage | |
| ICH | 20 (91) |
| IVH | 11 (50) |
| SAH | 1 (4.6) |
| Size of nidus | |
| 0–3 cm | 20 (91) |
| 3–6 cm | 2 (9.1) |
| >6 cm | 0 |
| Eloquent location | 7 (31.8) |
| Deep venous drainage | 9 (41) |
| Spetzler-Martin grade | |
| I | 9 (41) |
| II | 6 (27.3) |
| III | 3 (13.6) |
| IV | 4 (18.2) |
| V | 0 |
| Supplementary SM grade | |
| 2 | 8 (36.4) |
| 3 | 7 (31.8) |
| 4 | 0 |
| 5 | 3 (13.6) |
| 6 | 4 (18.2) |
| 7 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 |
| No. of Patients (%) | Surgery | Embolization | Radiosurgery | Embolization + Surgery | Embolization + Radiosurgery | Surgery + Radiosurgery | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of patients | 22 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Low-grade AVMs | |||||||
| I | 9 | 6 (66.7) | 1 (11.1) | 0 | 0 | 2 (22.2) | 0 |
| II | 6 | 2 (33.3) | 2 (33.3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 1 (16.7) |
| III | 3 | 1 (33.3) | 0 | 0 | 2 (66.7) | 0 | 0 |
| High-grade AVMs | |||||||
| IV | 4 | 0 | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| V | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antkowiak, L.; Putz, M.; Rogalska, M.; Mandera, M. Multimodal Treatment of Pediatric Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Single-Center Study. Children 2021, 8, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8030215
Antkowiak L, Putz M, Rogalska M, Mandera M. Multimodal Treatment of Pediatric Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Single-Center Study. Children. 2021; 8(3):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8030215
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntkowiak, Lukasz, Monika Putz, Marta Rogalska, and Marek Mandera. 2021. "Multimodal Treatment of Pediatric Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Single-Center Study" Children 8, no. 3: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8030215
APA StyleAntkowiak, L., Putz, M., Rogalska, M., & Mandera, M. (2021). Multimodal Treatment of Pediatric Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations: A Single-Center Study. Children, 8(3), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8030215







