Reconstruction of the Hip in Multiple Hereditary Exostoses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
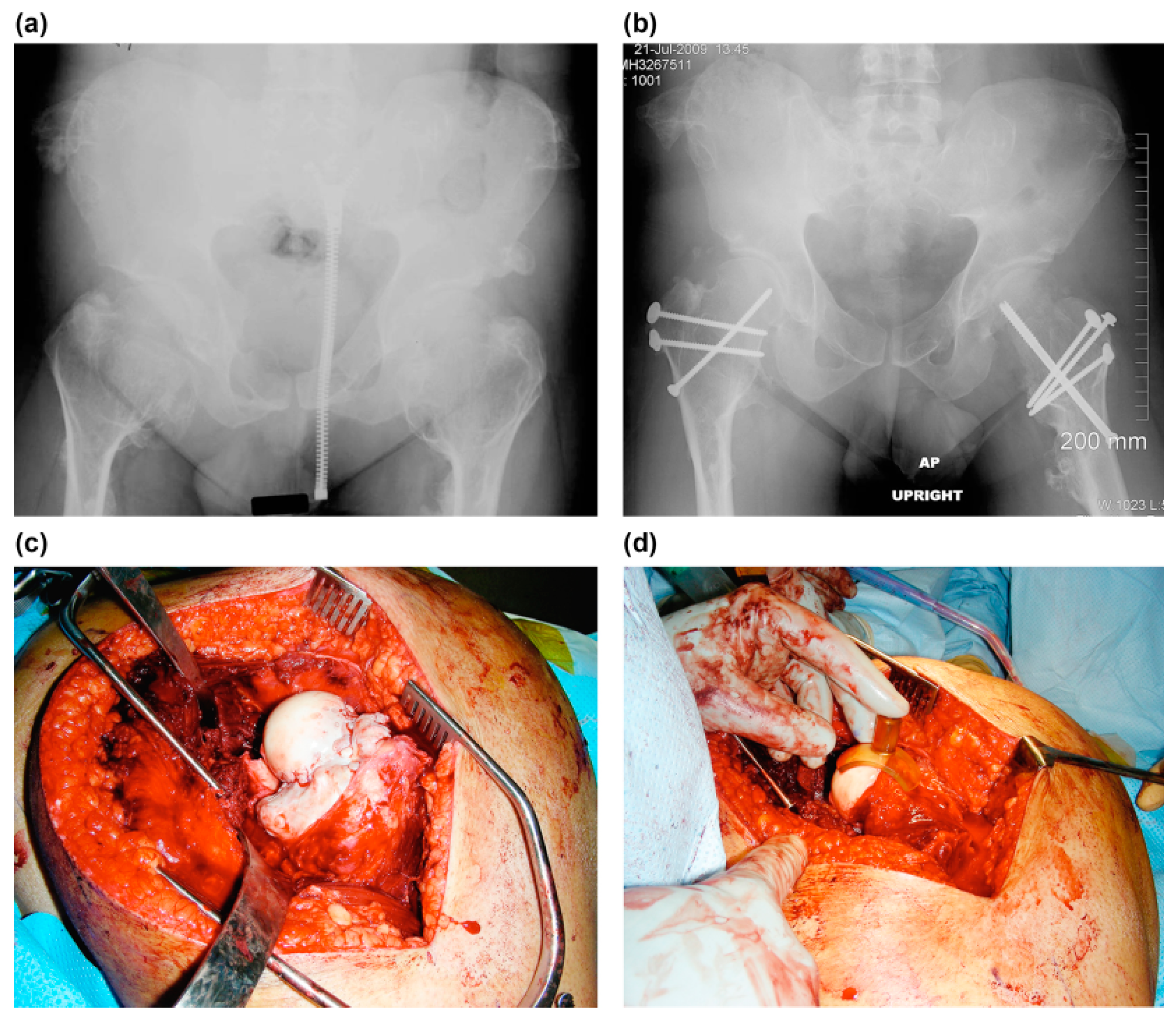
2.1. Surgical Procedure
2.2. Postoperative Management
2.3. Ethical Considerations
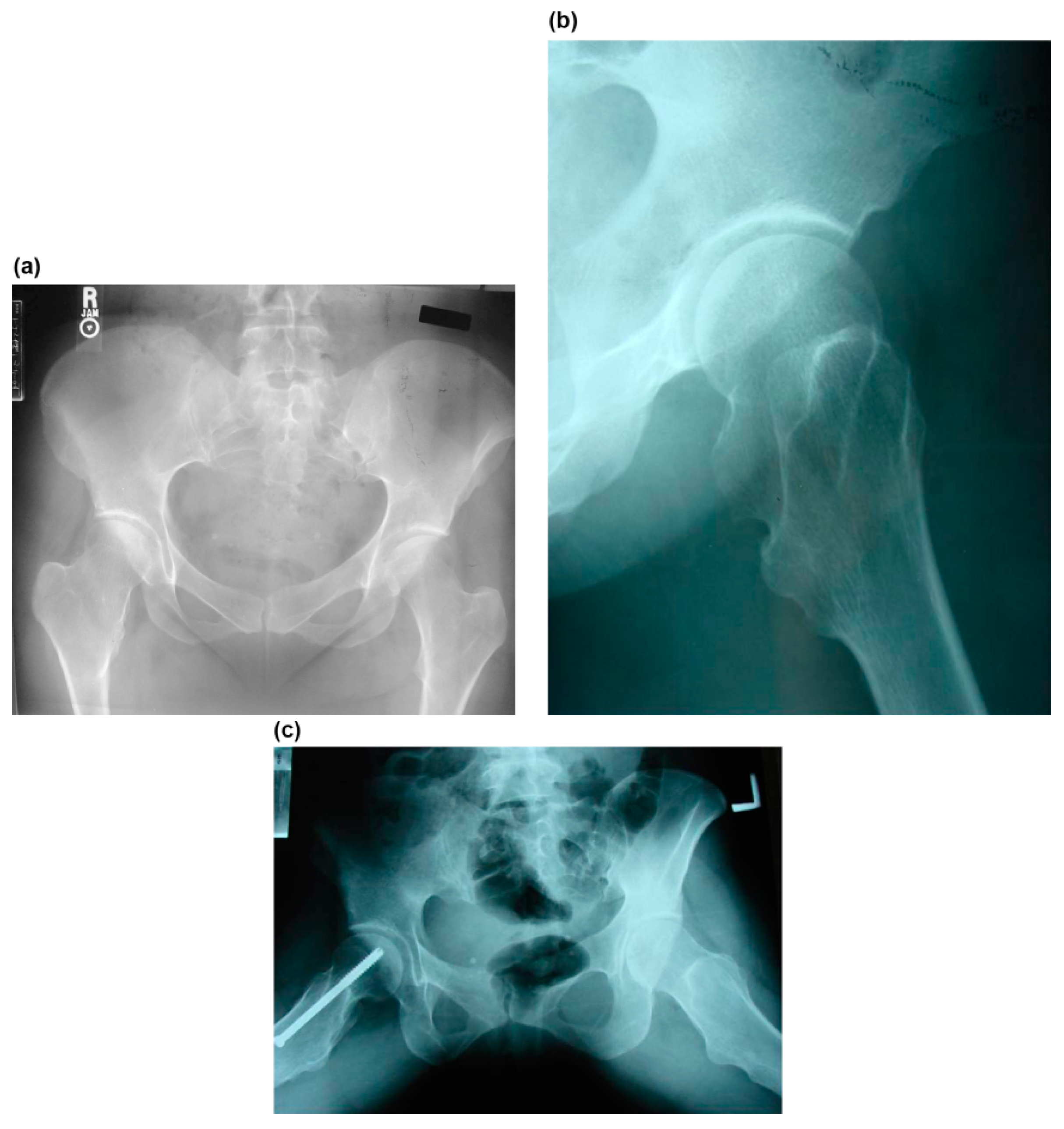
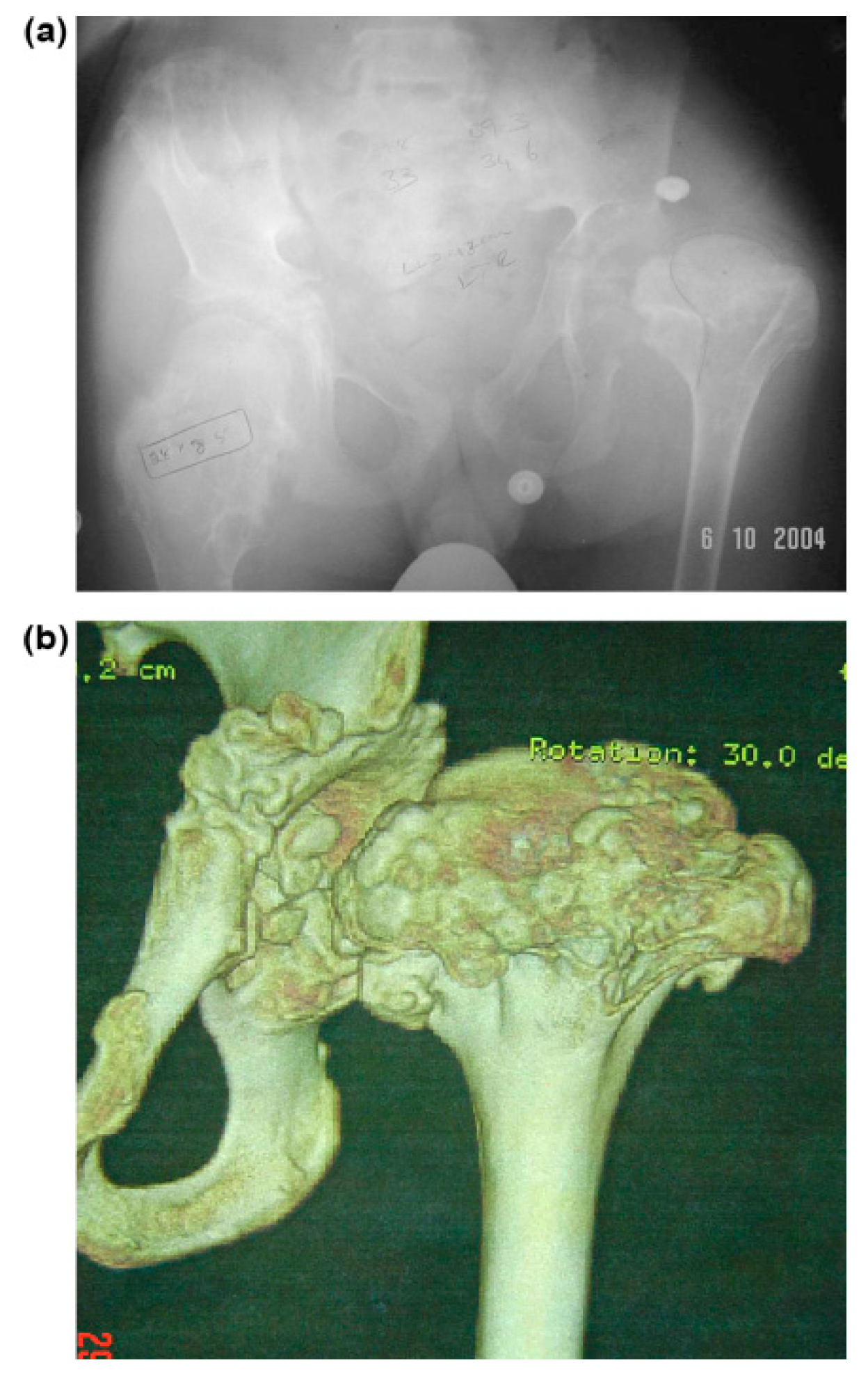
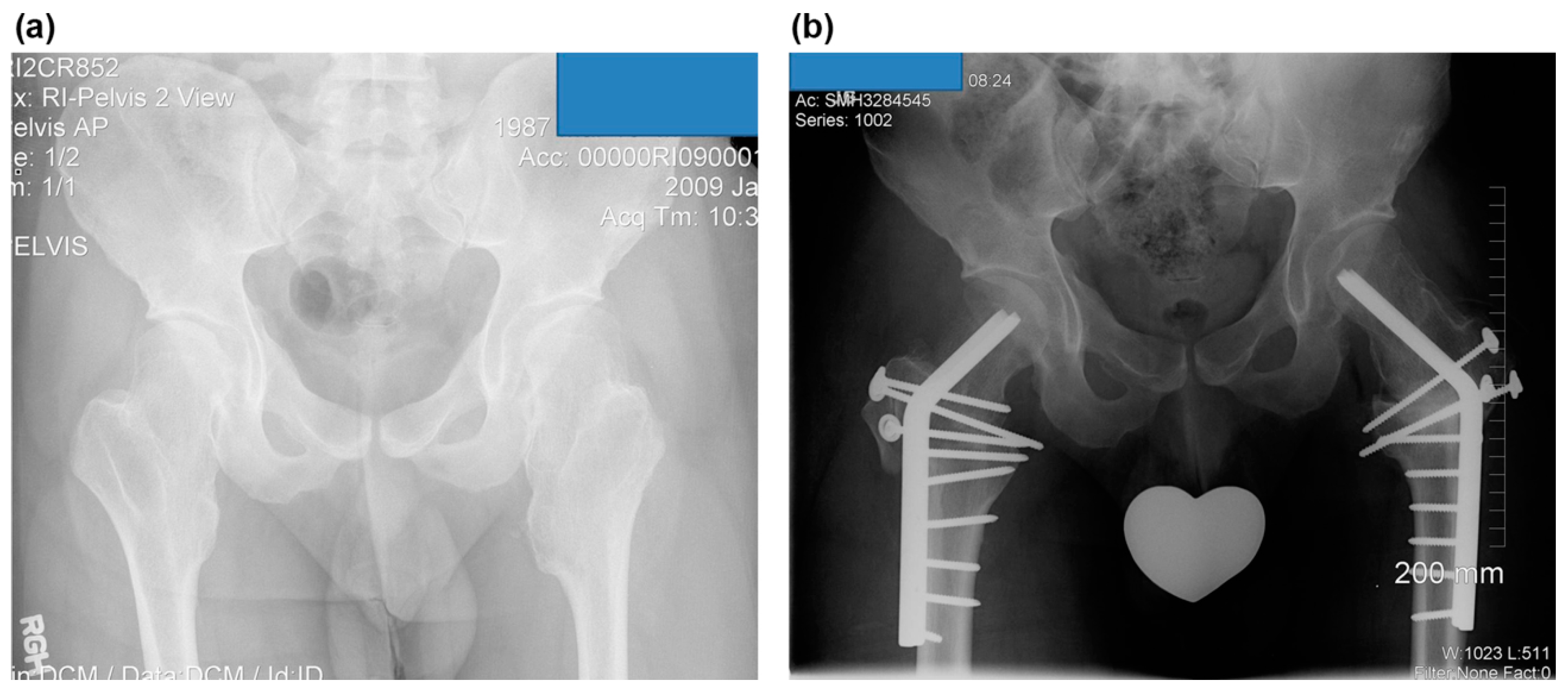
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Results
3.2. Radiographic Results
3.3. Combined Surgery and Complications
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmale, G.A.; Conrad, E.U.; Raskind, W.H. The natural history of hereditary multiple exostoses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1994, 76, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Lüdecke, H.J.; Lindow, S.; Horton, W.A.; Lee, B.; Wagner, M.J.; Horsthemke, B.; Wells, D.E. Cloning of the putative tumour suppressor gene for hereditary multiple exostoses (EXT1). Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickens, D.; Clines, G.; Burbee, D.; Ramos, P.; Thomas, S.; Hogue, D.; Hecht, J.T.; Lovett, M.; Evans, G.A. The EXT2 multiple exostoses gene defines a family of putative tumour suppressor genes. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieber, J.R.; Dormans, J.P. Manifestations of hereditary multiple exostoses. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2005, 13, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, D.E.; Benson, M.K.; Hosney, G.A. The hip in hereditary multiple exostoses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2001, 83, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, L. Hereditary multiple exostosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1964, 16, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, F.; Simon, S.; Glimcher, M.J. Hereditary multiple exostoses. Anthropometric, roentgenographic, and clinical aspects. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1979, 61, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, D.S.; Hoyt, W.A., Jr. The development of the upper end of the femur in multiple hereditary exostosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1978, 137, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, N.A.; Mazur, J.M.; Loveless, E.A. Acetabular dysplasia associated with hereditary multiple exostoses. A case report. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2000, 82, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofiram, E.; Porat, S. Progressive subluxation of the hip joint in a child with hereditary multiple exostosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2004, 13, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellicoe, P.; Son-Hing, J.; Hopyan, S.; Thompson, G.H. Surgical hip dislocation for removal of intraarticular exostoses: Report of two cases. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2009, 29, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.N.; Daly, K.E.; Dodds, R.D.; Fixsen, J.A. Subluxation of the hip joint in multiple hereditary osteochondromatosis: Report of two cases. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1999, 19, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, M.T.; Moreau, G. Benign cartilage tumors. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 27, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.; Krieg, A.H.; Boyle, R.A.; Stalley, P.D. Bilateral total hip arthroplasty in Severe Hereditary Multiple Exostosis: A report of two cases. Hip Int. 2009, 19, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, D.R. Intra-articular osteochondromas of the hip joint in a child with multiple osteochondromas. Case report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1985, 199, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnomet, F.; Clavert, P.; Abidine, F.Z.; Gicquel, P.; Clavert, J.M.; Kempf, J.F. Hip arthroscopy in hereditary multiple exostoses: A new perspective of treatment. Arthroscopy 2001, 17, E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Kwak, H.S.; Cho, T.J.; Park, M.S.; Yoo, W.J.; Chung, C.Y.; Choi, I.H. Application of Ganz surgical hip dislocation approach in pediatric hip diseases. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2009, 1, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauermeister, S.; Letts, M. The orthopaedic manifestations of the Langer-Giedion syndrome. Orthop. Rev. 1992, 21, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredensborg, N. The CE angle of normal hips. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1976, 47, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooperman, D.R.; Wallensten, R.; Stulberg, S.D. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1983, 175, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ganz, R.; Gill, T.J.; Gautier, E.; Ganz, K.; Krügel, N.; Berlemann, U. Surgical dislocation of the adult hip a technique with full access to the femoral head and acetabulum without the risk of avascular necrosis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2001, 83, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, C.L.; Erickson, J.A. Treatment of femoro-acetabular impingement with surgical dislocation and debridement in young adults. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2006, 88, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulé, P.E.; Le Duff, M.J.; Zaragoza, E. Quality of life following femoral head-neck osteochondroplasty for femoroacetabular impingement. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laude, F.; Sariali, E.; Nogier, A. Femoroacetabular impingement treatment using arthroscopy and anterior approach. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Ganz, R.; Parvizi, J.; Beck, M.; Leunig, M.; Nötzli, H.; Siebenrock, K.A. Femoroacetabular impingement: A cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 417, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger, M.; Brunner, A.; Herzog, R.F. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement of the hip: A new technique to access the joint. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clohisy, J.C.; St John, L.C.; Schutz, A.L. Surgical treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Bedi, A.; Dolan, M.; Hetsroni, I.; Magennis, E.; Lipman, J.; Buly, R.; Kelly, B.T. Surgical treatment of femoroacetabular impingement improves hip kinematics: A computer-assisted model. Am. J. Spots Med. 2011, 39, 43S–49S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippon, M.J.; Weiss, D.R.; Kuppersmith, D.A.; Briggs, K.K.; Hay, C.J. Arthroscopic labral repair and treatment of femoroacetabular impingement in professional hockey players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilizaliturri, V.M.; Nossa-Barrera, J.M.; Rodriguez, E.A.; Galindo, J.C. Arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement secondary to paediatric hip disorders. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2007, 89, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domb, B.G.; Stake, C.E.; Botser, I.B.; Jackson, T.J. Surgical dislocation of the hip Versus arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement: A prospective matched-pair study With average 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 2013, 29, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawabi, D.H.; Degen, R.M.; Fields, K.G.; McLawhorn, A.; Ranawat, A.S.; Sink, E.L.; Kelly, B.T. Outcomes After arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement for patients With borderline hip dysplasia. Am. J. Spots Med. 2016, 44, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwachukwu, B.U.; Chang, B.; Kahlenberg, C.A.; Fields, K.; Nawabi, D.H.; Kelly, B.T.; Ranawat, A.S. ASArthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents provides clinically significant outcome improvement. Arthroscopy 2017, 33, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.J.; Lim, J.H.; Jung, S.T. Characteristics of hip impingement syndrome in patients with multiple hereditary exostoses. BMC. Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifici, M. Hereditary Multiple Exostoses: New Insights into Pathogenesis, Clinical Complications, and Potential Treatments. Curr. Osteoporos Rep. 2017, 15, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagón, V. Development of hip dysplasia in hereditary multiple exostosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2001, 21, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorel, J.C.; Schaeffer, M.F.; Homan, A.S.; Scholtes, V.A.B.; Kempen, D.H.R.; Ham, S.J. Surgical hip dislocation according to Ganz for excision of osteochondromas in patients with multiple hereditary exostoses. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2016, 98–B, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindani, N.; Eberhardt, O.; Wirth, T.; Surace, M.F.; Fernandez, F.F. Surgical dislocation for pediatric and adolescent hip deformity: Clinical and radiographical results at 3 years follow-up. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2017, 137, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Case | Gender | Involved Side | Age at Operation (Years) | Follow-Up Period (Months) | Site of Tumor at Hip | Symptoms at Presentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | R | 6 | 84 | A/M/P | Hip pain, LOM |
| 2 | Female | R | 39 | 80 | M/P | Sciatic nerve Sx., Hip pain |
| 3 | Male | L | 14 | 97 | FH | Hip pain, LOM |
| 4 | Female | L | 11 | M/P | Hip pain, LOM | |
| 5 | Male | B | R: 23 | 50 | A/M/P | Hip pain, LOM |
| L: 26 | 13 | A/M/P | Hip pain, LOM | |||
| 6 | Male | B | R: 22 L: 25 R: 26 | 12 | A/M/P | Hip pain, LOM |
| 7 | Female | B | L: 22 | 19 | A/M/P | Hip pain, LOM |
| R: 28 | A/M | Hip pain, LOM | ||||
| L: 27 | 40 | A/M/P | Hip pain, LOM |
| Case | Range of Motion (°) | Additional Procedure | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexion | Extension | Adduction | Abduction | IR | ER | |||||||||
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |||
| 1 | 10 | 110 | −10 | 0 | 5 | 20 | 45 | 45 | 10 | 35 | 60 | 50 | VIO | |
| 2 | 110 | 110 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 45 | 45 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 20 | Sciatic nerve decompression | |
| 3 | 60 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 20 | Langer–Giedion syndrome VaIO; DFVO | |
| 4 | 60 | 130 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 60 | 60 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 40 | VIO | |
| 5 | R | 60 | 100 | −20 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 30 | 60 | 0 | 15 | 20 | 40 | |
| L | 60 | 105 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 30 | ||
| 6 | R | 70 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 45 | VIO |
| L | 70 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 45 | 45 | 10 | 10 | VIO | |
| 7 | R | 90 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 45 | 40 | 45 | 20 | 30 | VIO |
| L | 60 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 40 | 20 | 45 | 45 | 45 | 30 | 30 | ||
| Case | NSA (°) | NSR | SL | SAA (°) | CEA (°) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | Postoperative | AP | Lateral | Preoperative | Postoperative | +82- | Posterative | |||||
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |||||||||
| 1 | 180 | 135 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 2.1 | Broken (sublux.) | Reduced | 45 | 0 | 25 | |
| 2 | 145 | 145 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.9 | 0.8 | Intact | Intact | 45 | 30 | 30 | |
| 3 | 135 | 135 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 4.3 | 1.9 | Broken (dislocation) | Reduced | 40 | <0 | 30 | |
| 4 | 155 | 140 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 1.3 | Broken (sublux.) | Reduced | 45 | 15 | 25 | |
| 5 | R | 140 | 140 | 6.7 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 1.2 | Intact | Intact | 45 | 25 | 30 |
| L | 150 | 150 | 3.6 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 1.3 | Intact | Intact | 45 | 25 | 30 | |
| 6 | R | 170 | 140 | 2.3 | 1.6 | 2.9 | 1.4 | Broken (sublux.) | Reduced | 45 | 25 | 40 |
| L | 180 | 130 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 1.3 | Broken (sublux.) | Reduced | 45 | 20 | 30 | |
| 7 | R | 160 | 140 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 1.5 | Broken (sublux.) | Reduced | 40 | 10 | 25 |
| L | 150 | 135 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 1.5 | Intact | Intact | 40 | 30 | 30 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.H.; Paley, D. Reconstruction of the Hip in Multiple Hereditary Exostoses. Children 2021, 8, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060490
Lee DH, Paley D. Reconstruction of the Hip in Multiple Hereditary Exostoses. Children. 2021; 8(6):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060490
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong Hoon, and Dror Paley. 2021. "Reconstruction of the Hip in Multiple Hereditary Exostoses" Children 8, no. 6: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060490
APA StyleLee, D. H., & Paley, D. (2021). Reconstruction of the Hip in Multiple Hereditary Exostoses. Children, 8(6), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8060490






