Dynamic and Static Splinting for Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
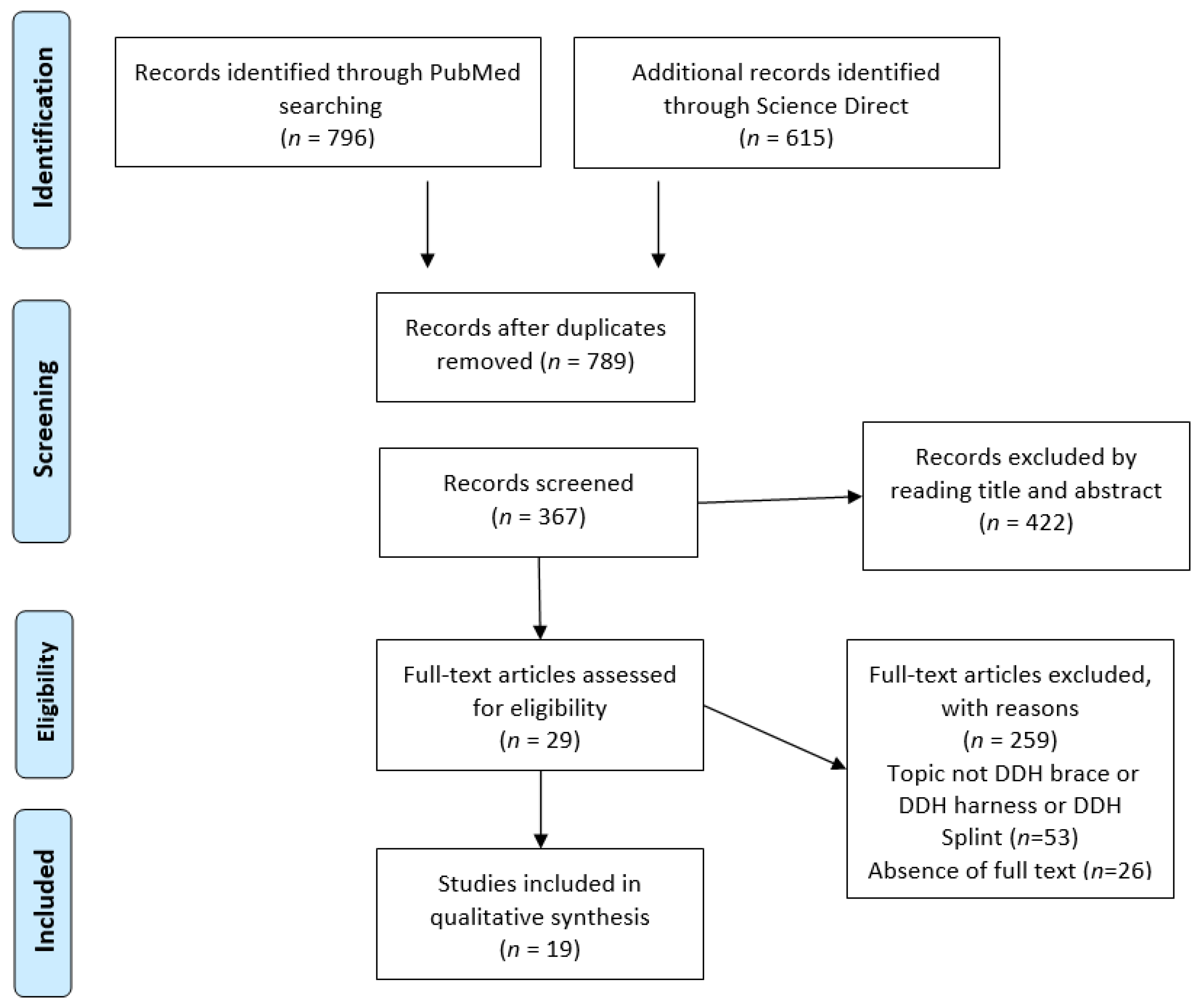
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Definition of Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
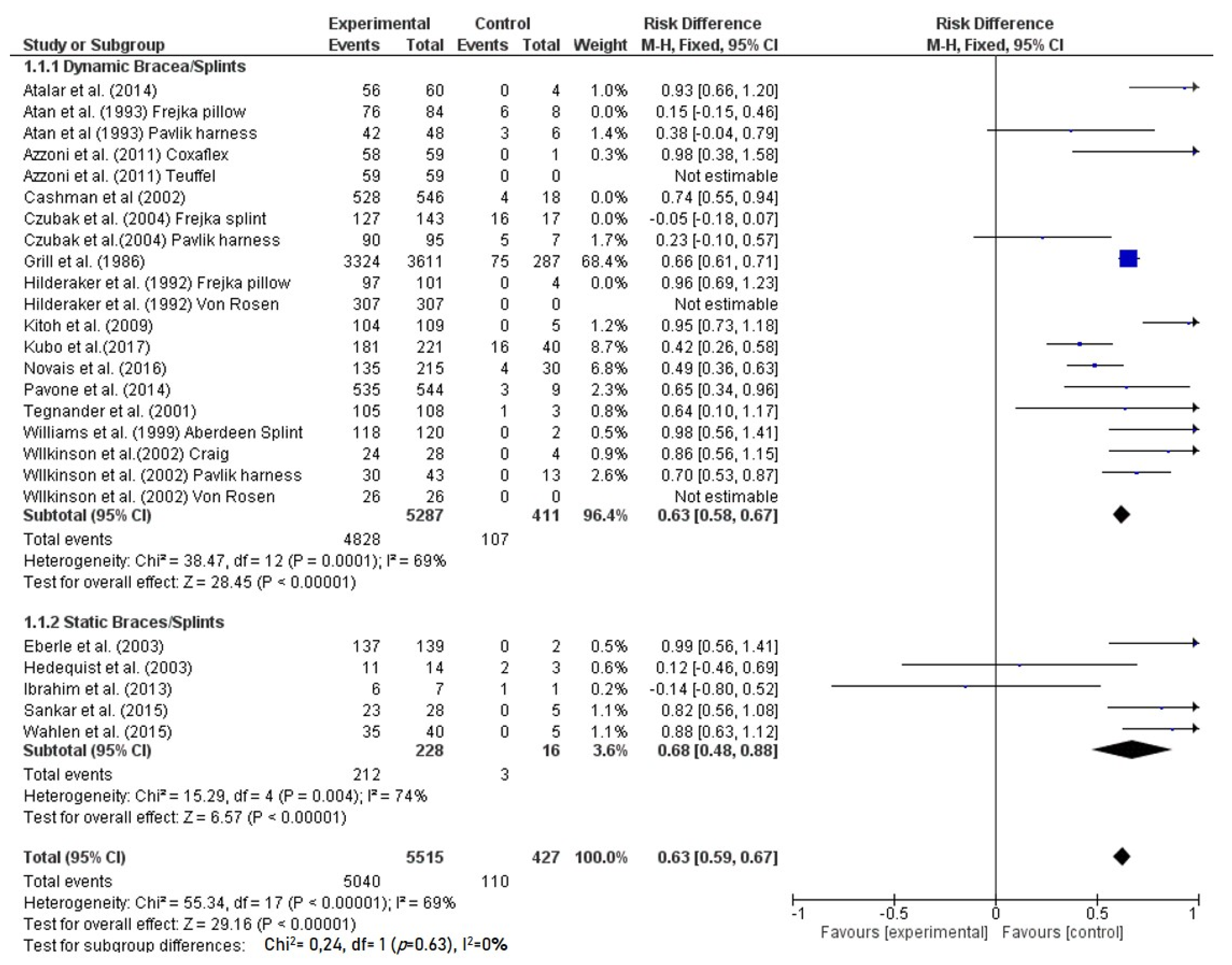
3. Results
3.1. Abduction Brace
3.2. Aberdeen Splint
3.3. Coxaflex splint
3.4. Craig Splint
3.5. Frejka pillow
3.6. Ilfeld Splint
3.7. Pavlik harness
3.8. Rhino-Style Splint
3.9. Teuffel Splint
3.10. Tubingen Splint
3.11. Von Rosen Splint
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loder, R.T.; Skopelja, E.N. The epidemiology and demographics of hip dysplasia. ISRN Orthop. 2011, 2011, 238607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R. The diagnosis of congenital hip-joint dislocation by the ultrasonic Combound treatment. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 1980, 97, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, R. Hip Sonography: Diagnosis and Management of Infant Hip Dysplasia, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–114. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, B.A.; Segal, L.S. Section on Orthopaedics. Evaluation and referral for developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20163107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, V.; Vescio, A.; Montemagno, M.; de Cristo, C.; Lucenti, L.; Pavone, P.; Testa, G. Perinatal Femoral Fracture: A Ten-Year Observational Case Series Study. Children 2020, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Truong, W.H.; Thompson, M.V.; Suryavanshi, J.R.; Penny, C.L.; Do, H.T.; Dodwell, E.R. Diagnostic and treatment preferences for developmental dysplasia of the hip: A survey of EPOS and POSNA members. J. Child. Orthop. 2018, 12, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, V.; Eseonu, K.; Sayani, J.; Ismail, N.; Uzoigwe, C.; Choudhury, M.Z.; Gulati, P.; Aqil, A.; Tibrewal, S. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in the newborn: A systematic review. World J. Orthop. 2013, 4, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernau, A. Die Tübinger Hüftbeugeschiene zur Behandlung der Hüftdysplasie. Z. Orthop. 1990, 128, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, H.; Pilge, H.; Weimann-Stahlschmidt, K.; Stefanovska, K.; Westhoff, B.; Krauspe, R. Use of the Tübingen splint for the initial management of severely dysplastic and unstable hips in newborns with DDH: An alternative to Fettweis plaster and Pavlik harness. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2018, 138, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwan, K.; Kirkham, J.; Paton, R.W.; Morley, E.; Newton, A.W.; Perry, D.C. Splinting for the non-operative management of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in children under six months of age. Coch. Data. Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, CD012717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinderaker, T.; Rygh, M.; Udén, A. The von Rosen splint compared with the Frejka pillow: A study of 408 neonatally unstable hips. Acta. Orthop. Scand. 1992, 63, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzoni, R.; Cabitza, P. A comparative study on the effectiveness of two different devices in the management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants. Min. Ped. 2011, 63, 355–361. [Google Scholar]
- Pagnotta, G.; Ruzzini, L.; Oggiano, L. Dynamic management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Arch. Ortop. Reumatol. 2012, 123, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, S.; Garfin, S.; Vance, R.; McKinnon, B.; Sutherland, D. Pitfalls in the use of the Pavlik harness for treatment of congenital dysplasia, subluxation, and dislocation of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1981, 63, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Mubarak, S.J.; Wenger, D.R. Developmental hip dysplasia and dislocation: Part II. Instr. Course Lect. 2004, 53, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnaghan, M.L.; Browne, R.H.; Sucato, D.J.; Birch, J. Femoral nerve palsy in Pavlik harness treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, V.; Pruijs, H.; Sakkers, R.; Castelein, R. Results of Pavlik harness treatment in children with dislocated hips between the age of six and twenty-four months. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2010, 30, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitoh, H.; Kawasumi, M.; Ishiguro, N. Predictive factors for unsuccessful treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip by the Pavlik harness. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2009, 29, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Yamamuro, T. Avascular necrosis in patients treated with the Pavlik harness for congenital dislocation of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1990, 72, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Naito, M.; Nomiyama, H. Treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hp with the Pavlik harness: Factors for predicting unsuccessful reduction. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2001, 10, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Lerman, J.A.; Emans, J.B.; Millis, M.B.; Share, J.; Zurakowski, D.; Kasser, J.R. Early failure of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental hip dysplasia: Clinical and ultrasound predictors. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2001, 21, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalar, H.; Gunay, C.; Komurcu, M. Functional treatment of developmental hip dysplasia with the Tübingen hip flexion splint. Hip Int. 2014, 24, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atar, D.; Lehman, W.B.; Tenenbaum, Y.; Grant, A.D. Pavlik harnes versus Frejka splint in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: Bicenter study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1993, 13, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, J.P.; Round, J.; Taylor, G.; Clarke, N.M. The natural history of developmental dysplasia of the hip after early supervised treatment in the Pavlik harness. A prospective, longitudinal follow-up. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2002, 84, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubak, J.; Piontek, T.; Niciejewski, K.; Magnowski, P.; Majek, M.; Płończak, M. Retrospective analysis of the non-surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip using Pavlik harness and Frejka pillow: Comparison of both methods. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2004, 6, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Eberle, C.F. Plastazote abduction orthosis in the management of neonatal hip instability. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2003, 23, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, F.; Bensahel, H.; Canadell, J.; Dungl, P.; Matasovic, T.; Vizkelety, T. The Pavlik harness in the treatment of congenital dislocating hip: Report on a multicenter study of the European Paediatric Orthopaedic Society. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1988, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedequist, D.; Kasser, J.; Emans, J. Use of an abduction brace for developmental dysplasia of the hip after failure of Pavlik harness use. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2003, 23, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.A.; Skaggs, D.L.; Choi, P.D. Abduction bracing after Pavlik harness failure: An effective alternative to closed reduction and spica casting? J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2013, 33, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novais, E.N.; Kestel, L.A.; Carry, P.M.; Meyers, M.L. Higher Pavlik harness treatment failure is seen in Graf type IV ortolani-positive hips in males. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, V.; Testa, G.; Riccioli, M.; Evola, F.R.; Avondo, S.; Sessa, G. Treatment of developmental dysplasia of hip with Tubingen hip flexion splint. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2015, 35, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, W.N.; Nduaguba, A.; Flynn, J.M. Ilfeld abduction orthosis is an effective second-line treatment after failure of Pavlik harness for infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegnander, A.; Holen, K.J.; Anda, S.; Terjesen, T. Good results after treatment with the Frejka pillow for hip dysplasia in newborns: A 3-year to 6-year follow-up study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2001, 10, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahlen, R.; Zambelli, P. Treatment of the developmental dysplasia of the hip with an abduction brace in children up to 6 months old. Adv. Orthop. 2015, 2015, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A.G.; Sherlock, D.A.; Murray, G.D. The efficacy of the Pavlik harness, the Craig splint and the von Rosen splint in the management of neonatal dysplasia of the hip: A comparative study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2002, 84, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.R.; Jones, D.A.; Bishay, M. Avascular necrosis and the Aberdeen splint in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1999, 81, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordin, S.; Umer, M.; Hafeez, K.; Nawaz, H. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthop. Rev. (Pavia) 2010, 2, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, I.; Flynn, J.M.; Sankar, W.N. Abduction bracing for residual acetabular dysplasia in infantile DDH. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2013, 33, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaroop, V.T.; Mubarak, S.J. Difficult-to-treat Ortolani-positive hip: Improved success with new treatment protocol. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2009, 29, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, E.A.; Brambrink, A.M. Anesthesia for the young child undergoing ambulatory procedures: Current concerns regarding harm to the developing brain. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 26, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viere, R.G.; Birch, J.G.; Herring, J.A. Use of the Pavlik harness in congenital dislocation of the hip: An analysis of failures of treatment. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1990, 72, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, P.L.; Lasser, S.; MacEwen, G.D. Congenital dislocation of the hip. Use of the Pavlik harness in the child during the first six months of life. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1976, 58, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, J.R.; Winter, R.B. Avascular necrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis as a complication of closed reduction of congenital dislocation of the hip: A critical review of twenty years’ experience at Gillette Children’s Hospital. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1972, 54, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamchi, A.; MacFarlane, R., 3rd. The Pavlik harness: Results in patients over three months of age. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1982, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.G.; Skaggs, D.L. Developmental dysplasia of the hip from six months to four years of age. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2001, 9, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabry, G. Clinical practice: The hip from birth to adolescence. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.E.; Dickens, R.; Menelaus, M.B. Use of the Pavlik harness for hip displacements. When to abandon treatment. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 281, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
| Ref | Author | No Participant Selection Took Place | Groups Are Comparable Regarding Age | Validated Measuring System Used | Independent (Blind) Determination of Outcomes | Clear Description of Groups Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [23] | Atalar H. et al. (2014) | + | + | + | ? | + |
| [24] | Atan D et al. (1993) | + | ? | − | ? | + |
| [12] | Azzoni et al. (2011) | + | ? | + | + | − |
| [25] | Cashman et al. (2002) | + | ? | + | ? | + |
| [26] | Czubak et al. (2004) | ? | + | + | ? | − |
| [27] | Eberle et al. 2003 | + | ? | − | ? | + |
| [28] | Grill et al. (1988) | − | + | + | ? | + |
| [29] | Hedequist et al. (2003) | + | − | + | ? | + |
| [11] | Hilderaker et al. (1992) | + | + | + | ? | + |
| [30] | Ibrahim et al. (2013) | + | ? | + | ? | + |
| [9] | Kubo et al. (2018) | + | + | − | ? | + |
| [18] | Kitoh et al. (2009) | + | ? | + | + | + |
| [31] | Novais et al. (2016) | + | ? | + | ? | + |
| [32] | Pavone et al. (2015) | + | ? | + | ? | + |
| [33] | Sankar et al. (2015) | + | + | + | ? | + |
| [34] | Tegnander et al. (2001) | + | ? | − | ? | + |
| [35] | Wahlen et al. (2015) | + | + | + | ? | + |
| [36] | Wilkinson et al. (2002) | − | ? | + | ? | + |
| [37] | Williams et al. (1999) | + | ? | + | ? | + |
| Ref | Author | Brace | No. of Patients (Females, Males) | No. of Hips | Mean Age of the Brace at Treatment Onset (Weeks) | Follow Up (Months) | Success Event (%) | Complications Event (%) | AVN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [23] | Atalar et al. (2014) | Tubingen splint | 49 (45 f, 4 m) | 60 | 18 | 24 | 56 (93.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [24] | Atan et al. (1993) | Frejka pillow | 70 (54 f, 16 m) | 84 | 0.7 | ? | 76 (90.5) | 6 (7) | 6 (7) |
| [24] | Atan et al. (1993) | Pavlik harness | 40 (29 f, 11 m) | 48 | 1.4 | ? | 42 (87.5) | 3 (6) | 3 (6) |
| [12] | Azzoni et al. (2011) | Teuffel | ? | 59 | 6.1 | ? | 59 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [12] | Azzoni et al. (2011) | Coxaflex | ? | 59 | 6.1 | ? | 58 (98.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [25] | Cashman et al. (2002) | Pavlik harness | 332 (275 f, 57 m) | 546 | ? | ? | 528 (96.7) | 4 (1) | 4 (1) |
| [26] | Czubak et al. (2004) | Pavlik harness | 95 (84 f; 11 m) | ? | 11.5 | ? | 90 (95) | 7 (7) | 7 (7) |
| [26] | Czubak et al. (2004) | Frejka splint | 143 (129 f; 14 m) | ? | 11.5 | ? | 127 (89) | 17 (12) | 17 (12) |
| [27] | Eberle et al. (2003) | Abduction brace | 113 | 139 | ? | 40 | 137 (99) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [28] | Grill et al. (1988) | Pavlik harness | 2636 (2343 f; 293 m) | 3611 | 5 | 53.5 | 3324 (92.1) | 75 (2) | 75 (2) |
| [29] | Hedequist et al. (2003) | Abduction brace | ? | 14 | 3.7 | 12 | 11 (79) | 2 (14) | 1 (7) |
| [11] | Hilderaker et al. (1992) | Frejka pillow | 101 | ? | ? | ? | 97 (96) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [11] | Hilderaker et al. (1992) | Von Rosen | 307 | ? | ? | ? | 307 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [30] | Ibrahim et al. (2013) | Abduction brace | 7 (7 f; 0 m) | 7 | 10.9 | 33.6 | 6 (86) | 1 (14) | 1 (14) |
| [9] | Kubo et al. (2018) | Tubingen splint | 79 (74 f; 5 m) | 109 | 3.1 | 24 | 104 (95.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [18] | Kitoh et al. (2009) | Pavlik harness | 210(190 f; 20 m) | 221 | 15.6 | 12 | 181 (81.9) | 16 (7) | 16 (7) |
| [31] | Novais et al. (2016) | Pavlik harness | 135 (107 f; 28 f) | 215 | 4.3 | 4 | 185 (86.0) | 4 (2) | 0 (0) |
| [32] | Pavone et al. (2015) | Tubingen splint | 351 (248 f, 103) | 544 | 9.7 | 76.8 | 535 (98.3) | 3 (0.6) | 3 (0.6) |
| [33] | Sankar et al. (2015) | Ilfeld | 19 | 28 | 4.6 | 12 | 23 (82.1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [34] | Tegnander et al. (2001) | Frejka pillow | 108 | ? | 16 | ? | 105 (97.2) | 1 (0.9) | 1 (0.9) |
| [35] | Wahlen et al. (2015) | Lausanne brace (rhino-style) | 33 | 40 | 11 | 40 | 35 (87.5) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [36] | Wilkinson et al. (2002) | Craig | 22 | 28 | 5.3 | ? | 24 (85.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [36] | Wilkinson et al. (2002) | Pavlik harness | 30 | 43 | 7 | ? | 30 (69.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [36] | Wilkinson et al. (2002) | Von Rosen | 16 | 26 | 3.7 | ? | 26 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| [37] | Williams et al. (1999) | Aberdeen Splint | 86 | 120 | ? | 108 | 118 (98.3) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) |
| Type of Dynamic Splint | Number of Hips | Proportion within Dynamic Group |
|---|---|---|
| Pavlik | 4779 | 73.2% |
| Tubingen | 713 | 14.9% |
| Frejka pillow | 436 | 9.1% |
| Von Rosen | 333 | 5.1% |
| Aberdeen | 120 | 1.8% |
| Coxaflex | 59 | 0.9% |
| Teufel | 59 | 0.9% |
| Craig | 28 | 0.4% |
| TOTAL | 6527 |
| Type of Static Brace | Number of Hips | Proportion within Static Group |
|---|---|---|
| Abduction brace | 160 | 70.2% |
| Rhino | 40 | 17.5% |
| Ilfeld | 28 | 12.3% |
| TOTAL | 228 |
| Dynamic Splint Group | Static Brace Group | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complication (No. of hips) | 138 | 3 | 141 |
| Complication rate | 2.1% | 1.3% | 2% |
| AVN (No. of hips) | 134 | 2 | 136 |
| AVN rate | 2% | 0.8% | 2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavone, V.; de Cristo, C.; Vescio, A.; Lucenti, L.; Sapienza, M.; Sessa, G.; Pavone, P.; Testa, G. Dynamic and Static Splinting for Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Systematic Review. Children 2021, 8, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020104
Pavone V, de Cristo C, Vescio A, Lucenti L, Sapienza M, Sessa G, Pavone P, Testa G. Dynamic and Static Splinting for Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Systematic Review. Children. 2021; 8(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020104
Chicago/Turabian StylePavone, Vito, Claudia de Cristo, Andrea Vescio, Ludovico Lucenti, Marco Sapienza, Giuseppe Sessa, Piero Pavone, and Gianluca Testa. 2021. "Dynamic and Static Splinting for Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Systematic Review" Children 8, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020104
APA StylePavone, V., de Cristo, C., Vescio, A., Lucenti, L., Sapienza, M., Sessa, G., Pavone, P., & Testa, G. (2021). Dynamic and Static Splinting for Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Systematic Review. Children, 8(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8020104









