Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Novel Regulator of Obesity and Its Associated Complications
Abstract
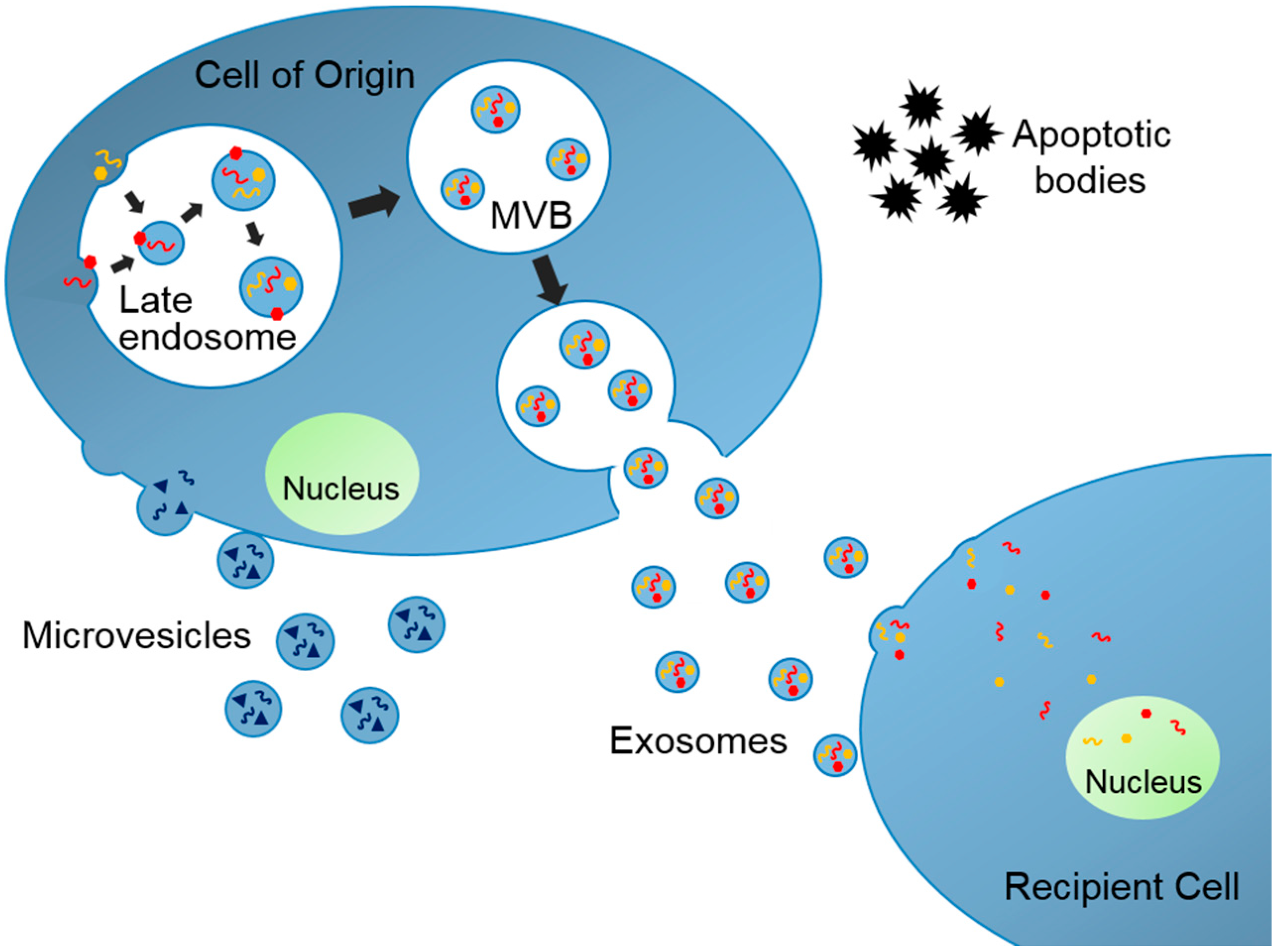
1. Introduction
2. EVs and Obesity
3. EVs and Insulin Resistance/Type 2 Diabetes
4. EVs and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, Z.J.; Long, M.W.; Resch, S.C.; Giles, C.M.; Cradock, A.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. Simulation of Growth Trajectories of Childhood Obesity into Adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon, J.J.; Martinez-Costa, O.H. Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rothman, D.L.; Magnusson, I.; Cline, G.; Gerard, D.; Kahn, C.R.; Shulman, R.G.; Shulman, G.I. Decreased muscle glucose transport/phosphorylation is an early defect in the pathogenesis of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Okumura, M.J.; Davis, M.M.; Herman, W.H.; Gurney, J.G. Prevalence and determinants of insulin resistance among U.S. adolescents: A population-based study. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Styne, D.M.; Arslanian, S.A.; Connor, E.L.; Farooqi, I.S.; Murad, M.H.; Silverstein, J.H.; Yanovski, J.A. Pediatric Obesity-Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 709–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang-Doran, I.; Zhang, C.Y.; Vidal-Puig, A. Extracellular Vesicles: Novel Mediators of Cell Communication in Metabolic Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Greening, D.W.; Zhu, H.J.; Takahashi, N.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: Toward clinical application. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, C.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Chen, D. Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanian, A.; Bourguignat, L.; Hennou, S.; Coupaye, M.; Hajage, D.; Salomon, L.; Alessi, M.C.; Msika, S.; de Prost, D. Microparticle increase in severe obesity: Not related to metabolic syndrome and unchanged after massive weight loss. Obesity 2013, 21, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, S.C.; Nadler, E.P.; Pillai, D.K.; Hubal, M.J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.M.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Koeck, E.; Sevilla, S.; Wiles, A.A.; et al. Adipocyte-derived exosomal miRNAs: A novel mechanism for obesity-related disease. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfeky, O.; Longo, S.; Lai, A.; Rice, G.E.; Salomon, C. Influence of maternal BMI on the exosomal profile during gestation and their role on maternal systemic inflammation. Placenta 2017, 50, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubal, M.J.; Nadler, E.P.; Ferrante, S.C.; Barberio, M.D.; Suh, J.H.; Wang, J.; Dohm, G.L.; Pories, W.J.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Freishtat, R.J. Circulating adipocyte-derived exosomal MicroRNAs associated with decreased insulin resistance after gastric bypass. Obesity 2017, 25, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Foundations of Immunometabolism and Implications for Metabolic Health and Disease. Immunity 2017, 47, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, I.; Clement, E.; Dauvillier, S.; Milhas, D.; Ducoux-Petit, M.; LeGonidec, S.; Moro, C.; Soldan, V.; Dalle, S.; Balor, S.; et al. Adipocyte Exosomes Promote Melanoma Aggressiveness through Fatty Acid Oxidation: A Novel Mechanism Linking Obesity and Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4051–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.B.; Poliakov, A.; Hardy, R.W.; Clements, R.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, X.; et al. Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranendonk, M.E.; Visseren, F.L.; van Balkom, B.W.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; van Herwaarden, J.A.; de Jager, W.; Schipper, H.S.; Brenkman, A.B.; Verhaar, M.C.; Wauben, M.H.; et al. Human adipocyte extracellular vesicles in reciprocal signaling between adipocytes and macrophages. Obesity 2014, 22, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.W.; Noren Hooten, N.; Eitan, E.; Green, J.; Mode, N.A.; Bodogai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lehrmann, E.; Zonderman, A.B.; Biragyn, A.; et al. Altered Extracellular Vesicle Concentration, Cargo and Function in Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Exosomes From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Attenuate Adipose Inflammation and Obesity Through Polarizing M2 Macrophages and Beiging in White Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2018, 67, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.; Ramstead, A.G.; Bauer, K.M.; Lee, S.H.; Runtsch, M.C.; Wallace, J.; Huffaker, T.B.; Larsen, D.K.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; et al. Rab27-Dependent Exosome Production Inhibits Chronic Inflammation and Enables Acute Responses to Inflammatory Stimuli. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.; Hu, R.; Runtsch, M.C.; Kagele, D.A.; Mosbruger, T.L.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Round, J.L.; Ward, D.M.; O’Connell, R.M. Exosome-delivered microRNAs modulate the inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Fisher, K.P.; Hammer, S.S.; Navitskaya, S.; Blanchard, G.J.; Busik, J.V. Plasma Exosomes Contribute to Microvascular Damage in Diabetic Retinopathy by Activating the Classical Complement Pathway. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatier, F.; Darmon, P.; Hugel, B.; Combes, V.; Sanmarco, M.; Velut, J.G.; Arnoux, D.; Charpiot, P.; Freyssinet, J.M.; Oliver, C.; et al. Type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients display different patterns of cellular microparticles. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2840–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Eguchi, A.; Tempaku, M.; Honda, T.; Togashi, K.; Iwasa, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Takei, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Taguchi, O. Circulating extracellular vesicles are associated with lipid and insulin metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E574–E582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesca, V.; Guay, C.; Jacovetti, C.; Menoud, V.; Peyot, M.L.; Laybutt, D.R.; Prentki, M.; Regazzi, R. Identification of particular groups of microRNAs that positively or negatively impact on beta cell function in obese models of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tattikota, S.G.; Rathjen, T.; Hausser, J.; Khedkar, A.; Kabra, U.D.; Pandey, V.; Sury, M.; Wessels, H.H.; Mollet, I.G.; Eliasson, L.; et al. miR-184 Regulates Pancreatic beta-Cell Function According to Glucose Metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20284–20294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalabert, A.; Vial, G.; Guay, C.; Wiklander, O.P.; Nordin, J.Z.; Aswad, H.; Forterre, A.; Meugnier, E.; Pesenti, S.; Regazzi, R.; et al. Exosome-like vesicles released from lipid-induced insulin-resistant muscles modulate gene expression and proliferation of beta recipient cells in mice. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantaluppi, V.; Biancone, L.; Figliolini, F.; Beltramo, S.; Medica, D.; Deregibus, M.C.; Galimi, F.; Romagnoli, R.; Salizzoni, M.; Tetta, C.; et al. Microvesicles derived from endothelial progenitor cells enhance neoangiogenesis of human pancreatic islets. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figliolini, F.; Cantaluppi, V.; De Lena, M.; Beltramo, S.; Romagnoli, R.; Salizzoni, M.; Melzi, R.; Nano, R.; Piemonti, L.; Tetta, C.; et al. Isolation, characterization and potential role in beta cell-endothelium cross-talk of extracellular vesicles released from human pancreatic islets. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, C.; Menoud, V.; Rome, S.; Regazzi, R. Horizontal transfer of exosomal microRNAs transduce apoptotic signals between pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.; Horvath, I.; Heath, N.; Hicks, R.; Forslow, A.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Extracellular vesicles from human pancreatic islets suppress human islet amyloid polypeptide amyloid formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11127–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, A.; Esguerra, J.L.; Eliasson, L. Islet microRNAs in health and type-2 diabetes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 43, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranendonk, M.E.; Visseren, F.L.; van Herwaarden, J.A.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; de Jager, W.; Wauben, M.H.; Kalkhoven, E. Effect of extracellular vesicles of human adipose tissue on insulin signaling in liver and muscle cells. Obesity 2014, 22, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, W.; Kang, M.; Chen, Q.; Qin, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wu, Y. Exosomes derived from pancreatic cancer cells induce insulin resistance in C2C12 myotube cells through the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomou, T.; Mori, M.A.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Konishi, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Wolfrum, C.; Rao, T.N.; Winnay, J.N.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Grinspoon, S.K.; et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature 2017, 542, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, W.; Riopel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dong, Y.; Birmingham, A.; Seo, J.B.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Wollam, J.; Hernandez-Carretero, A.; Fu, W.; et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate In Vivo and In Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell 2017, 171, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornek, M.; Popov, Y.; Libermann, T.A.; Afdhal, N.H.; Schuppan, D. Human T cell microparticles circulate in blood of hepatitis patients and induce fibrolytic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2011, 53, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeck, E.S.; Iordanskaia, T.; Sevilla, S.; Ferrante, S.C.; Hubal, M.J.; Freishtat, R.J.; Nadler, E.P. Adipocyte exosomes induce transforming growth factor beta pathway dysregulation in hepatocytes: A novel paradigm for obesity-related liver disease. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 192, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povero, D.; Eguchi, A.; Niesman, I.R.; Andronikou, N.; de Mollerat du Jeu, X.; Mulya, A.; Berk, M.; Lazic, M.; Thapaliya, S.; Parola, M.; et al. Lipid-induced toxicity stimulates hepatocytes to release angiogenic microparticles that require Vanin-1 for uptake by endothelial cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, E.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.S.; Yoo, Y.J.; Je, J.; Suh, S.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Exosomes derived from palmitic acid-treated hepatocytes induce fibrotic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrier, A.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Kemper, S.; Hattori, T.; Takigawa, M.; Brigstock, D.R. Exosomes mediate intercellular transfer of pro-fibrogenic connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) between hepatic stellate cells, the principal fibrotic cells in the liver. Surgery 2014, 156, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, L.; Giurato, G.; Cicchini, C.; Montaldo, C.; Mancone, C.; Tarallo, R.; Battistelli, C.; Alonzi, T.; Weisz, A.; Tripodi, M. The RNA-Binding Protein SYNCRIP Is a Component of the Hepatocyte Exosomal Machinery Controlling MicroRNA Sorting. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornek, M.; Lynch, M.; Mehta, S.H.; Lai, M.; Exley, M.; Afdhal, N.H.; Schuppan, D. Circulating microparticles as disease-specific biomarkers of severity of inflammation in patients with hepatitis C or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Momen-Heravi, F. Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Toyoda, H.; Tanahashi, T.; Tanaka, J.; Kumada, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Taguchi, Y.H. Comprehensive miRNA expression analysis in peripheral blood can diagnose liver disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, W.; Yoshida, T.; Diez, D.; Miyatake, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Imawaka, N.; Naruse, K.; Sadamura, Y.; Hanayama, R. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inge, T.H.; Jenkins, T.M.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Dixon, J.B.; Daniels, S.R.; Zeller, M.H.; Helmrath, M.A. Long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery in adolescents with severe obesity (FABS-5+): A prospective follow-up analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, A.; Shah, A.S.; Nakamura, T. Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Novel Regulator of Obesity and Its Associated Complications. Children 2018, 5, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5110152
Kim A, Shah AS, Nakamura T. Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Novel Regulator of Obesity and Its Associated Complications. Children. 2018; 5(11):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5110152
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ahlee, Amy S. Shah, and Takahisa Nakamura. 2018. "Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Novel Regulator of Obesity and Its Associated Complications" Children 5, no. 11: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5110152
APA StyleKim, A., Shah, A. S., & Nakamura, T. (2018). Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Novel Regulator of Obesity and Its Associated Complications. Children, 5(11), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/children5110152




