Idiopathic Flatfoot in Children and Adolescents Treated with Arthroereisis—Muscle Recession May Not Be Necessary in Feet with Mild Gastrocnemius Shortening
Abstract
Highlights
- Idiopathic flexible flatfeet in children and adolescents may be associated with shortening of gastrocnemius muscle.
- Gastrocnemius shortening affects the feet more in the sagittal plane.
- The kinematic deviations in the fore- and hindfoot tend to be more severe in flatfeet with gastrocnemius shortening.
- Gastrocnemius shortening prevents inversion of the hindfoot during push-off.
- Arthroereisis is effective in correcting flexible flatfeet, reduces pain, and restores the kinematics of the fore- and hindfoot.
- Following arthroereisis, there is a spontaneous stretching of the calf-muscle especially the gastrocnemius.
- Gastrocnemius recession is not necessary in mild shortening, as the muscle stretches after correction of the flatfoot.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients/Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Assessment
2.2. Radiological Assessment
2.3. Gait Analysis
2.4. Surgical Technique and Indication for Gastrocnemius Recession
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, U.; Joseph, B. The influence of footwear on the prevalence of flat foot. A survey of 2300 children. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 1992, 74-B, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Ceccarelli, F.; Berti, L.; Luciani, D.; Catani, F.; Boschi, M.; Giannini, S. Diagnosis of Flexible Flatfoot in Children: A Systematic Clinical Approach. Orthopedics 2011, 34, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, V.S. Flexible flatfoot in children and adolescents. J. Child. Orthop. 2010, 4, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdea, A.; Neculai, A.-G.; Ulici, A. The Role of Arthroereisis in Improving Sports Performance, Foot Aesthetics and Quality of Life in Children and Adolescents with Flexible Flatfoot. Children 2022, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, S.E.; Scannell, B.P. Pediatric Flatfoot. Foot Ankle Clin. 2017, 22, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, V.; Costarella, L.; Testa, G.; Conte, G.; Riccioli, M.; Sessa, G. Calcaneo-stop Procedure in the Treatment of the Juvenile Symptomatic Flatfoot. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013, 52, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döderlein, L.; Wenz, W.; Schneider, U. Der Knickplattfuß. In Fussdeformitäten, 1st ed.; Döderlein, L., Wenz, W., Schneider, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, M.; Kotz, R.; Ledl, T.; Hauser, G.; Sluga, M. Prevalence of Flat Foot in Preschool-Aged Children. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A.; Lintz, F.; Sadile, F. The role of arthroereisis of the subtalar joint for flatfoot in children and adults. EFORT Open Rev. 2017, 2, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pellegrin, M.; Moharamzadeh, D.; Strobl, W.M.; Biedermann, R.; Tschauner, C.; Wirth, T. Subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) for the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children. J. Child. Orthop. 2014, 8, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atik, A. Flexible flatfootness. North. Clin. Istanb. 2014, 1, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaggi, P.; Lullini, G.; Berti, L.; Giannini, S.; Leardini, A. Functional evaluation of bilateral subtalar arthroereisis for the correction of flexible flatfoot in children: 1-year follow-up. Gait Posture 2018, 64, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hösl, M.; Böhm, H.; Multerer, C.; Döderlein, L. Does excessive flatfoot deformity affect function? A comparison between symptomatic and asymptomatic flatfeet using the Oxford Foot Model. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, R.M.; Din, N. Correcting Pediatric Flatfoot with Subtalar Arthroereisis and Gastrocnemius Recession. Foot Ankle Spéc. 2013, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterian, A.G.; Ulici, A. Quality of Life after Flatfoot Surgery in the Pediatric Population. J. Med. Life 2020, 13, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pellegrin, M. Die subtalare Schrauben-Arthrorise beim kindlichen Plattfuß. Orthopade 2005, 34, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; He, W.; Yu, G.; Zhou, H.; Xia, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yu, T.; Yang, Y. Treatment for Flexible Flatfoot in Children With Subtalar Arthroereisis and Soft Tissue Procedures. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 656178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, V.S.; Bevan, W.P. Talocalcaneal Tarsal Coalitions and the Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy: The Role of Deformity Correction. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, V.S. Calcaneal lengthening for valgus deformity of the hindfoot. Results in children who had severe, symptomatic flatfoot and skewfoot. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1995, 77, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Coulon, G.; Turcot, K.; Canavese, F.; Dayer, R.; Kaelin, A.; Ceroni, D. Talonavicular Arthrodesis for the Treatment of Neurological Flat Foot Deformity in Pediatric Patients. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2011, 31, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yontar, N.S.; Ogut, T.; Guven, M.F.; Botanlioglu, H.; Kaynak, G.; Can, A. Surgical treatment results for flexible flatfoot in adolescents. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2016, 50, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, J.; Scutter, S.D.; Buckley, J. Static Ankle Joint Equinus. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2010, 100, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, X. Mid-term Results of Subtalar Arthroereisis with Talar-Fit Implant in Pediatric Flexible Flatfoot and Identifying the Effects of Adjunctive Procedures and Risk Factors for Sinus Tarsi Pain. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzman, S.; Irby, M.B.; Callahan, A.B.; Skelton, J.A. Pes planus and paediatric obesity: A systematic review of the literature. Clin. Obes. 2015, 5, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naal, F.D.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Huber, M.; Rippstein, P.F. Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Foot Function Index for Use in German-Speaking Patients with Foot Complaints. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, B.M.; Stasko, P.A.; Gesheff, M.G.; Bhave, A. Normal Foot and Ankle Radiographic Angles, Measurements, and Reference Points. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2016, 55, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, H.; Döderlein, L.; Fujak, A.; Dussa, C.U. Is there a correlation between static radiographs and dynamic foot function in pediatric foot deformities? Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D. Nils Silfverskiöld (1888–1957) and gastrocnemius contracture. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013, 19, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzenberg, J.E.; Lamm, B.M.; Corwin, C.; Sekel, J. Isolated Recession of the Gastrocnemius Muscle: The Baumann Procedure. Foot Ankle Int. 2007, 28, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.I.; Tan, S.H.S.; Lim, A.K.S.; Hui, J.H. The outcomes of subtalar arthroereisis in pes planus: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2021, 141, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.Y.; Macwilliams, B.A.; Hennessey, T.A.; Teske, N.; Stevens, P.M. Prospective comparison of subtalar arthroereisis with lateral column lengthening for painful flatfeet. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B 2015, 24, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| FFGR | FF | TD | ANOVA p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Group | Surgery | Interaction | |
| Anthropometry | ||||||||
| No. of subjects/feet | 13/21 | 14/24 | 18/18 | |||||
| Gender (m/f) | 7/14 | 7/14 | 12/12 | 12/12 | 8/10 | |||
| Age (years) | 12.4 (1.6) | 14.4 (1.7) | 12.2 (1.2) | 14.3 (2.1) | 12.1 (2.6) | 0.632 | <0.001 | 0.844 |
| Height | 155 (10) | 165 (9) | 159 (8) | 169 (10) | 155 (17) | 0.175 | <0.001 | 0.752 |
| Weight (kg) | 48.4 (8.8) | 60.2 (12.0) | 50.0 (11.1) | 60.3 (14.1) | 43.5 (14.5) | 0.812 | <0.001 | 0.396 |
| ) | 20.2 (3.7) | 22.0 (3.5) | 19.7 (3.4) | 20.9 (3.3) | 17.6 (2.6) | 0.437 | <0.001 | 0.109 |
| Clinical Assessment | ||||||||
| Passive ankle dorsiflexion [°] (0° knee flexion) | 2.9 (5.4) | 8.9 (6.2) | 4.4 (4.0) | 10.2 (7.4) | 17.9 (7.1) | 0.348 | <0.001 | 0.910 |
| Passive ankle dorsiflexion [°] (90° knee flexion) | 10.5 (8.2) | 14.5 (5.3) | 9.8 (5.6) | 15.0 (6.4) | 23.8 (8.4) | 0.961 | <0.001 | 0.570 |
| Silferskjöld test [°] | 7.6 (3.7) | 5.6 (4.0) | 5.4 (4.9) | 4.8 (3.8) | 5.9 (5.7) | 0.115 | 0.111 | 0.391 |
| Passive ankle plantarflexion [°] | 37.4 (7.4) | 31.9 (10.7) | 36.7 (8.8) | 32.5 (7.5) | 39.4 (8.3) | 0.978 | 0.002 | 0.664 |
| Ankle plantarflex. strength (1–5) | 4.9 (0.3) | 4.9 (0.3) | 4.9 (0.3) | 4.9 (0.5) | 5.0 (0.0) | 0.820 | 0.892 | 0.618 |
| Heel-raises (o.) | 15.1 (5.4) | 15.3 (5.2) | 17.3 (4.6) | 17.5 (5.7) | 19.4 (1.6) | 0.100 | 0.838 | 0.989 |
| Foot pain VAS [0, 10] | 3.5 (2.6) | 2.5 (2.6) | 4.2 (2.3) | 1.8 (2.9) | 0 (0) | 0.973 | 0.001 | 0.159 |
| FFGR | FF | TD | ANOVA p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Group | Surgery | Interaction | |
| Lateral Radiographs | ||||||||
| Talo-calcaneal [°] | 43.2 (10.4) | 37.9 (12.5) | 48.8 (10.5) | 38.7 (11.2) | 49 (7) | 0.313 | <0.001 | 0.064 |
| Talo-1 Metatarsal [°] | 21.4 (6.4) | 9.7 (9.9) | 18.3 (10.5) | 3.9 (8.3) | 13 (8) | 0.068 | <0.001 | 0.307 |
| Calcaneal pitch [°] | 8.7 (6.4) | 11.8 (5.6) | 14.1 (4.3) | 16.7 (5.1) | 17 (6) | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.628 |
| Talonavicular [°] | 6.4 (8.7) | −0.5 (10.2) | 4.7 (10.6) | −6.1 (8.3) | N/A | 0.172 | <0.001 | 0.095 |
| Naviculocuneiforme [°] | 20.1 (6.2) | 16.5 (7.6) | 18.3 (6.0) | 13.4 (5.2) | N/A | 0.146 | <0.001 | 0.510 |
| Metatarsal-1 declination [°] | −13.1 (3.1) | −16.4 (3.4) | −16.3 (3.1) | −18.1 (2.6) | N/A | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.112 |
| Naviculo-cuboid overlap (%) | 85.0 (7.5) | 69.8 (10.6) | 80.3 (9.8) | 62.3 (9.5) | 47 (14) | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.478 |
| Anterior–Posterior Radiographs | ||||||||
| Talo-calcaneal angle [°] | 20.9 (7.1) | 13.6 (8.8) | 22.2 (10.8) | 13.6 (7.3) | N/A | 0.759 | <0.001 | 0.688 |
| Talonavicular coverage [%] | 24.1 (11.0) | 7.7 (10.8) | 23.1 (11.8) | 2.4 (7.8) | 20 (10) | 0.218 | <0.001 | 0.267 |
| Talo-1 metatarsal [°] | 12.0 (6.3) | 0.4 (10.0) | 12.1 (12.1) | −1.4 (7.7) | 10 (7) | 0.724 | <0.001 | 0.574 |
| Talo-2 metatarsal 2 [°] | 23.0 (7.5) | 11.0 (11.0) | 21.9 (11.7) | 6.9 (8.1) | N/A | 0.304 | <0.001 | 0.371 |
| Calcaneal-4 metatarsal [°] | 8.2 (6.7) | 5.5 (6.3) | 5.5 (7.2) | 1.7 (6.6) | N/A | 0.086 | <0.001 | 0.498 |
| FFGR | FF | TD | ANOVA p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Group | Surgery | Interaction | |
| Spatio-temporal [non-dimensional units] | ||||||||
| Velocity | 45.4 (7.6) | 43.2 (4.1) | 45.6 (5.0) | 44.6 (5.3) | 47.0 (5.5) | 0.583 | 0.035 | 0.452 |
| Step length | 78.9 (9.1) | 75.2 (5.7) | 78.4 (5.3) | 76.5 (6.7) | 79.1 (8.0) | 0.819 | 0.003 | 0.336 |
| Cadence | 58.1 (5.5) | 58.1 (2.7) | 59.0 (4.2) | 58.5 (3.8) | 59.6 (3.2) | 0.559 | 0.598 | 0.611 |
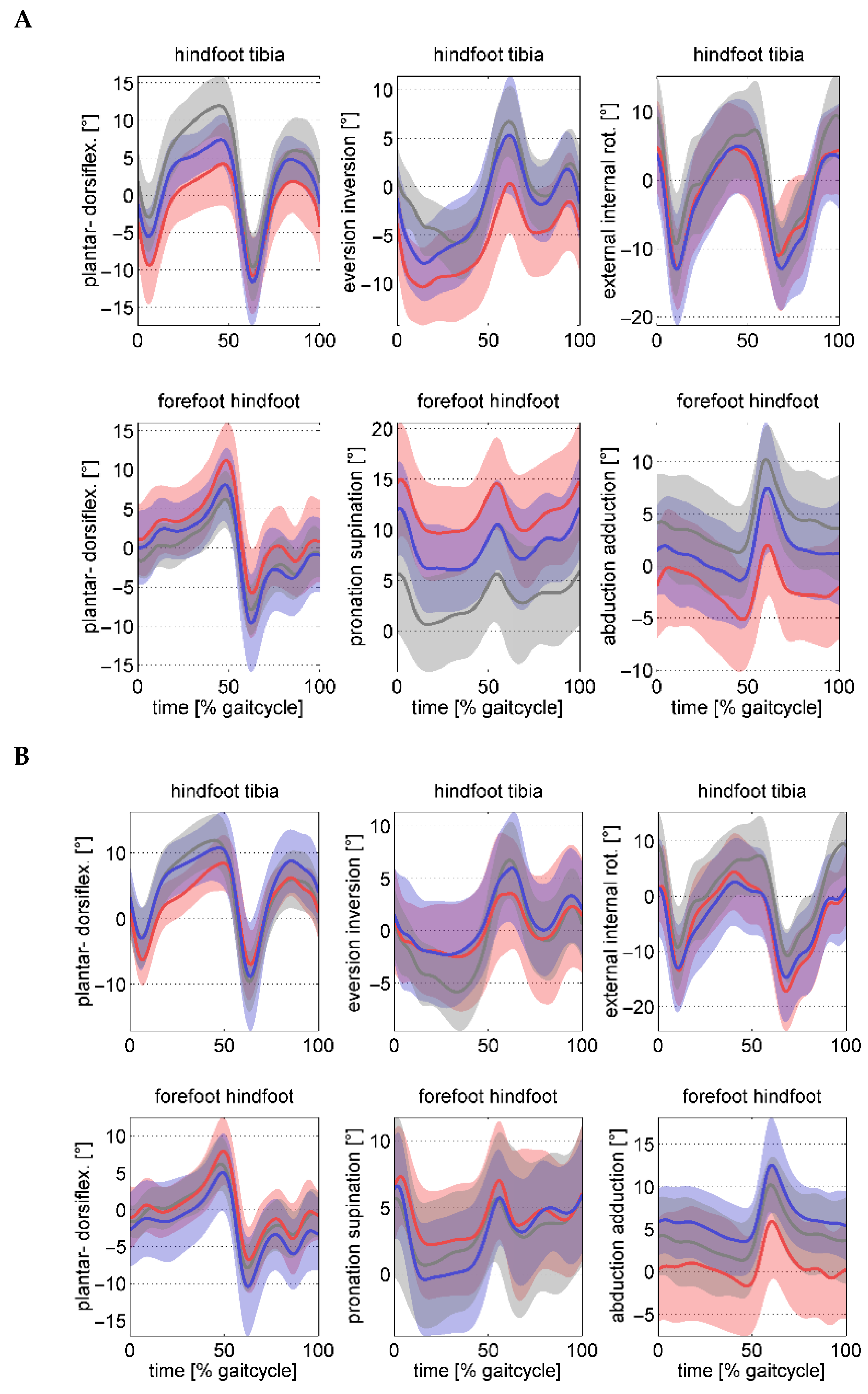
| Tibia-hindfoot kinematics [°] | ||||||||
| Peak dorsiflexion stance | 4.9 (5.0) | 9.7 (3.8) | 8.4 (3.0) | 11.6 (5.0) | 12.7 (5.0) | 0.014 | <0.001 | 0.243 |
| Peak ankle eversion stance | −11.5 (4.0) | −3.9 (4.7) | −8.6 (3.8) | −4.1 (4.8) | −7.3 (2.9) | 0.158 | <0.001 | 0.082 |
| Ankle inversion at take-off | −0.0 (5.0) | 3.7 (5.6) | 4.6 (5.3) | 5.9 (5.0) | 7.3 (3.9) | 0.007 | 0.015 | 0.221 |
| Hindfoot–forefoot kinematics [°] | ||||||||
| Peak midfoot dorsiflexion stance | 11.9 (4.8) | 8.6 (4.4) | 8.6 (4.6) | 5.6 (4.9) | 6.7 (3.2) | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.845 |
| Peak midfoot supination stance | 16.9 (4.7) | 9.0 (3.4) | 13.2 (4.4) | 8.4 (4.4) | 7.3 (5.3) | 0.023 | <0.001 | 0.080 |
| Peak midfoot abduction stance | −6.0 (4.9) | −2.5 (6.0) | −2.4 (4.8) | 1.9 (5.2) | 0.9 (4.3) | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.581 |
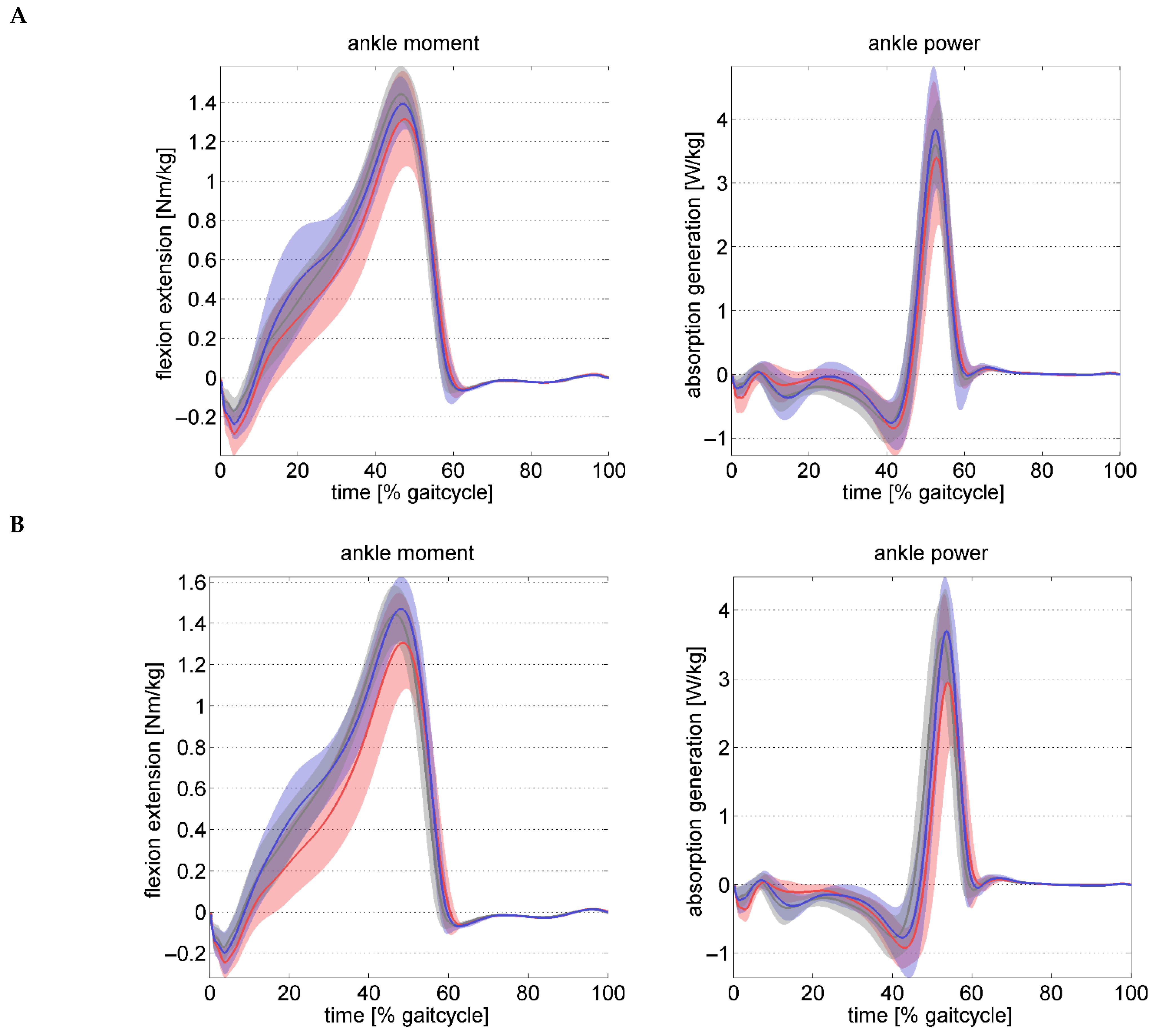
| Ankle kinetics | ||||||||
| Peak ankle moment stance [Nm/kg] | 1.34 (0.23) | 1.34 (0.22) | 1.42 (0.12) | 1.49 (0.16) | 1.47 (0.15) | 0.020 | 0.209 | 0.190 |
| Peak ankle power stance [W/kg] | 3.95 (1.10) | 3.56 (1.03) | 4.38 (0.77) | 4.20 (0.94) | 4.21 (0.47) | 0.044 | 0.029 | 0.392 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakobs, R.A.; Böhm, H.; Fujak, A.; Dussa, C.U. Idiopathic Flatfoot in Children and Adolescents Treated with Arthroereisis—Muscle Recession May Not Be Necessary in Feet with Mild Gastrocnemius Shortening. Children 2025, 12, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091239
Jakobs RA, Böhm H, Fujak A, Dussa CU. Idiopathic Flatfoot in Children and Adolescents Treated with Arthroereisis—Muscle Recession May Not Be Necessary in Feet with Mild Gastrocnemius Shortening. Children. 2025; 12(9):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091239
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakobs, Rebecca Alexandra, Harald Böhm, Albert Fujak, and Chakravarthy Ugandhar Dussa. 2025. "Idiopathic Flatfoot in Children and Adolescents Treated with Arthroereisis—Muscle Recession May Not Be Necessary in Feet with Mild Gastrocnemius Shortening" Children 12, no. 9: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091239
APA StyleJakobs, R. A., Böhm, H., Fujak, A., & Dussa, C. U. (2025). Idiopathic Flatfoot in Children and Adolescents Treated with Arthroereisis—Muscle Recession May Not Be Necessary in Feet with Mild Gastrocnemius Shortening. Children, 12(9), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12091239






