A 10-Year Review of the Efficacy of Cranial Remolding Orthosis Treatment and Factors That Influence Outcomes for Infants with Isolated Deformational Plagiocephaly
Abstract
Highlights
- Cranial remolding orthoses (CROs) are an effective, evidence-backed treatment for isolated deformational plagiocephaly in infants.
- Treatment efficacy has a negative relationship with infant age and severity rating, highlighting the need for earlier referrals to optimize treatment outcomes.
- This study provides useful information to pediatric health care providers regarding the significant clinical efficacy of CROs in treating plagiocephaly.
- Study findings help guide pediatric health care providers in the referral process by highlighting the main factors that impact CRO treatment outcomes in infants.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Source
2.4. Subject Identification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Demographics
3.2. Change in CVAI(S) and CI
3.3. Treatment Duration
3.4. Provider-Rated Outcome of Treatment
3.5. Pretreatment Versus Posttreatment Classification of Head Shape
3.6. Clinical Predictive Factors Associated with Change in CVAI(S)
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRO | Cranial remolding orthosis |
| IDP | Isolated deformational plagiocephaly |
| CVAI | Cranial vault asymmetry index |
| CVA | Cranial vault asymmetry |
References
- Argenta, L. Clinical classification of positional plagiocephaly. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2004, 15, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylton-Plank, L. The presentation of deformational plagiocephaly. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2004, 16, S28–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Kelly, K.M.; Reiff, J.L.; Pomatto, J.K. Car seats, infant carriers, and swings: Their role in deformational plagiocephaly. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2003, 15, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, F.; Braun, V.; Renz-Polster, H. Deformational plagiocephaly in normal infants: A systematic review of causes and hypotheses. Arch. Dis. Child. 2017, 102, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarren, S.K.; Smith, D.W.; Hanson, J.W. Helmet treatment for plagiocephaly and congenital muscular torticollis. J. Pediatr. 1979, 94, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Pomatto, J.K.; Beals, S.P.; Manwaring, K.H.; Joganic, E.F.; Ripley, C.E. Efficacy and stability of dynamic orthotic cranioplasty: An eight year investigation. In Proceedings of the Craniofacial Surgery VII: Proceedings, Santa Fe, New Mexico, 14–17 September 1997; pp. 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Teichgraeber, J.F.; Seymour-Dempsey, K.; Baumgartner, J.E.; Xia, J.J.; Waller, A.L.; Gateno, J. Molding helmet therapy in the treatment of brachycephaly and plagiocephaly. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2004, 15, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.M.; Kreutzman, J.; Earl, D.; Halberg, A.; Samayoa, C.; Guo, X. Deformational brachycephaly in supine-sleeping infants. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, J.B.; Vander Woude, D.L.; Hansen, M.; LaBrie, R.A.; Scott, M.R. Analysis of posterior plagiocephaly: Deformational versus synostotic. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 103, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.P.; Teichgraeber, J.F.; Baumgartner, J.E.; Waller, A.L.; English, J.D.; Lasky, R.E.; Miller, C.C.; Gateno, J.; Xia, J.J. Long-term treatment effectiveness of molding helmet therapy in the correction of posterior deformational plagiocephaly: A five-year follow-up. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2008, 45, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.M.; Joganic, E.F.; Beals, S.P.; Riggs, J.A.; McGuire, M.K.; Littlefield, T.R. Helmet treatment of infants with deformational brachycephaly. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2018, 5, 2333794X18805618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, C.J.; Petz, A.M.; Vallery, C.E.; Yosef, M.; Khalatbari, S.H.; Frank, C.J.; Richards, J.A.M. Success rates of cranial remolding orthosis treatment of plagiocephaly based on initial presentation. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2024, 36, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauc, S.C.; Long, A.S.; Littlefield, T.R.; Stephan, A.P.B.; Junn, A.H.B.; Rivera, J.C.B.; Dinis, J.B.; Junn, A.; Persing, J.A.; Alperovich, M.M. Role of state insurance policy in orthotic helmet access for deformational plagiocephaly. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 152, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, T.; Adams-Huet, B.; Gilbert, N.; Witthoff, K.; Gregory, T.; Walsh, M. Effects of initial age and severity on cranial remolding orthotic treatment for infants with deformational plagiocephaly. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, J.P.; Rawlani, R.; Humphries, L.S.; Rawlani, V.; Vicari, F.A. Effectiveness of conservative therapy and helmet therapy for positional cranial deformation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluba, S.; Kraut, W.; Reinert, S.; Krimmel, M. What is the optimal time to start helmet therapy in positional plagiocephaly? Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörhage, K.W.W.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.E.; von Grabe, V.; Sonntag, A.; Becker, S.T.; Wiltfang, J. Therapy effects of head orthoses in positional plagiocephaly. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Chae, K.Y. Effectiveness of Helmet therapy for infants with moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2024, 67, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.S.; Rah, D.K.; Kim, Y.O. Outcome analysis of cranial molding therapy in nonsynostotic plagiocephaly. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2012, 39, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.T.; David, L.R.; Wood, B.; Argenta, A.; Simpson, J.; Argenta, L.C. Outcome analysis of helmet therapy for positional plagiocephaly using a three-dimensional surface scanning laser. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2009, 20, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.G.; Ryu, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Yang, J.D.; Chung, H.Y.; Choi, K.Y. A study on the effectiveness of helmet therapy for cranial deformations according to cranial shape. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2024, 35, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Diaz, M.; Marcos-Alvarez, M.; Escobio-Prieto, I.; De la Fuente-Costa, M.; Perez-Dominguez, B.; Pinero-Pinto, E.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, A.M. Effectiveness of conservative treatments in positional plagiocephaly in infants: A systematic review. Children 2023, 10, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, F.; Schweitzer, T.; Kunz, J.; Waßmuth, N.; Stellzig-Eisenhauer, A.; Böhm, H.; Meyer-Marcotty, P.; Linz, C. Head orthosis therapy in positional plagiocephaly: Influence of age and severity of asymmetry on effect and duration of therapy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Bodem, J.P.; Kargus, S.; Castrillon-Oberndorfer, G.; Hoffman, J.; Engel, M. The incidence of complications associated with molding helmet therapy: An avoidable risk in the treatment of positional head deformities? J. Craniofacial Surg. 2015, 26, e299–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çevik, S.; Işık, S.; Özkılıç, A. The role of age on helmet therapy in deformational plagiocephaly and asymmetric brachycephaly. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matarazzo, C.G.; Pinto, F.C.G.; Peccin, M.S.; Schreen, G. Orthotic treatment of cranial asymmetries: Comparison between early and late interventions. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2016, 28, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamber, M.S.; Nikas, D.; Beier, A.; Baird, L.C.; Bauer, D.F.; Durham, S.; Klimo, P.; Lin, A.Y.; Mazzola, C.; McClung-Smith, C.; et al. Congress of Neurological Surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guideline on the role of cranial molding orthosis (helmet) therapy for patients with positional plagiocephaly. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, E632–E633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Babaee, T.; Moradi, V.; Bagheri, M.; Moghadam, M.J.; Ashkar, M.; Tavakoli, B.; Gordahani, A.A.; Habibi, Z. Cranial remolding orthosis for children with deformational skull deformities: A systematic review on the factors affecting success and duration of treatment. World Neurosurg. X 2024, 23, 100386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.T.; Kavyani, M. Evaluation of the effects of helmet therapy on head deformities: A systematic review of literature. J. Head Neck Physicians Surg. 2023, 11, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauc, S.C.; Junn, A.H.; Long, A.S.; Rivera, J.C.; Littlefield, T.R.; Ihnat, J.M.; Shah, H.P.; Pondugula, N.; Almeida, M.N.; Alper, D.P.; et al. Orthotic helmet therapy for deformational plagiocephaly: Stratifying outcomes by insurance. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2023, 61, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Kelly, K.M.; Pomatto, J.K.; Beals, S.P. Multiple-birth infants at higher risk for development of deformational plagiocephaly. Pediatrics 1999, 103, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.F.; Oh, A.K.; Mulliken, J.B. The role of congenital muscular torticollis in the development of deformational plagiocephaly. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Chalain, T.M.; Park, S. Torticollis associated with positional plagiocephaly: A growing epidemic. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2005, 16, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackel, C.E.; Bonnar, M.; Keeny, H.; Lipa, B.M.; Hwang, S.W. The role of age and initial deformation on final cranial asymmetry in infants with plagiocephaly treated with helmet therapy. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2017, 52, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, D.; Hinton, C.; Barrios, A. Revisiting the cephalic index: The origin, purpose, and current applicability—A narrative review. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2024, 36, e35–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabayashi, H.; Saito, K.; Kato, R.; Noto, T.; Nagano, N.; Morioka, I. Denominator of cranial vault asymmetry index: Choosing between longer and shorter diagonal lengths. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2023, 34, e369–e372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveday, B.P.; de Chalain, T.B. Active counterpositioning or orthotic device to treat positional plagiocephaly? J. Craniofacial Surg. 2001, 12, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Kelly, K.M.; Cherney, J.C.; Beals, S.P.; Pomatto, J.K. Development of a new three-dimensional cranial imaging system. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2004, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Cherney, J.C.; Luisi, J.N.; Beals, S.P.; Kelly, K.M.; Pomatto, J.K. Comparison of plaster casting with three-dimensional cranial imaging. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2005, 42, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flannery, A.M.; Tamber, M.S.; Mazzola, C.; Klimo, P., Jr.; Baird, L.C.; Tyagi, R.; Bauer, D.; Beier, A.; Durham, S.; Lin, A.Y.; et al. Summary: Evidence based guidelines for the treatment of pediatric positional plagiocephaly, part II. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2012, 26, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawji, A.; Vollman, A.R.; Hatfield, J.; McNeil, D.A.; Sauvé, R. The incidence of positional plagiocephaly: A cohort study. Pediatrics 2013, 132, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Beals, S.P.; Manwaring, K.H.; Pomatto, J.K.; Joganic, E.F.; Golden, K.A.; Ripley, C.E. Treatment of craniofacial asymmetry with dynamic orthotic cranioplasty. J. Craniofacial Surg. 1998, 9, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitsch, W.K.; Keefer, C.H.; LaBrie, R.A.; Mulliken, J.B. Incidence of cranial asymmetry in healthy newborns. Pediatrics 2002, 110, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, A.E.; McCarthy, J.G.; Thome, C.H.; Wisoff, J.H. The “Back to Sleep Campaign” and deformational plagiocephaly: Is there cause for concern? J. Craniofacial Surg. 1996, 7, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichgraeber, J.F.; Ault, J.K.; Baumgartner, J.; Waller, A.; Messersmith, M.; Gateño, J.; Bravenec, B.; Xia, J. Deformational posterior plagiocephaly: Diagnosis and treatment. Cleft Palate Craniofacial J. 2002, 39, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, I.F.; Losken, H.W.; Fasick, P. Diagnosis and management of posterior plagiocephaly. Pediatrics 1997, 99, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.S.; Klein, D.M.; Backstrom, J.W. Occipital plagiocephaly: Deformation or lambdoid synostosis? Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1996, 24, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, L.G.; Kesty, K.; Krebs, E.; Wright, L.; Leger, S.; David, L.R. Deformational plagiocephaly and craniosynostosis: Trends in diagnosis and treatment after the “Back to Sleep” campaign. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2015, 26, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, C.E.; Pomatto, J.; Beals, S.P.; Joganic, E.F.; Manwaring, K.H.; Moss, S.D. Treatment of positional plagiocephaly with Dynamic Orthotic Cranioplasty. J. Craniofacial Surg. 1994, 5, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.; Gilbert, N.; Witthoff, K.; Gregory, T.; Walsh, M. Significant factors influencing the effectiveness of cranial remolding orthoses in infants with deformational plagiocephaly. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 1710–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlefield, T.R.; Reiff, J.L.; Rekate, H.L. Diagnosis and management of deformational plagiocephaly. BNI Q. 2001, 17, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Thach, S.; Corso, J.; Cimorelli, A.; Owens, J.; Davis, C.L. Cranial remolding orthosis study on the use of a temperature sensor to measure wear time. JPO J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2025, 32, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karol, L.A.; Virostek, D.; Felton, K.; Wheeler, L. Effect of compliance counseling on brace use and success in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2016, 98, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemitsu, M.; Bowen, J.R.; Rahman, T.; Glutting, J.J.; Scott, C.B. Compliance monitoring of brace treatment for patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2004, 29, 2070–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
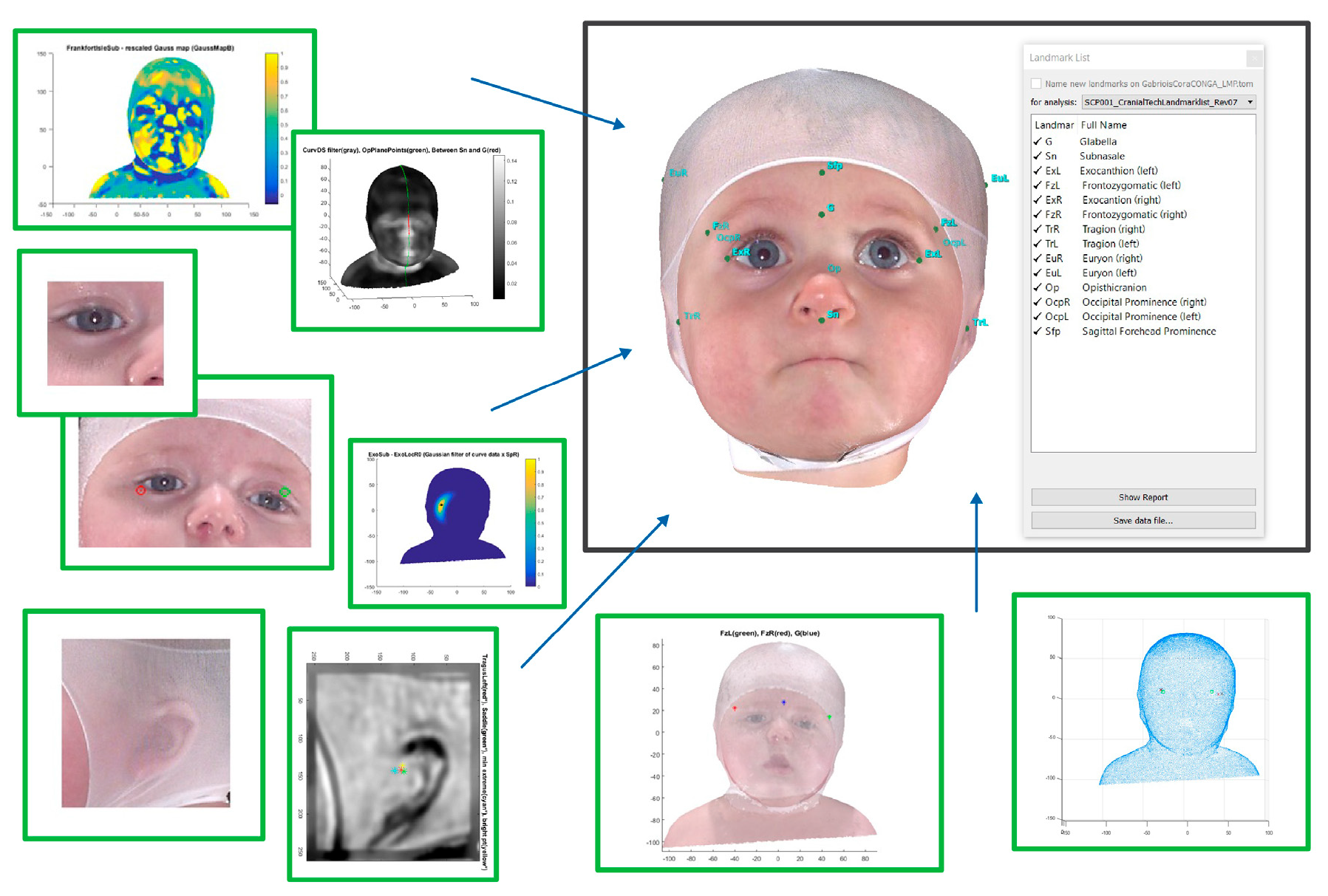
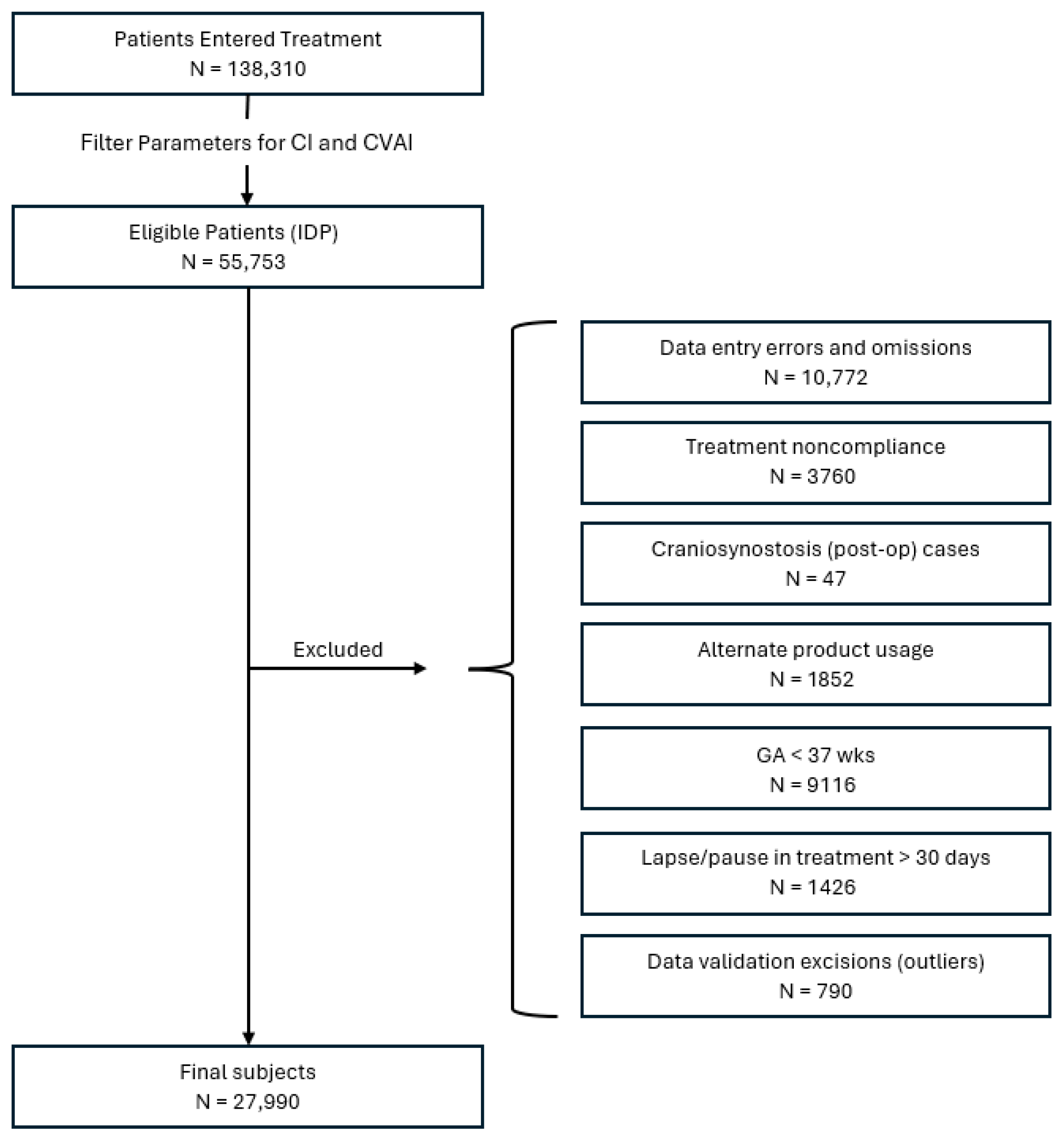
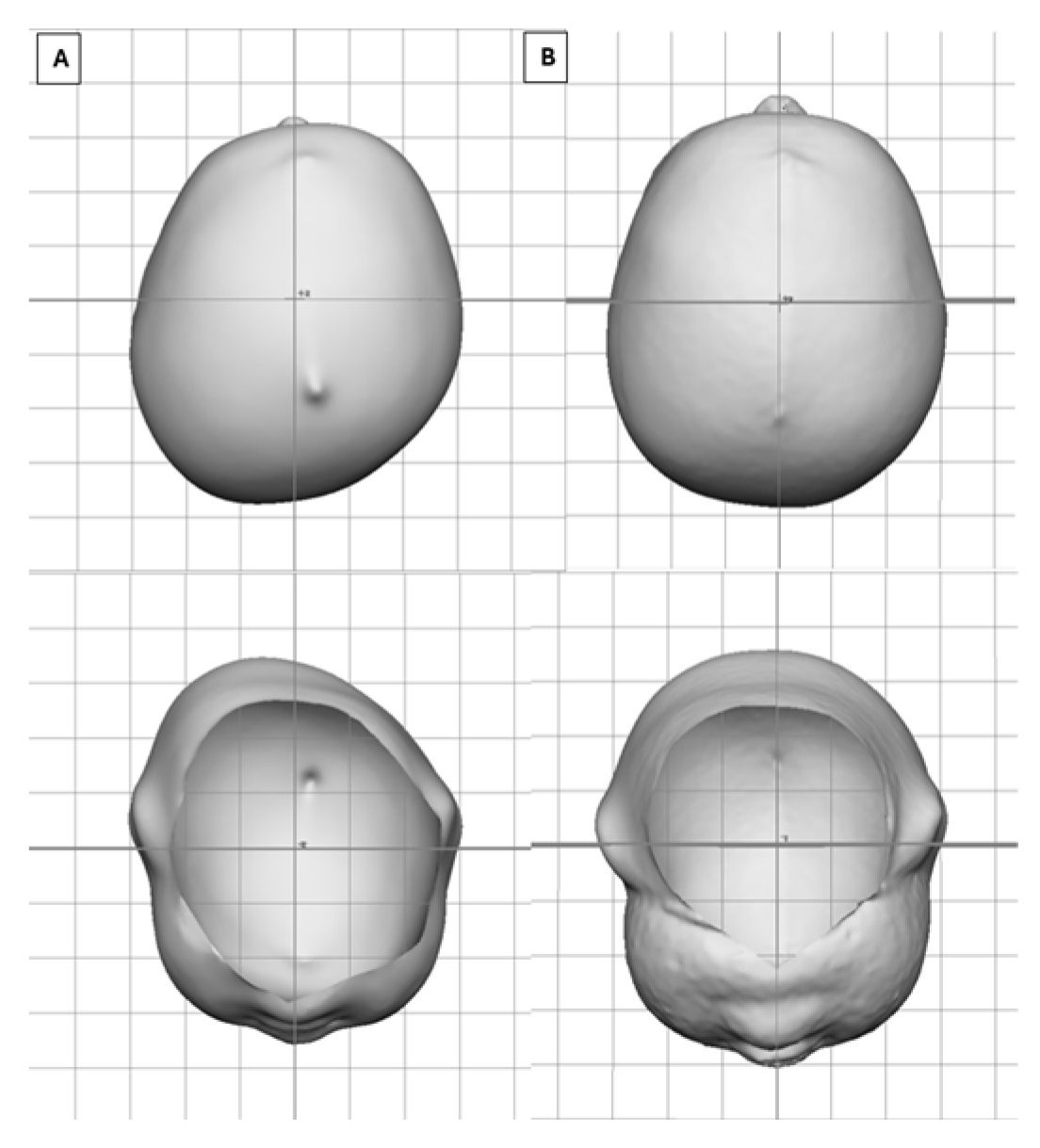
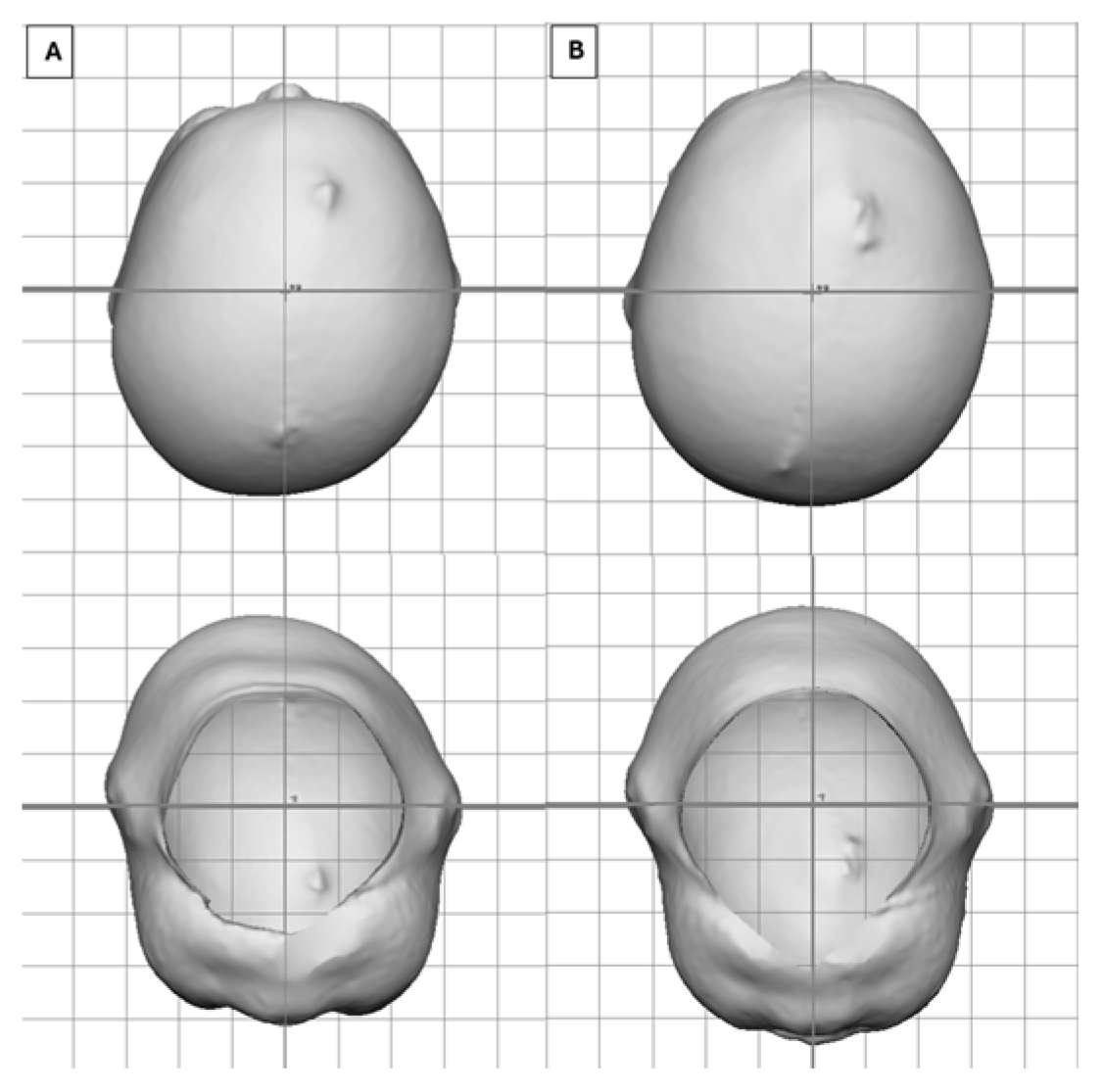
| Variable | All, N = 27,990 | <4, N = 1358 | ≥4 to <6, N = 13,249 | ≥6 to <8, N = 8617 | ≥8 to <11, N = 2866 | ≥11, N = 900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consult age (days) | 162 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Entry age (days) | 192 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Consult to Entry Lapse (days) | 30 | 25 | 26 | 34 | 38 | 40 |
| Duration (weeks) *** | 12.9 | 10 | 11.4 | 14 | 15 | 15.9 |
| Band Remake | 976 | 84 | 547 | 222 | 105 | 18 |
| Fit Modification | 7154 | 411 | 3281 | 2258 | 969 | 235 |
| Male | 18,412 | 948 | 8774 | 5593 | 2489 | 608 |
| Female | 9578 | 410 | 4475 | 3024 | 1377 | 292 |
| Frontal Flattening (Left) | 18,939 | 954 | 9130 | 5793 | 2488 | 574 |
| Frontal Flattening (Right) | 8253 | 382 | 3821 | 2544 | 1224 | 282 |
| Anterior Ear Shift (Left) | 7982 | 380 | 3698 | 2456 | 1172 | 276 |
| Anterior Ear Shift (Right) | 17,735 | 914 | 8630 | 5382 | 2283 | 526 |
| Anterior Orbit Shift (Left) | 6311 | 315 | 2948 | 1931 | 908 | 209 |
| Anterior Orbit Shift (Right) | 13,815 | 743 | 6789 | 4137 | 1753 | 393 |
| Head Height (Left) | 6978 | 353 | 3283 | 2141 | 979 | 222 |
| Head Height (Right) | 15,355 | 836 | 7595 | 4607 | 1891 | 426 |
| Eye Fissure Narrowed (Left) | 6995 | 409 | 3435 | 2059 | 894 | 198 |
| Eye Fissure Narrowed (Right) | 3533 | 181 | 1690 | 1041 | 494 | 127 |
| Limited Neck ROM (Includes Torticollis) | 13,550 | 812 | 6989 | 3954 | 1498 | 297 |
| Torticollis | 7331 | 427 | 3790 | 2139 | 802 | 173 |
| Multiple Birth | 1186 | 53 | 579 | 369 | 156 | 29 |
| Plagiocephaly (Left Sided) | 8492 | 393 | 3896 | 2645 | 1267 | 291 |
| Plagiocephaly (Right Sided) | 19,498 | 965 | 9353 | 5972 | 2599 | 609 |
| Repositioning Techniques | 13,735 | 923 | 7362 | 3911 | 1336 | 203 |
| Multiple Bands | 3197 | 318 | 2040 | 662 | 161 | 16 |
| Hematoma | 248 | 14 | 117 | 71 | 38 | 8 |
| Initial CVAI(S) | 8.327 | 9.569 | 8.723 | 7.968 | 7.507 | 7.585 |
| Final CVAI(S) | 4.908 | 4.814 | 4.864 | 4.908 | 4.960 | 5.463 |
| Mean Change in CVAI(S) *** | −3.420 | −4.755 | −3.859 | −3.060 | −2.547 | −2.122 |
| Initial CVA (mm) | 11.143 | 12.104 | 11.457 | 10.820 | 10.495 | 10.943 |
| Final CVA (mm) | 7.089 | 6.728 | 6.939 | 7.150 | 7.335 | 8.211 |
| Mean Change in CVA (mm) | −4.054 | −5.376 | −4.518 | −3.670 | −3.160 | −2.732 |
| Initial C.I. | 85.543 | 85.280 | 85.648 | 85.575 | 85.359 | 84.878 |
| Final C.I. | 83.688 | 84.091 | 83.827 | 83.552 | 83.447 | 83.378 |
| Change in C.I. *** | −1.855 | −1.189 | −1.821 | −2.023 | −1.912 | −1.500 |
| Consult Circumference (mm) | 431.097 | 409.244 | 423.305 | 435.793 | 447.713 | 462.428 |
| Exit Circumference (mm) | 452.724 | 437.047 | 446.658 | 456.899 | 464.743 | 474.082 |
| Change in Circumference (mm) *** | 21.628 | 27.803 | 23.353 | 21.106 | 17.030 | 11.653 |
| Entry Age | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Very Severe | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥3.5 to ≤6.25 | >6.25 to ≤8.75 | >8.75 to ≤11.0 | >11.0 | |||||
| <4 | 204 | (2.8%) | 369 | (4.0%) | 376 | (5.8%) | 409 | (8.5%) |
| ≥4 to <6 | 3017 | (40.8%) | 4049 | (43.8%) | 3377 | (51.8%) | 2806 | (58.0%) |
| ≥6 to <8 | 2509 | (33.9%) | 3045 | (33.0%) | 1897 | (29.1%) | 1166 | (24.1%) |
| ≥8 to <11 | 1359 | (18.4%) | 1444 | (15.6%) | 686 | (10.5%) | 377 | (7.8%) |
| ≥11 | 308 | (4.2%) | 330 | (3.6%) | 178 | (2.7%) | 84 | (1.7%) |
| Total | 7397 | 9237 | 6514 | 4842 | ||||
| Entry Age | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Very Severe | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (≥3.5 to ≤6.25) | >6.25 to ≤8.75 | >8.75 to ≤11.0 | >11.0 | |||||
| <4 | 197 | (96.6%) | 358 | (97.0%) | 367 | (97.6%) | 392 | (95.8%) |
| ≥4 to <6 | 2881 | (95.5%) | 3871 | (95.6%) | 3221 | (95.4%) | 2628 | (93.7%) |
| ≥6 to <8 | 2351 | (93.7%) | 2784 | (91.4%) | 1672 | (88.1%) | 995 | (85.3%) |
| ≥8 to <11 | 1199 | (88.2%) | 1182 | (81.9%) | 535 | (78.0%) | 258 | (68.4%) |
| ≥11 | 239 | (77.6%) | 228 | (69.1%) | 98 | (55.1%) | 41 | (48.8%) |
| Total | 6867 | 8423 | 5893 | 4314 | ||||
| Pretreatment Classification | Posttreatment Classification | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | WNL | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Very Severe | |||||||
| (<3.25) | (≥3.5 to ≤6.25) | (>6.25 to ≤8.75) | (>8.75 to ≤11.0) | (>11.0) | ||||||||
| Mild (≥3.5 to ≤6.25) | 7397 | (26.4%) | 5008 | (67.7%) | 2384 | (32.2%) | 5 | (0.1%) | 0 | (0.0%) | 0 | (0.0%) |
| Moderate (>6.25 to ≤8.75) | 9237 | (33.0%) | 2194 | (23.8%) | 6188 | (67.0%) | 853 | (9.2%) | 2 | (0.0%) | 0 | (0.0%) |
| Severe (>8.75 to ≤11.0) | 6514 | (23.3%) | 507 | (7.8%) | 3390 | (52.0%) | 2462 | (37.8%) | 153 | (2.4%) | 2 | (0.0%) |
| Very Severe (>11.0) | 4842 | (17.3%) | 97 | (2.0%) | 1277 | (26.4%) | 2361 | (48.8%) | 1037 | (21.4%) | 70 | (1.5%) |
| Final Multiple Linear Regression Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Statistics | ||||||
| Multiple R | 0.713 | |||||
| R Square | 0.508 | |||||
| Adjusted R Square | 0.508 | |||||
| Standard Error | 1.314 | |||||
| Observations | 27,990 | |||||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | ||
| Regression | 4 | 49,952.066 | 12,488.017 | 7231.067 | 0 | |
| Residual | 27,985 | 48,329.954 | 1.727 | |||
| Total | 27,989 | 98,282.020 | ||||
| Coefficients | Standard Error | t Stat | p-value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | |
| Intercept | −0.879 | 0.043 | −20.612 | <0.001 | −0.962 | −0.795 |
| Initial CVAI | −0.434 | 0.003 | −150.412 | <0.001 | −0.440 | −0.429 |
| Entry Age | 0.007 | 0.000 | 50.201 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 |
| No Torticollis | −0.170 | 0.018 | 9.398 | <0.001 | −0.205 | −0.135 |
| Laterality (Left) | −0.357 | 0.017 | −20.752 | <0.001 | −0.391 | −0.324 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trebilcock, A.L.; Findley, J.L.; Cherry, J.S.; Kasparek, J.A.; Gordon, M.M.; Beals, S.P.; Littlefield, T.R. A 10-Year Review of the Efficacy of Cranial Remolding Orthosis Treatment and Factors That Influence Outcomes for Infants with Isolated Deformational Plagiocephaly. Children 2025, 12, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081099
Trebilcock AL, Findley JL, Cherry JS, Kasparek JA, Gordon MM, Beals SP, Littlefield TR. A 10-Year Review of the Efficacy of Cranial Remolding Orthosis Treatment and Factors That Influence Outcomes for Infants with Isolated Deformational Plagiocephaly. Children. 2025; 12(8):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081099
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrebilcock, Anna L., Jill L. Findley, J. Suzanne Cherry, Jeffrey A. Kasparek, Melody M. Gordon, Stephen P. Beals, and Timothy R. Littlefield. 2025. "A 10-Year Review of the Efficacy of Cranial Remolding Orthosis Treatment and Factors That Influence Outcomes for Infants with Isolated Deformational Plagiocephaly" Children 12, no. 8: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081099
APA StyleTrebilcock, A. L., Findley, J. L., Cherry, J. S., Kasparek, J. A., Gordon, M. M., Beals, S. P., & Littlefield, T. R. (2025). A 10-Year Review of the Efficacy of Cranial Remolding Orthosis Treatment and Factors That Influence Outcomes for Infants with Isolated Deformational Plagiocephaly. Children, 12(8), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081099






