Long-Term Impact of Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury on Renal Function in Children Born Preterm: A Follow-Up Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
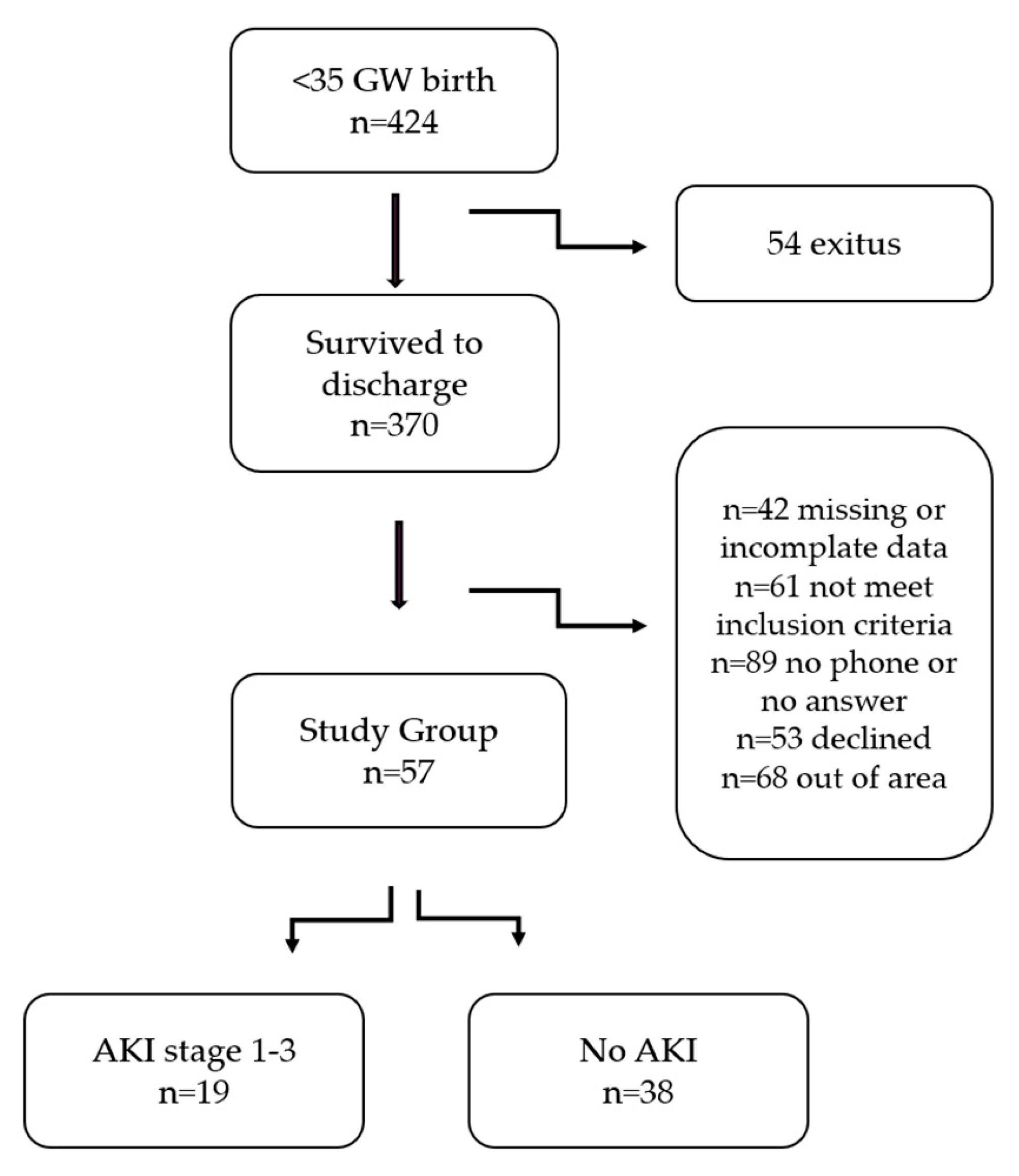
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Neonatal Period
2.3.2. School-Age Follow-Up Assessments
2.3.3. Clinical and Laboratory Assessments at School Age
2.3.4. Ultrasonographic Assessment at School Age
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Demographics During NICU Hospitalization
3.2. Anthropometric and Blood Pressure Findings at Follow-Up
3.3. Renal Ultrasound Findings at Follow-Up
3.4. Biomarkers of Renal Function and Injury in Comparison with the Term Cohort at Follow-Up
4. Discussion
4.1. Blood Pressure
4.2. Ultrasound Findings
4.3. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPM | Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring |
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| AHA | American Heart Association |
| BPD | Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia |
| BMI | BMI Body Mass Index |
| BP | BP Blood Pressure |
| CKD | CKD Chronic Kidney Disease |
| Cr | Cr Creatinine |
| DBP | DBP Diastolic Blood Pressure |
| eGFR | eGFR Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ELISA | ELISA Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ELBW | ELBW Extremely Low Birth Weight |
| IVH | IVH Intraventricular Hemorrhage |
| KIM-1 | KIM-1 Kidney Injury Molecule-1 |
| MBP | MBP Mean Blood Pressure |
| NEC | NEC Necrotizing Enterocolitis |
| NGAL | NGAL Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin |
| NICU | NICU Neonatal Intensive Care Unit |
| PDA | PDA Patent Ductus Arteriosus |
| RDS | RDS Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| SBP | SBP Systolic Blood Pressure |
| sCr | sCr Serum Creatinine |
| SNAPPE-II | SNAPPE-II Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology with Perinatal Extension-II |
| TFF3 | TFF3 Trefoil Factor 3 |
| uCr | uCr Urinary Creatinine |
| WHO | WHO World Health Organization |
| Z-score | Z-score Standard Deviation Score |
Appendix A
| Stage | Serum Creatinine |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.51.9 times baseline ≥0.3 mg/dL increase (48 h) |
| 2 | 2.02.9 times baseline |
| 3 | 3 times baseline ≥2.5 mg/d increase |
References
- Jetton, J.G.; Boohaker, L.J.; Sethi, S.K.; Wazir, S.; Rohatgi, S.; Soranno, D.E.; Chishti, A.S.; Woroniecki, R.; Mammen, C.; Swanson, J.R.; et al. Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury (AWAKEN): A multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2017, 1, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.S.; Kimmel, P.L. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: An integrated clinical syndrome. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.A.; Sawan, Z.A.; Nawawi, E.; Alsaedi, S.; Al-Wassia, H.; Kari, J.A. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of neonatal acute kidney injury: A prospective cohort study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018, 33, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruel, A.; Rozé, J.C.; Quere, M.P.; Flamant, C.; Boivin, M.; Roussey-Kesler, G.; Allain-Launay, E. Renal outcome in children born preterm with neonatal acute renal failure: IRENEO—A prospective controlled study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 2365–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Subcommittee on Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Sept. 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Garcia, D.L.; Anderson, S. Glomeruli and blood pressure. Less of one, more the other? Am. J. Hypertens. 1988, 1, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yu, J.; Prayogo, G.W.; Cao, W.; Wu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, A. Understanding kidney injury molecule 1: A novel immune factor in kidney pathophysiology. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolignano, D.; Lacquaniti, A.; Coppolino, G.; Donato, V.; Campo, S.; Fazio, M.R.; Nicocia, G.; Buemi, M. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Hwang, D.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Kuo, H.T.; Kuo, M.C.; Chang, J.M.; Tsai, J.C.; Hung, C.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Chen, H.C. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Nie, G.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Xing, C.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y. Assessment of urinary NGAL for differential diagnosis and progression of diabetic kidney disease. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2020, 34, 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.Y.; Luo, H.M.; Qin, H.C.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Circulating serum trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) is dramatically increased in chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebherz-Eichinger, D.; Tudor, B.; Ankersmit, H.J.; Reiter, T.; Haas, M.; Roth-Walter, F.; Krenn, C.G.; Roth, G.A. Trefoil factor 1 excretion is increased in early stages of chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.J.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Walsh, M.C. Fanaroff and Martin’s Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine: Diseases of the Fetus and Infant, 12th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Askenazi, D.J.; Ambalavanan, N.; Goldstein, S.L. Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: What do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Gauthier, B. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 1985, 75, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of aWHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004, 114 (Suppl. S2), 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, E.; Alpert, B.; Flynn, J.; Hayman, L.; Harshfield, G.A.; Jacobson, M.; Mahoney, L.; McCrindle, B.; Mietus-Snyder, M.; Steinberger, J.; et al. American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in Youth Committee. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children and adolescents: Recommendations for standard assessment: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, and Obesity in Youth Committee of the council on cardiovascular disease in the young and the council for high blood pressure research. Hypertension 2008, 52, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inker, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Tighiouart, H.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Feldman, H.I.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Manzi, J.; Van Lente, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrycki, Ł.; Sarnecki, J.; Lichosik, M.; Sopińska, M.; Placzyńska, M.; Stańczyk, M.; Mirecka, J.; Wasilewska, A.; Michalski, M.; Lewandowska, W.; et al. Kidney length normative values in children aged 0–19 years—A multicenter study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, C.L.; Bauer, C.R.; Montané, B.; Chandar, J.; Duara, S.; Zilleruelo, G. Long-term follow-up of extremely low birth weight infants with neonatal renal failure. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2003, 18, 887–893. [Google Scholar]
- Harer, M.; Pope, C.F.; Conaway, M.; Charlton, J. Follow-up of acute kidney injury in neonates during childhood years (FANCY): A prospective cohort study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017, 32, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangla, A.; Kandasamy, Y. Effects of prematurity on long-term renal health: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perico, N.; Cattaneo, D.; Remuzzi, G. Kidney injury molecule 1: In search of biomarkers of chronic tubulointerstitial damage and disease progression. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.H.; Abraham, A.G.; Xu, Y.; Schelling, J.R.; Feldman, H.I.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Ix, J.H.; Jogalekar, M.P.; Coca, S.; Waikar, S.S.; et al. Urine biomarkers of kidney tubule health, injury, and inflammation are associated with progression of CKD in children. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2664–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybi Szumińska, A.; Wasilewska, A.; Kamianowska, M. Protein Biomarkers in Chronic Kidney Disease in Children—What Do We Know So Far? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, J.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Jabłonowski, Z.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A. Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Mussap, M.; Noto, A.; Barberini, L.; Puddu, M.; Coni, E.; Murgia, F.; Lussu, M.; Fanos, V. Clinical metabolomics and urinary NGAL for the early prediction of chronic kidney disease in healthy adults born ELBW. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24 (Suppl. S2), 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmas, A.T.; Karadag, A.; Tabel, Y.I.; Ozdemir, R.; Otlu, G. Analysis of urine biomarkers for early determination of acute kidney injury in non-septic and non-asphyxiated critically ill preterm neonates. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017, 30, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussap, M.; Degrandi, R.; Fravega, M.; Fanos, V. Acute kidney injury in critically ill infants: The role of urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010, 23 (Suppl. S3), 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staub, E.; Urfer-Maurer, N.; Lemola, S.; Risch, L.; Evers, K.S.; Welzel, T.; Pfister, M. Comparison of blood pressure and kidney markers between adolescent former preterm infants and term controls. Children 2020, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, J.M.; Torres-Canchala, L.; Bonventre, J.V.; Arias, J.C.; Ferguson, M.; Villegas, A.; Ramirez, O.; Filler, G. Urinary KIM-1 is not correlated with gestational age among 5-year-old children born prematurely. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1038206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamianowska, M.; Rybi-Szumińska, A.; Kamianowska, A.; Maciejczyk, M.; Sołomianko, K.; Koput, A.; Wasilewska, A. The Urinary Concentration of Trefoil Factor 3 (TFF3) in the Term and Preterm Neonates. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, L.P.; Gatto, F.R.; Bressani, G.Y.; Lanza, K.; Simões e Silva, A.C. Nephrogenesis, renal function, and biomarkers in preterm newborns. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 4097–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogulska, K.; Wojciechowska-Koszko, I.; Krasnodębska-Szponder, B.; Kwiatkowski, P.; Roszkowska, P.; Dołęgowska, B.; Łuczkowska, K.; Machaliński, B.; Kosik-Bogacka, D. TFF3 as a Diagnostic Biomarker in Kidney Transplant Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainoglou, A.; Chrysaidou, K.; Kotsis, V.; Stabouli, S. Preterm birth, kidney function and cardiovascular disease in children and adolescents. Children 2022, 9, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| AKI (n = 19) | No AKI (n = 38) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perinatal Factors | |||
| Maternal age, year ** | 28 (23–32) | 32 (25–37) | 0.20 |
| Multiple birth, n (%) | 17 (44.7) | 5 (26.3) | 0.03 |
| Maternal hypertension, n (%) | 7 (38.9) | 15 (39.5) | 0.96 |
| Betamethasone (complete course) | 13 (68.4) | 22 (57.9 | 0.56 |
| Maternal diabetes, n (%) | 2 (10.5) | 9 (23.7) | 0.23 |
| PPROM, n (%) | 1 (5.3) | 4 (10.5) | 0.50 |
| Oligohydramnios, n (%) | 11 (57.9) | 6 (15.8) | 0.002 |
| Cesarean section, n (%) | 17 (89.5) | 34 (89.5) | 1 |
| Neonatal Factors | |||
| Gestational age ** | 30 (28–33) | 32 (31–33) | 0.01 |
| Birth weight (g) ** | 1335 (1015–1657) | 1615 (1318–1920) | 0.003 |
| Birth weight percentile, % * | 40.0 ± 6.2 | 47.2 ± 4.8 | 0.38 |
| IUGR, n (%) | 10 (52.6) | 16 (42.1) | 0.31 |
| Male, n (%) | 10 (52.6) | 18 (47.4) | 0.78 |
| Apgar score (1 min) ** | 7 (4–8) | 8.5 (7–9) | 0.007 |
| Apgar score (5 min) ** | 8.5 (7–10) | 10 (8–10) | 0.04 |
| Ph < 7.2, n (%) | 4 (21.1) | 1 (2.9) | 0.04 |
| BE mmol/L * | 7.5 ± 0.9 | 7,7 ± 0.6 | 0.93 |
| Lactate, mmol/L * | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 0.08 |
| SNAPPE II score ** | 34 (7–61) | 5 (2.5–21) | <0.001 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation, days ** | 3 (0.5–11) | 0 (0–1) | |
| Hypotension, n (%) | 9 (47.4) | 8 (21.1) | 0.04 |
| UVC, n (%) | 13 (68.4) | 18 (47.4) | 0.13 |
| UAC, n (%) | 4 (21.1) | 0 | |
| Parenteral nutrition, days ** | 28 (15–51) | 14 (5–23) | <0.001 |
| Early sepsis, n (%) | 7 (36.8) | 2 (5.3) | 0.004 |
| Treated PDA, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 4 (10.5) | 0.14 |
| NEC ≥ stage 2, n (%) | 3 (15.8) | 0 | |
| BPD, n (%) | 12 (63.2) | 8 (22.9) | 0.003 |
| IVH grade 3 or 4, n (%) | 3 (15.8) | 0 | |
| Length of hospitalization ** | 53 (36–66) | 32 (20–47) | <0.001 |
| Postmenstrual age at discharge, week ** | 38 (37–39) | 37 (35–38) | <0.001 |
| Weight at discharge, g ** | 2500 (2155–2715) | 2300 (2090–2440) | 0.05 |
| Weight percentile at discharge, % ** | 10 (1.5–18.5) | 11 (1–35) | 0.19 |
| Medications in NICU | |||
| Ibuprofen, mg/kg ** | 20 (15–20) | 20 (0–20) | 0.32 |
| Aminoglycoside, days * | 17 ± 4.4 | 9.1 ± 2.2 | 0.002 |
| Vancomycin, days ** | 11.5 (6–19) | 0 (0–14) | 0.01 |
| Caffeine, days * | 28.6 ± 7.9 | 19.4 ± 6.7 | 0.014 |
| Kidney history in NICU | |||
| Inıtial sCr, mg/dL ** | 0.62 (0.40–0.88) | 0.72 (0.47–0.84) | 0.71 |
| 1st week sCr, mg/dL * | 0.60 ± 0.06 | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 0.01 |
| 1st week eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 ** | 22.9 (16.2–28.2) | 29.0 (21.6–43.2) | 0.006 |
| Highest sCre during NICU stay, mg/dL ** | 0.86 (0.64–1.5) | 0.40 (0.23–0.56) | 0.006 |
| Lowest eGFR during NICU stay, mL/min/1.73 m2 ** | 24.2 (18.4–30.2) | 34.6 (23.8–49.9) | 0.003 |
| sCR at discharge, mg/dL ** | 0.3 (0.19–0.38) | 0.26 (0.2–0.33) | 0.42 |
| eGFR at discharge, mL/min/1.73 m2 ** | 50.0 (37.3–89.6) | 59.6 (49.5–87.4) | 0.17 |
| At the Time of Follow-Up (7–12 Years of Age) | AKI a (n = 19) | No-AKI b (n = 38) | Controls c (n = 44) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (month) * | 105 ± 2 | 97 ± 1 | 107 ± 4 | 0.06 |
| Male, n (%) | 10 (52.6) | 18 (45) | 28 (63.6) | 0.22 |
| Height (cm) * | 129 ± 2.2 | 125.5 ± 1.0 | 132.0 ± 2.0 | 0.02 pa-b: 0.33 pa-c: 0.61 pb-c: 0.01 |
| Height z-score ** | 129 (121–136) | 126 (122–130) | 129.5 (122.2–141.5) | 0.14 |
| Weight (kg) ** | 26 (23–37) | 25 (22.7–32.7) | 27.2 (21.2–31.7) | 0.77 |
| Weight z-score ** | 0.04 (−0.78–1.42) | −0.10 (−0.83–1.12) | −0.38 (−0.81–0.42) | 0.38 |
| BMI (kg/m2) ** | 16.8 (14.1–19.8) | 15.9 (14.6–19.2) | 15.9 (14.4–21.8) | 0.64 |
| BMI z-score * | 0.20 ± 0.35 | 0.22 ± 0.19 | −0.27 ± 0.16 | 0.13 |
| Blood pressure | ||||
| Systolic (mmHg) ** | 100 (95–108.5) | 100 (95.7–107.5) | 108 (100–115) | 0.06 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) ** | 60.5 (56–66) | 60 (55–62.2) | 60 (51–64) | 0.48 |
| Mean MP (mmHg) ** | 77 (73–82.7) | 76 (70–79.2) | 75 (70–82.6) | 0.27 |
| At the Time of Follow-Up (7–12 Years of Age) | AKI (n = 8) | No-AKI (n = 20) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambulatory BP (mmHg) | |||
| Awake SBP ** | 97.5(96–106) | 99.5 (95–106) | 0.80 |
| Awake DBP * | 61.3 ± 2.3 | 63.1 ± 1.3 | 0.64 |
| Awake MBP * | 79.3 ± 2.1 | 80.5 ± 1.2 | 0.56 |
| Sleep SBP * | 96.1 ± 2.4 | 93.6 ± 1.1 | 0.02 |
| Sleep DBP * | 55.3 ± 1.0 | 55.8 ± 1.1 | 0.20 |
| Sleep MBP * | 73.7 ± 1.4 | 73.0 ± 1.0 | 0.04 |
| Awake SBP Load (%) ** | 12.5 (3.2–19) | 5.5 (2–26.2) | 0.42 |
| Awake DBP Load (%) ** | 13.0 (0–19) | 13.5 (6–30.7) | 0.96 |
| Sleep SBP Load (%) * | 31.5 ± 8.2 | 15.7 ± 3.1 | 0.04 |
| Sleep DBP Load (%) * | 20.3 ± 5.4 | 15.6 ± 3.4 | 0.02 |
| At the Time of Follow-Up | AKI (n = 14) | No-AKI (n = 24) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney USG | |||
| Left kidney length, cm | 8.25 (7.72; 8.7) | 8.4 (7.5; 9.2) | 0.67 |
| Relative LK Length, cm | 6.69 (6.21; 7.07) | 6.45 (5.84; 6.78) | 0.19 |
| Left kidney length percentile, mm | 25 (4.5; 42) | 19.5 (4.2; 30.7) | 0.72 |
| Left kidney length z score | −0.67(−1.7; −0.2) | −0.86 (−1.77; −0.49) | 0.72 |
| Right Kidney length, cm | 8.2 (7.5–8.85) | 8.45 (8.17–9.2) | 0.19 |
| Relative RK Length, cm | 6.57 (6.07; 7.27) | 6.55 (6.07; 7.27) | 0.63 |
| Right kidney lenght percentile, mm | 21(10.2; 46.5) | 11.5 (1.2; 34.7) | 0.23 |
| Right kidney lenght z score | −0.60 ± 0.29 | −1.05 ± 0.29 | 0.14 |
| Mean kidney length/body length cm | 0.61 (0.59; 0.68) | 0.64 (0.58; 0.67) | 0.43 |
| AKI a (n = 19) | No AKI b (n = 38) | Controls c (n = 44) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum Cr, mg/dL ** | 0.52 (0.47–0.56) | 0.47 (0.43–0.50) | 0.51 (0.48–0.57) | 0.17 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 * | 118.12 ± 3.53 | 120.0 ± 2.53 | 128.8 ± 2.26 | 0.61 |
| Microalbumin/Cr, mg/mg ** | 10.48 (5.2–18.3) | 5.7 (4.1–10.1) | 6.5 (4.6–8.7) | 0.14 |
| Protein/Cr, mg/g * | 134.7 ± 9.7 | 129.6 ± 4.9 | 147.5 ± 7.8 | 0.50 |
| Cystatin C, serum, mg/L ** | 1.16 (0.74–2.24) | 0.95 (0.54–2.58) | 0.78 (0.52–1.05) | 0.04 pa-b: 0.10 pa-c: <0.001 pb-c: 0.10 |
| eGFR (CysC), mL/min/1.73 m2 * | 90 ± 9.7 | 98 ± 9.1 | 106 ± 6.7 | 0.002 pa-b: 0.04 pa-c: <0.001 pb-c: 0.21 |
| Serum TFF3, ng/mL * | 1.05 ± 0.05 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 0.77 ± 0.04 | <0.001 pa-b: 0.07 pa-c: <0.001 pb-c: 0.04 |
| Urinary NGAL/Cr, ng/mg Cr ** | 0.36 (0.22–1.15) | 0.07 (0.02–0.18) | 0.06 (0.03–0.14) | <0.001 pa-b: <0.001 pa-c: <0.001 pb-c: 0.94 |
| Urinary TFF3/Cr, ng/mg ** | 9.4 (4.0–12.48) | 7.0 (4.5–11.4) | 8.1 (5.3–12.8) | 0.63 |
| Urinary KIM1/Cr, ng/mg Cr ** | 0.42 (0.22–0.76) | 0.24 (0.19–0.28) | 0.21 (0.13–0.42) | 0.007 pa-b: 0.006 pa-c: 0.003 pb-c: 0.82 |
| Biomarker | Predictor | B (SE) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| uNGAL/creatinine | AKI | 7.537 (1.553) | <0.001 |
| Gestational Age | 0.259 (0.414) | 0.534 | |
| Birth weight | 0.000 (0.002) | 0.833 | |
| uKIM-1/creatinine | AKI | 0.003 (0.001) | 0.012 |
| Gestational Age | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.209 | |
| Birth weight | −0.000001 (0.000) | 0.491 | |
| uTFF3/creatinine | AKI | −0.004 (0.024) | 0.873 |
| Gestational Age | 0.010 (0.006) | 0.143 | |
| Birth weight | −0.00042(0.000) | 0.144 | |
| sTFF3 | AKI | 0.173 (0.075) | 0.024 |
| Gestational Age | 0.022 (0.019) | 0.259 | |
| Birth weight | −0.000081 (0.000) | 0.355 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barsan Kaya, T.; Aydemir, Ö.; Surmeli Onay, O.; Kocaturk, E.; Öztunalı, Ç.; Kavaz Tufan, A.; Cetin, N.; Alataş, Ö.; Tekin, A.N. Long-Term Impact of Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury on Renal Function in Children Born Preterm: A Follow-Up Study. Children 2025, 12, 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081018
Barsan Kaya T, Aydemir Ö, Surmeli Onay O, Kocaturk E, Öztunalı Ç, Kavaz Tufan A, Cetin N, Alataş Ö, Tekin AN. Long-Term Impact of Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury on Renal Function in Children Born Preterm: A Follow-Up Study. Children. 2025; 12(8):1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081018
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarsan Kaya, Tuğba, Özge Aydemir, Ozge Surmeli Onay, Evin Kocaturk, Çiğdem Öztunalı, Aslı Kavaz Tufan, Nuran Cetin, Özkan Alataş, and Ayşe Neslihan Tekin. 2025. "Long-Term Impact of Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury on Renal Function in Children Born Preterm: A Follow-Up Study" Children 12, no. 8: 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081018
APA StyleBarsan Kaya, T., Aydemir, Ö., Surmeli Onay, O., Kocaturk, E., Öztunalı, Ç., Kavaz Tufan, A., Cetin, N., Alataş, Ö., & Tekin, A. N. (2025). Long-Term Impact of Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury on Renal Function in Children Born Preterm: A Follow-Up Study. Children, 12(8), 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12081018






