Enhancing Physical Fitness in Primary School Children Through Inclusive Sports Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measuring Procedures
2.3. Testing
2.3.1. Handgrip Strength
2.3.2. Flamingo Balance Test
2.3.3. Hand Tapping
2.3.4. Sit-and-Reach
2.3.5. Sit-Ups for 30 s
2.3.6. Pull-Ups Test
2.3.7. Beep Test
2.3.8. Shuttle Run 10 × 5 m
2.3.9. Standing Broad Jump
2.4. Experimental Program
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BW | Body weight |
| BH | Body height |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| PBF | Percentage of body fat |
| HGR | Handgrip strength |
| FBL | Flamingo balance test |
| HTP | Hand tapping |
| SAR | Sit-and-reach |
| SUP | Sit-ups |
| PUP | Pull-ups test |
| BPT | Beep test/The 20 m endurance shuttle run test |
| SHR | Shuttle run 10 × 5 m |
| SBJ | Standing broad jump |
References
- Gibson, A.L.; Wagner, D.R.; Heyward, V.H. Advanced Fitness Assessment and Exercise Prescription; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ostojić, S.M. Seasonal alterations in body composition and sprint performance of elite soccer players. J. Exerc. Physiol. 2003, 6, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cvejić, D.; Pejović, T.; Ostojić, S. Assessment of physical fitness in children and adolescents. Facta Univ. Ser. Phys. Educ. Sport 2013, 11, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Masanovic, B.; Gardasevic, J.; Marques, A.; Peralta, M.; Demetriou, Y.; Sturm, D.J.; Popovic, S. Trends in physical fitness among school-aged children and adolescents: A systematic review. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 627529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, H.S.; Şahin, F.N.; Maksimovic, N.; Drid, P.; Bianco, A. School-based intervention programs for preventing obesity and promoting physical activity and fitness: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Castro-Piñero, J.; España-Romero, V.; Artero, E.G.; Ortega, F.B.; Cuenca, M.M.; Jimenez-Pavón, D.; Chillón, P.; Girela-Rejón, M.J.; Mora, J.; et al. Field-based fitness assessment in young people: The ALPHA health-related fitness test battery for children and adolescents. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, J.H.; Vanderbom, K.; Greene, M. Physical activity interventions for children and adolescents with disabilities. Disabil. Health J. 2012, 5, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.J.; Larkin, D. The effects of an adapted physical activity program on the health-related fitness and self-esteem of children with disabilities. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 2003, 20, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, M.N.; Krustrup, P.; Araújo Póvoas, S.C.; Castagna, C. Accuracy and reliability of the InBody 270 multi-frequency body composition analyser in 10–12-year-old children. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.; Hohmann, A.; Niessner, C.; Siener, M. Health-related motor testing of children in primary school: A Systematic review of criterion-referenced standards. Children 2021, 8, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, C.; Bortolami, O.; Bertucco, M.; Verlato, G.; Zancanaro, C. Anthropometry and motor fitness in children aged 6–12 years. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2010, 5, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, L.; Schulze, J.; Ohlendorf, D. Influence of additional exercise in class on the concentration behaviour of first grade primary school pupils. Man. Med. 2019, 57, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, M.; Croce, R.; Pesce, C.; Fallaize, A.E. Developmental and Adapted Physical Education: Making Ability Count; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Anaby, D.; Avery, L.; Gorter, J.W.; Levin, M.F.; Teplicky, R.; Turner, L.; Cormier, I.; Hanes, J. Improving body functions through participation in community activities among young people with physical disabilities. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, H.M.; Wen, L.M.; Peng, Y.Z.; Lin, L.Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, W.-H.; Wang, H.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the overall effects of school-based obesity prevention interventions and effect differences by intervention components. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.; Staples, K. The role of physical activity in improving physical fitness in children with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2017, 69, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlovic, M.; Roklicer, R.; Trivic, T.; Milic, R.; Maksimović, N.; Tabakov, R.; Sekulic, D.; Bianco, A.; Drid, P. Effects of school-based physical activity interventions on physical fitness and cardiometabolic health in children and adolescents with disabilities: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1180639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, J.H.; Riley, B. Evaluation of inclusive physical activity programs for children with and without disabilities: A systematic review. J. Phys. Act. Health 2014, 11, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, M. Instructional Models in Physical Education; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- La Greca, S.; Rapali, M.; Ciaprini, G.; Russo, L.; Vinciguerra, M.G.; Di Giminiani, R. Acute and chronic effects of supervised flexibility training in older adults: A comparison of two different conditioning programs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faigenbaum, A.D.; Bush, J.A.; McLoone, R.P.; Kreckel, M.C.; Farrell, A.; Ratamess, N.A.; Kang, J. Benefits of strength and skill-based training during primary school physical education. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, S.; Marinković, D.; Đorđić, V.; Pelemiš, V. Morphological characteristics and motor skills as predictors of physical activity of students in a physical education class. Facta Univ. Ser. Phys. Educ. Sport 2018, 16, 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Tahira, S. The association between sports participation and physical fitness. Int. J. Sport Stud. Health 2021, 4, e127001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branković, N.; Milanović, S.; Pavlović, B. The influence of regular physical education classes on the adaptive processes of motor agility and functional abilities. J. Anthropol. Soc. Serb. 2012, 47, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavčević, T.; Babin, J.; Prskalo, I. Complex group organizational forms—An optimizing factor in physical education instruction. Kinesiology 2006, 38, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Pozuelo-Carrascosa, D.P.; García-Hermoso, A.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Sánchez-López, M.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V. Effectiveness of school-based physical activity programmes on cardiorespiratory fitness in children: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogataj, Š.; Trajković, N.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Sember, V. Effects of school-based exercise and nutrition intervention on body composition and physical fitness in overweight adolescent girls. Nutrients 2021, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinđić, M.; Mačak, D.; Todorović, N.; Purda, B.; Batez, M. Effect of integrated neuromuscular exercise in physical education class on health-related fitness in female children. Healthcare 2021, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potempa-Jeziorowska, M.; Jonczyk, P.; Świętochowska, E.; Kucharzewski, M. The analysis of the nutritional status and dietary habits among children aged 6–10 years old attending primary schools in Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarzadeh Jenatabadi, H.; Shamsi, N.A.; Ng, B.K.; Abdullah, N.A.; Mentri, K.A.C. Adolescent obesity modeling: A framework of socio-economic analysis on public health. Healthcare 2021, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, E.D.S.; Gonçalves, E.M.; Morcillo, A.M.; Guerra-Júnior, G.; Amancio, O.M.S. Effects of programmed physical activity on body composition in post-pubertal schoolchildren. J. Pediatr. 2015, 91, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorås, H. The effects of physical education on motor competence in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports 2020, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardanova, Z.; Ponkratov, V.; Kuznetsov, N.; Nikitina, N.; Dudnik, O.; Latypova, E.; Shcherbatykh, S. A model for optimizing the structure of teaching techniques for distance learning in the Russian higher education system. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšić, D.; Mandić, S.; Maksimović, N.; Milošević, Z.; Roklicer, R.; Vuković, J.; Drid, P. Effects of a nine-month physical activity intervention on morphological characteristics and motor and cognitive skills of preschool children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawan, F.B.; Suharjana, R.L. The use of game as a strategy in strengthening the role of physical education teachers to improve the manipulative motion skills of elementary school students. Int. J. Hum. Mov. Sports Sci. 2021, 9, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Month | Week | Class | Learning Objective | Lesson Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| October | I | 1 | Testing | Testing |
| II | 2 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: passing and throwing | Ball handling, passing the ball stationary and in motion; passing the ball with one hand and both hands | |
| III | 3 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: positions and stances | Techniques for movement and positioning in defense and attack | |
| IV | 4 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: situational exercises 1 | Performing situational exercises, games with two goals | |
| November | I | 5 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: passing and throwing | Passing the ball stationary and in motion; passing the ball with one hand and both hands; passing the ball during running with one and both hands, blindfolded |
| II | 6 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: shooting techniques | Front technique shooting, rotational technique shooting | |
| III | 7 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: positions and stances | Squat position, lateral lunge from kneeling, on knees | |
| IV | 8 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: situational exercises 2 | Performing situational exercises, games with two goals with specific tasks | |
| December | I | 9 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: blocking and sliding techniques | Blocking technique, sliding technique on the floor |
| II | 10 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: shooting techniques | Front technique shooting, rotational technique shooting, shooting through the legs | |
| III | 11 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: penalty shooting and defense | Penalty shooting; penalty defense | |
| IV | 12 | Elements of sports for individuals with disabilities: situational exercises 3 | Performing situational exercises, games with two goals, applying all techniques and rules | |
| January | I | 13 | Testing | Testing |
| II | 14 | Testing | Testing |
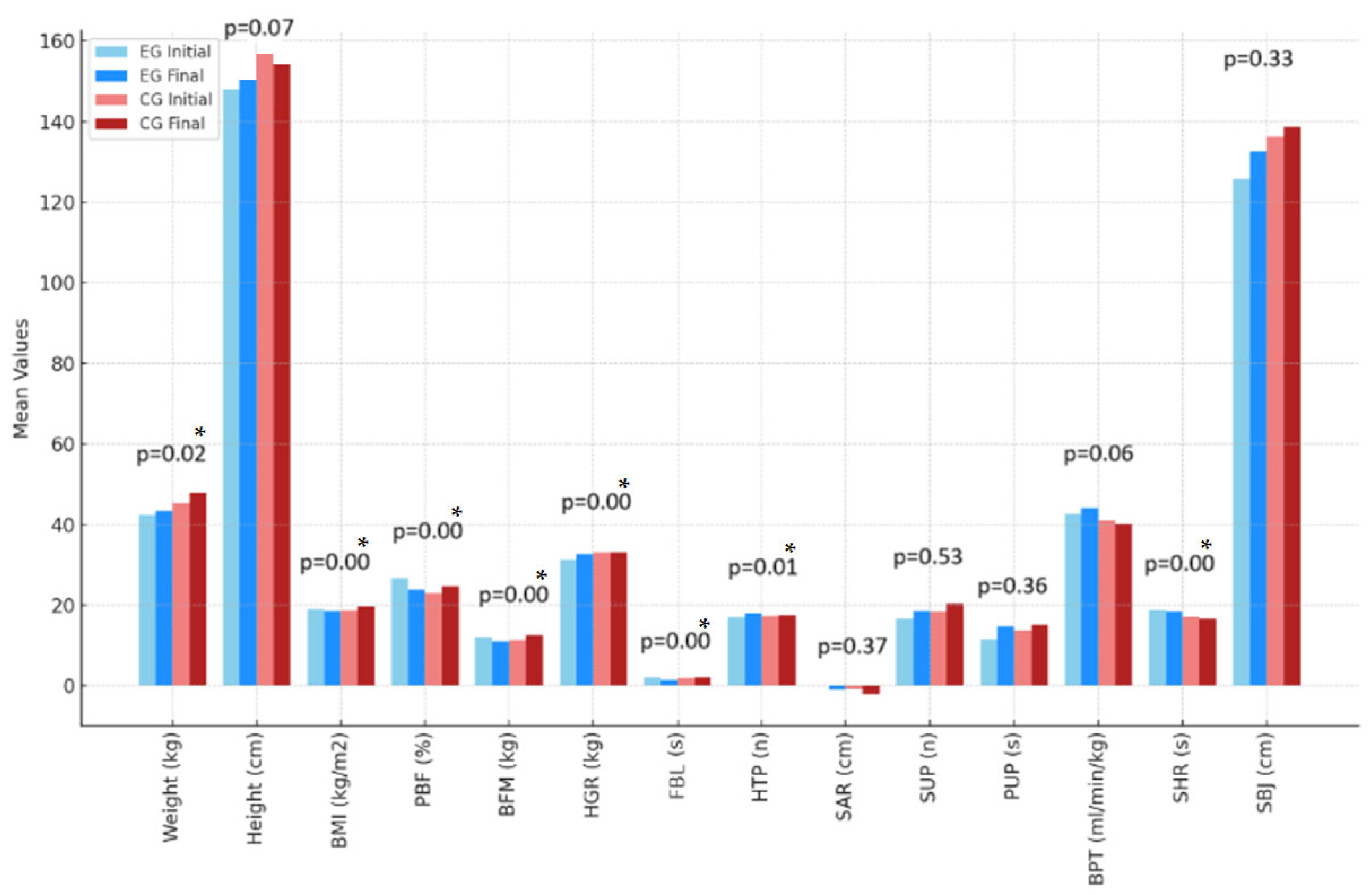
| Variables | Experimental Group | Control Group | p Value | η2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Measurements (M ± SD) | Final Measurements (M ± SD) | Initial Measurements (M ± SD) | Final Measurements (M ± SD) | |||
| Weight (kg) | 44.58 ± 9.06 | 46.26 ± 10.38 | 47.00 ± 13.41 | 50.30 ± 14.34 * | 0.10 | 0.01 (small) |
| Height (cm) | 149.19 ± 6.88 | 150.47 ± 6.69 * | 156.85 ± 21.00 | 155.30 ± 8.26 | 0.07 | 0.01 (small) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 19.59 ± 2.72 | 19.46 ± 3.14 | 19.30 ± 4.07 | 20.65 ± 4.40 * | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| PBF (%) | 26.21 ± 7.22 | 24.10 ± 9.12 * | 23.40 ± 10.19 | 25.45 ± 10.34 * | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| BFM (kg) | 12.17 ± 5.33 | 11.74 ± 6.16 | 12.26 ± 8.02 | 13.95 ± 8.82 * | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| HGR (kg) | 30.61 ± 5.59 | 32.06 ± 6.44 * | 34.68 ± 7.51 | 34.53 ± 7.19 | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| FBL (s) | 2.17 ± 1.15 | 1.44 ± 0.62 * | 1.70 ± 1.30 | 1.70 ± 1.13 | 0.06 | 0.01 (small) |
| HTP (n) | 17.39 ± 2.23 | 18.72 ± 2.44* | 18.35 ± 2.28 | 18.45 ± 1.85 | 0.06 | 0.01 (small) |
| SAR (cm) | 2.57 ± 5.86 | 1.03 ± 3.74 | −0.08 ± 3.76 | −1.63 ± 3.3.68 * | 0.18 | 0.01 (small) |
| SUP (n) | 18.39 ± 4.12 | 20.67 ± 4.59* | 21.75 ± 3.37 | 23.35 ± 3.22 * | 0.86 | 0.01 (small) |
| PUP (s) | 13.23 ± 18.59 | 17.07 ± 20.98 * | 18.79 ± 16.81 | 18.92 ± 17.68 | 0.12 | 0.01 (small) |
| BPT (mL/min/kg) | 43.75 ± 2.39 | 45.26 ± 2.65 * | 41.00 ± 11.26 | 41.37 ± 11.53 | 0.15 | 0.01 (small) |
| SHR (s) | 17.90 ± 1.63 | 17.67 ± 1.09 | 15.97 ± 1.28 | 15.76 ± 1.09 | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| SBJ (cm) | 132.50 ± 12.00 | 140.61 ± 15.02 * | 146.85 ± 21.00 | 152.40 ± 23.12 | 0.66 | 0.01 (small) |
| Variables | Experimental Group | Control Group | p Value | η2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Measurements (M ± SD) | Final Measurements (M ± SD) | Initial Measurements (M ± SD) | Final Measurements (M ± SD) | |||
| Weight (kg) | 40.65 ± 13.52 | 41.01 ± 12.53 | 43.78 ± 11.21 | 45.38 ± 11.29 * | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| Height (cm) | 149.88 ± 9.38 | 150.55 ± 8.80 | 155.65 ± 24.05 | 154.28 ± 10.11 * | 0.07 | 0.01 (small) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.56 ± 4.21 | 17.73 ± 3.87 * | 18.10 ± 3.08 | 18.65 ± 3.02 * | 0.11 | 0.01 (small) |
| PBF (%) | 26.97 ± 8.25 | 23.54 ±7.50 * | 22.61 ± 6.53 | 23.78 ± 6.77 | 0.71 | 0.01 (small) |
| BFM (kg) | 11.95 ± 7.00 | 10.42 ± 6.47 * | 10.38 ± 4.55 | 11.074.88 | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| HGR (kg) | 31.77 ± 8.52 | 33.09 ± 9.72 * | 31.45 ± 6.00 | 31.55 ± 5.54 | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| FBL (s) | 2.05 ± 0.65 | 1.36 ± 0.66* | 2.20 ± 1.51 | 2.30 ± 1.26 | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| HTP (n) | 16.68 ± 2.24 | 17.50 ± 2.54 * | 16.10 ± 1.83 | 16.45 ± 1.70 * | 0.16 | 0.01 (small) |
| SAR (cm) | −2.00 ± 4.82 | −2.45 ± 3.81 | −1.68 ± 7.38 | −2.65 ± 7.44 | 0.61 | 0.01 (small) |
| SUP (n) | 14.95 ± 5.49 | 16.86 ± 4.16 * | 15.15 ± 4.69 | 17.45 ± 4.90 | 0.67 | 0.01 (small) |
| PUP (s) | 9.89 ± 13.85 | 12.85 ± 16.95 | 8.67 ± 9.21 | 11.30 ± 12.22 | 0.88 | 0.01 (small) |
| BPT (mL/min/kg) | 41.66 ± 2.10 | 43.12 ± 1.81 * | 41.12 ± 1.68 | 39.15 ± 1.50 | 0.14 | 0.01 (small) |
| SHR (s) | 19.56 ± 2.14 | 19.16 ± 2.18 | 18.31 ± 1.43 | 17.25 ± 0.79 * | 0.00 | 0.14 (large) |
| SBJ (cm) | 120.14 ± 20.83 | 126.05 ± 20.64 * | 125.65 ± 24.05 | 124.95 ± 23.74 | 0.29 | 0.01 (small) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Utvić, N.; Marković, L.; Arsenijević, R.; Aksović, N.; Bjelica, B.; Stojljković, S.; Bubanj, S.; Raveica, G.; Dobreci, D.-L.; Voinea, N.-L.; et al. Enhancing Physical Fitness in Primary School Children Through Inclusive Sports Activities. Children 2025, 12, 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060758
Utvić N, Marković L, Arsenijević R, Aksović N, Bjelica B, Stojljković S, Bubanj S, Raveica G, Dobreci D-L, Voinea N-L, et al. Enhancing Physical Fitness in Primary School Children Through Inclusive Sports Activities. Children. 2025; 12(6):758. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060758
Chicago/Turabian StyleUtvić, Nikola, Lidija Marković, Radenko Arsenijević, Nikola Aksović, Bojan Bjelica, Stanimir Stojljković, Saša Bubanj, Gabriela Raveica, Daniel-Lucian Dobreci, Nicolae-Lucian Voinea, and et al. 2025. "Enhancing Physical Fitness in Primary School Children Through Inclusive Sports Activities" Children 12, no. 6: 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060758
APA StyleUtvić, N., Marković, L., Arsenijević, R., Aksović, N., Bjelica, B., Stojljković, S., Bubanj, S., Raveica, G., Dobreci, D.-L., Voinea, N.-L., Ciocan, V.-C., Anghel, M., Antohe, B.-A., & Dobrescu, T. (2025). Enhancing Physical Fitness in Primary School Children Through Inclusive Sports Activities. Children, 12(6), 758. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12060758









