Hip Involvement in Pediatric Scurvy: Early Magnetic Imaging Signs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. MRI Image Evaluation
2.3. MRI Protocol
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
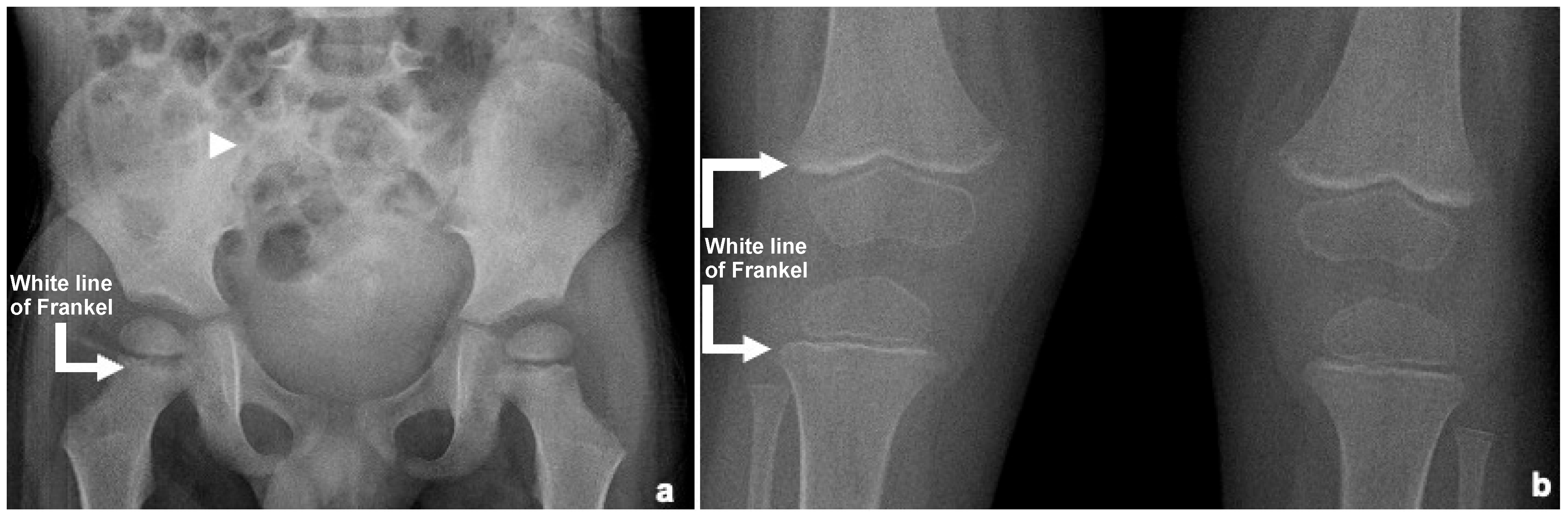
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trapani, S.; Rubino, C.; Indolfi, G.; Lionetti, P. A Narrative Review on Pediatric Scurvy: The Last Twenty Years. Nutrients 2022, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Shaharyar, A.; Kumar, A.; Bhat, M.S.; Mishra, M. Scurvy in pediatric age group—A disease often forgotten? J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2015, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, P.; Tate, A.; Adewumi, A.; Kinlin, L.M.; Ritwik, P. The risk for scurvy in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Spec. Care Dentist. 2020, 40, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, W.G.; Berry, R.C.; Burrell, L.; Scahill, L.; McElhanon, B.O. Scurvy as a Sequela of Avoidant-Restrictive Food Intake Disorder in Autism: A Systematic Review. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2020, 41, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deirawan, H.; Fakhoury, J.W.; Zarka, M.; Bluth, M.H.; Moossavi, M. Revisiting the pathobiology of scurvy: A review of the literature in the context of a challenging case. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, D.; Rubino, C.; Basile, M.; Indolfi, G.; Trapani, S. When the limp has a dietary cause: A retrospective study on scurvy in a tertiary Italian pediatric hospital. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 981908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, W.R. Scurvy in children. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.; Elfeky, O.; Ertugrul, H.; Chela, H.K.; Daglilar, E. Scurvy: Rediscovering a Forgotten Disease. Diseases 2023, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, S.; Cimorelli, V.; Bajwa, N.M. Case Report: Uncommon cause of limp in the 21st century. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 968015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, R.; Khani, F.; Sturmlechner, I.; Dehghani, S.S.; Denbeigh, J.M.; Zhou, X.; Pichurin, O.; Dudakovic, A.; Jerez, S.S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Vitamin C epigenetically controls osteogenesis and bone mineralization. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanian, P.; Hall, S.; Wongworawat, M.D.; Mohan, S. The Roles and Mechanisms of Actions of Vitamin C in Bone: New Developments. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, R.C.; Cheng, S.; Mohan, S. Vitamin C effects on 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and gene expression in osteoblasts and chondrocytes: Potential involvement of PHD2. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fain, O. Musculoskeletal manifestations of scurvy. Jt. Bone Spine 2005, 72, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Jamil, R.T.; Attia, F.N. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Bray, T.J.P.; Hall-Craggs, M.A. Quantifying bone structure, micro-architecture, and pathophysiology with MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwetje, D.; Zillekens, A.; Kieback, J.D.; Koob, S.; Placzek, R. Infantile scurvy: Still a relevant differential diagnosis in Western medicine. Nutrition 2020, 75–76, 110726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Mitchell, D.M.; Handa, A.; Kattapuram, S.V.; Huang, A.J. Imaging Findings of Metabolic Bone Disease. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 1871–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenetz, Z.J.; Al-Jaberi, L.; Brescia, A.C.; Saul, D.; Holton, R.S. An Atypical Case of Scurvy in an Adolescent With Sacroiliitis. Clin. Pediatr. 2022, 61, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swed-Tobia, R.; Haj, A.; Militianu, D.; Eshach, O.; Ravid, S.; Weiss, R.; Aviel, Y.B. Highly Selective Eating in Autism Spectrum Disorder Leading to Scurvy: A Series of Three Patients. Pediatr. Neurol. 2019, 94, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergill, K.K.; Shergill, G.S.; Pillai, H.J. Gelatinous transformation of bone marrow: Rare or underdiagnosed? Autops. Case Rep. 2017, 7, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.M.; Atkins, K.A.; Druzgal, C.H.; Gaskin, C.M. Magnetic resonance imaging appearance of scurvy with gelatinous bone marrow transformation. Skelet. Radiol. 2012, 41, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Miller, S.; Cohen, H.L. Scurvy in A Malnourished Child: Atypical Imaging Findings. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 16, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganske, A.; Kolbe, A.B.; Thomas, K.; Hull, N. Pediatric scurvy MRI appearance. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 16, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.C.; Davidson, A.M.; Beyda, R.M.; Eissa, M.A. Scurvy, abnormal MRI, and gelatinous bone marrow in an adolescent with avoidant restrictive food intake disorder. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, J. Gelatinous transformation of the bone marrow: The spectrum of underlying diseases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tall, M.A.; Thompson, A.K.; Vertinsky, T.; Palka, P.S. MR imaging of the spinal bone marrow. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2007, 15, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckow, C.; Thomas, A.A. Scurvy in a pediatric patient with autism and limp: A Case Report. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 60, e53–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.M.; Becker, M.L.; Shapiro, S.; Allison, T.; Harris, J.G. Scurvy presenting with limp and weakness: A case report. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, R.R.; Patro, P.; Agarwal, V.; Misra, D.P. Enthesitis-related arthritis: Current perspectives. Open Access Rheumatol. 2019, 11, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzola, G.; Possemato, N.; Germanò, G.; Salvarani, C. Scurvy mimicking spondyloarthritis in a young man. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 795. [Google Scholar]
- Rudwaleit, M.; Jurik, A.G.; Hermann, K.G.; Landewé, R.; van der Heijde, D.; Baraliakos, X.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Ostergaard, M.; Braun, J.; Sieper, J. Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: A consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herregods, N.; Dehoorne, J.; Joos, R.; Jaremko, J.L.; Baraliakos, X.; Leus, A.; Van den Bosch, F.; Verstraete, K.; Jans, L. Diagnostic value of MRI features of sacroiliitis in juvenile spondyloarthritis. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoddy, A.M.E.; Buckley, H.R.; Elliott, G.E.; Standen, V.G.; Arriaza, B.T.; Halcrow, S.E. Macroscopic features of scurvy in human skeletal remains: A literature synthesis and diagnostic guide. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2018, 167, 876–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Cousin, E.; Chouklati, K.; Bruneau, B.; Proisy, M. Scurvy in a 3-year-old autistic girl: Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging findings. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino, M.R.; Tse, S.M.; Gupta, S.; Rachlis, A.C.; Stimec, J. Whole-body MRI of juvenile spondyloarthritis: Protocols and pictorial review of characteristic patterns. Pediatr. Radiol. 2015, 45, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient N | Age at Disease Onset (Months) | Diagnostic Delay (Months) | Associated Disease | Signs/Symptomps of Scurvy | Initial Diagnostic Suspicion | Elevated CRP/ESR | Anemia | Plasma Vitamin C Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limping | Back Pain | Bleeding | Hypertrophic Gums | Fever | Other | ||||||||
| 1 | 48 | 2 | Autism, ED | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | Bilateral thigh swelling | Spondylodiscitis, neoplastic disease | Both | YES | 36 mcg/dL |
| 2 | 29 | 6 | Multiple food allergies (milk, egg, fish) | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | Thigh swelling, hypovolemic shock, polyserositis, irritability | Osteomyelitis, myosarcoma | CRP | YES | 3 mcg/dL |
| 3 | 17 | 3 | None | NO | NO | YES | YES | N | NO | Transient hip arthritis, osteomyelitis, CRMO, JIA | Both | YES | 26 mcg/dL |
| 4 | 133 | 1 | Severe developmental delay, spastic tetraparesis, focal epilepsy | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | Tooth pain, refusal to walk, nocturnal lower limb pain | Osteomyelitis, muscle contracture | Both | YES | Undetectable |
| 5 | 45 | 1 | None | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | Right thigh pain, refusal to walk, irritability | Transient hip arthritis, osteomyelitis, CRMO | NO | YES | 53 mcg/dL |
| 6 | 43 | 1 | Autism, ED | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | Spondylodiscitis | ESR | YES | Undetectable |
| 7 | 120 | 2 | Rett syndrome | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | Right leg pain, swelling, and irritability | Osteomyelitis | Both | YES | Undetectable |
| 8 | 45 | 2 | Autism | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | JIA (ERA subtype) | NO | Unknown | Undetectable |
| 9 | 38 | 1 | Psycomotor delay, G6PD, drepanocytotosis | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | JIA (ERA subtype) | NO | YES | Undetectable |
| 10 | 44 | 33 | Language delay | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | JIA | Both | YES | Undetectable |
| Patient N | Interval Between Symptoms and MRI (Months) | MRI: Whole Body/Targeted | Pelvic Involvement: Bilateral/Monolateral | Pelvic Marrow Signal Pattern | Sacroiliac Gadolinium Enhancement | Additional Radiological Signs | Previous X-Ray: Anatomical Area and Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | Whole Body | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | Edema of adjacent soft tissues and symmetrical signal changes in vertebrae and long bone metaphyses | Pelvis: Negative Lower limbs: positive |
| 2 | 6 | Pelvis | Bilateral | Patchy | Absent | none | Not perfmormed |
| 3 | 3 | Rachis and pelvis | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | Bilateral hip joint effusion with signal changes in the proximal femora | Not performed |
| 4 | 1 | Pelvis | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | Symmetrical signal changes in pelvic bones and proximal femora, with left hip joint effusion | Pelvis: Negative |
| 5 | 1 | Rachis, pelvis and lower limbs | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | Symmetrical signal changes in proximal femoral metaphyses and lumbar vertebrae | Pelvis: Negative Lower limbs: aspecific signs |
| 6 | 1 | Rachis and pelvis | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | none | Pelvis: Negative Lower limbs: aspecific signs |
| 7 | 1 | Pelvis and lower limbs | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | Symmetrical metaphyseal signal changes of the lower limbs with periosteal reaction and Edema of adjacent soft tissues | Pelvis: Negative |
| 8 | 2 | Pelvis | Bilateral | Patchy | Present | none | Pelvis: Negative |
| 9 | 33 | Pelvis | Bilateral | Patchy | Absent | none | Not performed |
| 10 | 1 | Rachis, pelvis and lower limbs | Bilateral | Homogeneous | Present | Sacroiliac joint effusion; symmetrical metaphyseal alterations of the lower limbs with periosteal reactions and soft tissue involvement | Pelvis: Negative |
| PELVIC MRI FINDINGS | SCURVY | JIA/ERA |
|---|---|---|
| Occasional, mild | Mild to intense |
| Mild, periosteal | Mild to intense, synovial |
| Absent | Mild to intense |
| Patchy, abnormal water-like signals (corresponding to gelatinous marrow subversion) Bilateral and symmetric | Bone marrow edema Focal and symmetric |
| Well-demarcated | Possible erosive signs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamalero, L.; Perrone, A.; Macucci, C.; Meneghel, A.; Balzarin, M.; Trapani, S.; Indolfi, G.; Martini, G.; Giani, T. Hip Involvement in Pediatric Scurvy: Early Magnetic Imaging Signs. Children 2025, 12, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050642
Gamalero L, Perrone A, Macucci C, Meneghel A, Balzarin M, Trapani S, Indolfi G, Martini G, Giani T. Hip Involvement in Pediatric Scurvy: Early Magnetic Imaging Signs. Children. 2025; 12(5):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050642
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamalero, Lisa, Anna Perrone, Chiara Macucci, Alessandra Meneghel, Marta Balzarin, Sandra Trapani, Giuseppe Indolfi, Giorgia Martini, and Teresa Giani. 2025. "Hip Involvement in Pediatric Scurvy: Early Magnetic Imaging Signs" Children 12, no. 5: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050642
APA StyleGamalero, L., Perrone, A., Macucci, C., Meneghel, A., Balzarin, M., Trapani, S., Indolfi, G., Martini, G., & Giani, T. (2025). Hip Involvement in Pediatric Scurvy: Early Magnetic Imaging Signs. Children, 12(5), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050642






