Effect of Relative Age on Gross Motor Coordination Development, Considering Biological Maturity and Sex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Anthropometry
2.4. Biological Maturity Assessment
2.5. Gross Motor Coordination Assessment
2.5.1. Hand-Foot Test (HF Test)
2.5.2. Dribbling-Targeting Test (DT Test)
2.5.3. T Test
2.5.4. Total Gross Motor Coordination Score (SGMC)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Relative Age and GMC
4.2. Biological Maturity and Sex in GMC
4.3. Subtest Analysis
4.4. Individual Differences in GMC
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Practical Applications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopes, V.P.; Stodden, D.F.; Bianchi, M.M.; Maia, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.P. Correlation between BMI and motor coordination in children. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2012, 15, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L.E.; Stodden, D.F.; Barnett, L.M.; Lopes, V.P.; Logan, S.W.; Rodrigues, L.P.; D’Hondt, E. Motor competence and its effect on positive developmental trajectories of health. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, L.M.; Lai, S.K.; Veldman, S.L.; Hardy, L.L.; Cliff, D.P.; Morgan, P.J.; Zask, A.; Lubans, D.R.; Shultz, S.P.; Ridgers, N.D. Correlates of gross motor competence in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 1663–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.M.; Van Beurden, E.; Morgan, P.J.; Brooks, L.O.; Beard, J.R. Does childhood motor skill proficiency predict adolescent fitness? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubans, D.R.; Morgan, P.J.; Cliff, D.P.; Barnett, L.M.; Okely, A.D. Fundamental movement skills in children and adolescents: Review of associated health benefits. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, S.; O’Donoghue, P. Season of birth distribution of elite tennis players. J. Sports Sci. 2005, 23, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, F.; Ballester, R.; Gines, H.J.; Hamidi, A.K.; Moratal, C.; Lupiáñez, J. Relative age effect in the sport environment. Role of physical fitness and cognitive function in youth soccer players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musch, J.; Grondin, S. Unequal competition as an impediment to personal development: A review of the relative age effect in sport. Dev. Rev. 2001, 21, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobley, S.; Baker, J.; Wattie, N.; McKenna, J. Annual age-grouping and athlete development: A meta-analytical review of relative age effects in sport. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, D.J.; Adler, A.L.; Côté, J. A proposed theoretical model to explain relative age effects in sport. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsen, W.F.; Van Winckel, J.; Williams, A.M. The relative age effect in youth soccer across Europe. J. Sports Sci. 2005, 23, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.; Barnsley, R.; Stebelsky, G. Baseball performance and the relative age effect: Does Little League neutralize birthdate selection bias. Nine 1992, 1, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, J.L.; Mutimer, B.T. The relative age phenomenon in sport: A replication and extension with ice-hockey players. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1994, 65, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadžić, A.; Milojević, A.; Stanković, V.; Vučković, I. Relative age effects on motor performance of seventh-grade pupils. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2017, 23, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattie, N.; Tietjens, M.; Schorer, J.; Ghanbari, M.-C.; Strauss, B.; Seidel, I.; Baker, J. Does relative age influence motor test performance of fourth grade pupils? Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2014, 20, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, H.; Akido, M.; Naruse, K.; Fujiwara, M. Relative age effect in physical fitness among elementary and junior high school students. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2017, 124, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vučković, I.; Kukrić, A.; Gadžić, A.; Petrović, B.; Marković, S.; Zlojutro, N. Motor abilities and relative age effect of adolescents. Phys. Cult. 2018, 72, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M. Growth, Maturation, and Physical Activity; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sherar, L.B.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.; Faulkner, R.A.; Russell, K.W. Do physical maturity and birth date predict talent in male youth ice hockey players? J. Sports Sci. 2007, 25, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, W.M.A.; Silva, K.G.d.; Silva, R.K.P.; Souza, A.P.d.S.; Silva, A.B.J.d.; Silva, M.R.M.; Fernandes, M.S.d.S.; Souza, S.L.d.; Souza, V.d.O.N. Effects of overweight/obesity on motor performance in children: A systematic review. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 759165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.P.; Maia, J.A.; Silva, R.G.; Morais, F.P. Estudo do nível de desenvolvimento da coordenação motora da população escolar (6 a 10 anos de idade) da Região Autónoma dos Açores. Rev. Port. Ciências Desporto 2003, 3, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuriato, M.; Lovecchio, N.; Pellino, V.C.; Mieszkowski, J.; Kawczyński, A.; Nevill, A.; Biino, V. Gross motor coordination and their relationship with body mass and physical activity level during growth in Children aged 8–11 years old: A longitudinal and allometric approach. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, G.; Giustino, V.; Tabacchi, G.; Lanza, M.; Schena, F.; Biino, V.; Giuriato, M.; Gallotta, M.C.; Guidetti, L.; Baldari, C. Interrelationship between age, gender, and weight status on motor coordination in Italian children and early adolescents aged 6–13 years old. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 738294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hondt, v.; Deforche, B.; Vaeyens, R.; Vandorpe, B.; Vandendriessche, J.; Pion, J.; Philippaerts, R.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Lenoir, M. Gross motor coordination in relation to weight status and age in 5-to 12-year-old boys and girls: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, N.; Raspaud, M. The relative age effect in young French basketball players: A study on the whole population. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.L.; Weir, P.L.; Till, K.; Romann, M.; Cobley, S. Relative age effects across and within female sport contexts: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 1451–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Till, K.; Cobley, S.; Wattie, N.; O’Hara, J.; Cooke, C.; Chapman, C. The prevalence, influential factors and mechanisms of relative age effects in UK Rugby League. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirwald, R.L.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.; Bailey, D.A.; Beunen, G.P. An assessment of maturity from anthropometric measurements. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Patón, R.; Lago-Ballesteros, J.; Arufe-Giráldez, V.; Sanmiguel-Rodríguez, A.; Lago-Fuentes, C.; Mecías-Calvo, M. Gender differences on motor competence in 5-year-old preschool children regarding relative age. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macun, A.; Söğüt, M. Influence of relative age effect (RAE) on motor performance of preschool children: A systematic review. Early Child Dev. Care 2024, 194, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Cumming, S.P.; Ribeiro, B.; Aroso, J. Maturity-associated variation in the growth and functional capacities of youth football (soccer) players 13–15 years. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 91, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malina, R.M. Growth and Maturity Status of Young Soccer Players; Routledge: London, UK, 2003; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar]
- Philippaerts, R.M.; Vaeyens, R.; Janssens, M.; Van Renterghem, B.; Matthys, D.; Craen, R.; Bourgois, J.; Vrijens, J.; Beunen, G.; Malina, R.M. The relationship between peak height velocity and physical performance in youth soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattuzzo, M.T.; dos Santos Henrique, R.; Ré, A.H.N.; de Oliveira, I.S.; Melo, B.M.; de Sousa Moura, M.; de Araújo, R.C.; Stodden, D. Motor competence and health related physical fitness in youth: A systematic review. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.L.; Rose, J.D. Motor skills of typically developing adolescents: Awkwardness or improvement? Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2000, 20, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.R.; French, K.E. Gender differences across age in motor performance: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 1985, 98, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Negro, J.; Huertas-Delgado, F.J.; Yanci, J. Motor skills differences by gender in early elementary education students. Early Child Dev. Care 2021, 191, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, J. Sex differences in the games children play. Soc. Probl. 1976, 23, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.J.; Allison, K.R.; Goldenberg, E.R.; Fein, A.J. Adolescent girls’perceived barriers to participation in physical activity. Adolescence 2006, 41, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Bardid, F.; Rudd, J.R.; Lenoir, M.; Polman, R.; Barnett, L.M. Cross-cultural comparison of motor competence in children from Australia and Belgium. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, R.S.; Oliver, J.L.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Howard, R.; Croix, M.B.D.S.; Williams, C.A.; Best, T.M.; Alvar, B.A.; Micheli, L.J.; Thomas, D.P. Long-term athletic development-part 1: A pathway for all youth. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
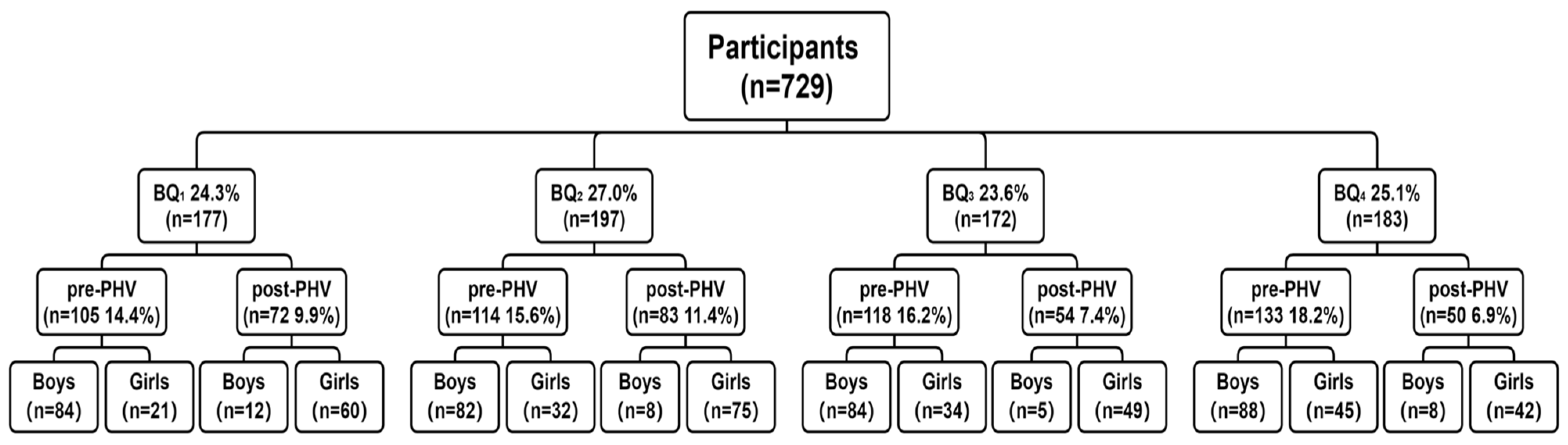
| BQ1 (n = 177) 1 | BQ2 (n = 197) 2 | BQ3 (n = 172) 3 | BQ4 (n = 183) 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pre-PHV (n = 105) | post-PHV (n = 72) | pre-PHV (n = 114) | post-PHV (n = 83) | pre-PHV (n = 118) | post-PHV (n = 54) | pre-PHV (n = 133) | post-PHV (n = 50) | ||
| Age (years) | Girls | 12.0 ± 0.4 | 13.0 ± 1.0 | 12.0 ± 0.3 | 12.8 ± 1.0 | 11.7 ± 0.3 | 12.7 ± 1.1 | 11.6 ± 0.1 | 12.9 ± 1.1 |
| Boys | 12.5 ± 0.7 | 14.8 ± 0.5 | 12.2 ± 0.7 | 14.7 ± 0.5 | 12.1 ± 0.8 | 14.6 ± 0.5 | 11.9 ± 0.8 | 13.9 ± 0.5 | |
| Height (cm) | Girls | 149.3 ± 3.6 | 160.0 ± 5.9 | 147.3 ± 5.0 | 161.0 ± 6.6 | 149.0 ± 4.8 | 158.2 ± 5.5 | 150.0 ± 5.8 | 160.3 ± 5.4 |
| Boys | 153.8 ± 8.9 | 173.5 ± 8.6 | 153.7 ± 8.6 | 175.4 ± 6.4 | 152.5 ± 8.0 | 172.2 ± 8.1 | 152.2 ± 7.9 | 173 ± 3.0 | |
| Body mass (kg) | Girls | 37.0 ± 5.2 | 50.3 ± 11.7 | 36.0 ± 4.6 | 50.6 ± 9.8 | 36.8 ± 5.3 | 48.8 ± 6.2 | 39.6 ± 5.8 | 52.6 ± 11.1 |
| Boys | 44.7 ± 12.0 | 56.9 ± 8.5 | 43.5 ± 10.2 | 57.8 ± 6.1 | 42.7 ± 10.4 | 59.8 ± 7.7 | 42.4 ± 8.0 | 62.8 ± 8.9 | |
| MO (years) 5 | Girls | −0.35 ± 0.25 | 0.95 ± 0.69 | −0.56 ± 0.34 | 0.89 ± 0.72 | −0.57 ± 0.28 | 0.72 ± 0.77 | −0.51 ± 0.33 | 0.95 ± 0.67 |
| Boys | −1.64 ± 0.77 | 0.93 ± 0.74 | −1.72 ± 0.71 | 1.06 ± 0.69 | −1.92 ± 0.80 | 0.54 ± 0.65 | −1.99 ± 0.73 | 0.66 ± 0.31 | |
| APHV (years) 6 | Girls | 12.0 ± 0.5 | 12.0 ± 0.6 | 12.3 ± 0.6 | 11.9 ± 0.6 | 12.1 ± 0.5 | 11.9 ± 0.6 | 11.8 ± 0.6 | 12.0 ± 0.6 |
| Boys | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 13.9 ± 0.6 | 13.9 ± 0.7 | 13.6 ± 0.7 | 13.9 ± 0.8 | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 13.8 ± 0.7 | 13.2 ± 0.3 | |
| HF Test Score 7 | Girls | 164 ± 92 | 146 ± 67 | 134 ± 82 | 146 ± 75 | 113 ± 78 | 150 ± 78 | 137 ± 83 | 141 ± 71 |
| Boys | 156 ± 88 | 154 ± 99 | 157 ± 86 | 131 ± 67 | 146 ± 81 | 196 ± 84 | 147 ± 94 | 173 ± 77 | |
| DT Test Score 8 | Girls | 85 ± 49 | 118 ± 50 | 85 ± 44 | 111 ± 48 | 76 ± 47 | 110 ± 49 | 78 ± 49 | 111 ± 35 |
| Boys | 113 ± 53 | 108 ± 46 | 114 ± 50 | 113 ± 32 | 110 ± 52 | 97 ± 26 | 110 ± 47 | 135 ± 21 | |
| T Test Score | Girls | 173 ± 109 | 177 ± 69 | 178 ± 94 | 195 ± 87 | 152 ± 89 | 173 ± 84 | 140 ± 91 | 204 ± 74 |
| Boys | 180 ± 103 | 247 ± 103 | 168 ± 95 | 255 ± 49 | 165 ± 107 | 244 ± 30 | 191 ± 98 | 258 ± 116 | |
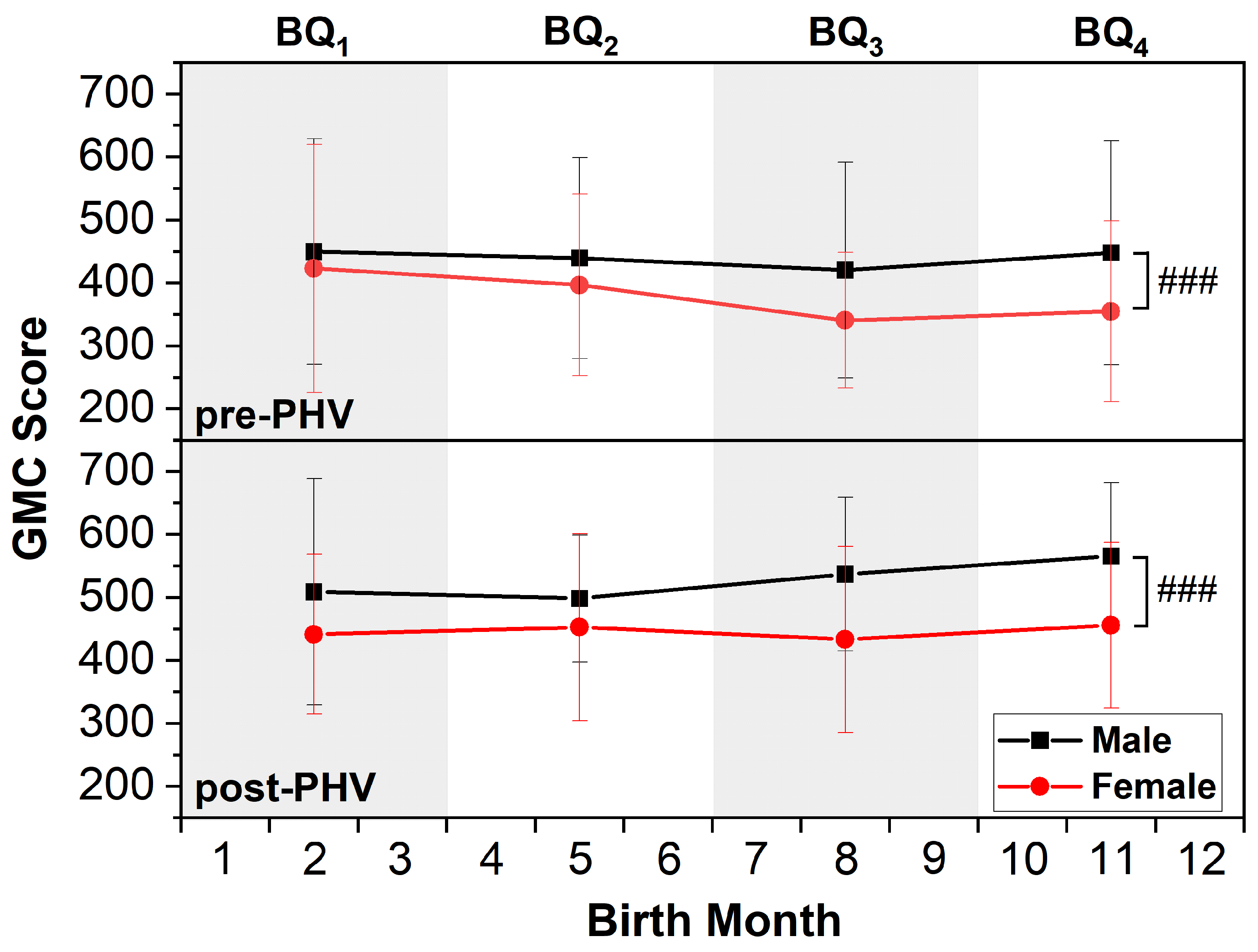
| GMC Score 9 | Girls | 423 ± 197 | 441 ± 127 | 397 ± 144 | 453 ± 148 | 341 ± 107 | 433 ± 148 | 355 ± 144 | 456 ± 132 |
| Boys | 450 ± 179 | 509 ± 179 | 439 ± 160 | 498 ± 100 | 420 ± 171 | 536 ± 122 | 448 ± 177 | 566 ± 116 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Ennequin, G.; Blazevich, A.J.; Ratel, S. Effect of Relative Age on Gross Motor Coordination Development, Considering Biological Maturity and Sex. Children 2025, 12, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050619
Zhang X, Ennequin G, Blazevich AJ, Ratel S. Effect of Relative Age on Gross Motor Coordination Development, Considering Biological Maturity and Sex. Children. 2025; 12(5):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050619
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoyu, Gaël Ennequin, Anthony J. Blazevich, and Sébastien Ratel. 2025. "Effect of Relative Age on Gross Motor Coordination Development, Considering Biological Maturity and Sex" Children 12, no. 5: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050619
APA StyleZhang, X., Ennequin, G., Blazevich, A. J., & Ratel, S. (2025). Effect of Relative Age on Gross Motor Coordination Development, Considering Biological Maturity and Sex. Children, 12(5), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050619







