Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease: Mind the Gap Between Reality and Expectations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
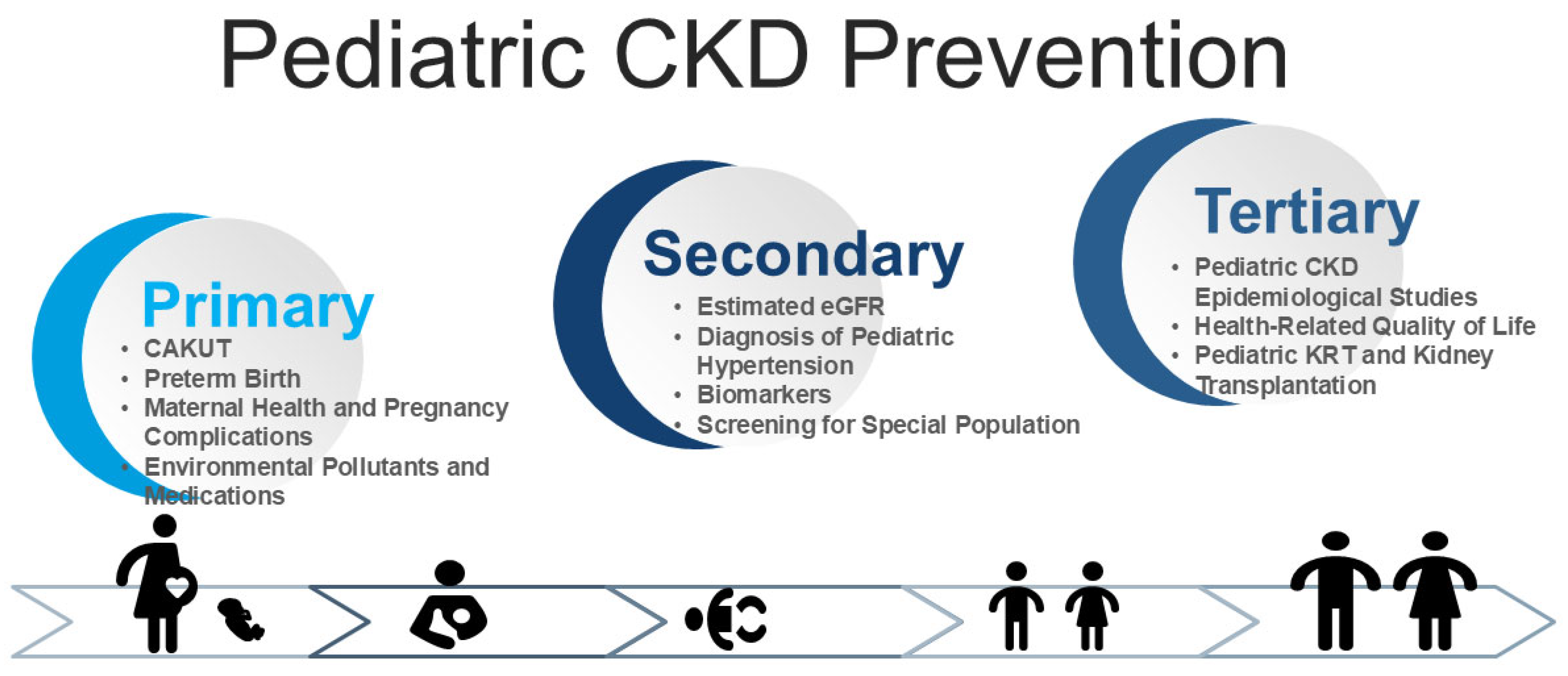
3. Challenges in Primary Prevention
3.1. CAKUT
3.2. Preterm Birth
3.3. Maternal Health and Pregnancy Complications
3.4. Environmental Pollutants and Medications
4. Challenges in Secondary Prevention
4.1. Estimated GFR
4.2. Diagnosis of Pediatric Hypertension
4.3. Biomarkers
4.4. Screening for Special Population
5. Challenges in Tertiary Prevention
5.1. Pediatric CKD Epidemiological Studies
5.2. Health-Related Quality of Life
5.3. Pediatric KRT and Kidney Transplantation
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jager, K.J.; Kovesdy, C.; Langham, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Jha, V.; Zoccali, C. A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1803–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; Pletcher, M.A.; Smith, A.E.; Tang, K.; Yuan, C.W.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelfinger, J.R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Schaefer, F.; World Kidney Day Steering Committee. World Kidney Day 2016: Averting the legacy of kidney disease-focus on childhood. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Developmental Origins of Chronic Kidney Disease: Should We Focus on Early Life? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Eriksson, J.G.; Forsén, T.; Osmond, C. Fetal origins of adult disease: Strength of effects and biological basis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 31, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Buklijas, T. A Conceptual Framework for the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2010, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Garcia Sanchez, J.J.; Carrero, J.J.; Kumar, S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Nolan, S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Chen, H.; Kanda, E.; et al. Low Adherence to Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes 2012 CKD Clinical Practice Guidelines Despite Clear Evidence of Utility. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, B.; Muenz, D.; Tu, C.; Speyer, E.; Alencar de Pinho, N.; Combe, C.; Yamagata, K.; Reichel, H.; Fliser, D.; Massy, Z.A.; et al. Adherence to the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes CKD Guideline in Nephrology Practice Across Countries. Kidney Int Rep. 2020, 6, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L. Advocacy for DOHaD research optimizing child kidney health. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2024, 66, S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.K.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Lui, S.F.; Andreoli, S.; Fung, W.W.; Hradsky, A.; Kumaraswami, L.; Liakopoulos, V.; Rakhimova, Z.; Saadi, G.; et al. Kidney health for everyone everywhere-from prevention to detection and equitable access to care. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassalotti, J.A.; Francis, A.; Soares Dos Santos, A.C., Jr.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Abdellatif, D.; Hsiao, L.L.; Roumeliotis, S.; Haris, A.; Kumaraswami, L.A.; Lui, S.F.; et al. Are your kidneys Ok? Detect early to protect kidney health. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waith, F.M.; Bresolin, N.L.; Antwi, S. Detect early, protect kidney health: World Kidney Day 2025. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2025, 40, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.T.; Su, G.; Zhang, L.; Qin, X.; Marshall, S.; González-Ortiz, A.; Clase, C.M.; Campbell, K.L.; Xu, H.; Carrero, J.J. Modifiable Lifestyle Factors for Primary Prevention of CKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Allen, N.B.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Black, T.; Brewer, L.C.; Foraker, R.E.; Grandner, M.A.; Lavretsky, H.; Perak, A.M.; Sharma, G.; et al. Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct of Cardiovascular Health: A Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 146, e18–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.L. Evolution, kidney development, and chronic kidney disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 91, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, C.; Sundquist, J.; Winkleby, M.A.; Sundquist, K. Preterm birth and risk of chronic kidney disease from childhood into mid-adulthood: National cohort study. BMJ 2019, 365, l1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Adverse Impact of Environmental Chemicals on Developmental Origins of Kidney Disease and Hypertension. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 745716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugapoopathy, V.; Gupta, I.R. A primer on congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tracts (CAKUT). Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, S.A.; Sargent, P.H.; Howard, C.V.; Chan, Y.F.; van Velzen, D. Human intrauterine renal growth expressed in absolute number of glomeruli assessed by the disector method and Cavalieri principle. Lab. Investig. 1991, 64, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Luh, H.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsu, C.N. Incidence and risks of congenital anomalies of kidney and urinary tract in newborns: A population-based case-control study in Taiwan. Medicine 2016, 95, e2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, G.; Tsuboi, N.; Shimizu, A.; Yokoo, T. Human nephron number, hypertension, and renal pathology. Anat. Rec. 2020, 303, 2537–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeman, S.C.; Cullen-McEwen, L.A.; Puelles, G.; Zhang, M.; Wu, T.; Baldelomar, E.J.; Dowling, J.; Charlton, J.R.; Forbes, M.S.; Ng, A.; et al. MRI-based glomerular morphology and pathology in whole human kidneys. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F1381–F1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelomar, E.J.; Charlton, J.R.; Beeman, S.C.; Bennett, K.M. Measuring rat kidney glomerular number and size in vivo with MRI. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 314, F399–F406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, W.A. Age terminology during the perinatal period. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Keijzer-Veen, M.G.; Schrevel, M.; Finken, M.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Nauta, J.; Hille, E.T.; Frölich, M.; van der Heijden, B.J. Dutch POPS19 Collaborative Study Group. Microalbuminuria and lower glomerular filtration rate at young adult age in subjects born very premature and after intrauterine growth retardation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2762–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwinta, P.; Klimek, M.; Drozdz, D.; Grudzień, A.; Jagła, M.; Zasada, M.; Pietrzyk, J.J. Assessment of long-term renal complications in extremely low birth weight children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, K.; Klimek, M.; Grudzień, A.; Jagła, M.; Kwinta, P. Longitudinal assessment of renal size and function in extremely low birth weight children at 7 and 11 years of age. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, A.; Abe, Y.; Koike, D.; Hirade, T.; Nariai, A.; Ito, T.; Katou, F. Long-term renal follow up of preterm neonates born before 35 weeks of gestation. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A.M.; Nixon, P.A.; Chappell, M.C.; Diz, D.I.; Russell, G.B.; Jensen, E.T.; Shaltout, H.A.; O’Shea, T.M.; Washburn, L.K. Renal function and blood pressure are altered in adolescents born preterm. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Preterm Birth and Kidney Health: From the Womb to the Rest of Life. Children 2024, 11, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.P.; Al-Hasan, Y. Impact of oxidative stress in fetal programming. J. Pregnancy 2012, 2012, 582748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisiadis, V.G.; Matthews, S.G. Glucocorticoids and fetal programming part 2: Mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, V.; Lacquaniti, A.; Tripodi, F.; Conti, G.; Marseglia, L.; Monardo, P.; Gitto, E.; Chimenz, R. Acute Kidney Injury in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Risk Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Pei, J.; Jiang, X.; Tang, J. Acute kidney injury in premature and low birth weight neonates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, A.D.; Griffin, R.L.; Vincent, K.; Askenazi, D.J.; Segar, J.L.; Kupferman, J.C.; Rastogi, S.; Selewski, D.T.; Steflik, H.J. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes Associated with Recurrent Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury in the AWAKEN Study. JAMA 2024, 7, e2355307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muk, T.; Jiang, P.P.; Stensballe, A.; Skovgaard, K.; Sangild, P.T.; Nguyen, D.N. Prenatal Endotoxin Exposure Induces Fetal and Neonatal Renal Inflammation via Innate and Th1 Immune Activation in Preterm Pigs. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 565484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, J.W.; Groeneveld, A.B.; Slutsky, A.S.; Plötz, F.B. Mechanical ventilation and acute renal failure. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H.J.; Thomas, B.; Van Wyk, B.; Tierney, S.B.; Selewski, D.T.; Jetton, J.G. Nephrotoxic medications and acute kidney injury risk factors in the neonatal intensive care unit: Clinical challenges for neonatologists and nephrologists. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.H.; Abdi, H.H.; Magers, J.; Prusakov, P.; Slaughter, J.L. Nephrotoxic medications and associated acute kidney injury in hospitalized neonates. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, M.B.; Gruneir, A.; Rochon, P.A.; Howard, A.W.; Koren, G.; Parshuram, C.S. Identifying high-risk medications associated with acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: A pharmacoepidemiologic evaluation. Paediatr. Drugs 2017, 19, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, G.; Farrent, S.; Gilroy, M.; Page, D.; Oliver, C.J.; Richmond, F.; Cormack, B.E. Variation in neonatal nutrition practice and implications: A survey of Australia and New Zealand neonatal units. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.N.; Barker, D.J. The thrifty phenotype hypothesis. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 60, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfarani, S.; Germani, D.; Branca, F. Low birthweight and adult insulin resistance: The “catch-up growth” hypothesis. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal. 1999, 81, F71–F73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embleton, N.D.; Korada, M.; Wood, C.L.; Pearce, M.S.; Swamy, R.; Cheetham, T.D. Catch-Up growth and metabolic outcomes in adolescents born preterm. Arch. Dis. Child. 2016, 101, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauzzo, C.; Chiavaroli, V.; Di Valerio, S.; Chiarelli, F. Birth size, growth trajectory and later cardio-metabolic risk. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1187261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tian, J.; Jose, M.D.; Dwyer, T.; Venn, A.J. BMI Trajectories from Childhood to Midlife are Associated with Subclinical Kidney Damage in Midlife. Obesity 2021, 29, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumele, C.E.; RAngaswami, J.; Chow, S.L.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Mathew, R.O.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; et al. Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health: A Presidential Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1606–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S.A.; Padda, I.; Johal, G. Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) syndrome: A state-of-the-art review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladunewich, M.A. Chronic Kidney Disease and Pregnancy. Semin. Nephrol. 2017, 37, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khalaf, S.; Bodunde, E.; Maher, G.M.; O’Reilly, É.J.; McCarthy, F.P.; O’Shaughnessy, M.M.; O’Neill, S.M.; Khashan, A.S. Chronic kidney disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 656–670.e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraman, D.; Walters, B.; Bramham, K.; Fish, R.; Lambie, M.; Wu, P. Adverse pregnancy outcomes in pregnant women with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2024, 131, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiles, K.; Chappell, L.; Clark, K.; Elman, L.; Hall, M.; Lightstone, L.; Mohamed, G.; Mukherjee, D.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Webster, P.; et al. Clinical practice guideline on pregnancy and renal disease. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attini, R.; Cabiddu, G.; Ciabatti, F.; Montersino, B.; Carosso, A.R.; Gernone, G.; Gammaro, L.; Moroni, G.; Torreggiani, M.; Masturzo, B.; et al. Chronic kidney disease, female infertility, and medically assisted reproduction: A best practice position statement by the Kidney and Pregnancy Group of the Italian Society of Nephrology. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Stracke, S.; Schneider, U.; Kuschel, B.; Feldkamp, T.; Habbig, S.; Mayer-Pickel, K.; Hartung, A.; Bader, B.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease and Pregnancy. Guideline of the DGGG, OEGGG, DGfN (S2k Level, AWMF Registry No. 015-090). Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2022, 82, 795–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lee, W.C.; Hsu, C.N.; Lee, W.C.; Huang, L.T.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, C.Y. Asymmetric dimethylarginine is associated with developmental programming of adult kidney disease and hypertension in offspring of streptozotocin-treated mothers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, Y.J.; Tsai, C.C. N-Acetylcysteine prevents programmed hypertension in male rat offspring born to suramin-treated mothers. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 95, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, G.D.; Walton, S.L.; Gazzard, S.E.; van der Wolde, J.; Mathias, P.C.F.; Moritz, K.M.; Cullen-McEwen, L.A.; Bertram, J.F. Maternal hypoxia developmentally programs low podocyte endowment in male, but not female offspring. Anat. Rec. 2020, 303, 2668–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlet-Bénichou, C.; Gilbert, T.; Muffat-Joly, M.; Lelièvre-Pégorier, M.; Leroy, B. Intrauterine growth retardation leads to a permanent nephron deficit in the rat. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1994, 8, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Q.; Zhang, H.G.; Yuan, Z.B.; Yang, D.L.; Hao, L.Y.; Li, X.H. Prenatal exposure to lipopolysaccharide alters the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system and renal damage in offspring rats. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.G.; Morgenstern, H.; Bennett, P.H. Intrauterine diabetes exposure and the risk of renal disease in diabetic Pima Indians. Diabetes 1998, 47, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.; Kandasamy, Y.; Rudd, D.M.; Schneider, M.E.; Jones, R.E.; Watson, D.L. The effect of diabetes during pregnancy on fetal renal parenchymal growth. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macumber, I.; Schwartz, S.; Leca, N. Maternal obesity is associated with congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract in offspring. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 32, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Slotkin, T. Cholinergic systems in brain development and disruption by neurotoxicants: Nicotine, environmental tobacco smoke, organophosphates. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-Costa, L.; Schaefer, F.; Afonso, A.C.; Correia, S.; Guimarães, J.T.; Guerra, A.; Barros, H.; Azevedo, A. Prenatal alcohol exposure affects renal function in overweight schoolchildren: Birth cohort analysis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 35, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; McIntyre, H.D.; Alati, R.; Al Mamun, A. Maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy and its association with offspring renal function at 30 years: Observation from a birth cohort study. Nephrology 2017, 24, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.P.; Denton, K.; Cullen-McEwen, L.; Bertram, J.; Moritz, K.M. Prenatal exposure to alcohol reduces nephron number and raises blood pressure in progeny. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, D.B.; Mesquita, F.F.; De Lima, I.P.; Boer, P.A.; Gontijo, J.A. Fetal kidney programming by maternal smoking exposure: Effects on kidney structure, blood pressure and urinary sodium excretion in adult offspring. Nephron 2015, 129, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taal, H.R.; Geelhoed, J.J.M.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Hofman, A.; Moll, H.A.; Lequin, M.; Van Der Heijden, A.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.V. Maternal smoking during pregnancy and kidney volume in the offspring: The generation R study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.D.; Bazzano, L.A.; Xie, D.; Cohan, J.; Dolata, J.; Fink, J.C.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Jamerson, K.; Lash, J.; Makos, G.; et al. Self-reported tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drug use and progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. The First Thousand Days: Kidney Health and Beyond. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder, M.F.; Bueters, R.R.; Huigen, M.C.; Russel, F.G.; Masereeuw, R.; van den Heuvel, L.P. Effect of drugs on renal development. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Song, L.; Wei, J.; Chen, T.; Chen, J.; Lin, Y.; Xia, W.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Maternal exposure to di-(2ethylhexyl)phthalate alters kidney development through the renin-angiotensin system in offspring. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal exposure to bisphenol A combined with high-fat diet-induced programmed hypertension in adult male rat offspring: Effects of resveratrol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, Y.J.; Lu, P.C.; Tain, Y.L. Maternal resveratrol therapy protects male rat offspring against programmed hypertension induced by TCDD and dexamethasone exposures: Is it relevant to aryl hydrocarbon receptor? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.J.; Jiang, Q.H.; Bei, X.Y.; Sun, W.L.; Xia, S.J.; Jiang, J.T. Maternal exposure to di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) induces renal fibrosis in adult rat offspring. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31101–31111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Li, L.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, C.N. Gestational Exposure to Maternal Systemic Glucocorticoids and Childhood Risk of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2024, 84, 215–223.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, L.A.; Quan, A.; Weinberg, A.; Baum, M. Effect of prenatal dexamethasone on rat renal development. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Li, L.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Chen, C.J.; Hsu, C.N. Gestational Exposure to Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease in Childhood. JAMA Pediatr. 2025, 179, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.C.; Wang, H.; Ang, Y.G.; Lim, C.K.; Ooi, X.Y. Cost-effectiveness of screening for chronic kidney disease in the general adult population: A systematic review. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 17, sfad137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, K.; Iseki, K.; Nitta, K.; Imai, H.; Iino, Y.; Matsuo, S.; Makino, H.; Hishida, A. Chronic kidney disease perspectives in Japan and the importance of urinalysis screening. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2008, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Sheng, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chou, P. Mass urinary screening and follow-up for school children in Taiwan Province. Acta Paediatr. Taiwan 2001, 42, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yap, H.K.; Quek, C.M.; Shen, Q.; Joshi, V.; Chia, K.S. Role of urinary screening programmes in children in the prevention of chronic kidney disease. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2005, 34, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, R.J. Screening for CKD in children: A global controversy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar, D.L.; Wang, L.; Hollenbeak, C.S.; Widome, M.D.; Paul, I.M. A cost-effectiveness analysis of screening urine dipsticks in well-child care. Pediatrics 2010, 125, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htay, H.; Alrukhaimi, M.; Ashuntantang, G.E.; Bello, A.K.; Bellorin-Font, E.; Gharbi, M.B.; Braam, B.; Feehally, J.; Harris, D.C.; Jha, V.; et al. Global access of patients with kidney disease to health technologies and medications: Findings from the Global Kidney Health Atlas project. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2018, 8, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottel, H.; Schwartz, G.J. Measuring and estimating the GFR in children: State of the art in 2025. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Haycock, G.B.; Edelmann, C.M.; Spitzer, M. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 1976, 58, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Muñoz, A.; Schneider, M.F.; Mak, R.H.; Kaskel, F.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.L. New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottel, H.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Zaman, Z.; Martens, F. On the relationship between glomerular filtration rate and serum creatinine in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2010, 25, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottel, H.; Hoste, L.; Martens, F. A simple height-independent equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012, 27, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottel, H.; Björk, J.; Bökenkamp, A.; Berg, U.; Åsling-Monemi, K.; Selistre, L.; Dubourg, L.; Hansson, M.; Littmann, K.; Jones, I.; et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate at the transition from pediatric to adult care. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottel, H.; Björk, J.; Courbebaisse, M.; Couzi, L.; Ebert, N.; Eriksen, B.O.; Dalton, R.N.; Dubourg, L.; Gaillard, F.; Garrouste, C.; et al. Development and validation of a modified full age spectrum creatinine-based equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate: A cross-sectional analysis of pooled data. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, J.M. Evidence Gaps in the Identification and Treatment of Hypertension in Children. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallibois, C.M.; Jawa, N.A.; Noone, D.G. Hypertension in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease: Management challenges. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2017, 10, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Zapata, P.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Burckart, G.; Daniels, S.R.; Flynn, J.T.; Giacoia, G.; Green, D.; Kelly, A.S.; Khurana, M.; Li, J.S.; et al. Research Gaps in Primary Pediatric Hypertension. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20183517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hirth, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabi, D.M.; McBrien, K.A.; Sapir-Pichhadze, R.; Nakhla, M.; Ahmed, S.B.; Dumanski, S.M.; Butalia, S.; Leung, A.A.; Harris, K.C.; Cloutier, L.; et al. Hypertension Canada’s 2020 Comprehensive Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, Risk Assessment, and Treatment of Hypertension in Adults and Children. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 596–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Committee for Guideline Revision. 2018 Chinese Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension-A report of the Revision Committee of Chinese Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 182–241. [Google Scholar]
- Umemura, S.; Arima, H.; Arima, S.; Asayama, K.; Dohi, Y.; Hirooka, Y.; Horio, T.; Hoshide, S.; Ikeda, S.; Ishimitsu, T.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2019). Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 1235–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.C.; Flynn, J.T. Blood pressure in children with chronic kidney disease: Lessons learned from the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children Cohort Study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Smith, C.M.; Flynn, J.T. 2023 European Pediatric Hypertension Guidelines: Has anything changed? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, N.; Shatat, I.F. Antihypertensive agents: A long way to safe drug prescribing in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 2049–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.R.; Parikh, C.R. Biomarkers of Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lousa, I.; Reis, F.; Beirão, I.; Alves, R.; Belo, L.; Santos-Silva, A. New Potential Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Management—A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.H.; Kakajiwala, A.; Parikh, C.R.; Furth, S. Emerging biomarkers of chronic kidney disease in children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandokji, I.; Greenberg, J.H. Plasma and Urine Biomarkers of CKD: A Review of Findings in the CKiD Study. Semin. Nephrol. 2021, 41, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) in Pediatric Renal Diseases: From Pathophysiological Phenomenon to Clinical Biomarker and Beyond. Children 2021, 8, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.H.; Dalla Gassa, A.; Mayer, G.; Zaza, G.; Brophy, P.D.; Gesualdo, L.; Pesce, F. The nephrologist of tomorrow: Towards a kidney-omic future. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuttke, M.; Wong, C.S.; Wuhl, E.; Epting, D.; Luo, L.; Hoppmann, A.; Doyon, A.; Li, Y.; Consortium, C.K.; Sozeri, B.; et al. Genetic loci associated with renal function measures and chronic kidney disease in children: The Pediatric Investigation for Genetic Factors Linked with Renal Progression Consortium. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.L.; Tain, Y.L.; Chen, H.E.; Hsu, C.N. Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease: Impact of Apolipoprotein C-II and Apolipoprotein C-III. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 706323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.T.; Chen, W.L.; Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Complement Factor H and Related Proteins as Markers of Cardiovascular Risk in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Liao, W.T.; Chen, W.L.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Tain, Y.L. Plasma and Urinary Platelet Factor 4 as Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Risk in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, E.R.; Lin, D.C.; Langman, C.B.; Thompson, J.W.; John-Williams, L.S.; Furth, S.L.; Warady, B.; Haymond, S. Metabolomic Patterns in Adolescents with Mild to Moderate CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheiss, U.T.; Sekula, P. The Promise of Metabolomics in Decelerating CKD Progression in Children. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Lin, S.; Hou, C.; Lu, P.C.; Tain, Y.L. Association of trimethylamine, trimethylamine N-oxide, and dimethylamine with cardiovascular risk in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, J.H.; Nashwan, A.J. Cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome: Understanding the interconnections and the need for holistic intervention. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2023, 1, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ostrominski, J.W.; Vaduganathan, M. Prevalence of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome Stages in US Adults, 2011–2020. JAMA 2024, 331, 1858–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, F.J.; Elder, J.S. CKD and bladder problems in children. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, R.L. Congenital urinary tract obstruction: The long view. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015, 22, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, R.; Hamasaki, Y.; Okuda, Y.; Hamada, R.; Ishikura, K. Epidemiology of pediatric chronic kidney disease/kidney failure: Learning from registries and cohort studies. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.J.; Moxey-Mims, M.; Jerry-Fluker, J.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.L. CKiD (CKD in children) prospective cohort study: A review of current findings. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfeld, U.; Anarat, A.; Bayazit, A.K.; Bakkaloglu, A.S.; Bilginer, Y.; Caliskan, S.; Civilibal, M.; Doyon, A.; Duzova, A.; Kracht, D.; et al. 4C Study Group. The cardiovascular comorbidity in children with chronic kidney disease (4C) study: Objectives, design, and methodology. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruidiaz-Gómez, K.S.; Higuita-Gutiérrez, L.F. Impact of chronic kidney disease on health-related quality of life in the pediatric population: Meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, A.C.; Wentz, A.; Abraham, A.G.; Mendley, S.R.; Hooper, S.R.; Butler, R.W.; Gipson, D.S.; Lande, M.B.; Shinnar, S.; Moxey-Mims, M.M.; et al. Health-related quality of life of children with mild to moderate chronic kidney disease. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e349–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lu, P.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, C.N. Differences in health-related quality of life in children with chronic kidney disease as reported by children and parent proxies. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Lin, H.W.; Pickard, A.S.; Tain, Y.L. EQ-5D-Y for the assessment of health-related quality of life among Taiwanese youth with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2018, 30, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L.; Lu, P.C.; Lin, H.W. Comparisons of EQ-5D-Y and PedsQL in pediatric patients with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease in longitudinal analyses. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2023, 21, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, L.; Schaefer, F.; Schmitt, C.P.; Shroff, R.; Warady, B.A. Chronic dialysis in children and adolescents: Challenges and outcomes. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2017, 1, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosa, M.R.; Kidd, M. The dangers of rationing dialysis treatment: The dilemma facing a developing country. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, L.; Bootsma-Robroeks, C.; Cornelissen, E.; de Wall, L.; Feitz, W. Pearls and Pitfalls in Pediatric Kidney Transplantation After 5 Decades. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 856630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzi, L.; Amore, A.; Coppo, R. Challenges in pediatric renal transplantation. World J. Transplant. 2014, 4, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.A.; Zafar, M.N.; Lanewala, A.A.; Naqvi, S.A. Challenges in pediatric renal transplantation in developing countries. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2009, 14, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Prevention |
| Long-Term Prospective Studies on CAKUT |
| Non-Invasive Methods for Nephron Number Assessment |
| High-Quality, Long-Term Studies on Preterm Birth and Kidney Outcomes |
| Inconsistencies in Nutritional Guidelines for Preterm Infants |
| Research on Maternal Health and Offspring Kidney Outcomes |
| Impact of Substance Abuse on Kidney Health |
| Research on Environmental Pollutants and Kidney Health |
| Screening and Prevention for Maternal Medication on Offspring CKD Risks |
| Secondary Prevention |
| Inadequate Pediatric-Specific eGFR Equations |
| Lack of Standardized International Definition for Pediatric Hypertension |
| Limited Global Use and Accessibility of 24-Hour ABPM |
| Limited Data on Pediatric Hypertension Treatment Goals |
| Need for Prospective Trials on BP Management in Children with CKD |
| Limited Research on Pediatric-Specific Biomarkers for CKD |
| Insufficient Screening for Preterm Infants at Risk of CKD |
| Lack of Early Screening and Intervention for CKMS in Children |
| Tertiary Prevention |
| Limited International and Long-term Pediatric CKD Cohort Data |
| No Consensus on Preferred HRQOL Assessment Tools |
| Inadequate Resources and Trained Personnel for Pediatric Dialysis in Some Regions |
| Technical Challenges in Dialysis for Neonates and Small Children |
| Lack of Consensus on Optimal Timing for Pediatric Kidney Transplantation |
| Insufficient Research on Risks Associated with Pediatric Kidney Transplantation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-N.; Lu, P.-C.; Liao, W.-T.; Tain, Y.-L. Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease: Mind the Gap Between Reality and Expectations. Children 2025, 12, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050614
Hsu C-N, Lu P-C, Liao W-T, Tain Y-L. Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease: Mind the Gap Between Reality and Expectations. Children. 2025; 12(5):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050614
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chien-Ning, Pei-Chen Lu, Wei-Ting Liao, and You-Lin Tain. 2025. "Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease: Mind the Gap Between Reality and Expectations" Children 12, no. 5: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050614
APA StyleHsu, C.-N., Lu, P.-C., Liao, W.-T., & Tain, Y.-L. (2025). Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease: Mind the Gap Between Reality and Expectations. Children, 12(5), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12050614







