Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscesses in Children: A Report of Eight Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNSIs | Deep neck space infections |
| MR | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| US | Ultrasound |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| CBC | Complete blood count |
References
- Kavanagh, K.R.; Valdez, T.A. Deep Neck Space Infections in Children: Has Anything Changed? Int. J. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 7, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, F.; Allen, S.M.; Stocks, R.M.S.; Thompson, J.W. Deep Neck Infection. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 41, 459–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, B.W.; Ryndin, S.; Mullen, K.M. Infections of Deep Neck Spaces. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2020, 41, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.; Bateman, N. Controversies in the Management of Deep Neck Space Infection in Children: An Evidence-Based Review. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2017, 42, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delides, A.; Manoli, E.; Papadopoulos, M.; Nikolopoulos, T. Ultrasound-Guided Transoral Drainage of a Paediatric Parapharyngeal Abscess. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2014, 128, 1120–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Lee, T.-J.; Chen, C.-W. Transnasal Endoscopic Approach for Drainage of Pediatric Parapharyngeal Space Abscess. Otolaryngol.–Head Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdim, İ.; Aksakal, C.; Sapmaz, E.; Gökçe, E. Bilateral Parapharyngeal Abscess Complicated with Trismus, Airway Obstruction and Bleeding. Turk. J. Ear Nose Throat 2022, 32, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georget, E.; Gauthier, A.; Brugel, L.; Verlhac, S.; Remus, N.; Epaud, R.; Madhi, F. Acute Cervical Lymphadenitis and Infections of the Retropharyngeal and Parapharyngeal Spaces in Children. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Lee, H.H.; Eun, Y.-G.; Lee, Y.C. Seasonality and Association with Climate Factors of Peritonsillar, Retropharyngeal, and Parapharyngeal Abscesses in Korea. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Khan, S.; Abbas, A.; Pasha, H.A.; Abbas, Q.; Siddiqui, N.U.R. Life-Threatening Complication of Retropharyngeal Abscess in an Infant: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2023, 17, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, T.M.; Chevalier, I.; Gauthier, M.; Carceller, A.M.; Bensoussan, A.; Tapiero, B. Acute Adenitis in Children: Clinical Course and Factors Predictive of Surgical Drainage. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2005, 41, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciello, F.; Crosetti, E.; Di Lisi, D.; Succo, G. Parapharyngeal Abscess Two Years After Elective Tonsillectomy. J. Med. Cases 2014, 5, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chowdhury, N.H.; Islam, M.A.; Mohammad, T.; Khan, S.R. Surgical Approach to Evaluate Neck Mass in Children Concerning Management Protocols. Magna Sci. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 8, 084–091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, J.; Velhonoja, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Happonen, T.; Nyman, M.; Irjala, H.; Soukka, T.; Mattila, K.; Hirvonen, J. Emergency Neck MRI: Feasibility and Diagnostic Accuracy in Cases of Neck Infection. Acta Radiol. 2020, 62, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Adam, S.; Goussard, P.; Venkatakrishna, S.S.B.; Andronikou, S.; Grobbelaar, J. Retropharyngeal Abscess Complicated by Mediastinitis in Infants. Respiration 2024, 103, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkinen, J.; Nurminen, J.; Velhonoja, J.; Irjala, H.; Happonen, T.; Soukka, T.; Mattila, K.; Hirvonen, J. Clinical and Prognostic Significance of Emergency MRI Findings in Neck Infections. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Happonen, T.; Nyman, M.; Sirén, A.; Vierula, J.-P.; Velhonoja, J.; Irjala, H.; Soukka, T.; Ivaska, L.; et al. Pictorial Review of MRI Findings in Acute Neck Infections in Children. Children 2023, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athirah, A.; Saniasiaya, J.; Hui, J.L.P.; Abidin, Z.A.Z. Traumatic Dental Extraction with Severe Complications. Pediatr. Med. Rodz. 2020, 16, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, S.; Baş, B.; Özden, B.; Selçuk, Ü.; Çengel Kurnaz, S. Deep Neck Infection after Third Molar Extraction. J. Istanb. Univ. Fac. Dent. 2015, 49, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulino, J.M.; Kirsch, C.F.E.; Burns, J.; Busse, P.M.; Chakraborty, S.; Choudhri, A.F.; Conley, D.B.; Jones, C.U.; Lee, R.K.; Luttrull, M.D.; et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria: Neck Mass-Adenopathy. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2019, 16, S150–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

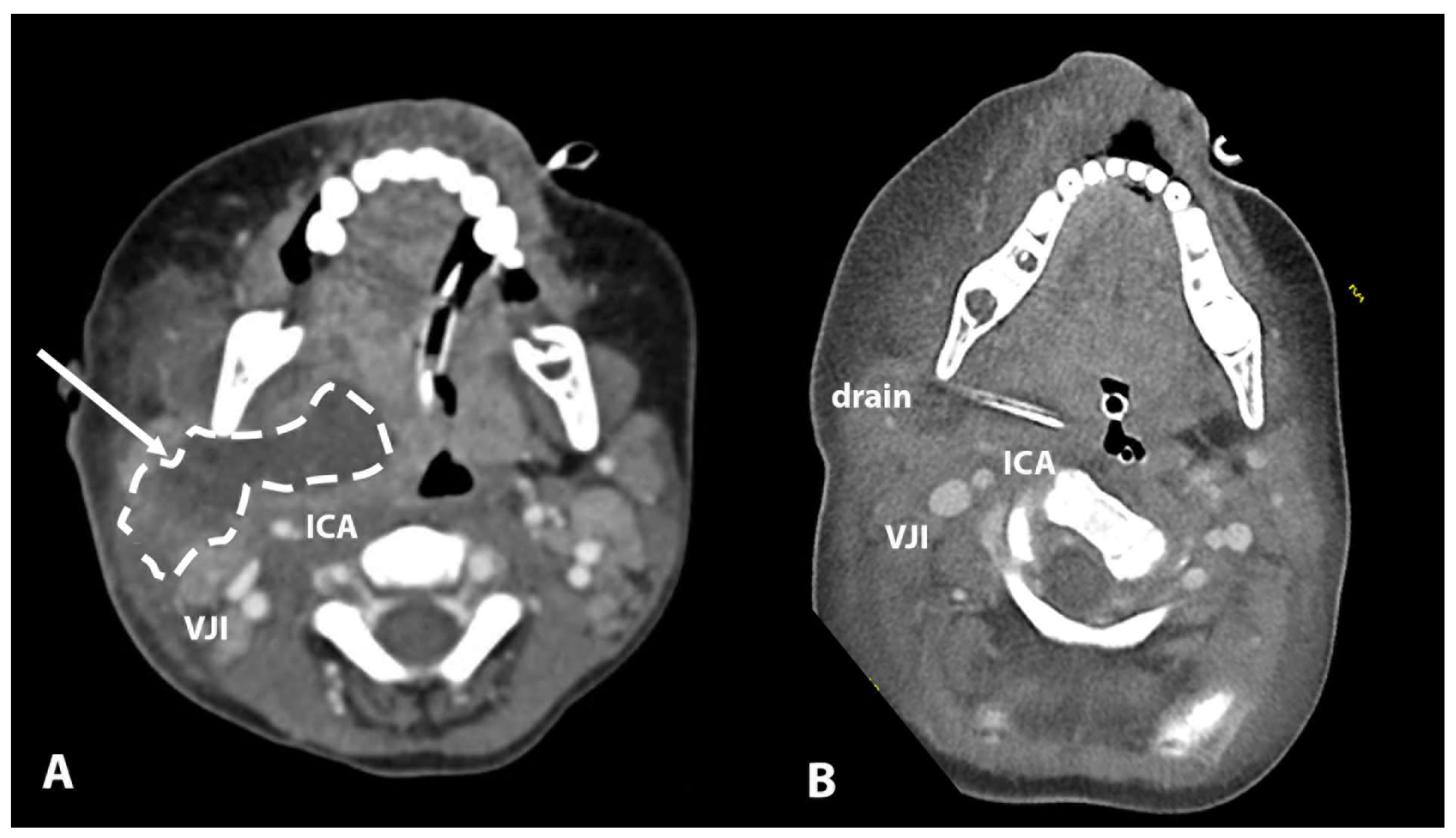
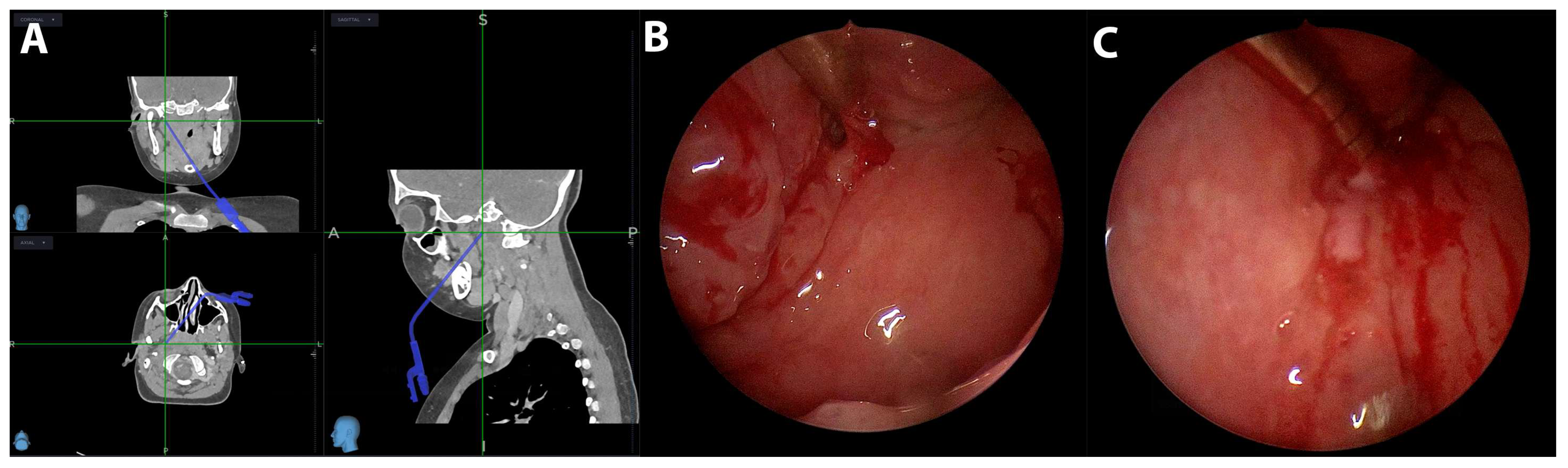
| Patient | Age | Abscess Location | Antibiotic at Admission | Symptom Duration (days) | Presentation at Admission | Primary and Ancillary Diagnostic Procedure | Relation to Vascular Space | Airway Obstruction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 years | Retropharyngeal | Clindamycin | 5 | Edema of the retropharyngeal space, high fever, regional lymphadenitis, stiff neck | US, CT, MRI | Medial | No |
| 2 | 7 years | Parapharyngeal | Flucloxacillin | 4 | High fever, lymphadenitis, torticollis | US, MRI | Medial | No |
| 3 | 6 years | Parapharyngeal | None | 5 | High fever, neck swelling, torticollis | US, CT | Medial | No |
| 4 | 9 months | Retropharyngeal | None | 4 | High fewer, swelling neck, torticollis | US, MRI | Medial | No |
| 5 | 18 months | Retropharyngeal | None | 4 | High fever, stiff neck, torticollis | US, MRI | Medial | No |
| 6 | 3 years | Parapharyngeal | Flucloxacillin | 4 | High fever, neck swelling | US, CT | Lateral | Yes |
| 7 | 7 years | Parapharyngeal | None | 4 | High fever, neck swelling | US | Lateral | No |
| 8 | 10 years | Retropharyngeal | None | 2 | High fever, torticollis | CT | Medial | No |
| Patient | Age (years) | Abscess Location | US | CT | MR | Airway Management During Imaging | Relation to Vascular Space | Conclusive Imaging Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 years | Retropharyngeal | Enlarged lymph nodes in level II, no vascular involvement, no pathology visible that could explain symptoms | Retropharyngeal collection 50 × 6 × 18, medial to ICA, C2-C6 | Retropharyngeal collection 25 × 6 × 40, medial to ICA, location oropharynx | Awake | Medial | CT, MRI |
| 2 | 7 years | Parapharyngeal | Enlarged lymph nodes in level II, no vascular involvement, no pathology visible that could explain symptoms | / | Parapharyngeal collection 27 × 22 × 35, anterior and medial to ICA | Awake | Medial | MRI |
| 3 | 6 years | Parapharyngeal | Enlarged lymph nodes in level II, no vascular involvement, no pathology visible that could explain symptoms | Parapharyngeal collection, medial to ICA, nasopharynx, below ICA canal, 18 × 15 × 12 | / | Awake | Medial | CT |
| 4 | 9 months | Retropharyngeal | Enlarged lymph nodes in level II, no vascular involvement, no pathology visible that could explain symptoms | / | Retropharyngeal inflammatory tissue 27 × 15 × 45 mm, medial to ICA with suspected central necrosis 11 × 6 × 27 mm | Sedation | Medial | MRI |
| 5 | 1.5 years | Retropharyngeal | Enlarged lymph node level II at 35 mm, 20 mm (4 mL) of pus collection in retropharyngeal space, consistent with MR findings | / | Retropharyngeal collection 18 × 20 × 18 mm, medial to ICA, reaching up to clivus | Sedation | Medial | MRI |
| 6 | 3 years | Parapharyngeal | Conglomerate of enlarged level II lymph nodes, area of collection in level II lateral to ICA | Major parapharyngeal collection 53 × 25 × 45, lateral and anterior to ICA | / | Intubation | Lateral | CT |
| 7 | 7 years | Retropharyngeal | Enlarged lymph nodes level II (22 × 10, 20 × 8,10 × 10), no colliquation, vessels OK | Edema of the retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal space, hypodense area 16 × 11 medial to the ICA suspected of abscess | MRI not performed | Awake | Lateral | CT |
| 8 | 10 years | Retropharyngeal | Enlarged level II lymph nodes, no vascular involvement, no pathology visible that could explain symptoms | 28 × 11 × 11 mm retropharyngeal abscess medial to ICA and IJV | / | Awake | Medial | CT |
| Patient | Age | Abscess Location | Relation to Vascular Space | Airway Management After Therapy | Treatment | Image Guidance | Microbiology | Antibiotic Inpatient | Intubation Duration (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 years | Retropharyngeal | Medial | Intubation | Transpharyngeal incision | - | S. intermedius, Achromobacter sp. | Clindamycin, Gentamycin, Ceftriaxone, Piperacillin | 6 |
| 2 | 7 years | Parapharyngeal | Medial | Intubation | Transpharyngeal incision | Image guidance | H. aphrophilus | Clindamycin | 2 |
| 3 | 6 years | Parapharyngeal | Medial | Intubation | Transpharyngeal incision | Image guidance | S. pyogenes, S. oralis | Clindamycin, Ceftriaxone | 2 |
| 4 | 9 months | Retropharyngeal | Medial | None | Conservative | - | - | Clindamycin, Ceftriaxone | - |
| 5 | 18 months | Retropharyngeal | Medial | Intubation | Transpharyngeal incision | - | S. parasanguinis, S. oralis, S. vestibularis | Amoxicillin/Clavunate | 4 |
| 6 | 3 years | Parapharyngeal | Lateral | Intubation | Transcervical incision | Image guidance | Staph. aureus | Piperacillin/Tazobactam | 4 |
| 7 | 7 years | Parapharyngeal | Lateral | None | Transcervical incision | - | Staph. aureus | Amoxicillin/Clavunate | - |
| 8 | 10 years | Retropharyngeal | Medial | None | Transpharyngeal incision | Image guidance | Staph. aureus | Amoxicillin/Clavunate | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glavan, M.; Dreu, L.; Lanišnik, B. Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscesses in Children: A Report of Eight Cases. Children 2025, 12, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040487
Glavan M, Dreu L, Lanišnik B. Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscesses in Children: A Report of Eight Cases. Children. 2025; 12(4):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040487
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlavan, Matic, Lara Dreu, and Boštjan Lanišnik. 2025. "Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscesses in Children: A Report of Eight Cases" Children 12, no. 4: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040487
APA StyleGlavan, M., Dreu, L., & Lanišnik, B. (2025). Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscesses in Children: A Report of Eight Cases. Children, 12(4), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040487





