Analysis of Factors Relevant to the Severity of Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
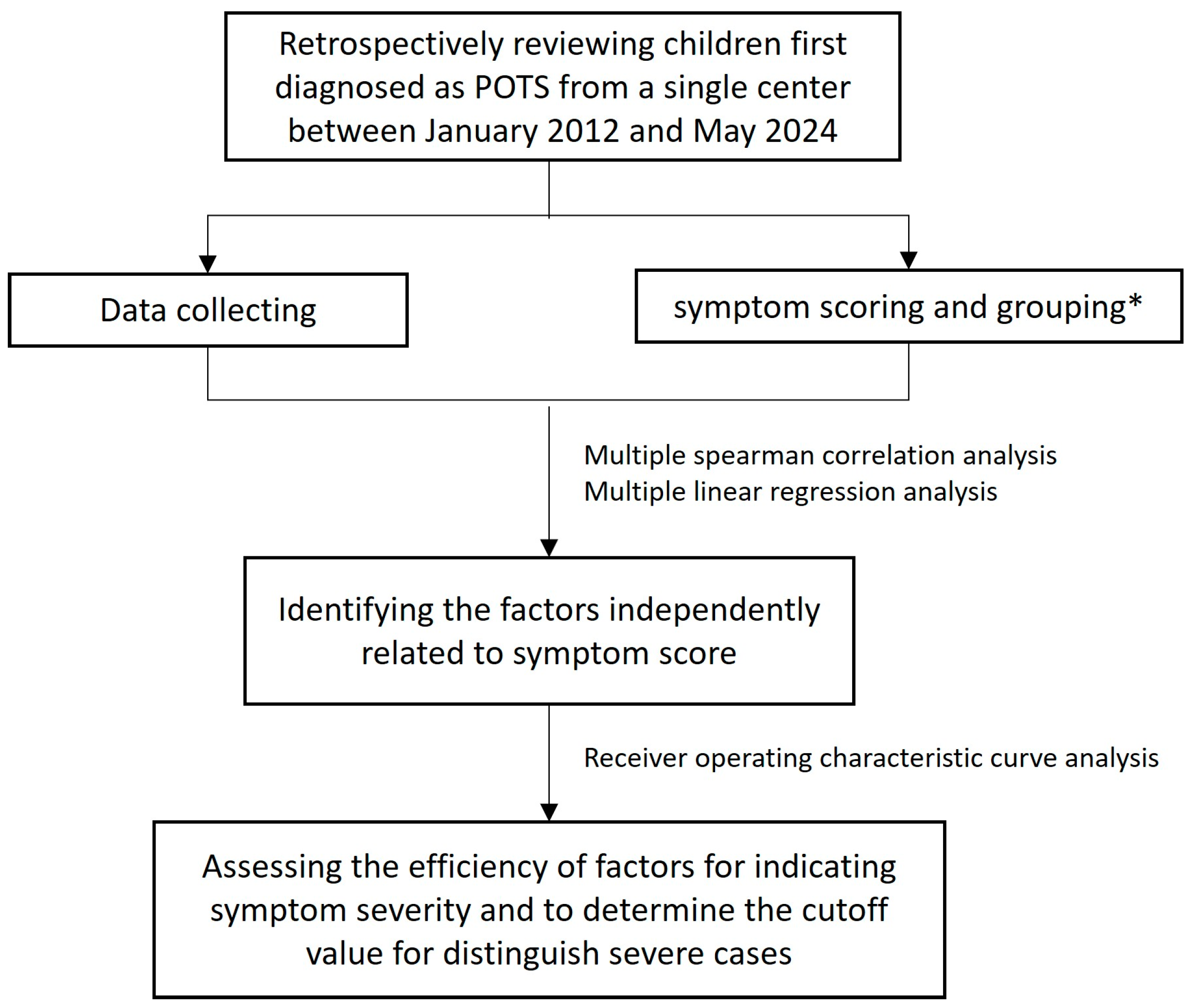
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Symptom Scores and Groupings
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Laboratory Examinations
2.6. Twelve-Lead ECG Tracings, Measurements, and Calculations
2.7. Ten-Minute Active Standing Test and HUTT
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Primary Characteristics of the Subjects
3.2. Multiple Spearman Correlation Analysis
3.3. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis of Factors Relevant to SS
3.3.1. Collinearity Statistics Among Variables
3.3.2. Excluding Variables That Show Collinearity
3.3.3. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
3.3.4. Obtaining the Regression Equation
3.4. ROC Analysis of QTcd Indicating the Symptom Severity in Children with POTS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huynh, P.; Brown, A.; Campisi, L.; Mruk, A.; Nguyen, T.; Raschka, M.; Afolabi, T. Management of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome in Pediatric Patients: A Clinical Review. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 29, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernino, S.; Bourne, K.M.; Stiles, L.E.; Grubb, B.P.; Fedorowski, A.; Stewart, J.M.; Arnold, A.C.; Pace, L.A.; Axelsson, J.; Boris, J.R.; et al. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS): State of the science and clinical care from a 2019 National Institutes of Health Expert Consensus Meeting-Part 1. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 235, 102828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngonge, A.L.; Nyange, C.; Ghali, J.K. Novel pharmacotherapeutic options for the treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2024, 25, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.K.; Sheldon, R.S.; Benditt, D.G.; Cohen, M.I.; Forman, D.E.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Grubb, B.P.; Hamdan, M.H.; Krahn, A.D.; Link, M.S.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the evaluation and management of patients with syncope: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm. 2017, 14, e155–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, N.M.; Yi, D.Y.; Yun, S.W.; Lim, I.S.; Chae, S.A. Awareness of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome is required in adolescent syncope. Medicine 2022, 101, e31513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, A.; Thompson, N.R.; Moodley, M. Pediatric-Onset Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome in a Single Tertiary Care Center. J. Child Neurol. 2020, 35, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, B.; Cannom, D.; Fedorowski, A.; Stewart, J.; Gibbons, C.; Sutton, R.; Shen, W.K.; Muldowney, J.; Chung, T.H.; Feigofsky, S.; et al. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS): A critical assessment. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 63, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Du, J.; Jin, H.; Huang, Y. Postural Tachycardia Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: Pathophysiology and Clinical Management. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, R. Orthostatische Intoleranz—Prävalenz, Diagnostik und die Bedeutung für die Arbeitsmedizin [Orthostatic intolerance—Prevalence, diagnostic management and its significance for occupational medicine]. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2004, 116, 40–46. (In Germany) [Google Scholar]
- Grubb, B.P.; Kanjwal, Y.; Kosinski, D.J. The postural tachycardia syndrome: A concise guide to diagnosis and management. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2006, 17, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Ochs, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, P.; Xiong, Z.; Gai, Y.; et al. Risk factors for postural tachycardia syndrome in children and adolescents. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeyasu, Y.; Okada, A.; Fujii, C.; Tanaka, C.; Sugihara, A.; Horiuchi, M.; Yorifuji, T.; Tsukahara, H. Quality of life and physical/psychosocial factors in children and adolescents with orthostatic intolerance. Biopsychosoc. Med. 2023, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.; Bourne, K.M.; Sheldon, R.S.; Vernino, S.; Raj, V.; Ng, J.; Okamoto, L.E.; Arnold, A.C.; Bryarly, M.; Phillips, L.; et al. A comparison of health-related quality of life in autonomic disorders: Postural tachycardia syndrome versus vasovagal syncope. Clin. Auton. Res. 2021, 31, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, W.S.; King, C.K.; Schaefer, M.R.; Decker, J.; Kuhn, B. “You Look Perfectly Healthy to Me”: Living with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Through Adolescents’ and Parents’ Eyes. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 62, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, J.R.; Shadiack III, E.C.; McCormick, E.M.; MacMullen, L.; George-Sankoh, I.; Falk, M.J. Long-Term POTS Outcomes Survey: Diagnosis, Therapy, and Clinical Outcomes. J. Am. Hear Assoc. 2024, 13, e033485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liao, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, H.; Huang, M.; Dong, X.Y.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.Q.; Sun, J.H.; Du, J.B.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of neurally mediated syncope in children and adolescents (revised 2024). World J. Pediatr. 2024, 20, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, B.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Deng, Y.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, L. Plasma metabolomic profile in orthostatic intolerance children with high levels of plasma homocysteine. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2024, 50, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Zheng, X.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Liao, Y.; Han, Z.H.; Huang, P.; Sun, C.F.; Liu, J.; Song, J.Y.; Tang, C.S.; et al. Increased Endogenous Sulfur Dioxide Involved in the Pathogenesis of Postural Tachycardia Syndrome in Children: A Case-Control Study. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Han, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Song, J.; Qi, J.; Liao, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Serum Resistin Negatively Correlates with Clinical Severity of Postural Tachycardia Syndrome in Children. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2017, 38, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryarly, M.; Phillips, L.T.; Fu, Q.; Vernino, S.; Levine, B.D. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1207–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.R.; Ottesen, J.T.; Mehlsen, J.; Olufsen, M.S. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome explained using a baroreflex response model. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Du, J.; Jin, H. Establishment and validation of a multivariate predictive model for the efficacy of oral rehydration salts in children with postural tachycardia syndrome. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapper, H.; Cheshire, W.P. Oral and intravenous hydration in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension and postural tachycardia syndrome. Auton. Neurosci. 2022, 238, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, E.M.; Gamboa, A.; Nwazue, V.C.; Celedonio, J.E.; Paranjape, S.Y.; Black, B.K.; Okamoto, L.E.; Shibao, C.A.; Biaggioni, I.; Robertson, D.; et al. Effect of High Dietary Sodium Intake in Patients With Postural Tachycardia Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.L.; Raj, S.R.; Schondorf, R.; Shen, W.K.; Wieling, W.; Claydon, V.E. Salt supplementation in the management of orthostatic intolerance: Vasovagal syncope and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 237, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, J.; Liao, Y.; Jin, H. Serum uric acid predicts therapeutic response to midodrine hydrochloride in children with vasovagal syncope: A pilot study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 183, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrom, C.J.; Foreman, N.A.; Biltz, G. Practices and Applications of Heart Rate Variability Monitoring in Endurance Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2022, 44, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.A. Heart rate-corrected QT interval prolongation is associated with decreased heart rate variability in patients with type 2 diabetes. Medicine 2022, 101, e31511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, H.; Zou, R.; Cai, H.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C. The value of QT interval in differentiating vasovagal syncope from epilepsy in children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2022, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zou, R.; Wang, C. Research progress on the predictive value of electrocardiographic indicators in the diagnosis and prognosis of children with vasovagal syncopeFront. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 916770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Yao, D.; Pan, Y.; Wang, M.; Meng, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Implication of heart rate variability on cerebral small vessel disease: A potential therapeutic target. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, R.; Chen, S.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C. The Relationship Between Unexplained Chest Pain in Children and Head-Up Tilt Test. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 901919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yuan, H.; Hu, C.; Liao, D.; Cai, H.; et al. Relationship between syncopal symptoms and head-up tilt test modes. Cardiol. Young 2024, 34, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimbo, S.; Fujita, Y.; Ishii, W.; Namiki, H.; Kato, M.; Komori, A.; Abe, Y.; Kamiyama, H.; Ayusawa, M.; Morioka, I. Decreased Stroke Volume and Venous Return in School Children with Postural Tachycardia Syndrome. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2021, 253, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S.A.; Co, E.L.; Panthangi, V.; Jain, E.; Ishak, A.; Shah, Y.; Vasavada, A.; Padda, I. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS): An Update for Clinical Practice. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zou, R.; Cai, H.; Wang, C. Predictive Value of Heart Rate and Blood Pressure on the Prognosis of Postural Tachycardia Syndrome in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 10802469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, M.; Maule, S.V.; Giudici, M.; Valente, M.; Ridolfi, L.; Scarsoglio, S. Cardiovascular Response to Posture Changes: Multiscale Modeling and in vivo Validation During Head-Up Tilt. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 826989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.J.; Lung, C.W.; Jan, Y.K.; Lee, L.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Liau, B.Y. The relationship between cardiovagal baroreflex and cerebral autoregulation in postural orthostatic tachycardia disorder using advanced cross-correlation function. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weperen, V.Y.H.; Ripplinger, C.M.; Vaseghi, M. Autonomic control of ventricular function in health and disease: Current state of the art. Auton. Res. 2023, 33, 491–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar, P.L.; Raj, S.R. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: Mechanisms and New Therapies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunami, Y.; Sugaya, K.; Takahashi, K.G. protein-coupled receptors related to autoimmunity in postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Immunol. Med. 2024, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, P.R.; Zadourian, A.; Lo, H.C.; Ormiston, C.K.; Golshan, S.; Hsu, J.C. Randomized Trial of Ivabradine in Patients with Hyperadrenergic Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2021, 77, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, A.L.; Peng, J. Defective recovery of QT dispersion due to no-reflow following acute interventional therapy in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 14, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederman, Y.S.; Balucani, C.; Steinberg, L.R.; Philip, C.; Lazar, J.M.; Weedon, J.; Mirchandani, G.; Weingast, S.Z.; Viticchi, G.; Falsetti, L.; et al. Does the Magnitude of the Electrocardiogram QT Interval Dispersion Predict Stroke Outcome? J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apoorva, M.; Atkar, C. A Study on Qt Dispersion before and after Thrombolysis in Acute Myocardial Infarction, and its Prognostic Implications. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2022, 70, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tonko, J.B.; Lambiase, P.D. The proarrhythmogenic role of autonomics and emerging neuromodulation approaches to prevent sudden death in cardiac ion channelopathies. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandstra, T.E.; Notenboom, R.G.E.; Wink, J.; Kiès, P.; Vliegen, H.W.; Egorova, A.D.; Schalij, M.J.; De Ruiter, M.C.; Jongbloed, M.R.M. Asymmetry and Heterogeneity: Part and Parcel in Cardiac Autonomic Innervation and Function. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 665298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, G.; Viola, E.; Nocco, M.; Santagada, E.; Durante, M.; Bucca, C.; Marigliano, V. Autonomic modulation and QT interval dispersion in hypertensive subjects with anxiety. Hypertension 1999, 34, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Takahashi, N.; Iwao, T.; Yonemochi, H.; Ooie, T.-H.; Hara, M.; Saikawa, T.; Ito, M. Evaluation of autonomic influences on QT dispersion using the head-up tilt test in healthy subjects. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1999, 22, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Shimizu, W.; Yan, G.X.; Sicouri, S. Cellular basis for QT dispersion. J. Electrocardiol. 1998, 30, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.; Miles, J.; Liebelt, J.; Christia, P.; Engstrom, K.; Thachil, R.; Grushko, M.; Faillace, R.T. QT Dispersion and Drug-Induced Torsade de Pointes. Cureus 2021, 13, e12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.; Racosta, J.M.; Kimpinski, K. Comparison of Heart Rate Variability Parameters to the Autonomic Reflex Screen in Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome and Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 35, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, G.; Diedrich, L.; Sato, K.; Brychta, R.J.; Raj, S.R.; Robertson, D.; Biaggioni, I.; Diedrich, A. Vagal and Sympathetic Function in Neuropathic Postural Tachycardia Syndrome. Hypertension 2019, 73, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
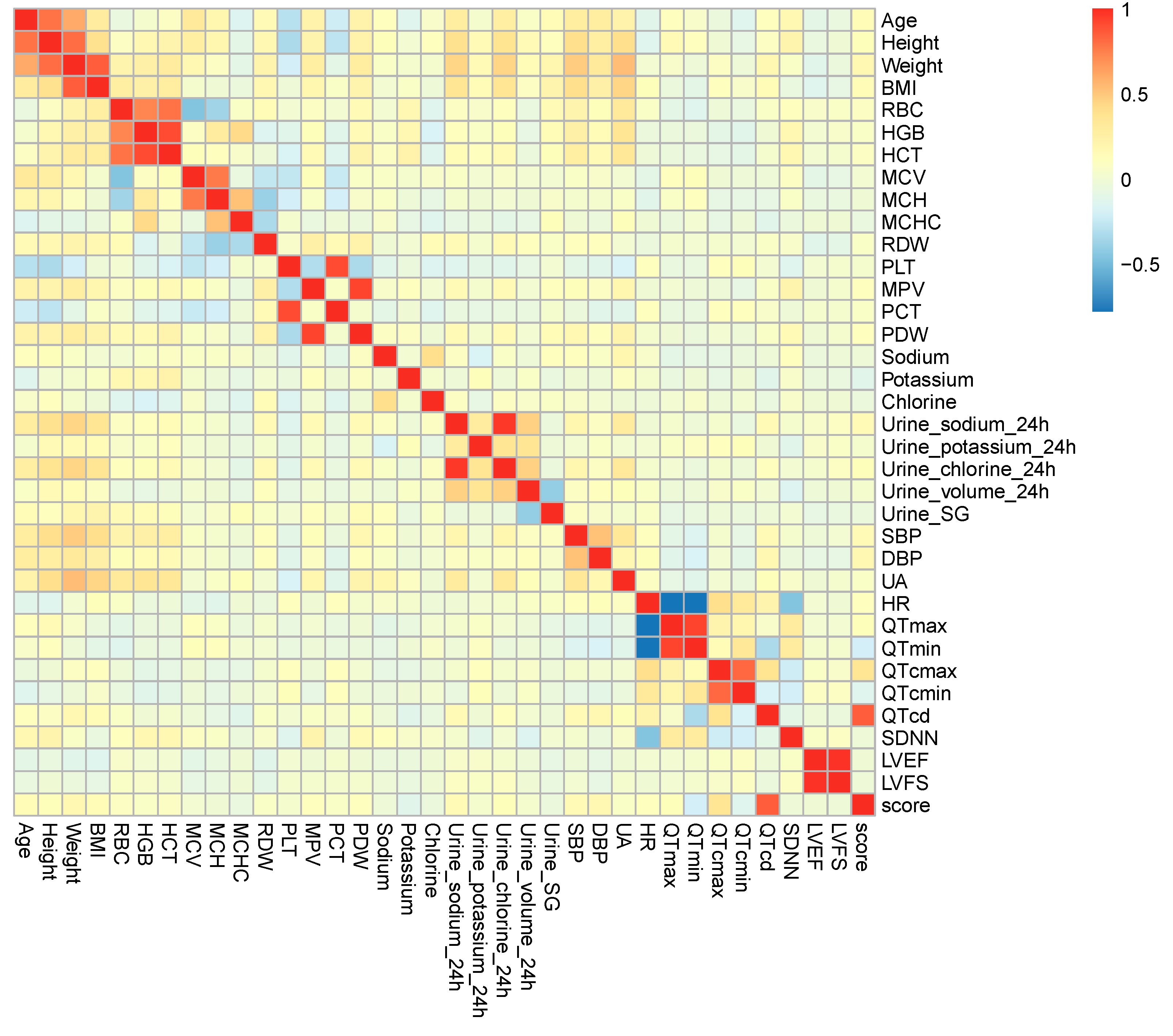

| Variables | rs | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline data | |||
| Age | 0.133 | 0.022 | |
| Height | 0.112 | 0.055 | |
| Weight | 0.172 | 0.003 | |
| BMI | 0.130 | 0.025 | |
| Variables related to blood volume | |||
| Blood cell count | RBC | 0.087 | 0.134 |
| HGB | 0.064 | 0.274 | |
| HCT | 0.082 | 0.160 | |
| MCV | 0.015 | 0.797 | |
| MCH | −0.015 | 0.797 | |
| MCHC | −0.063 | 0.282 | |
| RDW | 0.065 | 0.263 | |
| PLT | 0.030 | 0.603 | |
| MPV | 0.102 | 0.081 | |
| PCT | 0.062 | 0.286 | |
| PDW | 0.109 | 0.060 | |
| Serum ion | Sodium | −0.030 | 0.605 |
| Potassium | −0.117 | 0.045 | |
| Chlorine | −0.038 | 0.510 | |
| 24 h urine | 24 h urinary sodium | 0.148 | 0.011 |
| 24 h urinary potassium | 0.031 | 0.595 | |
| 24 h urinary chlorine | 0.117 | 0.045 | |
| 24 h urinary volume | 0.025 | 0.673 | |
| Urine SG | −0.045 | 0.445 | |
| Variables related to vascular function | |||
| SBP | 0.155 | 0.008 | |
| DBP | 0.167 | 0.004 | |
| UA | 0.073 | 0.210 | |
| Variables related to autonomic nervous function | |||
| 12-lead ECG | HR | 0.096 | 0.100 |
| QTmax | 0.116 | 0.046 | |
| QTmin | −0.195 | 0.001 | |
| QTcmax | 0.343 | <0.001 | |
| QTcmin | −0.136 | 0.019 | |
| QTcd | 0.849 | <0.001 | |
| 24 h Holter | SDNN | −0.018 | 0.754 |
| Echocardiography | LVEF | −0.006 | 0.919 |
| LVFS | −0.019 | 0.748 | |
| Variables | Collinearity Statistics | |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | VIF | |
| Age | 0.373 | 2.684 |
| Weight | 0.100 | 10.019 |
| BMI | 0.167 | 5.985 |
| Serum potassium | 0.913 | 1.095 |
| 24 h urinary sodium | 0.070 | 14.278 |
| 24 h urinary chlorine | 0.072 | 13.947 |
| SBP | 0.548 | 1.825 |
| DBP | 0.680 | 1.470 |
| QTmax | 0.001 | 914.549 |
| QTmin | 0.001 | 1058.700 |
| QTcmax | <0.001 | - |
| QTcmin | 0.151 | 6.626 |
| QTcd | 0.007 | 141.591 |
| Variables | Collinearity Statistics | |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | VIF | |
| Age | 0.777 | 1.286 |
| BMI | 0.709 | 1.410 |
| Serum potassium | 0.963 | 1.038 |
| 24 h urine sodium | 0.814 | 1.229 |
| SBP | 0.631 | 1.585 |
| DBP | 0.690 | 1.449 |
| QTmax | 0.884 | 1.131 |
| QTcmin | 0.868 | 1.152 |
| QTcd | 0.856 | 1.168 |
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | Collinearity Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | β | t Value | p Value | Tolerance | VIF | |
| Constant | −4.482 | 0.436 | −10.272 | <0.001 | |||
| QTcd | 0.242 | 0.009 | 0.839 | 26.425 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| F value 698.300; Adjusted R2 0.703; Durbin–Watson 2.038 | |||||||
| Mild Group | Severe Group | |
|---|---|---|
| SS (scores) | 3 (2, 4) | 11 (9, 12) |
| QTcd (ms) | 34.42 (30.98, 39.91) | 59.51 (52.04, 66.52) |
| Age (yrs) | 11 (10, 13) | 12 (11, 14) |
| Male [n(%)] | 55 (50.0%) | 34 (40.5%) |
| Female [n(%)] | 55 (50.0%) | 50 (59.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Jin, H.; Liao, Y. Analysis of Factors Relevant to the Severity of Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. Children 2025, 12, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040474
Cao Y, Liu P, Li B, Zhang Y, Du J, Jin H, Liao Y. Analysis of Factors Relevant to the Severity of Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. Children. 2025; 12(4):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040474
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yali, Ping Liu, Bo Li, Yingqian Zhang, Junbao Du, Hongfang Jin, and Ying Liao. 2025. "Analysis of Factors Relevant to the Severity of Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome" Children 12, no. 4: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040474
APA StyleCao, Y., Liu, P., Li, B., Zhang, Y., Du, J., Jin, H., & Liao, Y. (2025). Analysis of Factors Relevant to the Severity of Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome. Children, 12(4), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040474








