Application of Radiomics in Predicting the Prognosis of Medulloblastoma in Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohorts
2.2. Definition of Clinical Variables
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. MRI Imaging
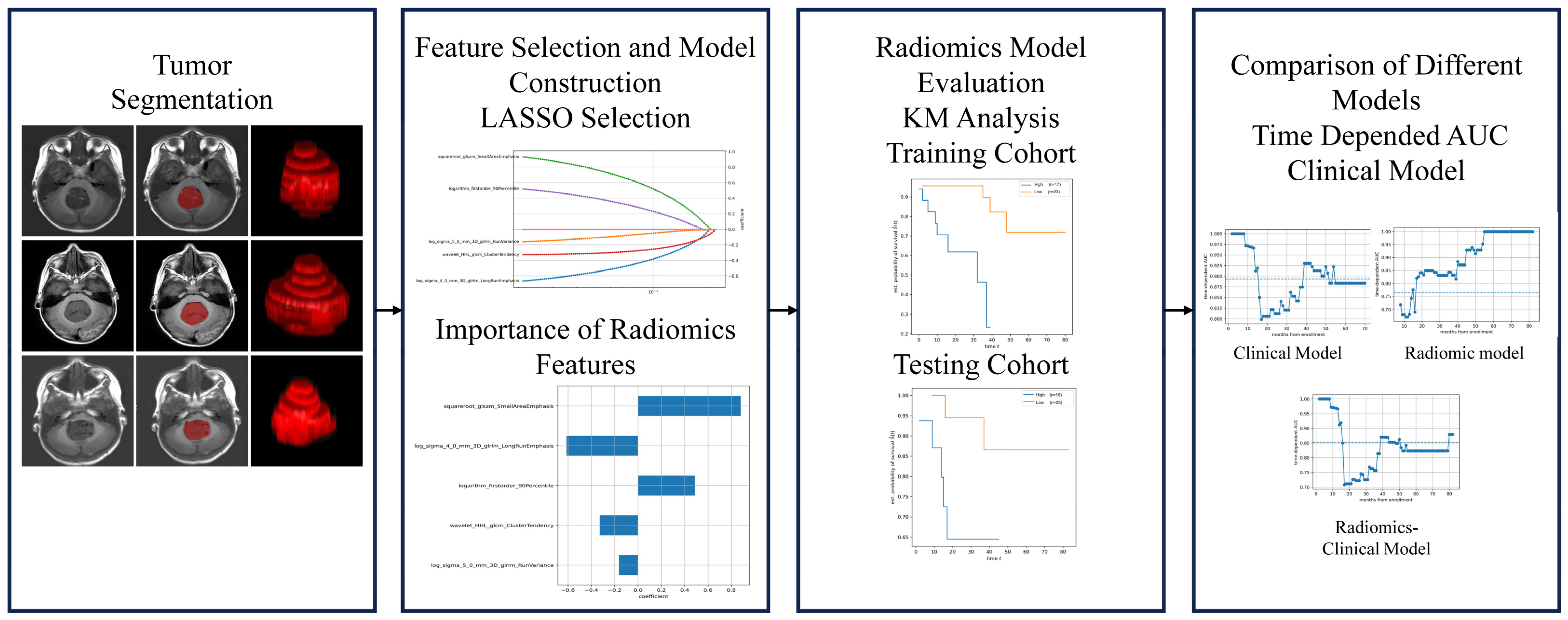
2.4.1. Image Segmentation
2.4.2. Radiomic Feature Extraction
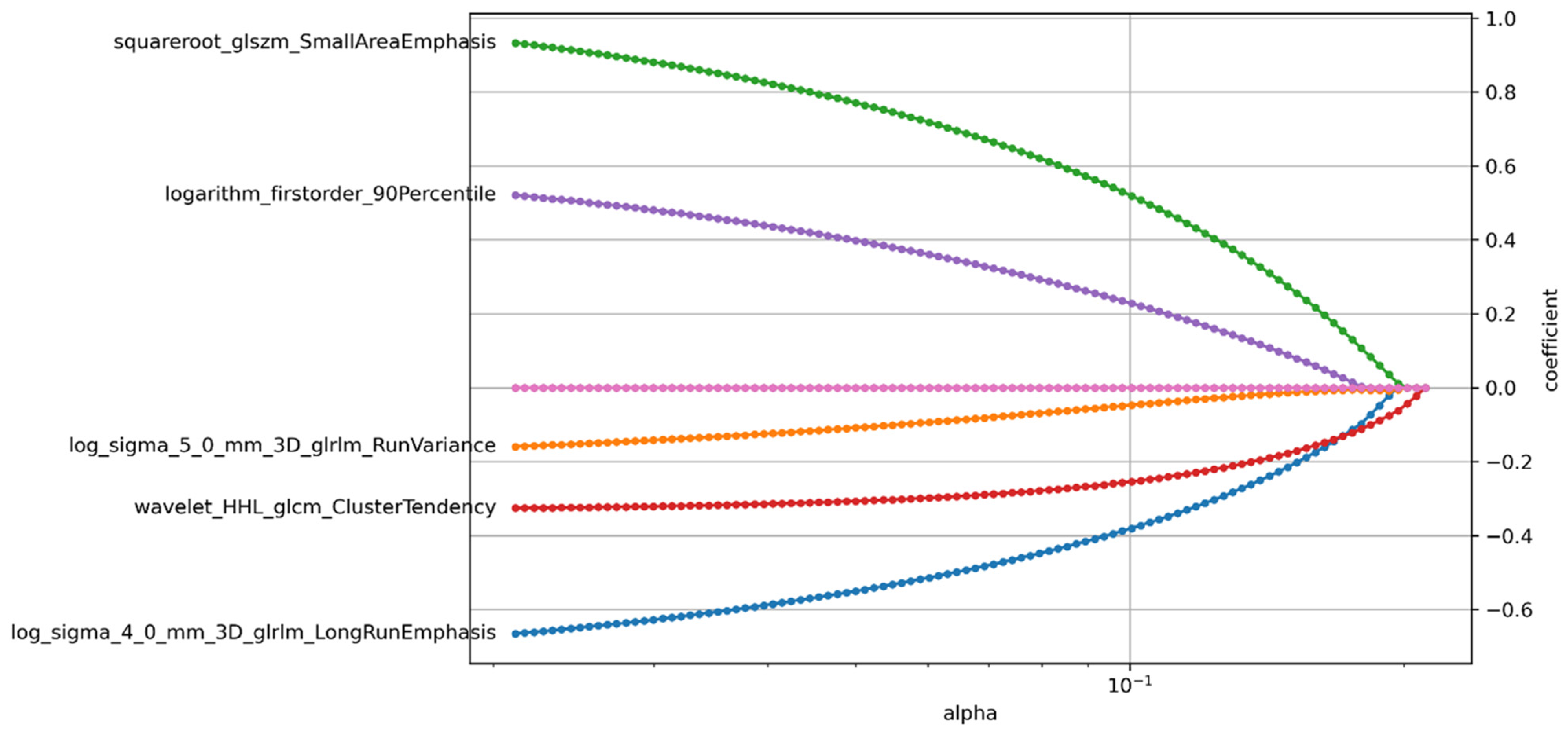
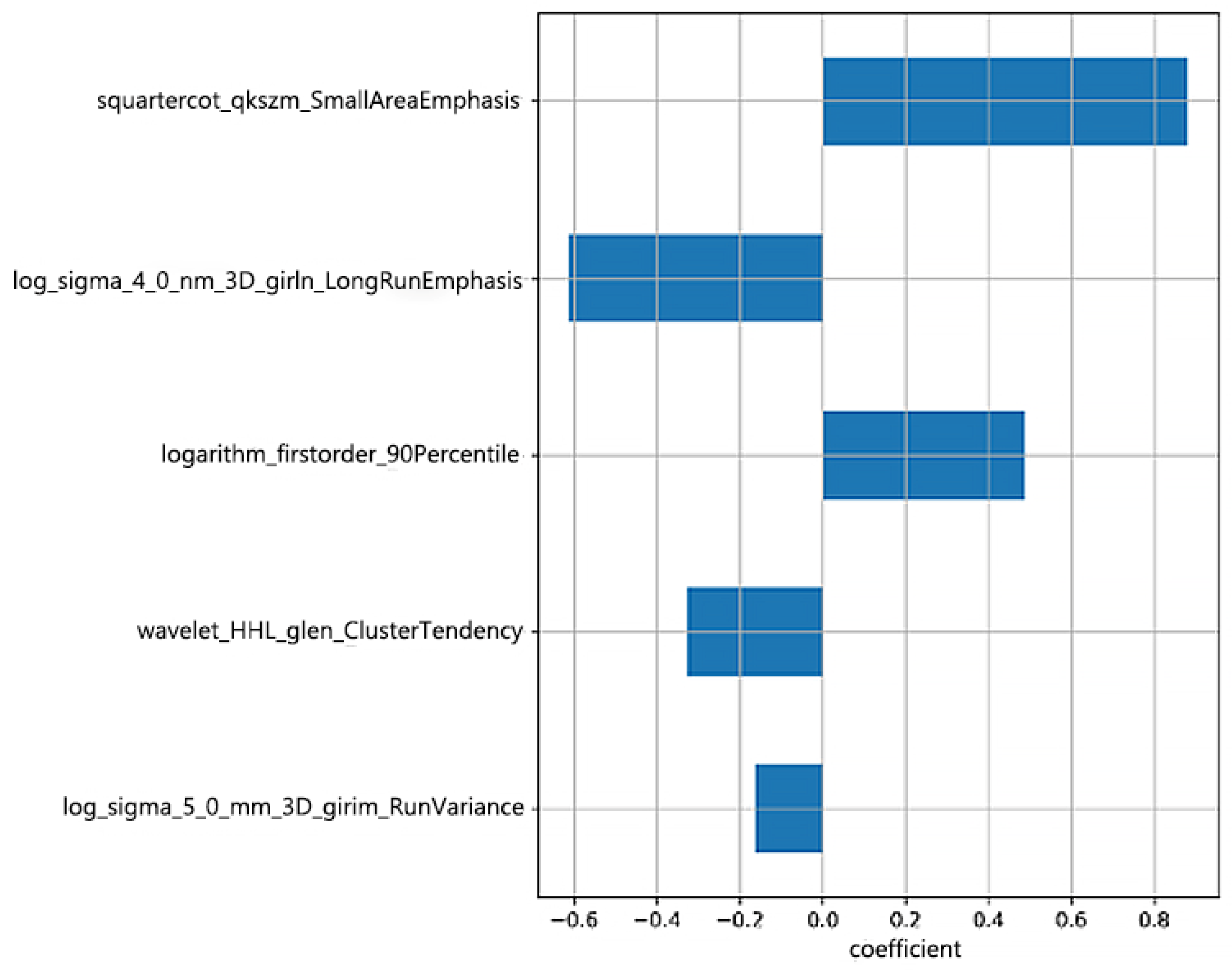
2.4.3. Feature Selection
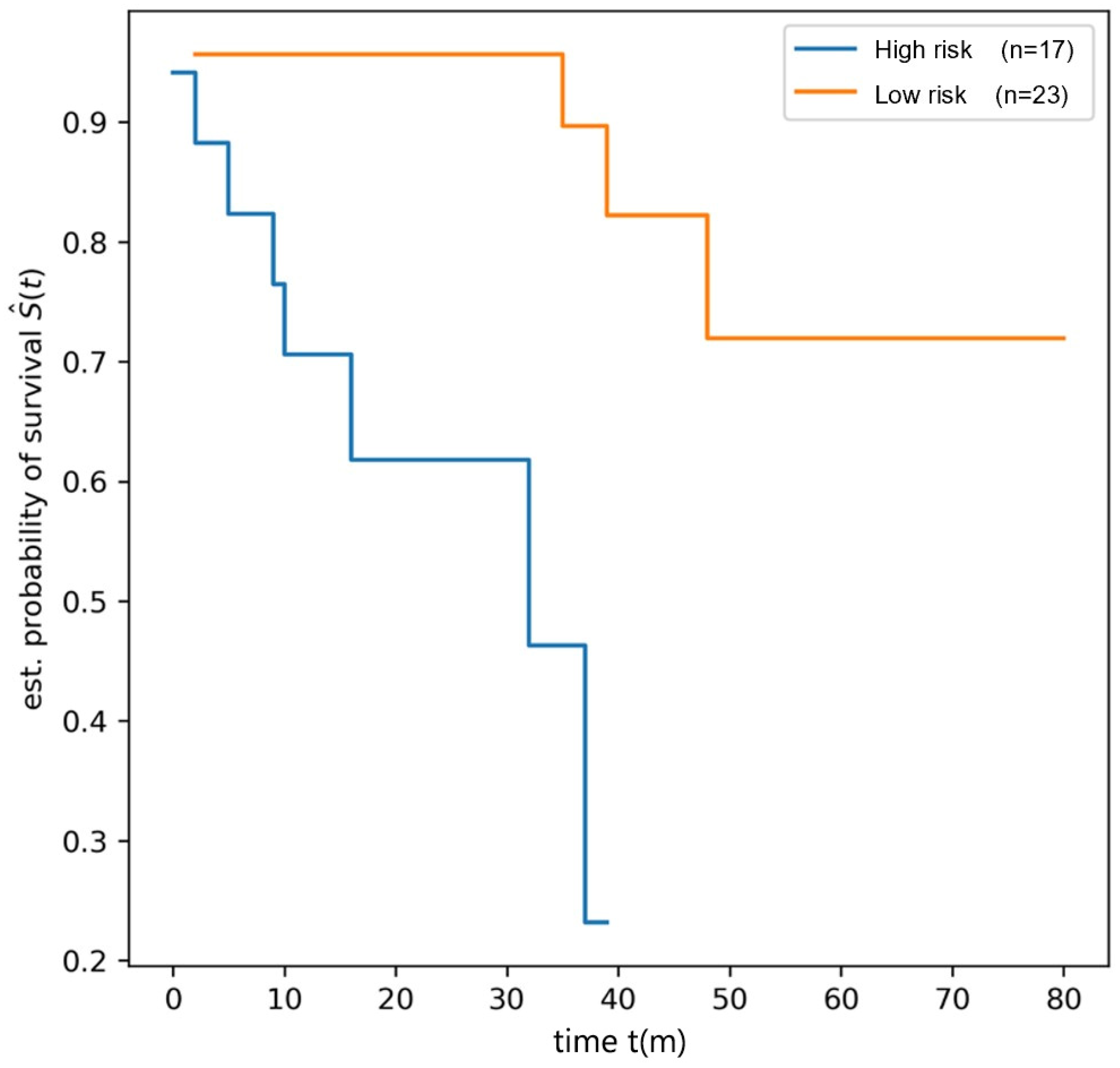
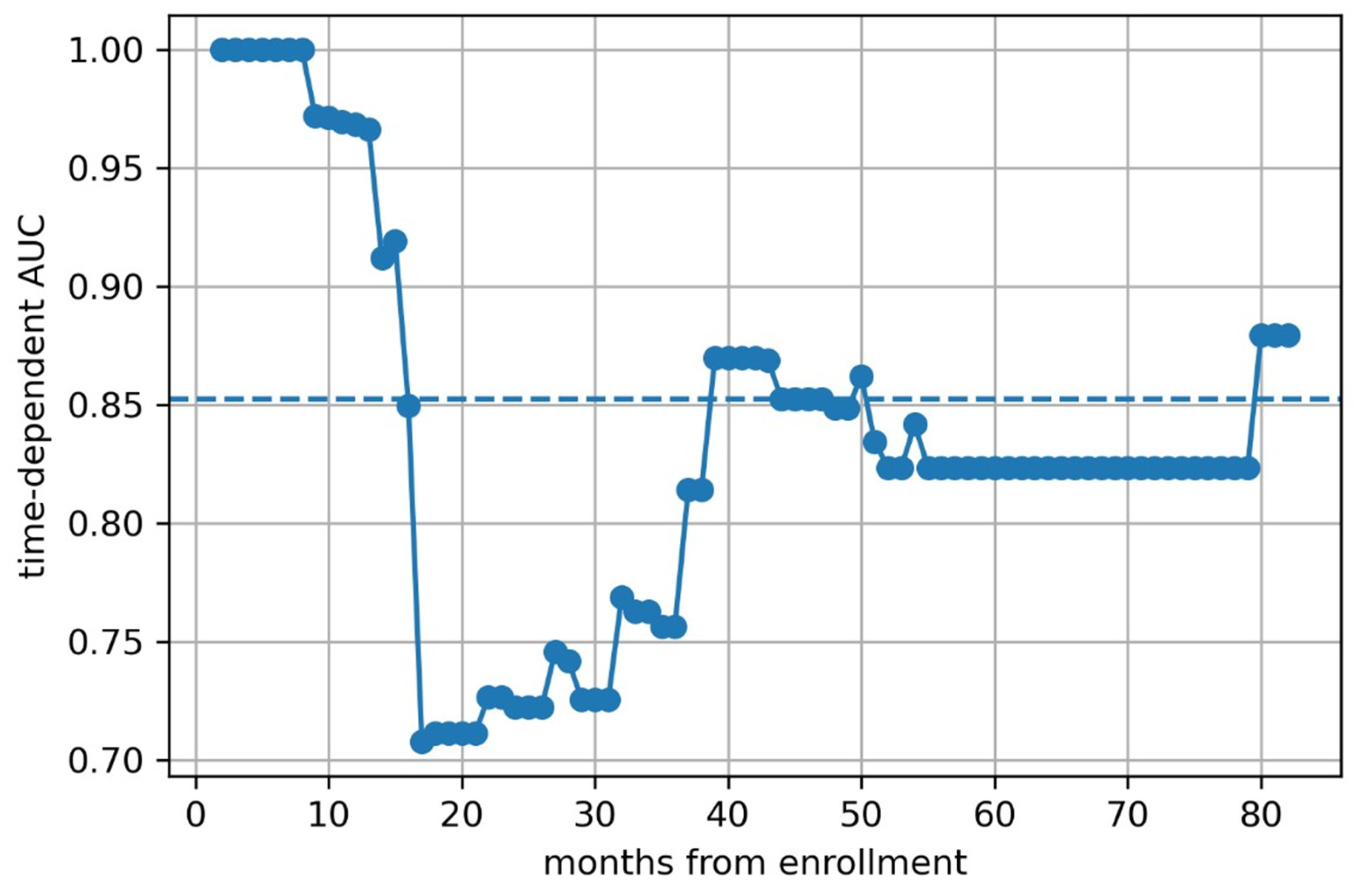
2.4.4. Radiomics Model Construction and Evaluation
2.4.5. Prediction Model Construction and Evaluation
2.4.6. Statistical Analysis
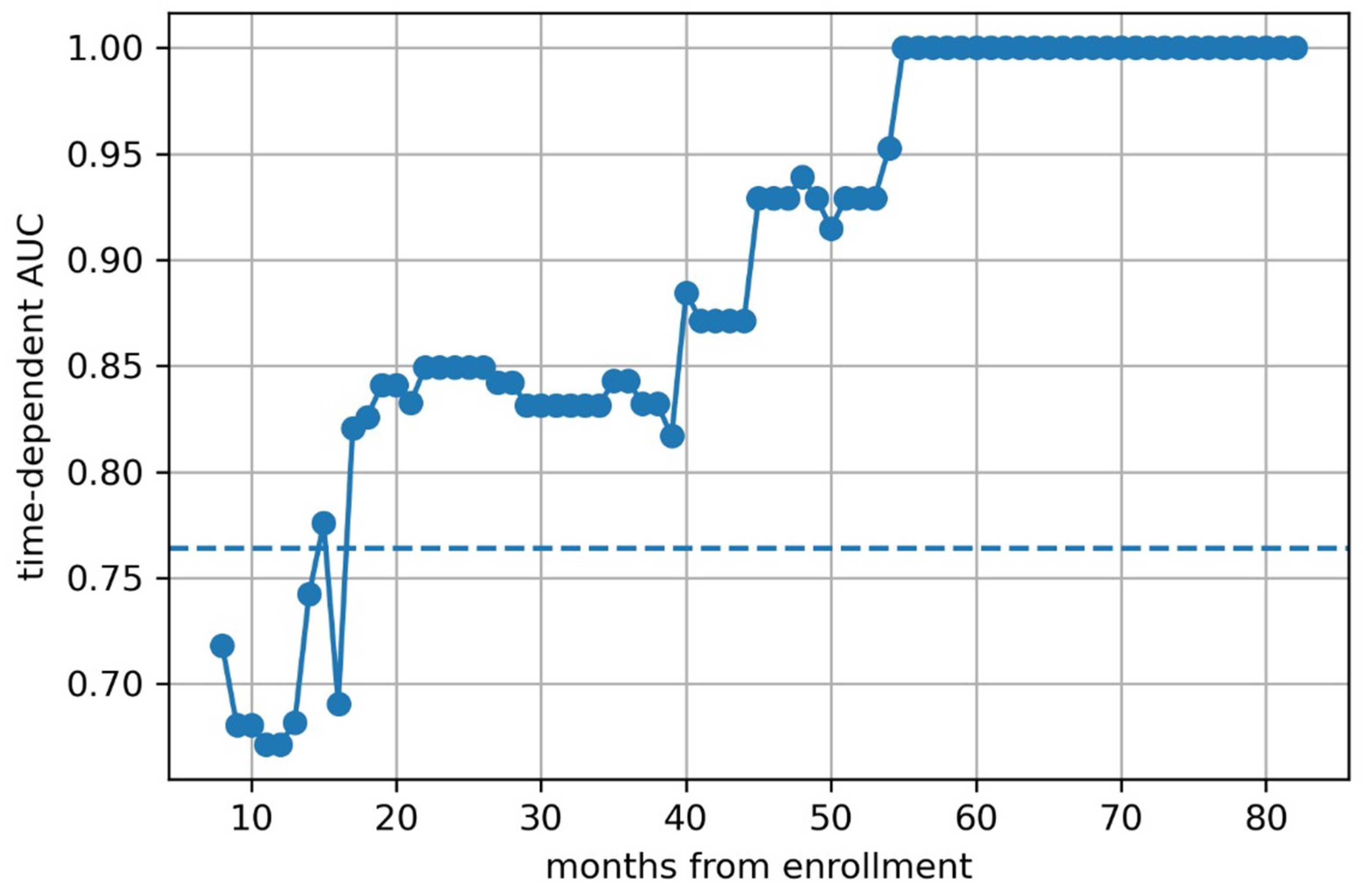
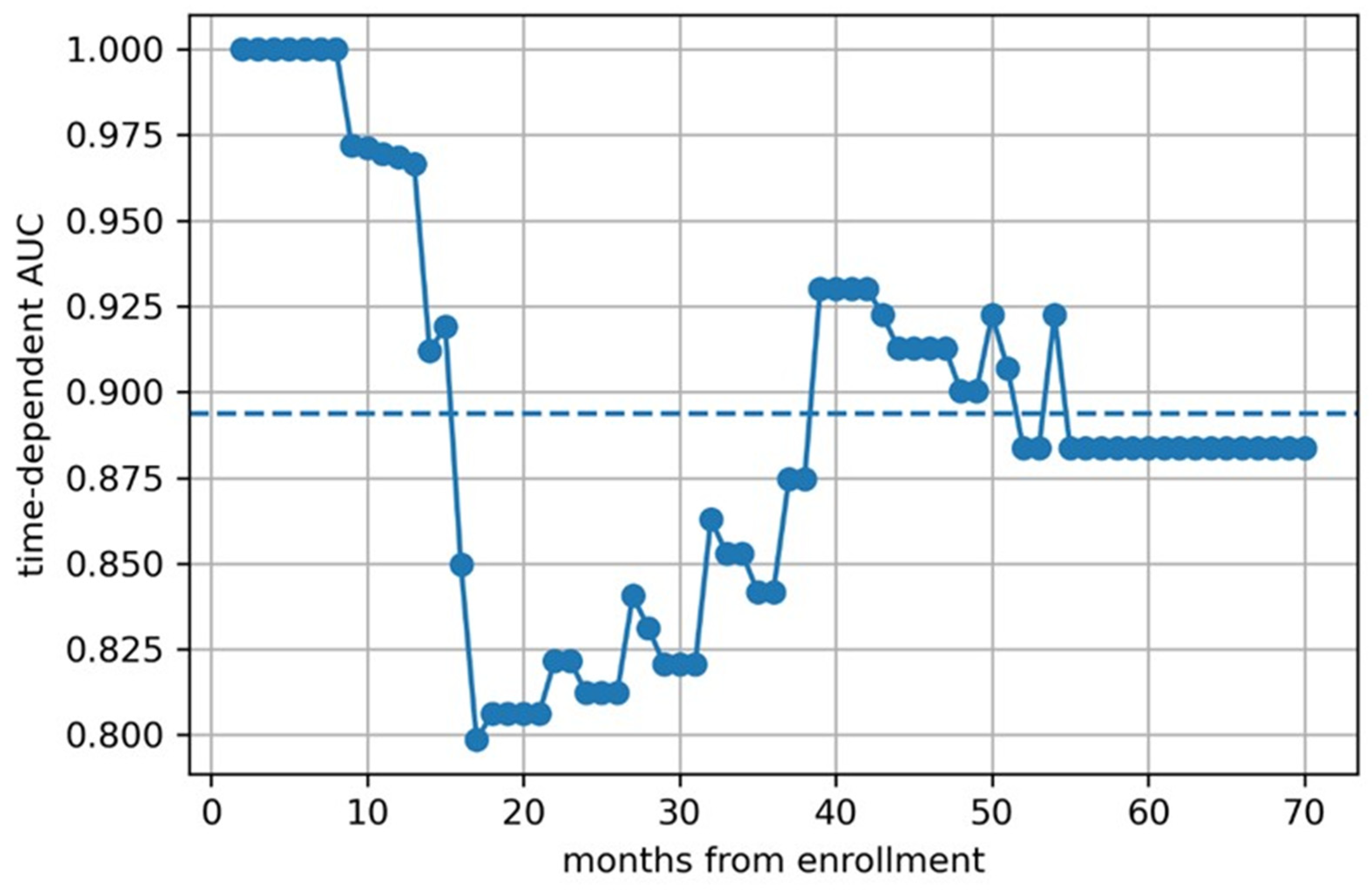
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Thompson, E.M.; Hielscher, T.; Bouffet, E.; Remke, M.; Luu, B.; Gururangan, S.; McLendon, R.E.; Bigner, D.D.; Lipp, E.S.; Perreault, S.; et al. Prognostic value of medulloblastoma extent of resection after accounting for molecular subgroup: A retrospective integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menyhart, O.; Gyorffy, B. Molecular stratifications, biomarker candidates and new therapeutic options in current medulloblastoma treatment approaches. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, K.; Packer, R.J. Recent Advances in Pediatric Medulloblastoma. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 23, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, V.; Sugur, H.; Jaiswal, J.; Arvinda, H.; Arivazhagan, A.; Somanna, S.; Santosh, V. Medulloblastoma: Distinctive Histo-Molecular Correlation with Clinical Profile, Radiologic Characteristics, and Surgical Outcome. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2019, 54, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, K.K.-W.; Wang, W.; Li, K.; Duan, W.; Yuan, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhan, Y.; et al. Incremental prognostic value and underlying biological pathways of radiomics patterns in medulloblastoma. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saju, A.C.; Chatterjee, A.; Sahu, A.; Gupta, T.; Krishnatry, R.; Mokal, S.; Sahay, A.; Epari, S.; Prasad, M.; Chinnaswamy, G.; et al. Machine-learning approach to predict molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma using multiparametric MRI-based tumor radiomics. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ma, W.; Huang, J.; Cai, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, D.; Zou, Z.; Sun, H.; Qi, X.; et al. Beijing Children’s Hospital guidelines on the design and conduction of the first standardized database for medulloblastoma. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyharcabal-Bourden, V.; Kalifa, C.; Gentet, J.; Frappaz, D.; Edan, C.; Chastagner, P.; Sariban, E.; Pagnier, A.; Babin, A.; Pichon, F.; et al. Standard-risk medulloblastoma treated by adjuvant chemotherapy followed by reduced-dose craniospinal radiation therapy: A French Society of Pediatric Oncology Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Chintagumpala, M.; Ashley, D.; Kellie, S.; Kun, L.E.; Merchant, T.E.; Woo, S.; Wheeler, G.; Ahern, V.; Krasin, M.J.; et al. Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): Long-term results from a prospective, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, R.J.; Gajjar, A.; Vezina, G.; Rorke-Adams, L.; Burger, P.C.; Robertson, P.L.; Bayer, L.; LaFond, D.; Donahue, B.R.; Marymont, M.H.; et al. Phase III study of craniospinal radiation therapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed average-risk medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4202–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandola, L.; Massimino, M.; Cefalo, G.; Solero, C.; Spreafico, F.; Pecori, E.; Riva, D.; Collini, P.; Pignoli, E.; Giangaspero, F.; et al. Hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy in the Milan strategy for metastatic medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakacki, R.I.; Burger, P.C.; Zhou, T.; Holmes, E.J.; Kocak, M.; Onar, A.; Goldwein, J.; Mehta, M.; Packer, R.J.; Tarbell, N.; et al. Outcome of children with metastatic medulloblastoma treated with carboplatin during craniospinal radiotherapy: A Children’s Oncology Group Phase I/II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, H.J. Medulloblastoma in children: Increasing survival rates and further prospects. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1982, 8, 2023–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seema Patel, Shiyang Wang, Matija Snuderl, Matthias A Karajannis, Pre-treatment lymphopenia and indication of tumor-induced systemic immunosuppression in medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 136, 541–544. [CrossRef]
- Margol, A.S.; Robison, N.J.; Gnanachandran, J.; Hung, L.T.; Kennedy, R.J.; Vali, M.; Dhall, G.; Finlay, J.L.; Erdreich-Epstein, A.; Krieger, M.D.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages in SHH subgroup of medulloblastomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, H.R.; Miller, K.; Samay, S.; Nellan, A.; Green, A.L. Investigation of white blood cell characteristics in cerebrospinal fluid samples at pediatric brain tumor diagnosis. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 159, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, D.R.; Awwad, A.; Meijer, L.; Manita, M.; Jaspan, T.; Dineen, R.A.; Grundy, R.G.; Auer, D.P. Metrics and textural features of MRI diffusion to improve classification of pediatric posterior fossa tumors. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quon, J.L.; Bala, W.; Chen, L.C.; Wright, J.; Kim, L.H.; Han, M.; Shpanskaya, K.; Lee, E.H.; Tong, E.; Iv, M.; et al. Deep Learning for Pediatric Posterior Fossa Tumor Detection and Classification: A Multi-Institutional Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, D.J.; Zeestraten, E.; Lawrence, A.J.; Barrick, T.R.; Markus, H.S. Texture Analysis of T1-Weighted and Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Images Detects Abnormalities That Correlate With Cognitive Decline in Small Vessel Disease. Stroke 2018, 49, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, H.; Qureshi, M.M.; Chapman, M.N.; Li, B.; Andreu-Arasa, V.C.; Onoue, K.; Truong, M.T.; Sakai, O. CT Texture Analysis Potentially Predicts Local Failure in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Chemoradiotherapy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Fang, M.; Li, Z.; Tu, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Tian, J.; Dong, D.; Liu, S. Radiomics signature: A biomarker for the preoperative discrimination of lung invasive adenocarcinoma manifesting as a ground-glass nodule. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Shi, D.; Li, Y.; Tong, T.; Peng, W. A clinical-radiomics nomogram for the preoperative prediction of lung metastasis in colorectal cancer patients with indeterminate pulmonary nodules. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Characteristics | Testing Cohort (n = 41) | Training Cohort (n = 40) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.947 | ||
| Median | 6.4 (4.1~9.6) | 6.8 (4.0~9.1) | |
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 27 (65.9%) | 26 (65.0%) | |
| Female | 14 (34.1%) | 14 (35.0%) | |
| Duration of disease (weeks) | 0.195 | ||
| Median | 14.0 (9.0~21.0) | 19.0 (11.0~25.0) | |
| Risk hierarchy | 0.429 | ||
| Low-risk | 21 (51.2%) | 24 (60.0%) | |
| High-risk | 20 (48.8%) | 19 (47.5%) | |
| Dissemination | 0.095 | ||
| (−) | 28 (68.3%) | 19 (47.5%) | |
| (+) | 13 (31.7%) | 21 (52.5%) | |
| Extent of resection | 0.965 | ||
| GTR | 36 (87.8%) | 34 (85.0%) | |
| STR | 5 (12.2%) | 6 (15.0%) | |
| V-P shunt before surgery | 0.180 | ||
| (−) | 38 (92.7%) | 32 (80.0%) | |
| (+) | 3 (7.3%) | 8 (20.0%) | |
| Pathologic classification | 0.475 | ||
| Classic | 29 (70.7%) | 31 (77.5%) | |
| Desmoplastic/nodular | 2 (4.9%) | 1 (2.5%) | |
| Extensive nodular | 5 (12.2%) | 7 (17.5%) | |
| Large-cell and anaplastic | 4 (9.8%) | 1 (2.5%) | |
| Unknown | 1 (2.4%) | ||
| Radiology | 1.000 | ||
| (−) | 7 (17.1%) | 7 (17.5%) | |
| (+) | 34 (82.9%) | 33 (82.5%) | |
| Chemotherapy | 0.406 | ||
| (−) | 9 (22.0%) | 5 (12.5%) | |
| (+) | 32 (78.0%) | 35 (87.5%) | |
| Preoperative blood lymphocytes (109/L) | 0.430 | ||
| Median | 2.4 (1.8~3.1) | 2.7 (1.9~3.5) | |
| Preoperative blood neutrophils (109/L) | 0.127 | ||
| Median | 3.4 (2.2~5.1) | 3.7 (3.0~6.9) | |
| Preoperative blood neutrophils to lymphocytes | 0.416 | ||
| Median | 1.2 (0.8~2.6) | 1.6 (0.9~3.7) | |
| Preoperative blood platelets to lymphocytes | 0.544 | ||
| Median | 110.3 (87.3~170.9) | 122.6 (85.6~193.5) | |
| Postoperative cerebrospinal fluid white blood cells (106/L) | 0.443 | ||
| Median | 10.0 (6.0~12.0) | 10.0 (8.2~14.0) | |
| Survival time (months) | 0.600 | ||
| Median | 22.0 (14.0~39.0) | 28.0 (15.0~40.2) |
| Factors | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 97.5%CI | p | |
| Finding-to-surgery time | 1.009 | [0.969;1.052] | 0.028 |
| Risk hierarchy | 1.591 | [0.098;25.764] | 0.001 |
| Dissemination | 14.695 | [1.455;148.42] | <0.001 |
| Radiotherapy | 0.205 | [0.053;0.795] | >0.001 |
| Chemotherapy | 0.219 | [0.063;0.760] | 0.086 |
| Postoperative cerebrospinal fluid white blood cells | HR = 0.999 | [0.996;1.002] | 0.019 |
| Model | C-Index | Brier |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical | 0.806 | 0.092 |
| Radiomics | 0.762 | 0.073 |
| Clinical–Radiomics | 0.860 | 0.087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Ying, Z.; Yang, P.; Liang, Y.; Liang, C.; Shang, B.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Y.; Peng, X.; et al. Application of Radiomics in Predicting the Prognosis of Medulloblastoma in Children. Children 2025, 12, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030387
Chen J, Yang W, Ying Z, Yang P, Liang Y, Liang C, Shang B, Zhang H, Cai Y, Peng X, et al. Application of Radiomics in Predicting the Prognosis of Medulloblastoma in Children. Children. 2025; 12(3):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030387
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiashu, Wei Yang, Zesheng Ying, Ping Yang, Yuting Liang, Chen Liang, Baojin Shang, Hong Zhang, Yingjie Cai, Xiaojiao Peng, and et al. 2025. "Application of Radiomics in Predicting the Prognosis of Medulloblastoma in Children" Children 12, no. 3: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030387
APA StyleChen, J., Yang, W., Ying, Z., Yang, P., Liang, Y., Liang, C., Shang, B., Zhang, H., Cai, Y., Peng, X., Sun, H., Ma, W., & Ge, M. (2025). Application of Radiomics in Predicting the Prognosis of Medulloblastoma in Children. Children, 12(3), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030387





