Clinical and Multivariate Predictors of Headaches Attributed to Rhinosinusitis in Pediatric Patients: A Comparative Study with Migraine and Tension-Type Headache
Highlights
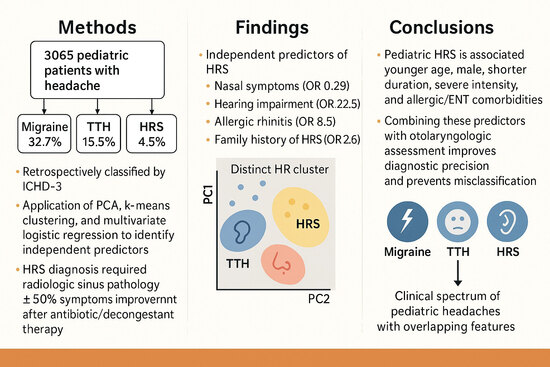
- Pediatric headache attributed to rhinosinusitis (HRS) was often misdiagnosed as migraine or tension-type headache, especially in younger children.
- Multivariate analysis identified distinct predictors of HRS, including nasal and auditory symptoms, allergic rhinitis, and family history of HRS.
- Incorporating otolaryngologic and allergic features into diagnostic evaluation can improve accuracy and reduce misclassification.
- These predictors may help clinicians avoid unnecessary neuroimaging and provide timely, targeted therapy for pediatric patients.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection and Variables
2.3. Headache Classification
2.4. Statistical and Analytical Methods
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Comparison Between HRS and Migraine
- Younger age at diagnosis (median 9 vs. 12 years, p < 0.001).
- Higher proportion of males (58.1% vs. 44.5%, p < 0.001).
- More preschool-age patients (28.5% vs. 7.1%, p < 0.001).
- Shorter headache duration (<1 h: 41.6% vs. 12.8%, p < 0.001).
- Fewer sensory symptoms such as photophobia and phonophobia, but more nasal and auditory symptoms (p < 0.001).
3.3. Comparison Between HRS and TTH
- Younger age at diagnosis in HRS (median 9 vs. 11 years, p < 0.001).
- Higher proportion of males (58.1% vs. 48.9%, p < 0.001).
- More preschool-age patients and fewer adolescents (p < 0.001).
- Greater headache intensity and more nasal/auditory symptoms (p < 0.001).
- Less frequent fatigue as a trigger (p = 0.045).
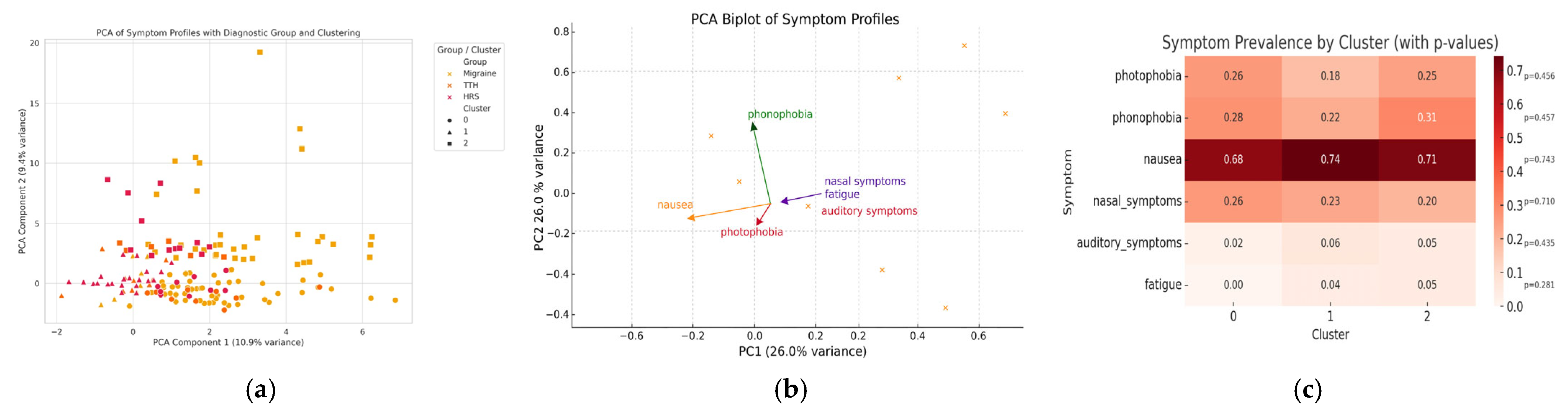
3.4. Symptom Profiling and Cluster Analysis
3.5. Supplementary Table S1: Three-Group Comparison
3.6. Multivariate Predictors of HRS
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.2. HRS Versus Primary Headaches: Shared and Distinguishing Features
4.3. Clinical Implications and Application of Predictors
4.4. Integration with Existing Literature
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HRS | Headache attributed to rhinosinusitis |
| TTH | Tension-type headache |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CL | Confidence interval |
| PC | Principal component |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristics |
| ICHD | International classification of headache disorders |
| IRB | Institutional review board |
References
- Mehle, M.E. What Do We Know about Rhinogenic Headache? The otolaryngologist’s challenge. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 47, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.; Ashwal, S.; Dahl, G.; Dorbad, D.; Hirtz, D.; Prensky, A.; Jarjour, I. Practice Parameter: Evaluation of Children and Adolescents with Recurrent Headaches: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2002, 59, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseh, K.; Makusidi, M. Rhinosinusitis: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Pattern and Outcome in North Western Nigeria. Ann. Afr. Med. 2010, 9, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenbil, N.; Gurer, Y.K.; Arslan, D.; Barlas, O.; Deda, G. Sinusitis in Children and Adolescents with Chronic or Recurrent Headache: A Case–Control Study. J. Headache Pain 2008, 9, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Gu, M. The Role of the Otolaryngologist in the Evaluation and Management of Headaches. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Arafeh, I.; Razak, S.; Sivaraman, B.; Graham, C. Prevalence of Headache and Migraine in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2010, 52, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, C.P.; Hutchinson, S.; Webster, C.J.; Ames, M.; Richardson, M.S.; Powers, C. Prevalence of Migraine in Patients with a History of Self-Reported or Physician-Diagnosed “Sinus” Headache. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onofri, A.; Chisari, C.; Martelletti, P. Primary Headache Epidemiology in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, Z.M.; Setzen, M.; Poetker, D.M.; DelGaudio, J.M. “Sinus Headache”: Rhinogenic Headache or Migraine? An Evidence-Based Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eross, E.; Dodick, D.; Eross, M. The Sinus, Allergy and Migraine Study (SAMS). Headache 2007, 47, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, C.E.; Silberstein, S.D. Headache and Rhinosinusitis: A Review. Cephalalgia 2021, 41, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C.; Adappa, N.D.; Palmer, J.N.; Kennedy, D.W.; Chiu, A.G. Rhinogenic Headache in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients: An Evidence-Based Review. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Liu, S.; Tao, F. Current Trends in Pediatric Migraine: Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini, B.; Arruda, M.; Cescut, A.; Saulle, C.; Persico, A.; Carotenuto, M.; Gatta, M.; Nacinovich, R.; Piazza, F.; Termine, C. Headache and Comorbidity in Children and Adolescents. J. Headache Pain 2013, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, K.; Irwin, S.L.; Gelfand, A.A. Pediatric Migraine: An Update. Neurol. Clin. 2019, 37, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.S. Sinus Headaches: Avoiding Over- and Mis-Diagnosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, A.H.; Kjaergaard, A.D.; Hansen, T.F.; Olesen, J. The Chronobiology of Migraine: A Systematic Review. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alstadhaug, K.; Salvesen, R.; Bekkelund, S. Seasonal Variation in Migraine. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriani, S.; Fiumana, E.; Manfredini, R.; Boari, B.; Scalas, C.; Battistella, P.A. Circadian and Seasonal Variation of Migraine Attacks in Children. Headache 2006, 46, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.J.; Lin, C.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Hsieh, Y.L.; Lin, Y.C. A Comparison of Clinical Features of Youth with and without Rhinitis Signs and Symptoms Who Are Hospitalized for Headache. Children 2022, 9, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner-Herwig, B.; Gassmann, J. Headache Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Their Association with Psychological, Behavioral, and Socio-Environmental Factors. Headache 2012, 52, 1387–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigal, M.E.; Lipton, R.B. The Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Daily Headaches: An Algorithm-Based Approach. J. Headache Pain 2007, 8, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robblee, J.; Secora, K.A. Debunking Myths: Sinus Headache. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, A. Clinical Study of Headache in Relation to Sinusitis and Its Management. J. Med. Life 2013, 6, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, E.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, J.Y. Headache Attributed to Rhinosinusitis in Pediatric Patients: Clinical Insights and Diagnostic Implications. Transl. Pediatr. 2025, 14, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Patawari, P.; Iftikhar, H.M.; Shimmi, S.C.; Hussain, S.S.; Sein, M.M. Acute and chronic rhinosinusitis: Pathophysiology and treatment. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cady, R.K.; Schreiber, C.P. Sinus Headache or Migraine? Considerations in Making a Differential Diagnosis. Neurology 2002, 58, S10–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loder, E.; Weizenbaum, E.; Giddon, D. Migraine Pain Location and Measures of Healthcare Use and Distress: An Observational Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 6157982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brna, P.M.; Dooley, J.M. Headaches in the Pediatric Population. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2006, 13, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, H.H.; Chaiban, R.; Makary, C. Pediatric Rhinosinusitis. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 69, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlı, N.; Akyol, A.; Uçler, S.; Baykan, B.; Zarifoğlu, M.; Siva, A.; Saip, S.; Ertaş, M.; Oğuz, H.; Özge, A. Clinical Characteristics of Tension-Type Headache and Migraine in Adolescents: A Student-Based Study. Headache 2006, 46, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl. S29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godley, F.A.; O’Brien, E.K.; Orlandi, R.R.; Smith, T.L.; Soler, Z.M. Update on the Diagnostic Considerations for Neurogenic Nasal and Sinus Symptoms: A Current Review Suggests Adding a Possible Diagnosis of Migraine. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Kalle, T.; Kaiser, W.A.; Mentzel, H.J. Incidental Findings in Paranasal Sinuses and Mastoid Cells: A Cross-Sectional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Study in a Pediatric Radiology Department. RoFo 2012, 184, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.T.; Spector, S.; Hsu, J.; Baroody, F.M.; Chandra, R.K.; Grammer, L.C.; Kennedy, D.W.; Cohen, N.A.; Kaliner, M.A.; Wald, E.R.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Rhinosinusitis: A Practice Parameter Update. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 113, 347–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, D.J.; Rosenfeld, R.M. Quality of Life for Children with Persistent Sinonasal Symptoms. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 128, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, R.M.; Smith, T.L.; Rudmik, L.; Mace, J.C.; Smith, S.B.; Schlosser, R.J.; Soler, Z.M. Primary Care and Upfront Computed Tomography Scanning in the Diagnosis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Cost-Based Decision Analysis. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Cho, S.J.; Chu, M.K. Analysis of Trigger Factors in Episodic Migraineurs Using a Smartphone Headache Diary Application. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.J.; Jin, J.O.; Lee, K.H. Evaluation of Pediatric Migraine Triggers: A Single-Center Study. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2024, 68, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziwon, J.; Waszak, P. Seasonal Changes of Internet Searching Suggest Circannual Rhythmicity of Primary Headache Disorders. Headache 2022, 62, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglioni, V.; D’Acunto, G.; Balestri, M.; Maestri, M.; Pochiero, G.; Zamponi, N.; Bravaccio, C.; Termine, C.; Cecchini, A.P.; Sansone, M.; et al. Tension-Type Headache in Children and Adolescents. Life 2023, 13, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubberud, A.; Alstadhaug, K.B.; Sand, T. Artificial Intelligence and Headache. Cephalalgia 2024, 44, 03331024241268290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Characteristics | Migraine (n = 1140) | HRS (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male (n, %) Female (n, %) | 471 (41.3) 669 (58.7) | 118 (58.1%) 85 (41.9%) | <0.001 |
| Age (years), median (range) | 12 (2–18) | 9 (3–17) | <0.001 |
| Age at diagnosis (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Pre-school age (≤6 years) | 81 (7.1) | 39 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| Children (7–12 years) | 450 (39.5) | 78 (56.9) | <0.001 |
| Adolescent (13–18 years) | 609 (53.4) | 20 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Onset type (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Acute (≤3 months) | 221 (19.4) | 43 (31.4) | 0.002 |
| Acute recurrent (≤3 months) | 227 (19.9) | 19 (13.9) | 0.114 |
| Chronic non-progressive (>3 months) | 214 (18.8) | 50 (36.5) | <0.001 |
| Chronic progressive (>3 months) | 478 (41.9) | 25 (18.2) | <0.001 |
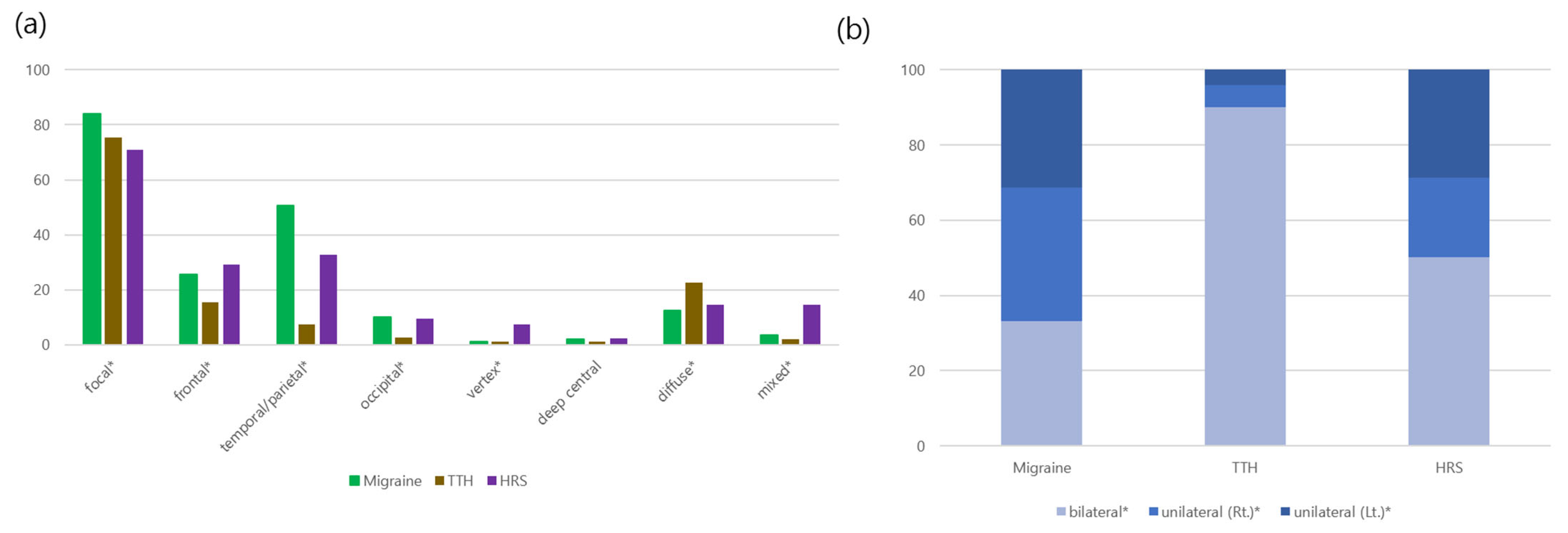
| Localization (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Diffuse | 144 (12.6) | 20 (14.6) | 0.607 |
| Localized | 956 (83.9) | 97 (70.8) | <0.001 |
| Mixed | 40 (3.5) | 20 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Duration (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| <30 min | 146 (12.8) | 38 (27.7) | <0.001 |
| 30–<60 min | 141 (12.4) | 35 (25.6) | <0.001 |
| ≥1 h | 853 (74.8) | 64 (46.7) | <0.001 |
| Frequency (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| <2/month | 131 (11.5) | 0 | <0.001 |
| 2–<4/month | 248 (21.8) | 49 (35.8) | <0.001 |
| 4–<15/month | 298 (26.2) | 50 (36.5) | 0.013 |
| ≥15/month | 161 (14.1) | 38 (27.7) | <0.001 |
| Daily | 151 (13.2) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Intensity (n, %) | 0.039 | ||
| Mild | 80 (7.0) | 18 (13.1) | 0.018 |
| Moderate | 749 (65.7) | 83 (60.6) | 0.274 |
| Severe | 311 (27.3) | 36 (26.3) | 0.883 |
| Sleep disturbance due to headache (n, %) | 158 (13.9) | 22 (16.1) | 0.569 |
| Morning headache (n, %) | 368 (32.3) | 33 (24.1) | 0.064 |
| Characteristics (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Throbbing | 727 (63.8) | 34 (24.8) | <0.001 |
| Sharp | 80 (7.0) | 9 (6.6) | 0.986 |
| Cramping | 24 (2.1) | 1 (0.7) | 0.440 |
| Prickling | 105 (9.2) | 10 (7.3) | 0.562 |
| Constant/dull | 33 (2.9) | 10 (7.3) | 0.014 |
| Pressure | 192 (16.8) | 33 (24.1) | 0.047 |
| Mixed | 34 (3.0) | 39 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| Others | 49 (4.3) | 1 (0.7) | 0.072 |
| Accompanied symptoms (n, %) | 998 (87.5) | 78 (56.9) | <0.001 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 796 (69.8) | 69 (50.4) | <0.001 |
| Abdominal pain | 66 (5.8) | 15 (11.0) | 0.031 |
| Photophobia | 266 (23.3) | 12 (8.8) | <0.001 |
| Phonophobia | 279 (24.5) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Dizziness | 394 (34.6) | 44 (32.1) | 0.653 |
| Nasal symptoms * | 21 (1.8) | 53 (38.7) | <0.001 |
| Neurologic manifestations (n, %) | 286 (25.1) | 30 (21.9) | <0.001 |
| Gait disturbance | 1 (0.09) | 2 (1.5) | 0.028 |
| Focal weakness | 33 (2.9) | 3 (2.2) | 0.843 |
| Visual disturbance | 224 (19.6) | 26 (19) | 0.942 |
| Auditory symptoms # | 10 (0.9) | 10 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| Dysarthria/aphasia | 9 (0.8) | 1 (0.7) | 1.000 |
| Dysesthesia | 38 (3.3) | 2 (2.5) | 0.352 |
| Decreased consciousness | 10 (0.9) | 2 (2.5) | 0.842 |
| Seizure | 3 (0.3) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Movement symptom † | 17 (1.5) | 4 (2.9) | 0.375 |
| Triggering factors (n, %) | 266 (23.3) | 25 (18.2) | <0.001 |
| Emotional stress | 182 (16.0) | 15 (11.0) | 0.158 |
| Hunger | 7 (0.6) | 0 | 0.759 |
| Weather | 37 (3.2) | 2 (2.5) | 0.376 |
| Fatigue | 43 (3.8) | 15 (11.0) | <0.001 |
| Exercise | 17 (1.5) | 4 (2.9) | 0.375 |
| Light | 11 (1.0) | 2 (1.5) | 0.924 |
| Noise | 8 (0.7) | 0 | 0.681 |
| Smell | 16 (1.4) | 0 | 0.323 |
| Season at diagnosis (n, %) | 0.694 | ||
| Spring | 288 (25.3) | 35 (25.6) | 1.000 |
| Summer | 365 (32.0) | 45 (32.8) | 0.921 |
| Fall | 296 (26.0) | 30 (21.9) | 0.353 |
| Winter | 191 (16.7) | 27 (19.7) | 0.454 |
| Family history of migraine (n, %) | 368 (32.3) | 9 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Family history of TTH (n, %) | 45 (3.9) | 3 (2.2) | 0.008 |
| Family history of HRS (n, %) | 12 (1.0) | 36 (26.3) | <0.001 |
| Family history of allergic rhinitis (n, %) | 23 (2.0) | 20 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Clinical Characteristics | TTH (n = 474) | HRS (n = 137) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male, (n, %) Female, (n, %) | 232 (48.9) 242 (51.1) | 118 (58.1%) 85 (41.9%) | 0.035 |
| Age (years), median (range) | 11 (3–18) | 9 (3–17) | <0.001 |
| Age at diagnosis (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Pre-school age (≤6 years) | 62 (13.1) | 39 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| Children (7–12 years) | 232 (48.9) | 78 (56.9) | 0.121 |
| Adolescent (13–18 years) | 180 (38.0) | 20 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Onset type (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Acute (≤3 months) | 65 (13.7) | 43 (31.4) | <0.001 |
| Acute recurrent (≤3 months) | 189 (39.9) | 19 (13.9) | <0.001 |
| Chronic non-progressive (>3 months) | 148 (31.2) | 50 (36.5) | 0.290 |
| Chronic progressive (>3 months) | 72 (15.2) | 25 (18.2) | 0.465 |
| Localization (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Diffuse | 107 (22.6) | 20 (14.6) | 0.056 |
| Localized | 357 (75.3) | 97 (70.8) | 0.340 |
| Mixed | 10 (2.1) | 20 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Duration (n, %) | 0.289 | ||
| <30 min | 132 (27.9) | 38 (27.7) | 1.000 |
| 30–<60 min | 93 (19.6) | 35 (25.6) | 0.167 |
| ≥1 h | 249 (52.5) | 64 (46.7) | 0.270 |
| Frequency (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| <2/month | 60 (12.7) | 0 | <0.001 |
| 2–<4/month | 96 (20.3) | 49 (35.8) | <0.001 |
| 4–<15/month | 146 (30.8) | 50 (36.5) | 0.249 |
| ≥15/month | 67 (14.1) | 38 (27.7) | <0.001 |
| Daily | 105 (22.1) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Intensity (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Mild | 175 (36.9) | 18 (13.1) | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 261 (55.1) | 83 (60.6) | 0.294 |
| Severe | 38 (8.0) | 36 (26.3) | <0.001 |
| Sleep disturbance due to headache (n, %) | 53 (11.2) | 22 (16.1) | 0.166 |
| Morning headache (n, %) | 113 (23.8) | 33 (24.1) | 1.000 |
| Characteristics (n, %) | <0.001 | ||
| Throbbing | 21 (4.4) | 34 (24.8) | <0.001 |
| Sharp | 1 (0.2) | 9 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Cramping | 3 (0.6) | 1 (0.7) | 1.000 |
| Prickling | 27 (5.7) | 10 (7.3) | 0.624 |
| Constant/dull | 83 (17.5) | 10 (7.3) | 0.005 |
| Pressure | 345 (72.8) | 33 (24.1) | <0.001 |
| Mixed | 7 (1.5) | 39 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| Others | 8 (1.7) | 1 (0.7) | 0.677 |
| Accompanied symptoms (n, %) | 168 (35.4) | 78 (56.9) | <0.001 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 22 (4.6) | 69 (50.4) | <0.001 |
| Abdominal pain | 15 (3.2) | 15 (11.0) | <0.001 |
| Photophobia | 29 (6.1) | 12 (8.8) | 0.371 |
| Phonophobia | 43 (9.1) | 0 | <0.001 |
| Dizziness | 96 (20.3) | 44 (32.1) | 0.005 |
| Nasal symptoms * | 11 (2.3) | 53 (38.7) | <0.001 |
| Neurologic manifestations (n, %) | 37 (7.8) | 30 (21.9) | <0.001 |
| Gait disturbance | 0 | 2 (1.5) | 0.074 |
| Focal weakness | 4 (0.8) | 3 (2.2) | 0.396 |
| Visual disturbance | 21 (4.4) | 26 (19) | <0.001 |
| Auditory symptoms # | 1 (0.2) | 10 (7.3) | <0.001 |
| Dysarthria/aphasia | 0 | 1 (0.7) | 0.508 |
| Dysesthesia | 2 (0.4) | 2 (1.5) | 0.468 |
| Decreased consciousness | 5 (1.1) | 2 (1.5) | 1.000 |
| Seizure | 1 (0.2) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Movement symptom † | 3 (0.6) | 4 (2.9) | 0.078 |
| Triggering factors (n, %) | 109 (23) | 25 (18.2) | <0.001 |
| Emotional stress | 79 (16.6) | 15 (11.0) | 0.134 |
| Hunger | 0 | 0 | - |
| Weather | 15 (3.2) | 2 (2.5) | 0.439 |
| Fatigue | 24 (5.1) | 15 (11.0) | 0.022 |
| Exercise | 8 (1.7) | 4 (2.9) | 0.572 |
| Light | 0 | 2 (1.5) | 0.074 |
| Noise | 2 (0.4) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Smell | 8 (1.7) | 0 | 0.270 |
| Season at diagnosis (n, %) | 0.458 | ||
| Spring | 107 (22.6) | 35 (25.6) | 0.541 |
| Summer | 133 (28.0) | 45 (32.8) | 0.327 |
| Fall | 125 (26.4) | 30 (21.9) | 0.343 |
| Winger | 109 (23.0) | 27 (19.7) | 0.485 |
| Family history of migraine (n, %) | 30 (6.8) | 9 (6.6) | 1.000 |
| Family history of TTH (n, %) | 114 (24.1) | 3 (2.2) | <0.001 |
| Family history of HRS (n, %) | 5 (1.1) | 36 (26.3) | <0.001 |
| Family history of allergic rhinitis (n, %) | 6 (1.3) | 20 (14.6) | <0.001 |
| Factors | OR | 95% Cl | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 0.567 | 0.334–0.963 | 0.036 |
| Age | 0.71 | 0.522–0.967 | 0.030 |
| Location | 1.57 | 0.794–3.102 | 0.194 |
| Duration | 0.62 | 0.484–0.793 | <0.001 |
| Frequency | 1.217 | 0.988–1.499 | 0.065 |
| Intensity | 2.165 | 1.380–3.397 | 0.001 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 1.046 | 0.609–1.796 | 0.870 |
| Photophobia | 0.412 | 0.145–1.172 | 0.097 |
| Phonophobia | 0.398 | 0.123–1.165 | 0.998 |
| Nasal symptoms | 9.836 | 4.548–21.273 | <0.001 |
| Auditory symptoms | 22.52 | 7.153–70.989 | <0.001 |
| Fatigue | 3.935 | 1.715–9.029 | 0.001 |
| Family history of HRS | 32.602 | 14.312–74.265 | <0.001 |
| Family history of allergic rhinitis | 8.468 | 3.484–20.582 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.B.; Park, E.G.; Han, J.Y. Clinical and Multivariate Predictors of Headaches Attributed to Rhinosinusitis in Pediatric Patients: A Comparative Study with Migraine and Tension-Type Headache. Children 2025, 12, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111557
Han SB, Park EG, Han JY. Clinical and Multivariate Predictors of Headaches Attributed to Rhinosinusitis in Pediatric Patients: A Comparative Study with Migraine and Tension-Type Headache. Children. 2025; 12(11):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111557
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Seung Beom, Eu Gene Park, and Ji Yoon Han. 2025. "Clinical and Multivariate Predictors of Headaches Attributed to Rhinosinusitis in Pediatric Patients: A Comparative Study with Migraine and Tension-Type Headache" Children 12, no. 11: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111557
APA StyleHan, S. B., Park, E. G., & Han, J. Y. (2025). Clinical and Multivariate Predictors of Headaches Attributed to Rhinosinusitis in Pediatric Patients: A Comparative Study with Migraine and Tension-Type Headache. Children, 12(11), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12111557