Nutritional Status in Pediatric Psoriasis: A Case–Control Study in a Tertiary Care Referral Centre
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Groups Characteristics
3.2. BMI-Psoriasis vs. Controls
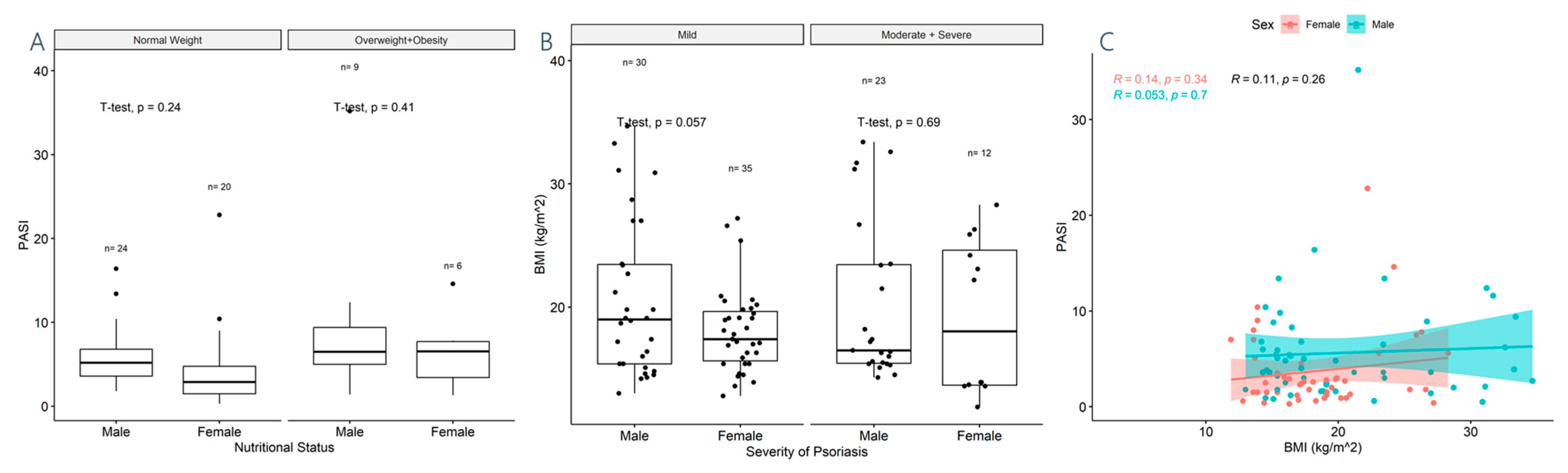
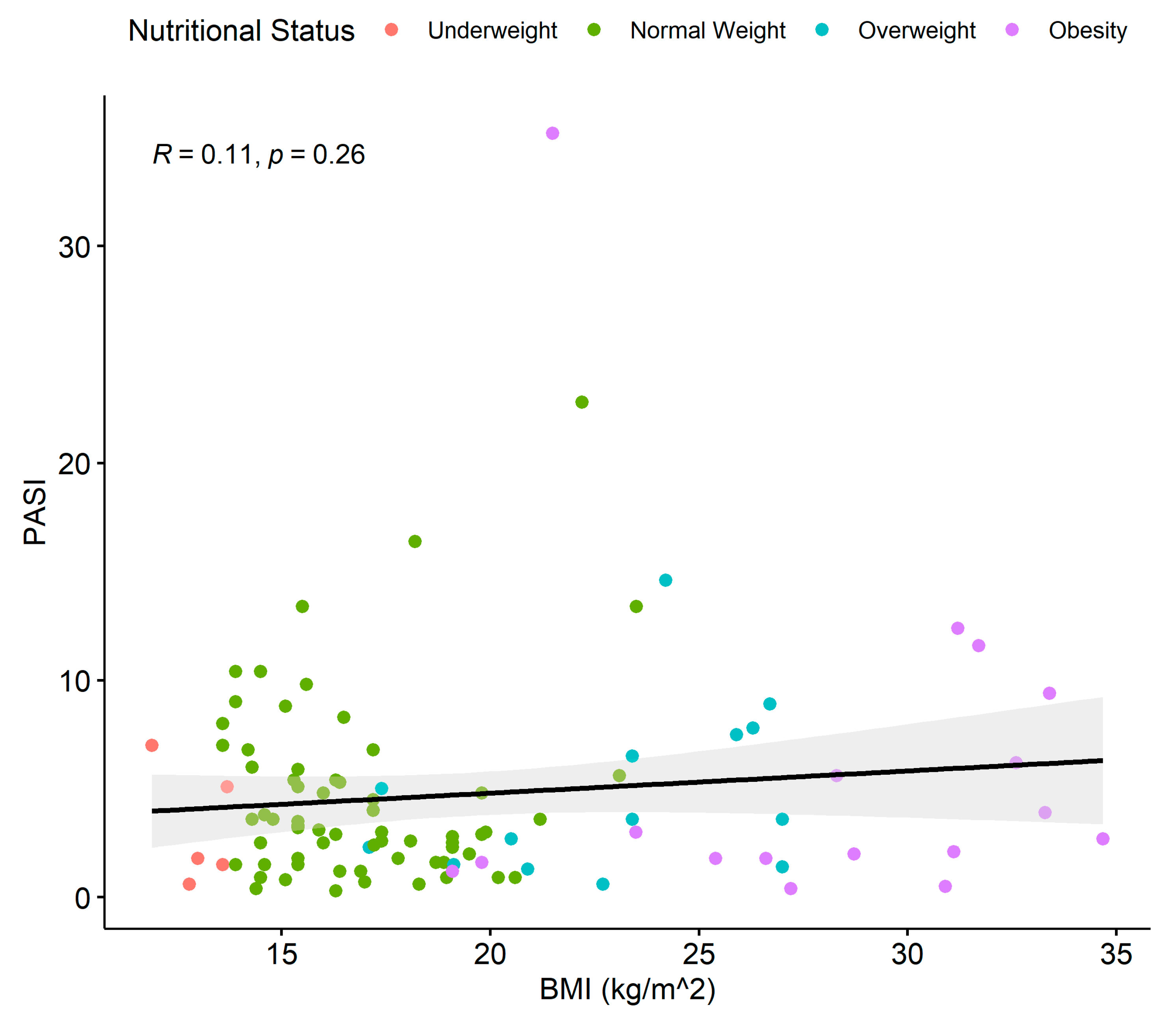
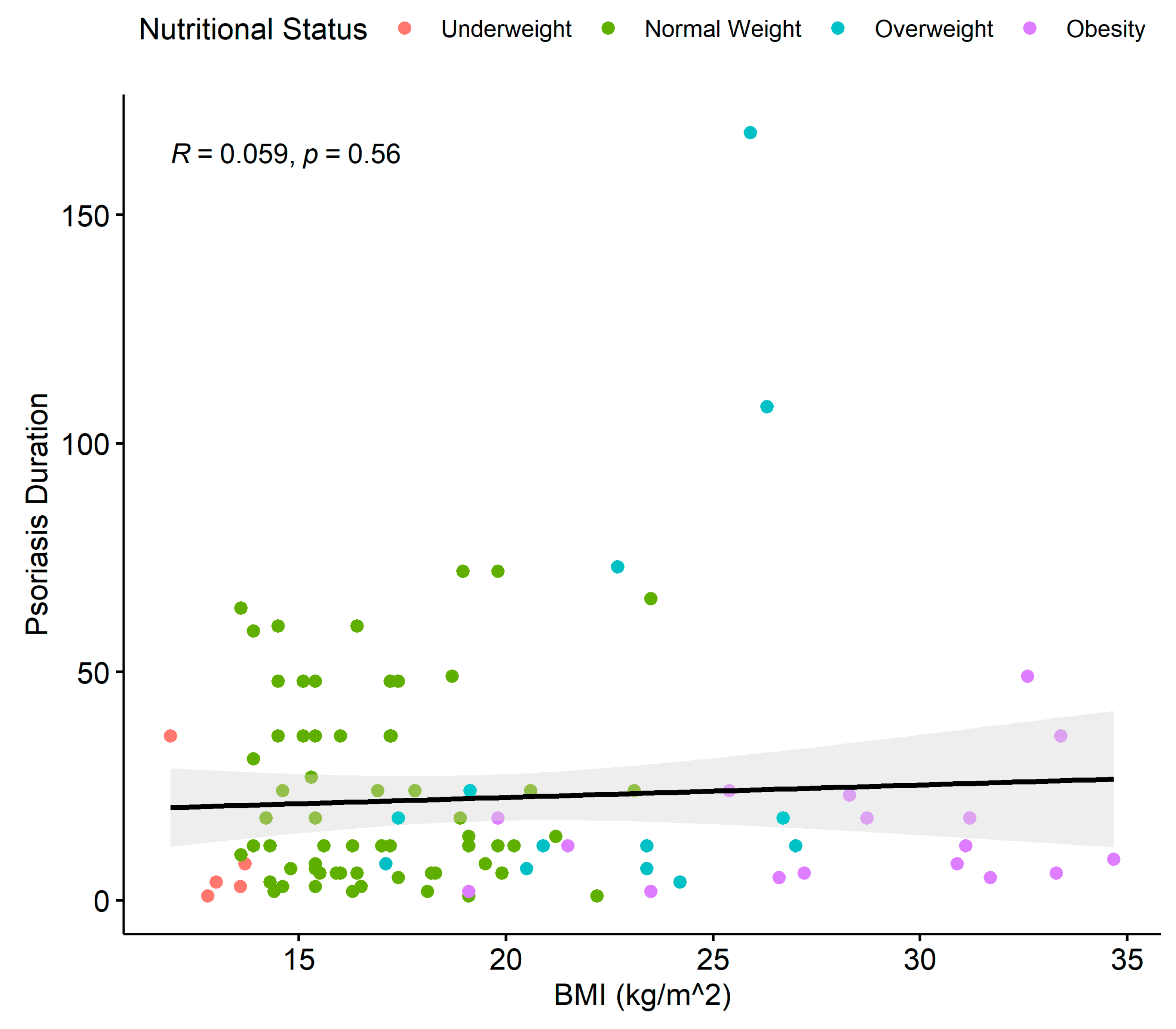
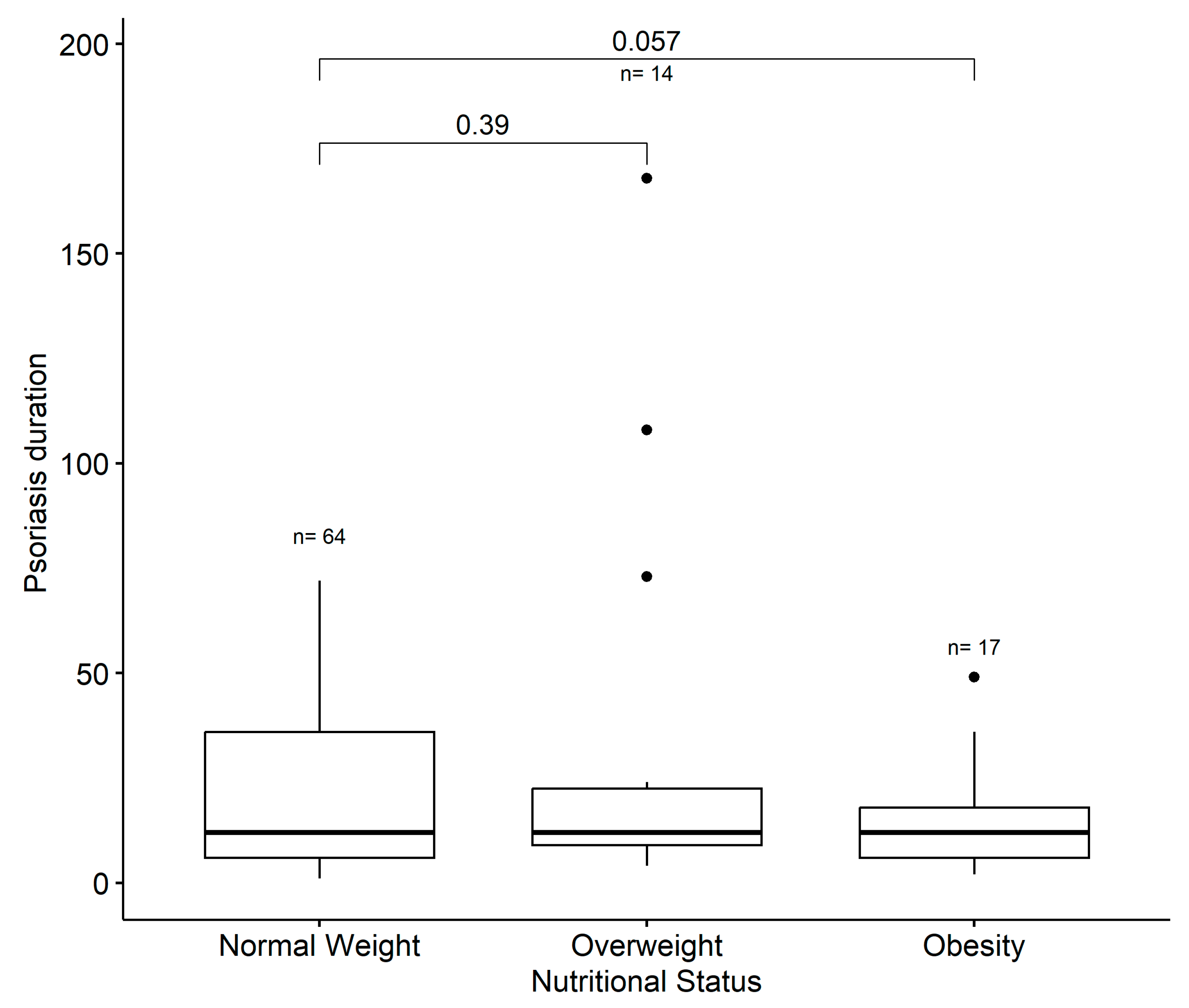
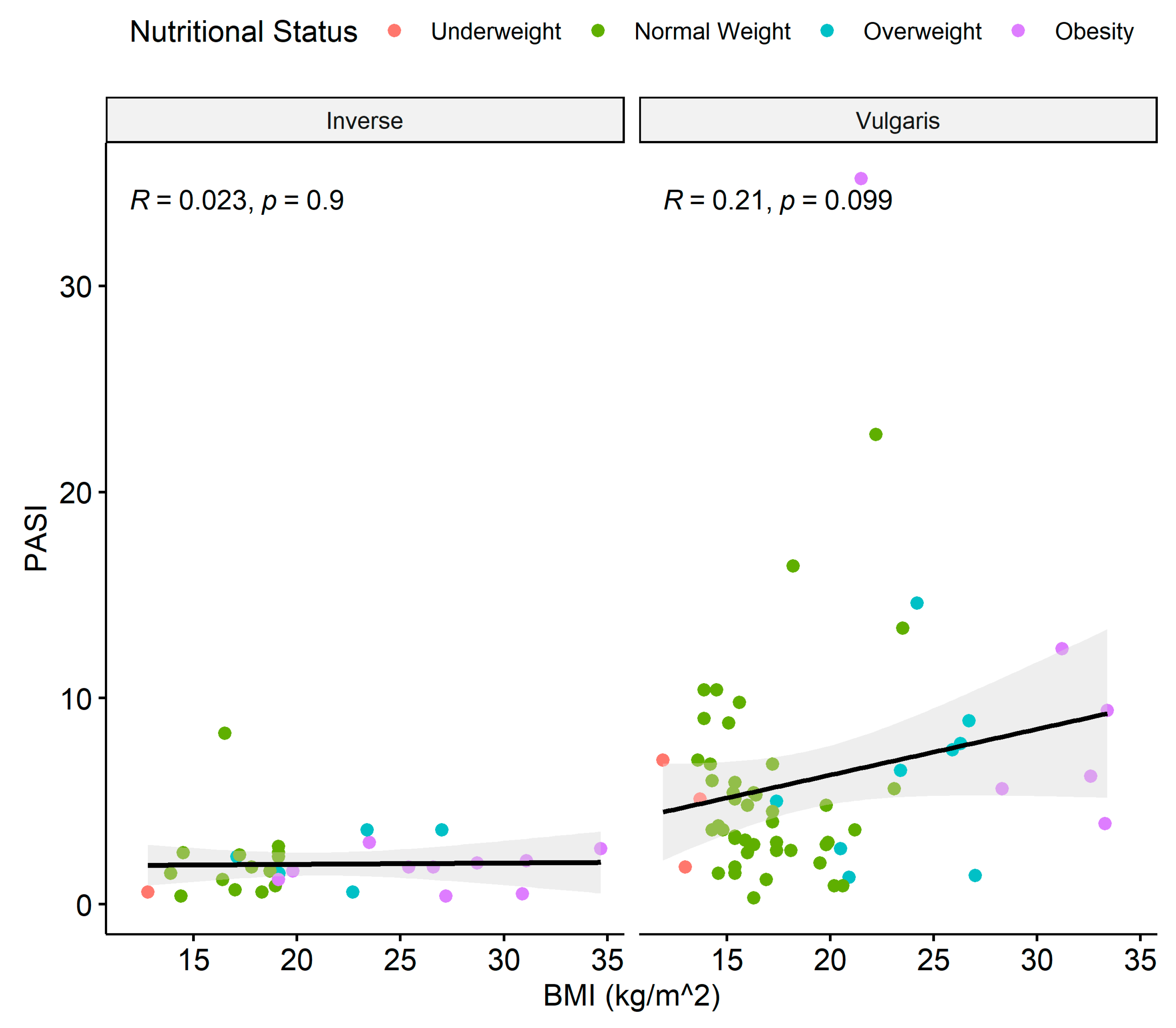
3.3. Association between BMI, PASI, Psoriasis Duration, and DLQI
3.4. BMI–Psoriasis Types Association
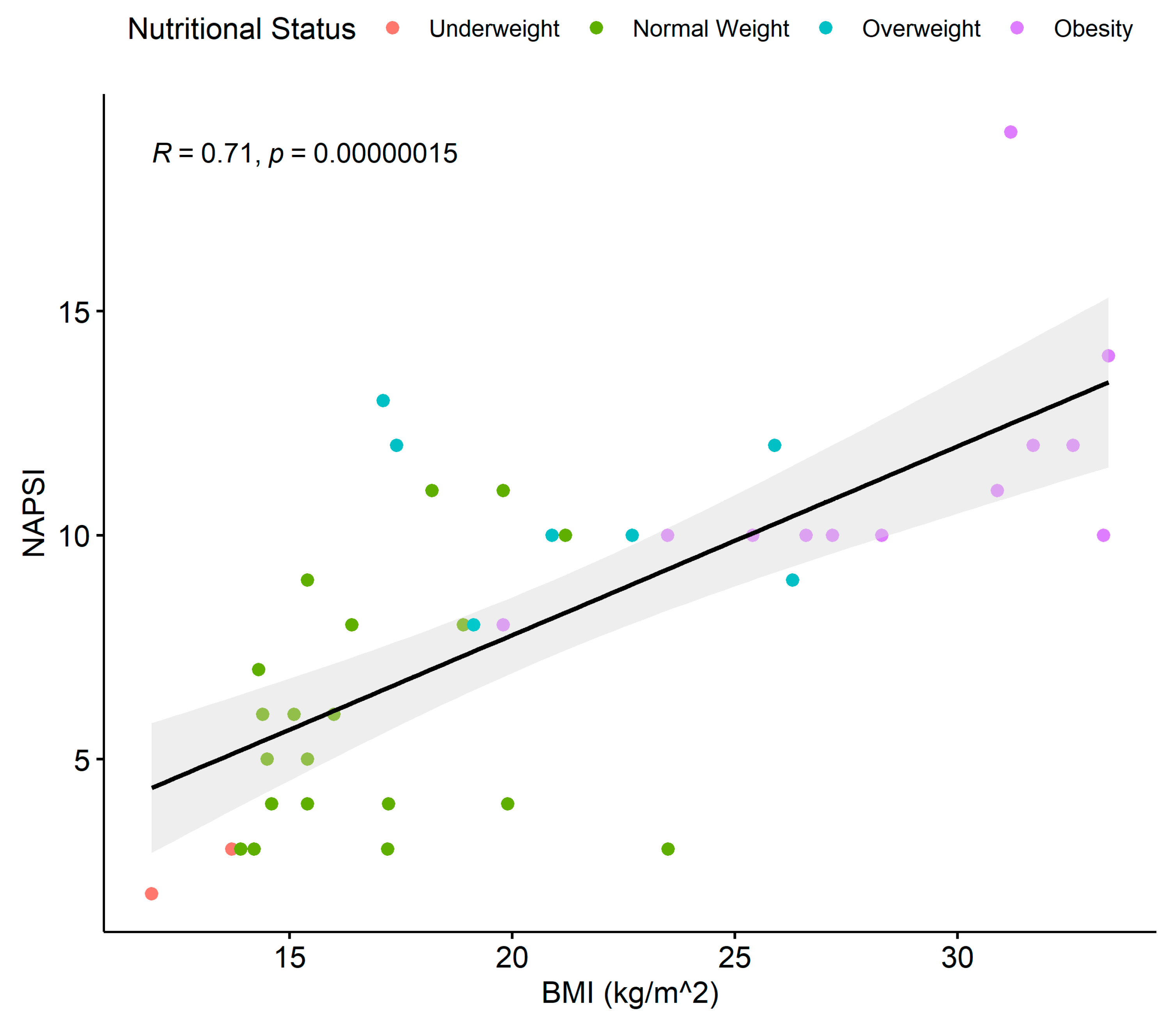
3.5. BMI–NAPSI Correlation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bronckers, I.M.G.J.; Paller, A.S.; van Geel, M.J.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.M.; Seyger, M.M.B. Psoriasis in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Management and Comorbidities. Pediatr. Drugs 2015, 17, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, C. Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: From keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, J.; Grewal, S.; Langan, S.M.; Mehta, N.N.; Ogdie, A.; Van Voorhees, A.S.; Gelfand, J.M. Psoriasis and comorbid diseases: Epidemiology. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovitwanichkanont, T.; Chong, A.H.; Foley, P. Beyond skin deep: Addressing comorbidities in psoriasis. Med. J. Aust. 2020, 212, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.; Skov, L. Psoriasis and Obesity. Dermatology 2016, 232, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaoui, A.; Tounian, P.; Mahé, E. Psoriasis and metabolic and cardiovascular comorbidities in children: A systematic review. Arch. Pediatr. 2019, 26, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaher, S.A.; Alyassiry, F. Screening for Comorbid Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Pediatric Psoriasis Among Iraqi Patients: A Case-Control Study. Cureus 2021, 13, e18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Smith, S.D.; Hong, E.; Garnett, S.; Fischer, G. Association Between Pediatric Psoriasis and Waist-to-Height Ratio in the Absence of Obesity: A Multicenter Australian Study. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Mercy, K.; Kwasny, M.J.; Choon, S.E.; Cordoro, K.M.; Girolomoni, G.; Menter, A.; Tom, W.L.; Mahoney, A.M.; Oostveen, A.M.; et al. Association of pediatric psoriasis severity with excess and central adiposity: An international cross-sectional study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Spain, S.L.; Knight, J.; Ellinghaus, E.; Stuart, P.E.; Capon, F.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Tejasvi, T.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; et al. Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisondi, P.; Fostini, A.C.; Fossà, I.; Girolomoni, G.; Targher, G. Psoriasis and the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakostelska, Z.; Málková, J.; Klimešová, K.; Rossmann, P.; Hornová, M.; Novosádová, I.; Stehlíková, Z.; Kostovcikova, M.; Hudcovic, T.; Štepánková, R.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Promotes Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation by Enhancing Th17 Response. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Boehncke, S.; Tobin, A.-M.; Kirby, B. The ‘psoriatic march’: A concept of how severe psoriasis may drive cardiovascular comorbidity. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M.; Kadono, T. “Inflammatory skin march” in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Soto, S.A.; Silva-Quintero, L.A.; Rojas-Zuleta, W.G. Psoriatic march: A view from pathophysiology to cardiovascular risk. Rev. Colomb. De Reumatol. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 31, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, A.; Khan, G. Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)-a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1994, 19, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevention CfDCa. BMI Percentile Calculator for Child and Teen: CDC. 2023. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/bmi/calculator.html (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Ped(z) Pediatric Calculator. Available online: https://pedz.de/de/pedz/bmi.html (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Radtke, M.A.; Langenbruch, A.K.; Schafer, I.; Herberger, K.; Reich, K.; Augustin, M. Nail psoriasis as a severity indicator: Results from the PsoReal study. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2010, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schons, K.R.R.; Knob, C.F.; Murussi, N.; Beber, A.A.C.; Neumaier, W.; Monticielo, O.A. Nail psoriasis: A review of the literature. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2014, 89, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, F.; Zhang, Z.; He, F.; Tu, J.; Yin, Z.; Xia, J.; Lu, Y.; Yin, Z. Dermoscopic features of nail psoriasis: Positive correlation with the severity of psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2021, 48, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, K.; Duan, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F. A Comparison of Clinical Characteristics in Overweight/Obese and Normal Weight Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris: A Bicentric Retrospective Observational Study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, B.M.; Berry, D.C. The regulation of adipose tissue health by estrogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 889923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmets, C.A.; Leonardi, C.L.; Davis, D.M.; Gelfand, J.M.; Lichten, J.; Mehta, N.N.; Armstrong, A.W.; Connor, C.; Cordoro, K.M.; Elewski, B.E.; et al. Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1073–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryld, L.; Sørensen, T.; Andersen, K.; Jemec, G.; Baker, J. high body mass index in adolescent girls precedes psoriasis hospitalization. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2010, 90, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidolin, L.; Borin, M.; Fontana, E.; Caroppo, F.; Piaserico, S.; Fortina, A. Central Obesity in Children with Psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2018, 98, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahé, E.; Beauchet, A.; Bodemer, C.; Phan, A.; Bursztejn, A.-C.; Boralevi, F.; Souillet, A.-L.; Chiaverini, C.; Bourrat, E.; Miquel, J.; et al. Psoriasis and obesity in French children: A case-control, multicentre study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunjan, M.K.; Kremers, H.M.; Lohse, C.; Tollefson, M. Association between obesity and pediatric psoriasis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, e304–e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.-C.; Goldminz, A.M.; Loo, D.S.; Dumont, N.; Levine, D.; Volf, E.; Michelon, M.; Wang, A.; Kim, N.; Yaniv, S.; et al. Association between pediatric psoriasis and the metabolic syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 1012–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Raimondo, A.; Lembo, S.; Fausti, F.; Dini, V.; Costanzo, A.; Monfrecola, G.; Balato, N.; Ayala, F.; Romanelli, M.; et al. Crosstalk between skin inflammation and adipose tissue-derived products: Pathogenic evidence linking psoriasis to increased adiposity. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cerdeira, C.; Cordeiro-Rodríguez, M.; Carnero-Gregorio, M.; López-Barcenas, A.; Martínez-Herrera, E.; Fabbrocini, G.; Sinani, A.; Arenas-Guzmán, R.; González-Cespón, J.L. Biomarkers of Inflammation in Obesity-Psoriatic Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, G.; Duran, P.; Vera, I.; Bermúdez, V. Exploring the Links between Obesity and Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Zhao, P.; Wu, C.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zeng, N.; Ding, Y. Casual association between childhood body mass index and risk of psoriasis: A Mendelian randomization study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 3491–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Zou, S.; Zhou, P.; Hu, Y.-W.; Zhao, Q.-X.; Gu, L.-N.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Metabolic Syndrome and Psoriasis: Mechanisms and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polic, M.V.; Miskulin, M.; Smolic, M.; Kralik, K.; Miskulin, I.; Berkovic, M.C.; Curcic, I.B. Psoriasis Severity—A Risk Factor of Insulin Resistance Independent of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnecka, A.; Purzycka-Bohdan, D.; Zabłotna, M.; Bohdan, M.; Nowicki, R.J.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A. Considerations of the Genetic Background of Obesity among Patients with Psoriasis. Genes 2023, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, H.A. Effects of Weight Loss on Psoriasis: A Review of Clinical Trials. Cureus 2018, 10, e3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglio, C.; Peltonen, M.; Rudin, A.; Carlsson, L.M. Bariatric Surgery and the Incidence of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. Obesity 2017, 25, 2068–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higa-Sansone, G.; Szomstein, S.; Soto, F.; Brasecsco, O.; Cohen, C.; Rosenthal, R.J. Psoriasis remission after laparoscopic roux-en-y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes. Surg. 2004, 14, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes Ettinger, J.E.; Azaro, E.; de Souza, C.A.; dos Santos Filho, P.V.; Mello, C.A.; Neves, M., Jr.; de Amaral, P.C.G.; Fahel, E. Remission of psoriasis after open gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Controls (Non-Psoriasis) (N = 100) | Cases (Psoriasis) (N = 100) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.99 | ||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 10.2 (4.43) [43.5%] | 10.2 (4.43) [43.5%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 10.0 [1.00, 17.0] | 10.0 [1.00, 17.0] | |
| Weight (kg) | 0.57 | ||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 38.7 (19.2) [49.5%] | 41.9 (23.2) [55.3%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 31.4 [10.5, 100] | 33.5 [8.50, 106] | |
| Sex | 0.99 | ||
| Female | 47 (47.0%) | 47 (47.0%) | |
| Male | 53 (53.0%) | 53 (53.0%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.68 | ||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 18.4 (3.95) [21.4%] | 19.4 (5.52) [28.4%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 17.7 [13.7, 40.1] | 17.4 [11.9, 34.7] | |
| Nutritional Status | <0.001 | ||
| Underweight | 0 (0%) | 5 (5.0%) | |
| Normal Weight | 95 (95.0%) | 64 (64.0%) | |
| Overweight | 3 (3.0%) | 14 (14.0%) | |
| Obesity | 2 (2.0%) | 17 (17.0%) | |
| Age Group | >0.99 | ||
| Toddler (1 ≤ 2 years) | 1 (1.0%) | 1 (1.0%) | |
| Early childhood (2 ≤ 6 years) | 18 (18.0%) | 18 (18.0%) | |
| Middle childhood (6 ≤ 12 years) | 41 (41.0%) | 41 (41.0%) | |
| Adolescents (12–17 years) | 40 (40.0%) | 40 (40.0%) | |
| Nail involvement | NA | ||
| No | 100 (100%) | 58 (58.0%) | |
| Yes | 0 (0%) | 42 (42.0%) |
| Mild (N = 65) | Moderate (N = 25) | Severe (N = 10) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.41 | |||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 10.4 (4.37) [42.1%] | 9.28 (4.34) [46.7%] | 11.2 (5.22) [46.6%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 10.0 [1.00, 17.0] | 8.00 [4.00, 17.0] | 13.5 [3.00, 17.0] | |
| Weight (kg) | 0.19 | |||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 41.5 (22.2) [53.5%] | 38.1 (22.8) [59.9%] | 53.6 (28.4) [52.9%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 38.0 [8.50, 105] | 25.0 [16.0, 84.0] | 53.4 [21.6, 106] | |
| Sex | 0.18 | |||
| Female | 35 (53.8%) | 9 (36.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | |
| Male | 30 (46.2%) | 16 (64.0%) | 7 (70.0%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.25 | |||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 19.3 (5.03) [26.1%] | 19.0 (6.38) [33.5%] | 21.6 (6.35) [29.4%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 18.1 [12.8, 34.7] | 16.3 [11.9, 33.4] | 21.9 [13.9, 31.7] | |
| Nutritional Status | 0.79 | |||
| Underweight | 3 (4.6%) | 2 (8.0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Normal Weight | 43 (66.2%) | 15 (60.0%) | 6 (60.0%) | |
| Overweight | 8 (12.3%) | 5 (20.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | |
| Obesity | 11 (16.9%) | 3 (12.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | |
| Age Group | 0.11 | |||
| Toddler (1 -< 2 years) | 1 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Early childhood (2 -< 6 years) | 8 (12.3%) | 7 (28.0%) | 3 (30.0%) | |
| Middle childhood (6 -< 12 years) | 29 (44.6%) | 11 (44.0%) | 1 (10.0%) | |
| Adolescents (12–17 years) | 27 (41.5%) | 7 (28.0%) | 6 (60.0%) | |
| Nail involvement | 0.27 | |||
| No | 41 (63.1%) | 11 (44.0%) | 6 (60.0%) | |
| Yes | 24 (36.9%) | 14 (56.0%) | 4 (40.0%) | |
| PASI Score | <0.001 | |||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 2.18 (1.17) [53.4%] | 6.89 (1.50) [21.8%] | 16.1 (7.64) [47.6%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 2.00 [0.300, 4.80] | 6.80 [5.00, 9.80] | 13.4 [10.4, 35.2] | |
| NAPSI | 0.40 | |||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 2.82 (4.17) [148%] | 3.56 (4.55) [128%] | 4.50 (6.93) [154%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 0 [0, 13.0] | 2.00 [0, 14.0] | 0 [0, 19.0] | |
| CDLQI Score | <0.001 | |||
| Mean (SD) [CV%] | 5.35 (5.21) [97.4%] | 9.28 (7.06) [76.1%] | 12.2 (5.35) [43.9%] | |
| Median [Min, Max] | 4.00 [1.00, 25.0] | 8.00 [1.00, 28.0] | 13.5 [5.00, 20.0] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sendrea, A.-M.; Cristea, S.; Salavastru, C.M. Nutritional Status in Pediatric Psoriasis: A Case–Control Study in a Tertiary Care Referral Centre. Children 2024, 11, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070885
Sendrea A-M, Cristea S, Salavastru CM. Nutritional Status in Pediatric Psoriasis: A Case–Control Study in a Tertiary Care Referral Centre. Children. 2024; 11(7):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070885
Chicago/Turabian StyleSendrea, Adelina-Maria, Sinziana Cristea, and Carmen Maria Salavastru. 2024. "Nutritional Status in Pediatric Psoriasis: A Case–Control Study in a Tertiary Care Referral Centre" Children 11, no. 7: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070885
APA StyleSendrea, A.-M., Cristea, S., & Salavastru, C. M. (2024). Nutritional Status in Pediatric Psoriasis: A Case–Control Study in a Tertiary Care Referral Centre. Children, 11(7), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11070885







