Epidemiological Features of Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Observational Study in Shandong Province, China, 2013–2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants with Infectious Diseases
3.2. Temporal Distribution of Infectious Diseases
3.3. Age Distribution of Infectious Diseases
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Infectious Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Effect of Communicable Diseases among Children. Available online: http://samphina.com.ng/effect-communicable-diseases-children/ (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Gibney, K.B.; Hall, R. Infectious diseases in China in the post-SARS era. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017, 17, 675–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Tsugawa, Y.; Mansbach, J.M.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Hasegawa, K. Trends in Infectious Disease Hospitalizations in US Children, 2000 to 2012. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, e158–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Xue, M.; Hellerstein, S.; Cai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, J.; Blustein, J.; Liu, J.-M. Association of China’s universal two child policy with changes in births and birth related health factors: National, descriptive comparative study. BMJ 2019, 366, l4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook-2018. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2018/indexch.htm (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Simon, A.K.; Hollander, G.A.; McMichael, A. Evolution of the immune system in humans from infancy to old age. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Chen, M.M.; Wang, L.P.; Xing, Y.; Song, Y.; Zou, Z.Y.; Dong, B.; Li, Z.J.; Ma, J. Epidemiological characteristics of infectious diseases of group, A.; B and C among Chinese students’ population. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2021, 53, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, L.; Burgner, D.P.; Miller, J.E.; Song, Y.; Ren, X.; Li, Z.; Xing, Y.; Ma, J.; Sawyer, S.M.; et al. Infectious diseases in children and adolescents in China: Analysis of national surveillance data from 2008 to 2017. BMJ 2020, 369, m1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Oza, S.; Hogan, D.; Perin, J.; Rudan, I.; Lawn, J.E.; Cousens, S.; Mathers, C.; Black, R.E. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000-13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: An updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015, 385, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Pei, Z.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Xu, L.; Gao, P.; Cao, B.; Zhan, S. Incidence of community-acquired pneumonia in urban China: A national population-based study. Vaccine 2020, 38, 8362–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhi, S.A.; De Wals, P.; Grijalva, C.G.; Grimwood, K.; Grossman, R.; Ishiwada, N.; Lee, P.-I.; Nascimento-Carvalho, C.; Nohynek, H.; O’brien, K.L.; et al. The burden of childhood pneumonia in the developed world: A review of the literature. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, e119–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Feng, L.; Cao, Y.; Peng, Z.; Yu, H. Epidemiological characteristics of influenza outbreaks in China, 2005–2013. Zhong Hua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2015, 36, 705–708. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolopoulou, G.B.; Maltezou, H.C. COVID-19 in Children: Where do we Stand? Arch. Med. Res. 2022, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoldas, M.A.; Yoldas, H. Pediatric COVID-19 Disease: A Review of the Recent Literature. Pediatr. Ann. 2020, 49, e319–e325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halasa, N.B. Update on the 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2010, 22, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.J.; Brouwer, S. Scarlet fever makes a comeback. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Wu, C.; Wu, H.; Lin, J. Analysis of Epidemiological Characteristics of Notifiable Diseases Reported in Children Aged 0–14 Years from 2008 to 2017 in Zhejiang Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.Y.; Yin, C.N.; Wang, H.T.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, W.J.; Xue, F.Z.; Zhao, L.; Cao, W.-C. Infectious diseases among elderly persons: Results from a population-based observational study in Shandong province, China, 2013–2017. J. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 08010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.T.; Zhang, H.; Xue, F.Z.; Zhao, L.; Cao, W.C. Associations of air pollutants with pneumonia hospital admissions in Qingdao, China: A prospective cohort study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 27779–27787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Available online: http://english.mofcom.gov.cn/article/lawsdata/chineselaw/200211/20021100050619.shtml (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Boice, J.D., Jr.; Monson, R.R. Breast cancer in women after repeated fluoroscopic examinations of the chest. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1977, 59, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Z.; Wang, C.; Shen, C.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, G.D.; Xue, X.D.; Xu, Z.L.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, G.H. Comparison of application of Cochran-Armitage trend test and linear regression analysis for rate trend analysis in epidemiology study. Zhong Hua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2017, 38, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesterbeek, H.; Anderson, R.M.; Andreasen, V.; Bansal, S.; De Angelis, D.; Dye, C.; Eames, K.T.D.; Edmunds, W.J.; Frost, S.D.W.; Funk, S.; et al. Modeling infectious disease dynamics in the complex landscape of global health. Science 2015, 347, aaa4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Silk, B.J.; Li, W.; Fleischauer, A.T.; Xing, X.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H.; Olsen, S.J.; Cohen, A.L. Pneumonia incidence and mortality in Mainland China: Systematic review of Chinese and English literature, 1985–2008. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roomaney, R.A.; Pillay-van Wyk, V.; Awotiwon, O.F.; Dhansay, A.; Groenewald, P.; Joubert, J.D.; Nglazi, M.D.; Nicol, E.; Bradshaw, D. Epidemiology of lower respiratory infection and pneumonia in South Africa (1997–2015): A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e012154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudan, I.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Biloglav, Z.; Mulholland, K.; Campbell, H. Epidemiology and etiology of childhood pneumonia. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Leng, K.; Lu, Y.; Wen, L.; Qi, Y.; Gao, W.; Chen, H.; Bai, L.; An, X.; Sun, B.; et al. Epidemiological features and time-series analysis of influenza incidence in urban and rural areas of Shenyang, China, 2010–2018. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila-Torres, J.; Chowell, G.; Borja-Aburto, V.H.; Viboud, C.; Grajalez-Muñiz, C.; Miller, M.A. Intense seasonal A/H1N1 influenza in Mexico, winter 2013–2014. Arch. Med. Res. 2015, 46, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cheong, H.K. Increasing Number of Scarlet Fever Cases, South Korea, 2011–2016. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2018, 24, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamagni, T.; Guy, R.; Chand, M.; Henderson, K.L.; Chalker, V.; Lewis, J.; Saliba, V.; Elliot, A.J.; Smith, G.E.; Rushton, S.; et al. Resurgence of scarlet fever in England, 2014–2016: A population-based surveillance study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chan, T.C.; Yap, L.W.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W.; Qin, S.; Zhao, N.; Yu, Z.; Geng, X.; Liu, S.-L. Resurgence of scarlet fever in China: A 13-year population-based surveillance study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, M. Spatiotemporal epidemiology of scarlet fever in Jiangsu Province, China, 2005–2015. BMC Infect Dis. 2017, 17, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y. China relaxes its one-child policy. Lancet 2013, 382, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, E.; Lu, M.; Kumar, H.; Wu, J. Epidemiology, treatment and prevention of herpes zoster: A comprehensive review. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2018, 84, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, H.M., Jr.; Hoss, D.M. Herpes zoster in otherwise healthy children. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2004, 23, 451–457, quiz 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civen, R.; Chaves, S.S.; Jumaan, A.; Wu, H.; Mascola, L.; Gargiullo, P.; Seward, J.F.M. The incidence and clinical characteristics of herpes zoster among children and adolescents after implementation of varicella vaccination. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2009, 28, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, S.; Naleway, A.L.; Koppolu, P.; Baxter, R.; Belongia, E.A.; Hambidge, S.J.; Irving, S.A.; Jackson, M.L.; Klein, N.P.; Lewin, B.; et al. Incidence of Herpes Zoster among Children: 2003–2014. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20182917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Committee of PRC. National Immunization Program for Children. Immunization Procedures and Instructions. 2016. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/jkj/s3581/201701/a91fa2f3f9264cc186e1dee4b1f24084.shtml (accessed on 15 February 2024).
- Jiang, Y.; Dou, X.; Yan, C.; Wan, L.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Epidemiological characteristics and trends of notifiable infectious diseases in China from 1986 to 2016. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 020803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Ou, R.; Xiang, H.; Hu, L.; Jing, D.; Sharma, M.; Ye, M. Epidemiological Characteristics and Spatiotemporal Analysis of Mumps from 2004 to 2018 in Chongqing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, Z.F.; Yang, X.H.; Pan, W.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.H.; Zheng, N.X.; Huang, L.F.; Zhou, Y. Epidemiological and pathogenic characteristics of mumps in Fujian province, 2005–2017. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2018, 39, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittrup, D.M.; Laursen, A.C.L.; Malon, M.; Soerensen, J.K.; Hjort, J.; Buus, S.; Svensson, J.; Stensballe, L.G. Measles-mumps-rubella vaccine at 6 months of age, immunology, and childhood morbidity in a high-income setting: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jia, K.M.; Sun, R.; Hu, P.; Wang, M.H.; Zee, B.C.; Liang, W.; Chong, K.C. Epidemiological changes in measles infections in southern China between 2009 and 2016: A retrospective database analysis. BMC Infect Dis. 2020, 20, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vynnycky, E.; Knapp, J.K.; Papadopoulos, T.; Cutts, F.T.; Hachiya, M.; Miyano, S.; Reef, S.E. Estimates of the global burden of Congenital Rubella Syndrome, 1996–2019. Int. J. Infect Dis. 2023, 137, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Ma, C.; Wen, N.; Fan, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Yin, Z.; Feng, Z.; Hao, L.; Yang, W. Epidemiological profile and progress toward rubella elimination in China. 10 years after nationwide introduction of rubella vaccine. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.K.; Moss, W.J. Rubella. Lancet 2022, 399, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team. The Epidemiological Characteristics of an Outbreak of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Diseases (COVID-19)—China, 2020. China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, J.R.; Moss, P.A.H. Systematic analysis of infectious disease outcomes by age shows lowest severity in school-age children. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.L.; Klausner, J.D. The growing epidemic of sexually transmitted infections in adolescents: A neglected population. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kagawa, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Hou, S.; et al. Air pollution and children’s respiratory symptoms in six cities of Northern China. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, R.J.; Hunter, B.M.; Rudge, J.W.; Liverani, M.; Hanvoravongchai, P. Emerging infectious diseases in southeast Asia: Regional challenges to control. Lancet 2011, 377, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.X.; Hansen, A.; Hanson-Easey, S.; Cameron, S.; Xiang, J.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Weinstein, P.; Han, G.-S.; Williams, C.; et al. Infectious Diseases, Urbanization and Climate Change: Challenges in Future China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 11025–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszl, S.M.; Froelich, B.A.; Vieira, C.R.; Blackwood, A.D.; Noble, R.T. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in South America: Water, seafood and human infections. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, B.; Liu, J.; He, R. A descriptive analysis of the Spatio-temporal distribution of intestinal infectious diseases in China. BMC Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.F.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.L.; Yan, J.B. Molecular evolution of GII.P17-GII.17 norovirus associated with sporadic acute gastroenteritis cases during 2013–2018 in Zhoushan Islands, China. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Xiang, L.; Kang, L.; Miao, L.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, C. Communicable disease mortality trends and characteristics of infants in rural China, 1996–2015. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, J.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Shibuya, K.; Black, R.E.; WHO Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet 2005, 365, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
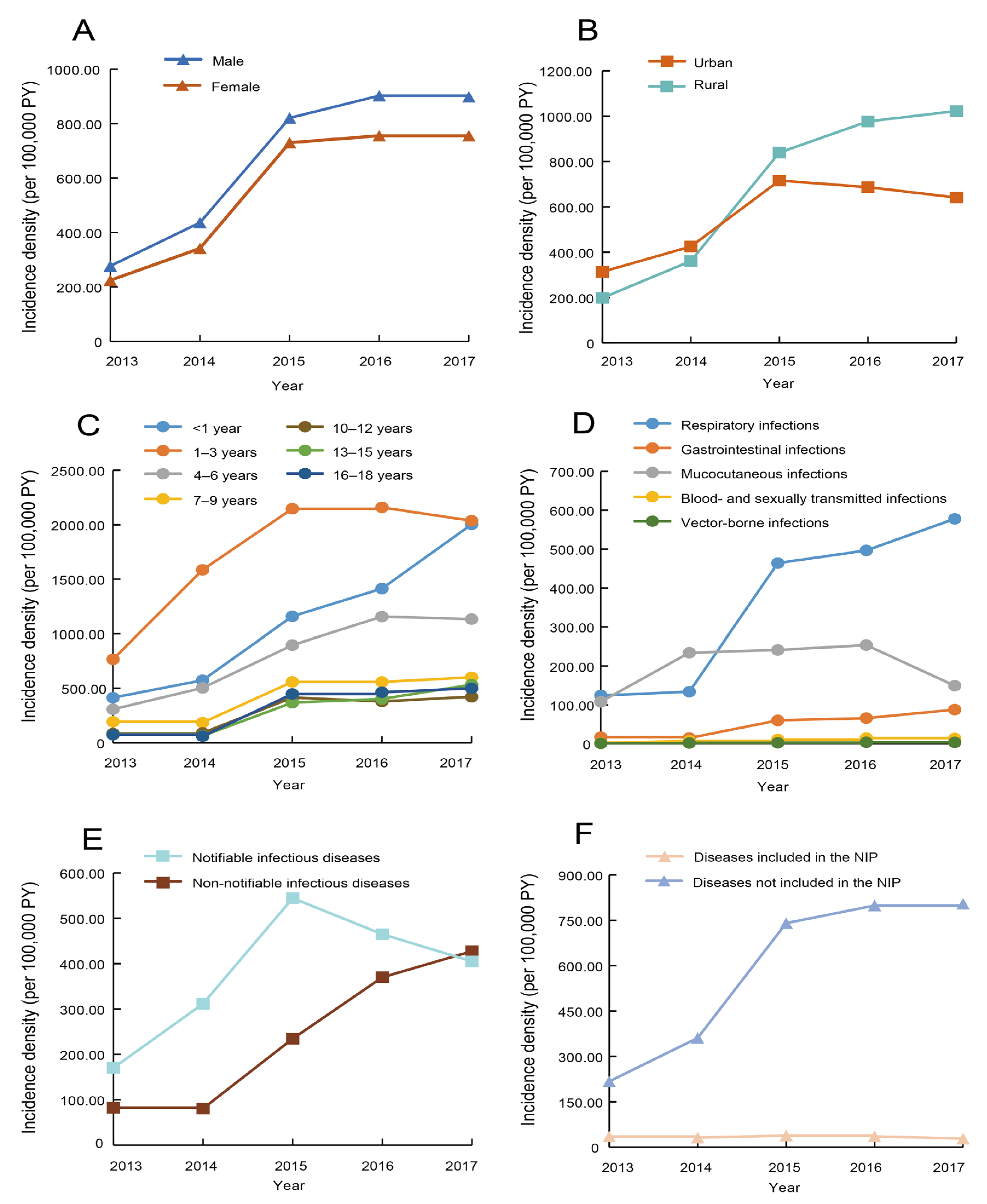

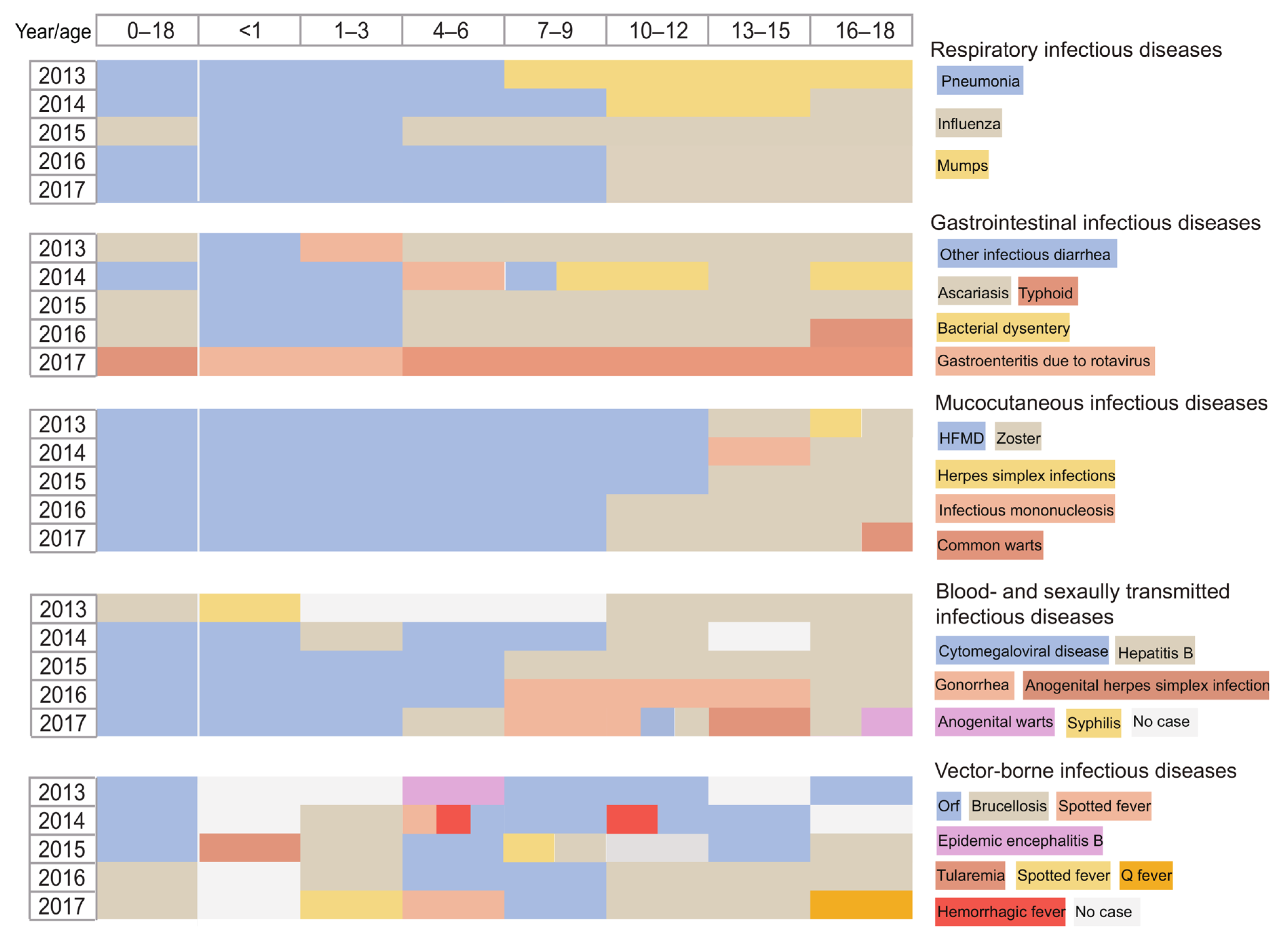
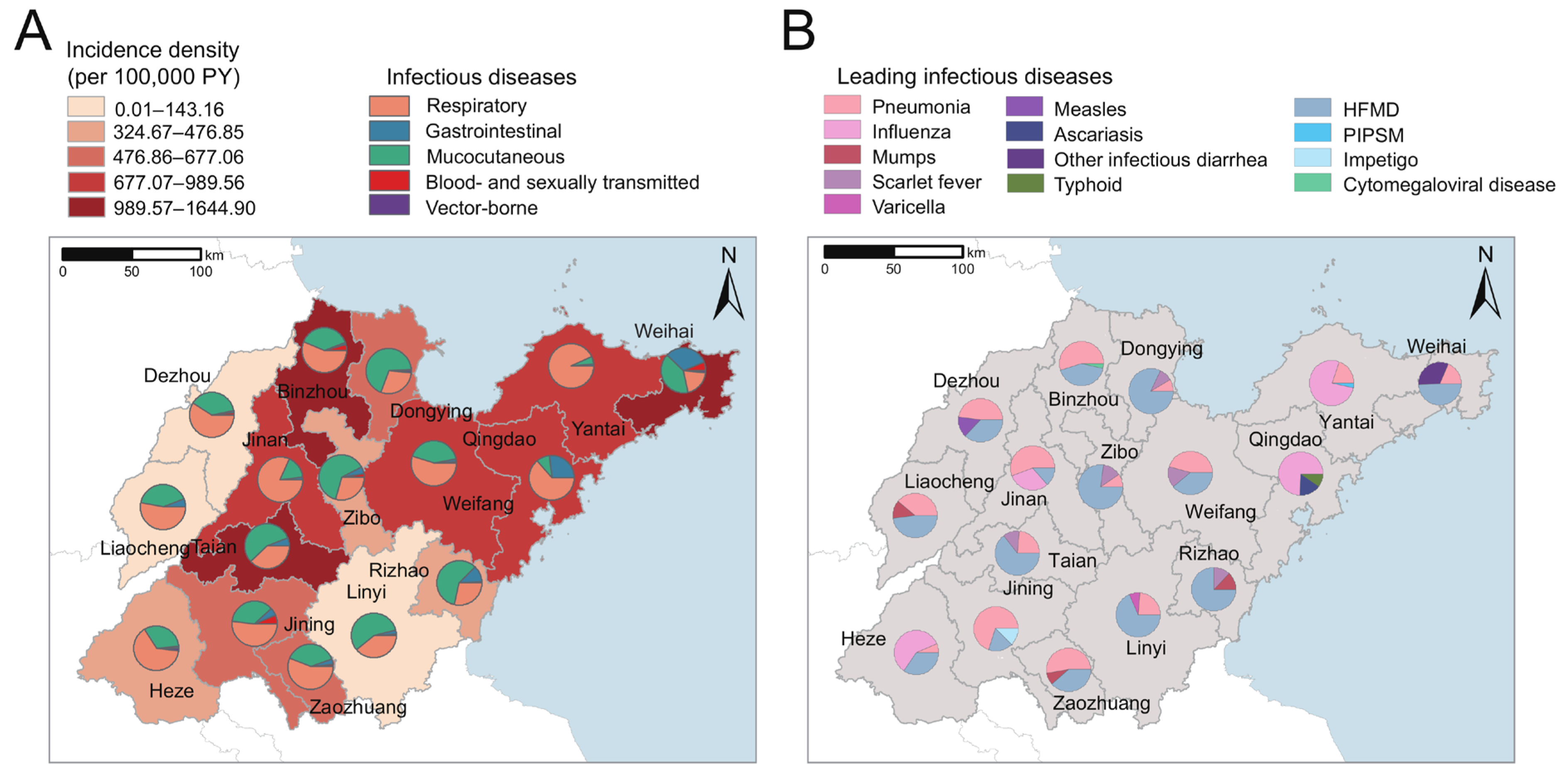
| Total (n = 18,183) | Male (n = 10,540) | Female (n = 7643) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (in years) at diagnosis, median (IQR) | 4 (2–9) | 4 (2–8) | 4 (2–9) |
| Incidence density of diseases by age group at diagnosis (per 100,000 PY) | |||
| Total (0–18) | 626.33 | 675.94 | 568.76 |
| <1 | 1015.66 | 1144.76 | 861.28 |
| 1–3 | 1771.97 | 1915.75 | 1596.53 |
| 4–6 | 779.44 | 834.47 | 713.34 |
| 7–9 | 422.02 | 428.19 | 414.76 |
| 10–12 | 287.85 | 300.21 | 273.79 |
| 13–15 | 292.49 | 306.77 | 276.62 |
| 16–18 | 318.59 | 350.37 | 283.80 |
| Incidence density of diseases by geographical region (per 100,000 PY) | |||
| Urban | 569.03 | 608.22 | 523.35 |
| Rural | 680.60 | 740.34 | 611.58 |
| Incidence density of diseases by diagnosis year (per 100,000 PY) | |||
| 2013 | 252.69 | 277.18 | 224.49 |
| 2014 | 392.45 | 436.40 | 341.69 |
| 2015 | 778.96 | 821.01 | 730.09 |
| 2016 | 834.79 | 902.77 | 755.49 |
| 2017 | 832.47 | 898.55 | 755.41 |
| Incidence density of diseases by transmission route (per 100,000 PY) | |||
| Respiratory | 358.30 | 373.95 | 340.16 |
| Gastrointestinal | 48.19 | 49.00 | 47.25 |
| Mucocutaneous | 207.19 | 239.08 | 170.19 |
| Blood-borne and sexually transmitted | 9.95 | 11.03 | 8.71 |
| Vector-borne | 2.69 | 2.89 | 2.46 |
| Incidence density of diseases by reporting type (per 100,000 PY) | |||
| Notifiable infectious diseases | 391.23 | 432.18 | 343.73 |
| Non-notifiable infectious diseases | 235.09 | 243.76 | 225.03 |
| Incidence density of diseases by whether included in the NIP (per 100,000 PY) | |||
| Infectious diseases included in the NIP | 34.38 | 41.36 | 26.27 |
| Infectious diseases not included in the NIP | 591.95 | 634.57 | 542.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Song, K.; Wang, B.; Xue, F.; Zhao, L.; Cao, W.; Cheeloo EcoHealth Consortium (CLEC). Epidemiological Features of Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Observational Study in Shandong Province, China, 2013–2017. Children 2024, 11, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030309
Wang W, Wang H, Song K, Wang B, Xue F, Zhao L, Cao W, Cheeloo EcoHealth Consortium (CLEC). Epidemiological Features of Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Observational Study in Shandong Province, China, 2013–2017. Children. 2024; 11(3):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030309
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenjing, Haitao Wang, Ke Song, Baoyu Wang, Fuzhong Xue, Lin Zhao, Wuchun Cao, and Cheeloo EcoHealth Consortium (CLEC). 2024. "Epidemiological Features of Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Observational Study in Shandong Province, China, 2013–2017" Children 11, no. 3: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030309
APA StyleWang, W., Wang, H., Song, K., Wang, B., Xue, F., Zhao, L., Cao, W., & Cheeloo EcoHealth Consortium (CLEC). (2024). Epidemiological Features of Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents: A Population-Based Observational Study in Shandong Province, China, 2013–2017. Children, 11(3), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11030309





