Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
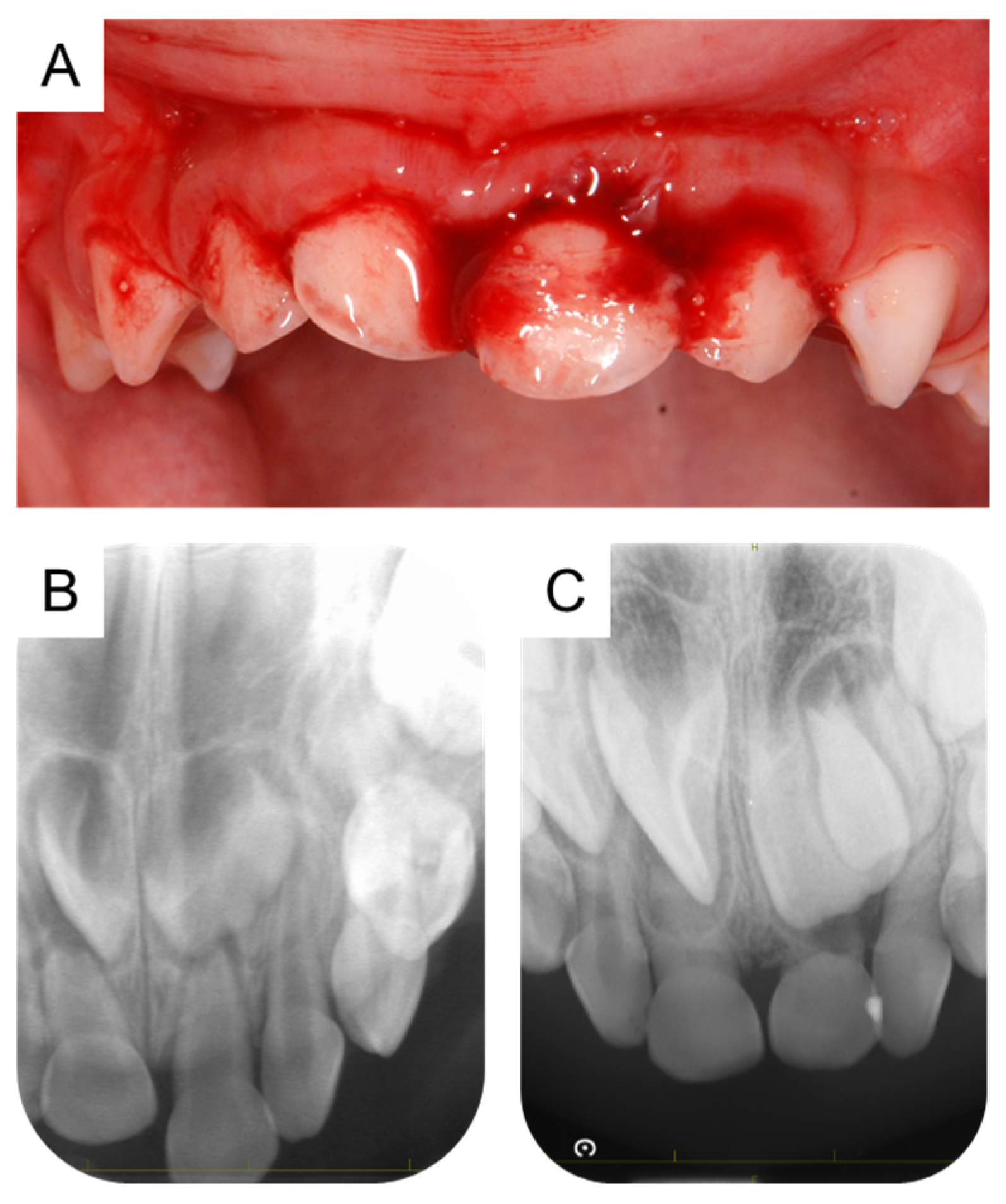
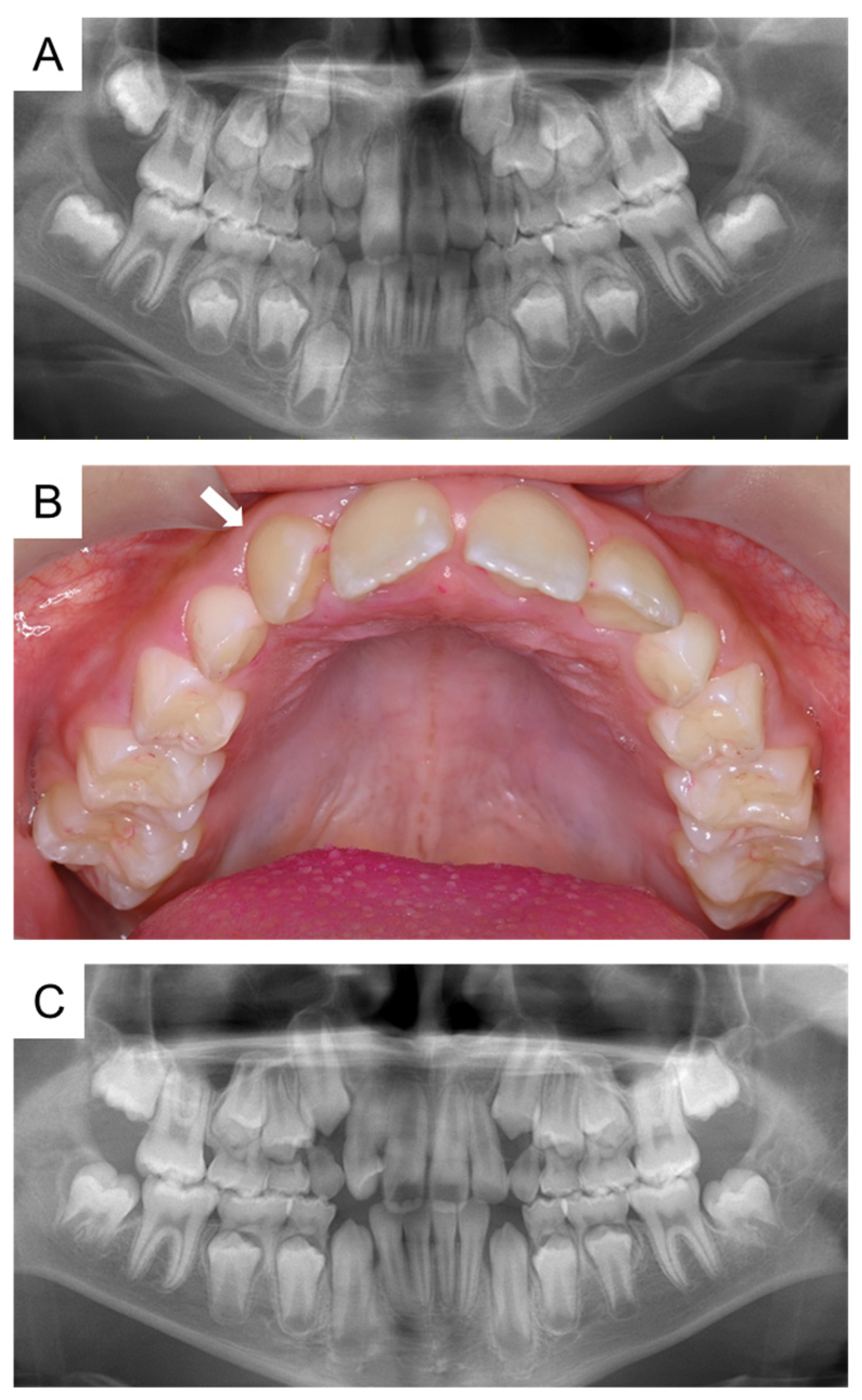
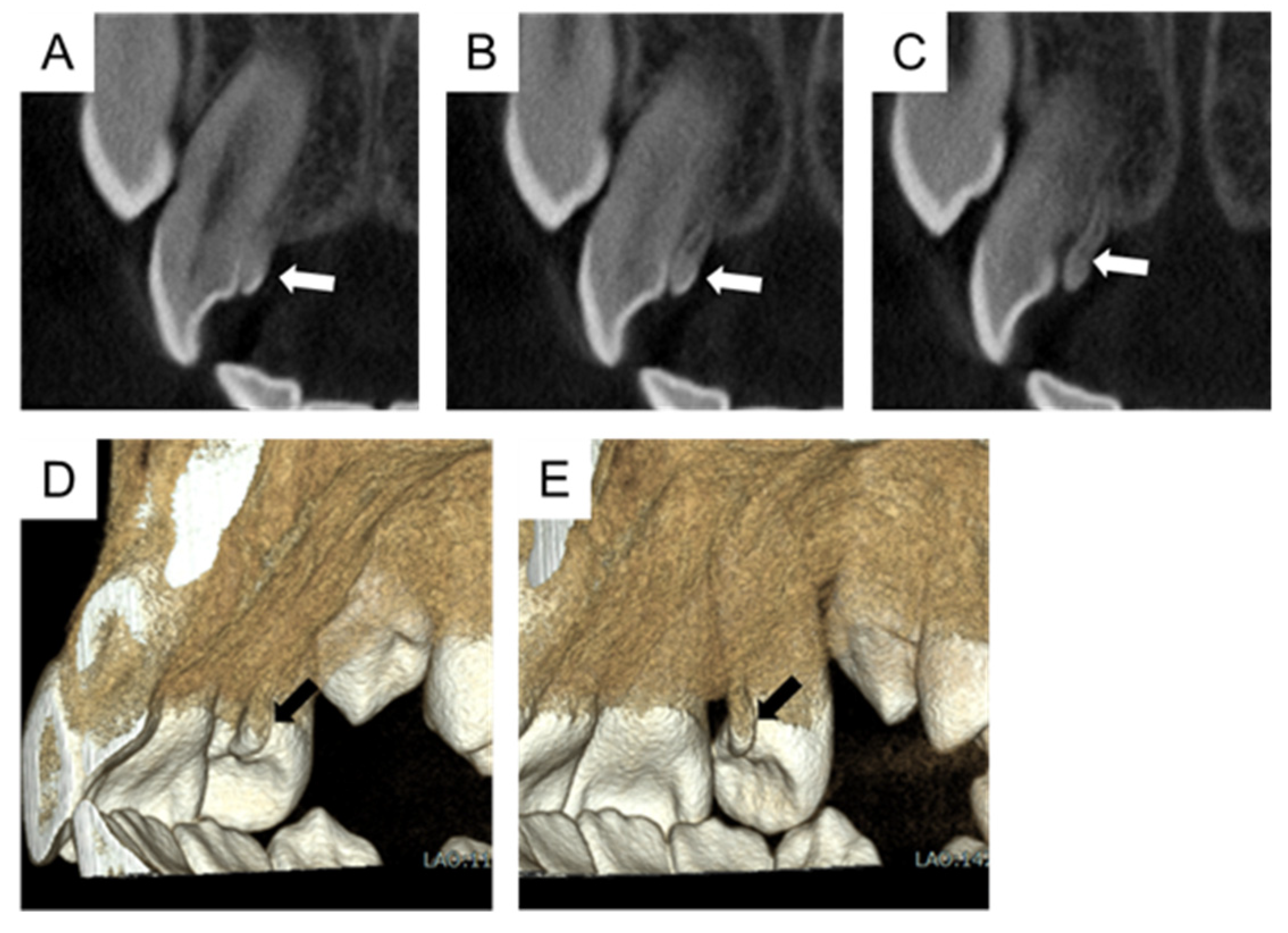
2. Case Presentation
3. Methods
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Data Extraction
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Fused Tooth
5.2. The Present Case
5.3. Literature Review
5.4. Occurrence and Region of Fusion
5.5. Prognosis
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilge, N.H.; Yeşiltepe, S.; Törenek Ağırman, K.; Çağlayan, F.; Bilge, O.M. Investigation of prevalence of dental anomalies by using digital panoramic radiographs. Folia Morphol. 2018, 77, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N.; Hernández, S.R.; Brisson-Suárez, K.; Baasch, A.C.; Pérez, A.R.; Alves, F.R.F. Dens Invaginatus: Clinical Implications and Antimicrobial Endodontic Treatment Considerations. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitomo, T.; Asao, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kusaka, S.; Usuda, M.; Kametani, M.; Ando, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Mitsuhata, C.; Kajiya, M.; et al. A Third Supernumerary Tooth Occurring in the Same Region: A Case Report. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitomo, T.; Kusaka, S.; Iwamoto, Y.; Usuda, M.; Kametani, M.; Asao, Y.; Nakano, M.; Tachikake, M.; Mitsuhata, C.; Nomura, R. Five-Year Follow-Up of a Child with Non-Syndromic Oligodontia from before the Primary Dentition Stage: A Case Report. Children 2023, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükgöze-Dindar, M.; Tekbaş-Atay, M. Prevalence of Dental Anomalies Assessed Using Panoramic Radiographs in a Sample of the Turkish Population. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 25, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Usuda, M.; Akitomo, T.; Kametani, M.; Kusaka, S.; Mitsuhata, C.; Nomura, R. Dens invaginatus of fourteen teeth in a pediatric patient. Pediatr. Dent. J. 2023, 33, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bağcı, N.; Pamukçu, U.; Altunkaynak, B.; Peker, İ. Dental Anomalies in Consanguineous Marriage: A Clinical-Radiological Study. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinjolli, F.; Zeqaj, M.; Dragusha, E.; Malara, A.; Danesi, C.; Laganà, G. Dental anomalies in an Albanian orthodontic sample: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, S.; Pathak, D.; Harrison, M.; Bhujel, N. Macrodontia and double teeth: A review and case series. Br. Dent. J. 2023, 234, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, D.B.; Deepak, B.S.; Selvamani, M.; Puneeth, H.K. Diagnostic dilemma of a double tooth: A rare case report and review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezević, A.; Travan, S.; Tarle, Z.; Sutalo, J.; Janković, B.; Ciglar, I. Double tooth. Coll. Antropol. 2002, 26, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujino, K.; Yonezu, T.; Shintani, S. Effects of different combinations of fused primary teeth on eruption of the permanent successors. Pediatr. Dent. 2013, 35, E64–E67. [Google Scholar]
- Yonezu, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Sasaki, J.; Machida, Y. Prevalence of congenital dental anomalies of the deciduous dentition in Japanese children. Bull. Tokyo Dent. Coll. 1997, 38, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujino, K.; Shintani, S. Management of a supernumerary tooth fused to a permanent maxillary central incisor. Pediatr. Dent. 2010, 32, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Gadimli, C.; Sari, Z. Interdisciplinary treatment of a fused lower premolar with supernumerary tooth. Eur. J. Dent. 2011, 5, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.K.; Chang, H.S.; Min, K.S. Endodontic management of supernumerary tooth fused with maxillary first molar by using cone-beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1901–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioglu Guler, D.; Sen Tunc, E.; Arici, N.; Ozkan, N. Multidisciplinary management of a fused tooth: A case report. Case Rep. Dent. 2013, 2013, 634052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Prakash, V.; Sharma, M. Endodontic and post-endodontic management of a fused molar. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2013, 24, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Gupta, J.; Acharya, S.R.; Ather, A. Mandibular lateral incisor with four root canals: A unique case of double tooth diagnosed using multidetector computed tomography. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2013, 43, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Venugopal, S.; Smitha, B.V.; Saurabh, S.P. Paramolar concrescence and periodontitis. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.M.; Jang, J.H.; Park, S.H. Clinical management of a fused upper premolar with supernumerary tooth: A case report. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2014, 39, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattab, F.N. Double talon cusps on supernumerary tooth fused to maxillary central incisor: Review of literature and report of case. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2014, 6, e400–e407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Ananthnarayan, K.; Ballal, S.; Natanasabapathy, V. Endodontic management of maxillary second molars fused with paramolar tubercles diagnosed by cone beam computed tomography—Two case reports. J. Dent. 2014, 11, 726–732. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbock, N.; Wigler, R.; Kaufman, A.Y.; Lin, S.; Abu-El Naaj, I.; Aizenbud, D. Fusion of central incisors with supernumerary teeth: A 10-year follow-up of multidisciplinary treatment. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagci, A.; Cantekin, K.; Buyuk, S.K.; Pala, K. The multidisciplinary management of fused maxillary lateral incisor with a supernumerary tooth in cleft lip adolescence. Case Rep. Dent. 2014, 2014, 459416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.S.; Junaid, A.; Mello, I. Unilateral fusion of a supernumerary tooth to a maxillary permanent lateral incisor: A report of a rare case. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Warhadpande, M.M.; Redij, S.A.; Sabir, H.; Shirude, T. Management of synodontia between dilacerated permanent maxillary central incisor and supernumerary tooth with aid of cone-beam computed tomography. J. Conserv. Dent. 2015, 18, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, T.; Shapira, Y.; Bechor, N.; Shpack, N. Fused and Geminated Permanent Maxillary Central Incisors: Prevalence, Treatment Options, and Outcome in Orthodontic Patients. J. Dent. Child. 2015, 82, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.; Kamio, T. Diagnosis and Endodontic Management of Fused Mandibular Second Molar and Paramolar with Concrescent Supernumerary Tooth Using Cone-Beam CT and 3-D Printing Technology: A Case Report. Bull. Tokyo Dent. Coll. 2015, 56, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Kariya, P.B.; Mallikarjuna, R.; Singh, A.N. Fusion of permanent maxillary right central incisor and mesiodens in an 8-year-old child. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014208541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Mutneja, A.R.; Nagpal, A.; Mutneja, P. Dens evaginatus and dens invaginatus in a double tooth: A rare case report. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2015, 26, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, C.; Ren, S.; Lin, Z.; Miao, L.; Sun, W. Fusion of a supernumerary tooth to right mandibular second molar: A case report and literature review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 11890–11895. [Google Scholar]
- Aydemir, S.; Ozel, E.; Arukaslan, G.; Tekce, N. Clinical management of a fused mandibular lateral incisor with supernumerary tooth: A case report. Dent. Res. J. 2016, 13, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Che, C.; Ding, Z.; Zeng, S.; Wang, W.; He, X. Precision diagnosis and antidiastole on supernumerary cusp of tooth by CBCT. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2016, 38, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, G.; Sekerci, A.E.; Soylu, E.; Nazlim, S.; Amuk, M.; Avci, F. Role of cone-beam computed tomography in the evaluation of a paradental cyst related to the fusion of a wisdom tooth with a paramolar: A rare case. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2016, 46, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smail-Faugeron, V.; Terradot, J.; Muller Bolla, M.; Courson, F. Management of non-syndromic double tooth affecting permanent maxillary central incisors: A systematic review. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016215482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, H.; Pasaoglu, A. Multidisciplinary management of a fused maxillary central incisor moved through the midpalatal suture: A case report. Korean J. Orthod. 2017, 47, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorielo, M.C.O.; Gonini-Junior, A.; de Oliveira, D.; Bordignon, R.T.; Borges, A.H. Root canal treatment of a fused mandibular incisor using cone-beam computed tomography as a diagnostic aid. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gera, N.; Tripathi, S.; Naik, N.S.; Astekar, M. Triplication in permanent teeth: A rare case report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2017, 21, 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Persic Bukmir, R.; Braut, A.; Brekalo Prso, I. Conservative endodontic management of a fused tooth: A case report. Gerodontology 2017, 34, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badole, G.P.; Shenoi, P.R.; Parlikar, A. Endodontic management of central incisor associated with large periapical lesion and fused supernumerary root: A conservative approach. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2018, 43, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.C.; Symington, O.; Kulkarni, G. Conservative Management of Fused and Geminated Permanent Anterior Teeth. J. Dent. Child. 2019, 86, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jarząbek, A.; Gońda-Domin, M.; Węsierska, K.; Aniko-Włodarczyk, M.; Trybek, G.; Nowicka, A. Multidisciplinary Management of a Double Immature Permanent Tooth: A Case Report. Iran. Endod. J. 2020, 15, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Šarac, Z.; Zovko, R.; Cvitanović, S.; Goršeta, K.; Glavina, D. Fusion of Unerupted Mesiodens with a Regular Maxillary Central Incisor: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2021, 55, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.; Sanchez, S.; Chen, I.P. Use of 3-dimensional-Printed Guide in Hemisection and Autotransplantation of a Fusion Tooth: A Case Report. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, W.; Alduraibi, M. Endodontic Management of a Fused Mandibular Third Molar with Supernumerary Tooth Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 23, e937224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Açıkel, H.; İbiş, S.; Şen Tunç, E. Primary Fused Teeth and Findings in Permanent Dentition. Med. Princ. Pract. 2018, 27, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, W.K.; Helpin, M.L. Bilateral fusion and gemination: A literature analysis and case report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1987, 64, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalamah, M.; Baroudi, K. Prevalence of oro-dental anomalies among schoolchildren in Sana’a city, Yemen. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2016, 22, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Kurahashi, M.; Mori, D.; Iinuma, M.; Tamura, Y.; Mizutani, K.; Shimpo, K.; Sonoda, S.; Azuma, K.; Kubo, K.Y. Hippocampus-dependent spatial memory impairment due to molar tooth loss is ameliorated by an enriched environment. Arch. Oral Biol. 2016, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruhisa, U.; Murakami, J.; Hisatomi, M.; Yanagi, Y.; Asaumi, J. A case of unerupted lower primary second molar associated with compound odontoma. Open Dent. J. 2009, 3, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Author | Objective | Sex | Tooth Number | Fused Region | Prognosis | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demircioglu Guler D, 2013 [18] | To report multidisciplinary management of a fused maxillary anterior tooth. | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction and Ortho | The technique described offers a simple and effective method for restoring a fused tooth that reestablishes function, shape, and esthetics. |
| Gupta R, 2013 [19] | To describe root canal treatment of a fused carious tooth presenting with apical periodontitis. | Female | 37 | Labiopalatal | RCT | The fused teeth were endodontically treated and restored using porcelain fused to a metal crown. |
| Gupta SK, 2013 [20] | To describe a unique case of a double tooth in relation to a mandibular lateral incisor exhibiting the presence of four root canals. | Female | 32 | Mesiodistal | RCT | The role of conventional radiography and advanced three-dimensional imaging techniques in the better assessment of complex root canal systems and their aid in endodontic management has also been highlighted. |
| Venugopal S, 2013 [21] | To describe the presence of a concrescence between the mandibular second molar and a supernumerary tooth, with its clinical and radiographic findings | Male | 47 | Labiopalatal | Partial extraction and RCT | A multidisciplinary approach is required for its management. |
| Cho KM, 2014 [22] | To present a rare case in which fusion of the maxillary left second premolar and a supernumerary tooth in a 13-year-old girl was diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography. | Female | 25 | Labiopalatal | RCT | Fused teeth can be effectively managed by the comprehensive treatment which includes both endodontic and periodontal procedures. |
| Hattab FN, 2014 [23] | To report the dental abnormalities which create clinical, pathological, and esthetic problems. | Female | 11 | Mesiodistal | Others | Dental practitioner should be aware of the clinical signs, associated problems, and treatment options for a given case. |
| Jain P, 2014 (Case 1) [24] | To present two case reports on the endodontic management of two maxillary second molars fused to paramolar tubercles. | Male | 27 | Labiopalatal | RCT | Use of cone-beam computed tomography provided valuable information about the root/root canal anatomy and the EndoVac irrigation system was useful in cleaning the communications that aided in the successful endodontic management. |
| Jain P, 2014 (Case 2) [24] | Male | 27 | Labiopalatal | RCT | ||
| Steinbock N, 2014 [25] | To describe a 10-year outcome of a combined treatment of a fused maxillary incisor by means of an orthodontic–endodontic–prosthodontic–oral surgery management protocol. | Female | 21 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction and Ortho | Proper interdisciplinary treatment planning of complicated cases such as anomalous teeth, which involve fusion to a supernumerary tooth, may lead to minimal invasive conservative procedures that maintain tooth vitality and result in a pleasing esthetic result. |
| Yagci A, 2014 [26] | To present the successful resolution of a fused maxillary lateral incisor with a supernumerary tooth using endodontic, surgical, restorative, and orthodontic management. | Female | 22 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction, RCT, and Ortho | The decision made in extracting or retaining the fused tooth depends on the arch discrepancy and esthetic needs. |
| Cunha RS, 2015 [27] | To describe a case of unilateral fusion of a supernumerary tooth to a maxillary permanent lateral incisor in which a conservative approach was used to reach a favorable outcome. | Female | 12 | Labiopalatal | RCT | Clinicians should be aware of possible anatomic variations and that thorough diagnosis by using appropriate technology is crucial to determine the treatment option that will provide the best outcome. |
| Das S, 2015 [28] | To describe endodontic, surgical, and restorative management of fused and dilacerated maxillary central incisor. | Male | 21 | Labiopalatal | Partial extraction and RCT | Three-dimensional imaging with cone-beam computed tomography for accurate diagnosis and interdisciplinary treatment planning for correction of esthetics and function is needed for the successful management of malformed teeth. |
| Finkelstein T, 2015 (Case1) [29] | To evaluate the prevalence of fused/geminated teeth in the maxillary anterior region of orthodontically treated patients and present treatment options and their outcomes. | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | Ortho | Esthetic consideration is a determining factor for various treatment alternatives. A multidisciplinary approach is imperative for the successful treatment of these dental abnormalities. |
| Finkelstein T, 2015 (Case2) [29] | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | Ortho | ||
| Finkelstein T, 2015 (Case3) [29] | Male | 21 | Mesiodistal | Ortho | ||
| Finkelstein T, 2015 (Case4) [29] | Female | 11 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction | ||
| Kato H, 2015 [30] | To report a case of a mandibular second molar fused with a paramolar, necessitating dental pulp treatment. | Male | 47 | Labiopalatal | Others | Evalualuation using cone-beam computed tomography and modeling with a printer markedly facilitated a three-dimensional understanding of the complicated morphology of the region involved. |
| Khan R, 2015 [31] | To describe an 8-year-old boy presented with a ‘large tooth’ in the upper front region of his jaw. | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | Others | A multidisciplinary approach is required to treat such a condition. |
| Sharma G, 2015 [32] | To report a rare case of dens invaginatus and dens evaginatus on fused permanent maxillary central incisor with supernumerary tooth in a 40-year-old male, and also focuses on the differentiating fusion from gemination and reviews preventive and management strategies for tooth with complex dental anatomy. | Male | 21 | Mesiodistal | Others | The rarity of all these dental anomalies occurring together on the same tooth makes it a unique case. A detailed and accurate radiographic examination is required for diagnosis and subsequent management. |
| Zhu M, 2015 [33] | To report endodontic management and the periodontal therapy of a mandibular second molar that appeared to have been fused with a supernumerary tooth and the importance of the use of cone-beam computed tomography as a valuable diagnostic aid in the treatment of such complex cases. | Female | 47 | Labiopalatal | RCT | A multispecialty approach with dentists of various specialties teaming up for better treatment outcomes can result in a successful culmination of a complicated treatment plan. |
| Aydemir S, 2016 [34] | To present a rare case of a fused mandibular lateral incisor with a supernumerary tooth with a follow-up for 18 months. | Female | 42 | Mesiodistal | RCT | Because of the abnormal morphology of the crown and the complexity of the root canal system in fused teeth, treatment protocols require special attention. |
| Jiang K, 2016 [35] | Based on a case of supernumerary cusp on the bucca of the left maxillary second molar diagnosed by cone-beam computed tomography, its genesis, diagnosis, and antidiastole are to be analyzed. | Male | 27 | Labiopalatal | Others | Cone-beam computed tomography can improve the accuracy of diagnosis. |
| Ozcan G, 2016 [36] | To describe the use of cone-beam computed tomography to visualize the fusion of the mandibular third molar and a supernumerary tooth in relation to a paradental cyst and in the presence of a retromolar canal in the same region. | Male | 48 | Labiopalatal | Extraction | An accurate assessment of morphological and pathological formations was carried out using cone-beam computed tomography. |
| Smail-Faugeron V, 2016 (Case1) [37] | To report an 11-year-old boy with bilateral fusion of the two maxillary central incisors and a 9-year-old boy with a double left central incisor and a supernumerary lateral right incisor. | Male (2 teeth) | 11 | Mesiodistal | RCT and Ortho | A multidisciplinary approach is key to the management of permanent maxillary central incisors affected by coronary anomalies. |
| 21 | Mesiodistal | Ortho | ||||
| Smail-Faugeron V, 2016 (Case2) [37] | Male | 21 | Mesiodistal | Extraction | ||
| Bulut H, 2017 [38] | To present the management of a fused maxillary central incisor with labial and palatal talon cusps that was moved through the midpalatal suture to obtain an appropriate dental midline by using a multidisciplinary approach. | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | Ortho | A multidisciplinary approach, including orthodontics, periodontics, endodontics, and prosthodontics, could be used to achieve successful and satisfying treatment results. |
| Dorielo MCO, 2017 [39] | To describe a case of successful root canal treatment of an anomalous, fused inferior anterior mandibular incisor, using cone-beam computed tomography as a diagnostic aid. | Male | 32 | Mesiodistal | RCT | It confirms that anomalous teeth requiring root canal treatment pose many challenges to dental practitioners. In addition, it also reveals that new tools and materials are useful and can greatly improve treatment success. |
| Gera N, 2017 [40] | To present a rare case of triple teeth in permanent dentition in a 15-year-old female with associated periapical pathology. | Female | 21 | Mesiodistal | Extraction | Triple teeth also complicate endodontic, oral surgical procedures, and periodontal treatment apart from being unesthetic. Since the longitudinal grooves created by the fusion of three teeth are susceptible to caries, sealant therapy, and fluoride application may be necessary. |
| Persic Bukmir R, 2017 [41] | To report a conservative treatment of a rare developmental anomaly. | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | RCT | It illustrates the importance of an individual approach when treating anomalous teeth. Priorities in pain and infection management to properly and functionally restore teeth should be unaffected by age. |
| Badole GP, 2018 [42] | To describe the endodontic management of upper central incisor fused with supernumerary root by using cone-beam computed tomography as a diagnostic aid. | Male | 21 | Mesiodistal | RCT | Cone-beam computed tomography helped in revealing complex tooth anatomy and the level of fusion of supernumerary teeth which was not visible in radiographs. |
| Kim EC, 2019 [43] | To present an eight-year-old patient with a permanent right central incisor that was fused with a supernumerary tooth as well as a geminated permanent left central incisor, and to describe the surgical-orthodontic-restorative management of the resultant malocclusion in the developing dentition. | Male | 11 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction | It highlights physiological principles and demonstrates conservative, cost-effective, and clinically effective procedures in the management of developing malocclusions resulting from dental anomalies of fusion and gemination affecting permanent incisors. |
| Jarząbek A, 2020 [44] | To describe the multidisciplinary/minimally invasive treatment of fused immature permanent teeth. | Female | 22 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction | The proposed multidisciplinary and minimally invasive treatment of the double tooth using a bioactive cement may facilitate the maturation of immature teeth and result in a desirable aesthetic and function. |
| Šarac Z, 2021 [45] | To describe a case of incomplete fusion of an unerupted mesiodens with a permanent maxillary central incisor, aligned in the dental arch. | Male | 21 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction | A multidisciplinary collaboration is necessary for precise diagnosis and predictable treatment outcomes. |
| Sato M, 2021 [46] | To present the treatment of a fusion tooth by combining three-dimensional printing technology and endodontic intervention in a 10-year-old patient. | Female | 12 | Mesiodistal | Partial extraction and RCT | Techniques in modern endodontics, such as cone-beam computed tomographic imaging and three-dimensional printing, should be adapted when it is beneficial to patients. |
| Almutairi W, 2022 [47] | To present the clinical management of a fused mandibular third molar with a supernumerary tooth, wherein abnormal anatomy was ascertained using cone-beam computed tomography. | Male | 48 | Mesiodistal | Extraction | Successful treatment can be predicted when clinicians use a proper treatment plan and utilize all available diagnostic tools. |
| Present case | Male | 12 | Labiopalatal | Others |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akitomo, T.; Kusaka, S.; Usuda, M.; Kametani, M.; Kaneki, A.; Nishimura, T.; Ogawa, M.; Mitsuhata, C.; Nomura, R. Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases. Children 2024, 11, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010006
Akitomo T, Kusaka S, Usuda M, Kametani M, Kaneki A, Nishimura T, Ogawa M, Mitsuhata C, Nomura R. Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases. Children. 2024; 11(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkitomo, Tatsuya, Satoru Kusaka, Momoko Usuda, Mariko Kametani, Ami Kaneki, Taku Nishimura, Masashi Ogawa, Chieko Mitsuhata, and Ryota Nomura. 2024. "Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases" Children 11, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010006
APA StyleAkitomo, T., Kusaka, S., Usuda, M., Kametani, M., Kaneki, A., Nishimura, T., Ogawa, M., Mitsuhata, C., & Nomura, R. (2024). Fusion of a Tooth with a Supernumerary Tooth: A Case Report and Literature Review of 35 Cases. Children, 11(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010006




