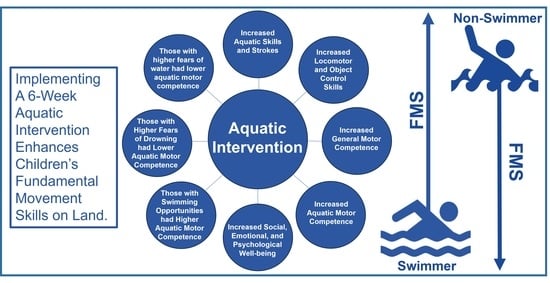
The Effects of a 6-Week Swimming Intervention on Gross Motor Development in Primary School Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.2.1. Control Group
2.2.2. Intervention Group
2.3. Anthropometry
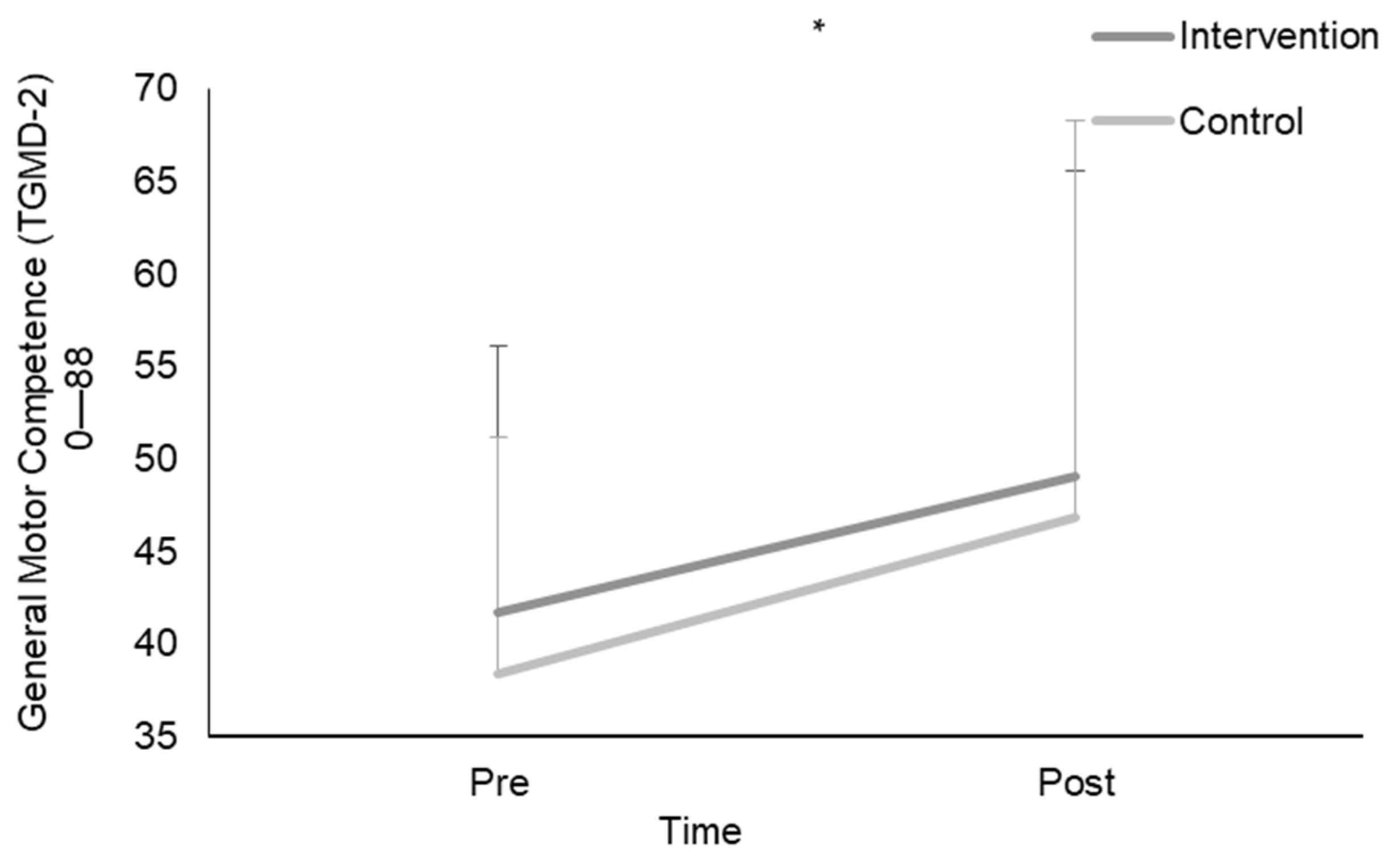
2.4. General Motor Competence
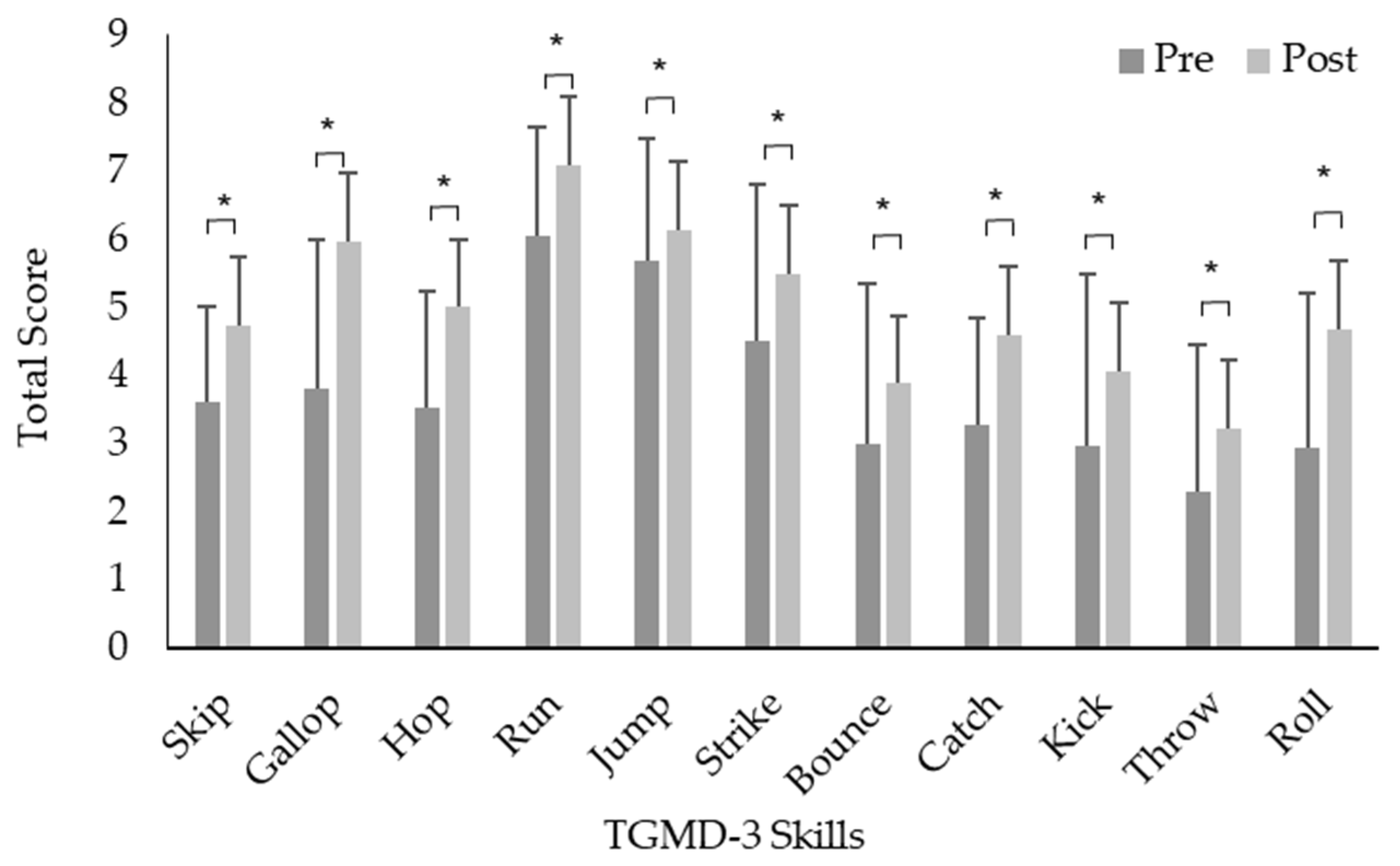
2.5. Aquatic Motor Competence
2.6. Fear of Drowning and Swimming Opportunities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
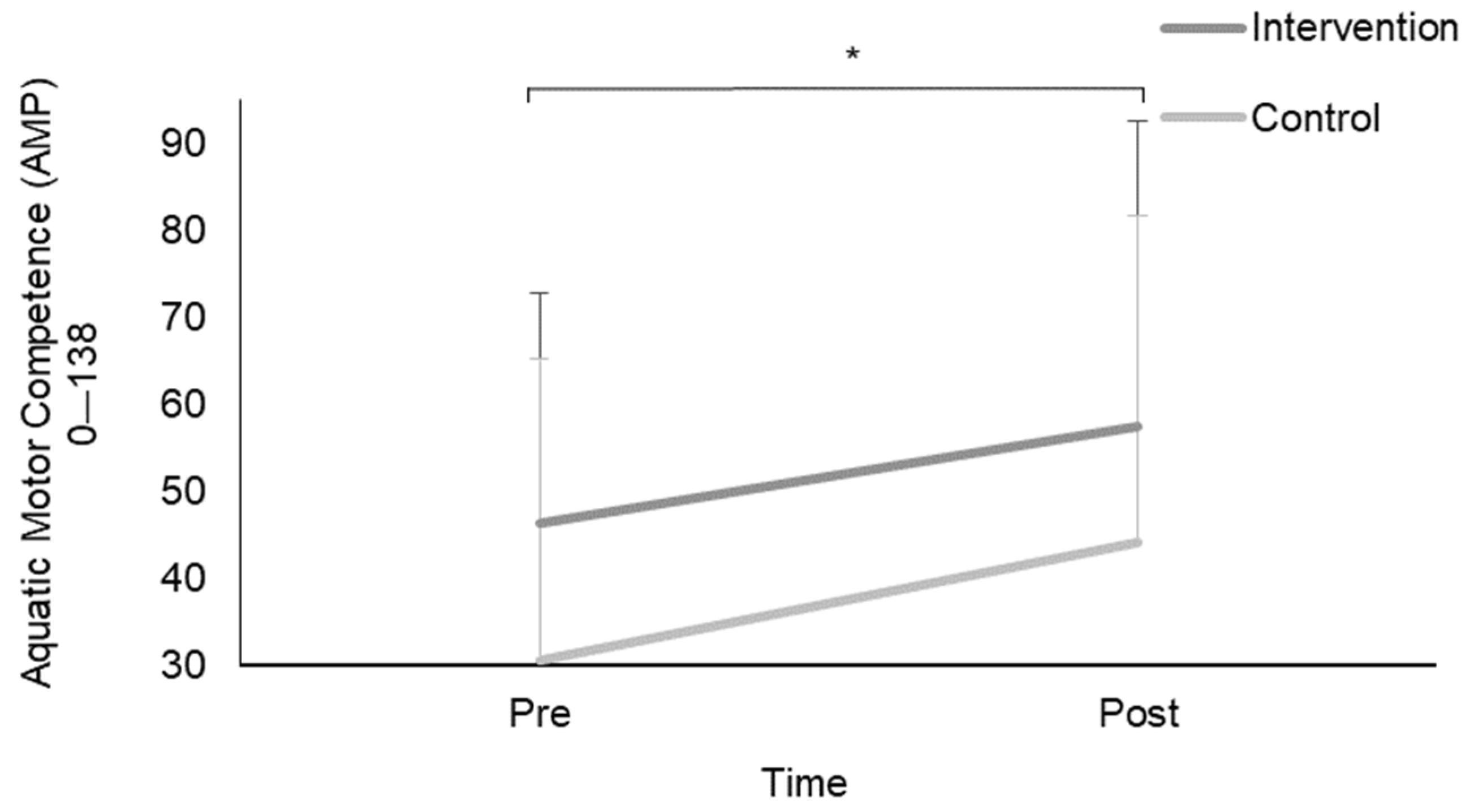
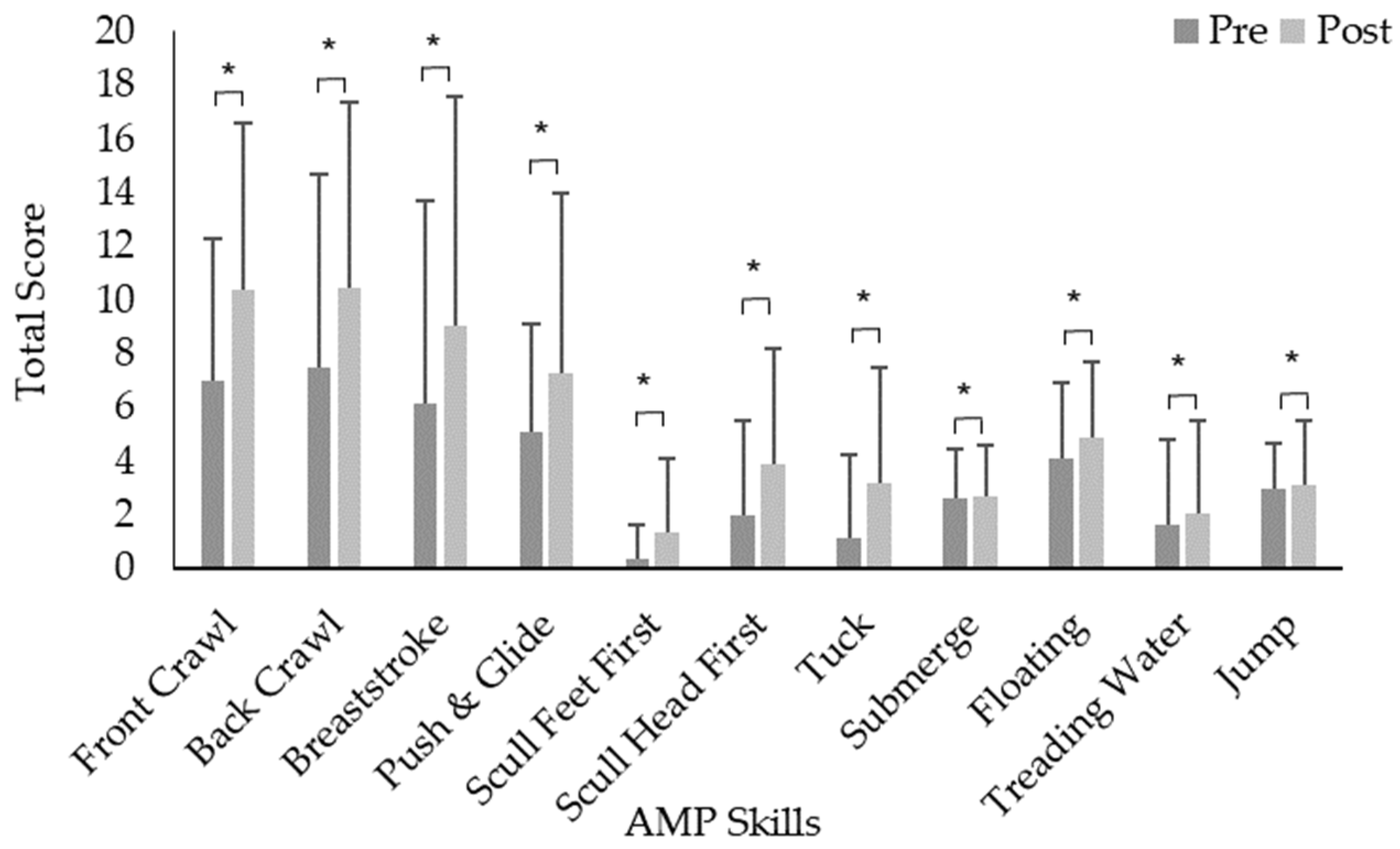
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lubans, D.R.; Morgan, P.J.; Cliff, D.P.; Barnett, L.M.; Okely, A.D. Fundamental Movement Skills in Children and Adolescents. Sport. Med. 2010, 40, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, D. TGMD 2—Test of Gross Motor Development Examiner’s Manual; PRO-ED 2: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Stodden, D.F.; Goodway, J.D.; Langendorfer, S.J.; Roberton, M.A.; Rudisill, M.E.; Garcia, C.; Garcia, L.E. A developmental perspective on the role of motor skill competence in physical activity: An emergent relationship. Quest 2008, 60, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundvall, S. Physical literacy in the field of physical education—A challenge and a possibility. J. Sport Health Sci. 2015, 4, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Dudley, D.; Kwan, M.; Bulten, R.; Kriellaars, D. Physical literacy, physical activity and health: Toward an evidence-informed conceptual model. Sport. Med. 2019, 49, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department for Education. National Curriculum in England: PE Programmes of Study. 2013. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-curriculum-in-england-physical-education-programmes-of-study (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Tun, M.T.; Aye, T.; Htut, T.Z.C.; Tin, W.M.; Khin, M.T. Fundamental motor skill proficiency among 7- to 10-year-old children with Down syndrome. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2023, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loprinzi, P.D.; Davis, R.E.; Fu, Y.-C. Early motor skill competence as a mediator of child and adult physical activity. Prev. Med. Rep. 2015, 2, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.M.; Morgan, P.J.; VAN Beurden, E.; Ball, K.; Lubans, D.R. A reverse pathway? Actual and perceived skill proficiency and physical activity. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2011, 43, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okely, A.D.; Booth, M.L.; Patterson, J.W. Relationship of cardiorespiratory endurance to fundamental movement skill proficiency among adolescents. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2001, 13, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, C.; Okely, A.; Bagley, S.; Telford, A.; Booth, M.; Crawford, D.; Salmon, J. Does weight status influence associations between children’s fundamental movement skills and physical activity? Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2008, 79, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, M.E.; Fragala-Pinkham, M.; Lennon, N.; George, A.; Forman, J.; Trost, S.G. Reliability and validity of objective measures of physical activity in youth with cerebral palsy who are ambulatory. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, W.O.; Belton, S.; Issartel, J. Fundamental movement skill proficiency amongst adolescent youth. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2016, 21, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Childhood Overweight and Obesity. Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/nmh/wha/59/dpas/en/ (accessed on 10 April 2019).
- Spessato, B.C.; Gabbard, C.; Valentini, N.; Rudisill, M. Gender differences in Brazilian children’s fundamental movement skill performance. Early Child Dev. Care 2013, 183, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, S.W.; Robinson, L.E.; Wilson, A.E.; Lucas, W.A. Getting the fundamentals of movement: A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of motor skill interventions in children. Child Care Health Dev. 2012, 38, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Capelle, A.; Broderick, C.R.; van Doorn, N.; Ward, R.; Parmenter, B.J. Interventions to improve fundamental motor skills in pre-school aged children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompsett, C.; Sanders, R.; Taylor, C.; Cobley, S. Pedagogical approaches to and effects of fundamental movement skill interventions on health outcomes: A systematic review. Sport. Med. 2017, 47, 1795–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.E.; Metcalfe, J.S. The mountain of motor development: A metaphor. Mot. Dev. Res. Rev. 2002, 2, 183–202. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, M.J.; Noon, M.; Lawson, C.; Hurst, J.; Eyre, E.L.J. The Effectiveness of a primary school based badminton intervention on children’s fundamental movement skills. Sports 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, H.A.; Marinho, D.A.; Jidovtseff, B.; Silva, A.J.; Costa, A.M. Influence of Regular Soccer or Swimming Practice on gross Motor Development in Childhood. J. Mot. 2016, 12, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.; Eyre, E.L.; Tallis, J.; Duncan, M.J. Fundamental movement skill proficiency among British primary school children: Analysis at a behavioural component level. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2021, 128, 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, D.J.; Liu, W.; Gao, Z. Effects of physical activity on children’s motor skill development: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8160756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Association for Sport and Physical Education. Active Start: A Statement of Physical Activity Guidelines for Children from Birth to Age 5, 2nd ed.; SHAPE America: Annapolis Junction, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman, K. Physical education in schools: A global perspective. Kinesiology 2008, 40, 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich, D.A. The test of gross motor development-3 (TGMD-3): Administration, scoring, and international norms. Spor Bilim. Derg. 2013, 24, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cumming, I. The Health & Wellbeing Benefits of Swimming 2017. Available online: http://tinyurl.com/y8qs9mv3 (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Escalante, Y.; Saavedra, J. Swimming and aquatic activities: State of the art. J. Hum. Kinet. 2012, 32, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepore, M.; Gayle, G.W.; Stevens, S.F. Adapted Aquatics Programming: A Professional Guide; ERIC: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, N.L.; Sui, X.; Blair, S.N. Comparison of the health aspects of swimming with other types of physical activity and sedentary lifestyle habits. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2008, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.E.; Stodden, D.F.; Barnett, L.M.; Lopes, V.P.; Logan, S.W.; Rodrigues, L.P.; D’Hondt, E. Motor competence and its effect on positive developmental trajectories of health. Sport. Med. 2015, 45, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.; Silva, A.J.; Marinho, D.A.; Costa, A.M. Desenvolvimento Motor Global De Crianças do 1º Ciclo do Ensino Básico Com e Sem Prática Prévia De Natação Em Contexto Escolar. Motricidade 2015, 11, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendorfer, S.; Bruya, L.D. Aquatic Readiness: Developing Water Competence in Young Children; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bunker, D.; Thorpe, R. A model for the teaching of games in secondary schools. Bull. Phys. Educ. 1982, 18, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gllareva, I.; Trajković, N.; Mačak, D.; Šćepanović, T.; Zobenica, A.K.; Pajić, A.; Halilaj, B.; Gallopeni, F.; Madić, D.M. Anthropometric and motor competence classifiers of swimming ability in preschool children—A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, C.; Irwin, R.; Martin, N.; Ross, S. Constraints Impacting Minority Swimming Participation, Phase II. 2010. Available online: http://www.usaswimming.org/_Rainbow/Documents/121d4497-c4be-44a6-8b28-12bf64f36036/2010%20Swim%20ReportUSA%20Swimming-5-26-10.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Cole, A.J.; Becker, B.E. Comprehensive Aquatic Therapy; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Berukoff, K.D.; Hill, G.M. A study of factors that influence the swimming performance of hispanic high school students. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2010, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, F.J. Games, Sports, and Exercises for the Physically Disabled. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 1991, 8, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, C.C.; Pharr, J.R.; Irwin, R.L. Understanding factors that influence fear of drowning in children and adolescents. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2015, 9, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, M.A. Self-Efficacy: The Key to Success in Sports. Excel at Life. 2001. Available online: http://www.excelatlife.com/self-efficacy.htm (accessed on 4 April 2009).
- Chase, M.A. Children’s self-efficacy, motivational intentions, and attributions in physical education and sport. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2001, 72, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 1977, 84, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, N.A.; Duncan, M.J.; Morris, M.G.; Oxford, S.W. The Reliability and Validation of the Aquatic Movement Protocol as an Instrument for Assessing Aquatic Motor Competence in Primary Aged Children. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2021, 9, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, E.S.; Duncan, M.J.; Birch, S.L.; James, R.S. Can Fundamental Movement Skill Mastery Be Increased via a Six Week Physical Activity Intervention to Have Positive Effects on Physical Activity and Physical Self-Perception? Sports 2016, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, K.K.; Chinn, K.M.; Robinson, L.E. The effect of the CHAMP intervention on fundamental motor skills and outdoor physical activity in preschoolers. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.K.; Stodden, D.F.; Ulrich, D.A.; Robinson, L.E. Using process- and product-oriented measures to evaluate changes in motor skills across an intervention. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2021, 25, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvin, A.; Barral, J.; Kakebeeke, T.H.; Kriemler, S.; Longchamp, A.; Schindler, C.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Puder, J.J. Effect of a governmentally-led physical activity program on motor skills in young children attending child care centers: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swim England. Swim England Learn to Swim Framework Stages 1–7. 2020. Available online: https://www.swimming.org/learntoswim/swim-england-learn-to-swim-framework/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Preston, N.; Magallón, S.; Hill, L.J.; Andrews, E.; Ahern, S.M.; Mon-Williams, M. A systematic review of high quality randomized controlled trials investigating motor skill programmes for children with developmental coordination disorder. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 31, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, T.J. Swimming and Water Safety: Reaching All Children in Australian Primary Schools. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2012, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Life Saving Society Australia. Keep Watch Programme History. 2011. Available online: http://www.royallifesaving.com.au/www/html/149-keep-watch-overview.asp (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Sibert, J.R.; Lyons, R.; Smith, B.; Cornall, P.; Sumner, V.; Craven, M.; Kemp, A.M. Preventing deaths by drowning in children in the United Kingdom: Have we made progress in 10 years? Population based incidence study. BMJ 2002, 324, 1070–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, S.P.; Hobbs, M.; Tipton, M.J.; Barwood, M.J. The water incident database (WAID) 2012 to 2019: A systematic evaluation of the documenting of UK drownings. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, J.D.; Knowles, Z.; Fairclough, S.J.; Stratton, G.; O’Dwyer, M.; Ridgers, N.D.; Foweather, L. Fundamental movement skills of preschool children in Northwest England. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2015, 121, 260–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmundsson, H.; Hopkins, B. Baby swimming: Exploring the effects of early intervention on subsequent motor abilities. Child Care Health Dev. 2010, 36, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, L.E.; Bolger, L.A.; Neill, C.O.; Coughlan, E.; O’brien, W.; Lacey, S.; Burns, C. Age and sex differences in fundamental movement skills among a cohort of irish school children. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2018, 6, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ye, W.; Korivi, M.; Liu, Y.; Hong, F. Gender Differences in Fundamental Motor Skills Proficiency in Children Aged 3–6 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senefeld, J.W.; Clayburn, A.J.; Baker, S.E.; Carter, R.E.; Johnson, P.W.; Joyner, M.J. Sex differences in youth elite swimming. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardid, F.; Lenoir, M.; Huyben, F.; De Martelaer, K.; Seghers, J.; Goodway, J.D.; Deconinck, F.J. The effectiveness of a community-based fundamental motor skill intervention in children aged 3–8 years: Results of the “Multimove for Kids” project. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, A.; Goodway, J.D.; Logan, J.A.; Sutherland, S. SKIPing with teachers: An early years motor skill intervention. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2017, 22, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, E.; Rommers, N.; Bardid, F.; Deconinck, F.J.; De Martelaer, K.; D’Hondt, E.; Lenoir, M. Long-term effectiveness of a fundamental motor skill intervention in Belgian children: A 6-year follow-up. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2021, 31, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.; O’Connor, S.; Harrison, A.J.; Ní Chéilleachair, N.J. Effects of an 8-week school-based intervention programme on Irish school children’s fundamental movement skills. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2021, 26, 593–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.H.; Rudisill, M.E.; Hastie, P.A. Motivational climate and fundamental motor skill performance in a naturalistic physical education setting. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedagog. 2009, 14, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deli, E.; Bakle, I.; Zachopoulou, E. Implementing intervention movement programs for kindergarten children. J. Early Child. Res. 2006, 4, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, N.C.; Rudisill, M.E. An Inclusive mastery climate intervention and the motor skill development of children with and without disabilities. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 2004, 21, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apache, R.G. Activity-based intervention in motor skill development. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2005, 100, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.E.; Palmer, K.K.; Meehan, S.K. Dose–response relationship: The effect of motor skill intervention duration on motor performance. J. Mot. Learn. Dev. 2017, 5, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swim England. About the Swim England Learn to Swim Programme [Online]. 2023. Available online: https://www.swimming.org/swimengland/learn-to-swim-programme/ (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- Department for Education. PE and Sport Premium for Primary Schools. GOV.UK. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/guidance/pe-and-sport-premium-for-primary-schools (accessed on 11 December 2023).
| Intervention | Control | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Girls | Boys | Girls | Boys | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |||||||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | Mean | SD | 95% CI | |
| TGMD-2 | 40.1 | 1.4 | 37.3–42.9 | 51.1 | 1.6 | 47.6–54.5 | 46.6 | 2.9 | 40.5–52.6 | 57 | 3.1 | 50.6–63.5 | 38.6 | 1.6 | 35.3–41.8 | 52.5 | 2.1 | 48.1–56.9 | 42 | 2.6 | 36.5–47.4 | 58.5 | 3.8 | 50.3–66.6 |
| Locomotor | 23 | 0.7 | 21.5–24.5 | 28.9 | 0.8 | 27.2–30.5 | 22.6 | 1.5 | 19.6–25.7 | 28.3 | 1.4 | 25.3–31.3 | 23.9 | 0.9 | 22–25.8 | 28.9 | 0.7 | 27.4–30.5 | 21.2 | 1.4 | 18.2–24.2 | 30.1 | 1.2 | 27.4–32.7 |
| Skip | 3.8 | 0.2 | 3.3–4.3 | 4.7 | 0.3 | 4.2–5.2 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 3.1–4.5 | 47 | 0.4 | 3.9–5.5 | 3.7 | 0.2 | 3.4–4.1 | 4.6 | 0.2 | 4.1–5.1 | 3 | 0.4 | 2.2–3.9 | 5.1 | 0.2 | 4.6–5.5 |
| Gallop | 3.5 | 0.4 | 2.6–4.4 | 5.6 | 0.5 | 4.5–6.6 | 3 | 0.5 | 2–4 | 5.2 | 0.5 | 4.1–6.3 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 3.9–5.4 | 6.6 | 0.2 | 6.2–7 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 2.9–3.9 | 6.7 | 0.4 | 5.9–7.6 |
| Hop | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3–4.4 | 5 | 0.3 | 4.3–5.7 | 4.1 | 0.4 | 3.4–4.8 | 5 | 0.3 | 4.5–5.6 | 3.2 | 0.3 | 2.6–3.8 | 4.7 | 0.3 | 4.1–5.3 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 2.3–3.9 | 5.4 | 0.4 | 4.5 -6.2 |
| Run | 6.0 | 0.3 | 5.5–6.6 | 7.1 | 0.3 | 6.5–7.6 | 6.0 | 0.3 | 5.3–6.7 | 7 | 0.3 | 6.3–7.6 | 6.2 | 0.3 | 5.6–6.8 | 7.2 | 0.2 | 6.7–7.7 | 5.9 | 0.4 | 5–6.7 | 7.1 | 0.3 | 6.4–7.8 |
| Jump | 6.2 | 0.3 | 5.5–6.8 | 6.6 | 0.3 | 5.9–7.2 | 5.6 | 0.5 | 4.6–6.6 | 6.4 | 0.4 | 5.6–7.2 | 5.4 | 0.3 | 4.9–6 | 5.8 | 0.3 | 5.3–6.4 | 5.6 | 0.3 | 5–6.2 | 5.8 | 0.5 | 4.9–6.8 |
| Object Control | 17.2 | 1.1 | 14.8–19.5 | 22.3 | 1.1 | 19.9–24.7 | 23.9 | 1.7 | 20.3–27.5 | 28.7 | 1.9 | 24.9–32.6 | 14.6 | 1 | 12.7–16.6 | 23.6 | 1.6 | 20.3–26.8 | 20.8 | 1.8 | 17–24.5 | 28.4 | 3 | 22.1–34.7 |
| Strike | 4.5 | 0.3 | 3.9–5.1 | 4.3 | 0.5 | 3.2–5.4 | 5.4 | 0.6 | 4.2–6.7 | 6.3 | 0.5 | 5.2–7.4 | 3.3 | 0.3 | 2.7–4 | 5 | 0.6 | 3.9–6.2 | 5.1 | 0.5 | 4–6.2 | 6.1 | 0.7 | 4.5–7.6 |
| Bounce | 2.3 | 0.4 | 1.6–3 | 3.7 | 0.5 | 2.7–4.7 | 3.5 | 0.4 | 2.7–4.3 | 4.8 | 0.5 | 3.7–5.9 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 2.1–4.1 | 3.7 | 0.5 | 2.7–4.7 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 1.7–4.1 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 2.2–4.8 |
| Catch | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3.0–4.3 | 4.7 | 0.3 | 4.1–5.3 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 2.7–4.1 | 4.7 | 0.4 | 3.9–5.6 | 2.8 | 0.3 | 2.3–3.4 | 4.4 | 0.3 | 3.7–5. | 3.2 | 0.3 | 2.5–4 | 4.4 | 0.5 | 3.3–5.4 |
| Kick | 2.7 | 0.4 | 1.9–3.5 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 2.4–3.9 | 4.9 | 0.5 | 3.7–6.0 | 5.3 | 0.6 | 4.2–6.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.8–1.7 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 2.1–3.6 | 3.2 | 0.5 | 2.1–4.3 | 4.9 | 0.7 | 3.4–6.4 |
| Throw | 1.8 | 0.3 | 1.2–2.5 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 2–3.2 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 2.8–4.9 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 2.3–4.7 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.6–1.7 | 2.4 | 0.5 | 1.4–3.3 | 2.4 | 0.5 | 1.4–3.4 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 2.8–6.3 |
| Roll | 2.2 | 0.4 | 1.3 -3.1 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 2.9–4.8 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 1.5–3.2 | 4.5 | 0.6 | 3.3–5.7 | 3 | 0.4 | 2.2–3.8 | 5.2 | 0.5 | 4.3–6.2 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 2.8–5 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 3.6–6.7 |
| AMP | 42.4 | 6.1 | 29.2–55.6 | 49.8 | 7.4 | 34.3–65.3 | 57 | 5.3 | 46–68 | 75.2 | 5.3 | 64.1–86.2 | 29.8 | 6.1 | 17.4–42.2 | 48 | 6.4 | 34.8–61.1 | 36.8 | 8.2 | 19.6–53.9 | 58 | 9.7 | 37.4–78.6 |
| Strokes | 22.3 | 3.8 | 14.1–30.5 | 28.9 | 4.3 | 19.8–38 | 31.6 | 3.4 | 24.2–39 | 42.4 | 3.4 | 35.4–49.4 | 14.1 | 3.4 | 7.2–20.9 | 22.3 | 0.6 | 14.9–29.8 | 16.9 | 4.7 | 7–26.7 | 28.1 | 4.8 | 17.8–38.3 |
| Front Crawl | 7.7 | 0.9 | 5.7–9.7 | 9.0 | 1.2 | 6.4–11.6 | 9.7 | 1.0 | 7.7–11.7 | 14 | 1.1 | 11.7–16.4 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 3.2–7 | 8.7 | 1.1 | 6.3–11 | 6.2 | 1.5 | 3.1–9.2 | 10.7 | 1.6 | 7.3–14.1 |
| Back Crawl | 9.9 | 1.7 | 6.1–13.7 | 9.9 | 0.6 | 6.5–13.4 | 11.3 | 1.3 | 8.6–14 | 14.4 | 1 | 12.3 -16.6 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 1.9–6.9 | 8.1 | 0.3 | 5.4–10.7 | 6 | 1.8 | 2.3–9.7 | 10.8 | 1.7 | 7.2–14.5 |
| Breaststroke | 4.7 | 1.6 | 1.2–8.2 | 10.5 | 0.9 | 6.6–14.4 | 10.6 | 1.7 | 7.1–14.1 | 15.6 | 1.3 | 13–18.2 | 4.5 | 0.3 | 2–7.1 | 4.9 | 1.5 | 1.8–7.9 | 4.7 | 1.7 | 1.1–8.3 | 6.5 | 2 | 2.4–10.7 |
| Aquatic Skills | 20.1 | 2.6 | 14.3–25.8 | 21.1 | 3.2 | 14.4–27.8 | 25.4 | 2.0 | 21.4–29.5 | 32.9 | 2.3 | 28.1–37.7 | 15.7 | 2.7 | 10.2–21.3 | 25.6 | 3.2 | 19.1–32.1 | 19.9 | 3.6 | 12.4–27.4 | 29.9 | 5.2 | 19–40.9 |
| Glide | 5.6 | 0.9 | 3.7–7.5 | 5.9 | 0.9 | 4–7.8 | 6.7 | 0.6 | 5.6–7.9 | 8.5 | 0.6 | 7.1–9.8 | 4.0 | 0.9 | 2.2–5.8 | 7.8 | 2.1 | 3.6–12 | 5.2 | 1 | 3–7.4 | 7 | 1 | 4.8–9.2 |
| Scull Feet-first | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2–0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | −0.1–0.7 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.2–2.2 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.9–3 | 0.8 | 0.5 | -0.1–1.7 | 2.5 | 1 | 0.3–4.6 | ||||||
| Scull Head-first | 0.9 | 0.8 | -0.8–2.6 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 1.1–5.4 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.8 -3.6 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 2.5–5.9 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 0.7–3.5 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 1.8–5.3 | 2.3 | 0.9 | 0.3–4.3 | 4.7 | 1.1 | 2.3 -7.1 |
| Tuck | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.3–0.7 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.2–3.5 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 1.8–5.5 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.2–2.9 | 3.4 | 0.9 | 1.6–5.1 | 3 | 1.1 | 0.8–5.2 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 1.7–6.6 | |||
| Submerge | 3.4 | 0.3 | 2.6–4.1 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.8–3.2 | 3.6 | 0.2 | 3.14–4.1 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 2.4–4.1 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 1.1–2.5 | 2.7 | 0.3 | 2.1–3.3 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 1.4–3.1 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 1.7–3.5 |
| Floating | 6.0 | 0.7 | 4.5–7.5 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 3.7–6.5 | 5.8 | 0.4 | 5–6.5 | 5.4 | 0.5 | 4.3–6.4 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 1.7–3.6 | 5 | 0.6 | 3.9–6.2 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 1.4–4.2 | 3.5 | 0.7 | 2–5.1 |
| Treading Water | 1.2 | 0.8 | −0.6–3 | 0.8 | 0.6 | −0.4–2.1 | 2.3 | 0.7 | 0.9–3.8 | 3 | 0.8 | 1.4–4.6 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.3–2.0 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 0.4–3.0 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.3–3.7 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 0.4–4.3 |
| Aquatic Jump | 2.8 | 0.5 | 1.7–3.8 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 0.9–3.3 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 3–4.4 | 3.5 | 0.5 | 2.6–4.4 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 2.0–3.3 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 2.7–4.5 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 1.8–2.9 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 1.84–4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pratt, N.A.; Duncan, M.J.; Oxford, S.W. The Effects of a 6-Week Swimming Intervention on Gross Motor Development in Primary School Children. Children 2024, 11, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010001
Pratt NA, Duncan MJ, Oxford SW. The Effects of a 6-Week Swimming Intervention on Gross Motor Development in Primary School Children. Children. 2024; 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010001
Chicago/Turabian StylePratt, Nicole A., Michael J. Duncan, and Samuel W. Oxford. 2024. "The Effects of a 6-Week Swimming Intervention on Gross Motor Development in Primary School Children" Children 11, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010001
APA StylePratt, N. A., Duncan, M. J., & Oxford, S. W. (2024). The Effects of a 6-Week Swimming Intervention on Gross Motor Development in Primary School Children. Children, 11(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010001