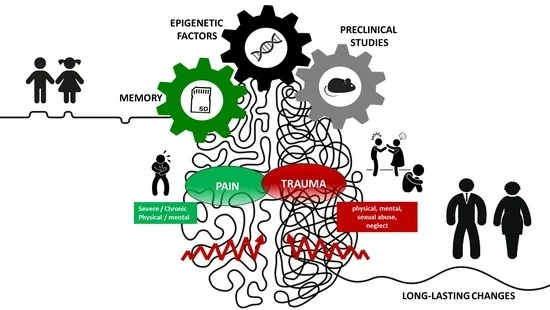
Narrative Review of the Complex Interaction between Pain and Trauma in Children: A Focus on Biological Memory, Preclinical Data, and Epigenetic Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How might painful and/or traumatic experiences affect the memory-forming abilities of a developing brain?
- How might trauma and pain and their emotional sequelae affect children’s memory?
- Are there strategies to correct maladaptive behaviors?
- What is the role of epigenetic factors in pain?
- What is the role of epigenetic factors in traumatic experiences?
- Can epigenetics be considered a new paradigm for developing drugs or strategies for pain and trauma management?
- What are the best model organisms to study traumatic and/or painful events during childhood?
- What are the most valuable paradigms to mimic painful and/or traumatic early-life events?
- How can we translate data from preclinical studies to the clinical setting?

2. Methods
3. The Double-Edged Sword in Defining the Relationship between Pain and Trauma
3.1. Definition of Trauma
3.2. Definition of Pain
3.3. Pain, Trauma, and Their Complex and Multifaced Relationship
4. Pain, Trauma, and Biological Memory: A Complex Trinomen
4.1. How Painful and/or Traumatic Experiences May Affect the Memory-Forming Abilities of a Developing Brain?
4.2. How Might Trauma and Pain and Their Emotional Sequelae Affect Children’s Memory?
4.3. Strategies to Correct Maladaptive Behaviors: From Retrieval-Induced Forgetting to Enriched Environments
5. Preclinical Studies to Decipher the Relationship between Pain and Trauma
5.1. Importance of Pre-Clinical Studies to Investigate the Conserved Molecular, Cellular, and Behavioral Effects of Pain
5.2. Importance of Pre-Clinical Studies to Investigate the Conserved Molecular, Cellular, and Behavioral Effects of Trauma
5.3. Early-Life Stress and Consequences of Trauma and Pain-Related Disorders
Maternal Separation as an Example of ELS
5.4. What Are the Possible Barriers That May Limit Preclinical Studies?
6. Epigenetics of Childhood Trauma and Pain
6.1. Epigenetics and Pain: New Insights about an Old Problem
6.1.1. Understanding Pain Perception or Distortion from an Epigenetics Point of View
- By modulating the expression of ion channels leading to changes in the excitability of neural circuits;
- By inducing or repressing postsynaptic receptors and signaling molecules;
- By altering cell numbers involved in pain transmission circuits, thus affecting their responsiveness;
- By maladapting the structural plasticity at the pre- or post-synaptic level [16].
6.1.2. DNA Methylation in Pain
6.1.3. Histone Modifications in Pain
6.1.4. Non-Coding RNA
6.2. Epigenetics of Childhood Trauma: Long-Term Sequelae and Potential for Treatment
6.3. Epigenetics as a New Paradigm for Developing Drugs or Strategies for Pain and Trauma Management
7. Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, S.; Bento, S.; Enlow, M.B. Biomarkers of Allostatic Load as Correlates of Impairment in Youth with Chronic Pain: An Initial Investigation. Children 2021, 8, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; Borsook, D.; Bosquet Enlow, M. Targeting the Stress Response in Pediatric Pain: Current Evidence for Psychosocial Intervention and Avenues for Future Investigation. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, T.O.; Macmillan, H.L. Resilience Following Child Maltreatment: A Review of Protective Factors. Can. J. Psychiatry 2011, 56, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Kadosh, K.; Linden, D.E.J.; Lau, J.Y.F. Plasticity during Childhood and Adolescence: Innovative Approaches to Investigating Neurocognitive Development. Dev. Sci. 2013, 16, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fandakova, Y.; Hartley, C.A. Mechanisms of Learning and Plasticity in Childhood and Adolescence. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 42, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laube, C.; van den Bos, W.; Fandakova, Y. The Relationship between Pubertal Hormones and Brain Plasticity: Implications for Cognitive Training in Adolescence. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 42, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyandt, L.L.; Clarkin, C.M.; Holding, E.Z.; May, S.E.; Marraccini, M.E.; Gudmundsdottir, B.G.; Shepard, E.; Thompson, L. Neuroplasticity in Children and Adolescents in Response to Treatment Intervention: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2020, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Postovit, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Binder, E.B.; Aitchison, K.J. Epigenetic Modifications in Stress Response Genes Associated with Childhood Trauma. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S. Human Pain and Genetics: Some Basics. Br. J. Pain 2013, 7, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenz, L.; Schechter, D.S.; Serpa, S.R.; Paoloni-Giacobino, A. Intergenerational Transmission of DNA Methylation Signatures Associated with Early Life Stress. Curr. Genom. 2018, 19, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradt, E.; Adkins, D.E.; Crowell, S.E.; Raby, K.L.; Diamond, L.M.; Ellis, B. Incorporating Epigenetic Mechanisms to Advance Fetal Programming Theories. Dev. Psychopathol. 2018, 30, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; Miller, J.V.; Timmers, I.; Simons, L.E.; Meldrum, K.; Noel, M. Paediatric Chronic Pain as a Catalyst for Toxic Stress. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2022, 6, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, M.L.; Goodman, G.S.; Qin, J.; Davis, S.; Crayton, J. Maltreated Children’s Memory: Accuracy, Suggestibility, and Psychopathology. Dev. Psychol. 2007, 43, 1275–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otgaar, H.; Candel, I. Children’s False Memories: Different False Memory Paradigms Reveal Different Results. Psychol. Crime Law 2011, 17, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumfart, K.M.; Jawaid, A.; Bright, K.; Flachsmann, M.; Mansuy, I.M. Epigenetics of Childhood Trauma: Long Term Sequelae and Potential for Treatment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirvanie-Persaud, L.; Millis, R.M. Epigenetics and Pain: New Insights to an Old Problem. Cureus 2022, 14, e29353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisagno, E.; Cadamuro, A.; Dierickx, S.; Mosleh, D.B.; Linde-Ozola, Z.; Kandāte, A.; Varga-Sabjan, D.; Morva, D.; Laszlo, N.; Rozsa, M.; et al. A European Comparison of Screening and Referral by Childcare Professionals of Maltreatment in Children Aged 0–3: A Wild Goose Chase or Maybe Not. Child Abus. Rev. 2023, 32, e2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, J.L.; Ownsworth, T.; Dawe, S. Development of a Framework for Classifying Threat and Neglect in Childhood: A Qualitative Study. Child Abus. Rev. 2023, 32, e2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddoe, L.; Ferguson, H.; Warwick, L.; Disney, T.; Leigh, J.; Cooner, T.S. Supervision in Child Protection: A Space and Place for Reflection or an Excruciating Marathon of Compliance? Eur. J. Soc. Work 2022, 25, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAMHSA—Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/ (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Gradus, J.L.; Galea, S. Reconsidering the Definition of Trauma. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 608–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.V.; Lopez, R.A.; King, K.C. Blunt Force Trauma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lubit, R.; Rovine, D.; Defrancisci, L.; Eth, S. Impact of Trauma on Children. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2003, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.; Spinazzola, J.; Ford, J.; Lanktree, C.; Blaustein, M.; Cloitre, M.; DeRosa, R.; Hubbard, R.; Kagan, R.; Liautaud, J.; et al. Complex Trauma in Children and Adolescents. Psychiatr. Ann. 2005, 35, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, J.L.; Bush, K.A.; Kersevich, S.E. Trauma-Sensitive Schools: An Evidence-Based Approach. Sch. Soc. Work J. 2016, 40, 37–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.L.; Sharma-Patel, K.; Brown, E.J.; Huntt, J.S.; Chaplin, W.F. Complex Trauma and Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: How Do Trauma Chronicity and PTSD Presentation Affect Treatment Outcome? Child Abus. Negl. 2021, 111, 104734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Substance Abuse Treatment. Understanding the Impact of Trauma; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, H.N.; Moran, G.; Pederson, D.R. Childhood Maltreatment, Complex Trauma Symptoms, and Unresolved Attachment in an At-Risk Sample of Adolescent Mothers. Attach. Hum. Dev. 2007, 9, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonagy, P.; Gergely, G.; Target, M. The Parent-Infant Dyad and the Construction of the Subjective Self. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2007, 48, 288–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The Revised International Association for the Study of Pain Definition of Pain: Concepts, Challenges, and Compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thill, B. The Fetal Pain Paradox. Front. Pain Res. 2023, 4, 1128530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellieni, C.V. New Insights into Fetal Pain. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 24, 101001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, L. Pain in Children: Neglected, Unaddressed and Mismanaged. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2011, 17, S70–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.E.; McGrath, P.J. The Epidemiology of Pain in Children and Adolescents: A Review. Pain 1991, 46, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonhard, S.E.; Mandarakas, M.R.; Gondim, F.A.A.; Bateman, K.; Ferreira, M.L.B.; Cornblath, D.R.; van Doorn, P.A.; Dourado, M.E.; Hughes, R.A.C.; Islam, B.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Guillain-Barré Syndrome in Ten Steps. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvenile Arthritis—Types and Treatments—OrthoInfo—AAOS. Available online: https://www.orthoinfo.org/en/diseases--conditions/juvenile-arthritis/ (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Morris, C.; Ross, A.; Greene, K.; Irwin, S.; Wagstaff, A.; Gelfand, A. Outcomes that Matter to Adolescents with Continuous Headache Due to Chronic Migraine and Their Parents: A Pilot Survey Study. Neurology 2022, 98, e2347–e2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, N.; Naser, B.; Hanley, J.; Peliowski, A.; Hayes, J.; Aoyama, K. A Practical Guide to Acute Pain Management in Children. J. Anesth. 2020, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, J.M.C.; Barisone, E.; Bertolotti, M.; Caprino, D.; Cellini, M.; Clerici, C.A.; Colliva, C.; Favara-Scacco, C.; Di Giuseppe, S.; Jankovic, M.; et al. The Use of Psychotropic Medication in Pediatric Oncology for Acute Psychological and Psychiatric Problems: Balancing Risks and Benefits. Children 2022, 9, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, L.M.; Zayfert, C.; Gross, R.T. The Pain Anxiety Symptoms Scale: Development and Validation of a Scale to Measure Fear of Pain. Pain 1992, 50, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pate, J.W.; Hush, J.M.; Hancock, M.J.; Moseley, G.L.; Butler, D.S.; Simons, L.E.; Pacey, V. A Child’s Concept of Pain: An International Survey of Pediatric Pain Experts. Children 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, N.L.; Key, A.P.; Chorna, O.D.; Slaughter, J.C.; Matusz, P.J.; Wallace, M.T.; Murray, M.M. The Dual Nature of Early-Life Experience on Somatosensory Processing in the Human Infant Brain. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.C.; Cheong, J.L.Y.; Doyle, L.W. Biological and Social Influences on the Neurodevelopmental Outcomes of Preterm Infants. Clin. Perinatol. 2018, 45, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, M.; Zwicker, J.G.; Chau, C.M.Y.; Park, M.T.M.; Chakravarthy, M.M.; Poskitt, K.; Miller, S.P.; Bjornson, B.H.; Tam, E.W.Y.; Chau, V.; et al. Neonatal Pain and Infection Relate to Smaller Cerebellum in Very Preterm Children at School Age. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 292–298.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.M.Y.; Ranger, M.; Bichin, M.; Park, M.T.M.; Amaral, R.S.C.; Chakravarty, M.; Poskitt, K.; Synnes, A.R.; Miller, S.P.; Grunau, R.E. Hippocampus, Amygdala, and Thalamus Volumes in Very Preterm Children at 8 Years: Neonatal Pain and Genetic Variation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, L.J.; Cooke, R.W.I.; Foulder-Hughes, L. Caudate and Hippocampal Volumes, Intelligence, and Motor Impairment in 7-Year-Old Children Who Were Born Preterm. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.E.; Minhas, D.; Clauw, D.J.; Lee, Y.C. Identifying and Managing Nociplastic Pain in Individuals with Rheumatic Diseases: A Narrative Review. Arthritis Care Res. 2023. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, S.A.; Herr, M.J. Physiology, Nociception. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosek, E.; Clauw, D.; Nijs, J.; Baron, R.; Gilron, I.; Harris, R.E.; Mico, J.-A.; Rice, A.S.C.; Sterling, M. Chronic Nociplastic Pain Affecting the Musculoskeletal System: Clinical Criteria and Grading System. Pain 2021, 162, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Association for the Study of Pain|IASP. Available online: https://www.iasp-pain.org/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Grichnik, K.P.; Ferrante, F.M. The Difference between Acute and Chronic Pain. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 1991, 58, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Voscopoulos, C.; Lema, M. When Does Acute Pain Become Chronic? Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 105 (Suppl. S1), i69–i85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.M.; Cunningham, N.R.; Kashikar-Zuck, S. A Conceptual Framework for Understanding the Role of Adverse Childhood Experiences in Pediatric Chronic Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, M.; Alberts, N.; Langer, S.L.; Levy, R.L.; Walker, L.S.; Palermo, T.M. The Sensitivity to Change and Responsiveness of the Adult Responses to Children’s Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Chronic Pain. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2016, 41, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.L.; Jackson, N.L.; Ballestas, M.E.; Webb, W.M.; Lubin, F.D.; Clinton, S.M. Amygdalar Expression of the MicroRNA MiR-101a and Its Target Ezh2 Contribute to Rodent Anxiety-like Behaviour. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinall, J.; Pavlova, M.; Asmundson, G.J.G.; Rasic, N.; Noel, M. Mental Health Comorbidities in Pediatric Chronic Pain: A Narrative Review of Epidemiology, Models, Neurobiological Mechanisms and Treatment. Children 2016, 3, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierickx, S.; Malisse, L.; Bisagno, E.; Cadamuro, A.; Van Haeken, S.; Wuyts, D.; Linde-Ozola, Z.; Kandãte, A.; Morva, D.; Rozsa, M.; et al. Care When It Counts: Establishing Trauma-Sensitive Care as a Preventative Approach for 0-3-Year-Old Children Suffering from Trauma and Chronic Stress. Children 2023, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, G.S.; Bhandari, R.P.; Huestis, S.E.; Golianu, B. Traumatic Stress and Pediatric Pain: Towards a Neurobiological Stress-Health Perspective. J. Child Adolesc. Trauma 2017, 11, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elman, I.; Borsook, D. Threat Response System: Parallel Brain Processes in Pain Vis-à-Vis Fear and Anxiety. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, D.; Adhia, D.; Vanneste, S. The Anatomy of Pain and Suffering in the Brain and Its Clinical Implications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 130, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ridder, D.; Vanneste, S.; Smith, M.; Adhia, D. Pain and the Triple Network Model. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 757241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarponi, D.; Sarti, P.; Rivi, V.; Colliva, C.; Marconi, E.; Pession, A.; Blom, J.M.C. Emotional, Behavioral, and Physical Health Consequences in Caregivers of Children with Cancer: A Network Analysis Differentiation in Mothers’ and Fathers’ Reactivity. Cancers 2023, 15, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.; Simons, L.E.; Logan, D. The Incidence of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and Their Association with Pain-Related and Psychosocial Impairment in Youth with Chronic Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2018, 34, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriquez, E.J.; Kim, E.N.; Sumner, A.E.; Nápoles, A.M.; Pérez-Stable, E.J. Allostatic Load: Importance, Markers, and Score Determination in Minority and Disparity Populations. J. Urban Health. 2019, 96 (Suppl. 1), 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charuvastra, A.; Cloitre, M. Social Bonds and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakamata, Y.; Mizukami, S.; Izawa, S.; Moriguchi, Y.; Hori, H.; Matsumoto, N.; Hanakawa, T.; Inoue, Y.; Tagaya, H. Childhood Trauma Affects Autobiographical Memory Deficits through Basal Cortisol and Prefrontal-Extrastriate Functional Connectivity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 127, 105172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbriano, G.; Waszczuk, M.; Rajaram, S.; Ruggero, C.; Miao, J.; Clouston, S.; Luft, B.; Kotov, R.; Mohanty, A. Association of Attention and Memory Biases for Negative Stimuli with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms. J. Anxiety Disord. 2022, 85, 102509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olff, M. Bonding after Trauma: On the Role of Social Support and the Oxytocin System in Traumatic Stress. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol. 2012, 3, 18597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Soderlund, A.L.; Braungart-Rieker, J.M. Early Individual Differences in Temperamental Reactivity and Regulation: Implications for Effortful Control in Early Childhood. Infant Behav. Dev. 2008, 31, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waikamp, V.; Serralta, F.B.; Ramos-Lima, L.F.; Zatti, C.; Freitas, L.H.M. Relationship between Childhood Trauma, Parental Bonding, and Defensive Styles and Psychiatric Symptoms in Adult Life. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2021, 43, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BREM, A.-K.; RAN, K.; PASCUAL-LEONE, A. Learning and Memory. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 116, 693–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornstein, P.A.; Haden, C.A. Memory Development or the Development of Memory? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 10, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.; Ornstein, P.A. Determinants of Memory Development in Childhood and Adolescence. Int. J. Psychol. 2019, 54, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, M.; Edorsson, A.; Sundqvist, A.; Koch, F.-S. Thirteen- to Sixteen-Months Old Infants Are Able to Imitate a Novel Act from Memory in Both Unfamiliar and Familiar Settings but Do Not Show Evidence of Rational Inferential Processes. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camina, E.; Güell, F. The Neuroanatomical, Neurophysiological, and Psychological Basis of Memory: Current Models and Their Origins. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.J.; Hoffmann, A.M. Autobiographical Memory in Childhood. In The Encyclopedia of Child and Adolescent Development; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-1-119-17149-2. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, S.E.; Ford, J.H.; Kensinger, E.A. The Power of Negative and Positive Episodic Memories. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 22, 869–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, B.; Gibb, R. Brain Plasticity and Behaviour in the Developing Brain. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 20, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Tafà, M.; Cerniglia, L.; Cimino, S.; Ballarotto, G.; Marzilli, E.; Tambelli, R. Predictive Values of Early Parental Loss and Psychopathological Risk for Physical Problems in Early Adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, E.G.; Friedenberg, S.L.; Swenson, C.C.; LaRosa, A.; De Bellis, M.D.; Macias, M.M.; Summer, A.P.; Hulsey, T.C.; Runyan, D.K.; Brady, K.T. The Effects of Early Neglect on Cognitive, Language, and Behavioral Functioning in Childhood. Psychology 2012, 3, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majer, M.; Nater, U.M.; Lin, J.-M.S.; Capuron, L.; Reeves, W.C. Association of Childhood Trauma with Cognitive Function in Healthy Adults: A Pilot Study. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liming, K.W.; Grube, W.A. Wellbeing Outcomes for Children Exposed to Multiple Adverse Experiences in Early Childhood: A Systematic Review. Child Adolesc. Soc. Work J. 2018, 35, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, A.L.; Wilson, A.C.; Noel, M.; Palermo, T.M. Post-Traumatic Stress Symptoms in Children and Adolescents with Chronic Pain: A Topical Review of the Literature and a Proposed Framework for Future Research. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorastos, A.; Pervanidou, P.; Chrousos, G.P.; Baker, D.G. Developmental Trajectories of Early Life Stress and Trauma: A Narrative Review on Neurobiological Aspects Beyond Stress System Dysregulation. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, J.K. Cognitive Deficits in Psychiatric Disorders: Current Status. Indian J. Psychiatry 2006, 48, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, C. Disorders of Memory and Plasticity in Psychiatric Disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 15, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, A.; Zorkina, Y.; Abramova, O.; Pavlova, O.; Pavlov, K.; Soloveva, K.; Volkova, M.; Alekseeva, P.; Andryshchenko, A.; Kostyuk, G.; et al. Neurobiological Highlights of Cognitive Impairment in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivi, V.; Benatti, C.; Colliva, C.; Radighieri, G.; Brunello, N.; Tascedda, F.; Blom, J.M.C. Lymnaea Stagnalis as Model for Translational Neuroscience Research: From Pond to Bench. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 108, 602–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia, D.A.; Crossman, A.M.; Segovia, D.A.; Crossman, A.M. Cognition and the Child Witness: Understanding the Impact of Cognitive Development in Forensic Contexts; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; Corpus ID: 142946954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainerd, C.J.; Reyna, V.F. Reliability of Children’s Testimony in the Era of Developmental Reversals. Dev. Rev. 2012, 32, 224–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard-Gilligan, M.; Zoellner, L.A. Dissociation and Memory Fragmentation in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: An Evaluation of the Dissociative Encoding Hypothesis. Memory 2012, 20, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, C.R. Memory and Forgetting. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kolk, B.A. The Body Keeps the Score: Memory and the Evolving Psychobiology of Posttraumatic Stress. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 1994, 1, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, B.; Wallott, F.; Ehlers, A. Are Trauma Memories Disjointed from Other Autobiographical Memories in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder? An Experimental Investigation. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2008, 36, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, A.; Clark, D.M. A Cognitive Model of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Behav. Res. Ther. 2000, 38, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, C.R. A Cognitive Neuroscience Account of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Its Treatment. Behav. Res. Ther. 2001, 39, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.D.; Shobe, K.K.; Kihlstrom, J.F. False Memories in Women with Self-Reported Childhood Sexual Abuse: An Empirical Study. Psychol. Sci. 2000, 11, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoellner, L.A.; Foa, E.B.; Brigidi, B.D.; Przeworski, A. Are Trauma Victims Susceptible to “False Memories”? J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2000, 109, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.M.G. Depression and the Specificity of Autobiographical Memory. In Remembering Our Past: Studies in Autobiographical Memory; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 244–267. ISBN 978-0-521-46145-0. [Google Scholar]
- Brewin, C.R.; Andrews, B. Creating Memories for False Autobiographical Events in Childhood: A Systematic Review. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2017, 31, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D.; Krystal, J.H.; Charney, D.S.; Southwick, S.M. Neural Mechanisms in Dissociative Amnesia for Childhood Abuse: Relevance to the Current Controversy Surrounding the “False Memory Syndrome”. Am. J. Psychiatry 1996, 153, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hallford, D.J.; Rusanov, D.; Yeow, J.J.J.; Barry, T. Reduced Specificity and Increased Overgenerality of Autobiographical Memory Persist as Cognitive Vulnerabilities in Remitted Major Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2022, 29, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otgaar, H.; Howe, M.L.; Dodier, O.; Lilienfeld, S.O.; Loftus, E.F.; Lynn, S.J.; Merckelbach, H.; Patihis, L. Belief in Unconscious Repressed Memory Persists. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2021, 16, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otgaar, H.; Howe, M.L.; Patihis, L.; Merckelbach, H.; Lynn, S.J.; Lilienfeld, S.O.; Loftus, E.F. The Return of the Repressed: The Persistent and Problematic Claims of Long-Forgotten Trauma. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 14, 1072–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, R.J.; Geraerts, E. A New Solution to the Recovered Memory Debate. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 4, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otgaar, H.; Candel, I.; Merckelbach, H. Children’s False Memories: Easier to Elicit for a Negative than for a Neutral Event. Acta Psychol. 2008, 128, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman-Brown, T.B.; Edelstein, R.S.; Goodman, G.S.; Jones, D.P.H.; Gordon, D.S. Why Children Tell: A Model of Children’s Disclosure of Sexual Abuse. Child Abus. Negl. 2003, 27, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, M.C.; Palombo, D.J.; Nazarov, A.; Kumar, N.; Khuu, W.; Levine, B. Threat of Death and Autobiographical Memory: A Study of Passengers from Flight AT236. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 3, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, R.J. Debunking Myths about Trauma and Memory. Can. J. Psychiatry 2005, 50, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremner, J.D. Traumatic Stress: Effects on the Brain. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.I.; Clark, D.M. Predictors of Analogue Post-Traumatic Intrusive Cognitions. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 1998, 26, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bücken, C.A.; Otgaar, H.; London, K.; Riesthuis, P.; Battista, F.; Mangiulli, I. ‘Nothing Happened’: Legal Implications of False Denials among Abused Children. Child Abus. Rev. 2023, 32, e2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffee, S.R. Child Maltreatment and Risk for Psychopathology in Childhood and Adulthood. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2017, 13, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellis, M.D.; Zisk, A. The Biological Effects of Childhood Trauma. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 23, 185–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Lambert, H.K. Child Trauma Exposure and Psychopathology: Mechanisms of Risk and Resilience. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2017, 14, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.C.; Joseph, J.; Feit, M.; Committee on Child Maltreatment Research, Policy, and Practice for the Next Decade: Phase II; Board on Children, Youth, and Families; Committee on Law and Justice; Institute of Medicine; National Research Council (Eds.) Consequences of Child Abuse and Neglect. In New Directions in Child Abuse and Neglect Research; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Marche, T.A.; Briere, J.L.; von Baeyer, C.L. Children’s Forgetting of Pain-Related Memories. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2016, 41, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, C.J.; Aagaard, L.; Burcu, M.; Glaeske, G.; Kalverdijk, L.J.; Petersen, I.; Schuiling-Veninga, C.C.M.; Wijlaars, L.; Zito, J.M.; Hoffmann, F. Trends and Patterns of Antidepressant Use in Children and Adolescents from Five Western Countries, 2005–2012. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, L.S.; Chan, M.F.; Al-Azri, M. Prevalence of Anxiety, Depression, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder among Children and Adolescents with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. Nurs. 2022, 39, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Sheridan, M.A.; Gold, A.L.; Duys, A.; Lambert, H.K.; Peverill, M.; Heleniak, C.; Shechner, T.; Wojcieszak, Z.; Pine, D.S. Maltreatment Exposure, Brain Structure, and Fear Conditioning in Children and Adolescents. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milad, M.R.; Pitman, R.K.; Ellis, C.B.; Gold, A.L.; Shin, L.M.; Lasko, N.B.; Zeidan, M.A.; Handwerger, K.; Orr, S.P.; Rauch, S.L. Neurobiological Basis of Failure to Recall Extinction Memory in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craske, M.G.; Waters, A.M.; Bergman, R.L.; Naliboff, B.; Lipp, O.V.; Negoro, H.; Ornitz, E.M. Is Aversive Learning a Marker of Risk for Anxiety Disorders in Children? Behav. Res. Ther. 2008, 46, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, J.D.; Yehuda, R. Comorbidity between Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Major Depressive Disorder: Alternative Explanations and Treatment Considerations. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 17, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslau, N.; Davis, G.C.; Peterson, E.L.; Schultz, L. Psychiatric Sequelae of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Women. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, I.; Brennen, T. Intentional Forgetting of Emotional Words after Trauma: A Study with Victims of Sexual Assault. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzi, M.; Cianfanelli, B.; Santirocchi, A.; Lasaponara, S.; Spataro, P.; Rossi-Arnaud, C.; Cestari, V. Forgetting Unwanted Memories: Active Forgetting and Implications for the Development of Psychological Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyadurai, L.; Visser, R.M.; Lau-Zhu, A.; Porcheret, K.; Horsch, A.; Holmes, E.A.; James, E.L. Intrusive Memories of Trauma: A Target for Research Bridging Cognitive Science and Its Clinical Application. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2019, 69, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, S.J.; Mather, M. Forgetting in Context: The Effects of Age, Emotion, and Social Factors on Retrieval-Induced Forgetting. Mem. Cognit. 2012, 40, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yuan, M.; Guo, Y.-S.; Shen, X.-Y.; Gao, Z.-K.; Bi, X. The Role of Enriched Environment in Neural Development and Repair. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 890666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter-Levin, G.; Stork, O.; Schmidt, M.V. Animal Models of PTSD: A Challenge to Be Met. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1135–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghans, B.; Homberg, J.R. Animal Models for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: An Overview of What Is Used in Research. World J. Psychiatry 2015, 5, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, J.I. The Future of Preclinical Animal Models in Pharmaceutical Discovery and Development: A Need to Bring in Cerebro to the in Vivo Discussions. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howland, J.G.; Greenshaw, A.J.; Winship, I.R. Practical Aspects of Animal Models of Psychiatric Disorders. Can. J. Psychiatry 2019, 64, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S.; Davis, K.D.; Derbyshire, S.W. The Necessity of Animal Models in Pain Research. Pain 2010, 151, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S. The Translatability of Pain across Species. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20190286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberg, D.E.; Bustamante, H.A.; Herzberg, D.E.; Bustamante, H.A. Animal Models of Chronic Pain. Are Naturally Occurring Diseases a Potential Model for Translational Research? Austral. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 53, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdowsian, H.; Merskin, D. Parallels in Sources of Trauma, Pain, Distress, and Suffering in Humans and Nonhuman Animals. J. Trauma Dissociation 2012, 13, 448–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.; Deol, H.K.; Martin, L.J. Bridging the Translational Divide in Pain Research: Biological, Psychological and Social Considerations. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 603186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, C.; Hu, X.; Ni, J.; Lu, H.; Zhao, H. Calcitonin Gene–Related Peptide Monoclonal Antibody Versus Botulinum Toxin for the Preventive Treatment of Chronic Migraine: Evidence from Indirect Treatment Comparison. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 631204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, C.F.; Phifer, J.; Bradley, B.; Ressler, K.J. Risk and Resilience: Genetic and Environmental Influences on Development of the Stress Response. Depress. Anxiety 2009, 26, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brust, V.; Schindler, P.M.; Lewejohann, L. Lifetime Development of Behavioural Phenotype in the House Mouse (Mus Musculus). Front. Zool. 2015, 12, S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill, L.A.; Abdallah, C.G.; Fenton, L.R.; Fasula, M.K.; Jiang, L.; Rothman, D.L.; Mason, G.F.; Sanacora, G. Early Life Stress and Glutamate Neurotransmission in Major Depressive Disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 35, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benatti, C.; Radighieri, G.; Alboni, S.; Blom, J.M.C.; Brunello, N.; Tascedda, F. Modulation of Neuroplasticity-Related Targets Following Stress-Induced Acute Escape Deficit. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 364, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti, C.; Blom, J.M.C.; Rigillo, G.; Alboni, S.; Zizzi, F.; Torta, R.; Brunello, N.; Tascedda, F. Disease-Induced Neuroinflammation and Depression. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 15, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti, C.; Alboni, S.; Montanari, C.; Caggia, F.; Tascedda, F.; Brunello, N.; Blom, J.M.C. Central Effects of a Local Inflammation in Three Commonly Used Mouse Strains with a Different Anxious Phenotype. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 224, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboni, S.; Benatti, C.; Colliva, C.; Radighieri, G.; Blom, J.M.C.; Brunello, N.; Tascedda, F. Vortioxetine Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Memory Impairment without Inhibiting the Initial Inflammatory Cascade. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 603979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras, I.; Río-Álamos, C.; Cañete, T.; Blázquez, G.; Martínez-Membrives, E.; Giorgi, O.; Corda, M.G.; Tobeña, A.; Fernández-Teruel, A. Prepulse Inhibition Predicts Spatial Working Memory Performance in the Inbred Roman High- and Low-Avoidance Rats and in Genetically Heterogeneous NIH-HS Rats: Relevance for Studying Pre-Attentive and Cognitive Anomalies in Schizophrenia. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swick, D.; Cayton, J.; Ashley, V.; Turken, A.U. Dissociation Between Working Memory Performance and Proactive Interference Control in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Neuropsychologia 2017, 96, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, S.; Dalgleish, T. Emotional Working Memory Capacity in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Behav. Res. Ther. 2011, 49, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Herman, J.P. Neural Regulation of Endocrine and Autonomic Stress Responses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.P.; Figueiredo, H.; Mueller, N.K.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.; Ostrander, M.M.; Choi, D.C.; Cullinan, W.E. Central Mechanisms of Stress Integration: Hierarchical Circuitry Controlling Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Responsiveness. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2003, 24, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juruena, M.F. Early-Life Stress and HPA Axis Trigger Recurrent Adulthood Depression. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 38, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, A.; Belliveau, C.; Mechawar, N.; Walker, C.-D. Effects of Early Life Stress on the Developing Basolateral Amygdala-Prefrontal Cortex Circuit: The Emerging Role of Local Inhibition and Perineuronal Nets. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 669120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juruena, M.F.; Bourne, M.; Young, A.H.; Cleare, A.J. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Dysfunction by Early Life Stress. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 759, 136037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Williams, A.V.; Bangasser, D.A.; Peña, C.J. Impact of Early Life Stress on Reward Circuit Function and Regulation. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 744690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschdorf, J.P.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetics/Programming in the HPA Axis. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 6, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryce, C.R.; Feldon, J. Long-Term Neurobehavioural Impact of the Postnatal Environment in Rats: Manipulations, Effects and Mediating Mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2003, 27, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldji, C.; Tannenbaum, B.; Sharma, S.; Francis, D.; Plotsky, P.M.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal Care during Infancy Regulates the Development of Neural Systems Mediating the Expression of Fearfulness in the Rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5335–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orso, R.; Creutzberg, K.C.; Wearick-Silva, L.E.; Wendt Viola, T.; Tractenberg, S.G.; Benetti, F.; Grassi-Oliveira, R. How Early Life Stress Impact Maternal Care: A Systematic Review of Rodent Studies. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tractenberg, S.G.; Levandowski, M.L.; de Azeredo, L.A.; Orso, R.; Roithmann, L.G.; Hoffmann, E.S.; Brenhouse, H.; Grassi-Oliveira, R. An Overview of Maternal Separation Effects on Behavioural Outcomes in Mice: Evidence from a Four-Stage Methodological Systematic Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, F.A.; Francis, D.D.; Mar, A.; Meaney, M.J. Variations in Maternal Care in the Rat as a Mediating Influence for the Effects of Environment on Development. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 79, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.D.; Kuhar, M.J. Frequency of Maternal Licking and Grooming Correlates Negatively with Vulnerability to Cocaine and Alcohol Use in Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudani, S.; Torrisi, S.A.; Alboni, S.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Benatti, C.; Rivi, V.; Moloney, R.D.; Fuochi, V.; Furneri, P.M.; Drago, F.; et al. Gut Microbiota Alterations Promote Traumatic Stress Susceptibility Associated with P-Cresol-Induced Dopaminergic Dysfunctions. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2023, 107, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugher, B.J.; Sachs, B.D. Early Life Maternal Separation Induces Sex-Specific Antidepressant-like Responses but Has Minimal Effects on Adult Stress Susceptibility in Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 941884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.; Gould, E. Early Life Stress in Rodents: Animal Models of Illness or Resilience? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millstein, R.A.; Holmes, A. Effects of Repeated Maternal Separation on Anxiety- and Depression-Related Phenotypes in Different Mouse Strains. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichev, M.; Easterling, K.W.; Plotsky, P.M.; Holtzman, S.G. Long-Lasting Changes in Stress-Induced Corticosterone Response and Anxiety-like Behaviors as a Consequence of Neonatal Maternal Separation in Long–Evans Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundakovic, M.; Champagne, F.A. Early-Life Experience, Epigenetics, and the Developing Brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.; Denk, F.; McMahon, S.B. Genes and Epigenetic Processes as Prospective Pain Targets. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessans, S.; Dorsey, S.G. The Role for Epigenetic Modifications in Pain and Analgesia Response. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 961493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descalzi, G.; Ikegami, D.; Ushijima, T.; Nestler, E.; Zachariou, V.; Narita, M. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Chronic Pain. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Gu, X.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Wu, S.; Miao, X.; Xiao, J.; Mo, K.; Zhang, J.; Lutz, B.M.; Bekker, A.; et al. G9a Participates in Nerve Injury-Induced Kcna2 Downregulation in Primary Sensory Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Xu, M.; Mo, C.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, X. JMJD6 Exerts Function in Neuropathic Pain by Regulating NF-κB Following Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Gu, X.; Liang, L.; Wu, S.; Mo, K.; Feng, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, J.; Bekker, A.; et al. Nerve Injury-Induced Epigenetic Silencing of Opioid Receptors Controlled by DNMT3a in Primary Afferent Neurons. Pain 2017, 158, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sahbaie, P.; Liang, D.-Y.; Li, W.-W.; Li, X.-Q.; Shi, X.-Y.; Clark, J.D. Epigenetic Regulation of Spinal CXCR2 Signaling in Incisional Hypersensitivity in Mice. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Chao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, J.; Li, S.; Wei, H.; Xue, R.; Li, F.; Li, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in a Mouse Model of Brain Ischemic/Reperfusion Injury via Anti-apoptotic Mechanisms Based on the Akt Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-C.; He, L.-N.; Wu, X.-B.; Shi, H.; Zhang, W.-W.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Cao, D.-L.; Li, C.-H.; Gu, J.; Gao, Y.-J. Promoted Interaction of C/EBPα with Demethylated Cxcr3 Gene Promoter Contributes to Neuropathic Pain in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-C.; Zhang, W.-W.; Yang, T.; Guo, C.-Y.; Cao, D.-L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Gao, Y.-J. Demethylation of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor 151 Promoter Facilitates the Binding of Krüppel-Like Factor 5 and Enhances Neuropathic Pain after Nerve Injury in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10535–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauceri, D. Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Chronic Pain. Cells 2022, 11, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Ren, X.; Su, S.; Bai, Q.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; et al. MicroRNA-182 Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Regulating Nav1.7 Following Spared Nerve Injury in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Tao, J.; Gu, J.; Jiang, X.; Xu, G.-Y. Promoter Demethylation of Cystathionine-β-Synthetase Gene Contributes to Inflammatory Pain in Rats. Pain 2013, 154, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.; Chaloner, A.; Sawalha, A.H.; Greenwood Van-Meerveld, B. Importance of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Visceral Pain Induced by Chronic Water Avoidance Stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzarides, T. Chromatin Modifications and Their Function. Cell 2007, 128, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannister, A.J.; Kouzarides, T. Regulation of Chromatin by Histone Modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Song, F.; Li, W.; Xie, G.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J. Epigenetic Modifications in Neuropathic Pain. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 17448069211056768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lu, J.; Mori, T.; Smith-Powell, L.; Synold, T.W.; Chen, S.; Wen, W. Baicalin Increases VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis by Activating the ERR/PGC-1 Pathway. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Matsushita, Y.; Ueda, H. Epigenetic Regulation of BDNF Expression in the Primary Sensory Neurons after Peripheral Nerve Injury: Implications in the Development of Neuropathic Pain. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhao, G.-Q.; Li, L.-Y.; Wu, G.-Z.; Cui, S. Epigenetic Upregulation of Cdk5 in the Dorsal Horn Contributes to Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Neuroreport 2014, 25, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Saika, F.; Kishioka, S. Epigenetic Upregulation of CCL2 and CCL3 via Histone Modifications in Infiltrating Macrophages after Peripheral Nerve Injury. Cytokine 2013, 64, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiguchi, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Maeda, T.; Fukazawa, Y.; Tohya, K.; Kimura, M.; Kishioka, S. Epigenetic Augmentation of the Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 2/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 2 Axis through Histone H3 Acetylation in Injured Peripheral Nerves Elicits Neuropathic Pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.-Y.; Li, X.; Clark, J.D. Epigenetic Regulation of Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia, Dependence, and Tolerance in Mice. J. Pain 2013, 14, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Lutz, B.M.; Bekker, A.; Tao, Y.-X. Epigenetic Regulation of Chronic Pain. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Rong, L.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, L.; Yu, W.; Zhang, M.; Ren, X.; et al. Epigenetic Restoration of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel Kv1.2 Alleviates Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain. J. Neurochem. 2021, 156, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigillo, G.; Vilella, A.; Benatti, C.; Schaeffer, L.; Brunello, N.; Blom, J.M.C.; Zoli, M.; Tascedda, F. LPS-induced histone H3 phospho(Ser10)-acetylation(Lys14) regulates neuronal and microglial neuroinflammatory response. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Shen, X.; Bao, S.; Feng, S.-W.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Shen, R.; et al. Dopaminergic Inhibition by G9a/Glp Complex on Tyrosine Hydroxylase in Nerve Injury-Induced Hypersensitivity. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916663731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.-R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, G.; Pan, H.-L. Histone Methyltransferase G9a Diminishes Expression of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in Primary Sensory Neurons in Neuropathic Pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3553–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; He, M.; Xu, Q.; Tian, W. Advances with Non-Coding RNAs in Neuropathic Pain. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 760936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Du, S.; Wang, K.; Guo, X.; Mao, Q.; Feng, X.; Huang, L.; Wu, S.; Hou, B.; Chang, Y.; et al. Downregulation of a Dorsal Root Ganglion-Specifically Enriched Long Noncoding RNA Is Required for Neuropathic Pain by Negatively Regulating RALY-Triggered Ehmt2 Expression. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Su, S.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zang, W. MicroRNA-30b Regulates Expression of the Sodium Channel Nav1.7 in Nerve Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain in the Rat. Mol. Pain 2016, 12, 1744806916671523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, A.; Saitow, F.; Miyake, N.; Miyake, K.; Shimada, T.; Suzuki, H. MiR-7a Alleviates the Maintenance of Neuropathic Pain through Regulation of Neuronal Excitability. Brain 2013, 136, 2738–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinders, M.; Üçeyler, N.; Pritchard, R.A.; Sommer, C.; Sorkin, L.S. Increased MiR-132-3p Expression Is Associated with Chronic Neuropathic Pain. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, A.; Saitow, F.; Maruyama, M.; Miyake, N.; Miyake, K.; Shimada, T.; Okada, T.; Suzuki, H. MicroRNA Cluster MiR-17-92 Regulates Multiple Functionally Related Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Chronic Neuropathic Pain. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahchop, E.L.; Branton, W.G.; Krishnan, A.; Chen, P.A.; Yang, D.; Kong, L.; Zochodne, D.W.; Brew, B.J.; Gill, M.J.; Power, C. HIV-Associated Sensory Polyneuropathy and Neuronal Injury Are Associated with MiRNA-455-3p Induction. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.; Hermanns, H.; Barthel, F.; Werdehausen, R.; Brandenburger, T. Expression Changes of MicroRNA-1 and Its Targets Connexin 43 and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Peripheral Nervous System of Chronic Neuropathic Rats. Mol. Pain 2015, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manners, M.T.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ajit, S.K. MicroRNAs Downregulated in Neuropathic Pain Regulate MeCP2 and BDNF Related to Pain Sensitivity. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.-R.; Chen, J.; Yi, H.; Peng, L.-Y.; Hu, X.-L.; Guo, Q.-L. MicroRNA-7a Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain in a Rat Model of Spinal Nerve Ligation via the Neurofilament Light Polypeptide-Dependent Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Signaling Pathway. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919842464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jiang, K.; Li, Z. MiR-145 Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Inhibiting Inflammatory Responses and MTOR Signaling Pathway by Targeting Akt3 in a Rat Model. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 134, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, J.; Naumova, O.; Hunter, S.; Barbot, B.; Lee, M.; Luthar, S.S.; Raefski, A.; Grigorenko, E.L. Childhood Adversity and DNA Methylation of Genes Involved in the Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis and Immune System: Whole-Genome and Candidate-Gene Associations. Dev. Psychopathol. 2012, 24, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A.M.; Koliada, A.K. Early-Life Adversity and Long-Term Neurobehavioral Outcomes: Epigenome as a Bridge? Hum. Genom. 2017, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondar, N.P.; Merkulova, T.I. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Early-Life Stress: Multifaceted Interplay. J. Biosci. 2016, 41, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracz, S.J.; Everett, N.A.; Cornish, J.L. The Impact of Early Life Stress on the Central Oxytocin System and Susceptibility for Drug Addiction: Applicability of Oxytocin as a Pharmacotherapy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 110, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houwing, D.J.; Buwalda, B.; van der Zee, E.A.; de Boer, S.F.; Olivier, J.D.A. The Serotonin Transporter and Early Life Stress: Translational Perspectives. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, O.D.; McCutcheon, R.; Owen, M.J.; Murray, R.M. The Role of Genes, Stress, and Dopamine in the Development of Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, I.C.G.; Cervoni, N.; Champagne, F.A.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Sharma, S.; Seckl, J.R.; Dymov, S.; Szyf, M.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic Programming by Maternal Behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, I.C.G.; Meaney, M.J.; Szyf, M. Maternal Care Effects on the Hippocampal Transcriptome and Anxiety-Mediated Behaviors in the Offspring That Are Reversible in Adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosten, T.A.; Huang, W.; Nielsen, D.A. Sex and Litter Effects on Anxiety and DNA Methylation Levels of Stress and Neurotrophin Genes in Adolescent Rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perroud, N.; Salzmann, A.; Prada, P.; Nicastro, R.; Hoeppli, M.E.; Furrer, S.; Ardu, S.; Krejci, I.; Karege, F.; Malafosse, A. Response to Psychotherapy in Borderline Personality Disorder and Methylation Status of the BDNF Gene. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Blanco, A.; Ferrer, M.; Soler, J.; Salazar, J.; Vega, D.; Andión, O.; Sanchez-Mora, C.; Arranz, M.J.; Ribases, M.; Feliu-Soler, A.; et al. Association between Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene, Childhood Maltreatment, and Clinical Severity in Borderline Personality Disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 57, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrka, A.R.; Price, L.H.; Marsit, C.; Walters, O.C.; Carpenter, L.L. Childhood Adversity and Epigenetic Modulation of the Leukocyte Glucocorticoid Receptor: Preliminary Findings in Healthy Adults. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, N.; Pape, J.C.; Engel, M.; Zannas, A.S.; Cattane, N.; Cattaneo, A.; Binder, E.B.; Chen, A. Amygdalar MicroRNA-15a Is Essential for Coping with Chronic Stress. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1882–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramo-Fernández, L.; Boeck, C.; Koenig, A.M.; Schury, K.; Binder, E.B.; Gündel, H.; Fegert, J.M.; Karabatsiakis, A.; Kolassa, I.-T. The Effects of Childhood Maltreatment on Epigenetic Regulation of Stress-Response Associated Genes: An Intergenerational Approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattane, N.; Mora, C.; Lopizzo, N.; Borsini, A.; Maj, C.; Pedrini, L.; Rossi, R.; Riva, M.A.; Pariante, C.M.; Cattaneo, A. Identification of a MiRNAs Signature Associated with Exposure to Stress Early in Life and Enhanced Vulnerability for Schizophrenia: New Insights for the Key Role of MiR-125b-1-3p in Neurodevelopmental Processes. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 205, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frach, L.; Tierling, S.; Schwaiger, M.; Moser, D.; Heinrichs, M.; Hengstler, J.G.; Walter, J.; Kumsta, R. The Mediating Role of KITLG DNA Methylation in the Association between Childhood Adversity and Cortisol Stress Reactivity Does Not Replicate in Monocytes. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 116, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, C.; Su, Z.; Lin, D. DGCR5 Attenuates Neuropathic Pain through Sponging MiR-330-3p and Regulating PDCD4 in CCI Rat Models. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7292–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachim, H.A.; Corsi-Zuelli, F.; Loureiro, C.M.; Iamjan, S.-A.; Shuhama, R.; Joca, S.; Menezes, P.R.; Heald, A.; Louzada-Junior, P.; Dalton, C.F.; et al. Early-Life Stress Effects on BDNF DNA Methylation in First-Episode Psychosis and in Rats Reared in Isolation. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 108, 110188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Strachan, E.; Fowler, E.; Bacus, T.; Roy-Byrne, P.; Goldberg, J.; Vaccarino, V.; Zhao, J. Childhood Trauma, DNA Methylation of Stress-Related Genes, and Depression: Findings from Two Monozygotic Twin Studies. Psychosom. Med. 2018, 80, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, L.; Gauvin, L.; Joober, R.; Groleau, P.; de Guzman, R.; Ambalavanan, A.; Israel, M.; Wilson, S.; Steiger, H. Methylation of BDNF in Women with Bulimic Eating Syndromes: Associations with Childhood Abuse and Borderline Personality Disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 54, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bales, K.L.; Perkeybile, A.M. Developmental Experiences and the Oxytocin Receptor System. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, A.K.; McEwen, L.M.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Francis, D.D.; Kobor, M.S. Natural Variation in Maternal Care and Cross-Tissue Patterns of Oxytocin Receptor Gene Methylation in Rats. Horm. Behav. 2016, 77, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smearman, E.L.; Almli, L.M.; Conneely, K.N.; Brody, G.H.; Sales, J.M.; Bradley, B.; Ressler, K.J.; Smith, A.K. Oxytocin Receptor Genetic and Epigenetic Variation: Association with Child Abuse and Adult Psychiatric Symptoms. Child Dev. 2016, 87, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womersley, J.S.; Hemmings, S.M.J.; Ziegler, C.; Gutridge, A.; Ahmed-Leitao, F.; Rosenstein, D.; Domschke, K.; Seedat, S. Childhood Emotional Neglect and Oxytocin Receptor Variants: Association with Limbic Brain Volumes. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, J.; Li, G.; Sun, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Xu, G.; Duan, S. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Gene Promoter Methylation as a Peripheral Biomarker in Male Schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 44, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janusek, L.W.; Tell, D.; Gaylord-Harden, N.; Mathews, H.L. Relationship of Childhood Adversity and Neighborhood Violence to a Proinflammatory Phenotype in Emerging Adult African American Men: An Epigenetic Link. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 60, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y. Epigenetic Reduction of MiR-214-3p Upregulates Astrocytic Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 and Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Induced by Nerve Injury. Pain 2020, 161, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issler, O.; Haramati, S.; Paul, E.D.; Maeno, H.; Navon, I.; Zwang, R.; Gil, S.; Mayberg, H.S.; Dunlop, B.W.; Menke, A.; et al. MicroRNA 135 Is Essential for Chronic Stress Resiliency, Antidepressant Efficacy, and Intact Serotonergic Activity. Neuron 2014, 83, 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasagawa, T.; Horii-Hayashi, N.; Okuda, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Azuma, C.; Nishi, M. Long-Term Effects of Maternal Separation Coupled with Social Isolation on Reward Seeking and Changes in Dopamine D1 Receptor Expression in the Nucleus Accumbens via DNA Methylation in Mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 641, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X. Dopamine Receptor D2 and Associated MicroRNAs Are Involved in Stress Susceptibility and Resistance to Escitalopram Treatment. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 18, pyv025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayendran, M.; Beach, S.R.H.; Plume, J.M.; Brody, G.H.; Philibert, R.A. Effects of Genotype and Child Abuse on DNA Methylation and Gene Expression at the Serotonin Transporter. Front. Psychiatry 2012, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-J.; Kim, J.-M.; Stewart, R.; Kim, S.-Y.; Bae, K.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Shin, I.-S.; Shin, M.-G.; Yoon, J.-S. Association of SLC6A4 Methylation with Early Adversity, Characteristics and Outcomes in Depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 44, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groleau, P.; Joober, R.; Israel, M.; Zeramdini, N.; DeGuzman, R.; Steiger, H. Methylation of the Dopamine D2 Receptor (DRD2) Gene Promoter in Women with a Bulimia-Spectrum Disorder: Associations with Borderline Personality Disorder and Exposure to Childhood Abuse. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 48, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engdahl, E.; Alavian-Ghavanini, A.; Forsell, Y.; Lavebratt, C.; Rüegg, J. Childhood Adversity Increases Methylation in the GRIN2B Gene. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 132, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checknita, D.; Ekström, T.J.; Comasco, E.; Nilsson, K.W.; Tiihonen, J.; Hodgins, S. Associations of Monoamine Oxidase A Gene First Exon Methylation with Sexual Abuse and Current Depression in Women. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, A.; Marinova, Z.; Robinson, M.D.; Kühnel, B.; Waldenberger, M.; Wahl, S.; Kunze, S.; Gieger, C.; Livshits, G.; Williams, F. Are Epigenetic Factors Implicated in Chronic Widespread Pain? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladish, N.; Merrill, S.M.; Kobor, M.S. Childhood Trauma and Epigenetics: State of the Science and Future. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sundquist, K.; Hedelius, A.; Palmér, K.; Memon, A.A.; Sundquist, J. Circulating MicroRNA-144-5p Is Associated with Depressive Disorders. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.E.; Watson, E.D. Unravelling the Complex Mechanisms of Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2016, 33, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Grevet, E.H.; Figueira da Silva, N.A.; Bandeira, C.E.; Barbosa, E.; Vitola, E.S.; Charão, M.F.; Linden, R.; Rohde, L.A.; Ramos, J.K.N.; et al. Global DNA Methylation Changes in Adults with Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder and Its Comorbidity with Bipolar Disorder: Links with Polygenic Scores. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari-Javan, S.; Varbanov, H.; Halder, R.; Benito, E.; Kaurani, L.; Burkhardt, S.; Anderson-Schmidt, H.; Anghelescu, I.; Budde, M.; Stilling, R.M.; et al. HDAC1 Links Early Life Stress to Schizophrenia-like Phenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4686–E4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.-S. Therapeutic Advances of MiRNAs: A Preclinical and Clinical Update. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 28, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goell, J.H.; Hilton, I.B. CRISPR/Cas-Based Epigenome Editing: Advances, Applications, and Clinical Utility. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, L.M.; Gerra, M.C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Time Course of DNA Methylation in Pain Conditions: From Experimental Models to Humans. Eur. J. Pain 2021, 25, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivi, V.; Rigillo, G.; Toscano, Y.; Benatti, C.; Blom, J.M.C. Narrative Review of the Complex Interaction between Pain and Trauma in Children: A Focus on Biological Memory, Preclinical Data, and Epigenetic Processes. Children 2023, 10, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071217
Rivi V, Rigillo G, Toscano Y, Benatti C, Blom JMC. Narrative Review of the Complex Interaction between Pain and Trauma in Children: A Focus on Biological Memory, Preclinical Data, and Epigenetic Processes. Children. 2023; 10(7):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071217
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivi, Veronica, Giovanna Rigillo, Ylenia Toscano, Cristina Benatti, and Johanna Maria Catharina Blom. 2023. "Narrative Review of the Complex Interaction between Pain and Trauma in Children: A Focus on Biological Memory, Preclinical Data, and Epigenetic Processes" Children 10, no. 7: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071217
APA StyleRivi, V., Rigillo, G., Toscano, Y., Benatti, C., & Blom, J. M. C. (2023). Narrative Review of the Complex Interaction between Pain and Trauma in Children: A Focus on Biological Memory, Preclinical Data, and Epigenetic Processes. Children, 10(7), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071217