Study of the Effects of Physical-Activity Practice and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet on Emotional Intelligence in Elementary School Education Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Instruments and Variables
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerekes, N.; Bador, K.; Sfendla, A.; Belaatar, M.; Mzadi, A.E.; Jovic, V.; Damjanovic, R.; Erlandsson, M.; Nguyen, H.T.M.; Nguyen, N.T.A.; et al. Changes in Adolescents’ Psychosocial Functioning and Well-Being as a Consequence of Long-Term COVID-19 Restrictions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynor, H.A.; Mazzeo, S.E.; LaRose, J.G.; Adams, E.L.; Thornton, L.M.; Caccavale, L.J.; Bean, M.K. Effect of a High-Intensity Dietary Intervention on Changes in Dietary Intake and Eating Pathology during a Multicomponent Adolescent Obesity Intervention. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Boraita, R.; Gargallo-Ibort, E.; Dalmau-Torres, J.M.; Arriscado-Alsina, D. Gender Differences Relating to Lifestyle Habits and Health-Related Quality of Life of Adolescents. Child Ind. Res. 2020, 13, 1937–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Ricardo, L.I.; Wendt, A.; dos Santos-Costa, C.; Mielke, G.I.; Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Khan, A.; Kolbe-Alexander, T.L.; Crochemore-Silva, I. Gender inequalities in physical activity among adolescents from 64 Global South countries. J. Sport Health Sci. 2022, 11, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melguizo-Ibáñez, E.; González-Valero, G.; Badicu, G.; Filipa-Silva, A.; Clemente, F.M.; Sarmento, H.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L. Mediterranean Diet Adherence, Body Mass Index and Emotional Intelligence in Primary Education Students—An Explanatory Model as a Function of Weekly Physical Activity. Children 2022, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, S.; Carayanni, V.; Notara, V.; Chaniotis, D. Anthropometric, Lifestyle Characteristics, Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, and COVID-19 Have a High Impact on the Greek Adolescents’ Health-Related Quality of Life. Foods 2022, 11, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre-Moral, A.; Fàbregues, S.; Bach-Faig, A.; Fornieles-Deu, A.; Medina, F.X.; Aguilar-Martínez, A.; Sánchez-Carracedo, D. Family Meals, Conviviality, and the Mediterranean Diet among Families with Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochantaridou, A.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Merakou, K.; Vassilakou, T.; Kornarou, E. Food Advertisement and Dietary Choices in Adolescents: An Overview of Recent Studies. Children 2023, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muros, J.J.; Cofre-Bolados, C.; Arriscado, D.; Zurita, F.; Knox, E. Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with lifestyle, physical fitness, and mental wellness among 10-y-olds in Chile. Nutrition 2017, 35, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Ortega, F.; San Román-Mata, S.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Muros, J.J. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with Physical Activity, Self-Concept and Sociodemographic Factors in University Student. Nutrients 2018, 10, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Nutrient adequacy and Mediterranean Diet in Spanish school children and adolescents. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, S35–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventriglio, A.; Sancassiani, F.; Contu, M.P.; Latorre, M.; Di Salvatore, M.; Fornaro, M.; Bhugra, D. Mediterranean Diet and its Benefits on Health and Mental Health: A Literature Review. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2020, 16, S156–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnes, L.T.; Økland, J.M.; Haaland, Ø.A.; Johansson, K.A. Correction: Estimating impact of food choices on life expectancy: A modeling study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1003962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jurado, J.A. La Actividad Física Orientada a la Promoción de la Salud. Esc. Abierta Rev. Investig. Educ. 2007, 7, 73–96. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-López, E.J.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Moral-García, J.E.; Grao-Cruces, A.; Ruiz, J.R.; Redecillas-Peiró, M.T.; Martínez-Amat, A. Association of low weekly physical activity and sedentary lifestyle with self-perceived health, pain, and well-being in a Spanish teenage population. Sci. Sports 2015, 30, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arundell, L.; Salmon, J.; Veitch, J.; Timperio, A. The Relationship between Objectively Measured and Self-Reported Sedentary Behaviours and Social Connectedness among Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.J.; Welk, G.J. Definitions and measurement. In Youth Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior: Challenges and Solutions; Smith, A.L., Biddle, J.H., Eds.; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2008; Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.5040/9781492595601.ch-001 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: At a Glance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Malm, C.; Jakobsson, J.; Isaksson, A. Physical Activity and Sports—Real Health Benefits: A Review with Insight into the Public Health of Sweden. Sports 2019, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Si, W.; Shao, T. The Effects of Physical Activity on Positive Emotions in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleman, D. Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More than IQ; Bantam: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Puertas-Molero, P.; González-Valero, G.; Sánchez-Zafra, M. Influence of Sports Physical Practice on the Emotional Intelligence of Students: A Systematic Review. Educ. Sport Health Phys. Activ. 2017, 1, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Perpiñà-Martí, G.; Sidera, F.; Senar-Morerea, F.; Serrat-Sellabona, E. Executive functions are important for academic achievement, but emotional intelligence too. Scand. J. Psychol. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melguizo-Ibáñez, E.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; González-Valero, G. Study of the relationship between motivation towards physical activity and its relationship with anxiety and self-concept in the educational setting. A systematic review. Ansiedad Estrés 2023, 29, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; San Román-Mata, S.; Puertas-Molero, P.; González-Valero, G. Impact of Physical Activity Practice and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Relation to Multiple Intelligences among University Students. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salovey, P.; Mayer, J.D.; Goldman, S.L.; Turvey, C.; Palfai, T.P. Emotional attention, clarity, and repair: Exploring emotional intelligence using the Trait Meta-Mood Scale. In Emotion, Disclosure and Health; Pennebaker, J.W., Ed.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 125–154. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Berrocal, P.; Extremera, N.; Ramos, N. Validity and reliability of the Spanish modified version of the Trait Meta-Mood Scale. Psychol. Rep. 2004, 94, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean diet quality index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchola-González, J.; Bagur-Calafat, C.; Girabent-Farrés, M. Fiabilidad de la versión española del Cuestionario de actividad física PAQ-C/Reliability of the Spanish Version of Questionnaire of Physical Activity PAQ-C. Rev. Int. Med. Cienc. Act. Física Deporte 2017, 65, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Pieper, T.M.; Ringle, C.M. The use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in strategic management research: A review of past practices and recommendations for future applications. Long Range Plann. 2012, 45, 320–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydeu-Olivares, A. Maximum likelihood estimation of structural equation models for continuous data: Standard errors and goodness of fit. Struct. Equ. Model. 2017, 24, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazos, T.A. Applied psychometrics: Sample size and sample power considerations in factor analysis (EFA, CFA) and SEM in general. Psychology 2018, 9, 2207–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, G.; Eklund, R.C. Handbook of Sport Psychology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Melguizo-Ibáñez, E.; Badicu, G.; Clemente, F.M.; Silva, A.F.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; González-Valero, G. Impact of emotional intelligence on adherence to the Mediterranean diet in elementary education school students. A structural equation model. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Pipó, J.; Bouzas, C.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Tur, J.A.; Mariscal-Arcas, M. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet Pattern, Physical Activity, and Physical Self-Concept in Spanish Older Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, T.L.; Whatnall, M.C.; Patterson, A.J.; Hutchesson, M.J. Associations between Dietary Intake and Academic Achievement in College Students: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2017, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubičić, M.; Matek Sarić, M.; Klarin, I.; Rumbak, I.; Colić Barić, I.; Ranilović, J.; Dželalija, B.; Sarić, A.; Nakić, D.; Djekic, I.; et al. Emotions and Food Consumption: Emotional Eating Behavior in a European Population. Foods 2023, 12, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Martins, F.; Santos, A.F.; Fernandes, M.; Veríssimo, M. Complementary Feeding Methods: Associations with Feeding and Emotional Responsiveness. Children 2023, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrozy, T.; Rydzik, L.; Obmisnki, Z.; Blach, W.; Serafin, N.; Blach, B.; Jaszczur-Nowicki, J.; Ozimek, M. The effect of high-intensity interval training periods on morning serum testosterone and cortisol levels and physical fitness in men aged 35–40 years. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, L.; Nelius, A.-K.; Pastor, G.G.; Sillero-Quintana, M.; Veiga, Ó.L.; Homeyer, D.; Kück, M. Comparison of Adherence to Mediterranean Diet between Spanish and German School-Children and Influence of Gender, Overweight, and Physical Activity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Cascales, R.; Albaladejo-Blázquez, N.; Ruiz-Robledillo, N.; Clement-Carbonell, V.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; Zaragoza-Martí, A. Higher Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet is Related to More Subjective Happiness in Adolescents: The Role of Health-Related Quality of Life. Nutrients 2019, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melguizo-Ibáñez, E.; González-Valero, G.; Puertas-Molero, P.; Alonso-Vargas, J.M. Emotional Intelligence, Physical Activity Practice and Mediterranean Diet Adherence-An Explanatory Model in Elementary Education School Students. Children 2022, 9, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qiu, L. Gender and Age Association with Physical Activity and Mood States of Children and Adolescents in Social Isolation during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Luo, J. The Relationship among College Students’ Physical Exercise, Self-Efficacy, Emotional Intelligence, and Subjective Well-Being. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Sánchez, M.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; González-Valero, G.; García-Mármol, E.; Chacón-Cuberos, R. Relationships between Anxiety, Emotional Intelligence, and Motivational Climate among Adolescent Football Players. Sports 2019, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela-Pino, I.; López-Castedo, A.; Martínez-Patiño, M.J.; Valverde-Esteve, T.; Domínguez-Alonso, J. Gender Differences in Motivation and Barriers for The Practice of Physical Exercise in Adolescence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo-Ramos, J.; Franco-García, J.M.; Mayordomo-Pinilla, N.; Pazzi, F.; Galán-Arroyo, C. Physical Activity and Emotional Regulation in Physical Education in Children Aged 12–14 Years and Its Relation with Practice Motives. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sllujis, E.M.F.; Ekelund, U.; Crochemore-Silva, I.; Guthold, R.; Ha, A.; Lubans, D.; Oyeyemi, A.L.; Ding, D.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Physical activity behaviours in adolescence: Current evidence and opportunities for intervention. Lancet 2021, 398, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilardell-Dávila, A.; Martínez-Andrade, G.; Klünder-Klünder, M.; Miranda-Lora, A.L.; Mendoza, E.; Flores-Huerta, S.; Vargas-González, J.E.; Duque, X.; Vilchis-Gil, J. A Multi-Component Educational Intervention for Addressing Levels of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviors of Schoolchildren. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Shi, L.; Peng, L.; Chen, S.; Hong, J.; Liu, Y. Associations between socioeconomic status and physical activity: A cross-sectional analysis of Chinese children and adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 904506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigueros, R.; Mínguez, L.A.; González-Bernal, J.J.; Jahouh, M.; Soto-Camara, R.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M. Influence of Teaching Style on Physical Education Adolescents’ Motivation and Health-Related Lifestyle. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.M.; Koulanova, A.; Sabiston, C.M. Understanding Girls’ Motivation to Participate in Sport: The Effects of Social Identity and Physical Self-Concept. Front. Sports Act. Living 2022, 3, 787334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Chico, L.; González-Peño, A.; Hernández-Cuadrado, E.; Franco, E. The Impact of a Challenge-Based Learning Experience in Physical Education on Students’ Motivation and Engagement. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redig, L.; Feter, N.; Dumith, S.C.; Domingues, M.R.; Rombaldi, A.J. Physical inactivity from childhood to adolescence and incident depression. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 62, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.C.; Tebar, W.R.; Lemes, I.R.; Sasaki, J.E.; Mota, J.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Vanderlei, L.C.M.; Christofaro, D.G.D. Can Sports Practice in Childhood and Adolescence Be Associated with Higher Intensities of Physical Activity in Adult Life? A Retrospective Study in Community-Dwelling Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintle, J. Physical Education and Physical Activity Promotion: Lifestyle Sports as Meaningful Experiences. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branquinho, L.; Forte, P.; Ferraz, R. Pedagogical Concerns in Sports and Physical Education for Child Growth and Health Promotion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; González-Valero, G.; Puertas-Molero, P.; García-Martínez, I. Development of Emotional Intelligence through Physical Activity and Sport Practice. A Systematic Review. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CFI | IFI | GFI | TLI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire Sample Model | 0.972 | 0.978 | 0.963 | 0.949 |
| Male Model | 0.968 | 0.970 | 0.944 | 0.909 |
| Female Model | 0.990 | 0.995 | 0.927 | 0.900 |
| Effect Direction | Regression Weights | Standardised Regression Weights | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimations | Error Estimation | Critical Ratio | p | Estimations | |
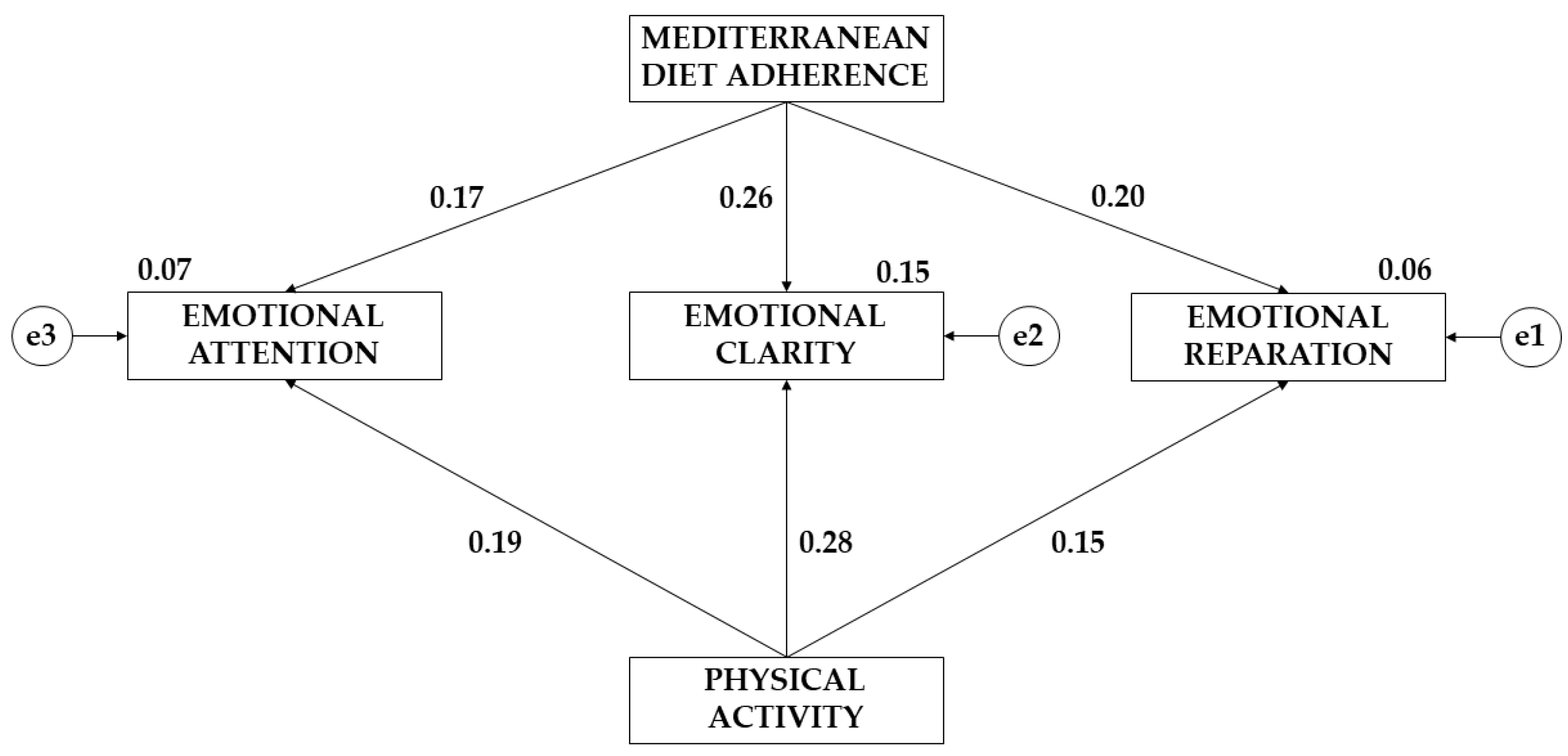
| EA←MDA | 0.612 | 0.326 | 1.879 | 0.060 | 0.109 |
| EC←MDA | 0.651 | 0.272 | 2.392 | 0.017 | 0.138 |
| ER←MDA | 0.803 | 0.264 | 3.039 | 0.002 | 0.175 |
| EA←PA | 0.017 | 0.147 | 0.114 | 0.909 | 0.007 |
| EC←PA | 0.155 | 0.123 | 1.267 | 0.205 | 0.073 |
| ER←PA | 0.164 | 0.119 | 1.377 | 0.168 | 0.079 |
| Effect Direction | Regression Weights | Standardised Regression Weights | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimations | Error Estimation | Critical Ratio | p | Estimations | |
| EA←MDA | 0.891 | 0.411 | 2.171 | 0.030 | 0.174 |
| EC←MDA | 1.107 | 0.326 | 3.392 | 0.001 | 0.259 |
| ER←MDA | 0.850 | 0.347 | 2.451 | 0.014 | 0.197 |
| EA←PA | 0.516 | 0.221 | 2.332 | 0.020 | 0.187 |
| EC←PA | 0.654 | 0.176 | 3.722 | 0.001 | 0.284 |
| ER←PA | 0.352 | 0.187 | 1.883 | 0.060 | 0.151 |
| Effect Direction | Regression Weights | Standardised Regression Weights | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimations | Error Estimation | Critical Ratio | p | Estimations | |
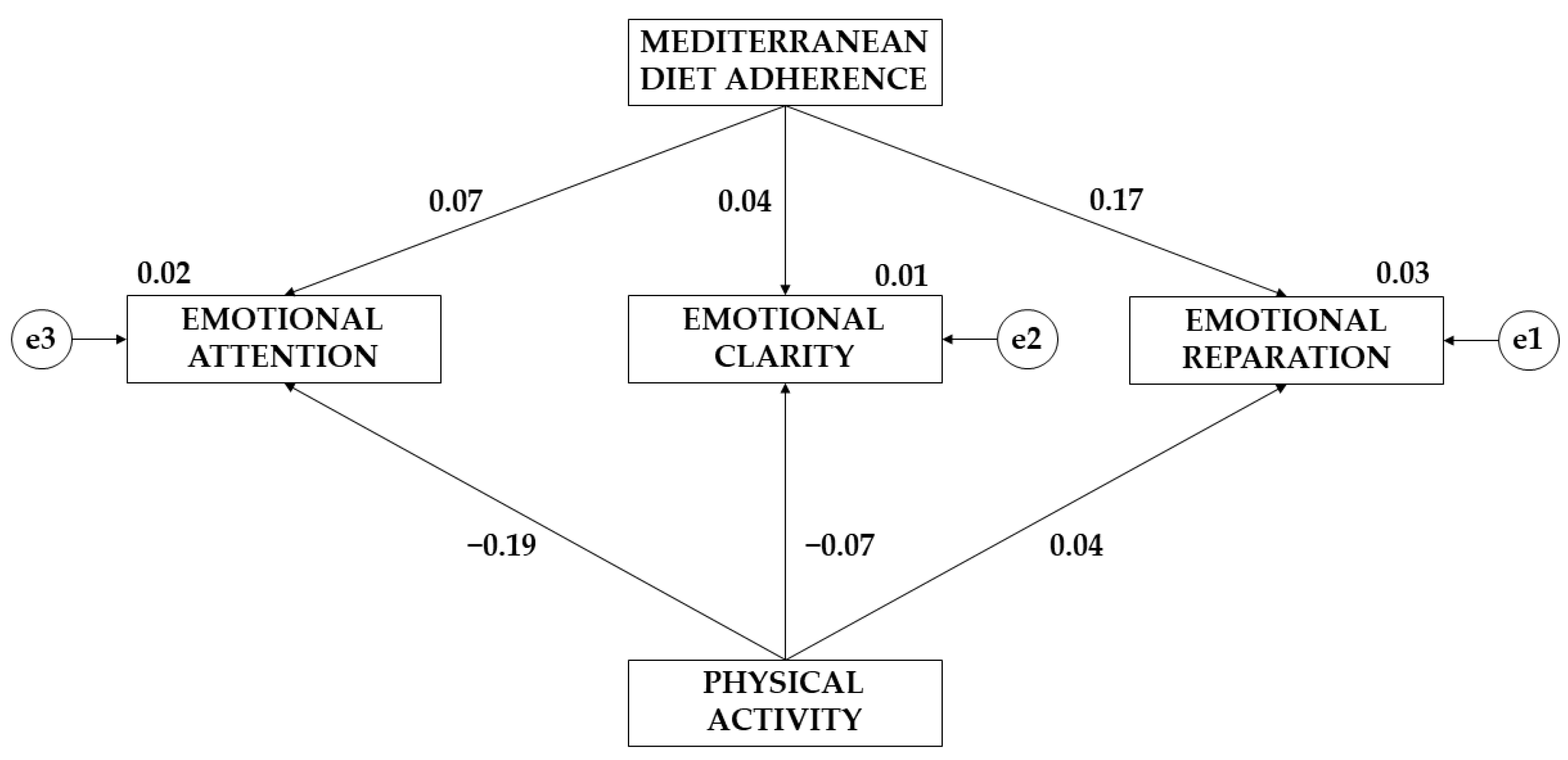
| EA←MDA | 0.415 | 0.507 | 0.818 | 0.413 | 0.667 |
| EC←MDA | 0.198 | 0.433 | 0.457 | 0.648 | 0.038 |
| ER←MDA | 0.823 | 0.403 | 2.043 | 0.041 | 0.167 |
| EA←PA | −0.278 | 0.195 | −1.423 | 0.155 | −0.117 |
| EC←PA | −0.133 | 0.167 | −0.797 | 0.425 | −0.066 |
| ER←PA | 0.068 | 0.155 | 0.439 | 0.661 | 0.036 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melguizo-Ibáñez, E.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; González-Valero, G.; Badicu, G.; Al-Mhanna, S.B.; Puertas-Molero, P. Study of the Effects of Physical-Activity Practice and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet on Emotional Intelligence in Elementary School Education Students. Children 2023, 10, 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071211
Melguizo-Ibáñez E, Ubago-Jiménez JL, González-Valero G, Badicu G, Al-Mhanna SB, Puertas-Molero P. Study of the Effects of Physical-Activity Practice and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet on Emotional Intelligence in Elementary School Education Students. Children. 2023; 10(7):1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071211
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelguizo-Ibáñez, Eduardo, José Luis Ubago-Jiménez, Gabriel González-Valero, Georgian Badicu, Sameer Badri Al-Mhanna, and Pilar Puertas-Molero. 2023. "Study of the Effects of Physical-Activity Practice and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet on Emotional Intelligence in Elementary School Education Students" Children 10, no. 7: 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071211
APA StyleMelguizo-Ibáñez, E., Ubago-Jiménez, J. L., González-Valero, G., Badicu, G., Al-Mhanna, S. B., & Puertas-Molero, P. (2023). Study of the Effects of Physical-Activity Practice and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet on Emotional Intelligence in Elementary School Education Students. Children, 10(7), 1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071211









