Different Protocols for Low Whole-Body Vibration Frequency for Spasticity and Physical Performance in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
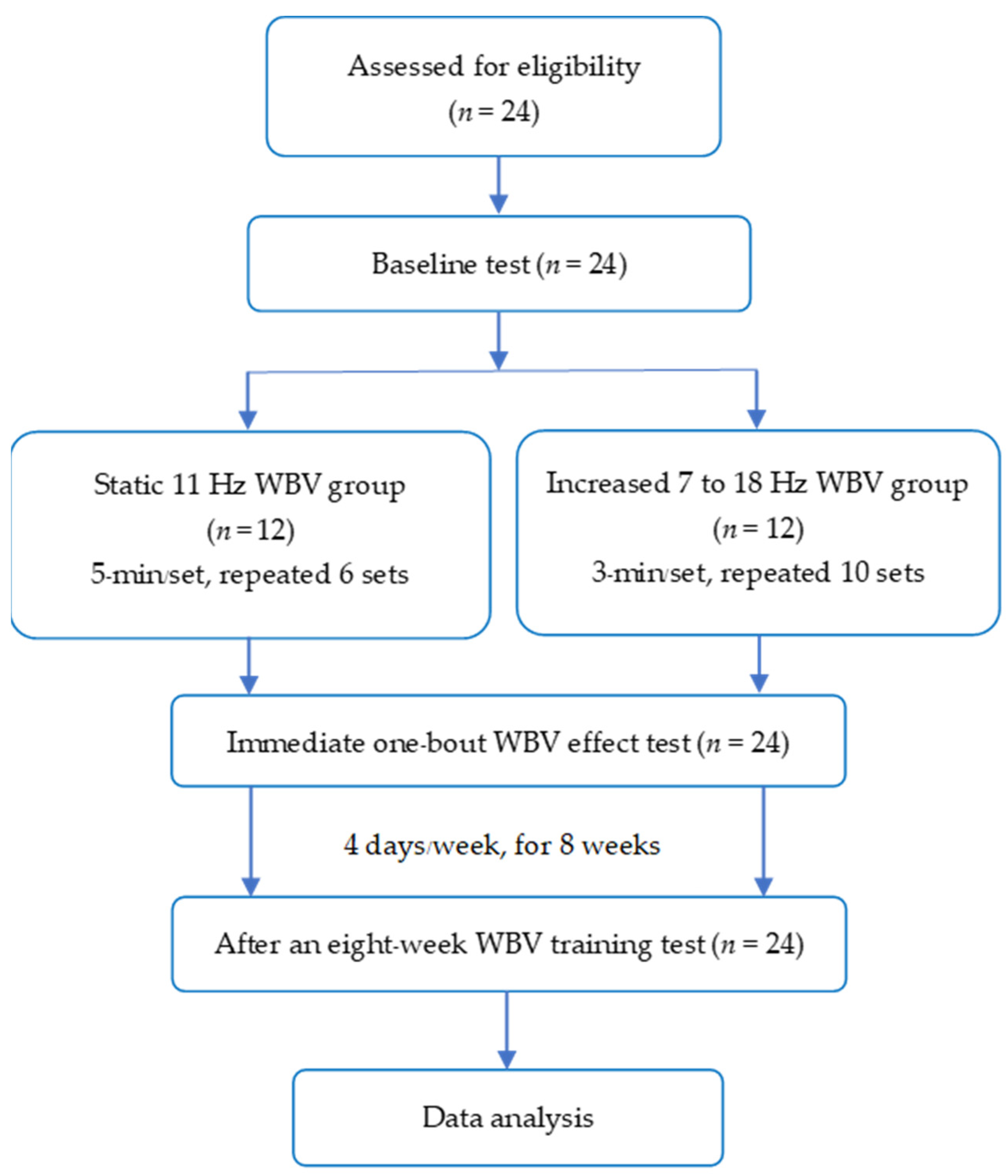
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Protocols
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.4.1. Modified Ashworth Scale
2.4.2. Five Times Sit to Stand Test
2.4.3. Functional Reach Test
2.4.4. Timed Up and Go Test
2.4.5. Ten Metre Walk Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of Participants
3.2. Immediate and after 8-Week WBV Training Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Leviton, A.; Goldstein, M.; Bax, M.; Damiano, D.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B. A report: The definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 49, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Krigger, K.W. Cerebral palsy: An overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2006, 73, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.J.; Park, S.W.; Lee, H.S. Comparison of the Effectiveness of Whole Body Vibration in Stroke Patients: A Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5083634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arauz, Y.L.A.; Ahuja, G.; Kamsma, Y.P.T.; Kortholt, A.; van der Zee, E.A.; van Heuvelen, M.J.G. Potential of Whole-Body Vibration in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human and Animal Studies. Biology 2022, 11, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, M.H.; Hase, R.; Yamaguchi, N.; Hiroshige, K.; Harada, N.; Bhuiyan, A.N.M.N.H.; Tanabe, T. Acute Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Peripheral Blood Flow, Vibrotactile Perception and Balance in Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhde, L.; Hulla, R. An overview of the effects of whole-body vibration on individuals with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Rehabilitation Med. 2022, 15, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlborg, L.; Andersson, C.; Julin, P. Whole-Body Vibration Training Compared with Resistance Training: Effect on Spasticity, Muscle Strength and Motor Performance in Adults with Cerebral Palsy. J. Rehabil. Med. 2006, 38, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-Y.K.; Yu, Y.-C.; Wong, A.M.-K.; Tsai, Y.-S.; Ju, Y.-Y. Effects of an eight-week whole body vibration on lower extremity muscle tone and function in children with cerebral palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 38, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shamy, S. Effect of Whole-Body Vibration on Muscle Strength and Balance in Diplegic Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2014, 93, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Eid, M.A.; Moawd, S.A. Effect of whole-body vibration on muscle strength, spasticity, and motor performance in spastic diplegic cerebral palsy children. Egypt. J. Med Hum. Genet. 2014, 15, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupimai, T.; Peungsuwan, P.; Prasertnoo, J.; Yamauchi, J. Effect of combining passive muscle stretching and whole body vibration on spasticity and physical performance of children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saquetto, M.; Carvalho, V.; Silva, C.; Conceição, C.; Gomes-Neto, M. The effects of whole body vibration on mobility and balance in children with cerebral palsy: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2015, 15, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-K.; Chon, S.-C. Effect of whole body vibration training on mobility in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled experimenter-blinded study. Clin. Rehabil. 2013, 27, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruck, J.; Chabot, G.; Rauch, F. Vibration treatment in cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2010, 10, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- del Pozo-Cruz, B.; Adsuar, J.C.; Parraca, J.A.; del Pozo-Cruz, J.; Olivares, P.R.; Gusi, N. Using Whole-Body Vibration Training in Patients Affected with Common Neurological Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater Reliability of a Modified Ashworth Scale of Muscle Spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumban, W.; Amatachaya, S.; Emasithi, A.; Siritaratiwat, W. Five-times-sit-to-stand test in children with cerebral palsy: Reliability and concurrent validity. Neurorehabilitation 2013, 32, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niznik, T.M.; Turner, D.; Worrell, T.W. Functional Reach as a Measurement of Balance for Children with Lower Extremity Spasticity. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 1996, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhote, S.N.; Khatri, P.A.; Ganvir, S.S. Reliability of “Modified timed up and go” test in children with cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2012, 7, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.; Beath, T.; Bell, J.; Jacobson, G.; Phair, T.; Salbach, N.M.; Wright, F.V. Test-retest reliability of the 10-metre fast walk test and 6-minute walk test in ambulatory school-aged children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008, 50, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lee, K.; Jung, S.; Park, S.; Cho, H.; Lee, G. Effect of Horizontal Whole-Body Vibration Training on Trunk and Lower-Extremity Muscle Tone and Activation, Balance, and Gait in a Child with Cerebral Palsy. Am. J. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Park, E.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, Y.; Rha, D.-W. Immediate Effect of a Single Session of Whole Body Vibration on Spasticity in Children With Cerebral Palsy. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, A.; Schönau, E.; Gollhofer, A.; Duran, I.; Ferrari-Malik, A.; Freyler, K.; Ritzmann, R. Alleviation of Motor Impairments in Patients with Cerebral Palsy: Acute Effects of Whole-body Vibration on Stretch Reflex Response, Voluntary Muscle Activation and Mobility. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickin, D.C.; A Faust, K.; Wang, H.; Frame, J. The acute effects of whole-body vibration on gait parameters in adults with cerebral palsy. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2013, 13, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.-G.; Lee, S.-W.; Yun, C.-K. The immediate influence of various whole-body vibration frequency on balance and walking ability in children with cerebral palsy: A pilot study. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2019, 15, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.; Stebbins, J.; Seniorou, M.; Newham, D. Muscle strength and walking ability in Diplegic Cerebral Palsy: Implications for assessment and management. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SVF Group Static 11 Hz | min | IVF Group Increased 7–18 Hz | min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1: | Warm-up: 5 to 7 Hz | 1 | 7 to 10 Hz | 1 |
| Step 2: | Warm-up: 7 to <9 Hz | 1 | 11 to 15 Hz | 1 |
| Step 3: | 11 Hz | 3 | 16 to 18 Hz | 1 |
| rest | Seated on chair | 1 | Seated on chair | 1 |
| Total 6 repetitions | 30 | Total 10 repetitions | 30 | |
| Characteristics | SVF Group (n = 12) | IVF Group (n = 12) | p-Value | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 11.67 ± 2.43 | 11.5 ± 2.64 | 0.49 | −3.32 to 1.65 |
| Weight, kg | 33.89 ± 11.67 | 38.12 ± 12.59 | 0.40 | −14.50 to 6.06 |
| High, cm | 132.6 ± 11.10 | 141.9 ± 12.57 | 0.07 | −19.35 to 0.73 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 19.15 | 18.90 | 0.12 | −9.35 to 2.56 |
| GMFCS I/II/III, n | 2/2/8 | 2/2/8 | - | - |
| No aids/walker/crutches, n | 3/9/0 | 4/7/1 | - | - |
| Muscles/Groups | Immediate Effects | After 8-Weeks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decreased MAS n (%) | Improved Difference between Groups n (%), (95% CI) | p-Value | Decreased MAS n (%) | Improved Difference between Groups n (%), (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| HE | ||||||
| Stronger spastic leg | ||||||
| 4 (33.33) | 3 (25.00) | 0.219 | 7 (58.33) | 1 (8.33) | 0.682 |
| 7 (58.33) | (−13.59 to 63.59) | 6 (50.00) | (−31.4 to 48.06) | ||
| Weaker spastic leg | ||||||
| 3 (25) | 2 (16.67) | 0.387 | 3 (25) | 3 (25) | 0.206 |
| 5 (41.67) | (−20.46 to 53.79) | 6 (50.00) | (−21.42 to 62.42) | ||
| HF | ||||||
| Stronger spastic leg | ||||||
| 4 (33.33) | 3 (25.00) | 0.219 | 5 (41.67) | 2 (16.67) | 0.414 |
| 7 (58.33) | (−13.59 to 63.59) | 7 (58.33) | (−22.78 to 56.11) | ||
| Weaker spastic leg | ||||||
| 6 (50.00) | 1 (8.33) | 0.682 | 5 (41.67) | 1 (8.33) | 0.682 |
| 5 (41.67) | (−31.4 to 48.06) | 6 (50.00) | (−31.4 to 48.06) | ||
| HAD | ||||||
| Stronger spastic leg | 2 (16.67) | 5 (41.67) | 0.035 * | 2 (16.67) | 2 (16.67) | 0.346 |
| 7 (58.33) | (6.70 to 76.63) | 4 (33.33) | (−17.33 to 50.67) | ||
| ||||||
| Weaker spastic leg | ||||||
| 2 (16.67) | 1 (8.33) | 0.615 | 2 (16.67) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| 3 (25) | (−23.99 to 40.66) | 2 (16.67) | (−29.82 to 29.82) | ||
| KE | ||||||
| Stronger spastic leg | ||||||
| 2 (16.67) | 4 (33.33) | 0.083 | 4 (33.33) | 2 (16.67) | 0.408 |
| 6 (50.00) | (−1.95 to 68.62) | 6 (50.00) | (−22.21 to 55.55) | ||
Weaker spastic leg
| ||||||
| 1 (8.33) | 5 (41.67) | 0.025 * | 4 (33.33) | 2 (16.67) | 0.408 | |
| 6 (50.00) | (9.43 to 73.99) | 6 (50.00) | (−22.21 to 55.55) | |||
| KF | ||||||
| Stronger spastic leg | 6 (50.00) | 1 (8.33) | 0.682 | 9 (75.00) | 3 (25.00) | 0.206 |
| 5 (41.67) | (−31.4 to 48.06) | 6 (50.00) | (−12.42 to 62.42) | ||
| ||||||
| Weaker spastic leg | ||||||
| 5 (41.67) | 3 (25.00) | 0.178 | 7 (58.33) | 3 (25.00) | 0.219 |
| 2 (16.67) | (−9.67 to 59.97) | 4 (33.33) | (−13.59 to 63.59) | ||
| APF | ||||||
| Stronger spastic leg | 2 (16.67) | 1 (8.33) | 0.615 | 6 (50.00) | 3 (25) | 0.206 |
| 3 (25) | (−23.99 to 40.66) | 3 (25) | (−12.42 to 62.42) | ||
| ||||||
| Weaker spastic leg | ||||||
| 5 (41.67) | 3 (25) | 0.178 | 4 (33.33) | 4 (33.33) | 0.029 * |
| 2 (16.67) | (−9.97 to 59.97) | 0 (0) | (6.66 to 60.00) | ||
| Functional Ability Test | Groups | Within the SVF and IVF Groups’ Baselines and after 8 Weeks | Between SVF and IVF Groups after 8 Weeks $ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After 8 Weeks | Change (95% CI) | p-Value | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| FTSTS | SVF | 17.07 ± 3.66 | 11.33 ± 3.21 | −5.74 ± 3.44 (−7.92 to −3.55) | 0.0001 # | −1.65 (−3.81 to 0.52) | 0.13 |
| IVF | 17.26 ± 6.00 | 13.06 ± 3.53 | −4.20 ± 3.88 (−6.66 to −1.74) | 0.003 ** | |||
| TUG | SVF | 19.59 ± 10.97 | 17.15 ± 10.49 | −2.44 ± 1.76 (−3.56 to −1.32) | 0.0006 # | −0.65 (−5.01 to 3.71) | 0.76 |
| IVF | 19.43 ± 10.39 | 17.66 ± 11.49 | −1.77 ± 6.99 (−6.22 to 2.67) | 0.40 | |||
| FRT | SVF | 17.08 ± 08 | 20.64 ± 5.84 | 3.56 ± 5.16 (0.27 to 6.84) | 0.036 * | 0.53 (−3.43 to 4.49) | 0.78 |
| IVF | 17.55 ± 3.1 | 20.26 ± 3.35 | 2.71 ± 5.08 (−0.51 to 5.94) | 0.09 | |||
| 10 MW | SVF | 13.28 ± 4.13 | 12.27 ± 4.61 | −1.01 (−2.31 to 0.30) | 0.12 | −1.71 (−6.02 to 2.60) | 0.42 |
| IVF | 14.66 ± 11.55 | 14.81 ± 9.04 | 0.15 (−5.11 to 5.42) | 0.95 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peungsuwan, P.; Chatchawan, U.; Donpunha, W.; Malila, P.; Sriboonreung, T. Different Protocols for Low Whole-Body Vibration Frequency for Spasticity and Physical Performance in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Children 2023, 10, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030458
Peungsuwan P, Chatchawan U, Donpunha W, Malila P, Sriboonreung T. Different Protocols for Low Whole-Body Vibration Frequency for Spasticity and Physical Performance in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Children. 2023; 10(3):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030458
Chicago/Turabian StylePeungsuwan, Punnee, Uraiwan Chatchawan, Wanida Donpunha, Pisamai Malila, and Thanyaluck Sriboonreung. 2023. "Different Protocols for Low Whole-Body Vibration Frequency for Spasticity and Physical Performance in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy" Children 10, no. 3: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030458
APA StylePeungsuwan, P., Chatchawan, U., Donpunha, W., Malila, P., & Sriboonreung, T. (2023). Different Protocols for Low Whole-Body Vibration Frequency for Spasticity and Physical Performance in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy. Children, 10(3), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10030458





