Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Showing Unilateral Motor Dysfunction Prior to Chemotherapy: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Functional Evaluation
2.3. Diffusion Tensor Imaging
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Functional Data
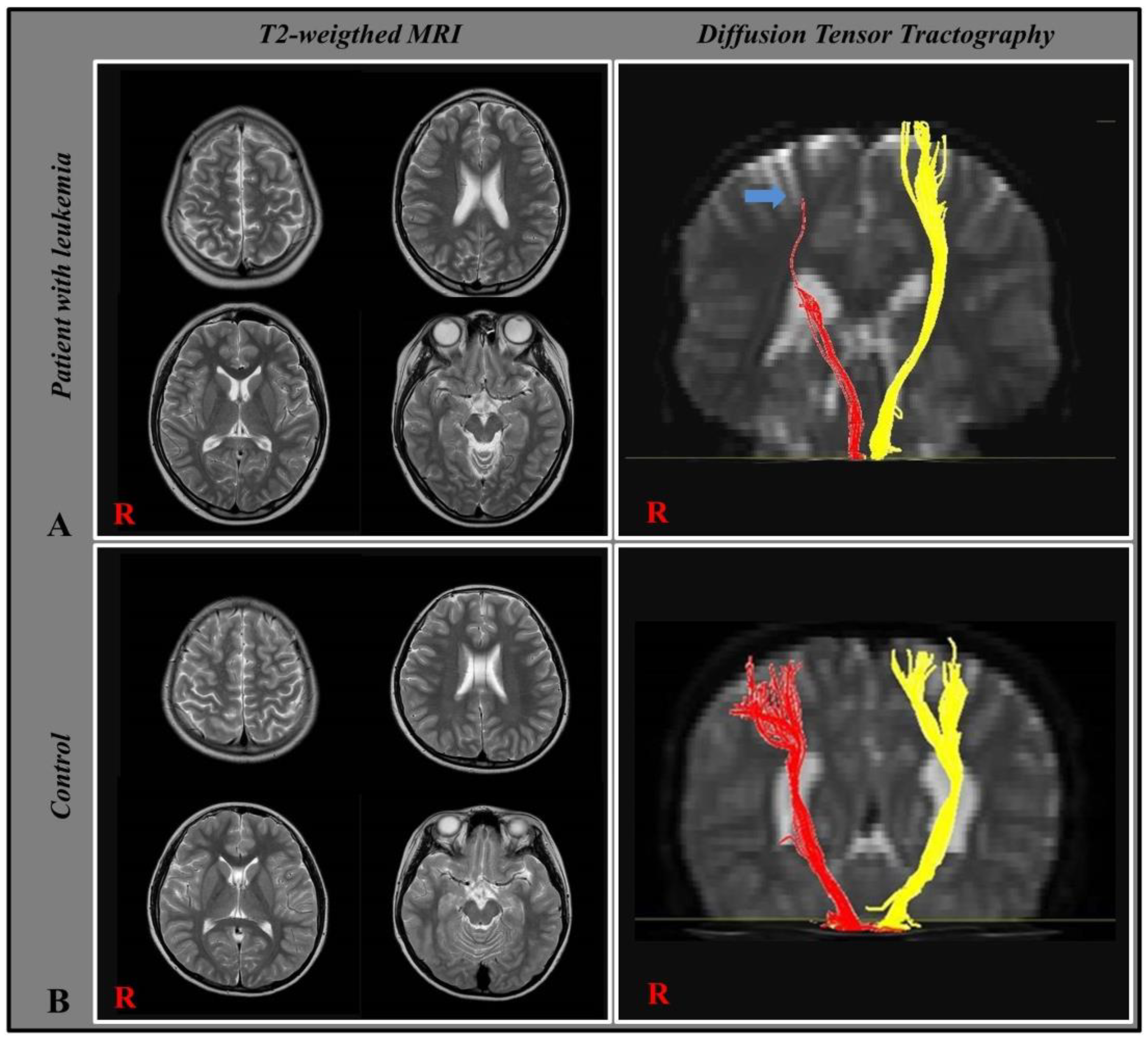
3.2. Diffusion Tensor Tractography
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leukemia in Children. Dana Farber Boston Children’s Cancer and Blood Disorders Center. Available online: https://www.danafarberbostonchildrens.org/ (accessed on 3 December 2018).
- Cortes, J. Central nervous system involvement in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2001, 15, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.B.; Hudson, M.M.; Ledet, D.S.; Morris, E.B.; Pui, C.H.; Howard, S.C.; Krull, K.R.; Hinds, P.S.; Crom, D.; Browne, E.; et al. Neurologic morbidity and quality of life in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A prospective cross-sectional study. J. Cancer Surviv. 2014, 8, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baytan, B.; Evim, M.S.; Guler, S.; Gunes, A.M.; Okan, M. Acute central nervous system complications in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 53, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofstad, G.E.; Reinfjell, T.; Hestad, K.; Diseth, T.H. Cognitive outcome in children and adolescents treated for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with chemotherapy only. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, S.G.; Kembhavi, S.; Arora, B. Hemiparesis and aphasia in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann. Indian Acad. Neur. 2011, 14, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krull, K.R.; Cheung, Y.T.; Liu, W.; Fellah, S.; Reddick, W.E.; Brinkman, T.M.; Kimberg, C.; Ogg, R.; Srivastava, D.; Pui, C.H.; et al. Chemotherapy pharmacodynamics and neuroimaging and neurocognitive outcomes in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.K.; Scaduto, M.; Sharp, W.; Dufton, L.; Van Slyke, D.; Whitlock, J.A.; Compas, B. A meta-analysis of the neurocognitive sequelae of treatment for childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 49, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, S.; Yetgin, S.; Tavil, B. Acute and long-term neurologic complications in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Turk. J. Pediatr 2006, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, A.; Harrison, P.L.; Sandlund, J.T.; Rivera, G.K.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Razzouk, B.; Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E.; Boyett, J.M.; et al. Traumatic lumbar puncture at diagnosis adversely affects outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2000, 96, 3381–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thastrup, M.; Marquart, H.V.; Schmiegelow, K. Flow Cytometric Detection of Malignant Blasts in Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Biomarker of Central Nervous System Involvement in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.A.; Johnson, W.W. The central nervous system in childhood leukemia. I. The arachnoid. Cancer 1973, 31, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Laperche, C.; Gomez-Garcia, A.M.; Lassaletta, A.; Moscardo, C.; Vivanco, J.L.; Molina, J.; Fuster, J.L.; Couselo, J.M.; de Toledo, J.S.; Bureo, E.; et al. Detection of occult cerebrospinal fluid involvement during maintenance therapy identifies a group of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at high risk for relapse. Am. J. Hematol. 2013, 88, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinsen, M.; Marquart, H.V.; Groth-Pedersen, L.; Abrahamsson, J.; Albertsen, B.K.; Andersen, M.K.; Frandsen, T.L.; Harila-Saari, A.; Pronk, C.; Ulvmoen, A.; et al. Leukemic blasts are present at low levels in spinal fluid in one-third of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cases. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Crain, B.J.; Chacko, V.P.; van Zijl, P.C. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guye, M.; Parker, G.J.; Symms, M.; Boulby, P.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Salek-Haddadi, A.; Barker, G.J.; Duncan, J.S. Combined functional MRI and tractography to demonstrate the connectivity of the human primary motor cortex in vivo. Neuroimage 2003, 19, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, S.S.; Jang, S.H.; Son, S.M. The different maturation of the corticospinal tract and corticoreticular pathway in normal brain development: Diffusion tensor imaging study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.M.; Ahn, Y.H.; Sakong, J.; Moon, H.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, H.; Yu, I.K.; Shin, Y.J.; Jang, S.H. Diffusion tensor imaging demonstrates focal lesions of the corticospinal tract in hemiparetic patients with cerebral palsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 420, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Jang, S.H.; Lee, E.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Kwon, Y.H.; Son, S.M. Diffusion tensor imaging-demonstrated differences between hemiplegic and diplegic cerebral palsy with symmetric periventricular leukomalacia. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, S.R.; Yin, C.H.; Matloub, Y.H.; Sabaawy, H.E.; Sandoval, C.; Levendoglu-Tugal, O.; Ozkaynak, M.F.; Jayabose, S. Detection of central nervous system leukemia in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia by real-time polymerase chain reaction. J. Mol. Diagn. 2005, 7, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werring, D.J.; Toosy, A.T.; Clark, C.A.; Parker, G.J.M.; Barker, G.J.; Miller, D.H.; Thompson, A.J. Diffusion tensor imaging can detect and quantify corticospinal tract degeneration after stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 69, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, J.; Harada, K.; Mano, T. Differentiation of dys- and demyelination using diffusion anisotropy. Pediatr. Neurol. 1997, 16, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Son, S.M. Limb length discrepancy and corticospinal tract disruption in hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Children 2022, 9, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlow, B.L.; Haynes, R.L.; Takahashi, E.; Klein, J.P.; Cummings, P.; Benner, T.; Greer, D.M.; Greenberg, S.M.; Wu, O.; Kinney, H.C.; et al. Disconnection of the ascending arousal system in traumatic coma. J Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 2013, 72, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haas, V.; Vet, R.J.; Verhagen, O.J.; Kroes, W.; van den Berg, H.; van der Schoot, C.E. Early detection of central nervous system relapse by polymerase chain reaction in children with B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2002, 81, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijano, S.; Lopez, A.; Manuel Sancho, J.; Panizo, C.; Deben, G.; Castilla, C.; Antonio Garcia-Vela, J.; Salar, A.; Alonso-Vence, N.; Gonzalez-Barca, E.; et al. Identification of leptomeningeal disease in aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Improved sensitivity of flow cytometry. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, U.; Filie, A.; Little, R.F.; Janik, J.E.; Grant, N.; Steinberg, S.M.; Dunleavy, K.; Jaffe, E.S.; Abati, A.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; et al. High incidence of occult leptomeningeal disease detected by flow cytometry in newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas at risk for central nervous system involvement: The role of flow cytometry versus cytology. Blood 2005, 105, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brem, S.S.; Bierman, P.J.; Black, P.; Brem, H.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Chiocca, E.A.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Fenstermaker, R.A.; Friedman, A.; Gilbert, M.R.; et al. Central nervous system cancers. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2008, 6, 456–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, M.J.; Devidas, M.; Hunger, S.P.; Bowman, W.P.; Carroll, A.J.; Carroll, W.L.; Linda, S.; Martin, P.L.; Pullen, D.J.; Viswanatha, D.; et al. Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its relationship to other prognostic factors: A Children’s Oncology Group study. Blood 2008, 111, 5477–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.A.; Zhou, S.; Higley, H.; Mukundan, L.; Fu, S.; Reaman, G.H.; Wood, B.L.; Kelloff, G.J.; Jessup, J.M.; Radich, J.P. Association of Minimal Residual Disease With Clinical Outcome in Pediatric and Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e170580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subira, D.; Castanon, S.; Roman, A.; Aceituno, E.; Jimenez-Garofano, C.; Jimenez, A.; Garcia, R.; Bernacer, M. Flow cytometry and the study of central nervous disease in patients with acute leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 112, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biojone, E.; Queiróz Rde, P.; Valera, E.T.; Odashima, N.S.; Takayanagui, O.M.; Viana, M.B.; Tone, L.G.; Scrideli, C.A. Minimal residual disease in cerebrospinal fluid at diagnosis: A more intensive treatment protocol was able to eliminate the adverse prognosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeer, J.L.; Schmiegelow, K. Management of CNS Disease in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2022, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winick, N.; Devidas, M.; Chen, S.; Maloney, K.; Larsen, E.; Mattano, L.; Borowitz, M.J.; Carroll, A.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Impact of Initial CSF Findings on Outcome Among Patients With National Cancer Institute Standard- and High-Risk B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, K.R.; Pullen, D.J.; Sather, H.N.; Shuster, J.J.; Devidas, M.; Borowitz, M.J.; Carroll, A.J.; Heerema, N.A.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Loh, M.L.; et al. Risk- and response-based classification of childhood B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A combined analysis of prognostic markers from the Pediatric Oncology Group (POG) and Children’s Cancer Group (CCG). Blood 2007, 109, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürger, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Mann, G.; Kühl, J.; Löning, L.; Riehm, H.; Reiter, A.; Schrappe, M. Diagnostic cerebrospinal fluid examination in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Significance of low leukocyte counts with blasts or traumatic lumbar puncture. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinsen, M.; Taskinen, M.; Abrahamsson, J.; Forestier, E.; Frandsen, T.L.; Harila-Saari, A.; Heyman, M.; Jonsson, O.G.; Lähteenmäki, P.M.; Lausen, B.; et al. Clinical features and early treatment response of central nervous system involvement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Wade, R.; Moorman, A.V.; Mitchell, C.; Kinsey, S.E.; Eden, T.O.; Parker, C.; Vora, A.; Richards, S.; Saha, V. Temporal changes in the incidence and pattern of central nervous system relapses in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated on four consecutive Medical Research Council trials, 1985–2001. Leukemia 2010, 24, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancela, C.S.P.; Murao, M.; Assumpção, J.G.; Souza, M.E.L.; de Macedo, A.V.; Viana, M.B.; De Oliveira, B.M. Immunophenotyping of the cerebrospinal fluid as a prognostic factor at diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 34, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.; Henze, G.; Verzhbitskaya, T.; Roumiantseva, J.; Lagoyko, S.; Khlebnikova, O.; Streneva, O.; Bidanov, O.; Tsaur, G.; Inaba, H.; et al. Absolute count of leukemic blasts in cerebrospinal fluid as detected by flow cytometry is a relevant prognostic factor in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelli, M.; Disarò, S.; Scarparo, P.; Francescato, S.; Zangrando, A.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Putti, M.C.; Basso, G.; Buldini, B. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis by 8-color flow cytometry in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2825–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, S.; Nilsson, F.; Harila-Saari, A.; Saft, L.; Tani, E.; Söderhäll, S.; Porwit, A.; Hultdin, M.; Noren-Nyström, U.; Heyman, M. Detection of central nervous system involvement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia by cytomorphology and flow cytometry of the cerebrospinal fluid. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Loo, D.M.; Kamps, W.A.; van der Does-van den Berg, A.; van Wering, E.R.; de Graaf, S.S. Prognostic significance of blasts in the cerebrospinal fluid without pleiocytosis or a traumatic lumbar puncture in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Experience of the Dutch Childhood Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2332–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, A.; Andreano, A.; Pui, C.H.; Hunger, S.P.; Schrappe, M.; Moericke, A.; Biondi, A.; Escherich, G.; Silverman, L.B.; Goulden, N.; et al. Influence of Cranial Radiotherapy on Outcome in Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated With Contemporary Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.J.; Galea, V.; Barr, R.D. Proficiency of balance in children and youth who have had acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Physics 2005, 85, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, A.; Hop, W.; Takken, T.; Pieters, R.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M. Motor performance and functional exercise capacity in survivors of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.L.; Knight, S.J.; McCarthy, M.; De Luca, C.R. Motor functioning during and following treatment with chemotherapy for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, L.; Preibisch, C.; Hattingen, E.; Bartels, M.; Lehrnbecher, T.; Dewitz, R.; Zanella, F.; Good, C.; Lanfermann, H.; DuMesnil, R.; et al. Voxel-based morphometry and diffusion-tensor MR imaging of the brain in long-term survivors of childhood leukemia. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, M.N.; Krull, K.R.; Liu, W.; Glass, J.O.; Ji, Q.; Ogg, R.J.; Sabin, N.D.; Srivastava, D.K.; Robison, L.L.; Hudson, M.M.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and neurocognition in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Brain 2014, 137, 2973–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.W.; Su, L.Z.; Xu, J.J.; Xiang, L.; Wang, L.S.; Zhai, Z.M.; Zheng, S.S. Structural brain alteration in survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with chemotherapy treatment: A voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain Res. 2017, 1658, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjalldal, S.; Follin, C.; Svard, D.; Rylander, L.; Gabery, S.; Petersen, A.; van Westen, D.; Sundgren, P.C.; Bjorkman-Burtscher, I.M.; Latt, J.; et al. Microstructural white matter alterations and hippocampal volumes are associated with cognitive deficits in craniopharyngioma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.T.; Sabin, N.D.; Reddick, W.E.; Bhojwani, D.; Liu, W.; Brinkman, T.M.; Glass, J.O.; Hwang, S.N.; Srivastava, D.; Pui, C.H.; et al. Leukoencephalopathy and long-term neurobehavioural, neurocognitive, and brain imaging outcomes in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated with chemotherapy: A longitudinal analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e456–e466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.B.; Byun, D.H.; Son, S.M. Disruption of the corticospinal tract in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A case series. Children 2022, 9, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients Group (n = 19) | Control Group (n = 20) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 7.483 ± 3.1 | 7·534 ± 4.12 | 0.845 | |
| Sex (male: female) | 16:3 | 17:3 | 0.607 | |
| Gestational age at birth (weeks) | 39.6 ± 1.2 | 38.7 ± 2.1 | 0.135 | |
| Birth weight (kg) | 3.6 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 0.264 | |
| Hand dominance (n, Right/left) | 19 (14:5) | 20 (16:4) | 0.531 | |
| Acute leukemia type (B-cell/T-cell) | 19 (17:2) | |||
| Intrathecal chemotherapy | 19 | 0 | ||
| Cranial irradiation | 2 | 0 | ||
| Duration of chemotherapy and CSF study (days) | 4.36 ± 3.2 | |||
| CNS state | CNS 1 | 14 (73.6%) | ||
| CNS 2 | 2 (10.5%) | |||
| CNS 3 | 1 (5.3%) | |||
| Traumatic lumbar puncture | 2 (10.5%) | |||
| CST | Patients Group (n = 19) | Control Group (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA | |||
| Affected side | 0.309 ± 0.052 | 0.579 ± 0.05 | 0.001 * |
| Unaffected side | 0.528 ± 0.053 | 0.579 ± 0.05 | 0.005 * |
| p-value | 0.003 * | - | - |
| FV | |||
| Affected side | 289.8 ± 100 | 1081.8 ± 171 | 0.001 * |
| Unaffected side | 869.6 ± 131 | 1081.8 ± 171 | 0.002 * |
| p-value | 0.005 * | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.B.; Lee, J.M.; Son, S.M. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Showing Unilateral Motor Dysfunction Prior to Chemotherapy: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study. Children 2023, 10, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020224
Kim JB, Lee JM, Son SM. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Showing Unilateral Motor Dysfunction Prior to Chemotherapy: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study. Children. 2023; 10(2):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020224
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jong Bum, Jae Min Lee, and Su Min Son. 2023. "Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Showing Unilateral Motor Dysfunction Prior to Chemotherapy: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study" Children 10, no. 2: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020224
APA StyleKim, J. B., Lee, J. M., & Son, S. M. (2023). Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Showing Unilateral Motor Dysfunction Prior to Chemotherapy: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study. Children, 10(2), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10020224







