NF-κB-Dependent and -Independent (Moonlighting) IκBα Functions in Differentiation and Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Altered IκBα Activity in Cancer
3. IκBα Activation and Functions
4. IκBα in Hematologic Diseases
5. IκBα Loss in Glioma
6. IκBα Alterations in Other Solid Tumors
7. Targeting NF-κB or/and Chromatin Editing Enzymes for Treating IκBα-Deficient Tumors
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S.; May, M.J.; Kopp, E.B. NF-κB and Rel Proteins: Evolutionarily Conserved Mediators of Immune Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, C.; Sundqvist, A.; Mudie, S.; Melvin, A.; Xirodimas, D.; Rocha, S. Mechanism of Hypoxia-Induced NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4901–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desterro, J.M.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Hay, R.T. SUMO-1 modification of IkappaBalpha inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livolsi, A.; Busuttil, V.; Imbert, V.; Abraham, R.T.; Peyron, J.-F. Tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent activation of NF-κB. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontoriero, M.; Fiume, G.; Vecchio, E.; de Laurentiis, A.; Albano, F.; Iaccino, E.; Mimmi, S.; Pisano, A.; Agosti, V.; Giovannone, E.; et al. Activation of NF-κB in B cell receptor signaling through Bruton’s tyrosine kinase-dependent phosphorylation of IκB-α. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) activates nuclear factor-κB through IκBα kinase-independent but EGF receptor-kinase dependent tyrosine 42 phosphorylation of IκBα. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, Y.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Kundu, G.C.; Mahabeleshwar, G.H.; Singh, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Hydrogen Peroxide Activates NF-κB through Tyrosine Phosphorylation of IκBα and Serine Phosphorylation of p65. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24233–24241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Manna, S.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Pervanadate-induced Nuclear Factor-κB Activation Requires Tyrosine Phosphorylation and Degradation of IκBα. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8549–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rayet, B.; Gélinas, C. Aberrant rel/nfkb genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6938–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, M.M.; Sung, B.; Yadav, V.R.; Kannappan, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. NF-κB addiction and its role in cancer: ‘one size does not fit all’. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viatour, P.; Legrand-Poels, S.; van Lint, C.; Warnier, M.; Merville, M.-P.; Gielen, J.; Piette, J.; Bours, V.; Chariot, A. Cytoplasmic IκBα Increases NF-κB-independent Transcription through Binding to Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) 1 and HDAC3. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46541–46548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguilera, C.; Hoya-Arias, R.; Haegeman, G.; Espinosa, L.; Bigas, A. Recruitment of I B to the hes1 promoter is associated with transcriptional repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16537–16542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulero, M.; Ferres-Marco, D.; Islam, A.; Margalef, P.; Pecoraro, M.; Toll, A.; Drechsel, N.; Charneco, C.; Davis, S.; Bellora, N.; et al. Chromatin-bound IκBα regulates a subset of polycomb target genes in differentiation and cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marruecos, L.; Bertran, J.; Guillén, Y.; González, J.; Batlle, R.; López-Arribillaga, E.; Garrido, M.; Ruiz-Herguido, C.; Lisiero, D.; González-Farré, M.; et al. IκBα deficiency imposes a fetal phenotype to intestinal stem cells. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.J.; Ohta, S.; Sheu, K.M.; Spreafico, R.; Adelaja, A.; Taylor, B.; Hoffmann, A. NF-κB dynamics determine the stimulus specificity of epigenomic reprogramming in macrophages. Science 2021, 372, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brena, D.; Bertran, J.; Porta-de-la-Riva, M.; Guillén, Y.; Cornes, E.; Kukhtar, D.; Campos-Vicens, L.; Fernández, L.; Pecharroman, I.; García-López, A.; et al. Ancestral function of Inhibitors-of-kappaB regulates Caenorhabditis elegans development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.M.; Roff, M.; Hay, R.T. Defective IκBα in Hodgkin cell lines with constitutively active NF-κB. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabannes, E.; Khan, G.; Aillet, F.; Jarrett, R.F.; Hay, R.T. Mutations in the IkBa gene in Hodgkin’s disease suggest a tumour suppressor role for IκBα. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jungnickel, B.; Staratschek-Jox, A.; Bräuninger, A.; Spieker, T.; Wolf, J.; Diehl, V.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Rajewsky, K.; Küppers, R. Clonal Deleterious Mutations in the Iκbα Gene in the Malignant Cells in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krappmann, D.; Emmerich, F.; Kordes, U.; Scharschmidt, E.; Dörken, B.; Scheidereit, C. Molecular mechanisms of constitutive NF-κB/Rel activation in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells. Oncogene 1999, 18, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emmerich, F.; Meiser, M.; Hummel, M.; Demel, G.; Foss, H.-D.; Jundt, F.; Mathas, S.; Krappmann, D.; Scheidereit, C.; Stein, H.; et al. Overexpression of I Kappa B Alpha Without Inhibition of NF-κB Activity and Mutations in the I Kappa B Alpha Gene in Reed-Sternberg Cells. Blood 1999, 94, 3129–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkozy, C.; Hung, S.; Takata, K.; Chavez, E.; Aoki, T.; Duns, G.; Slack, G.W.; Telenius, A.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Viganò, E.; et al. Mutational Landscape of Grey Zone Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.K.; Wickenhauser, C.; Tawadros, S.; Diehl, V.; Küppers, R.; Wolf, J.; Schmitz, R. Mutational analysis of the I κ B α gene in activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidis, D.; Davis, R.E.; Rosenwald, A.; Staudt, L.M.; Gilmore, T.D. The human B-cell lymphoma cell line RC-K8 has multiple genetic alterations that dysregulate the Rel/NF-κB signal transduction pathway. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8759–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalaitzidis, D.; Gilmore, T.D. Genomic organization and expression of the rearrangedREL proto-oncogene in the human B-cell lymphoma cell line RC-K8. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2002, 34, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, K.J. The molecular signature of mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma differs from that of other diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and shares features with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2003, 102, 3871–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Feuerhake, F.; Monti, S.; Kutok, J.L.; Aster, J.C.; Shipp, M.A. Lack of IKBA coding region mutations in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma and the host response subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2006, 107, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivellaro, S.; Carrà, G.; Panuzzo, C.; Taulli, R.; Guerrasio, A.; Saglio, G.; Morotti, A. The non-genomic loss of function of tumor suppressors: An essential role in the pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia chronic phase. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marruecos, L.; Manils, J.; Moreta, C.; Gómez, D.; Filgaira, I.; Serafin, A.; Cañas, X.; Espinosa, L.; Soler, C. Single loss of a Trp53 allele triggers an increased oxidative, DNA damage and cytokine inflammatory responses through deregulation of IκBα expression. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Gu, L.; Zhu, N.; Woods, W.G.; Findley, H.W. Transfection of a dominant-negative mutant NF-kB inhibitor (IkBm) represses p53-dependent apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells: Interaction of IkBm and p53. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8137–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Granados, E.; Keenan, J.E.; Kinney, M.C.; Leo, H.; Jain, N.; Ma, C.A.; Quinones, R.; Gelfand, E.W.; Jain, A. A novel mutation in NFKBIA/IKBA results in a degradation-resistant N-truncated protein and is associated with ectodermal dysplasia with immunodeficiency. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, K.M.; Ma, M.H.; Manyak, S.; Altamirano, C.V.; Tang, Y.M.; Frantzen, M.; Mikail, A.; Roussos, E.; Sjak-Shie, N.; Vescio, R.A.; et al. Identification of polymorphisms of the IκBα gene associated with an increased risk of multiple myeloma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2002, 137, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spink, C.F.; Gray, L.C.; Davies, F.E.; Morgan, G.J.; Bidwell, J.L. Haplotypic structure across the IκBα gene (NFKBIA) and association with multiple myeloma. Cancer Lett. 2007, 246, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angileri, F.F.; Aguennouz, M.; Conti, A.; La Torre, D.; Cardali, S.; Crupi, R.; Tomasello, C.; Germanò, A.; Vita, G.; Tomasello, F. Nuclear factor-κB activation and differential expression of survivin and Bcl-2 in human grade 2-4 astrocytomas. Cancer 2008, 112, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkolopoulou, P.; Levidou, G.; Saetta, A.A.; El-Habr, E.; Eftichiadis, C.; Demenagas, P.; Thymara, I.; Xiromeritis, K.; Boviatsis, E.; Thomas-Tsagli, E.; et al. Expression of nuclear factor-κB in human astrocytomas: Relation to pIκBa, vascular endothelial growth factor, Cox-2, microvascular characteristics, and survival. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredel, M.; Scholtens, D.M.; Yadav, A.K.; Alvarez, A.A.; Renfrow, J.J.; Chandler, J.P.; Yu, I.L.Y.; Carro, M.S.; Dai, F.; Tagge, M.J.; et al. NFKBIA Deletion in Glioblastomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinker, G.S.; Thomas, A.M.; Carvalho, V.J.; Lima, F.P.; Fujita, A. Deletion and low expression of NFKBIA are associated with poor prognosis in lower-grade glioma patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyar, A.; Habibi, I.; Ebrahimi, A.; Mansourpour, D.; Mokarizadeh, A.; Rajabi, A.; Farshgar, R.; Eshaghzadeh, M.; Zamani-Ahmadmahmudi, M.; Nodushan, S.M.H.T. Predictive and prognostic value of TLR9 and NFKBIA gene expression as potential biomarkers for human glioma diagnosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 368, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Recombinant I κ B α -loaded curcumin nanoparticles for improved cancer therapeutics. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 345102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhong, X.; Wu, T.; Yang, T.; Chen, G.; Xie, X.; Wei, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Z. Identification of a NFKBIA polymorphism associated with lower NFKBIA protein levels and poor survival outcomes in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loercher, A.; Lee, T.L.; Ricker, J.L.; Howard, A.; Geoghegen, J.; Chen, Z.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Sitcheran, R.; Chuang, E.Y.; Mitchell, J.B.; et al. Nuclear Factor-κB is an Important Modulator of the Altered Gene Expression Profile and Malignant Phenotype in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6511–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palayoor, S.T.; Youmell, M.Y.; Calderwood, S.K.; Coleman, C.N.; Price, B.D. Constitutive activation of IκB kinase α and NF-κB in prostate cancer cells is inhibited by ibuprofen. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7389–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo-Domenech, J.; Mellado, B.; Ferrer, B.; Truan, D.; Codony-Servat, J.; Sauleda, S.; Alcover, J.; Campo, E.; Gascon, P.; Rovira, A.; et al. Activation of nuclear factor-κB in human prostate carcinogenesis and association to biochemical relapse. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sovak, M.A.; Bellas, R.E.; Kim, D.W.; Zanieski, G.J.; Rogers, A.E.; Traish, A.M.; Sonenshein, G.E. Aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression and the pathogenesis of breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2952–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakshatri, H.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Martin, D.A.; Goulet, R.J.; Sledge, G.W. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 3629–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sau, A.; Lau, R.; Cabrita, M.A.; Nolan, E.; Crooks, P.A.; Visvader, J.E.; Pratt, M.A.C. Persistent Activation of NF-κB in BRCA1-Deficient Mammary Progenitors Drives Aberrant Proliferation and Accumulation of DNA Damage. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, N.; Morisaki, T.; Hashizume, K.; Yao, T.; Tsuneyoshi, M.; Noshiro, H.; Nakamura, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Uchiyama, A.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Nuclear factor-κB p65 (RelA) transcription factor is constitutively activated in human gastric carcinoma tissue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 4136–4142. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Majada, V.; Aguilera, C.; Villanueva, A.; Vilardell, F.; Robert-Moreno, A.; Aytés, A.; Real, F.X.; Capella, G.; Mayo, M.W.; Espinosa, L.; et al. Nuclear IKK activity leads to dysregulated Notch-dependent gene expression in colorectal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007, 104, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margalef, P.; Fernández-Majada, V.; Villanueva, A.; Garcia-Carbonell, R.; Iglesias, M.; López, L.; Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Villà-Freixa, J.; Mulero, M.C.; Andreu, M.; et al. A Truncated Form of IKKα Is Responsible for Specific Nuclear IKK Activity in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, X.; Liu, D.; Shishodia, S.; Ozburn, N.; Behrens, C.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, W.K.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Wistuba, I.I. Nuclear factor-κB (nf-κB) is frequently expressed in lung cancer and preneoplastic lesions. Cancer 2006, 107, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujiang, P.; Mori, T.J.; Takahashi, T.; Tanaka, F.; Kasyu, I.; Hitomi, S.; Hiai, H. Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at 17q and 14q in human lung cancers. Oncogene 1998, 17, 3029–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, M.; Soh, J.; Yamamoto, H.; Ichimura, K.; Shien, K.; Maki, Y.; Muraoka, T.; Tanaka, N.; Ueno, T.; Asano, H.; et al. Silenced expression of NFKBIA in lung adenocarcinoma patients with a never-smoking history. Acta Med. Okayama 2013, 67, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Haverty, P.M.; Guan, Y.; Stinson, J.; Yue, P.; Zhang, Y.; Pant, K.P.; Bhatt, D.; et al. The mutation spectrum revealed by paired genome sequences from a lung cancer patient. Nature 2010, 465, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivona, T.G.; Hieronymus, H.; Parker, J.; Chang, K.; Taron, M.; Rosell, R.; Moonsamy, P.; Dahlman, K.; Miller, V.A.; Costa, C.; et al. FAS and NF-κB signalling modulate dependence of lung cancers on mutant EGFR. Nature 2011, 471, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrà, G.; Ermondi, G.; Riganti, C.; Righi, L.; Caron, G.; Menga, A.; Capelletto, E.; Maffeo, B.; Lingua, M.F.; Fusella, F.; et al. IκBα targeting promotes oxidative stress-dependent cell death. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Guan, X.; Guo, Y.; Sham, J.; Deng, M.; Liang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Trent, J. Analysis of genetic alterations in primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma by comparative genomic hybridization. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2001, 30, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chung, G.T.Y.; Lui, V.W.Y.; To, K.-F.; Ma, B.B.Y.; Chow, C.; Woo, J.K.S.; Yip, K.Y.; Seo, J.; Hui, E.P.; et al. Exome and genome sequencing of nasopharynx cancer identifies NF-κB pathway activating mutations. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, R.; Liu, Y.-P.; Lin, D.-C.; Li, Q.; Yu, T.; Zou, X.; Lin, M.; Zhang, X.-L.; He, G.-P.; Yang, Q.; et al. Clonal Mutations Activate the NF-κB Pathway to Promote Recurrence of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5930–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Dai, W.; Cheung, A.K.L.; Ko, J.M.Y.; Kan, R.; Wong, B.W.Y.; Leong, M.M.L.; Deng, M.; Kwok, T.C.T.; Chan, J.Y.-W.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies multiple loss-of-function mutations of NF-κB pathway regulators in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11283–11288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phoon, Y.P.; Cheung, A.K.L.; Cheung, F.M.F.; Chan, K.F.; Wong, S.; Wong, B.W.Y.; Tung, S.Y.; Yau, C.C.; Ng, W.T.; Lung, M.L. IKBB tumor suppressive role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via NF-κB-mediated signalling. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Pfeifer, D.; He, L.-J.; Qiao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Arbman, G.; Wang, Z.-L.; Jia, C.-R.; Carstensen, J.; Sun, X.-F. Association of NFKBIA polymorphism with colorectal cancer risk and prognosis in Swedish and Chinese populations. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewander, A.; Butchi, A.K.R.; Gao, J.; He, L.-J.; Lindblom, A.; Arbman, G.; Carstensen, J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; The Swedish Low-Risk Colorectal Can; Sun, X.-F. Polymorphism in the promoter region of the NFKB1 gene increases the risk of sporadic colorectal cancer in Swedish but not in Chinese populations. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, C.; Cai, Y.; Liu, B. Association of NFKB1 and NFKBIA gene polymorphisms with susceptibility of gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 101042831771710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, K.L.; Vierkant, R.A.; Phelan, C.M.; Fridley, B.L.; Anderson, S.; Knutson, K.L.; Schildkraut, J.M.; Cunningham, J.M.; Kelemen, L.E.; Pankratz, V.S.; et al. Polymorphisms in NF-κB Inhibitors and Risk of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, H.; Rosdahl, I.; Sun, X.-F.; Zhang, H. Importance of polymorphisms in NF-κB1 and NF-κBIα genes for melanoma risk, clinicopathological features and tumor progression in Swedish melanoma patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 133, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Xie, J.; Tan, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; et al. IkappaBalpha gene promoter polymorphisms are associated with hepatocarcinogenesis in patients infected with hepatitis B virus genotype C. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. Polymorphisms in NFKB1 and NFKBIA Genes Modulate the Risk of Developing Prostate Cancer among Han Chinese. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, J.S.; Kallakury, B.V.S.; Sheehan, C.E.; Fisher, H.A.G.; Kaufman, R.P.; Kaur, P.; Gray, K.; Stringer, B. Expression of Nuclear Factor-κB and IκBα Proteins in Prostatic Adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatlekar, S.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. Role of HOX Genes in Stem Cell Differentiation and Cancer. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.; Zyoud, A.; Allegrucci, C. A Case of Identity: HOX Genes in Normal and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Hogerlinden, M.; Rozell, B.L.; Toftgård, R.; Sundberg, J.P. Characterization of the Progressive Skin Disease and Inflammatory Cell Infiltrate in Mice with Inhibited NF-κB Signaling. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seitz, C.S.; Lin, Q.; Deng, H.; Khavari, P.A. Alterations in NF- B function in transgenic epithelial tissue demonstrate a growth inhibitory role for NF- B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dajee, M.; Lazarov, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cai, T.; Green, C.L.; Russell, A.J.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Tao, S.; Lin, Q.; Kubo, Y.; et al. NF-κB blockade and oncogenic Ras trigger invasive human epidermal neoplasia. Nature 2003, 421, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, K.J.; Amato, S.; Noberini, R.; Toscani, C.; Fernández-Pérez, D.; Rossi, A.; Conforti, P.; Zanotti, M.; Bonaldi, T.; Tamburri, S.; et al. Intestinal differentiation involves cleavage of histone H3 N-terminal tails by multiple proteases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marruecos, L.; Bertran, J.; Álvarez-villanueva, D.; Floor, M.; Villà-freixa, J.; Ghosh, G.; Bigas, A. Dynamic association of IκBα to chromatin is regulated by acetylation and cleavage of histone H4. EMBO Rep. 2021, e52649. [Google Scholar]
- Nacev, B.A.; Feng, L.; Bagert, J.D.; Lemiesz, A.E.; Gao, J.; Soshnev, A.A.; Kundra, R.; Schultz, N.; Muir, T.W.; Allis, C.D. The expanding landscape of ‘oncohistone’ mutations in human cancers. Nature 2019, 567, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatori, S.; Tavolaro, S.; Gambardella, S.; Fanelli, M. The dark side of histones: Genomic organization and role of oncohistones in cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, V.; Karin, M. Is NF-κB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitsiades, N.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Richardson, P.G.; Poulaki, V.; Tai, Y.-T.; Chauhan, D.; Fanourakis, G.; Gu, X.; Bailey, C.; Joseph, M.; et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 potentiates sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to conventional chemotherapeutic agents: Therapeutic applications. Blood 2003, 101, 2377–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Arkan, M.C.; Bollrath, J.; Hsu, L.-C.; Goode, J.; Miething, C.; Göktuna, S.I.; Neuenhahn, M.; Fierer, J.; Paxian, S.; et al. NF-κB Is a Negative Regulator of IL-1β Secretion as Revealed by Genetic and Pharmacological Inhibition of IKKβ. Cell 2007, 130, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eich, M.-L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E.; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiacchiera, F.; Rossi, A.; Jammula, S.; Zanotti, M.; Pasini, D. PRC 2 preserves intestinal progenitors and restricts secretory lineage commitment. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 2301–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koppens, M.A.J.; Bounova, G.; Gargiulo, G.; Tanger, E.; Janssen, H.; Cornelissen-Steijger, P.; Blom, M.; Song, J.-Y.; Wessels, L.F.A.; van Lohuizen, M. Deletion of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 From Mouse Intestine Causes Loss of Stem Cells. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 684–697.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
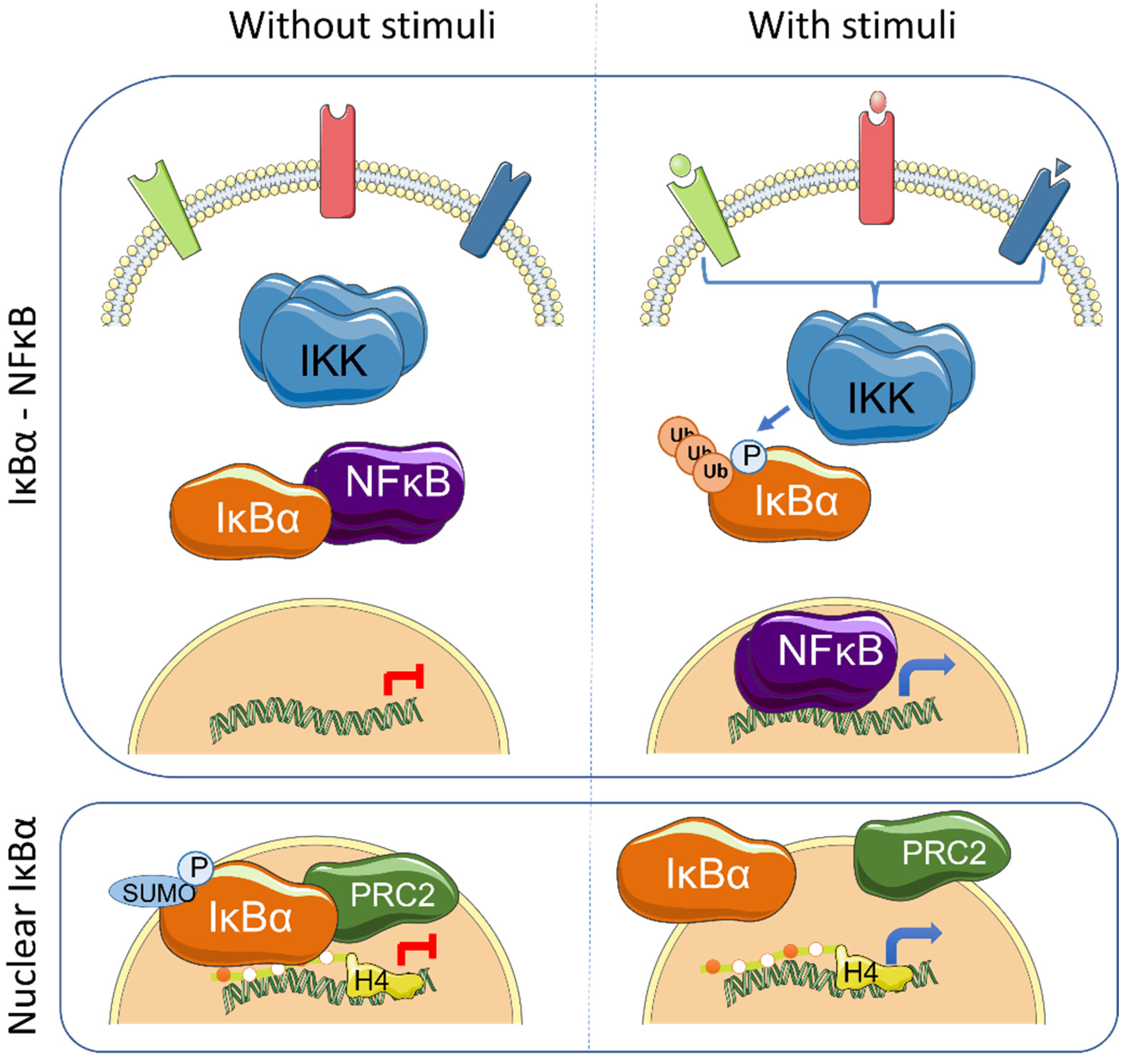
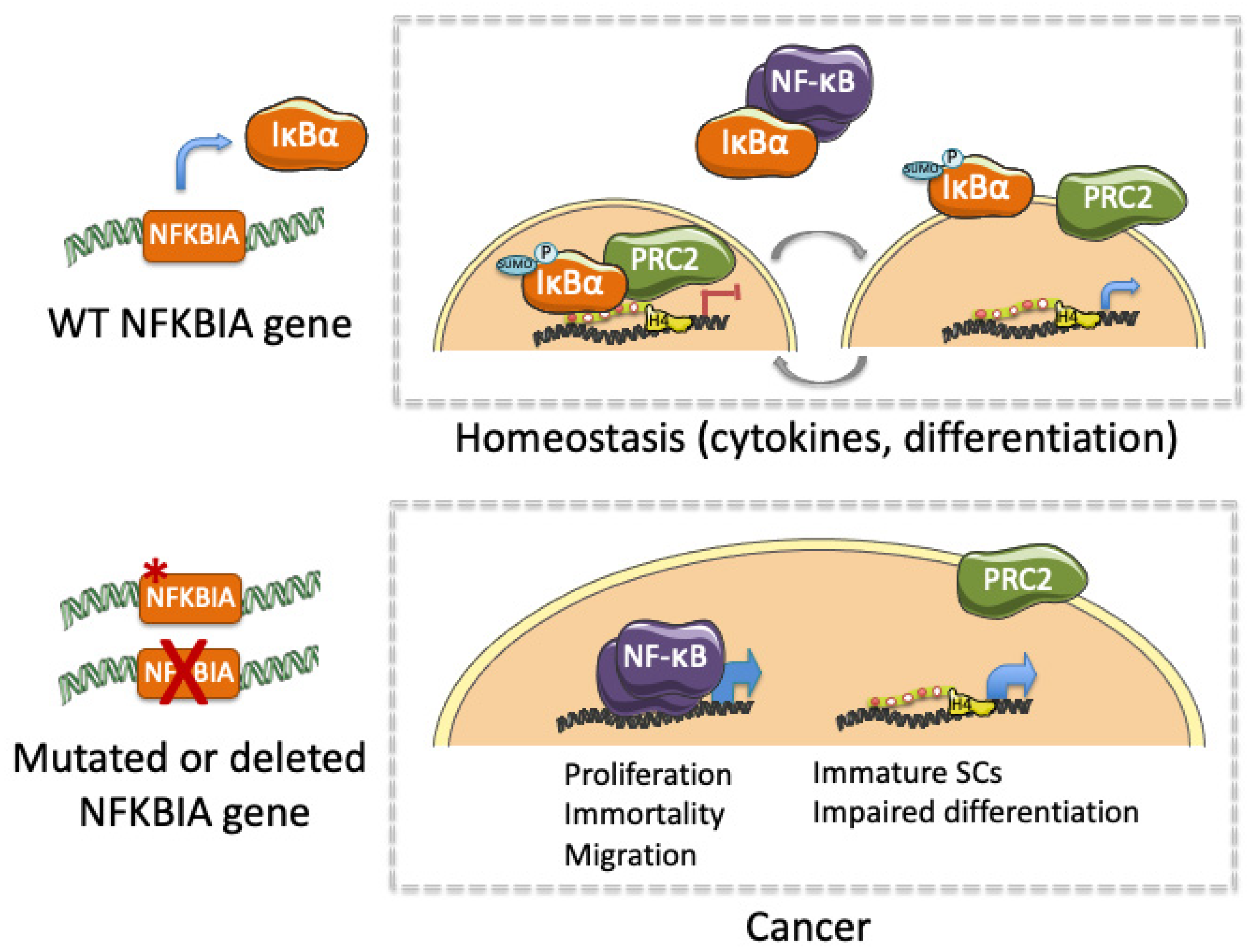
| Tissue | Cancer | IκBα Alteration | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematopoietic | Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) | Inactivating mutations that produce non-functional protein | NF-κB constitutive activation | [16,17,18,19,20] |
| Gray zone lymphoma (GZL) | Inactivating mutations | No evaluated | [22] | |
| B-cell lymphoma (DCLBL) | Inactivating mutations with absence of the protein | NF-κB constitutive activation | [22,23] | |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) | High expression | Complex with BCR-ABL and p53, avoiding its nuclear activity as tumor-suppressor | [24] | |
| Brain | Glioblastoma | Reduced gene copy number | No evaluated | [27,28,36] |
| Low-grade glioma | Reduced gene copy number | No evaluated | [37] | |
| Lung | Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) | Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) or inactivating mutations | No evaluated | [39,40] |
| Head and neck | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Inactivating mutations and loss of 14q region | NF-κB constitutive activation | [5,56,57,58,59,60] |
| Skin | Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) | Loss of nuclear IκBα and cytoplasmic accumulation | Altered IκBα /PRC2 target gene transcription | [12] |
| IκBα super-repressor (SR) mutant | Constitutive NF-κB inhibition | [47,48] | ||
| IκBα super-repressor (SR) mutant + mutant KRAS (G12V) | Invasiveness of tumor | [50] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espinosa, L.; Marruecos, L. NF-κB-Dependent and -Independent (Moonlighting) IκBα Functions in Differentiation and Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091278
Espinosa L, Marruecos L. NF-κB-Dependent and -Independent (Moonlighting) IκBα Functions in Differentiation and Cancer. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091278
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspinosa, Lluís, and Laura Marruecos. 2021. "NF-κB-Dependent and -Independent (Moonlighting) IκBα Functions in Differentiation and Cancer" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091278
APA StyleEspinosa, L., & Marruecos, L. (2021). NF-κB-Dependent and -Independent (Moonlighting) IκBα Functions in Differentiation and Cancer. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091278







