Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.1.1. Extracellular Vesicle Isolation
2.1.2. Extracellular Vesicle Characterisation
2.2. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry
Mass Spectrometry
2.3. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.3.1. cDNA Synthesis
2.3.2. MiRNA Array Profiling
2.3.3. Validation of Selected miRNAs
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Study
3.2. Extracellular Vesicle Characterisation
3.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
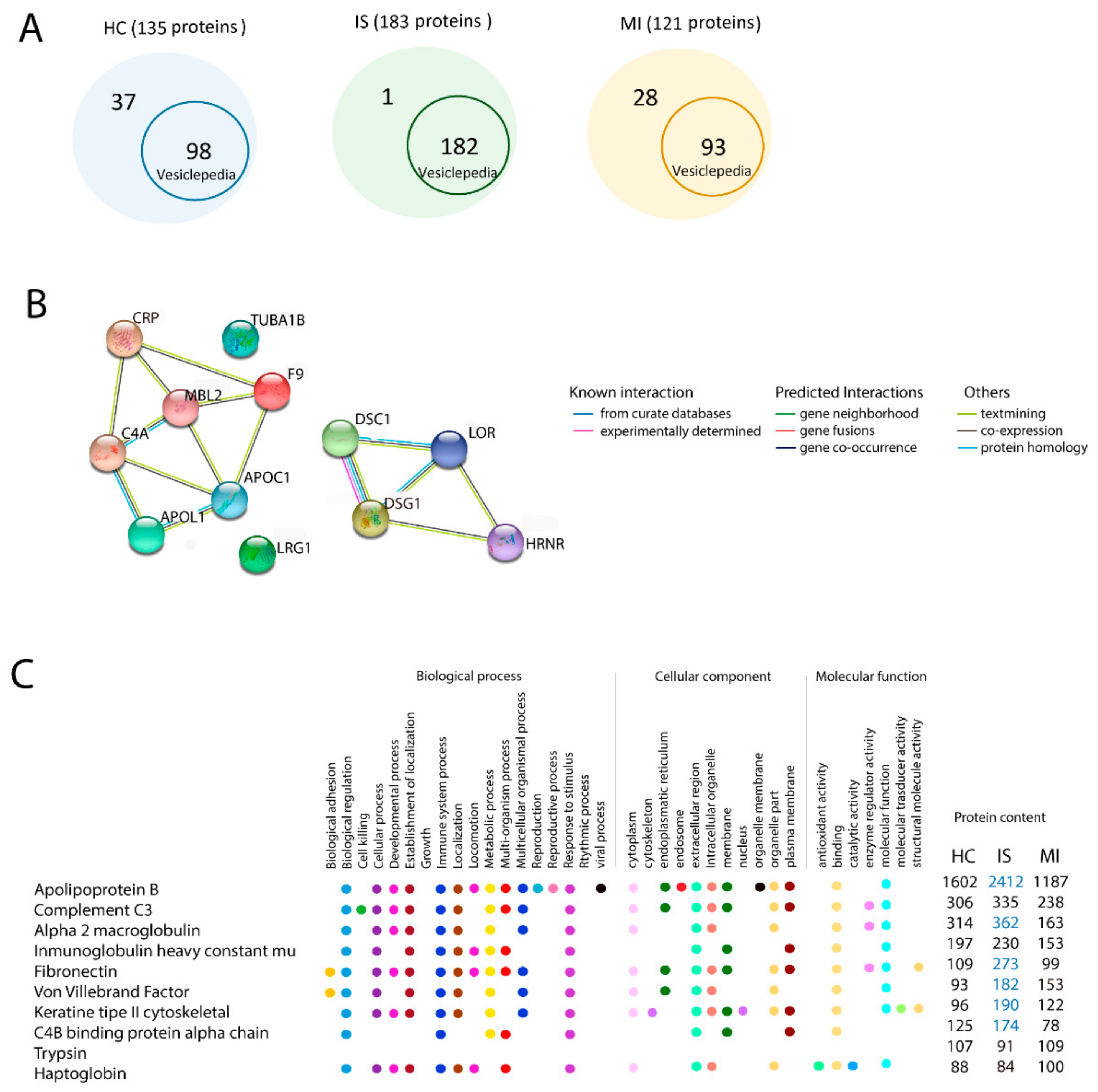
3.3.1. Vesiclepedia
3.3.2. In Silico Gene Ontology Analysis of the Total Proteins of Each Group
3.3.3. Similarities in Gene Ontology Terms in Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction
3.3.4. Differences in Gene Ontology Terms in the 10 Most Enriched Proteins among the Ischaemic Stroke, Myocardial Infarction, and Healthy Control Groups
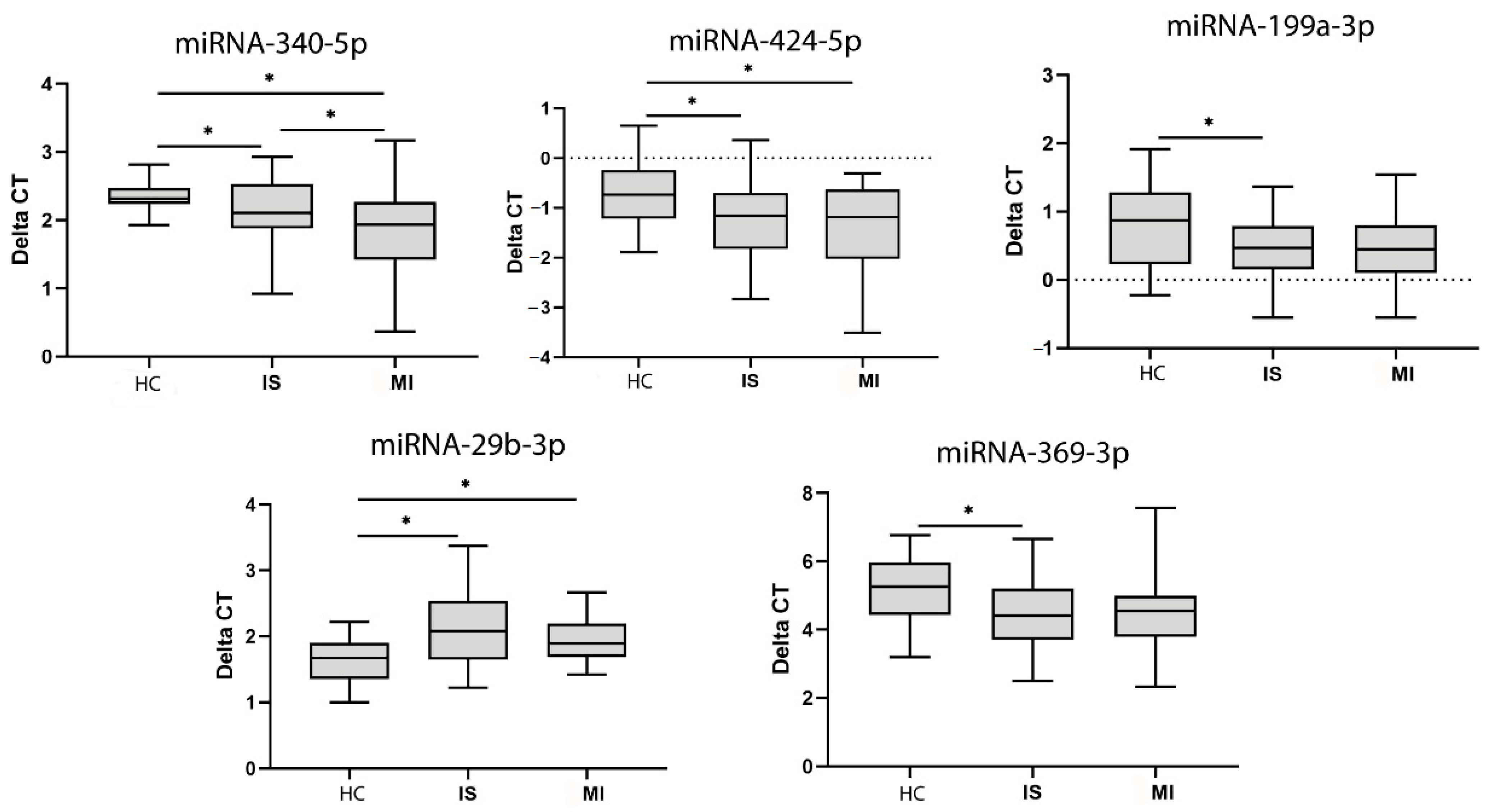
3.4. MiRNA Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Shared Proteins and miRNAs
4.2. Specific Proteins and miRNAs
4.3. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Neurological Disorders. Available online: http://www.who.int/mental_health/neurology/neurodiso/en/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Méloux, A.; Béjot, Y.; Rochette, L.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Brain-Heart Interactions during Ischemic Processes: Clinical and Experimental Evidences. Stroke 2020, 51, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesselli, D.; Parisse, P.; Aleksova, A.; Veneziano, C.; Cervellin, C.; Zanello, A.; Beltrami, A.P. Extracellular vesicles: How drug and pathology interfere with their biogenesis and function. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kralingen, J.C.; McFall, A.; Ord, E.N.J.; Coyle, T.F.; Bissett, M.; McClure, J.D.; McCabe, C.; Macrae, I.M.; Dawson, J.; Work, L.M. Altered Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Expression in Ischemic Stroke and Small Vessel Disease. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Ji, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y. Increased brain specific MiR-9 and MiR-124 in the serum exosomes of acute ischemic stroke patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.; Qu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.Y. Increased circulating exosomal miRNA-223 is associated with acute ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, R.Y.; Yu, D.J.; Lan, X.Y.; Li, J.P. Plasma exosomal miR-422a and miR-125b-2-3p serve as biomarkers for ischemic stroke. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2017, 14, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, M.Y.S.; Alsop, E.; Meechoovet, B.; Beecroft, T.; Agrawal, K.; Whitsett, T.G.; Huentelman, M.J.; Spetzler, R.F.; Nakaji, P.; Kim, S.; et al. Extracellular microRNAs in blood differentiate between ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke subtypes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1713540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Feng, Y.S.; Tan, Z.X.; Xing, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, F. The Role of Exosomes in Stroke. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankam, F.G.; Agrawal, D.K. Infarct Zone: A Novel Platform for Exosome Trade in Cardiac Tissue Regeneration. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2020, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluijter, J.P.G.; Verhage, V.; Deddens, J.C.; van den Akker, F.; Doevendans, P.A. Microvesicles and exosomes for intracardiac communication. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 102, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suades, R.; Padró, T.; Crespo, J.; Ramaiola, I.; Martin-Yuste, V.; Sabaté, M.; Sans-Roselló, J.; Sionis, A.; Badimon, L. Circulating microparticle signature in coronary and peripheral blood of ST elevation myocardial infarction patients in relation to pain-to-PCI elapsed time. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 202, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyer, X.; Vion, A.C.; Tedgui, A.; Boulanger, C.M. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, C.; Bruce, K.D.; Burgy, O.; Boyd, T.D.; Michel, C.R.; Garcia-Perez, J.E.; Adame, V.; Anton, P.; Bettcher, B.M.; Chial, H.J.; et al. Exosome Isolation by Ultracentrifugation and Precipitation and Techniques for Downstream Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2020, 88, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.C.; Diekhorst, L.; Martínez-Arroyo, A.; Alonso-López, E.; García-Bermejo, M.L.; Rodríguez-Serrano, M.; Arrúe-Gonzalo, M.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; et al. Low dose of extracellular vesicles identified that promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K.; Breyne, K.; Ughetto, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Breakefield, X.O. RNA delivery by extracellular vesicles in mammalian cells and its applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 26, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Illei, G.G. The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Sáez-Martínez, P.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; López-Cánovas, J.L.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Herrera-Martínez, A.D.; García-Bermejo, L.; Macías-González, M.; López-Miranda, J.; et al. Influence of obesity in the miRNome: miR-4454, a key regulator of insulin response via splicing modulation in prostate. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 25, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesiclepedia. Available online: http://microvesicles.org/ (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- KEGG. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/kegg/ (accessed on 19 September 2020).
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Poudel, S.; Muruganujan, A.; Casagrande, J.T.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 10: Expanded protein families and functions, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D336–D342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIRBD. Available online: http://www.mirdb.org/ (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- UNIPROT. Available online: www.uniprot.org (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- STRING. Available online: https://string-db.org/ (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Otero-Ortega, L.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.; Fuentes, B.; Diekhorst, L.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. Role of Exosomes as a Treatment and Potential Biomarker for Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Ni, J.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, B.; Graham, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer: Recent advances in circulating extracellular vesicle detection for early diagnosis and monitoring progression. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4130–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, J.; Thompson, J.; Malouf, D.; Bucci, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Extracellular vesicles: The next generation of biomarkers for liquid biopsy-based prostate cancer diagnosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2309–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughson, M.D.; Hoy, W.E.; Mott, S.A.; Puelles, V.G.; Bertram, J.F.; Winkler, C.L.; Kopp, J.B. APOL1 Risk Alleles Are Associated With More Severe Arteriosclerosis in Renal Resistance Vessels with Aging and Hypertension. Kidney Int. Rep. 2016, 1, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, B.; Gigante, B.; Mehlig, K.; Bergsten, A.; Leander, K.; de Faire, U.; Lissner, L.; Thelle, D.S.; Carlsson, L.M. Apolipoprotein C-I genotype and serum levels of triglycerides, C-reactive protein and coronary heart disease. Metabolism 2010, 59, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, R.; Tiwari, H.K.; Arnett, D.K.; Ovbiagele, B.; Irvin, M.R.; Wahab, K.; Sarfo, F.; Srinivasasainagendra, V.; Adeoye, A.; Perry, R.T.; et al. APOL1, CDKN2A/CDKN2B and HDAC9 polymorphisms and small vessel ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2018, 137, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittas, K.; Vrachatis, D.A.; Angelidis, C.; Tsoucala, S.; Giannopoulos, G.; Deftereos, S. The Role of Calcium Handling Mechanisms in Reperfusion Injury. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 4077–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. Toast. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkowska-Jastrzębska, I.; Karliński, M.A.; Błażejewska-Hyżorek, B.; Sarzynska-Dlugosz, I.; Filipiak, K.J.; Czlonkowska, A. Carotid intima media thickness and blood biomarkers of atherosclerosis in patients after stroke or myocardial infarction. Croat. Med. J. 2016, 57, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Risks of Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, Diabetes, and Total Mortality: Implications for Longevity. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, S253–S259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yi, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Sung, J.H. Association of High-sensitivity C-reactive Protein with Patient Prognosis Following Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2020. in Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anrather, J.; Iadecola, C. Inflammation and stroke: An overview. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, T.P.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S. MicroRNA-29b alleviates oxygen and glucose deprivation/reperfusion-induced injury via inhibition of the p53-dependent apoptosis pathway in N2a neuroblastoma cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegele, R.A.; Ban, M.R.; Anderson, C.M.; Spence, J.D. Infection-susceptibility Alleles of Mannose-Binding Lectin Are Associated with Increased Carotid Plaque Area. J. Investig. Med. 2000, 48, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalani, R.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Deepa, D.; Gopala, S.; Prabhakaran, D.; Tirschwell, D.; Sylaja, P.N. Apolipoproteins B and A1 in Stroke Subtypes. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezu, T.; Hosomi, N.; Aoki, S.; Deguchi, K.; Masugata, H.; Ichihara, N.; Ohyama, H.; Ohtsuki, T.; Kohno, M.; Matsumoto, M. Alpha2-macroglobulin as a promising biomarker for cerebral small vessel disease in acute ischemic stroke patients. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2642–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanesha, N.; Chorawala, M.R.; Jain, M.; Bhalla, A.; Thedens, D.; Nayak, M.; Doddapattar, P.; Chauhan, A.K. Fn-EDA (Fibronectin Containing Extra Domain A) in the Plasma, but Not Endothelial Cells, Exacerbates Stroke Outcome by Promoting Thrombo-Inflammation. Stroke 2019, 50, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, P.; Herz, J. Signaling through LRP1: Protection from atherosclerosis and beyond. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, A.R.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, O.J.; Kim, J.K.; Oh, S.H. Alteration of microRNA 340-5p and Arginase-1 Expression in Peripheral Blood Cells During Acute Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3211–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, R.; Baaken, M.; Horn, P.; Schuler, D.; Westenfeld, R.; Amabile, N.; Kelm, M.; Heiss, C. Endothelial microparticles and vascular parameters in subjects with and without arterial hypertension and coronary artery disease. Data Brief. 2018, 19, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrieger, F.W.; Vitale, N. Cholesterol and the journey of extracellular vesicles. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjeti, A.K.; Ariyarajah, A.; D’Crus, A.; Seldon, M.; Lincz, L.F. Circulating microvesicle number, function and small RNA content vary with age, gender, smoking status, lipid and hormone profiles. Thromb. Res. 2017, 156, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.D.; Shah, S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods 2015, 87, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendergast, E.N.; de Souza Fonseca, M.A.; Dezem, F.S.; Lester, J.; Karlan, B.Y.; Noushmehr, H.; Lin, X.; Lawrenson, K. Optimizing exosomal RNA isolation for RNA-Seq analyses of archival sera specimens. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoshenko, M.Y.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 8545347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Variables | HC N = 22 | IS N = 81 | MI N = 37 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age, years (SD) | 61 (12.74) | 67.675(14.88) * | 55.95 (13.95) | 0.001 |
| Males, N (%) | 7 (31.8) | 42 (51.9) | 27 (73) † | 0.005 |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 3 (13.63) | 54 (69.2)*,† | 17 (45.9) | 0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 2 (9.09) | 15 (19.2) | 4 (10.8) | 0.411 |
| Dyslipidaemia, N (%) | 3 (13.63) | 36 (46.2) *,† | 18 (48.6) † | 0.007 |
| Smokers, N (%) | 3 (13.63) | 18 (22.2)* | 22 (59.5) † | 0.001 |
| Alcohol use, N (%) | 1 (4.54) | 6 (7.4) | 1 (2.7) | 0.761 |
| Previous ischaemic Cardiomyopathy, N (%) | 0 (0) | 9 (11.8) | 4 (10.8) | 0.244 |
| Median Charlson Comorbidity index (IQR) | 0.00 (1) | 1 (1.25) † | 1 (1) † | 0.001 |
| HC | IS | MI |
|---|---|---|
| Biological regulation | Biological regulation | Biological regulation |
| Biogenesis | Biogenesis | Biogenesis |
| Cellular process | Cellular process | Cellular process |
| Immune system process | Cellular developmental process | Cellular developmental process |
| Localization | Immune system process | Immune system process |
| Metabolic Process | Localization | Localization |
| Multiorgan process | Metabolic Process | Metabolic Process |
| Multicellular organismal process | Multiorgan process | Multiorgan process |
| Response to stimulus | Response to stimulus | Response to stimulus |
| Signalling | Signalling | Signalling |
| HC | IS | MI |
|---|---|---|
| Binding | Binding | Binding |
| Catalytic activity | Catalytic activity | Catalytic activity |
| Molecular function regulation | Molecular function regulation | Molecular function regulation |
| Structural molecule activity | Structural molecule activity | Structural molecule activity |
| Transcription regulator activity | Transcription regulator activity | Transcription regulator activity |
| Transporter activity | Transporter activity | Transporter activity |
| miRNAs HC vs. MI | Fold Change | p |
| miR-376a-3p | 2.804 | 0.001 |
| miR-369-3p | 4.055 | 0.005 |
| miR-376c-3p | 2.510 | 0.006 |
| miR-150-5p | −2.485 | 0.010 |
| miR-375 | −3.007 | 0.029 |
| miR-326 | 2.829 | 0.033 |
| miR-197-3p | 2.035 | 0.035 |
| miRNAs HC vs. IS | Fold Change | p |
| miR-376a-3p | 3.772 | 0.001 |
| miR-376c-3p | 3.353 | 0.001 |
| miR-33a-5p | 2.237 | 0.001 |
| miR-100-5p | −2.181 | 0.001 |
| miR-199a-5p | 3.844 | 0.001 |
| miR-369-3p | 6.741 | 0.001 |
| miR-326 | 4.287 | 0.001 |
| miR-340-5p | 2.304 | 0.004 |
| miR-424-5p | 2.588 | 0.009 |
| miR-423-3p | 2.000 | 0.036 |
| miR-197-3p | 2.320 | 0.042 |
| miR-1537-3p | 3.331 | 0.046 |
| miRNAs IS vs. MI | Fold Change | p |
| miR-339-5p | −2.954 | 0.001 |
| miR-181a-5p | −2.150 | 0.001 |
| miR-194-5p | 2.134 | 0.001 |
| miR-100-5p | 2.909 | 0.004 |
| miR-29b-3p | −2.327 | 0.005 |
| miR-15a-5p | 2.004 | 0.012 |
| miR-1537-3p | −3.148 | 0.034 |
| miR-199a-5p | −2.168 | 0.040 |
| miRNA | Patient Group | Patient Group | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MI | HC | |||
| miR-424-5p | −1.331 ± 0.813 | > | −0.773 ± 0.663 | 0.023 |
| miR-340-5p | 1.824 ± 0.7139 | > | 2.417 ± 0.372 | 0.003 |
| miR-29b-3p | 1.930 ± 0.3614 | < | 1.640 ± 0.362 | 0.019 |
| IS | HC | |||
| miR-424-5p | −1.273 ± 0.747 | < | −0.773 ± 0.663 | 0.014 |
| miR-369-3p | 4.510 ± 1.052 | < | 5.141 ± 0.976 | 0.029 |
| miR-340-5p | 2.168 ± 0.486 | < | 2.417 ± 0.372 | 0.049 |
| miR-199a-3p | 0.463 ± 0.451 | < | 0.796 ± 0.593 | 0.019 |
| miR-29b-3p | 2.093 ± 0.551 | > | 1.640 ± 0.362 | 0.0001 |
| IS | MI | |||
| miR-340-5p | 2.168 ± 0.486 | > | 1.824 ± 0.713 | 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otero-Ortega, L.; Alonso-López, E.; Pérez-Mato, M.; Laso-García, F.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.C.; Diekhorst, L.; García-Bermejo, M.L.; Conde-Moreno, E.; Fuentes, B.; Alonso de Leciñana, M.; et al. Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010008
Otero-Ortega L, Alonso-López E, Pérez-Mato M, Laso-García F, Gómez-de Frutos MC, Diekhorst L, García-Bermejo ML, Conde-Moreno E, Fuentes B, Alonso de Leciñana M, et al. Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtero-Ortega, Laura, Elisa Alonso-López, María Pérez-Mato, Fernando Laso-García, Mari Carmen Gómez-de Frutos, Luke Diekhorst, María Laura García-Bermejo, Elisa Conde-Moreno, Blanca Fuentes, María Alonso de Leciñana, and et al. 2021. "Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction" Biomedicines 9, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010008
APA StyleOtero-Ortega, L., Alonso-López, E., Pérez-Mato, M., Laso-García, F., Gómez-de Frutos, M. C., Diekhorst, L., García-Bermejo, M. L., Conde-Moreno, E., Fuentes, B., Alonso de Leciñana, M., Armada, E., Buiza-Palomino, L., Díez-Tejedor, E., & Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. (2021). Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction. Biomedicines, 9(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9010008








